Abstract
As an essential infrastructure that provides positioning, navigation, and timing services, China constructed the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS). The last BDS satellite was launched in June 2020, which represents the completion of BDS. BDS’s constellation consists of Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), Inclined Geosynchronous Orbit (IGSO), and Geostationary Orbit satellites. The precise modeling of non-conservative forces for BDS satellites is a challenging task. As an independent observation, Satellite Laser Ranging (SLR) is an important validation method of GNSS orbit modeling. In this paper, we validated the precise orbit products of different Analysis Centers (ACs) by using SLR observations, focusing on the BDS orbit modeling. By comparing BDS precise orbit products generated by four ACs with respect to SLR observations for the period of February 2017 to March 2021, we proved that an obvious satellite signature effect exists in the SLR residuals of BDS observed by multi-photon stations. The result indicates that multi-photon stations have a root mean square (RMS) of SLR residuals about 5 mm lower than that of single-photon detectors. The slope of SLR residuals with regard to nadir angle of IGSO satellites for single-photon and multi-photon stations is −2.0 and −2.5 mm/deg, respectively, while the slope of MEO satellites for these stations is about −0.6 to −0.3 and −1.0 to −0.4 mm/deg, respectively. To assess the effect of non-conservative force modeling, we selected seven high-performing stations, including five single-photon and two multi-photon stations. By comparing the SLR residuals of four ACs’ orbits, we analyzed the effect of the solutions of orbit processing, especially solar radiation pressure (SRP) models. We found that some centers may have modeling defects, including BDS-3 orbits of the Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum and BDS-2 orbits of the European Space Agency, inferred from the large RMS of SLR residuals. Modeling the SRP of BDS satellites is challenging, while an appropriate prior box-wing model can improve the accuracy of SRP modeling and provide a more stable performance.
1. Introduction
The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) is a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) independently constructed by China [1]. BDS combines a variety of satellite constellations and is deployed in three generations [1]. The first generation of BDS consisted of three GEO satellites, which are currently retired. Construction of the regional BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS-2) began in 2004. A total of 20 satellites manufactured by the China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) provide regional services, and 15 satellites are fully operational as of the preparation of this article [2]. In 2009, China began the construction of the global BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS-3). The launch of the final BDS-3 satellite on 23 June 2020 represented the full completion of BDS-3. The BDS-3 constellation consists of 30 satellites, including 24 MEO, 3 IGSO, and 3 GEO satellites. Ten MEO satellites were manufactured by the Shanghai Engineering Center for Microsatellites (SECM), while the other satellites were made by CAST.
BDS requires high-quality orbits to support its positioning, navigation, and timing accuracy. In 2012, the Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) was established by the International GNSS Service (IGS) [3] to release precise clock and orbit products through Analysis Centers (ACs) for operational services. Currently, several ACs, including the Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum (GFZ) [4], the European Space Agency (ESA) [5], the Center for Orbit Determination in Europe (CODE) [6,7], and Wuhan University (WU) [8] can provide precise clock and orbit products of BDS and other GNSSs. The precise orbit determination (POD) strategies and orbit models are important factors that affect the orbit accuracy of GNSS. However, due to the short construction time of BDS, the POD strategy and orbit dynamic models of BDS are still in the research stage. Thus, the processing strategies and force models of various ACs are still inconsistent at present. Currently, the 3D root mean square (RMS) of MEO and IGSO satellites is approximately 10 and 20 cm [9], respectively, whereas that of GEO satellites is at a meter level.
Improving the accuracy of BDS force models requires a thorough investigation of the accuracy performance and systematic errors of existing precise orbit products. One effective approach to validate the accuracy of BDS orbits is satellite laser ranging (SLR), which is an independent observation [10,11,12]. SLR offers several advantages, such as a high tracking precision, and is not affected by problems such as phase ambiguities. Therefore, SLR validation is considered a crucial accuracy index for refining BDS orbit modeling [13,14].
Despite their high accuracy, SLR observations are not entirely free of biases that may contain systematic errors in range measurements. The systematic errors have been identified from the differences among SLR stations tracking LAGEOS [15]. It has also been reported that a systematic error between single-photon and multi-photon stations exists in the SLR observations of GLONASS [16] and Galileo [17]. Previous studies have shown that the relative position between the station and satellite, as well as the quality of the SLR station, can affect the results of SLR residuals, suggesting that the SLR residuals may contain ranging bias. Therefore, evaluating SLR observations is essential before validating the orbits of BDS.
This paper validates BDS satellite precise orbit products using SLR observations, focusing on the systematic errors in SLR observations and the non-conservative force modeling effects of BDS orbits. Section 2 provides an overview of SLR tracking of BDS satellites, including laser retroreflector arrays (LRAs) onboard BDS satellites and SLR observations of BDS satellites. Additionally, the method of SLR validation is provided. Section 3 analyzes the systematic effects of SLR ranging related to different types of SLR detectors and different BDS satellites. We then select observations from high-performing stations to validate the BDS orbit modeling of non-conservative forces, including antenna thrust (AT), earth radiation pressure (ERP), and solar radiation pressure (SRP).
2. Materials and Methods
This section introduces the SLR tracking of BDS satellites, which includes LRAs onboard BDS satellites and SLR observations. In addition, the details of the SLR validation method used in our study are presented.
2.1. LRAs Onboard BDS Satellites
Currently, laser retroreflector arrays (LRAs) are deployed on all BDS-2 and BDS-3 satellites. Typically, LRAs consist of multiple corner cubes that increase the effective reflective area. Among the nine BDS satellites (one GEO, three IGSO, and five MEO) long-term tracked by the International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS) [18], three types of LRAs were used with different prism numbers and arrangements. LRAs onboard three BDS-2 IGSO satellites including COMPASS-I3, COMPASS-I5, and COMPASS-I6B and one BDS-2 GEO, i.e., COMPASS-G1, were manufactured by Shanghai Astronomical Observatory (SHAO) with 90 corner cubes. One BDS-2 MEO, i.e., COMPASS-M3, two BDS-3 SECM satellites, i.e., Beidou3-M9 and Beidou3-M10, manufactured by SHAO, have an LRAs with 42 corner cubes. The 38-corner-cube-LRAs made by North China Research Institute of Electro-Optics (NCRIEO) are equipped on BDS-3 CAST satellites, i.e., Beidou3-M2 and Beidou3-M3 [19,20]. Table 1 provides detailed information on the three types of LRAs. In 2023, ILRS started to track all BDS-3 MEO satellites. However, due to the limited number of observations available, the analysis does not incorporate the data obtained from recently tracked satellites. It is worth noting that the structure of LRAs will cause a systematic error in SLR observations. When SLR signal pulse is not perpendicular to the prism, the pulse may be reflected by other prisms nearby, which can result in a distance difference between LRAs and station. This systematic error caused by the characteristics of the SLR measurement mode is known as the satellite signature effect [15].

Table 1.
Parameters of LRAs equipped on the nine BDS satellites long-term tracked by ILRS.
2.2. SLR Observations of BDS Satellites
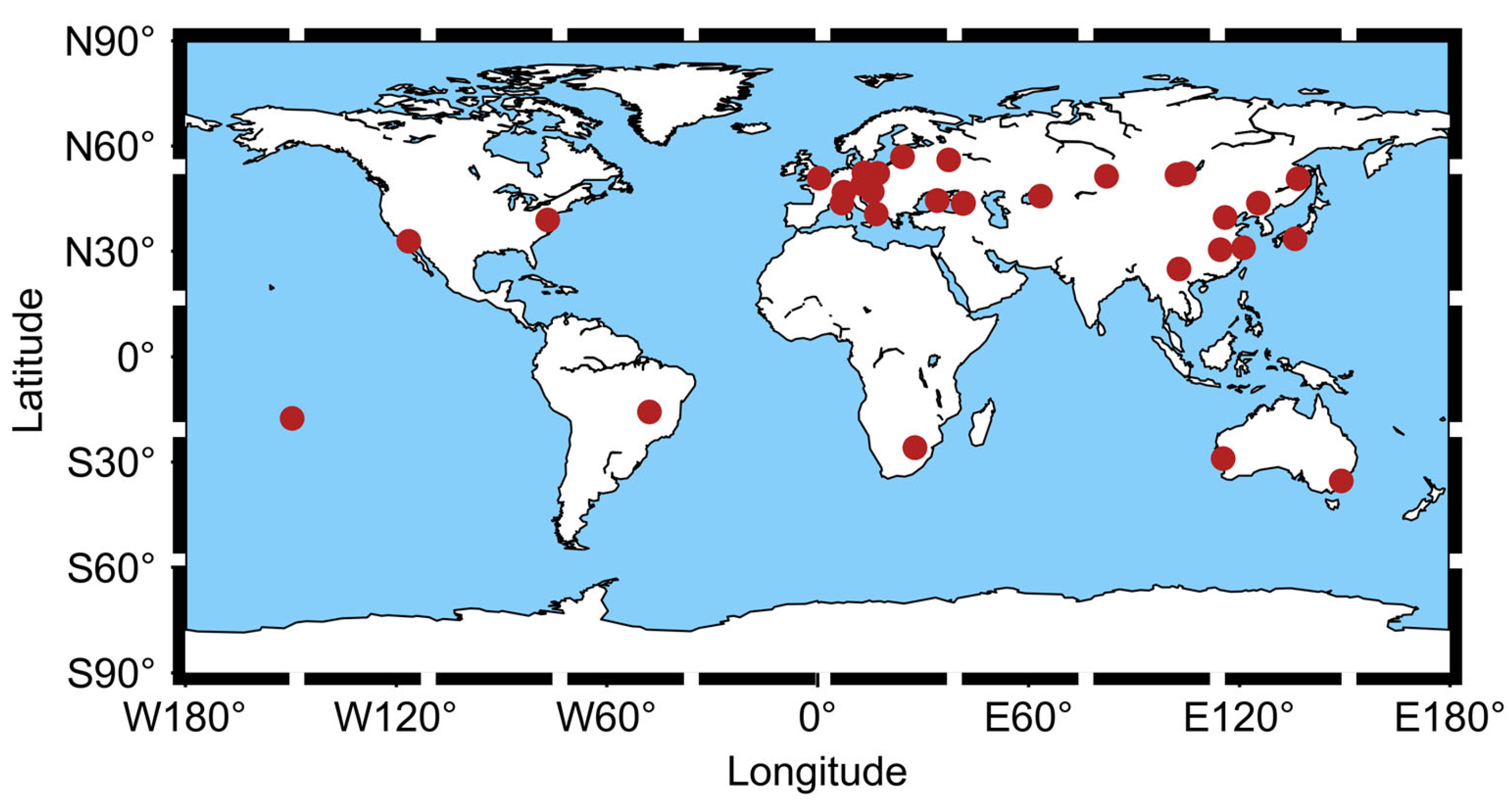
With an increasing number of satellites tracked by ILRS, tracking new GNSS satellites such as BDS is becoming more challenging for laser stations. To cope with the growing demand for observations, SLR stations are constantly optimizing their tracking strategies. Currently, SLR stations can track more than 140 different satellites by adjusting their tracking strategies [21]. Moreover, the number of available SLR stations has been increasing annually along with the development of ILRS [22]. As of August 2022, 34 stations can receive the return laser from BDS satellites, the distribution of which can be seen in Figure 1. Additionally, Table 2 lists their monument code, detector type, location name, and country.
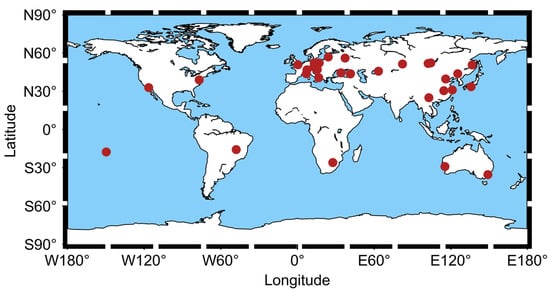
Figure 1.
The map of the distribution and condition of worldwide SLR stations tracking BDS.

Table 2.
SLR stations with BDS satellite tracking observations.
SLR stations typically employ three detector types including Photo-Multiplier Tube (PMT), Micro-Channel Plate (MCP), and Compensated Single-Photon Avalanche Diode (CSPAD). CSPAD has been improved over SPAD and both are capable of detecting single returning photons, making them single-photon stations. MCP and PMT can simultaneously detect multiple returning photons, making them multi-photon stations. Variations in detector types installed at SLR stations can lead to differences in their performance, as demonstrated in studies of center-of-mass corrections for spherical geodetic satellites [23] and the signature effect of GNSS satellites [16,17].
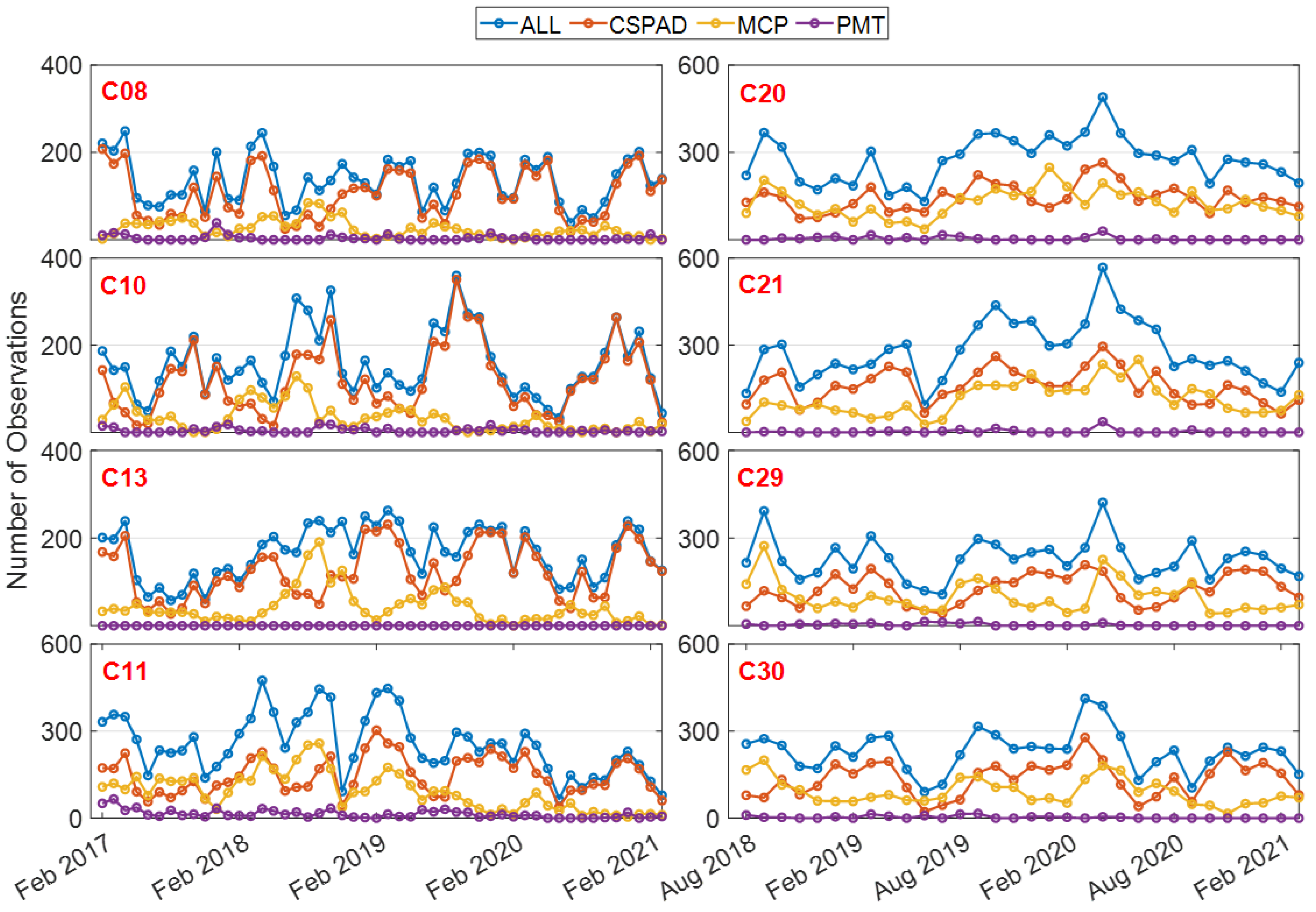
The number of monthly SLR observations of long-term tracked satellites in the period of February 2017 to March 2021 are presented in Figure 2. Please note that the GEO satellites are not prioritized due to meter-level variations in their orbits among the products released by ACs [24] On average, the number of monthly SLR observations of MEO and IGSO satellites are around 250 and 150, respectively, with maximum values of 568 and 360, respectively. Among them, the number of MEO and IGSO satellites observed by CSPAD, MCP, and PMT stations are around 140 and 120; 100 and 30; and 6 and 3, respectively.
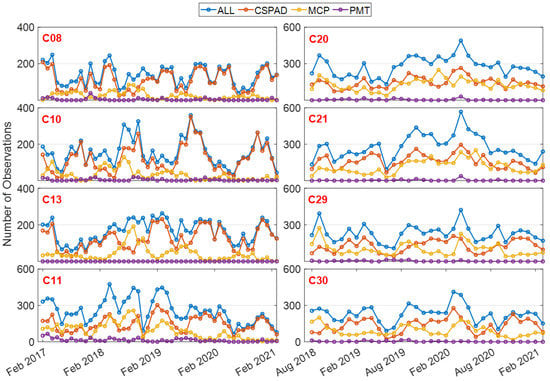
Figure 2.
Monthly statistics of SLR observations. ILRS has been tracking BDS-2 satellites since before 2017 (C08, C10, C11, and C13), while the SLR observations of BDS-3 MEO satellites began in August 2018 (C20 C21, C29, and C30).
2.3. SLR Validation Method
SLR stations record the turnaround time , which represents the interval of a signal emitted from the station and received after being reflected at LRAs of the target satellite. The time of flight multiplied by the speed of light in vacuum can be transformed into a range value. Throughout this paper, the SLR residual is defined as the difference between the observed range and the computed range obtained from Equations (1) and (2).
The range value denotes the computed distance between the SLR station and the LRAs of the target satellite. Although SLR measurements are relatively free from bias, some effects of signal propagation need to be accurately modeled to correct the range value. Thus, the corrected SLR range value measurement is given by Equation (2).
In Equation (2), the is the distance from the station to the satellite, while the is the distance from the satellite to the station. denotes the time delay related to the relativistic effect [25]. is the tropospheric delay due to the atmospheric friction. consists of observation noises and unmodeled errors.
Considering the relative motion between the station and the satellite caused by the Earth’s rotation and the satellite revolution, the value for the distance of uplink and downlink in an inertial reference frame can be obtained by Equation (3).
where and denote the time-dependent position vectors of the SLR station and the satellite, respectively.
In this case, is not strictly equal to and the difference is less than a millimeter [26]. Therefore, we used to assume that the time of uplink is approximately equal to that of downlink , which are half of the time measurement value . Thus, the simplified expressions of Equation (2) are obtained by Equation (4).
where the coordinates and the eccentricity correction of the SLR station are determined as part of the SLR contribution (SLRF2014 is used in this paper) to the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF) [27] and the position of the target satellite is derived from the precise orbit product in the International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF) with the added satellite-independent LRA center-of-mass correction in a spacecraft frame (SCF). The alternative equations are described by Equation (5).
where and are the time-dependent rotation matrices from SCF and ITRF to ICRF, respectively. is an LRA-special range correction between the position of LRAs center and reference point of LRAs. is the correction of station eccentricity according to SLRF2014.
In addition to the basic signal propagation model for SLR range measurement given by Equations (3)–(5), and in Equation (2) can be corrected through modeling. The relativistic correction on the SLR measurement is about 13 mm for MEO satellites at orbital altitudes of 22,000 km [25]. Tropospheric range delays which are in the order of meters must also be modeled in SLR range models, which can be modeled with an accuracy of a millimeter level [28,29].
3. Results
We will analyze the SLR residual results of different BDS satellites and SLR stations in this section. After evaluating the SLR observations of different satellites by different SLR stations, seven stations were selected as high-performing stations. Finally, we compared the effect of different non-conservative force models deployed on four ACs from a view of independent SLR validation tracked by high-performing stations.
3.1. Satellite Signature Effect of BDS
In this section, we used the method detailed in Section 2 to process the orbit products from WU to analyze the signature effect. A threshold with the value of ±0.5 m was set to eliminate gross errors in SLR residuals. While the POD strategies of different ACs differed, the signature effect remained consistent among them. Moreover, the precise orbit products released by WU for BDS were continuous, enabling the analysis of satellite signature effect through a wide distribution of SLR residuals.
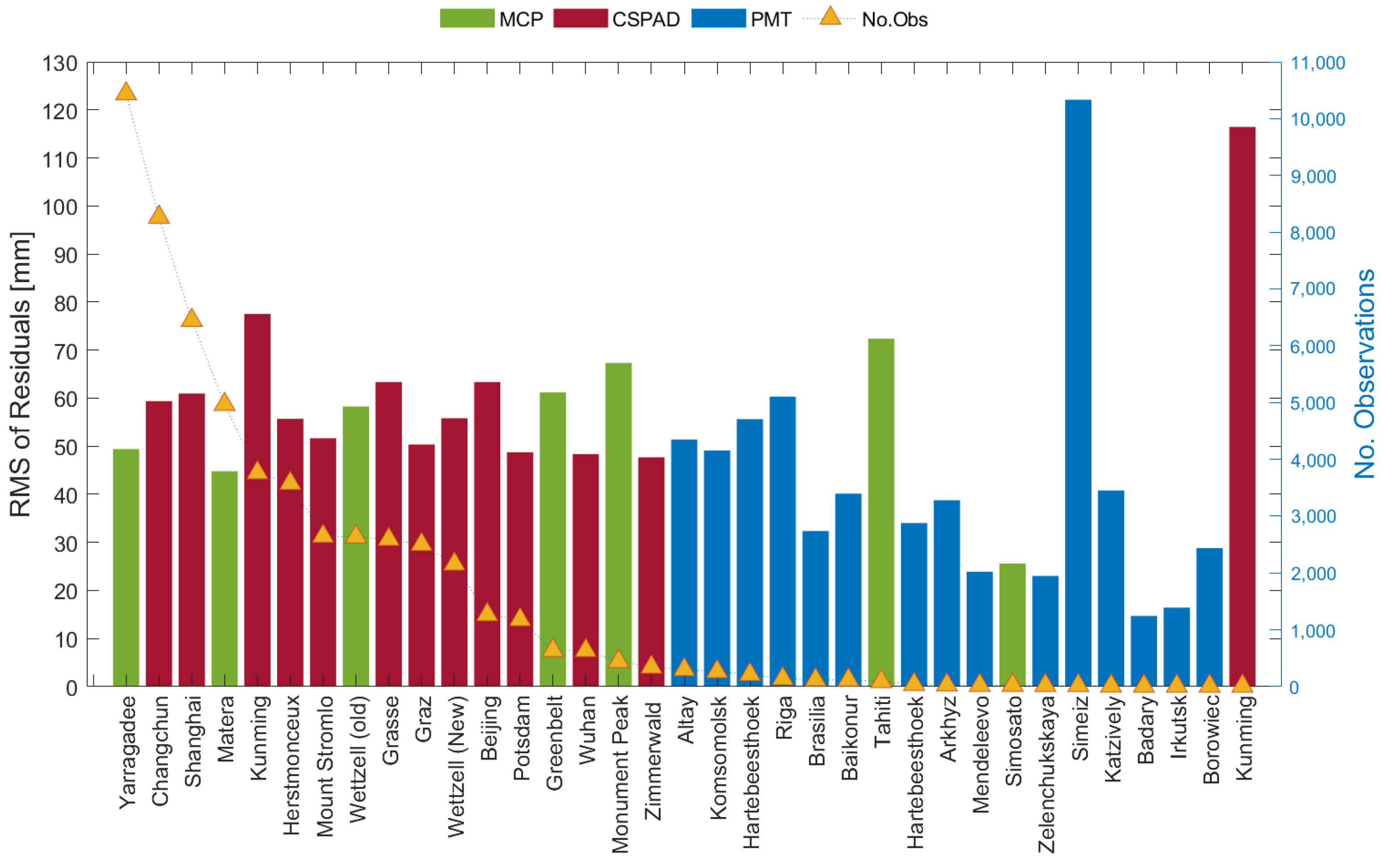
In consideration of the different systematic errors of three groups of stations, Figure 3 shows the number of observations and the RMS of the SLR residuals of the 34 stations listed in Table 2. Unlike other GNSSs, CSPAD and MCP stations provide more than 90% of the SLR observations for BDS, whereas a percentage of the observations are only tracked by PMT stations. This can be explained by the observation priority of SLR stations, while PMT stations concentrated in Russia and nearby countries mainly track GLONASS satellites. The number of SLR observations for MEO satellites is approximately the same for both CSPAD and MCP stations. However, for BDS-2 IGSO satellites, the number of CSPAD observations is three times greater than that of MCP observations. Several CSPAD stations located in China, e.g., Changchun and Shanghai, provide about half of CSPAD observations. The RMS of the SLR residuals from most CSPAD and MCP stations are similar and vary from 50 to 70 mm. The RMS of the residuals from four PMT stations i.e., Altay, Komsomolsk, Hartebeesthoek, and Riga, reached the same level as CSPAD and MCP stations, while the RMS of the residuals from some other PMT stations had a value lower than 40 mm. Despite having a smaller RMS value, the PMT stations with this characteristic had a limited number of SLR observations. As a result, the overall SLR residuals for these stations exceeded 80 mm in RMS.
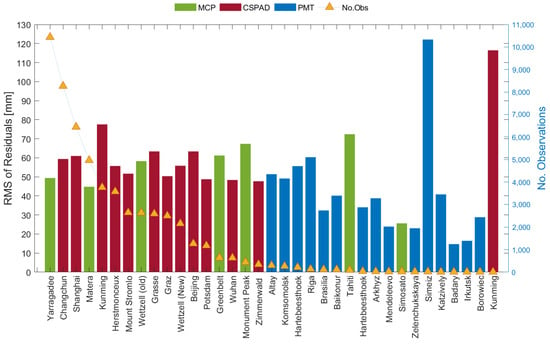
Figure 3.
The number and RMS of BDS SLR residuals tracked by 34 stations.
For the sake of accurately reflecting the satellite signature effect, it is necessary to exclude stations with limited observations. Therefore, we selected 20 stations according to the total number of observations from February 2017 to March 2021 with a threshold of 200. Among multi-photon stations, only two MCP stations, Yarragadee (7090) and Matera (7941), as well as two PMT stations, Altay (1879) and Komsomolsk (1868), could track BDS-2 IGSO satellites. Furthermore, each of the other three stations, except Yarragadee, had only a few hundred observations of BDS-2 IGSO.
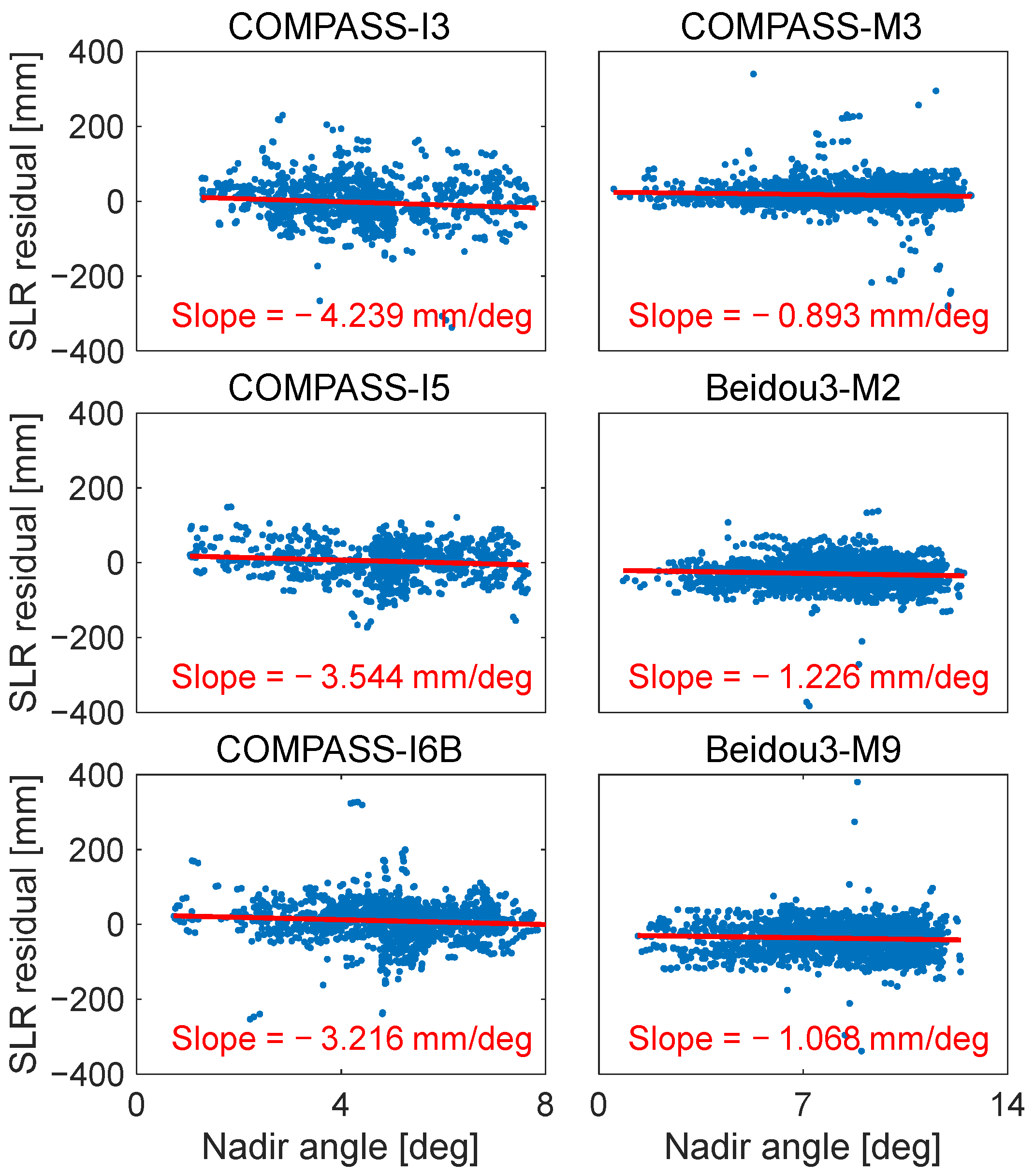
According to the installation method of LRAs, the nadir angle of SLR stations with respect to a satellite reference frame is equivalent to the incident angle of the laser beam on BDS satellites. To investigate the signature effect of multi-photon stations tracking BDS satellites, Figure 4 shows the variation in SLR residuals with respect to the nadir angle observed by Yarragadee. As a high-energy station, Yarragadee provides the majority of observations among the MCP and PMT stations, serving as a representative for multi-photon stations. The slope of COMPASS-I3, COMPASS-I5, COMPASS-I6B, COMPASS-M3, Beidou3-M2, and Beidou3-M9 with respect to the nadir angle was −4.24, −3.54, −3.21, −0.89, −1.23, and −1.07 mm/deg, respectively. The observed SLR residuals demonstrate a clear dependence on the nadir angle, caused by the laser pulses reflected from the nearer cube of the LRAs and a shorter collection time by the detectors. This explains why the slopes are negative values. Moreover, the slopes of IGSO satellites were larger than those of MEO satellites, which is attributed to the larger LRAs and the greater number of corner cubes deployed on IGSO satellites.
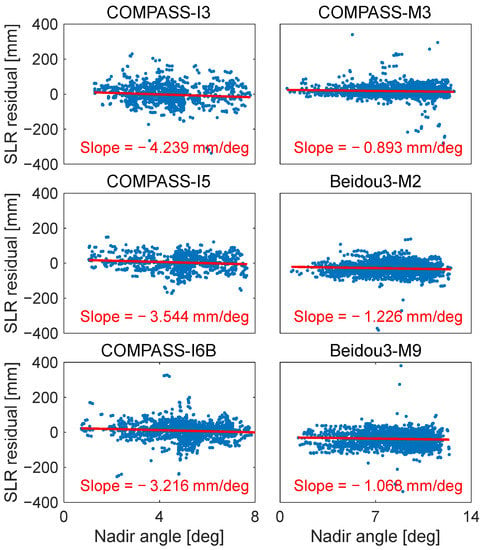
Figure 4.
The variation in SLR residuals for six satellites with regard to the nadir angle observed by Yarragadee.
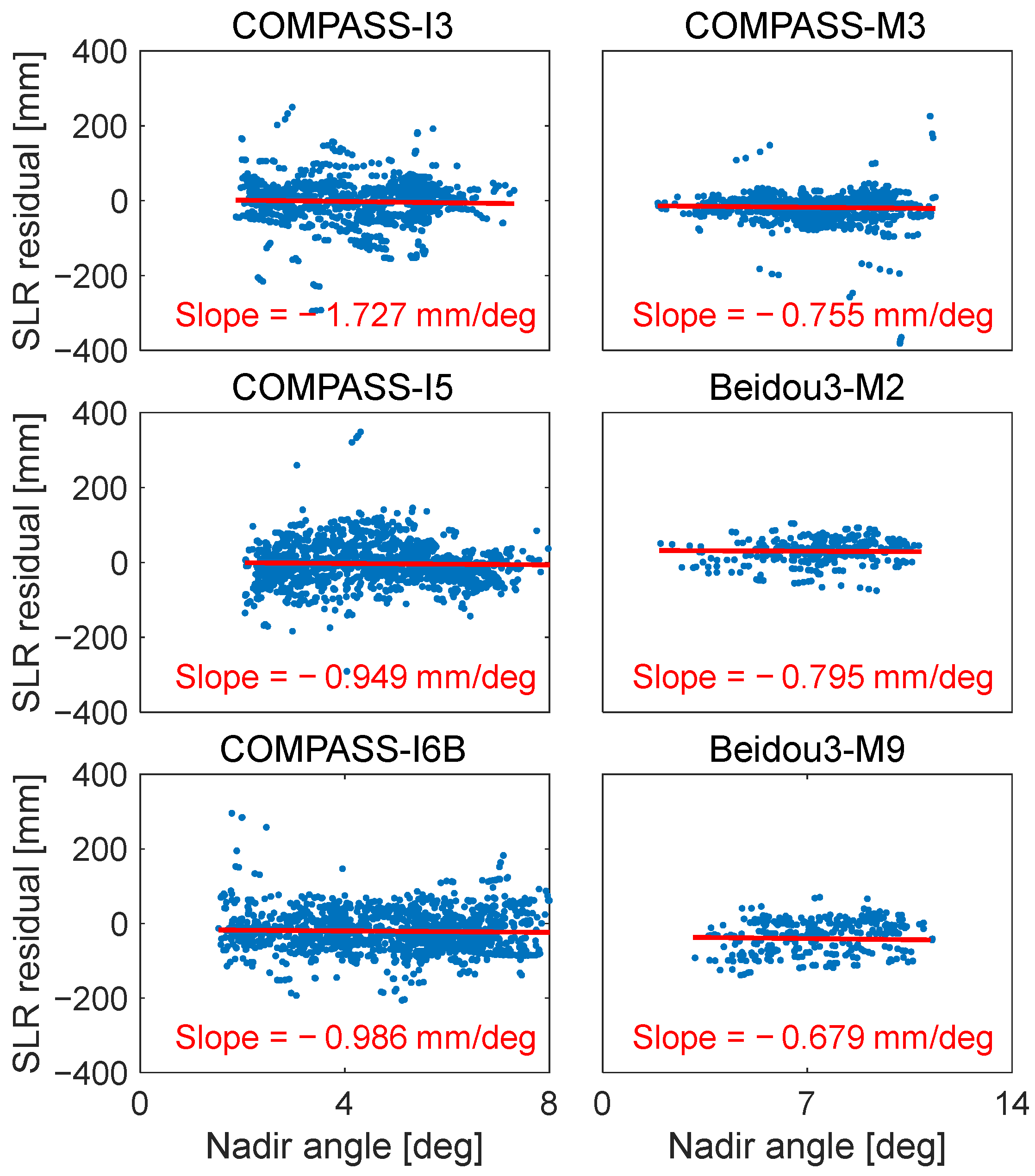
In order to compare the systematic error between multi-photon and single-photon stations, we selected Shanghai, which is equipped with a single-photon detector, to compare it to Yarragadee. Figure 5 shows the variation in the SLR residuals with regard to the nadir angle observed by Shanghai. The slope with regard to the nadir angle was −1.73, −0.95, −0.99, −0.76, −80, and −0.68 mm/deg for COMPASS-I3, COMPASS-I5, COMPASS-I6B, COMPASS-M3, Beidou3-M2, and Beidou3-M9. We found that the slopes of Yarragadee with regard to the nadir angle were larger than those of Shanghai. This suggests that the signature effect exists in the SLR residuals observed by multi-photon stations. In low-energy mode, single-photon stations are not subject to the issues of varying nadir angles since the probability of photon reflection is equal for every corner cube. However, it can be seen that the SLR residuals are also dependent on the nadir angle, which may be attributed to the requirement for post-processing rejection of high-rate data and changes in the optical path of the laser pulse as it passes through the troposphere during observations at different elevation angles [17].
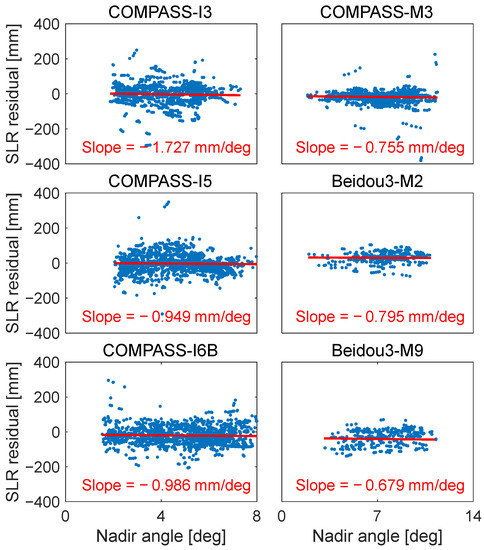
Figure 5.
The variation in SLR residuals for six satellites with regard to the nadir angle observed by Shanghai.
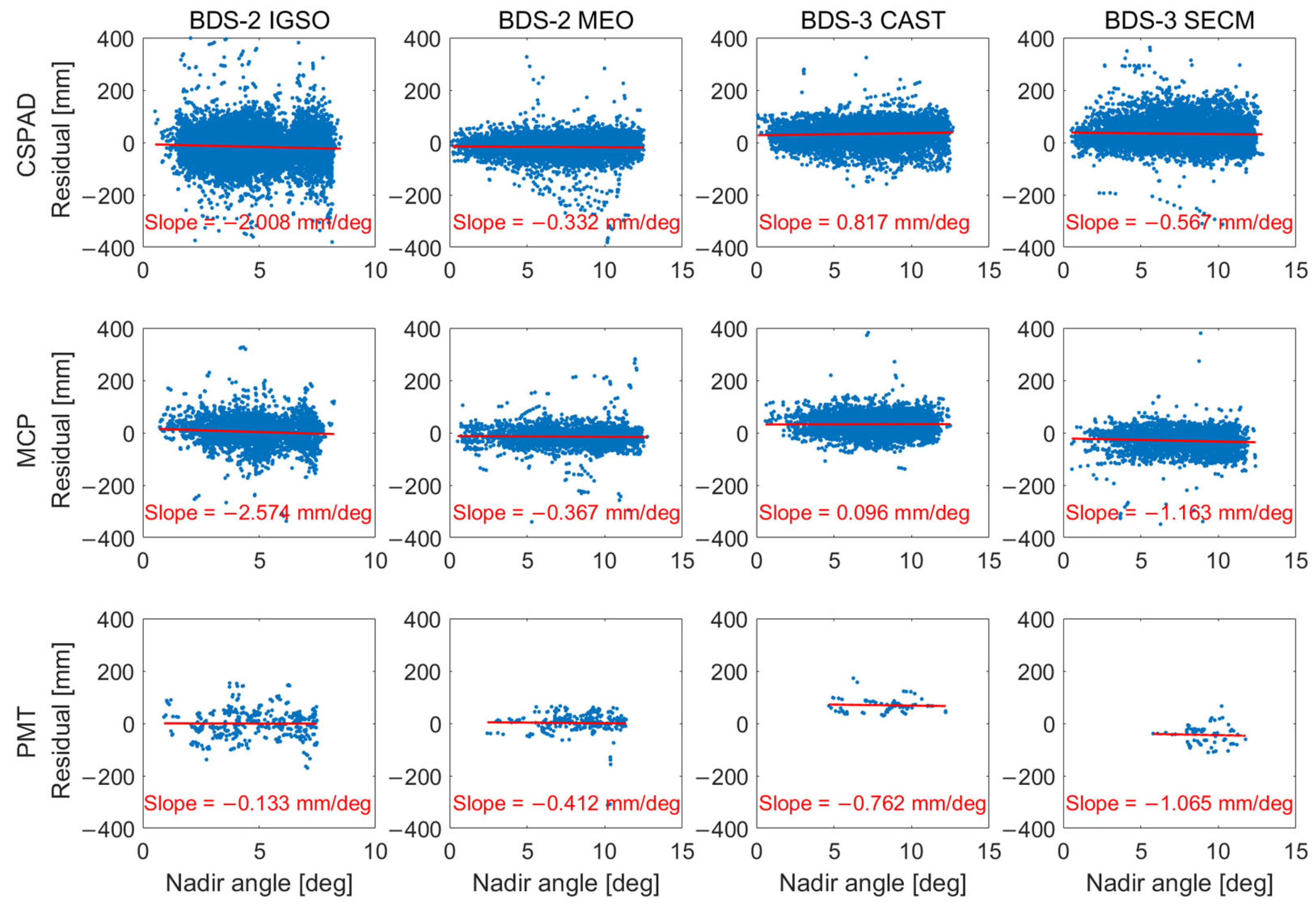
To further investigate the signature effect in SLR observations, we analyzed the residuals as a function of the nadir angle for four types of satellites (BDS-2 IGSO, BDS-2 MEO, BDS-3 CAST, and BDS-3 SECM) and divided them into three station groups (CSPAD, MCP, and PMT), as shown in Figure 6. For MCP and CSPAD stations, the slope with regard to the nadir angle was around −2.5 to −2.0, −0.4 to −0.3, and −1.2 to −0.6 mm/deg for BDS-2 IGSO, BDS-2 MEO, and BDS-3 SECM satellites, respectively. The results indicate that IGSO satellites exhibit a larger slope than MEO satellites. Moreover, it can be seen that MCP stations have a stronger correlation between the nadir angle and SLR residuals than CSPAD stations, and the difference in slope has a maximum of about 0.6 mm/deg for BDS SECM satellites. For BDS-3 CAST satellites, a slope with a positive value also existed in GFZ and ESA. Among eight long-term tracked satellites, the two CAST satellites were manufactured by NCRIEO, while the other six satellites were made by SHAO (see Table 1). According to the published information [30,31,32], the prism cubes on those three types of LRA are made of quartz. Additionally, all the surfaces of the corner cubes on the two types of LRAs made by SHAO are uncoated, while for the LRAs manufactured by NCRIEO, it is still unknown whether some surfaces of the prism cubes are coated or not, which may have an impact on the SLR residuals. For PMT stations, the slope with regard to the nadir angle was approximately −0.1, −0.4, −0.8, and −1.1 mm/deg for the four types of satellites, respectively. However, the reader should also note that the slope of the PMT stations may not be reliable, considering that the PMT stations only had a few BDS observations (about 2% and 4% of those by made CSPAD and MCP stations, respectively).
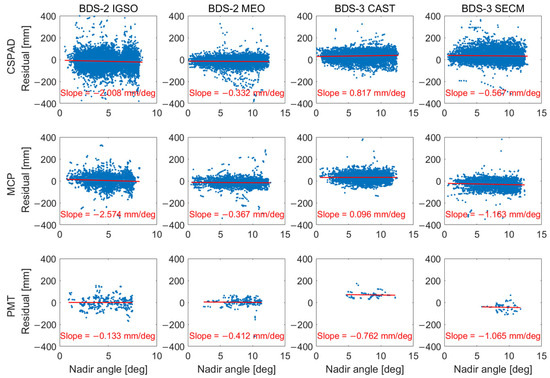
Figure 6.
The variation in SLR residuals with regard to nadir angle of four types of BDS satellites observed by different types of SLR stations.
After analyzing the SLR residuals of different constellations, we selected several stations with a significant number of observations to evaluate their performance in tracking BDS. Matera is another MCP station as well as Yarragadee, and can provide a large number of observations. The RMS of SLR residuals and the slope with regard to the nadir angle observed by Matera was approximately 45 mm and −2.21 mm/deg, respectively, which shows a good performance among multi-photon stations. Herstmonceux is equipped with an uncompensated SPAD and its SLR residuals had a positive slope. This phenomenon was also observed in Grasse, where a SPAD detector is installed. Changchun had an RMS of 59 mm and a large positive slope. The positive slope anomaly may indicate the presence of amplified noises at Changchun [33]. Shanghai had a slope of −0.40 mm/deg and a mean offset of 8 mm, which represents most high-performance CSPAD stations including Mt Stromlo, Beijing, and Wettzell. From the above phenomena shown by the results of different stations, some SLR stations have high performance in tracking BDS satellites. CSPAD stations including Mt Stromlo, Shanghai, Graz, Wettzell, and Beijing, as well as MCP stations Yarragadee and Matera, can be considered high-performing stations suitable for BDS. These high-performing stations have a sufficient number of stable observations for each BDS satellite, and the orientation of the satellite and station, such as elevation and nadir angles, have a smaller impact on the SLR residuals. Moreover, the RMS and mean offset of the SLR residuals of these seven stations were below 60 mm and 20 mm, respectively. Statistical results in Table 3 show that high-performing stations can reduce the RMS of SLR residuals by about 1 to 3 mm.

Table 3.
Mean offsets and RMS of the SLR residuals for precise orbit products of four ACs observed by high-performing SLR stations and all stations.
3.2. Non-Conservative Force Modeling Effect of BDS
After the identification of the SLR signature effect, SLR observations from seven high-performing stations were selected to analyze the modeling effect of non-conservative forces on SLR residuals. This section specifically focuses on the impact of non-conservative forces such as AT, ERP (albedo and infrared radiation), and SRP.
ACs use different non-conservative force models to generate precise orbit products. Depending on the different models used by ACs, the modeling difference in the final perturbation acceleration may reach several nanometers per square second, which ultimately affects the accuracy of the orbits. SRP is the primary consideration factor for the non-conservative force models of navigation satellites, which cause an of about 80 to 130 nm/s2. Four different SRP models, i.e., the empirical CODE orbit model (ECOM), the extended ECOM model (ECOM2), the a-priori box-wing (PBW) along with the ECOM model, and the PBW with estimated values along with the ECOM model, have been applied in GFZ, CODE, WU, and ESA, respectively. ECOM and ECOM2 are purely empirical models, which expressed the acceleration of SRP by estimating parameters in a DYB orthogonal frame [34]. PBW + ECOM adds an analytical model to the basis of ECOM, which is calculated by the solar radiation and characteristics of satellite surfaces. It is worth emphasizing that the perturbation generated by the thermal radiation pressure emitted from the materials of satellite surface is incorporated with SRP in a combined form [35]. The acceleration of ERP is a perturbation of 1 to 3 nm/s2 caused by reflected solar radiation and emitted infrared radiation. For ERP, the widely used model for the GNSS satellite is the ERPBOXW model presented by Rodriguez-Solano [36], which considers both the modeling of reflected radiation and infrared radiation. ESA and WU deployed the ERPBOXW model for all BDS satellites and the BDS-2 MEO satellite, respectively, while CODE and GFZ do not consider the modeling of BDS ERP. AT is a perturbation caused by the signal transmission of satellites. The acceleration caused by AT can be modeled by the transmitting power of antenna and the mass of the satellite, which varies from 0.3 to 0.4 nm/s2 for BDS-2 IGSO and BDS-2 MEO satellites. Because the China Satellite Navigation Office (CSNO) does not disclose the transmit power for BDS-3 satellites [5], the antenna thrust is only applied to BDS-2 MEO in WU. The different solutions for BDS among four ACs in non-conservative force modeling of interest are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Parts of non-conservative force modeling strategy among four ACs.
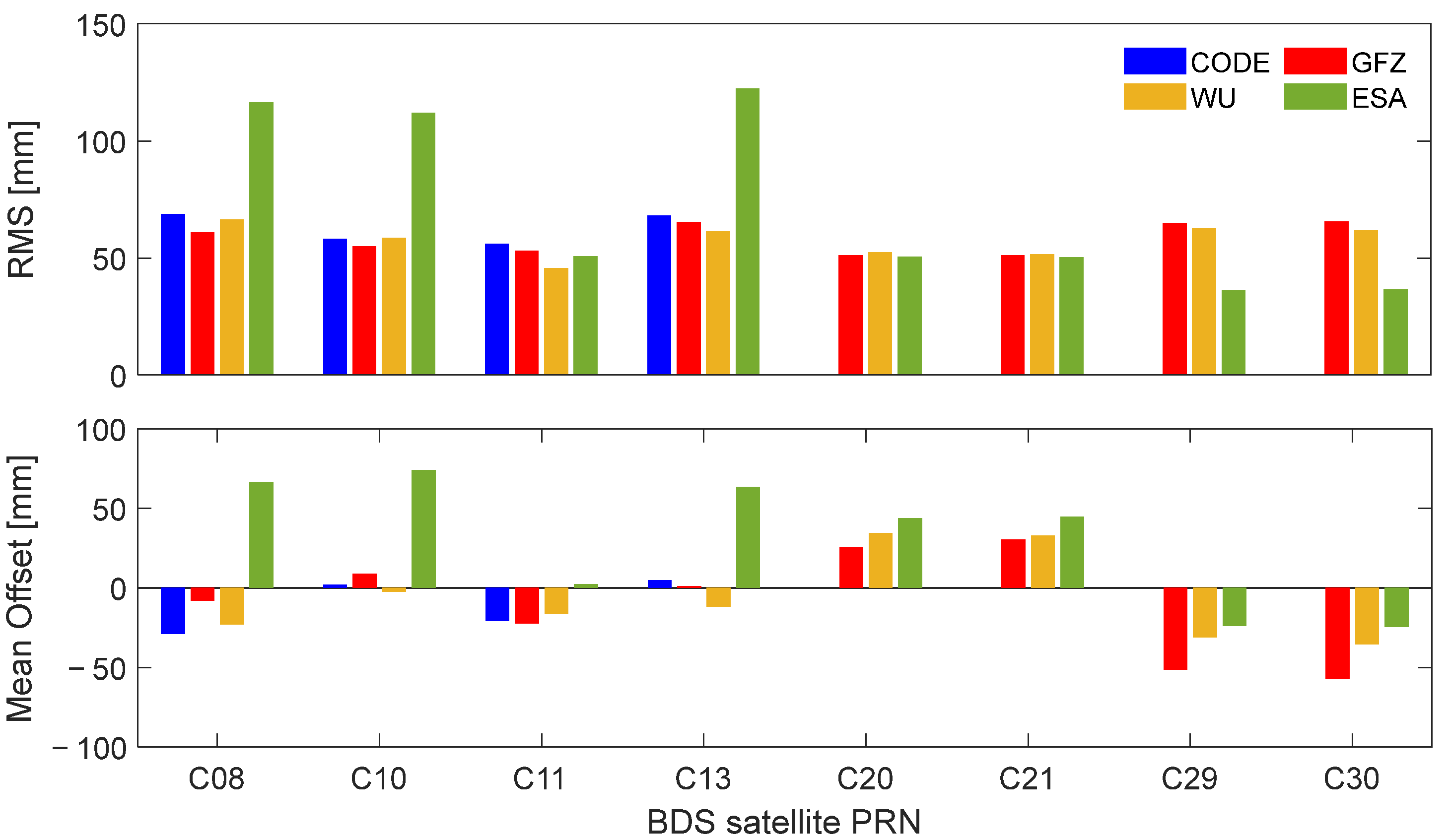
For earth radiation pressure and antenna thrust mainly imposing on the radial direction, which is basically consistent with the observation direction of SLR, the effect of these two forces can be reflected in SLR residuals. Figure 7 shows the statistical information, i.e., mean and RMS of SLR residuals of different satellites among the four ACs. For the three IGSO satellites, the RMS of ESA’s SLR residuals is notably larger than that of the other ACs (about a factor of 2), which could be attributed to the differences in the geometry parameters and optical coefficients of IGSO satellites. The mean offset of SLR residuals of WU for the BDS-2 MEO (C11) satellite is approximately 5 mm larger than that of CODE and GFZ (ESA’s non-conservative force modeling of BDS-2 satellites may have defects in the subsequent comparison), which may be related to the modeling of ERP and AT. Additionally, the RMS of WU for C11 is the smallest among WU, CODE, and GFZ. The mean offset of the SLR residuals of ESA for the BDS-3 CAST (C20 and C21) and SECM (C29 and C30) satellites are the largest, and they both have a positive centimeter-level offset compared with GFZ and WU. When antenna thrust and albedo were modeled, the mean value of SLR residuals had a positive offset with the range of 5 to 10 mm, while the RMS decreased by 1 to 5 mm.
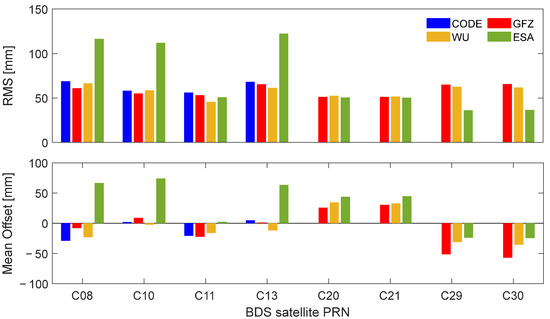
Figure 7.
RMS and mean offset of SLR residuals of long-termed tracked BDS satellites (eight satellites except C01 in Table 1) observed by high-performing stations for four ACs.
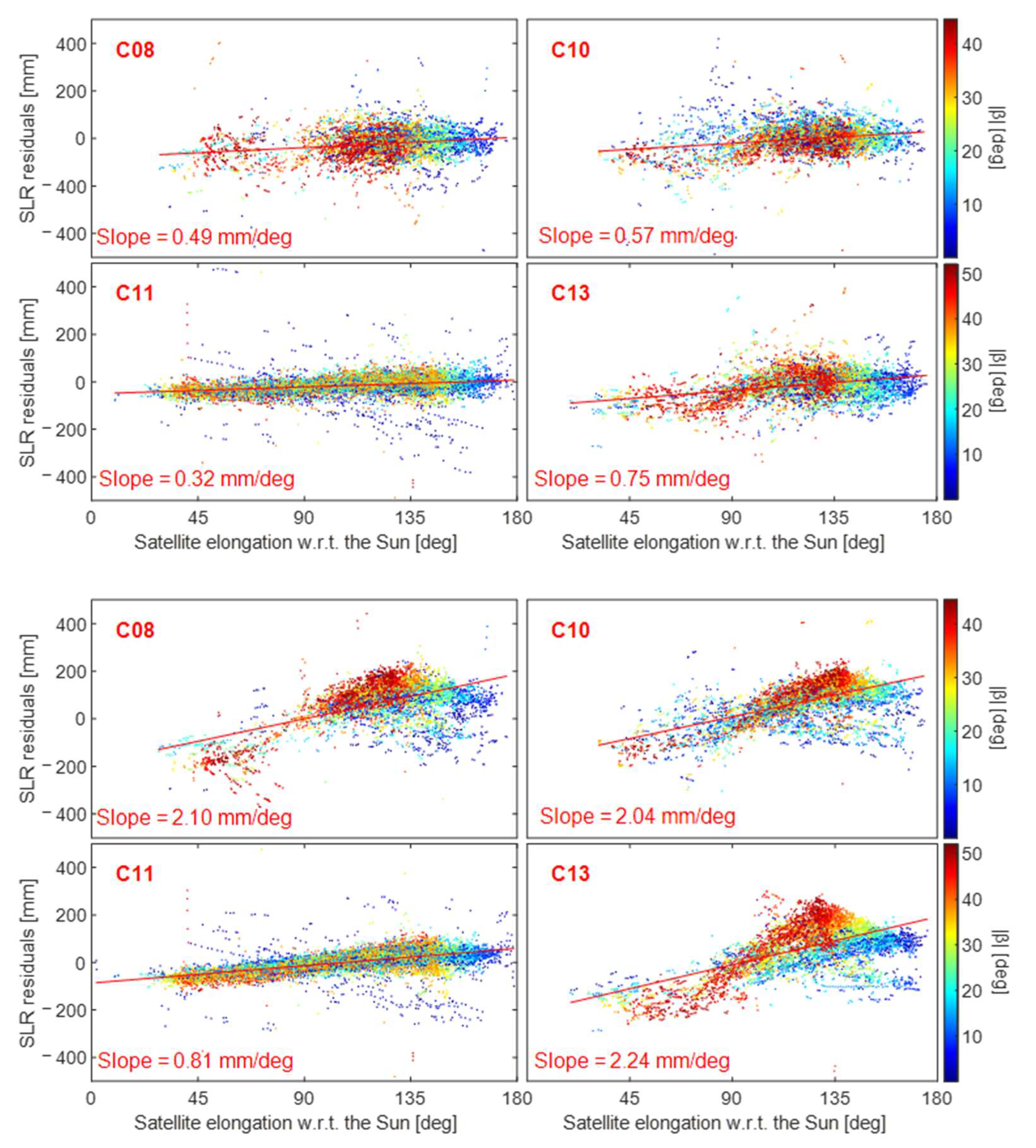
To compare the adaptability of SRP modeling, we validated BDS orbits by utilizing SLR observations, and the SLR residuals were then depicted as a function of the sun elevation and the satellite’s elongation angle relative to the sun. Comparing the relationship between elongation angle and SLR residual can effectively reflect the effect of SRP modeling. To better analyze the effect of SRP modeling, we generated pictures according to each satellite. Four BDS-2 satellites of WU and ESA are shown in Figure 8 to investigate the relationship between SLR residuals and elongation angle. According to the results, the SLR residual of the BDS-2 IGSO satellite is more dependent on the elongation angle, which indicates that the BDS-2 MEO satellite has a better performance than IGSO satellites. Additionally, the slope with regard to the elongation of the BDS-2 MEO of ESA is higher to that of the BDS-2 IGSO of WU. Combined with the above-mentioned results—that the RMS of the IGSO of ESA is too large—we infer that ESA may have some defects in the SRP modeling of BDS-2 satellites.
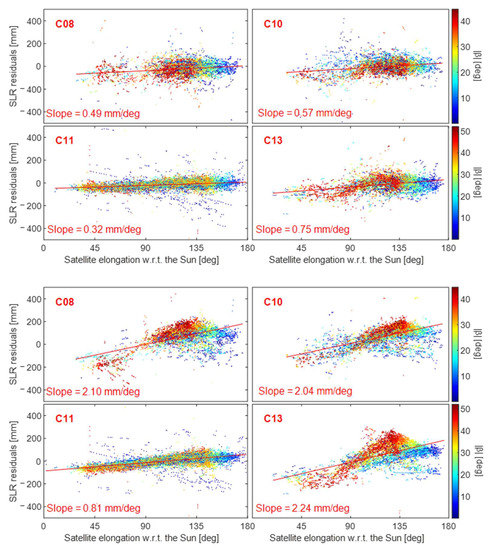
Figure 8.
SLR residuals as a function of the elongation angle and the sun elevation for four BDS-2 satellites (C08, C10, C11 and C13): (top): WU; (bottom): ESA.
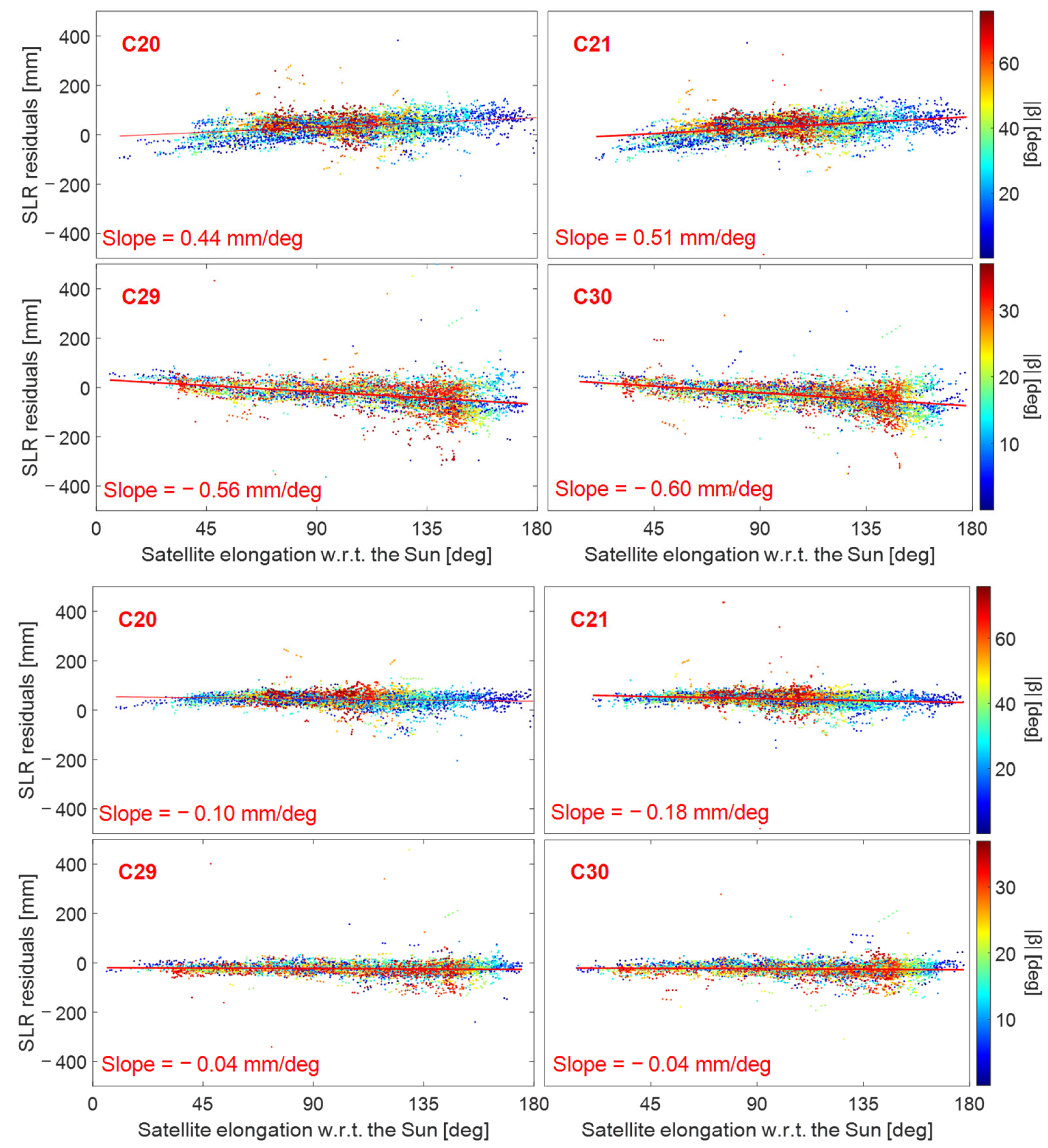
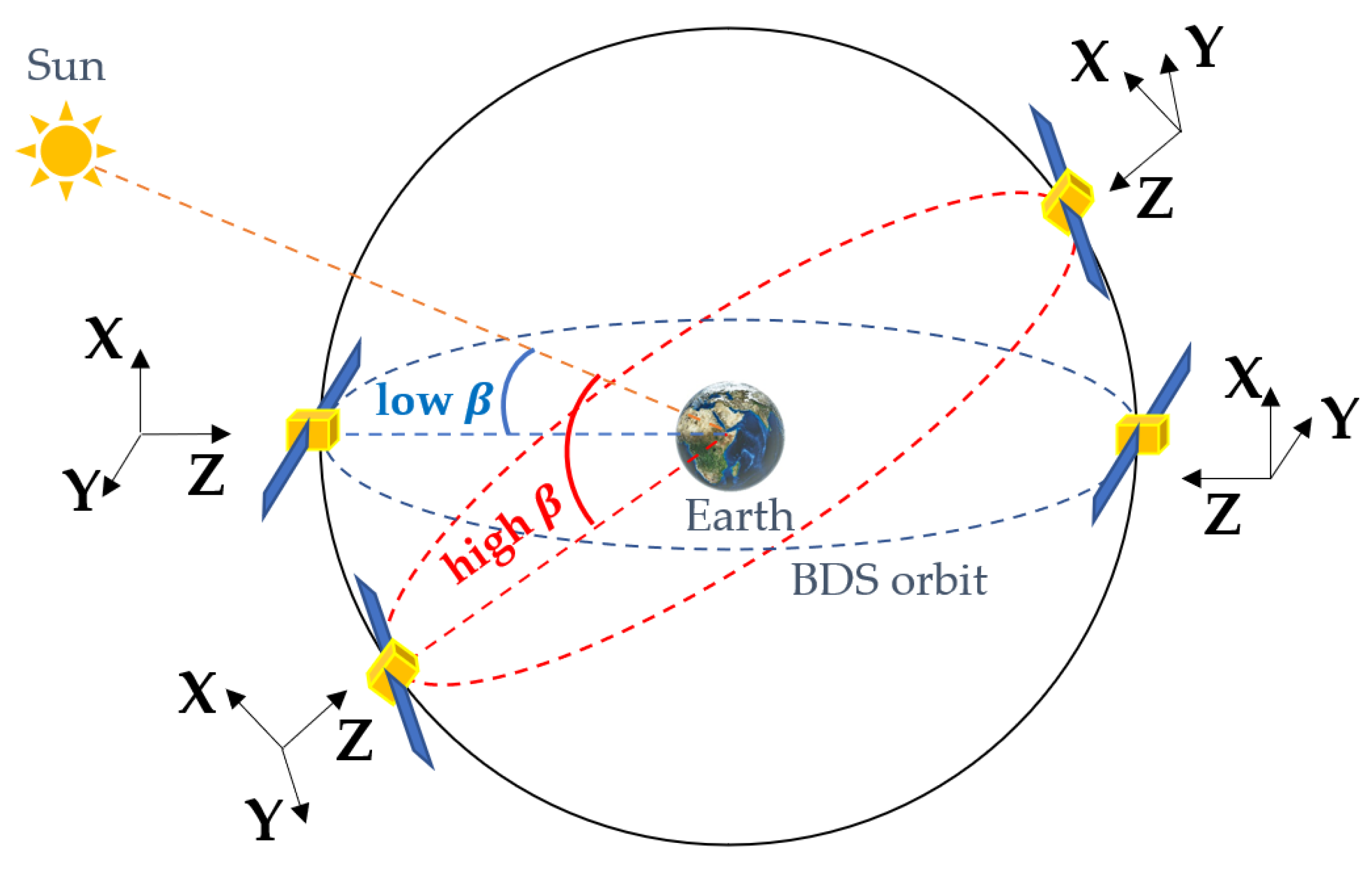
Figure 9 illustrates the relationship between SLR residuals and the elongation angle for four BDS-3 satellites, highlighting how modeling defects of SRP can be observed through the sun elevation. When the elongation angle is close to 90 degrees, the spread of SLR residuals is smaller for high sun elevations (red dots in Figure 9) than that for low sun elevations (blue dots in Figure 9). This phenomenon occurs because, when the satellite is at a high (the red orbit in Figure 10), the sunlight mainly illuminates the +X surface (the X and the following Z axes are defined in the SCF [37]). When the satellite is at a low (the blue orbit in Figure 10), the +Z and −Z surfaces are also alternatively illuminated apart from the +X surface, which makes accurately modeling the SRP difficult.
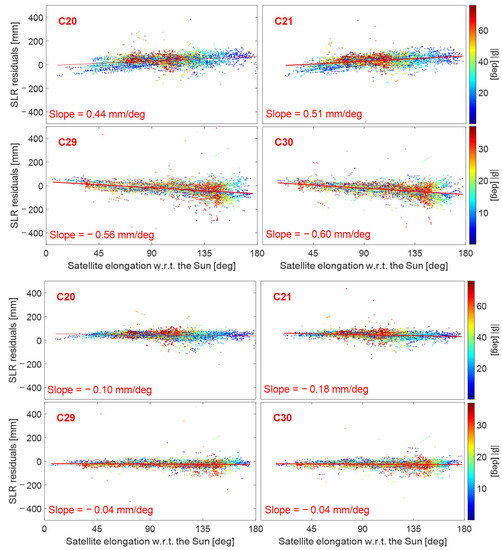
Figure 9.
SLR residuals as a function of the elongation angle and the sun elevation for four BDS-3 satellites (C20, C21, C29 and C30): (top): WU; (bottom): ESA.
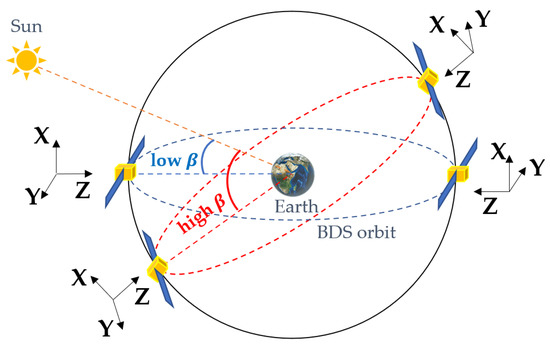
Figure 10.
BDS satellites orientation in orbits at different sun elevations. The X, Y, and Z vectors indicate the axes of the SCF.
As shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9, out of the three types of MEO satellites, only the slope of the SECM satellites (i.e., C29 and C30) was negative except for the ESA center, whereas the slopes of the other two types of satellites are positive. For BDS-3 SECM satellites, surface X has an area of 1.3 m2, while surface Z has a larger area of 2.6 m2. On the contrary, the X surface area of BDS-2 MEO and BDS-3 CAST satellites is larger than the area of the Z surface, with values of 3.8 and 3.4 m2, and 2.9 and 2.2 m2, respectively [38]. Compared with previous research, it was found that the slopes of SECM and Galileo (X area: 1.3 m2, Z area: 3.0 m2) satellites are negative [17], whereas the slopes of BDS-2 MEO, CAST, and GLONASS (X area: 4.2 m2, Z area: 1.7 m2) satellites are positive [39]. Thus, this phenomenon can be explained by the different shapes of satellites.
The slope of the ESA BDS-3 CAST orbit was similar to that of SECM satellites, both of which had a negative value that was close to 0. By comparing the strategies of ACs, we found that ESA and WU utilized a PBW model in their solutions, which differs from the approach used by other ACs. It was found that a proper PBW model can enhance the stability of SLR residuals. For instance, when the estimated PBW model was applied in ESA, the RMS of the SLR residuals of ™CAST and SECM satellites was 36 mm and 50 mm, respectively. The slopes of the CAST and SECM satellites were both −0.04 mm/deg, which is smaller than the slope of the WU CAST and SECM orbits of about −0.4 and 0.5 mm/deg. This phenomenon may be explained by the fact that ESA added a more accurate PBW model to the modeling of SRP, which is reflected in ESA’s BDS-3 satellite SLR residuals having the best statistical results.
4. Discussion
The POD strategy of BDS is in the research stage. It can be seen that BDS satellite precise orbit products still face some challenges from the view of SLR validation. Firstly, the BDS processing strategies and force models of various ACs are still inconsistent at present, and there is a discrepancy of about 10 mm between the precise orbit products among different ACs. Secondly, the orbit accuracy of different BDS constellations varies significantly. As an example, the difference in the RMS of SLR residuals between the orbits of BDS-3 CAST and BDS-3 SECM released by GFZ, WU, and ESA is about −13, −10, and 14 mm, respectively. This suggests that there are significant differences in the model adaptability of different BDS constellations, which may be the main challenge in improving BDS orbit accuracy. Furthermore, the pure empirical SRP models including ECOM and ECOM2 are not entirely applicable to BDS, whereas the estimated PBW model used by ESA can reduce the RMS of SLR residuals by 20 mm with regard to other ACs. Based on the results presented above, it is evident that there is still room for improvement in the non-conservative force modeling of BDS satellites, including but not limited to the accurate calibration of optical parameters of BDS satellites, the application of the modeling of ERP and AT for all BDS satellites, and considering some unmodeled non-conservative forces such as thermal radiation pressure. Fortunately, with the increasing number of observations tracked by ILRS and the continuous research of SLR technology for BDS, the modeling effect of BDS can be better evaluated and the accuracy of BDS orbit products can be further improved.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents a comparative analysis of SLR observations with regard to BDS satellite precise orbit products generated by CODE, GFZ, WU, and ESA as part of the IGS MGEX campaign. The analysis covers the period from February 2017 to March 2021.
The monthly number of SLR observations for MEO and IGSO satellites is around 250 and 150, respectively. CSPAD and MCP stations provide most of the observations, with roughly equal numbers for MCP observations and CSPAD observations of MEO satellites. For BDS-2 IGSO satellites, CSPAD observations outnumber MCP observations by a factor of two. However, there are only a few observations from PMT stations, which limits their ability to evaluate accuracy. This study primarily focuses on comparing the signature effects of CSPAD and MCP detectors.
The SLR residuals of IGSO satellites exhibit a greater dependence on nadir angle compared to MEO satellites, which can be attributed to the presence of more corner cubes on LRAs. The RMS of the SLR residuals of MCP stations is about 40 to 56 mm, which is about 5 mm smaller than that of CSPAD stations. As a representative of high-energy stations, Yarragadee provides most of the observations between MCP and PMT stations. The slope with regard to the nadir angle is approximately −1.0 and −3.5 mm/deg for MEO and IGSO satellites, respectively. Compared with Yarragadee, the slope of SLR residuals observed by Shanghai equipped with a single-photon detector is about −0.8 and −1.0 mm/deg, respectively. The correlation between SLR residuals and nadir angle of multi-photon stations is larger than that of single-photon stations, which may prove that the signature effect of multi-photon stations also exists in the SLR observations of BDS. The slope with regard to the nadir angle of BDS-3 CAST for single-photon and multi-photon stations is about 0.8 and 0.1 mm/deg, respectively, which may be caused by the material of the prism cubes or other components on LRAs. Considering the number and the quality consisting of signature effects for SLR stations, seven stations—five C-SPAD and two MCP station—can be regarded as high-performing stations. The results show that these stations can reduce the RMS of SLR residuals for all constellations by about 1 to 3 mm.
The RMS of the SLR residuals of CODE for the BDS-2 MEO and BDS-2 IGSO satellites is 56 and 65 mm, respectively. For GFZ, WU, and ESA, the resulting RMS of the SLR residuals are 61, 53, 51, and 65 mm; 62, 46, 52, 62 mm; 120, 51, 50, and 36 mm, for BDS-2 IGSO, BDS-2 MEO, BDS-3 CAST, and BDS-3 SECM, respectively. The mean offset of the SLR residuals varies significantly between ACs. Excluding the results for the BDS-2 satellites from ESA, the difference between the other three ACs is typically around 10 to 15 mm. This discrepancy is attributable to differences in both non-conservative force models and AC strategies for new GNSSs. Upon comparing the mean offset and RMS of each AC, it becomes evident that there are discrepancies. The RMS value above 110 mm suggests that ESA may have a modeling error with BDS-2 IGSO satellites. Additionally, GFZ and WU may have modeling defects with BDS-3 satellites due to the similarity in the slope with regard to elongation between BDS-3 MEO and BDS-2 IGSO. Through strategic analysis of the differences among ACs, it can be inferred that utilizing an appropriate PBW model could enhance the accuracy of SRP modeling and result in more consistent performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. and C.L.; methodology, X.L. and C.L.; software, C.L.; validation, C.L.; formal analysis, C.L.; investigation, C.L. and Y.Y.; resources, K.Z.; data curation, C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.L.; writing—review and editing, C.L. and Y.Y.; supervision, C.L.; project administration, X.L. and Y.Y.; funding acquisition, X.L. and Y.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41974027) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFB2501102).
Acknowledgments
We thank MGEX for providing precise orbit and earth rotation parameter products free of charge, which can be accessed at ftp://igs.ign.fr/pub/igs/products/ (accessed on 20 April 2023) and ftp://igs.gnsswhu.cn/pub/gnss/products/mgex/ (accessed on 20 April 2023). We also acknowledge ILRS for providing SLR observations, which can be accessed at ftp://edc.dgfi.tum.de/pub/slr/data/npt_crd/ (e.g., /beidou3m2/2021/beidou3m2_202101.npt for January 2021, accessed on 20 April 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, Y.; Tang, J.; Montenbruck, O. Chinese Navigation Satellite Systems. In Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 273–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSNO TARC Test and Assessment Research Center of China Satellite Navigation Office. Available online: http://csno-tarc.cn/system/constellation (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Montenbruck, O.; Rizos, C.; Weber, R.; Weber, G.; Neilan, R.; Hugentobler, U. Getting a grip on multi-GNSS: The international GNSS service MGEX campaign. GPS World 2013, 24, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlemann, M.; Gendt, G.; Ramatschi, M.; Deng, Z. GFZ Global Multi-GNSS Network and Data Processing Results//IAG 150 Years. In Proceedings of the IAG Scientific Assembly, Postdam, Germany, 1–6 September 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, T.A.; Otten, M.; Flohrer, C. Spreading the Usage of NAPEOS, the ESA Tool for Satellite Geodesy. In EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts; EGU: Vienna, Austria, 2012; p. 7099. [Google Scholar]
- Prange, L.; Dach, R.; Lutz, S.; Schaer, S.; Jaggi, A. The CODE MGEX Orbit and Clock Solution//IAG 150 Years. In Proceedings of the IAG Scientific Assembly, Postdam, Germany, 1–6 September 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, L.; Orliac, E.; Dach, R.; Arnold, D.; Beutler, G.; Schaer, S.; Jaggi, A. CODE’s five-system orbit and clock solution—The challenges of multi-GNSS data analysis. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Precise orbit determination for quad-constellation satellites at Wuhan University: Strategy, result validation, and comparison. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, K.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, G.; Xiong, Y. Precise orbit and clock products of Galileo, BDS and QZSS from MGEX since 2018: Comparison and PPP validation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U. Enhanced solar radiation pressure modeling for Galileo satellites. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlis, E.C. Comparison of GPS S/C orbits determined from GPS and SLR tracking data. Adv. Space Res. 1995, 16, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urschl, C.; Beutler, G.; Gurtner, W.; Hugentobler, U.; Schaer, S. Contribution of SLR tracking data to GNSS orbit determination. Adv. Space Res. 2007, 39, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, K. Galileo and QZSS precise orbit and clock determination using new satellite metadata. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajdel, R.; Sośnica, K.; Bury, G. A new online service for the validation of multi-GNSS orbits using SLR. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, G.; Rodríguez, J.; Altamimi, Z. Assessment of the accuracy of global geodetic satellite laser ranging observations and estimated impact on ITRF scale: Estimation of systematic errors in LAGEOS observations 1993–2014. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 1371–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sośnica, K.; Thaller, D.; Dach, R.; Steigenberger, P.; Beutler, G.; Arnold, D.; Jaggi, A. Satellite laser ranging to GPS and GLONASS. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 725–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sośnica, K.; Prange, L.; Kaźmierski, K.; Bury, G.; Drożdżewski, M.; Zajdel, R.; Hadas, T. Validation of Galileo orbits using SLR with a focus on satellites launched into incorrect orbital planes. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ILRS Study Group. LARGE: Laser Ranging to GNSS s/c Experiment Expanded SLR Tracking of GNSS Satellites. Available online: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/2014/GNSS_Pilot_Project_v2_20140311.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Lin, X.; Baojun, L.; Yingchun, L.; Sujie, X.; Tao, B. Satellite Geometry and Attitude Mode of BDS-3 MEO Satellites Developed by SECM. In Proceedings of the 31st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2018), Miami, FL, USA, 24–28 September 2018; pp. 1268–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, B.C.; Harris, I.B.; Beckman, T.J.; Reed, D.A.; Cook, D.A. Design and performances of laser retro-reflector arrays for Beidou navigation satellites and SLR observations. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, G.; Koidl, F. Maximizing the Output of SLR Station Graz: Tracking 140 Targets. In Proceedings of the 2015 ILRS Technical Workshop, Matera, Italy, 26–30 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman, M.R.; Degnan, J.J.; Bosworth, J.M. The international laser ranging service. Adv. Space Res. 2002, 30, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsubo, T.; Appleby, G.M. System-dependent center-of-mass correction for spherical geodetic satellites. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Assessment of precise orbit and clock products for Galileo, BeiDou, and QZSS from IGS Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX). GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IERS. IERS Conventions 2010: IERS Technical Note 36; Petit, G., Luzum, B., Eds.; Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, D.; Meindl, M.; Beutler, G.; Dach, R.; Schaer, S.; Lutz, S.; Prange, L.; Sośnica, K.; Mervart, L.; Jäggi, A. CODE’s new solar radiation pressure model for GNSS orbit determination. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamimi, Z.; Rebischung, P.; Métivier, L.; Collilieux, X. ITRF2014: A new release of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame modeling nonlinear station motions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 6109–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, V.B.; Prates, G.; Pavlis, E.C.; Pavlis, D.E.; Langley, R.B. Improved mapping functions for atmospheric refraction correction in SLR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 53-1–53-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, V.B.; Pavlis, E.C. High-accuracy zenith delay prediction at optical wavelengths. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L14602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ILRS International Laser Ranging Service. Available online: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/2012/COMPASS-I3_RRA_information.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- ILRS International Laser Ranging Service. Available online: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/2012/COMPASS-M3_RRA_information.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- ILRS International Laser Ranging Service. Available online: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/2015/ilrsmsr_1604_retro_v2-Compass-MS1.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Dong, X.; Han, X.; Fan, C.; Song, Q. Improvements of Changchun SLR Station. In Proceedings of the 20th International Workshop on Laser Ranging, Potsdam, Germany, 9–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Solano, C.; Hugentobler, U.; Steigenberger, P. Adjustable box-wing model for solar radiation pressure impacting GPS satellites. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 49, 1113–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Lyu, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, C.; Li, J. Precise orbit determination for BDS satellites. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Solano, C.J. Impact of Albedo Modelling on GPS Orbits; Technische Universität München: München, Germany, 2009; Available online: https://mediatum.ub.tum.de/doc/1368717/document.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Montenbruck, O.; Schmid, R.; Mercier, F.; Steigenberger, P.; Noll, C.; Fatkulin, R.; Kogure, S.; Ganeshan, A. GNSS satellite geometry and attitude models. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 1015–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. CSNO Satellite Information of BDS. Available online: http://en.beidou.gov.cn/SYSTEMS/Officialdocument/201912/P020200103556125703019.rar (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Fritsche, M.; Sośnica, K.; Rodriguez-Solano, C.J.; Steigenberger, P.; Wang, K.; Dietrich, R.; Dach, R.; Hugentobler, U.; Rothacher, M. Homogeneous reprocessing of GPS, GLONASS and SLR observations. J. Geod. 2014, 88, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).