Performance Assessment of Multi-GNSS PPP Ambiguity Resolution with LEO-Augmentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. LEO Constellation Design and Ground Observation Simulation
3. Methods
3.1. LEO-Enhanced GNSSs PPP
3.2. PPP-AR
4. Analysis
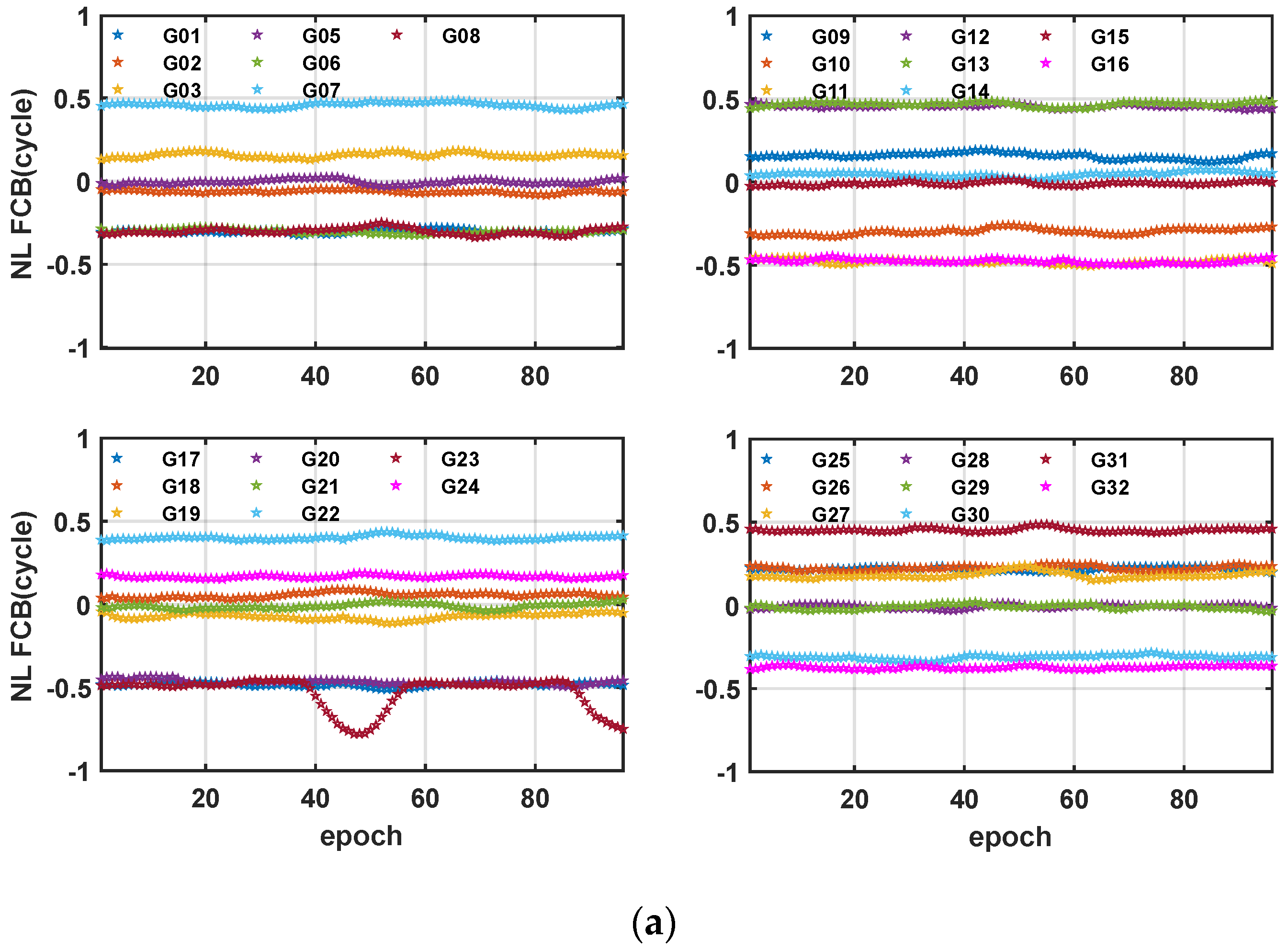
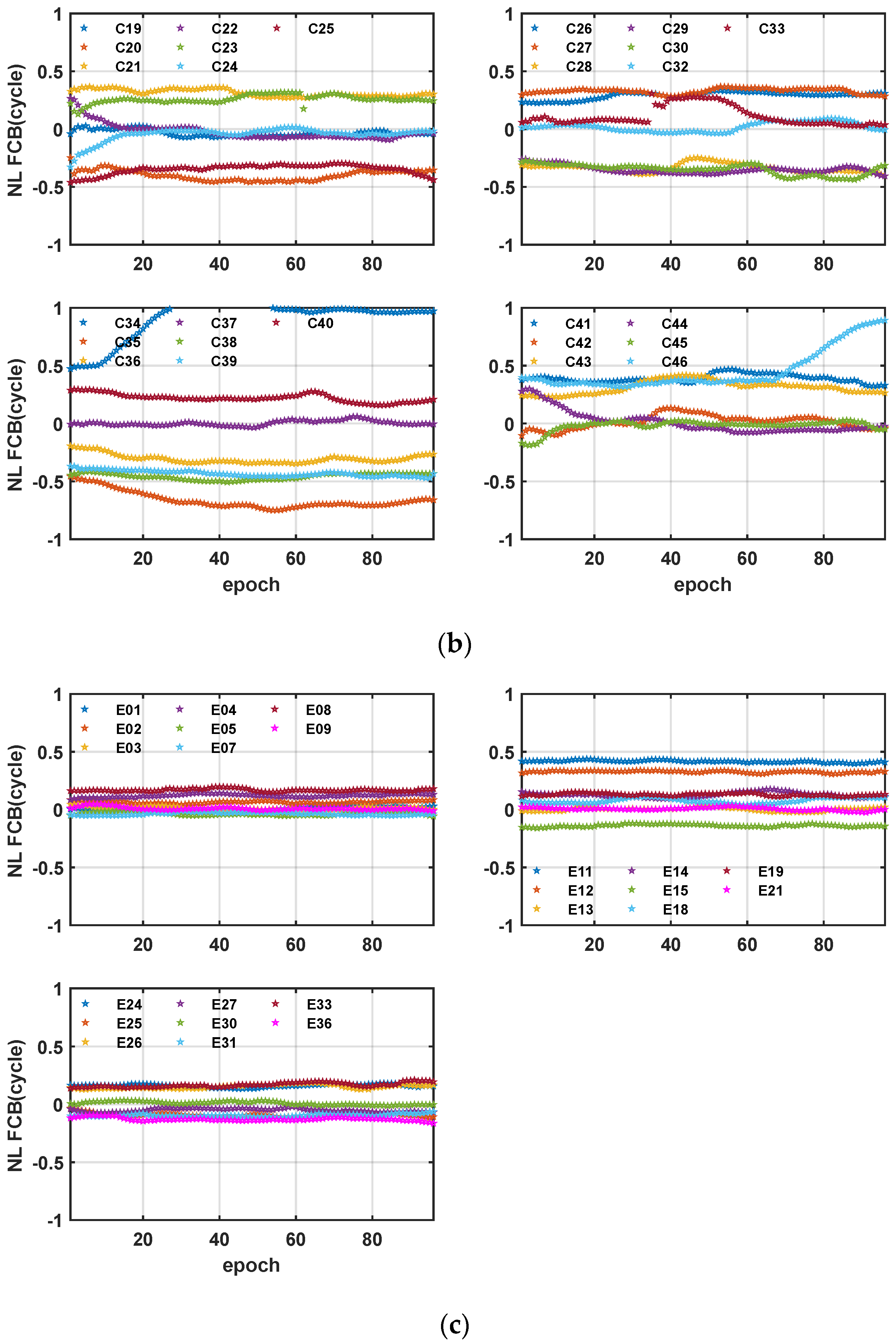
4.1. Quality of FCB Products
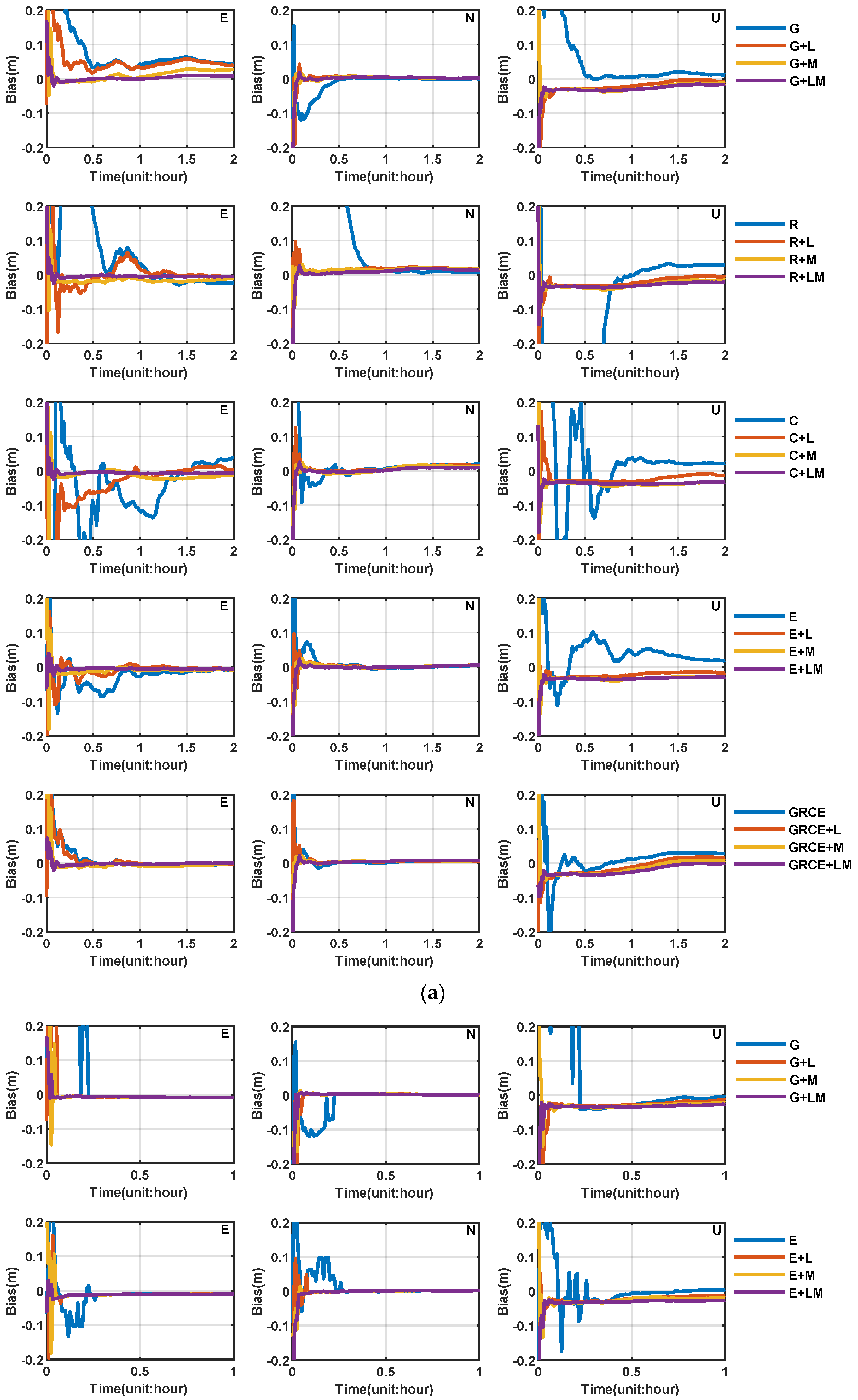
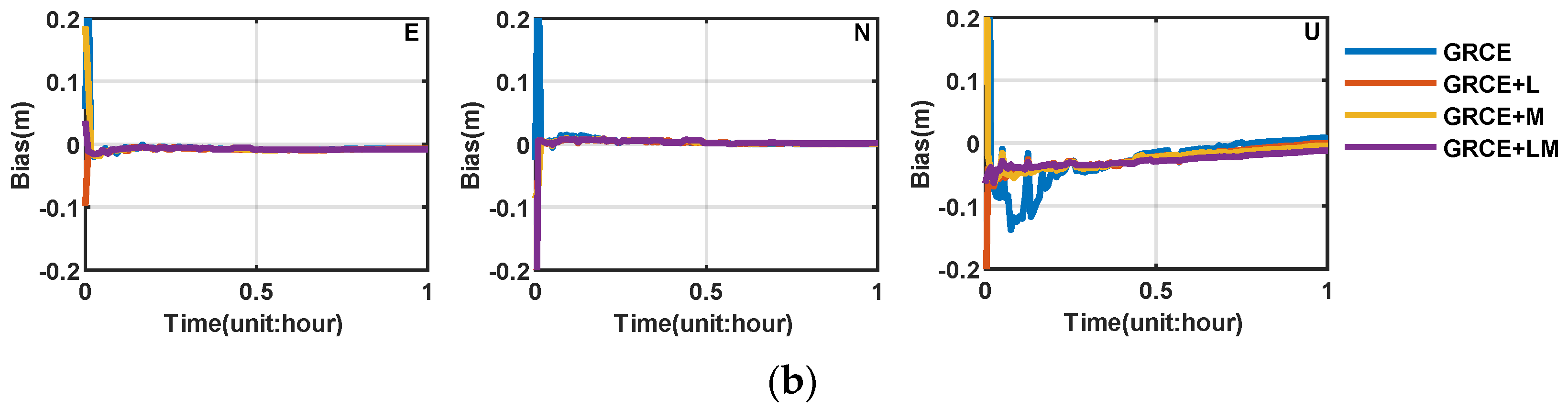
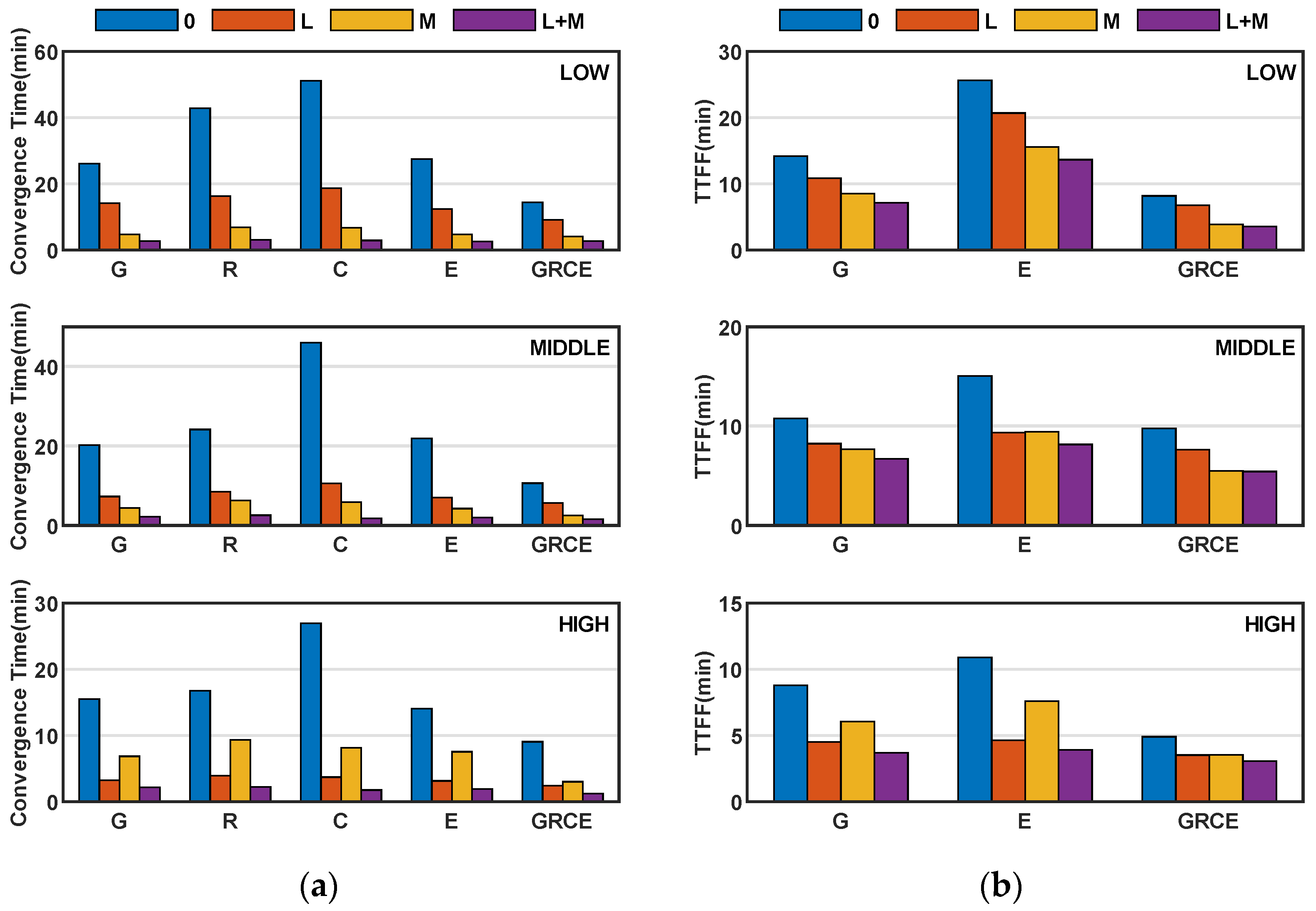
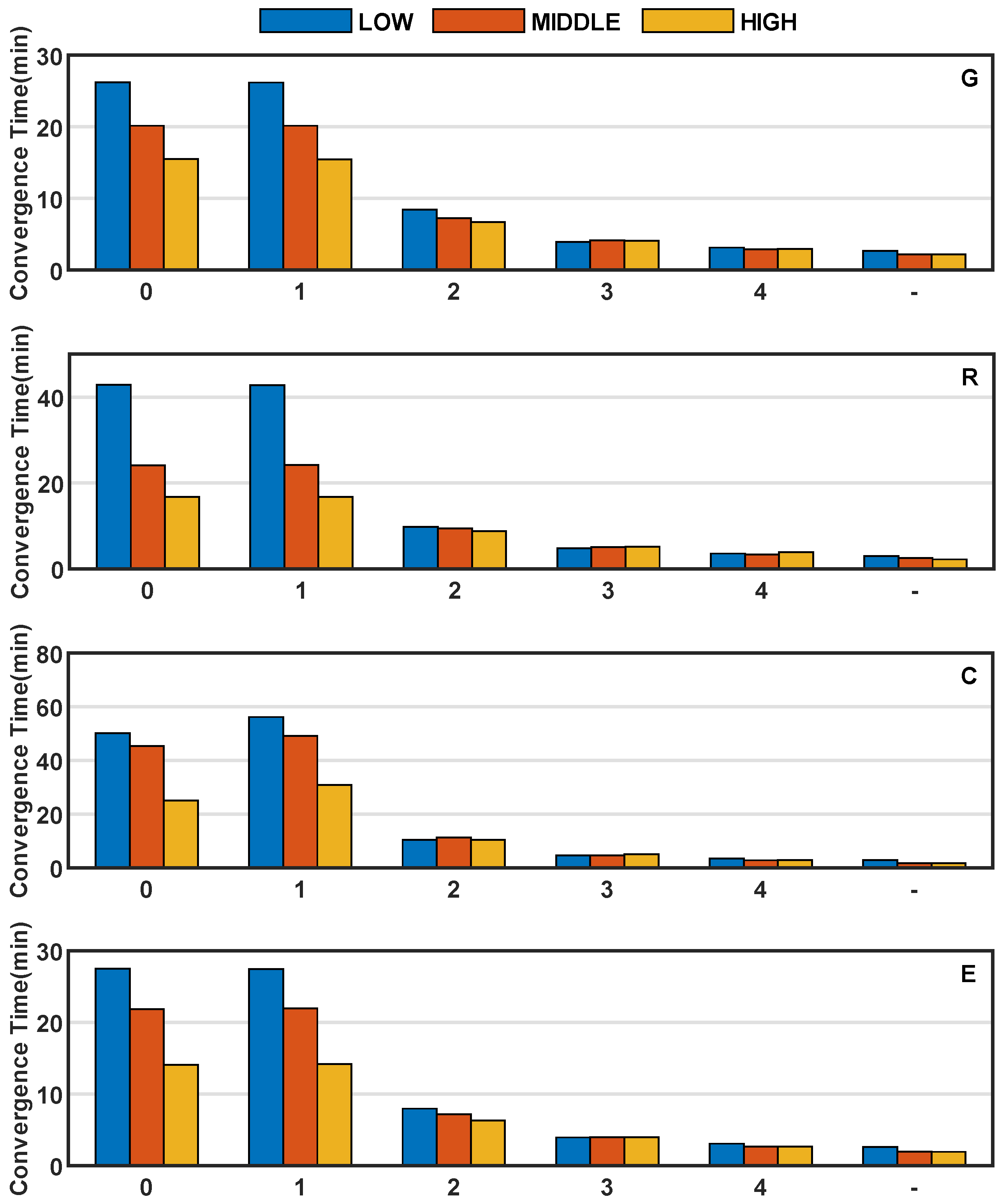
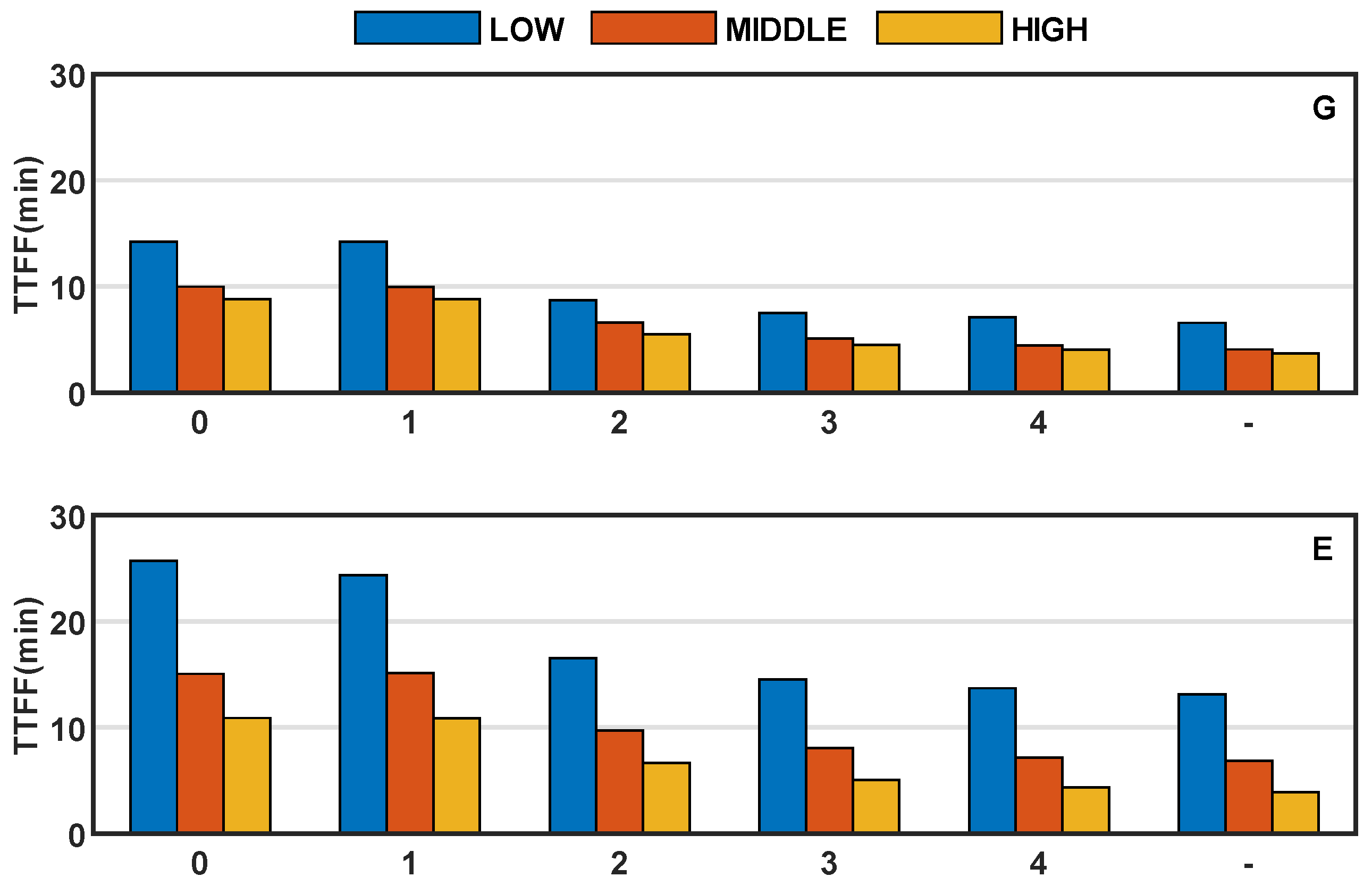
4.2. LEO-Enhanced PPP and PPP-AR
4.2.1. PPP and PPP-AR Enhanced with Different LEO Constellations
4.2.2. LEO-Enhanced PPP and PPP-AR in Different Latitudes
4.2.3. PPP and PPP-AR Enhanced by Different LEO Satellite Numbers
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, F.; Gong, X.; Jiang, X. GNSS High-Precision Augmentation for Autonomous Vehicles: Requirements, Solution, and Technical Challenges. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabor, M.J.; Nerem, R.S. GPS carrier phase AR using satellite-satellite single difference. In Proceedings of the 12th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (GPS 99), Nashville, TN, USA, 14–17 September 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, M.; Gendt, G.; Rothacher, M.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Resolution of GPS carrier phase ambiguities in precise point positioning (PPP) with daily observations. J. Geod. 2008, 82, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wübbena, G.; Schmitz, M.; Bagge, A. PPP-RTK: Precise point positioning using state-space representation in RTK networks. In Proceedings of the 18th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2005), Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–16 September 2005; pp. 2584–2594. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Khodabandeh, A. Review and principles of PPP-RTK methods. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C. Precise Point Positioning using Dual-Frequency GPS and GLONASS Measurements; University of Calgary: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tolman, B.W.; Kerkhoff, A.; Rainwater, D.; Munton, D.; Banks, J. Absolute precise kinematic positioning with GPS and GLONASS. In Proceedings of the 23th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2010), 21–24 September 2010; pp. 2565–2576. [Google Scholar]
- Jokinen, A.; Feng, S.; Schuster, W.; Ochieng, W.; Hide, C.; Moore, T.; Hill, C. GLONASS Aided GPS Ambiguity Fixed Precise Point Positioning. J. Navig. 2013, 66, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X. Integrating GPS and GLONASS to accelerate convergence and initialization times of precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegedor, J.; Øvstedal, O.; Vigen, E. Precise orbit determination and point positioning using GPS, Glonass, Galileo and BeiDou. J. Geod. Sci. 2014, 4, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Dai, X.; Ren, X.; Fritsche, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Accuracy and reliability of multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 607–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Wickert, J. Multi-GNSS phase delay estimation and PPP ambiguity resolution: GPS, BDS, GLONASS, Galileo. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 579–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Bock, Y. Triple-frequency GPS precise point positioning with rapid ambiguity resolution. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E. Precise Point Positioning using Triple-Frequency GPS Measurements. J. Navig. 2014, 68, 480–492. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. Three-frequency BDS precise point positioning ambiguity resolution based on raw observables. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Feng, G.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Ren, X. Triple-frequency PPP ambiguity resolution with multi-constellation GNSS: BDS and Galileo. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1105–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banville, S.; Collins, P.; Zhang, W.B.; Langley, R. Global and Regional Ionospheric Corrections for Faster PPP Convergence. Navigation 2014, 61, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychas, D.; Verhagen, S. Real-Time PPP-RTK Performance Analysis Using Ionospheric Corrections from Multi-Scale Network Configurations. Sensors 2020, 20, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, T.G.; Neish, A.M.; Walter, T.F.; Enge, P.K. Leveraging Commercial Broadband LEO Constellations for Navigation. In Proceedings of the 29th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2016), Portland, OR, USA, 12–16 September 2016; pp. 2300–2314. [Google Scholar]
- Enge, P.; Ferrell, B.; Bennet, J.; Whelan, D.; Gutt, G.; Lawrence, D. Orbital Diversity for Satellite Navigation. In Proceedings of the 25th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2012), Nashville, TN, USA, 17–21 September 2012; pp. 3834–3846. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Xu, T.; Guan, M.; Gao, F. LEO-constellation-augmented multi-GNSS real-time PPP for rapid re-convergence in harsh environments. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, M.; Lv, J.; Chang, J.; Dai, W.; Tong, K.; Zhu, M. Integrating GPS and LEO to accelerate convergence time of precise point positioning. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Proceeding (WCSP), Nanjing, China, 15–17 October 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, H.; Li, B.; Ge, M.; Zang, N.; Nie, L.; Shen, Y.; Schuh, H. Initial Assessment of Precise Point Positioning with LEO Enhanced Global Navigation Satellite Systems (LeGNSS). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Ma, F.; Li, X.; Lu, H.; Blan, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X. LEO constellation-augmented multi-GNSS for rapid PPP convergence. J. Geod. 2018, 93, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Ma, F.; Yuan, Y. Improved PPP ambiguity resolution with the assistance of multiple LEO constellations and signals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Pan, S.; Gao, C. BDS/GPS/LEO triple-frequency uncombined precise point positioning and its performance in harsh environments. Measurement 2020, 151, 107216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.G. Satellite constellations. J. Br. Interplanet. Soc. 1984, 37, 559–572. [Google Scholar]
- Saastamoinen, J. Atmospheric correction for the troposphere and stratosphere in radio ranging satellites. Use Artif. Satell. Geod. 1972, 15, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Böhm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kouba, J. A Guide to Using International GNSS Service (IGS) Products. 2009. Available online: http://igscb.jpl.nasa.gov/igscb/resource/pubs/UsingIGSProductsVer21.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- King, R.W. Documentation for the GAMIT GPS Analysis Software; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hatch, R. The synergism of GPS code and carrier measurements. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Satellite Doppler Positioning at Physical Sciences Laboratory of New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, NM, USA, 8–12 February 1982; pp. 1213–1231. [Google Scholar]
- Melbourne, W.G. The case for ranging in GPS-based geodetic systems. In Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Precise Positioning with the Global Positioning System, Rockville, MD, USA, 15–19 April 1985; pp. 373–386. [Google Scholar]
- Wübbena, G. Software developments for geodetic positioning with GPS using TI 4100 code and carrier measurements. In Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Precise Positioning with the Global Positioning System, Rockville, MD, USA, 15–19 April 1985; pp. 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.; Tu, R.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, R.; Fan, L.; Wang, S.; Lu, X. GNSS rapid precise point positioning enhanced by low Earth orbit satellites. Satell. Navig. 2023, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
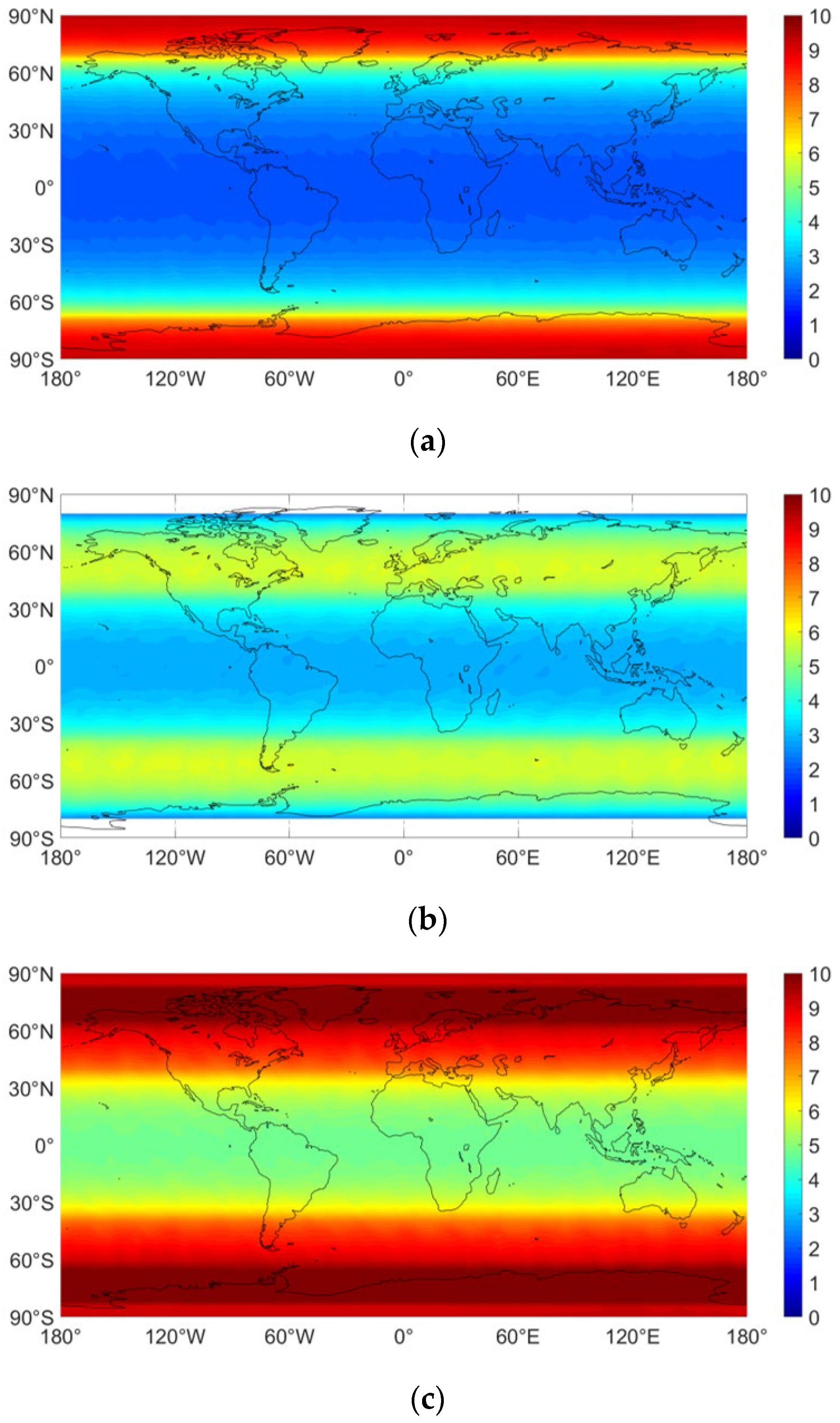




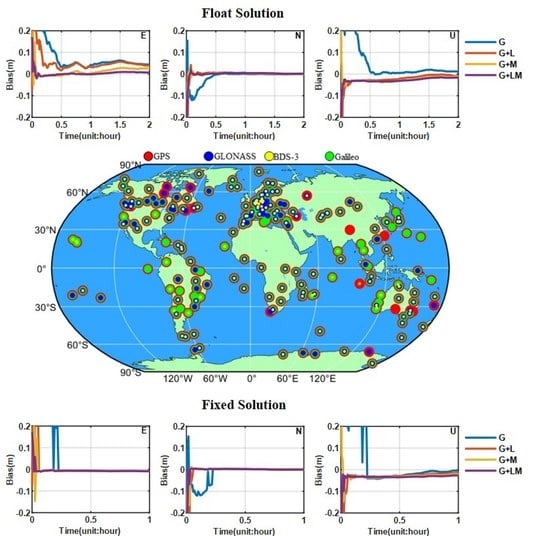
| Items | Data Processing Strategy |
|---|---|
| Frequency | GPS/LEO: L1/L2; BDS-3: B1/B3; Galileo: E1/E5a; GLONASS: G1/G2 |
| Sampling | 30 s |
| Observations | IF observations of carrier phase and code pseudorange |
| Cut-off elevation angle | Float: 7°; Fix: 10° |
| Ambiguities | LEO/GLONASS: constant estimation GPS/BDS-3/Galileo: constant estimation and ambiguities fixed |
| Receiver coordinates | Estimated as constants in static mode |
| Receiver clock offsets | Estimated as white noise |
| Tropospheric dry delay | Saastamoinen model + GMF projection function |
| Tropospheric wet delay in the zenith direction | LEO: Saastamoinen model correction GPS/GLONASS/BDS-3/Galileo: estimated by random walk |
| Ionospheric delay | Eliminated by IF observations |
| Satellite orbit and clock | Precise products |
| Satellite and receiver antenna phase center, and other modellable errors | Model correction |
| Constellations | Float Solution/cm | Fixed Solution/cm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | N | U | E | N | U | |
| G G+L G+M G+L+M | 0.3560 0.3254 0.2390 0.2130 | 0.2523 0.2381 0.2334 0.2220 | 0.8695 0.8139 0.7251 0.7103 | 0.3554 0.3378 0.2920 0.2668 | 0.2549 0.2413 0.2366 0.2239 | 0.8803 0.8245 0.7302 0.7131 |
| R R+L R+M R+L+M | 0.3214 0.2938 0.2727 0.2397 | 0.3072 0.2787 0.3086 0.2948 | 0.9848 0.8455 0.7377 0.7233 | |||
| C C+L C+M C+L+M | 0.8484 0.6016 0.4335 0.2925 | 0.5709 0.3748 0.4611 0.3811 | 2.0243 1.1799 0.8451 0.7211 | |||
| E E+L E+M E+L+M | 0.2628 0.2388 0.2374 0.2150 | 0.2755 0.2520 0.2860 0.2732 | 1.0658 0.9140 0.7660 0.7283 | 0.2447 0.2337 0.2245 0.2066 | 0.2740 0.2518 0.2810 0.2703 | 1.0661 0.9179 0.7712 0.7313 |
| GRCE GRCE+L GRCE+M GRCE+L+M | 0.2294 0.2173 0.2094 0.2020 | 0.2844 0.2787 0.2891 0.2786 | 1.0538 0.9864 0.8848 0.8171 | 0.2309 0.2204 0.2118 0.2056 | 0.2830 0.2781 0.2887 0.2777 | 1.0593 0.9915 0.8895 0.8214 |
| +0 +L +M +L+M | 0.4036 0.3354 0.2784 0.2324 | 0.3381 0.2845 0.3156 0.2899 | 1.1996 0.9479 0.7917 0.7400 | 0.2770 0.2640 0.2428 0.2263 | 0.2706 0.2571 0.2688 0.2573 | 1.0019 0.9113 0.7970 0.7553 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Yao, W.; Tu, R.; Du, Y.; Liu, M. Performance Assessment of Multi-GNSS PPP Ambiguity Resolution with LEO-Augmentation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15122958
Li Q, Yao W, Tu R, Du Y, Liu M. Performance Assessment of Multi-GNSS PPP Ambiguity Resolution with LEO-Augmentation. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(12):2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15122958
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qin, Wanqiang Yao, Rui Tu, Yanjun Du, and Mingyue Liu. 2023. "Performance Assessment of Multi-GNSS PPP Ambiguity Resolution with LEO-Augmentation" Remote Sensing 15, no. 12: 2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15122958
APA StyleLi, Q., Yao, W., Tu, R., Du, Y., & Liu, M. (2023). Performance Assessment of Multi-GNSS PPP Ambiguity Resolution with LEO-Augmentation. Remote Sensing, 15(12), 2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15122958