Layered SOTIF Analysis and 3σ-Criterion-Based Adaptive EKF for Lidar-Based Multi-Sensor Fusion Localization System on Foggy Days
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A layered quantitative SOTIF analysis method was proposed for the LMSFLS in foggy environments based on ISO 21448. The method includes static detection analysis for LiDAR and localization performance analysis for LMSFLS. Based on this, we identified the potential SOTIF-related harms and quantitative triggering conditions of LMSFLS on foggy days by quantitatively analyzing the component-level, system-level, and vehicle-level functional insufficiencies caused by fog in different concentrations.
- A functional modification strategy was proposed to address the SOTIF-related harms of LMSFLS. In this strategy, visibility recognition was first introduced to identify whether LiDAR odometry is interfered with by fog. Subsequently, the 3σ-criterion-based variance mismatch degree grading adaptive extended Kalman filter (3σ-VMDG-AEKF) was employed to accurately isolate abnormal measurement information in LiDAR odometry through sequential filtering and variance mismatch degree grading.
2. Related Work
2.1. Effects of Adverse Weather on LiDAR
2.2. LiDAR-Based Multi-Sensor Fusion Localization
2.3. SOTIF of the Automated Driving Function
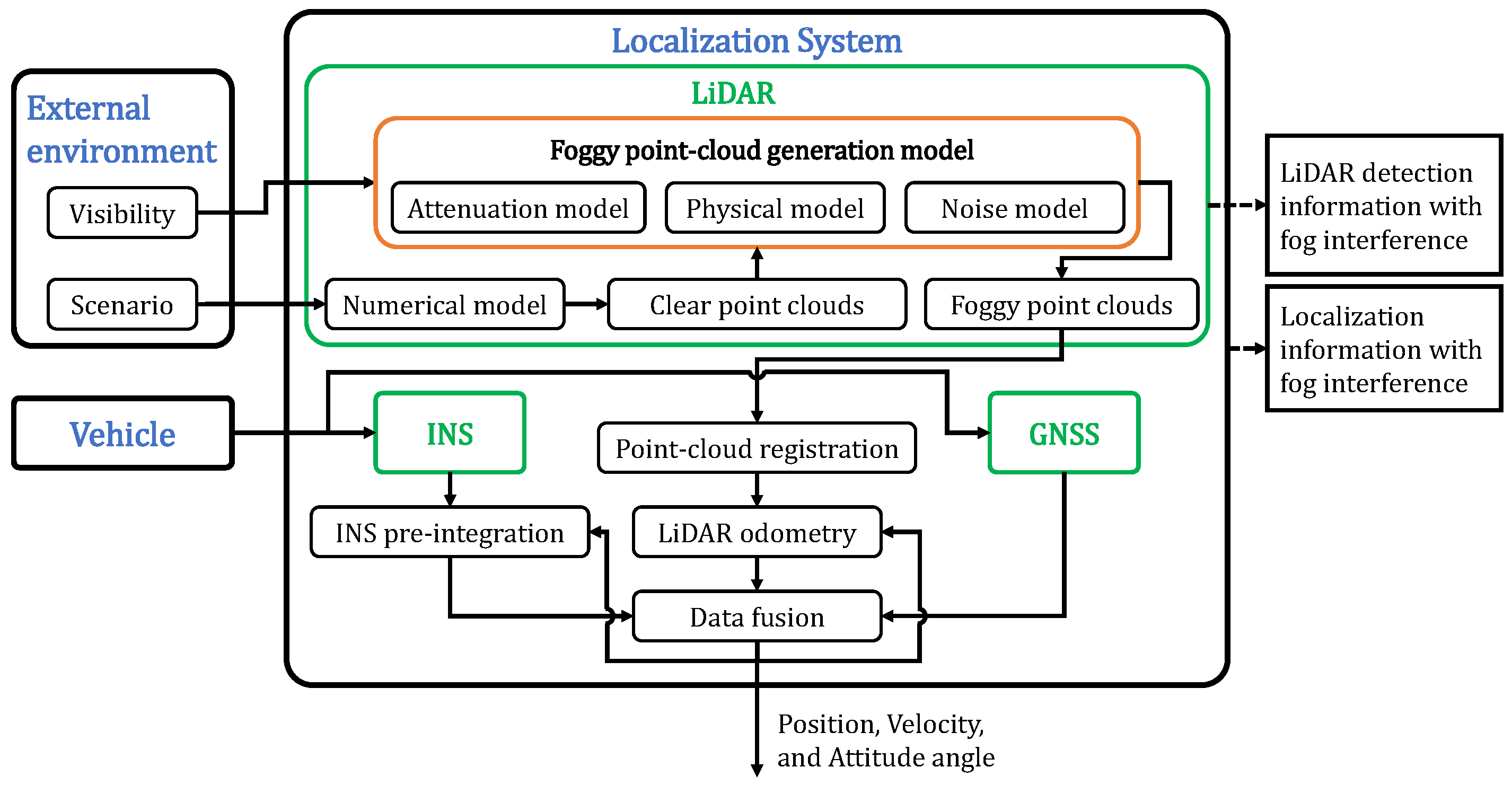
3. Fog Interference Simulation Method of LMSFLS
3.1. The Architecture of LMSFLS with Fog Interference Introduced
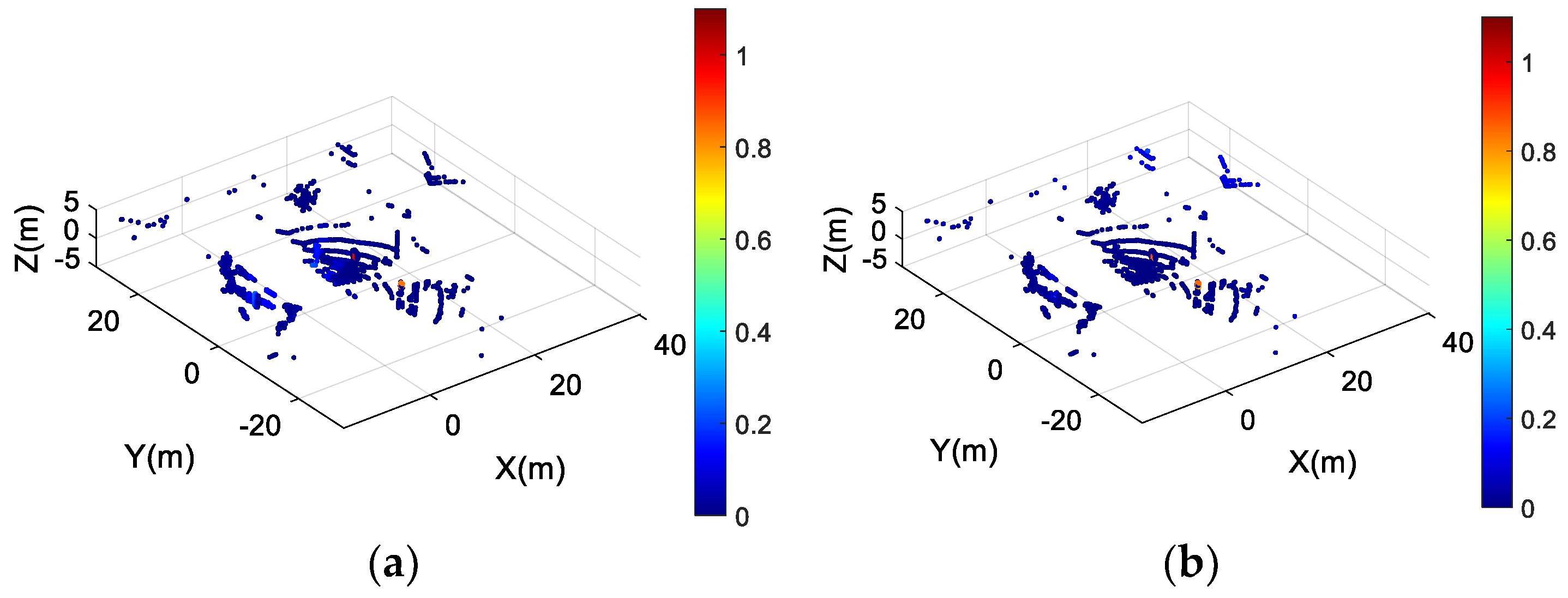
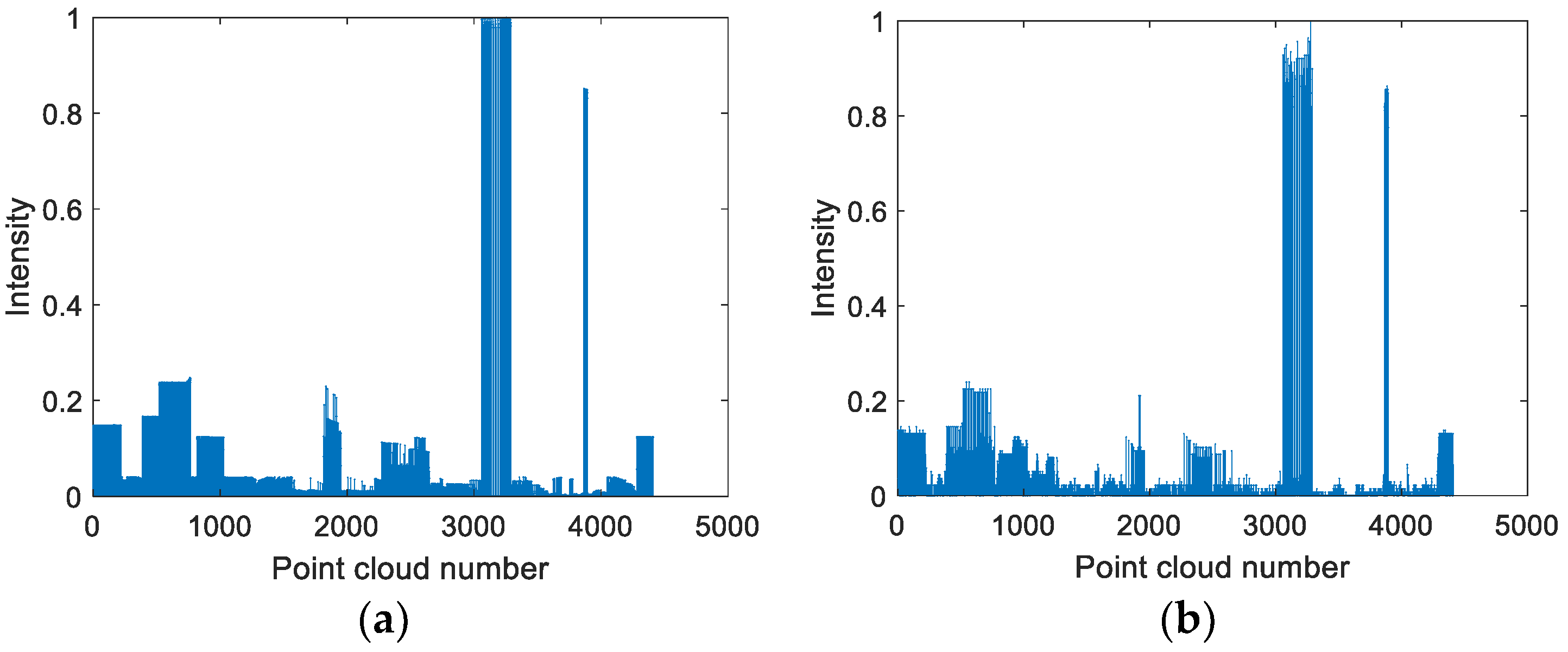
3.2. Foggy Point Clouds Generation
| Algorithm 1: Generation of foggy point clouds | |||
| 1 | Initialization: points | ||
| 2 | for | do | |
| 3 | using (A9) | ||
| 4 | using (A10) | ||
| 5 | using (A17) | ||
| 6 | if | then | |
| 7 | |||
| 8 | else | ||
| 9 | The point is invalid | ||
| 10 | end if | ||
| 11 | end for | ||
| 12 | return | One frame of foggy point cloud | |
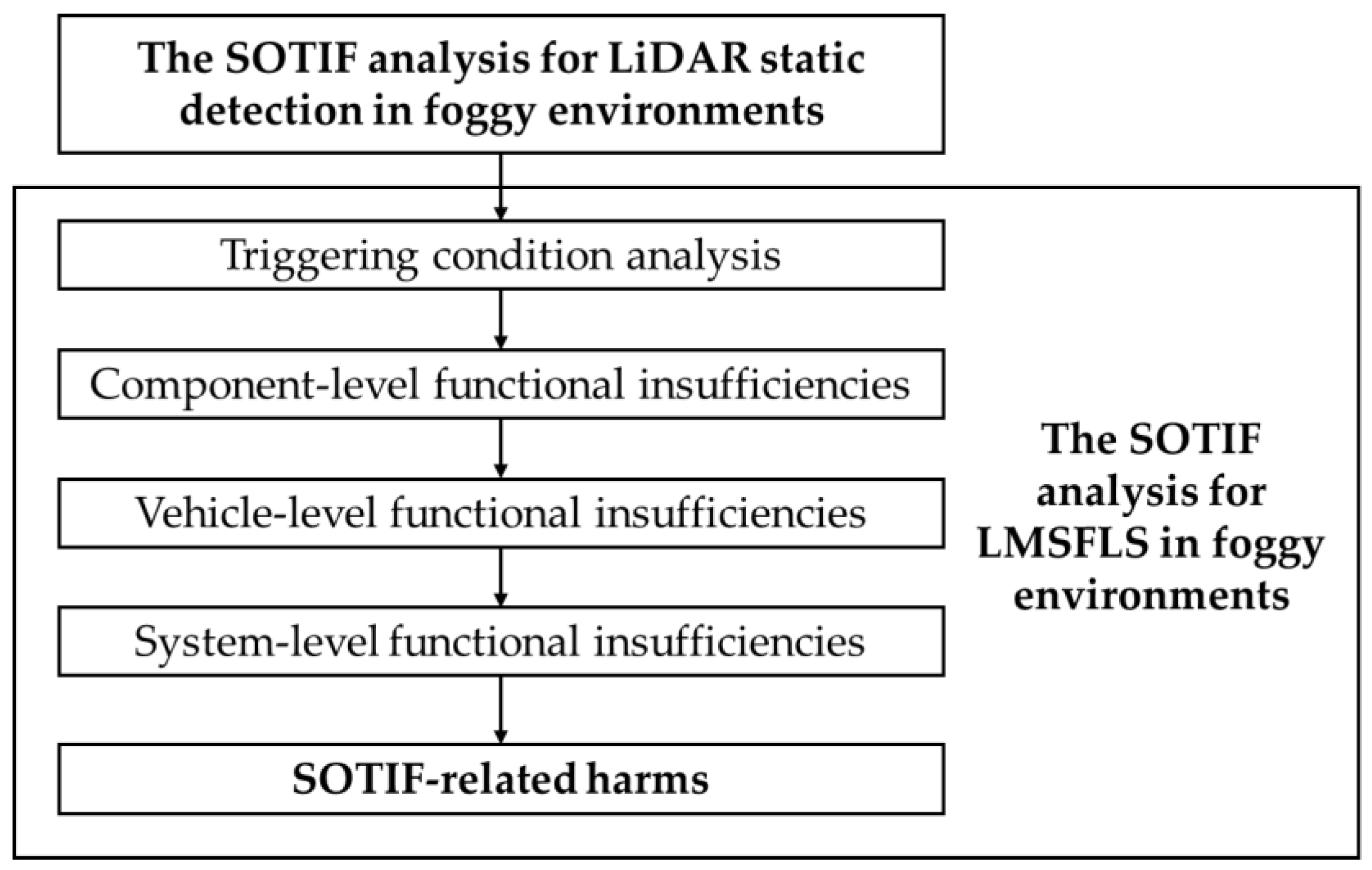
4. Fog Simulation-Based Layered SOTIF Analysis
4.1. The Analysis for LiDAR Static Detection in Foggy Environments
- Under the condition that the visibility remains constant, the and of the echo signals decreases and increases, respectively, with an increase in the LiDAR detection range.
- When the LiDAR detection range is constant, the decreases and increases with a decrease in visibility. The smaller the visibility, the faster the decrease rate of , and the quicker the increase rate of .
- With a reduction in visibility, the maximum detection range of LIDAR decreases. When the visibility was 10 km, 1 km, 0.8 km, 0.6 km, 0.5 km, 0.4 km, 0.3 km, and 0.2 km, the corresponding maximum detection ranges were 120 m, 88 m, 83 m, 76 m, 71 m, 65.5 m, 58 m, and 48 m.
- The number of point cloud clusters of obstacles in foggy point clouds decreases with reduced visibility.
4.2. The SOTIF Analysis for LMSFLS in Foggy Environments
- Simulation scenarios and parameters setting
- 2.
- Quantitative triggering condition analysis
- 3.
- Functional insufficiencies analysis
- 4.
- SOTIF-related harms analysis
5. Functional Modification Strategy
5.1. Strategy Process
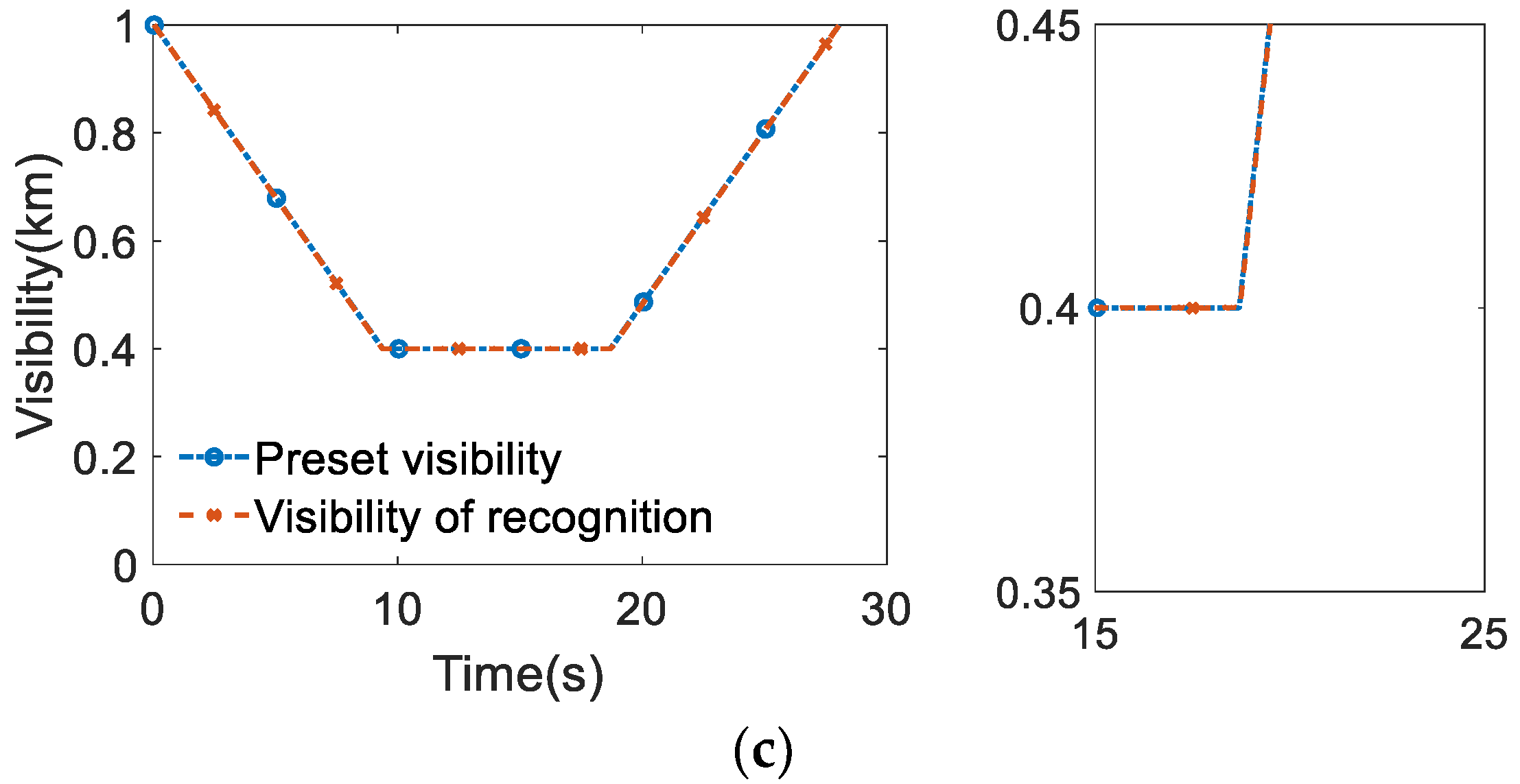
5.2. Recognition of Visibility
5.3. 3σ-Criterion-Based Variance Mismatch Degree Grading Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter
| Algorithm 2:-VMDG-AEKF | |||
| 1 | Initialization: | ||
| 2 | for | ||
| 3 | using (6) | ||
| 4 | using (7) | ||
| 5 | if | ||
| 6 | and using (13) and (14) | ||
| 7 | else if | ||
| 8 | using (11) | ||
| 9 | and using (12)–(14) | ||
| 10 | else | ||
| 11 | |||
| 12 | end if | ||
| 13 | end for | ||
| 14 | Return | and | |
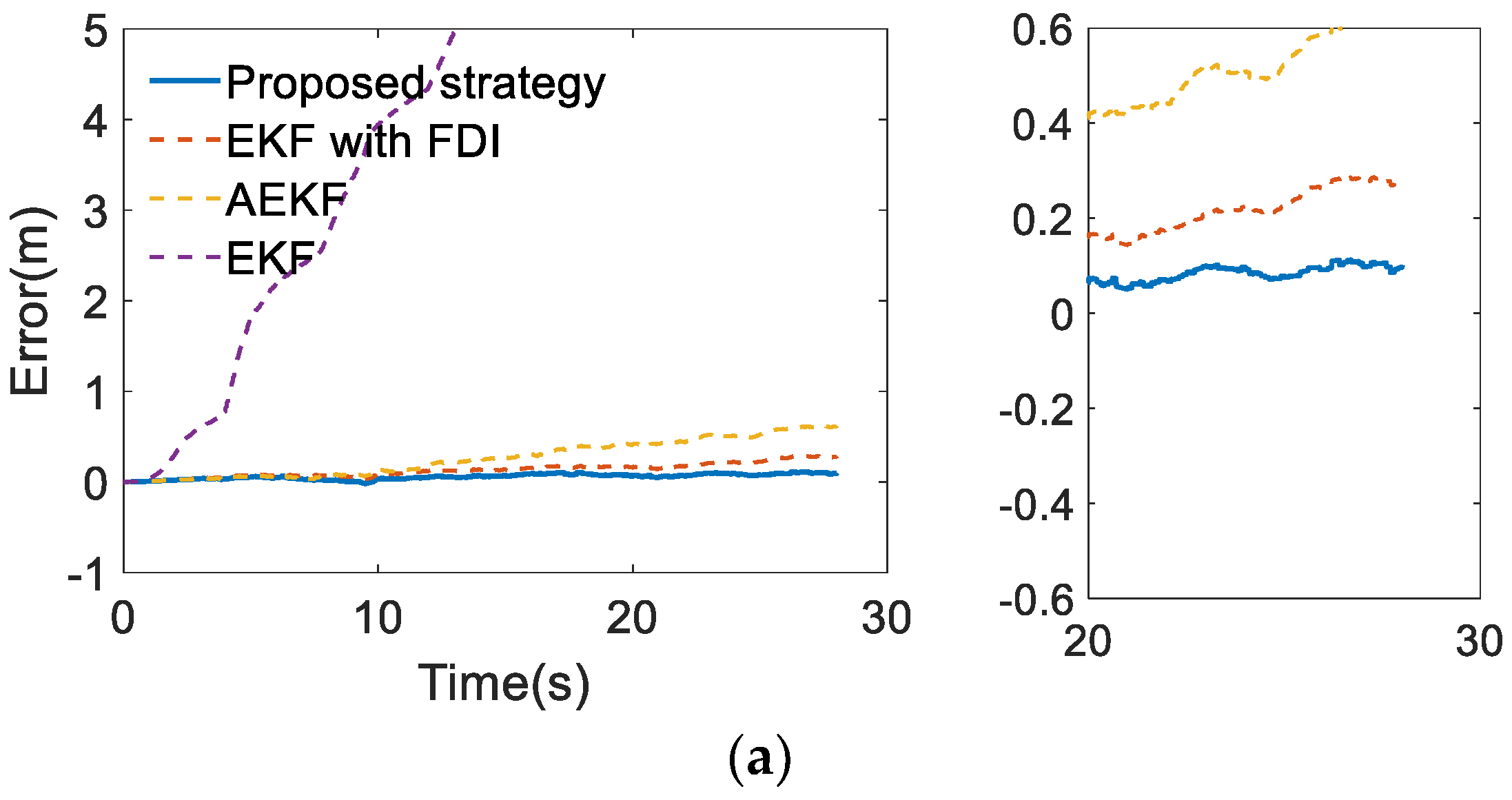
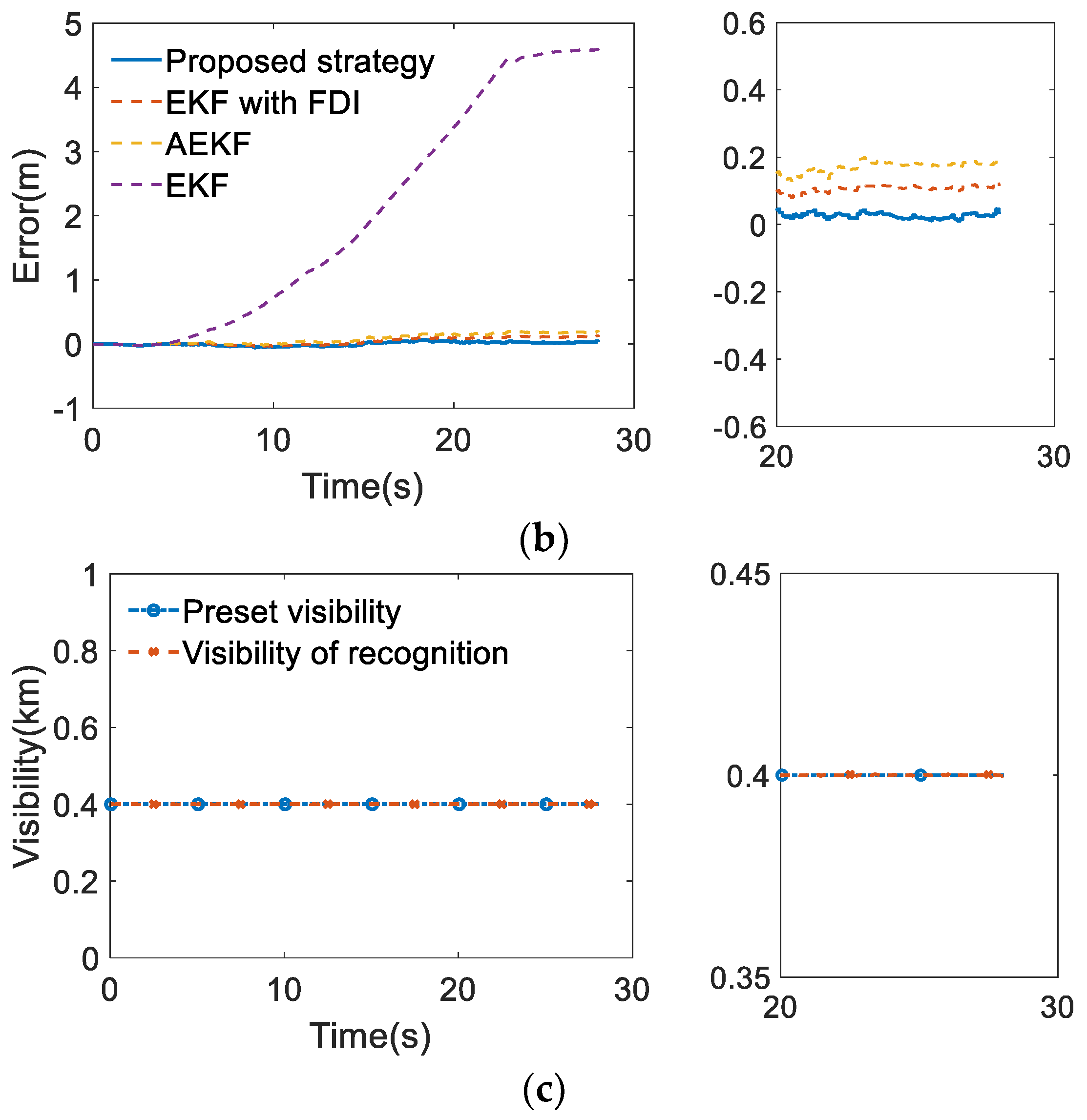
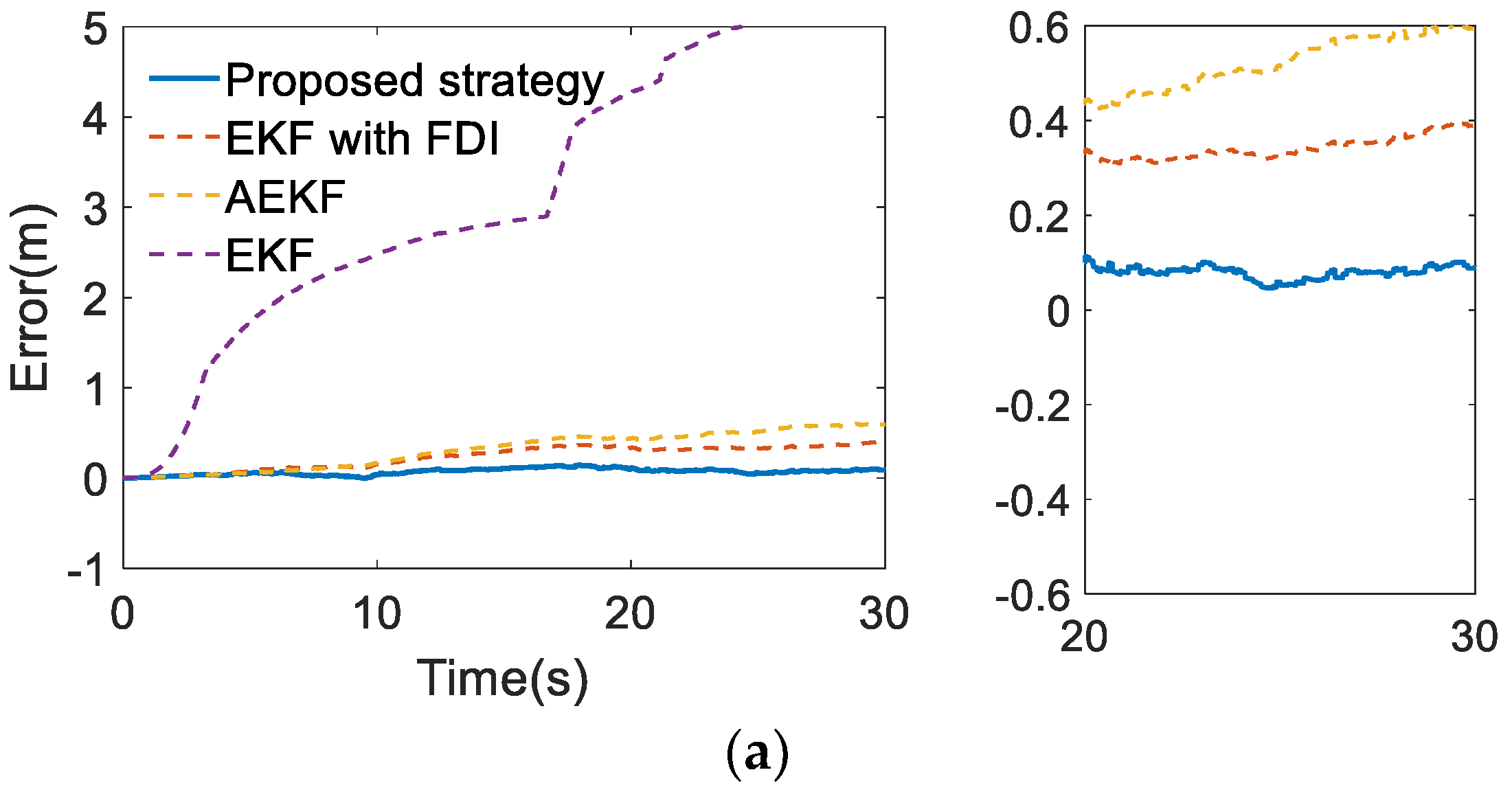
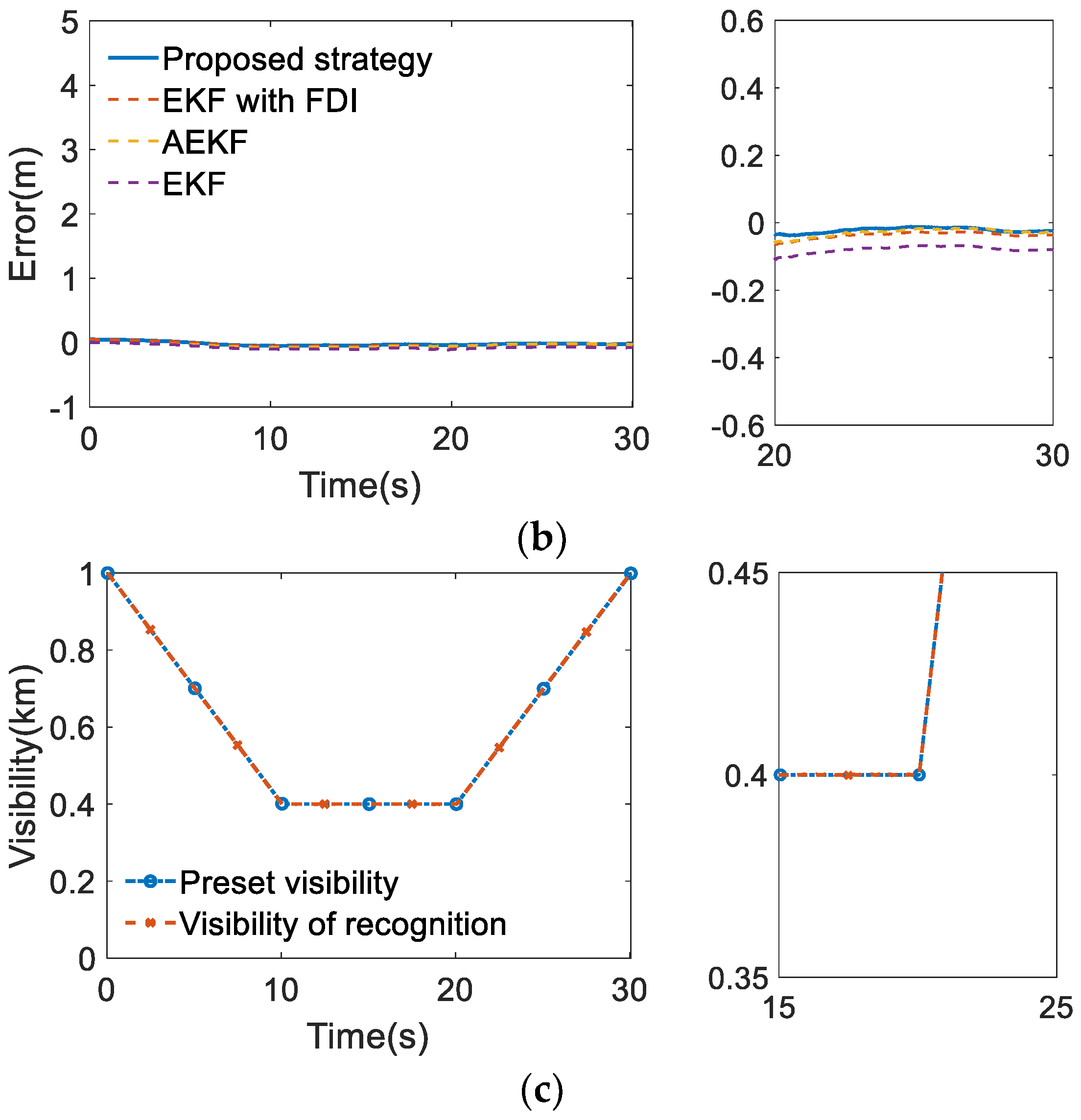
6. Validation of Functional Modification Strategy
6.1. Design of Validation Schemes
6.2. Analysis of Simulation Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. LiDAR Odometry
Appendix A.2. INS Pre-Integration
Appendix A.3. Data Fusion
Appendix B
- 1.
- To calculate the valid signal for each point . The formula is as follows:where is the number of valid signal photons, is the pulse time, is the spatial resolution, is the speed of light, is the energy of a single photon, is Planck’s constant, and is the quantum efficiency of the receiver.
- 2.
- To calculate the sunlight noise signal, which is given below:where is the number of background light photons received by the receiver, is the brightness of the sky background radiation, is the viewing angle of the receiving telescope, is the bandwidth of the optical filter, and is the total transmittance of the optical receiver system.
- 3.
- To calculate the dark counting signal. It can be expressed as follows:where is the number of dark counts and is the dark-counting rate of the laser receiver.
- 4.
- When combining steps 1–3, we can calculate the of each echo signal using the following formula [47]:where is the detector noise factor.
- 5.
- If the of point, is greater than , its standard deviation has the following relationship with [47]:where the is the smallest of the echo signals that can be received by LiDAR.
References
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Niu, Q. Multi-Sensor Fusion in Automated Driving: A Survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 2847–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorai, P.; Eskandarian, A.; Kim, Y.-K.; Mehr, G. State Estimation and Motion Prediction of Vehicles and Vulnerable Road Users for Cooperative Autonomous Driving: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 16983–17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Cao, C.; Wang, W.; Ran, Y.; Tan, Z.; Luo, M. A Review of Multi-Sensor Fusion SLAM Systems Based on 3D LIDAR. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, C.; Shang, G.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, C.; Hu, K. SLAM Overview: From Single Sensor to Heterogeneous Fusion. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; You, X.; Chen, L.; Tian, J.; Tang, F.; Zhang, L. A Scalable and Accurate De-Snowing Algorithm for LiDAR Point Clouds in Winter. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldibaja, M.; Yanase, R.; Kuramoto, A.; Kim, T.H.; Yoneda, K.; Suganuma, N. Improving Lateral Autonomous Driving in Snow-Wet Environments Based on Road-Mark Reconstruction Using Principal Component Analysis. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2021, 13, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Carballo, A.; Yang, H.; Takeda, K. Autonomous Driving in Adverse Weather Conditions: A Survey. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.08936. [Google Scholar]
- Hespel, L.; Riviere, N.; Huet, T.; Tanguy, B.; Ceolato, R. Performance Evaluation of Laser Scanners through the Atmosphere with Adverse Condition. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Electro-Optical Remote Sensing, Photonic Technologies, and Applications V, Prague, Czech Republic, 19–22 September 2011; pp. 64–78. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 21448; Road Vehicles—Safety of the Intended Functionality. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Yoneda, K.; Suganuma, N.; Yanase, R.; Aldibaja, M. Automated Driving Recognition Technologies for Adverse Weather Conditions. IATSS Res. 2019, 43, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, S.; Ding, M.; Smith, D.; Tyler, P.; Rakotoarivelo, T.; Kaafar, M.A. The Impact of Adverse Weather Conditions on Autonomous Vehicles: How Rain, Snow, Fog, and Hail Affect the Performance of a Self-Driving Car. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2019, 14, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasshofer, R.H.; Spies, M.; Spies, H. Influences of Weather Phenomena on Automotive Laser Radar Systems. Adv. Radio Sci. 2011, 9, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannheim, C.; Icking, C.; Mäder, M.; Sallis, P. Weather Detection in Vehicles by Means of Camera and LIDAR Systems. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computational Intelligence, Communication Systems and Networks, Tetova, Macedonia, 27–29 May 2014; pp. 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Hahner, M.; Sakaridis, C.; Dai, D.; Van Gool, L. Fog Simulation on Real LiDAR Point Clouds for 3D Object Detection in Adverse Weather. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 15283–15292. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, B.; Deng, W.; Sun, B. Method and Applications of Lidar Modeling for Virtual Testing of Intelligent Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 2990–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutila, M.; Pyykönen, P.; Ritter, W.; Sawade, O.; Schäufele, B. Automotive LIDAR Sensor Development Scenarios for Harsh Weather Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1–4 November 2016; pp. 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Bijelic, M.; Gruber, T.; Ritter, W. A Benchmark for Lidar Sensors in Fog: Is Detection Breaking Down? In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Changshu, China, 26–30 June 2018; pp. 760–767. [Google Scholar]
- Kutila, M.; Pyykönen, P.; Holzhüter, H.; Colomb, M.; Duthon, P. Automotive LiDAR Performance Verification in Fog and Rain. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 1695–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Heinzler, R.; Schindler, P.; Seekircher, J.; Ritter, W.; Stork, W. Weather Influence and Classification with Automotive Lidar Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Paris, France, 9 June 2019; pp. 1527–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Duthon, P.; Colomb, M.; Ibanez-Guzman, J. What Happens for a ToF LiDAR in Fog? IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 6670–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Li, Y.; Ruichek, Y.; Yan, Z. Performance Modeling a Near-Infrared ToF LiDAR Under Fog: A Data-Driven Approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 11227–11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Meng, Z.; Han, X.; Li, H.; Tsukiji, T.; Xu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J. Automated Driving Systems Data Acquisition and Processing Platfor. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.13425. [Google Scholar]
- Ghallabi, F.; El-Haj-Shhade, G.; Mittet, M.-A.; Nashashibi, F. LIDAR-Based Road Signs Detection For Vehicle Localization in an HD Map. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Paris, France, 9–12 June 2019; pp. 1484–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.-C.; Tartavull, I.; Bârsan, I.A.; Wang, S.; Bai, M.; Mattyus, G.; Homayounfar, N.; Lakshmikanth, S.K.; Pokrovsky, A.; Urtasun, R. Exploiting Sparse Semantic HD Maps for Self-Driving Vehicle Localization. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3 November 2019; pp. 5304–5311. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, Y.; Seo, S.-W.; Kim, S.-W. Curb Detection and Tracking in Low-Resolution 3D Point Clouds Based on Optimization Framework. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 3893–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fang, J.; Dai, X.; Zhang, H.; Vlacic, L. Intelligent Vehicle Self-Localization Based on Double-Layer Features and Multilayer LIDAR. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2020, 5, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, N.; Ritter, C.-N.; Goehring, D.; Rojas, R. Robust LiDAR Feature Localization for Autonomous Vehicles Using Geometric Fingerprinting on Open Datasets. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 2761–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Quijano, K.; Crawford, M.M. YOLOv5-Tassel: Detecting Tassels in RGB UAV Imagery With Improved YOLOv5 Based on Transfer Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8085–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wang, Y.; Ding, X.; Tang, L.; Huang, S.; Xiong, R. 3D LiDAR-Based Global Localization Using Siamese Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 1380–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wan, G.; Hou, S.; Song, S. L3-Net: Towards Learning Based LiDAR Localization for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 6382–6391. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Vizzo, I.; Läbe, T.; Behley, J.; Stachniss, C. Range Image-Based LiDAR Localization for Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 30 May 2021; pp. 5802–5808. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, L.; Xia, X.; Lu, Y.; Liu, W.; Gao, L.; Song, S.; Yu, Z. IMU-Based Automated Vehicle Body Sideslip Angle and Attitude Estimation Aided by GNSS Using Parallel Adaptive Kalman Filters. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 10668–10680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xiong, L.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Gao, L.; Xu, N.; Yu, Z. Estimation on IMU Yaw Misalignment by Fusing Information of Automotive Onboard Sensors. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 162, 107993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Hashemi, E.; Xiong, L.; Khajepour, A. Autonomous Vehicle Kinematics and Dynamics Synthesis for Sideslip Angle Estimation Based on Consensus Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2023, 31, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubača, J.; Stolz, M.; Watzenig, D. Extended H∞ Filter Adaptation Based on Innovation Sequence for Advanced Ego-Vehicle Motion Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 3rd Connected and Automated Vehicles Symposium (CAVS), Victoria, BC, Canada, 18 November 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Maaref, M.; Khalife, J.; Kassas, Z.M. Lane-Level Localization and Mapping in GNSS-Challenged Environments by Fusing Lidar Data and Cellular Pseudoranges. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2019, 4, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.; Winkler, B.; Grubmüller, S.; Watzenig, D. Identification of Performance Limitations of Sensing Technologies for Automated Driving. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Connected Vehicles and Expo (ICCVE), Graz, Austria, 4–8 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jianyu, D.; Zhang, H. Model-Based Systemic Hazard Analysis Approach for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles and Case Study Application in Automatic Emergency Braking System. SAE Intl. J. CAV 2021, 4, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaicenavicius, J.; Wiklund, T.; Grigaite, A.; Kalkauskas, A.; Vysniauskas, I.; Keen, S.D. Self-Driving Car Safety Quantification via Component-Level Analysis. SAE Intl. J. CAV 2021, 4, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, X.; He, X.; Li, P.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, D. Research on Safety of the Intended Functionality of Automobile AEB Perception System in Typical Dangerous Scenarios of Two-Wheelers. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2022, 173, 106709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulazim, A.; Elbahaey, M.; Mohamed, A. Putting Safety of Intended Functionality SOTIF into Practice; SAE Technical Paper 2021-01-0196; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA; pp. 1–11.
- Yan, M.; Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Liang, X.; Cai, B. Human–Machine Cooperative Control of Intelligent Vehicles for Lane Keeping—Considering Safety of the Intended Functionality. Actuators 2021, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Shang, S.; Haifeng, C.; Zhang, K.; Deng, W.; Zhang, X.; Yu, F. Control Model of Automated Driving Systems Based on SOTIF Evaluation; SAE Technical Paper 2020-01-1214; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 2900–2906. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, A.; Xing, X.; Zhou, T.; Chen, J. A Safety Analysis and Verification Framework for Autonomous Vehicles Based on the Identification of Triggering Events; SAE Technical Paper 2021-01-5010; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA; pp. 1–8.
- Wang, B.; Luo, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Li, K. Robust Non-Fragile Fault Tolerant Control for Ensuring the Safety of the Intended Functionality of Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 18746–18760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naboulsi, M.C.A.; Sizun, H.; Fornel, F.D.R. Fog Attenuation Prediction for Optical and Infrared Waves. Opt. Eng. 2004, 43, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltsavias, E.P. Airborne Laser Scanning: Basic Relations and Formulas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1999, 54, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheeny, M.; De Pellegrin, E.; Mukherjee, S.; Ahrabian, A.; Wang, S.; Wallace, A. RADIATE: A Radar Dataset for Automotive Perception in Bad Weather. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- China National GB/T 33673-2017; Grade of Horizontal Visibility. China National Standards: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Mori, D.; Sugiura, H.; Hattori, Y. Adaptive Sensor Fault Detection and Isolation Using Unscented Kalman Filter for Vehicle Positioning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Auckland, New Zealand, 27–30 October 2019; pp. 1298–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhappa, M.; Mahindrakar, A.D.; Guizilini, V.C.; Terra, M.H.; Sabat, S.L. MEMS-Based IMU Drift Minimization: Sage Husa Adaptive Robust Kalman Filtering. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, T.G.R.; Houts, S.E.; Cammarata, R.; Mills, G.; Agarwal, S.; Vora, A.; Pandey, G. Localization Requirements for Autonomous Vehicles. SAE Intl. J. CAV 2019, 2, 12-02-03-0012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.-L. Linear Least-Squares Optimization for Point-to-Plane ICP Surface Registration; Technical Report TR04-004; University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill: Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 2004; Volume 4, pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
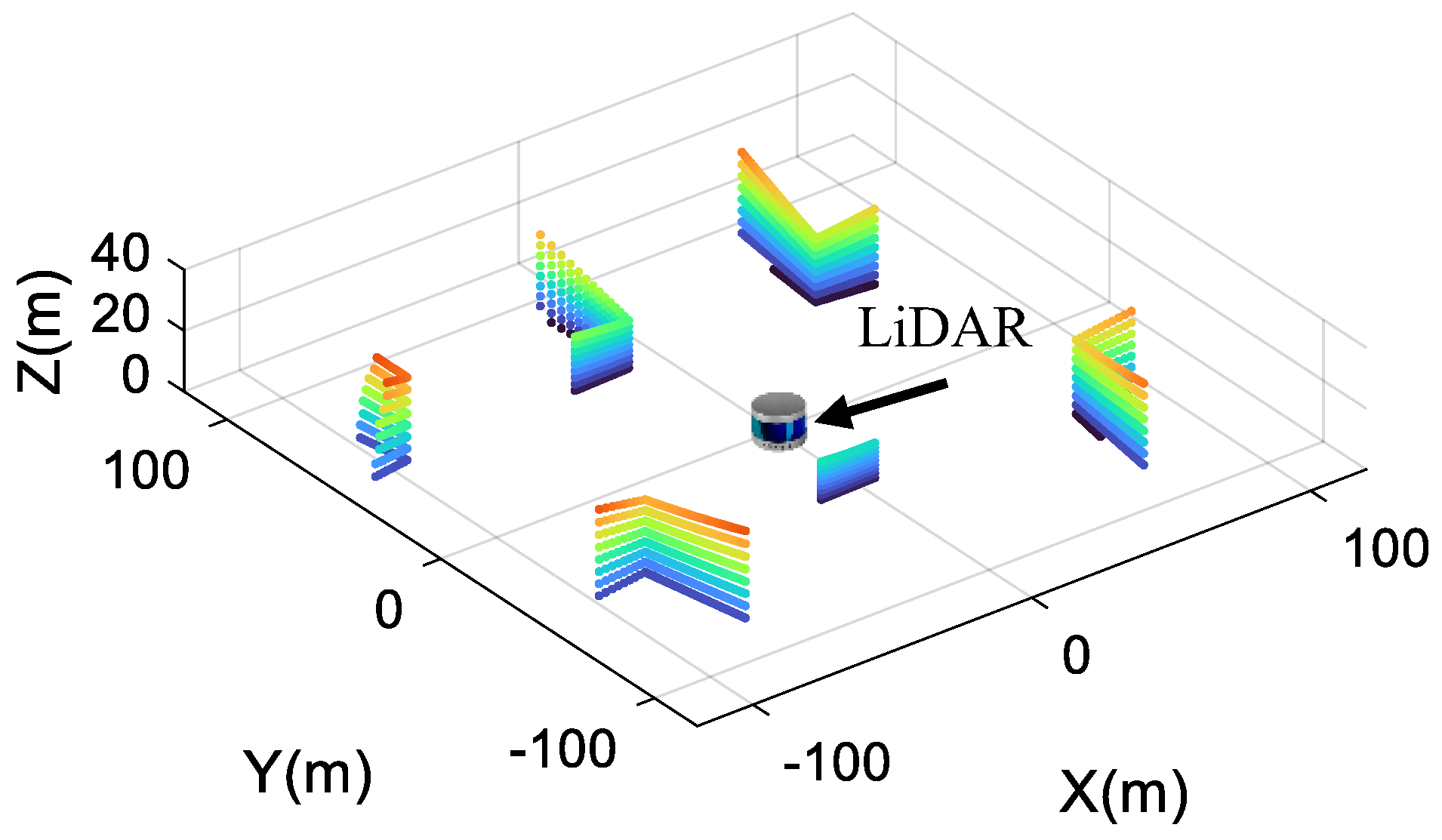
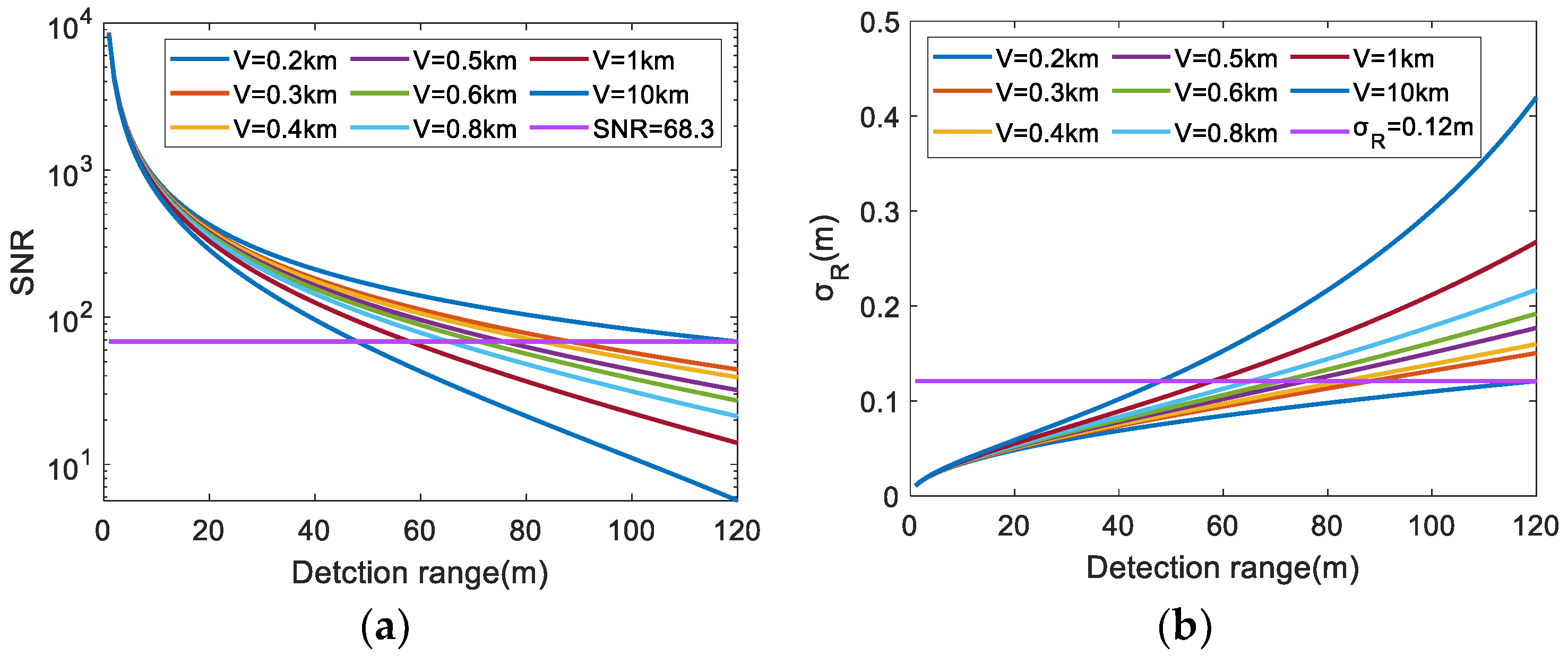



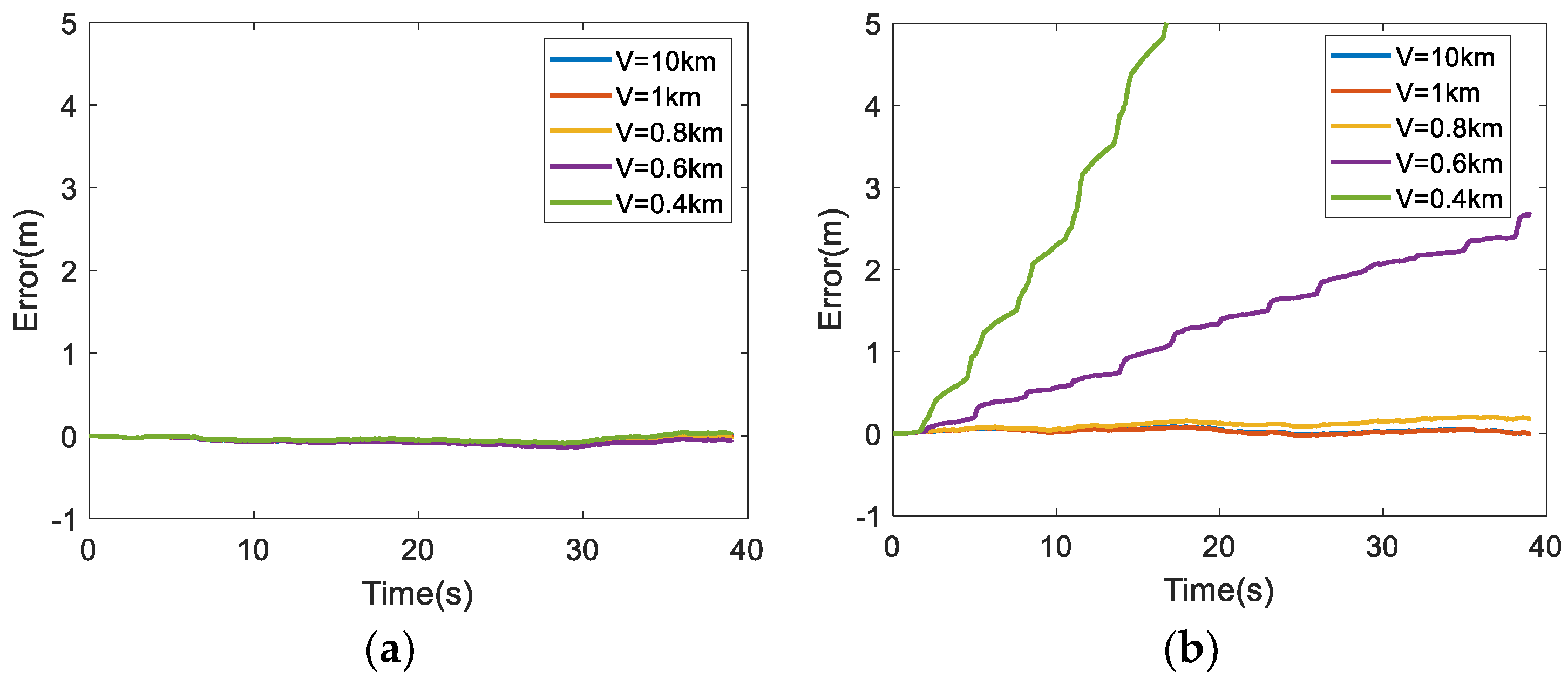
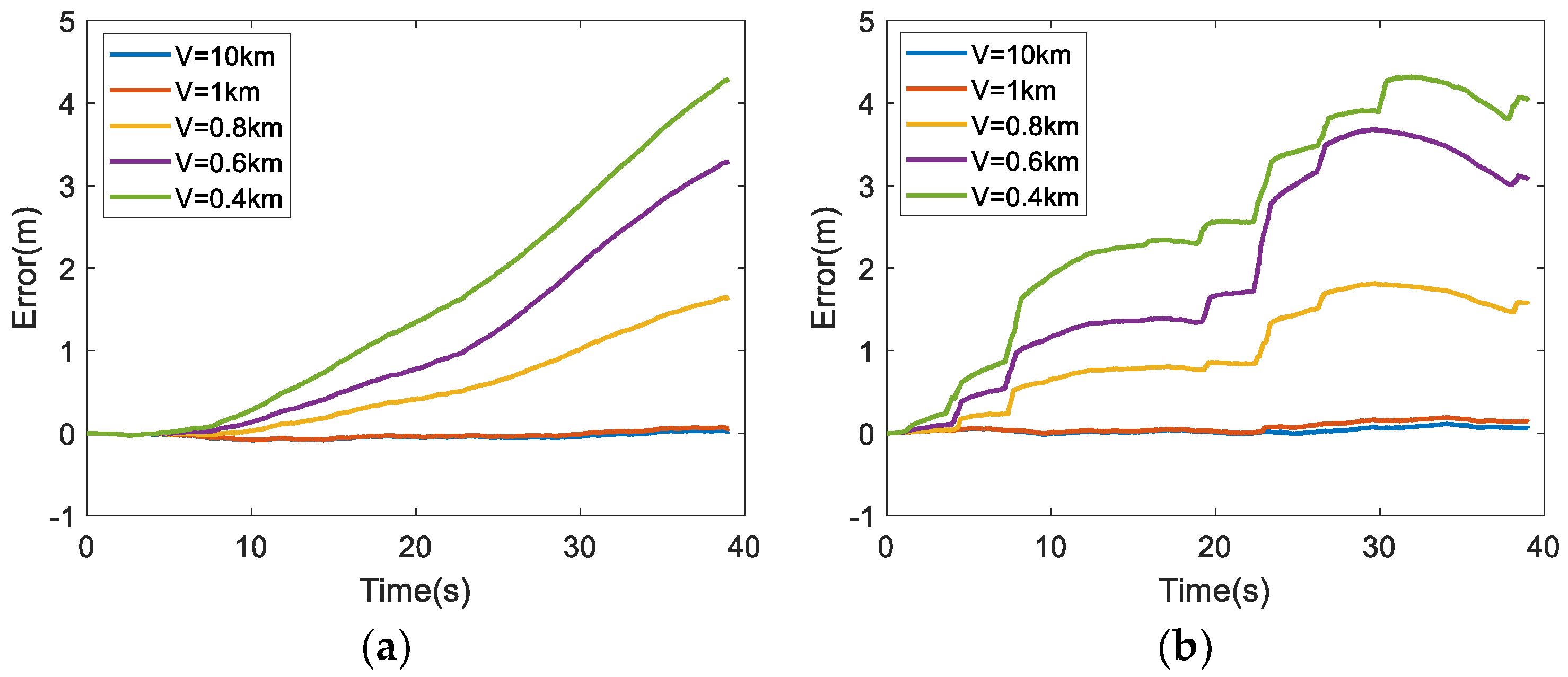


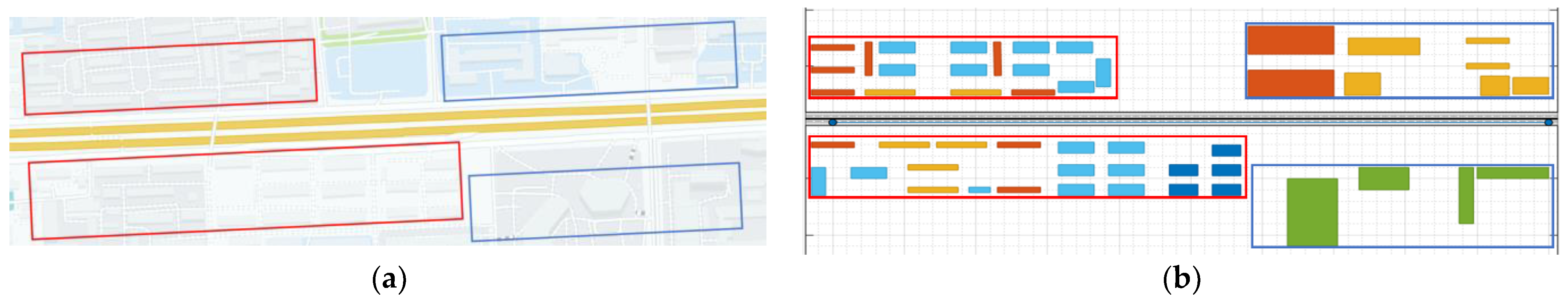
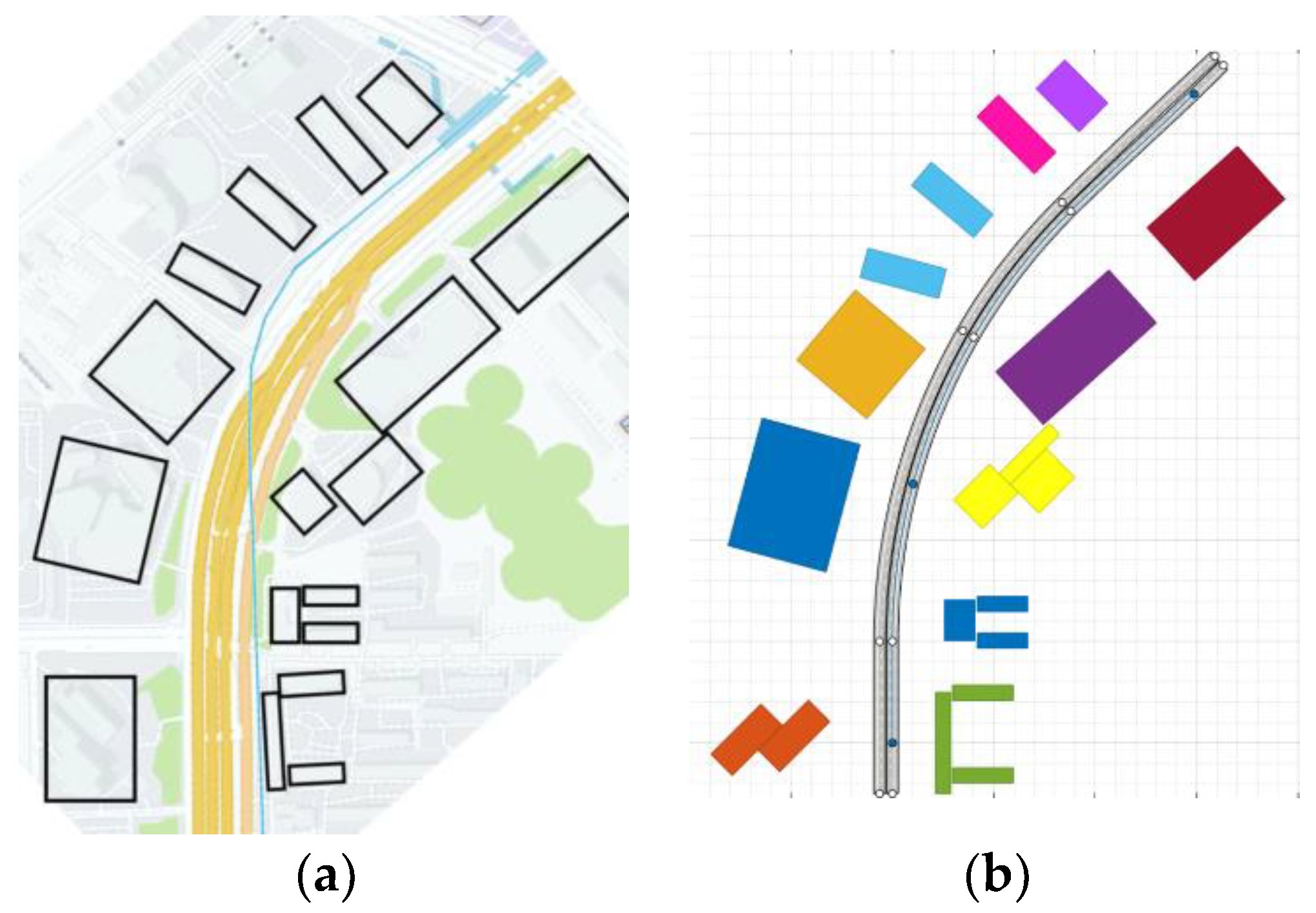


| Parameters | Descriptions | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Laser emitted energy | 1.6 μJ | |
| Spatial resolution | 15 m | |
| Laser emitter efficiency | 0.8 | |
| Laser receiver efficiency | 0.3 | |
| Receiver quantum efficiency | 0.1 | |
| Receiving telescope viewing angle | 0.0003 rad | |
| Receiver effective area | 10 cm2 | |
| Optical filter bandwidth | 60 nm | |
| Sky background radiation brightness | 0.6 W/(m2·nm·sr) | |
| Dark counting rate of the receiver | 300 |
| Sensors | Parameters |
|---|---|
| INS Gyroscope | Noise: 0.573 deg/s Frequency: 100 Hz |
| INS Accelerometer | Noise: 0.1 m/s2 Frequency: 100 Hz |
| GNSS Position | Noise: 2 m Frequency: 10 Hz |
| GNSS Velocity | Noise: 0.1 m/s Frequency: 10 Hz |
| LiDAR | Max Range: 120 m Range Accuracy: 0.002 m Azimuth: 0.4 deg Elevation: 1.875 deg Azimuthal Limits: [−180° 180°] Elevation Limits: [−15° 15°] Frequency: 20 Hz |
| Scenarios | Visibility (km) | Probability of Detecting Feature Degenerated Point Clouds (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Straight urban expressway | 10.0 | 0 |
| 1.0 | 0 | |
| 0.8 | 0 | |
| 0.6 | 6.7 | |
| 0.4 | 40.0 | |
| Curved urban expressway | 10.0 | 0 |
| 1.0 | 0.7 | |
| 0.8 | 4.6 | |
| 0.6 | 15.1 | |
| 0.4 | 40.8 |
| Scenarios | Triggering Condition | Functional Insufficiencies | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component-Level | System-Level | Vehicle-Level | ||
| Straight urban expressway | Visibility is 0.6 km or less. | Solution degradation of longitudinal localization | Divergence of longitudinal localization. | Unintended acceleration or deceleration |
| Curved urban expressway | Visibility is 0.8 km or less. | Solution degradation of longitudinal and lateral localization | Divergence of longitudinal and lateral localization. | Unintended acceleration, deceleration, or steering |
| Scenarios | SOTIF-Related Harms | |||
| Straight urban expressway |
| |||
| Curved urban expressway |
| |||
| Validation Scenarios | Road Length | Visibility | Comparison Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quasi-real straight urban expressway | 750 m | Case 1: 0.4 km | EKF AEKF EKF with FDI |
| Case 2: 0.4–1 km | |||
| Quasi-real curved urban expressway | 700 m | Case 1: 0.4 km | EKF AEKF EKF with FDI |
| Case 2: 0.4–1 km |
| Error Types | Requirements | Methods | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EKF | AEKF | EKF with FDI | Proposed Strategy | |||
| Longitudinal error (m) | Max | 1.40 | 11.85 | 0.62 | 0.31 | 0.12 |
| 95% accuracy | 0.48 | 8.88 | 0.51 | 0.27 | 0.10 | |
| Lateral error (m) | Max | 0.57 | 4.59 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0.10 |
| 95% accuracy | 0.24 | 4.17 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.10 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, L.; He, Y.; Luo, Y.; Chen, J. Layered SOTIF Analysis and 3σ-Criterion-Based Adaptive EKF for Lidar-Based Multi-Sensor Fusion Localization System on Foggy Days. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123047
Cao L, He Y, Luo Y, Chen J. Layered SOTIF Analysis and 3σ-Criterion-Based Adaptive EKF for Lidar-Based Multi-Sensor Fusion Localization System on Foggy Days. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(12):3047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123047
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Lipeng, Yansong He, Yugong Luo, and Jian Chen. 2023. "Layered SOTIF Analysis and 3σ-Criterion-Based Adaptive EKF for Lidar-Based Multi-Sensor Fusion Localization System on Foggy Days" Remote Sensing 15, no. 12: 3047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123047
APA StyleCao, L., He, Y., Luo, Y., & Chen, J. (2023). Layered SOTIF Analysis and 3σ-Criterion-Based Adaptive EKF for Lidar-Based Multi-Sensor Fusion Localization System on Foggy Days. Remote Sensing, 15(12), 3047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123047






