Quantitative Study on Salinity Estimation of Salt-Affected Soils by Combining Different Types of Crack Characteristics Using Ground-Based Remote Sensing Observation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
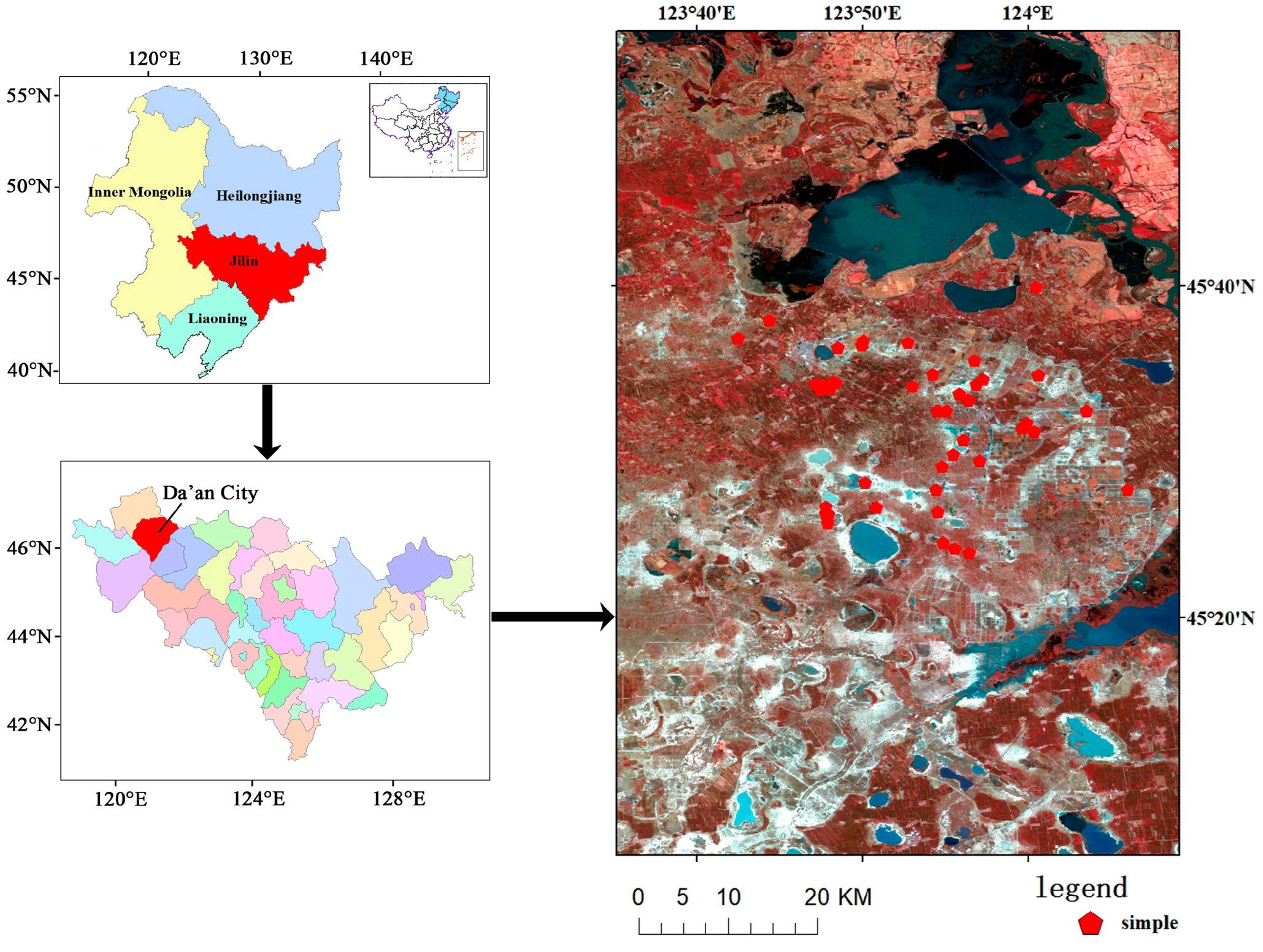
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Property Measurements
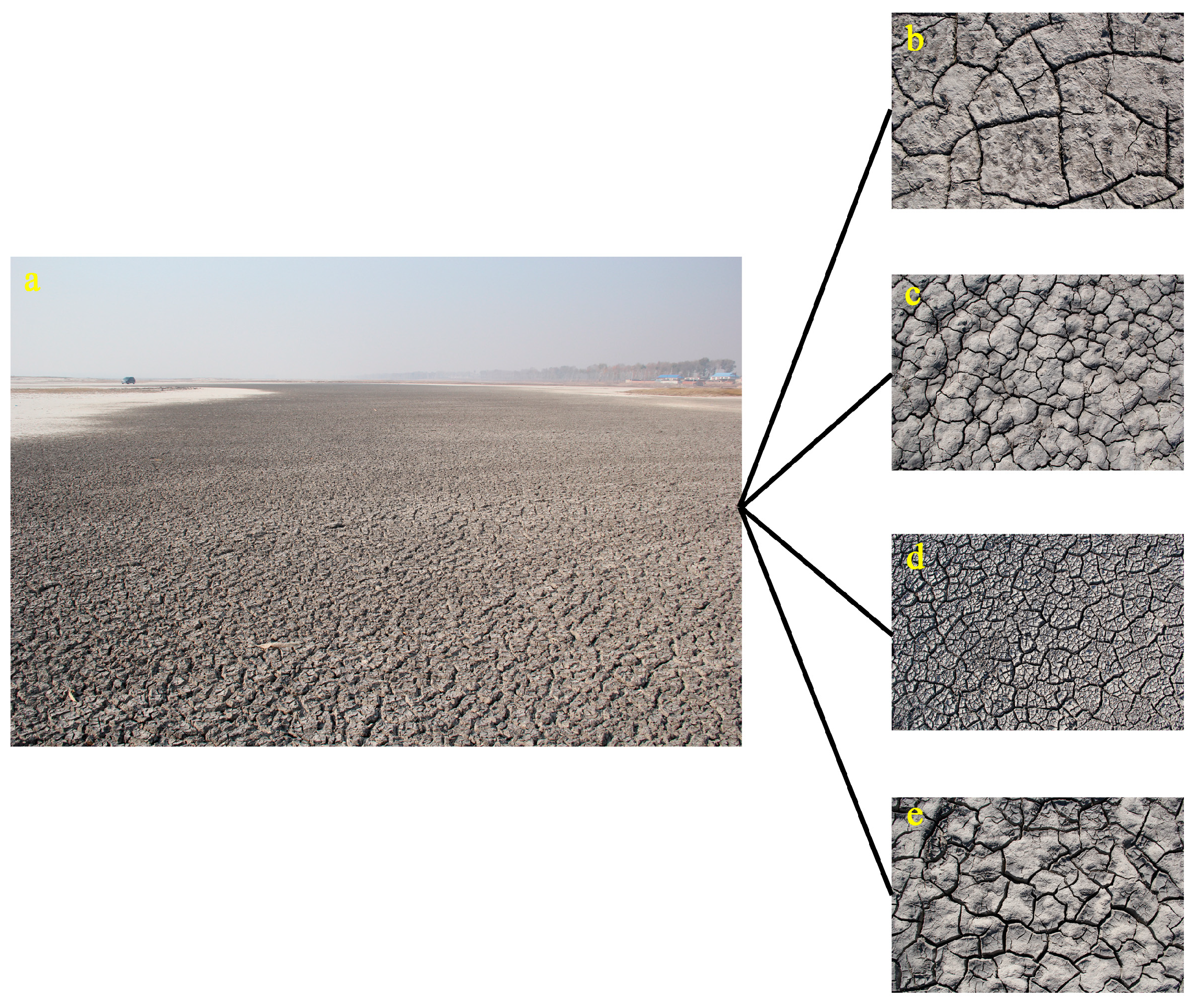
2.3. Soil Surface Cracking Experiments
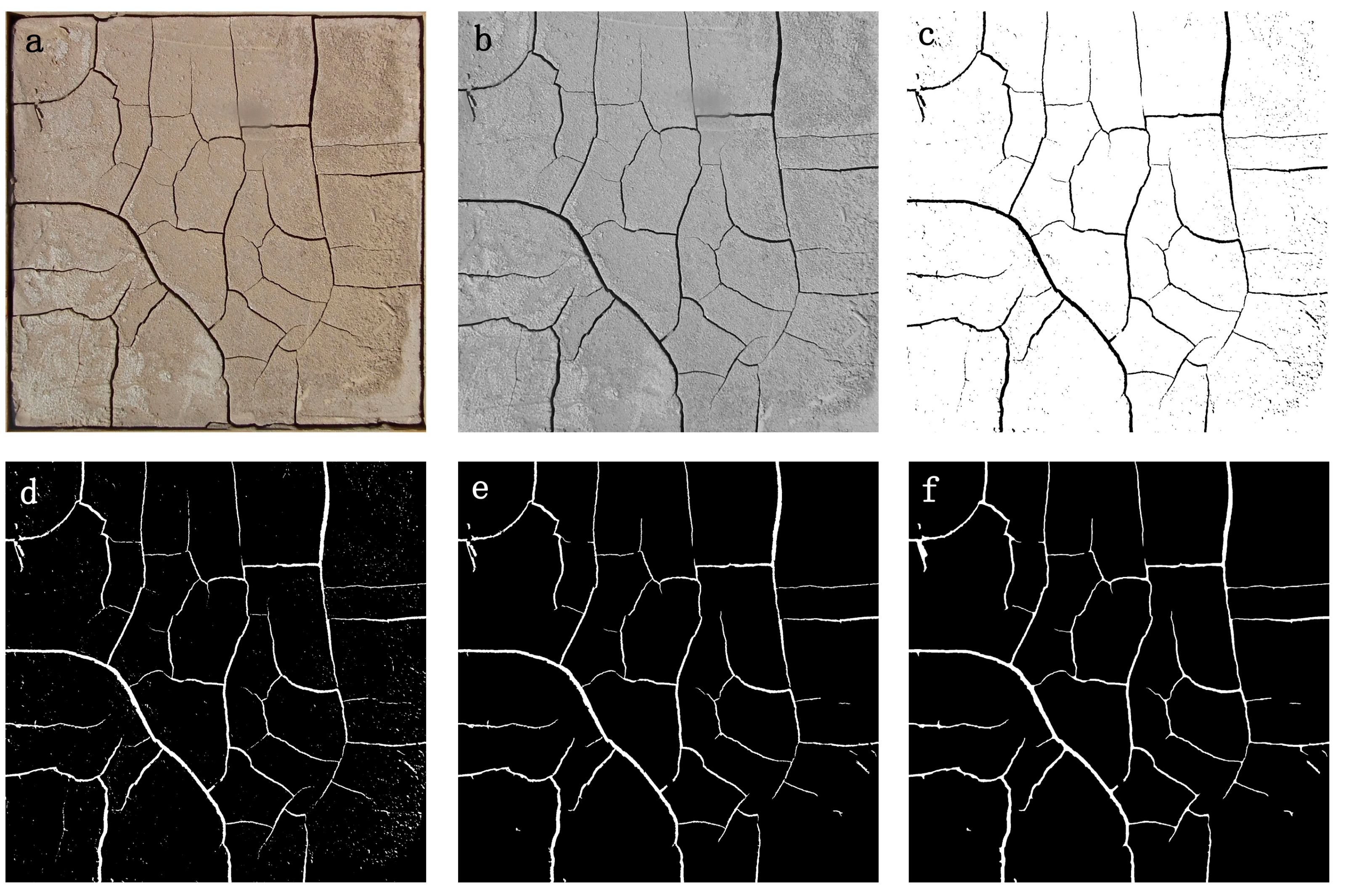
2.4. Standardized Preprocessing of Crack Images
2.5. Crack Feature Extraction
2.5.1. Crack Length
2.5.2. Fractal Dimension
2.5.3. Texture Feature
2.6. Correlation Analysis and Regression Model Establishment
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
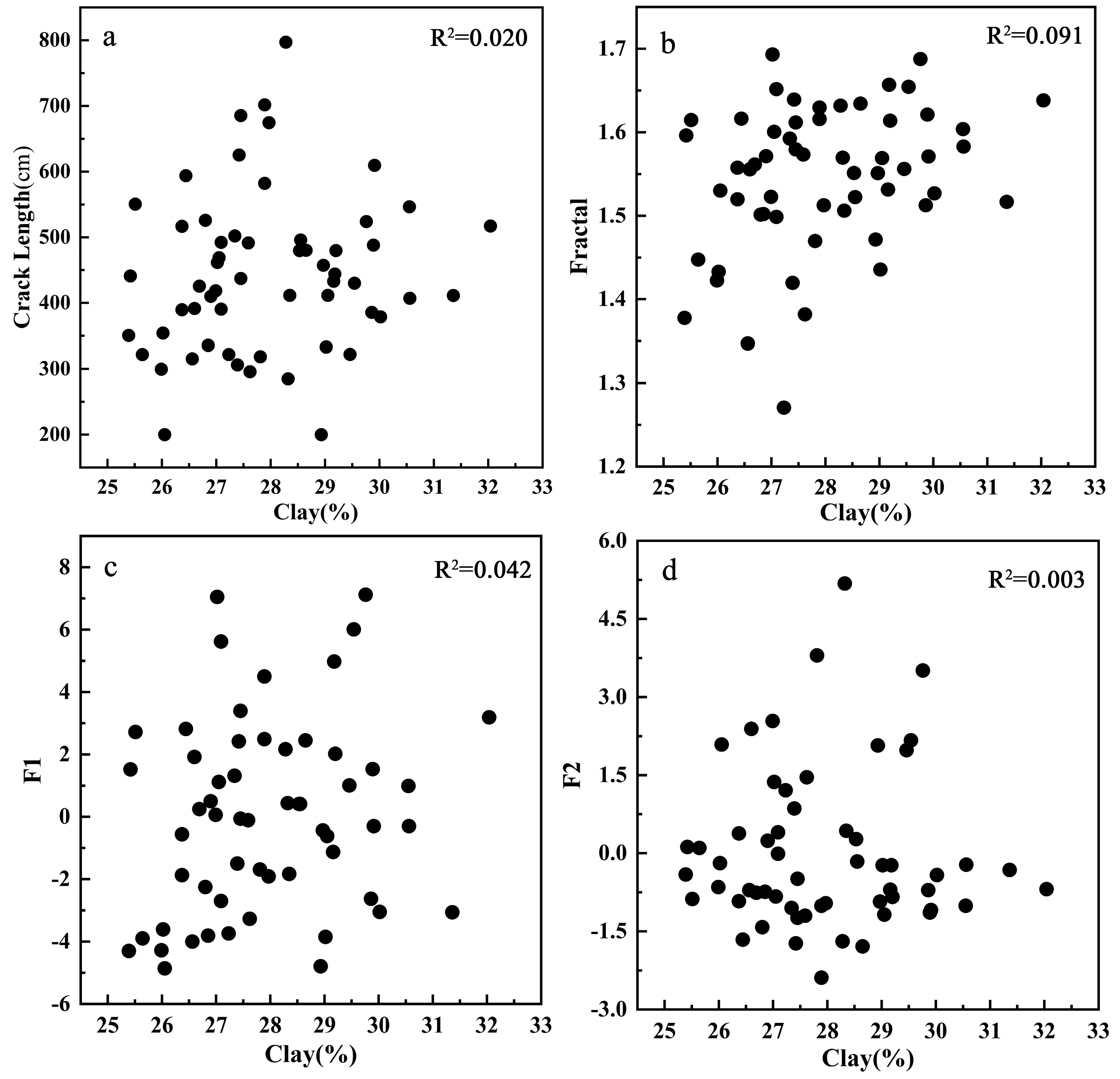
3.2. Crack Characteristic Parameters
3.2.1. Crack Length
3.2.2. Fractal Dimension
3.2.3. GLCM Texture Features
3.3. Correlation Analysis
3.4. Soil Salinity Parameter Prediction Models
3.4.1. Multiple Linear Regression Model
3.4.2. Multiple Stepwise Regression Model
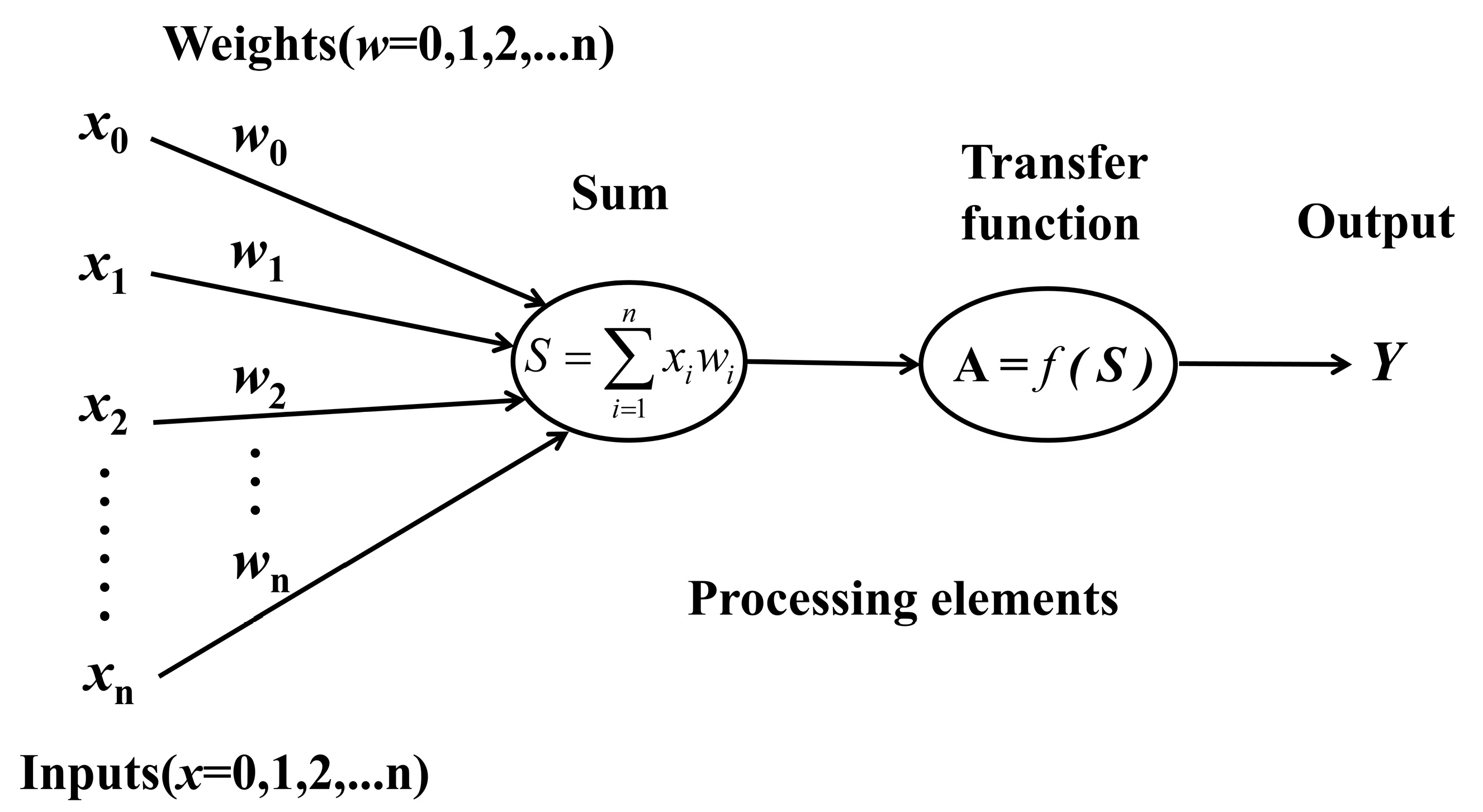
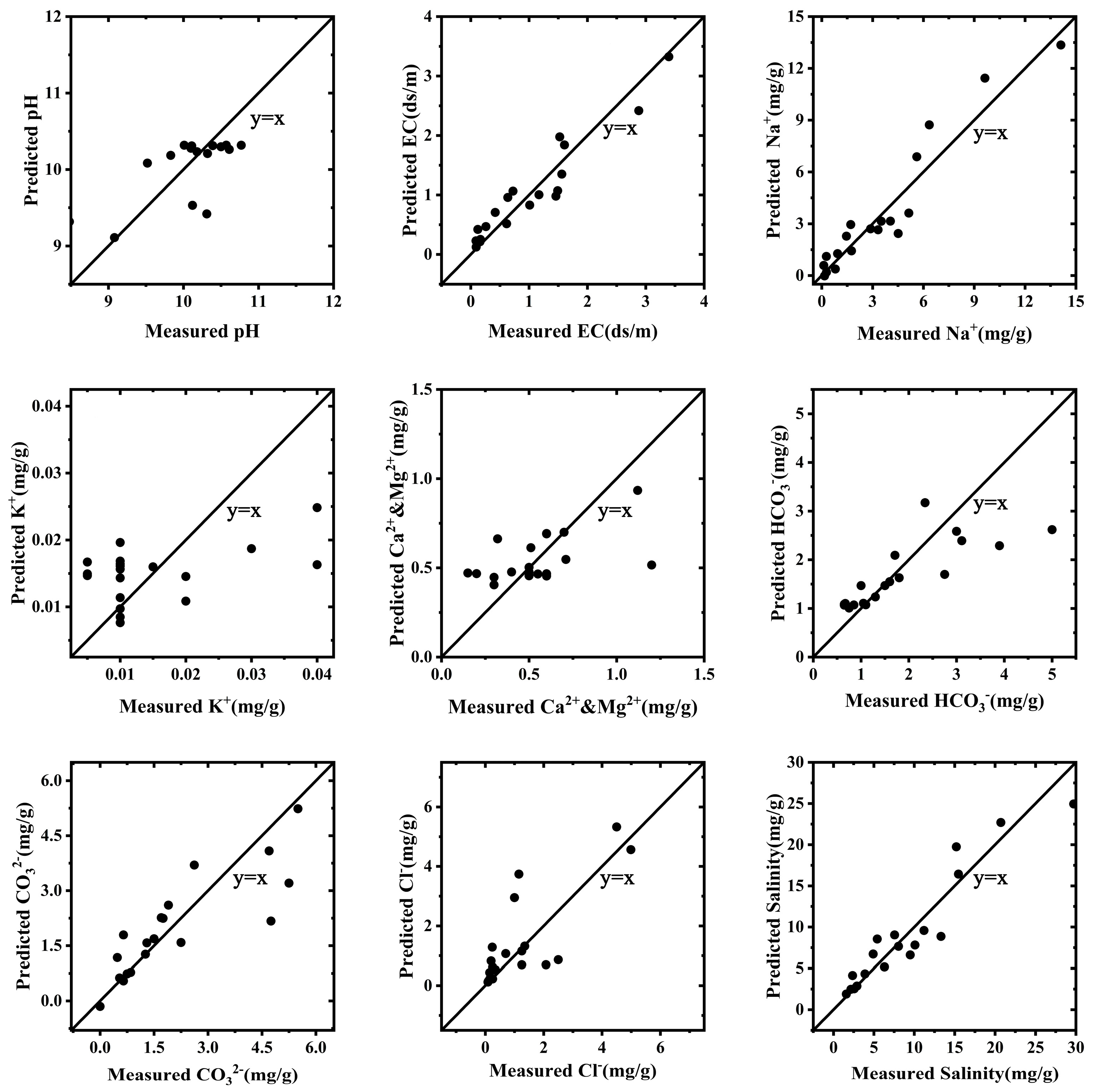
3.4.3. BP Neural Network Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Salinity on the Desiccation Cracking Process
4.2. Prediction Abilities of Different Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; He, X. Remote sensing monitoring and temporal and spatial characteristics of soil salinization in Aral Reclamation area. Arid Land. Geogr. 2022, 45, 1176–1185. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Boudibi, S.; Sakaa, B.; Benguega, Z.; Fadlaoui, H.; Othman, T.; Bouzidi, N. Spatial prediction and modeling of soil salinity using simple cokriging, artificial neural networks, and support vector machines in El Outaya plain, Biskra, southeastern Algeria. Acta Geochim. 2021, 40, 390–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.; Jeong, Y.; Baek, N.; Park, H.; Yang, H.; Park, S.; Choi, W. Soil texture affects the conversion factor of electrical conductivity from 1:5 soil-water to saturated paste extracts. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yu, D. Monitoring and evaluating spatial variability of soil salinity in dry and wet seasons in the Werigan–Kuqa Oasis, China, using remote sensing and electromagnetic induction instruments. Geoderma 2014, 235, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadim, F.K.; Su, H.; Xu, L.; Tian, J. Soil salinity mapping in Everglades National Park using remote sensing techniques and vegetation salt tolerance. Phys. Chem. Earth 2019, 110, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, S.; Wei, Y.; Shi, Q.; Ding, J. Characterizing soil salinity at multiple depth using electromagnetic induction and remote sensing data with random forest: A case study in Tarim River Basin of southern Xinjiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; An, F.; Ma, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z. Spatial variations of apparent soil electrical conductivity in the saline-sodic upland soil of the Songnen Plain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 1184–1190. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zarai, B.; Walter, C.; Michot, D.; Montoroi, J.P.; Hachicha, M. Integrating multiple electromagnetic data to map spatiotemporal variability of soil salinity in Kairouan region, Central Tunisia. J. Arid Land 2022, 14, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, K.; Schmidhalter, U. Comparison of the EM38 and EM38-MK2 electromagnetic induction-based sensors for spatial soil analysis at field scale. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 110, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, J.; Hudnall, W.H. Measurement of soil salinity using electromagnetic induction in a paddy with a densic pan and shallow water table. Paddy Water Environ. 2014, 12, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongnawang, T.; Zare, E.; Srihabun, P.; Triantafilis, J. Comparing electromagnetic induction instruments to map soil salinity in two-dimensional cross-sections along the Kham-rean Canal using EM inversion software. Geoderma 2020, 377, 114611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.D.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Panagea, I.S.; Tsanis, I.K. Assessing soil salinity using WorldView-2 multispectral images in Timpaki, Crete, Greece. Geocarto Int. 2016, 33, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Chan, N.; Wang, Y. Regional suitability prediction of soil salinization based on remote-sensing derivatives and optimal spectral index. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, M.F.; Wikantika, K.; Harto, A.B. Potential use of spectral analysis to delineate coastal boundary of a landmass based on estimation soil salinity and salt water intrusion: A preliminary result. J. Coast. Conserv. 2022, 26, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrayini, E.; Noroozi, A.A.; Eghbal, M.K. Prediction on soil properties by visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2020, 53, 1760–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Z.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Nyongesah, J.M. Estimation of soil salinity under various soil moisture conditions using laboratory based thermal infrared spectra. J. Indian Soc. Remote 2021, 49, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zovko, M.; Romić, D.; Colombo, C.; Iorio, E.D.; Romić, M.; Buttafuoco, G.; Castrignano, A. A geostatistical Vis-NIR spectroscopy index to assess the incipient soil salinization in the Neretva River valley, Croatia. Geoderma 2018, 332, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Tao, J.; Weng, Y. Soil salinity retrieval from advanced multi-spectral sensor with partial least square regression. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 488–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickam, L.; Subramanian, D.; Khandal, S.; Hegde, R. Modeling and mapping of salt-affected soils through spectral indices in inland plains of semi-arid agro-ecological region. J. Indian Soc. Remote 2021, 49, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Liou, Y.; Tran, H.; Hoang, P.; Nguyen, T. Soil salinity assessment by using near-infrared channel and vegetation soil salinity index derived from landsat 8 OLI data: A case study in the Tra Vinh Province, Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Prog. Earth Planet. Sc. 2020, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allbed, A.; Kumar, L.; Sinha, P. Soil salinity and vegetation cover change detection from multi-temporal remotely sensed imagery in Al Hassa Oasis in Saudi Arabia. Geocarto Int. 2018, 33, 830–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, T.; Sertel, E.; Tanik, A. Monitoring soil salinity via remote sensing technology under data scarce conditions: A case study from Turkey. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 74, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ma, F.; Li, J.; Gu, Q.; Yang, S.; Wu, D.; Feng, J.; Ding, J. Characterizing and modeling regional-scale variations in soil salinity in the arid oasis of Tarim Basin, China. Geoderma 2016, 305, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Battay, A.; Bannari, A.; Hameid, N.A.; Abahussain, A.A. Comparative study among different semi-empirical models for soil salinity prediction in an arid environment using OLI Landsat-8 data. Adv. Remote Sens. 2017, 6, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Webster, R.; Shi, Z. Mapping soil salinity in the Yangtze delta: REML and universal kriging (E-BLUP) revisited. Geoderma 2015, 237, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Al-Shafile, W.; Mhaimeed, A.; Ziadat, F.; Nangia, V.; Payne, W. Soil salinity mapping by multiscale remote sensing in Mesopotamia, Iraq. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 4442–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, S. Evaporation and cracked soda soil improved by fly ash from recycled materials. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhu, C.; Cheng, Q.; Zeng, H.; Xu, J.; Tian, B.; Shi, B. Desiccation cracking of soils: A review of investigation approaches, underlying mechanisms, and infuencing factors. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 216, 103586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.A.; Grismer, M.E. Soil crack morphology and soil salinity. Soil Sci. 1992, 153, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Tang, C.; Wang, P.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z.; Xu, S. Effect of salt content on desiccation cracking behavior of soil. J. Eng. Geol. 2015, 23, 77–83. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.; Xing, X. Water characteristic curve and shrinkage characteristics of different sodification degree. Chin. J. Irrig Drain. 2021, 40, 131–136. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Decarlo, K.F.; Shokri, N. Salinity effects on cracking morphology and dynamics in 3-D desiccating clays. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 3052–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Ma, X.; Kang, D. Impacts of type and concentration of salt cations on soil water retention and desiccation cracking. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 115–122. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zheng, Q.; Lin, J.; Jiang, F.; Ge, H.; Huang, Y. Quantitative Study on the Effect of Temperature on the Formation of Soil Desiccation Cracks in Red Soil Layer in Benggang Areas. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 53, 805–814. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, K.; Fu, B.; Tao, J. Study of an on-line measurement method for the salt parameters of soda-saline soils based on the texture features of cracks. Geoderma 2016, 263, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; An, F.; Yang, H. Soil water characteristics of saline-sodic soil in Songnen Plain. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2015, 35, 340–345. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Chi, C. Distribution characteristics of ions in sodic soil and correlation analysis. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 38, 653–656. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Xie, R.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Comparative study on the abilities of different crack parameters to estimate the salinity of soda saline-alkali soil in Songnen Plain, China. Catena 2022, 213, 106221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, S.; Bansal, P. Experimental analogy of different texture feature extraction techniques in image retrieval systems. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 27391–27406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, R.; Singal, G.; Nain, N. A texture feature based approach for person verification using footprint bio-metric. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 1581–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Zhong, S.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Z.; Luo, X. A simple texture feature for retrieval of medical images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 10853–10866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouat, S.; Ait-hammi, I.; Hamouchene, I. A new approach for texture segmentation based on the gray level co-occurrence matrix. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 24027–24052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.; Rajitha, B.; Agarwal, S.; Singh, S. Pattern-based image retrieval using GLCM. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 10819–10832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shamugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Texture features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, 3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Ren, J. Quantitative Response of Gray-Level Co-Occurrence Matrix Texture Features to the Salinity of Cracked Soda Saline–Alkali Soi. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6555–6556. [Google Scholar]
- Aneke, F.I.; Onyelowe, K.C.; Ebid, A.M.; Nwobia, L.I.; Adu, J.T. Predictive models of swelling stress-a comparative study between BP- and GRG-ANN. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Geng, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Zhu, B.; Li, Q.; Chen, Q. Using genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization BP neural network algorithm to improve marine oil spill prediction. Water Air Soil Poll. 2022, 233, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Panda, G. Performance evaluation of a new BP algorithm for a modified artificial neural network. Neural Process. Lett. 2020, 51, 1869–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeloye, A.J.; Munari, A.D. Artificial neural network based generalized storage-yield-reliability models using the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm. J. Hydrol. 2006, 326, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; You, L.; Xu, L.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Cui, X. Treatment of the saline-alkali soil with acidic corn stalk biochar and its effect on the sorghum yield in western Songnen Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, B.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, W.; Hu, W. Study on salinization characteristics of surface soil in western Songnen Plain. Soils 2013, 45, 332–338. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yan, B.; Zhu, L.; Ou, Y. The effect of reclamation on the distribution of heavy metals in saline-sodic soil of Songnen Plain, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USSLS. Diagnose and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Li, X.; Cao, J.; Li, F. Influence of salinity, sodicity and organic matter on some physical properties of salt-affected soils. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 35, 64–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, K.; Zheng, X.; Jiang, T. Quantitative research on the relationship between salinity and crack length of soda saline-alkali soil. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Ren, J.; Zhou, S. Study on the drying process and the influencing factors of desiccation cracking of cohesive soda saline-alkali soil in the Songnen Plain, China. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayhani, M.H.T.; Yanful, E.K.; Fakher, A. Physical modeling of desiccation cracking in plastic soils. Eng. Geol. 2008, 97, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Effect of clay content on plastic shrinkage cracking of cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppala, A.J.; Manosuthikij, T.; Chittoori, B.C.S. Swell and shrinkage characterizations of unsaturated expansive clays from Texas. Eng. Geol. 2013, 164, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vail, M.; Zhu, C.; Tang, C.; Anderson, L.; Moroski, M.; Montalbo-Lomboy, M.T. Desiccation cracking behavior of MICP-treated bentonite. Geosciences 2019, 9, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H. An Experiment Study of the Fundamental Property of the Carbonate-saline Soil in West of Jilin Province. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2011, 37, 217–224. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.H.; Yu, Q.C.; Wei, G.Q.; Chen, B.; Yang, L.S.; Hu, C.Y.; Li, J.P.; Chen, H.H. Interpretation of salinity characteristics of normal profile in estuarine region by using electromagnetic induction. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2007, 3, 37–40. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H. Effects of salinity on shear strength of saline alkali soils in Songnen plain. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 2008, 19, 128–131. [Google Scholar]
- Shokri, N.; Zhou, P.; Keshmiri, A. Patterns of desiccation cracks in saline bentonite layers. Transport Porous Med. 2015, 110, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farifteh, J.; Van der Meer, F.; Atzberger, C.; Carranzza, E.J.M. Quantitative analysis of salt-affected soil reflectance spectra: A comparison of two adaptive methods (PLSR and ANN). Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


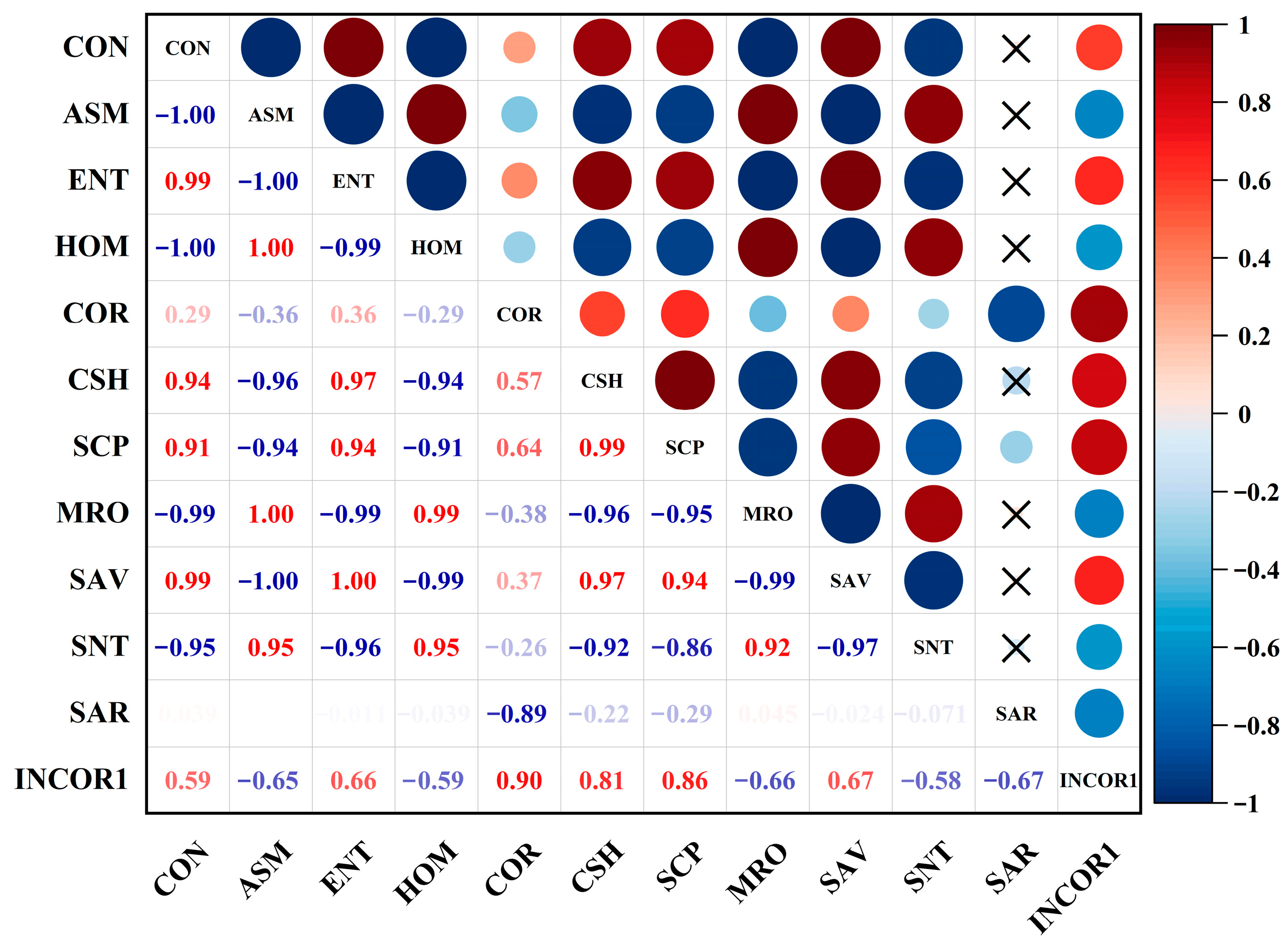
| Soil Parameters | Min | Max | Mean | SD | CV (%) | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.01 | 10.77 | 9.83 | 0.73 | 7.41 | −1.14 | 0.18 |
| EC (ds/m) | 0.06 | 3.39 | 0.97 | 0.84 | 86.64 | 1.02 | 0.56 |
| Na+ (mg/g) | 0.12 | 14.12 | 3.32 | 3.28 | 98.95 | 1.51 | 2.13 |
| K+ (mg/g) | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 67.41 | 2.14 | 5.49 |
| Ca2+ and Mg2+ (mg/g) | 0.10 | 1.60 | 0.53 | 0.32 | 59.75 | 1.19 | 1.67 |
| HCO3− (mg/g) | 0.12 | 5.00 | 1.57 | 0.99 | 63.40 | 1.11 | 1.38 |
| CO32− (mg/g) | 0.00 | 5.50 | 1.75 | 1.56 | 89.33 | 1.02 | 0.14 |
| Cl− (mg/g) | 0.08 | 5.25 | 1.32 | 1.46 | 110.44 | 1.34 | 0.86 |
| Salinity (mg/g) | 1.06 | 29.73 | 8.50 | 6.46 | 75.98 | 1.22 | 1.43 |
| SAR | 0.34 | 42.03 | 9.63 | 8.71 | 90.44 | 1.72 | 3.51 |
| ESP (%) | 0.26 | 47.30 | 10.58 | 9.91 | 93.67 | 1.67 | 3.43 |
| Clay (%) | 25.39 | 32.04 | 27.98 | 1.54 | 5.49 | 0.43 | −0.27 |
| Silt (%) | 28.72 | 40.4 | 35.19 | 3.18 | 9.03 | −0.12 | −0.82 |
| Sand (%) | 28.26 | 43.94 | 36.85 | 3.64 | 9.87 | −0.21 | −0.85 |
| Texture Features | Min | Max | Mean | SD | CV (%) | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 0.001 | 0.287 | 0.123 | 0.080 | 64.941 | 0.330 | −1.006 |
| ASM | 0.430 | 0.999 | 0.761 | 0.151 | 19.820 | −0.345 | −0.842 |
| ENT | 0.009 | 1.552 | 0.712 | 0.398 | 55.830 | 0.185 | −0.830 |
| HOM | 0.856 | 1.000 | 0.938 | 0.040 | 4.252 | −0.332 | −1.008 |
| COR | 0.007 | 0.297 | 0.089 | 0.065 | 72.981 | 1.452 | 1.894 |
| CS | 0.001 | 0.364 | 0.136 | 0.085 | 62.270 | 0.478 | −0.042 |
| SP | 0.001 | 0.638 | 0.199 | 0.146 | 73.550 | 1.019 | 1.098 |
| MP | 0.612 | 0.999 | 0.860 | 0.098 | 11.421 | −0.632 | −0.432 |
| SA | 0.008 | 1.265 | 0.589 | 0.319 | 54.051 | 0.154 | −0.757 |
| SE | 1.946 | 3.971 | 2.650 | 0.551 | 20.782 | 0.623 | −0.571 |
| SV | −0.156 | −0.001 | −0.029 | −0.033 | 113.430 | −1.853 | 3.401 |
| IC | 0.010 | 0.320 | 0.092 | 0.064 | 69.701 | 1.405 | 2.195 |
| Components | Initial Eigenvalue | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Eigenvalue λi | Variance (%) | Cumulative Contribution Rate (%) | |
| 1 | 9.45 | 78.75 | 78.75 |
| 2 | 2.30 | 19.15 | 97.90 |
| 3 | 0.13 | 1.06 | 98.96 |
| 4 | 0.09 | 0.77 | 99.73 |
| 5 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 99.92 |
| 6 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 99.98 |
| 7 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 100.00 |
| 8 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 |
| 9 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 |
| 10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 |
| 11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 |
| 12 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 |
| Variables | First Principal Component | Second Principal Component |
|---|---|---|
| CON | 0.96 | −0.23 |
| ASM | −0.98 | 0.16 |
| ENT | 0.98 | −0.16 |
| HOM | −0.96 | 0.23 |
| COR | 0.50 | 0.85 |
| CS | 0.99 | 0.06 |
| SP | 0.97 | 0.15 |
| MP | −0.98 | 0.13 |
| SA | 0.98 | −0.15 |
| SE | −0.93 | 0.24 |
| SV | −0.16 | −0.95 |
| IC | 0.77 | 0.60 |
| Soil Salinity Parameters | CL | D | F1 | F2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.64 | 0.50 | 0.59 | −0.26 |
| EC (ds/m) | 0.87 | 0.57 | 0.59 | −0.62 |
| Na+ (mg/g) | 0.87 | 0.51 | 0.52 | −0.40 |
| K+ (mg/g) | 0.24 | 0.29 | 0.29 | −0.05 |
| Ca2+ and Mg2+ (mg/g) | 0.24 | 0.10 | 0.26 | −0.02 |
| HCO3− (mg/g) | 0.60 | 0.51 | 0.65 | −0.08 |
| CO32− (mg/g) | 0.73 | 0.37 | 0.25 | −0.62 |
| Cl− (mg/g) | 0.82 | 0.48 | 0.46 | −0.41 |
| Salinity (mg/g) | 0.88 | 0.54 | 0.53 | −0.45 |
| Clay (%) | 0.14 | 0.30 | 0.20 | −0.05 |
| Soil Parameters | Formulas | R | R² |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Y = 13.272 + 0.003 X1 − 2.992 X2 + 0.126 X3 − 0.038 X4 | 0.69 | 0.48 |
| EC | Y = −3.443 + 0.008 X1 + 0.570 X2 − 0.054 X3 + 0.123 X4 | 0.93 | 0.86 |
| Na+ | Y = −13.421 + 0.034 X1 + 1.202 X2 − 0.299 X3 + 0.623 X4 | 0.91 | 0.83 |
| K+ | Y = 0.034 − 5.634 × 10−6 X1 − 0.01 X2−0.001 X3 | 0.26 | 0.07 |
| Ca2+ and Mg2+ | Y = 3.465 − 1.953 X2 + 0.079 X3 + 0.10 X4 | 0.42 | 0.18 |
| HCO3− | Y = 5.98 + 0.003 X1 − 3.807 X2 + 0.191 X3 + 0.079 X4 | 0.68 | 0.46 |
| CO32− | Y = −15.078 + 0.012 X1 + 7.361 X2 − 0.395 X3 − 0.004 X4 | 0.85 | 0.72 |
| Cl− | Y = −9.221 + 0.014 X1 + 2.903 X2 − 0.157 X3 − 0.182 X4 | 0.89 | 0.79 |
| Salinity | Y = −28.225 + 0.063 X1 + 5.689 X2 − 0.579 X3 + 0.89 X4 | 0.94 | 0.89 |
| Soil Parameters | CL | D | F1 | F2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | √ | × | × | × |
| EC | √ | × | × | √ |
| Na+ | √ | × | √ | √ |
| K+ | - | - | - | - |
| Ca2+ and Mg2+ | - | - | - | - |
| HCO3− | √ | × | × | × |
| CO32− | √ | √ | √ | × |
| Cl− | √ | × | × | × |
| Salinity | √ | × | × | × |
| Soil Parameters | Formulas | R | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Y = 8.197 + 0.004 X1 | 0.65 | 0.42 |
| EC | Y = −2.12 + 0.007 X1 + 0.08 X4 | 0.92 | 0.85 |
| Na+ | Y = −11.535 + 0.034 X1 + 0.613 X3 − 0.267 X4 | 0.91 | 0.83 |
| K+ | - | - | - |
| Ca2+ and Mg2+ | - | - | - |
| HCO3− | Y = 1.475 + 0.169 X3 | 0.60 | 0.36 |
| CO32− | Y = −15.128 + 0.012 X1 − 0.396 X3 + 7.378 X2 | 0.85 | 0.72 |
| Cl− | Y = −3.47 + 0.011 X1 | 0.87 | 0.76 |
| Salinity | Y = −12.908 + 0.049 X1 | 0.93 | 0.86 |
| Soil Parameters | Number of Iterations | Number of Neurons | R | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 13 | 4 | 0.79 | 0.62 |
| EC | 11 | 4 | 0.93 | 0.87 |
| Na+ | 10 | 4 | 0.96 | 0.92 |
| K+ | 14 | 3 | 0.52 | 0.27 |
| Ca2+ and Mg2+ | 12 | 3 | 0.49 | 0.24 |
| HCO3− | 10 | 4 | 0.69 | 0.47 |
| CO32− | 13 | 2 | 0.87 | 0.75 |
| Cl− | 9 | 3 | 0.92 | 0.85 |
| Salinity | 13 | 4 | 0.97 | 0.94 |
| Method | Index | pH | EC | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ and Mg2+ | HCO3− | CO32− | Cl− | Salinity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLR | R2 | 0.55 | 0.85 | 0.90 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.72 | 0.67 | 0.58 | 0.91 |
| RPD | 0.85 | 2.47 | 3.11 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.69 | 1.49 | 1.36 | 3.15 | |
| MSR | R2 | 0.49 | 0.89 | 0.87 | - | - | 0.53 | 0.66 | 0.63 | 0.92 |
| RPD | 1.32 | 3.06 | 2.21 | - | - | 1.33 | 1.69 | 1.44 | 3.38 | |
| ANN | R2 | 0.66 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.22 | 0.28 | 0.65 | 0.71 | 0.62 | 0.89 |
| RPD | 1.06 | 2.96 | 3.47 | 0.40 | 0.60 | 0.84 | 1.50 | 1.58 | 2.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, J. Quantitative Study on Salinity Estimation of Salt-Affected Soils by Combining Different Types of Crack Characteristics Using Ground-Based Remote Sensing Observation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133249
Zhang Z, Li X, Zhou S, Zhao Y, Ren J. Quantitative Study on Salinity Estimation of Salt-Affected Soils by Combining Different Types of Crack Characteristics Using Ground-Based Remote Sensing Observation. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(13):3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133249
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhuopeng, Xiaojie Li, Shuang Zhou, Yue Zhao, and Jianhua Ren. 2023. "Quantitative Study on Salinity Estimation of Salt-Affected Soils by Combining Different Types of Crack Characteristics Using Ground-Based Remote Sensing Observation" Remote Sensing 15, no. 13: 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133249
APA StyleZhang, Z., Li, X., Zhou, S., Zhao, Y., & Ren, J. (2023). Quantitative Study on Salinity Estimation of Salt-Affected Soils by Combining Different Types of Crack Characteristics Using Ground-Based Remote Sensing Observation. Remote Sensing, 15(13), 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133249








