Appraisal of the Magnetotelluric and Magnetovariational Transfer Functions’ Selection in a 3-D Inversion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. The 3-D Electromagnetic Inversion Method
2.2. The Explicit Forms of the Matrix L in Different Cases of Transfer Functions
3. Synthetic Model Study
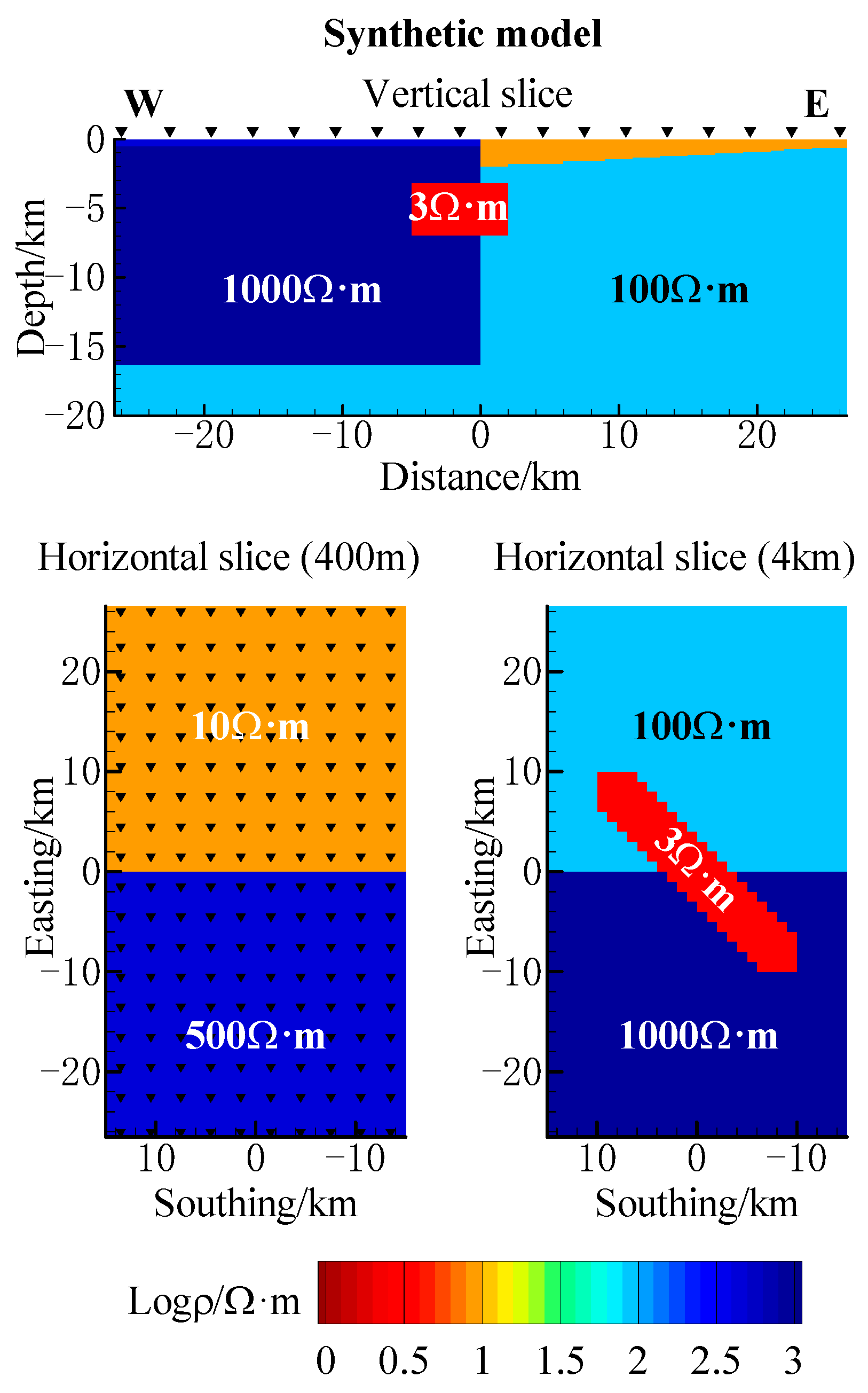
3.1. Synthetic Model
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis
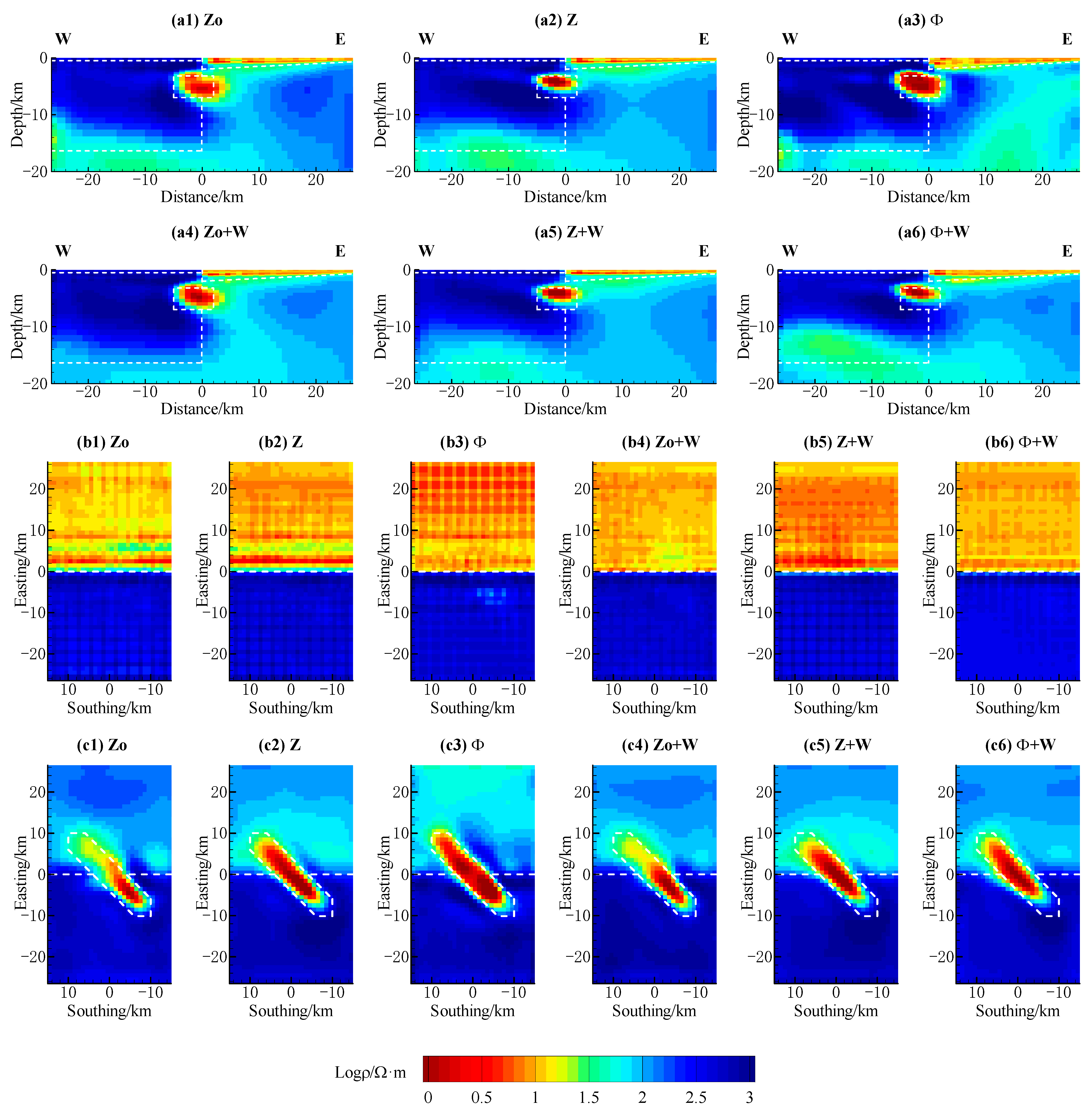
3.3. Three-Dimensional Inversion Tests
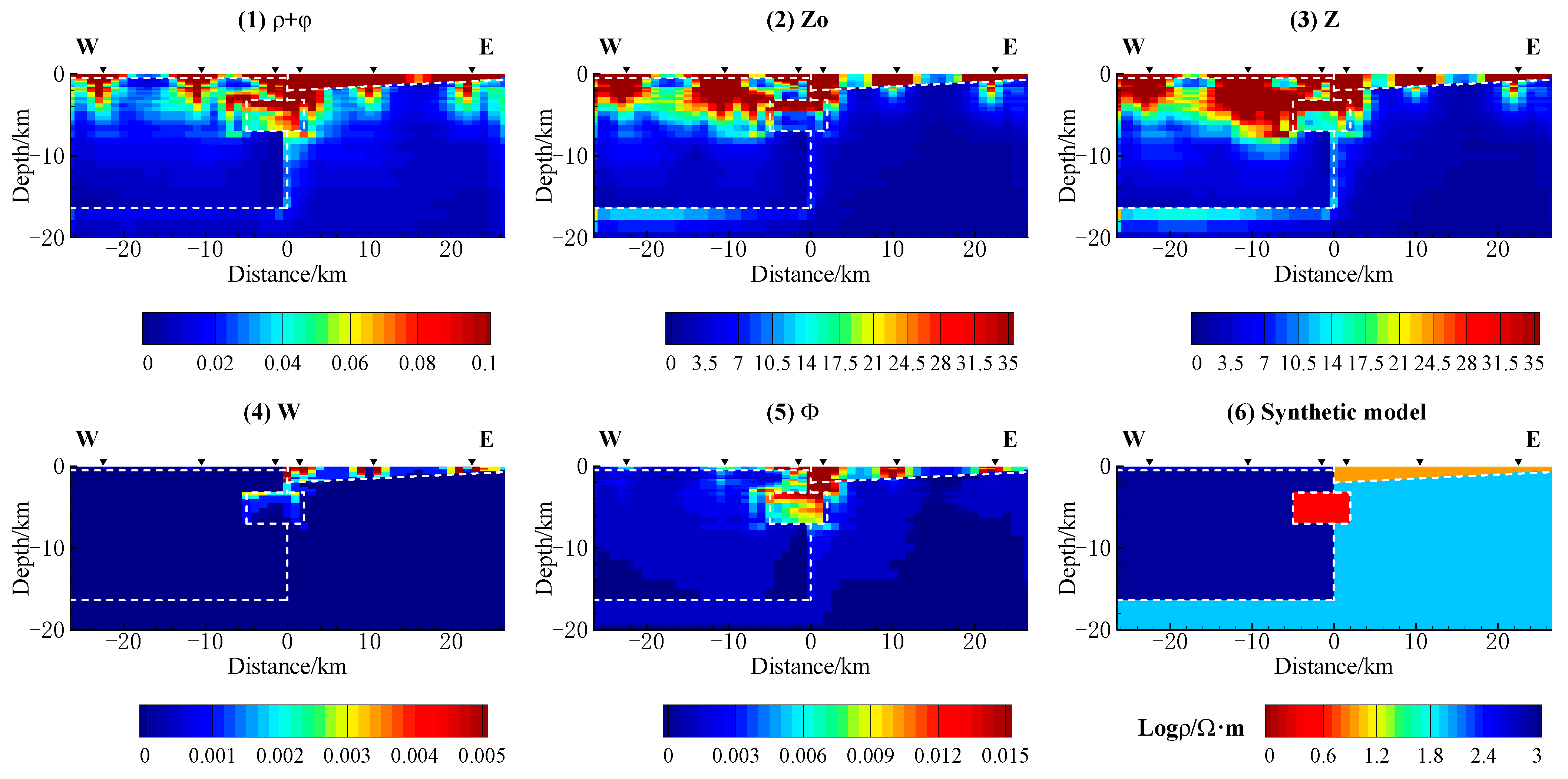
3.3.1. Results of Inverting the MT and MV Transfer Functions Individually
3.3.2. Results of Inverting the MT and MV Transfer Functions Jointly
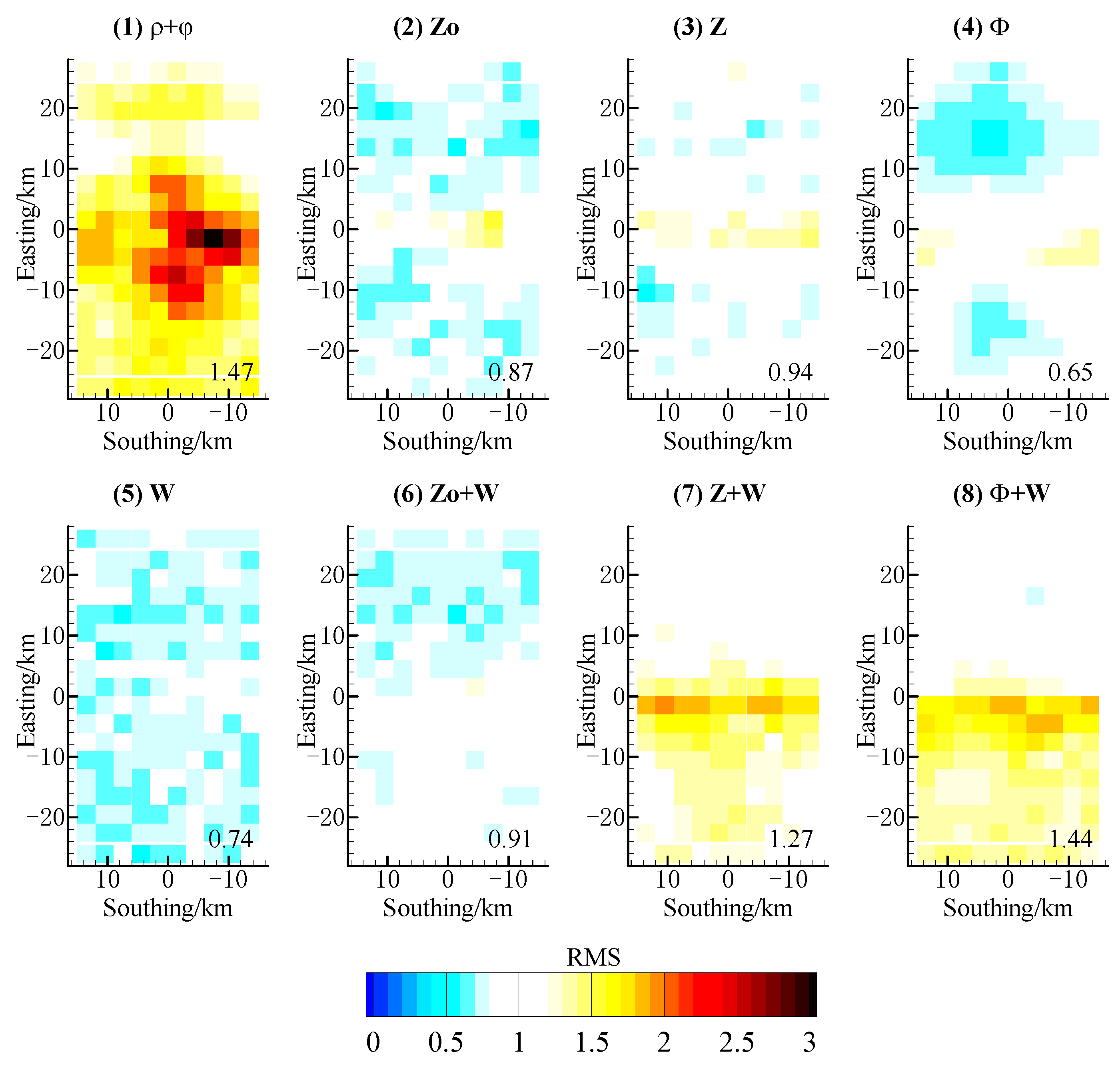
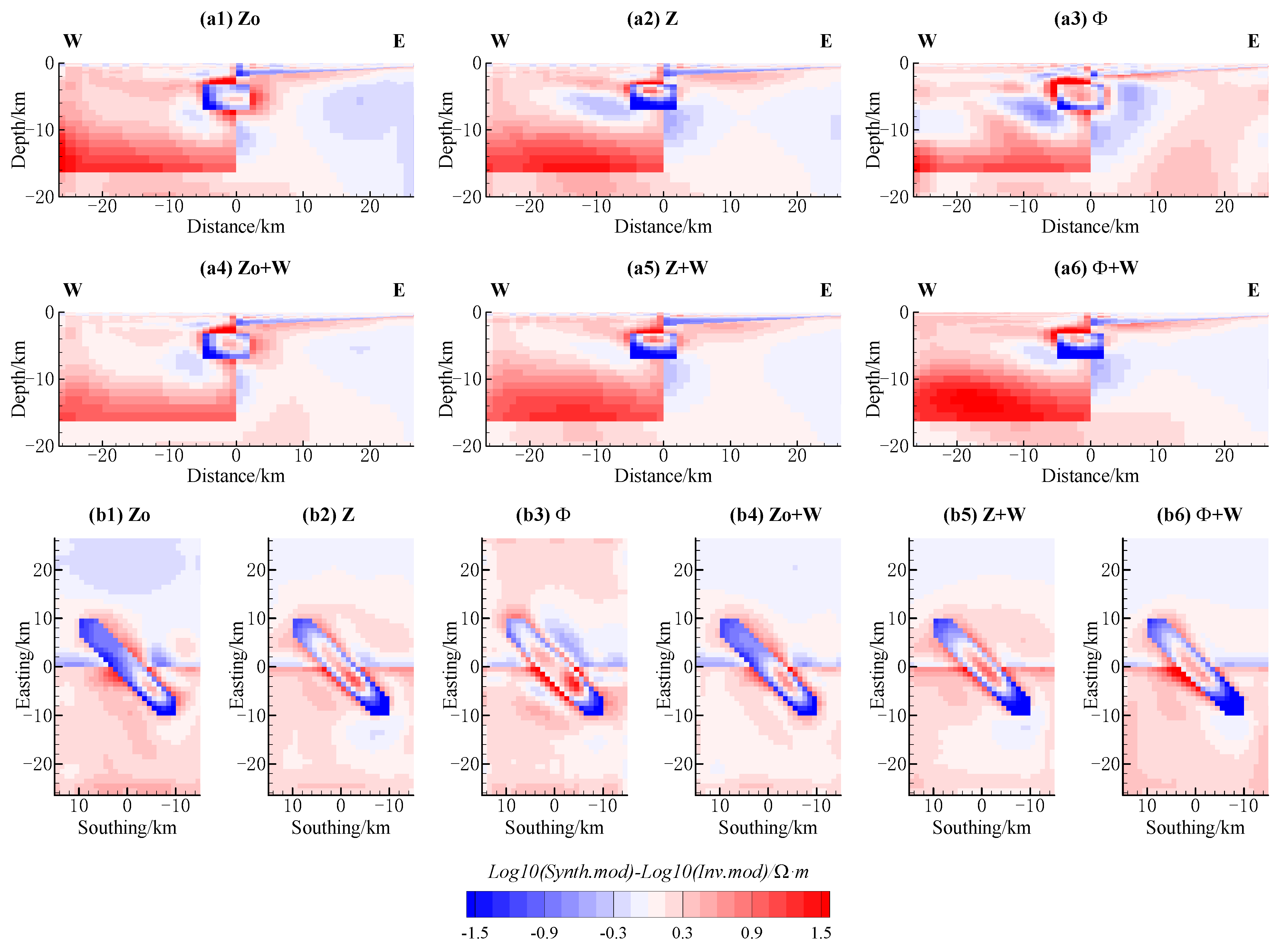
3.3.3. Assessment of the Model’s Accuracy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhdanov, M.S. Geophysical Electromagnetic Theory and Methods; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 43. [Google Scholar]
- Berdichevsky, M.N.; Zhdanov, M.S. Advanced Theory of Deep Geomagnetic Sounding; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA; Tokyo, Japan, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Berdichevsky, M.N.; Dmitriev, V.I. Models and Methods of Magnetotellurics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tikhonov, A.N. On determining electrical characteristics of the deep layers of earth’s crust. Doklady 1950, 73, 295–297. [Google Scholar]
- Cagniard, L. Basic theory of the magneto-telluric method of geophysical prospecting. Geophysics 1953, 18, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermance, J.F.; Thayer, R.E. The Telluric-Magnetotelluric Method. Geophysics 1975, 40, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruglyakov, M.; Kuvshinov, A. 3-D inversion of MT impedances and inter-site tensors, individually and jointly. New lessons learnt. Earth Planets Space 2019, 71, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berdichevsky, M.N. Electrical Prospecting with the Telluric Current Method; Colorado School of Mines: Golden, CO, USA, 1965; Volume 60, pp. 1–216. [Google Scholar]
- Yungul, S.H. Telluric Sounding-A Magnetotelluric Method Without Magnetic Measurements. Geophysics 1966, 31, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, T.G.; Bibby, H.M.; Brown, C. The magnetotelluric phase tensor. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 158, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araya Vargas, J.; Ritter, O. Source effects in mid-latitude geomagnetic transfer functions. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 204, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morschhauser, A.; Grayver, A.; Kuvshinov, A.; Samrock, F.; Matzka, J. Tippers at island geomagnetic observatories constrain electrical conductivity of oceanic lithosphere and upper mantle. Earth Planets Space 2019, 71, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jupp, D.L.B. Estimation of the magnetotelluric impedance functions. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1978, 17, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.L. The magnetotelluric inverse problem. Geophys. Surv. 1983, 6, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbert, G.D.; Kelbert, A. Computational recipes for electromagnetic inverse problems. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 189, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelbert, A.; Meqbel, N.; Egbert, G.D.; Tandon, K. ModEM: A modular system for inversion of electromagnetic geophysical data. Comput. Geosci. 2014, 66, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayver, A.V. Parallel three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion using adaptive finite-element method. Part I: Theory and synthetic study. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 202, 584–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kordy, M.; Wannamaker, P.; Maris, V.; Cherkaev, E.; Hill, G. 3-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion including topography using deformed hexahedral edge finite elements and direct solvers parallelized on symmetric multiprocessor computers–Part II: Direct data-space inverse solution. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 204, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conway, D.; Alexander, B.; King, M.; Heinson, G.; Kee, Y. Inverting magnetotelluric responses in a three-dimensional earth using fast forward approximations based on artificial neural networks. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 127, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I. Ten Lectures on Wavelets; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992; Volume 61. [Google Scholar]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A Practical Guide to Wavelet Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucciarelli, G. Wavelet Analysis in Volcanology: The Case of Phlegrean Fields. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 6, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nittinger, C.G.; Becken, M. Inversion of magnetotelluric data in a sparse model domain. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 206, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Farquharson, C.G.; Yin, C.; Baranwal, V.C. Wavelet-based 3-D inversion for frequency-domain airborne EM data. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 213, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miensopust, M.P. Application of 3-D Electromagnetic Inversion in Practice: Challenges, Pitfalls and Solution Approaches. Surv. Geophys. 2017, 38, 869–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasse, H.; Lezaeta, P.; Rath, V.; Schwalenberg, K.; Soyer, W.; Haak, V. The Bolivian Altiplano conductivity anomaly. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2002, 107, EPM 4-1–EPM 4-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripunvaraporn, W.; Egbert, G.; Lenbury, Y.; Uyeshima, M. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion: Data-space method. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2005, 150, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, K.; Ritter, O. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion in practice—The electrical conductivity structure of the San Andreas Fault in Central California. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 195, 130–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiyan, D.; Jones, A.G.; Vozar, J. The inability of magnetotelluric off-diagonal impedance tensor elements to sense oblique conductors in three-dimensional inversion. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 196, 1351–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, Y.; Meju, M.A. Three-dimensional joint inversion for magnetotelluric resistivity and static shift distributions in complex media. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2006, 111, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slezak, K.; Jozwiak, W.; Nowozynski, K.; Orynski, S.; Brasse, H. 3-D studies of MT data in the Central Polish Basin: Influence of inversion parameters, model space and transfer function selection. J. Appl. Geophys. 2019, 161, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, J.R. The magnetotelluric phase tensor: A critical review. Surv. Geophys. 2014, 35, 7–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanyà, J.; Ogaya, X.; Jones, A.G.; Rath, V.; Vozar, J.; Meqbel, N. The advantages of complementing MT profiles in 3-D environments with geomagnetic transfer function and interstation horizontal magnetic transfer function data: Results from a synthetic case study. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 207, 1818–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siripunvaraporn, W.; Egbert, G. WSINV3DMT: Vertical magnetic field transfer function inversion and parallel implementation. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2009, 173, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwer, A.; Junge, A. Magnetotelluric Transfer Functions: Phase Tensor and Tipper Vector above a Simple Anisotropic Three-Dimensional Conductivity Anomaly and Implications for 3D Isotropic Inversion. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2017, 174, 2089–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibby, H.M. Analysis of multiple-source bipole-quadripole resistivity surveys using the apparent resistivity tensor. Geophysics 1986, 51, 972–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, P.K.; Uyeshima, M.; Siripunvaraporn, W. Three-dimensional inversion of magnetotelluric phase tensor data. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 192, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tietze, K.; Ritter, O.; Egbert, G.D. 3-D joint inversion of the magnetotelluric phase tensor and vertical magnetic transfer functions. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 203, 1128–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samrock, F.; Grayver, A.V.; Eysteinsson, H.; Saar, M.O. Magnetotelluric Image of Transcrustal Magmatic System Beneath the Tulu Moye Geothermal Prospect in the Ethiopian Rift. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 12847–12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munch, F.D.; Grayver, A. Multi-scale imaging of 3-D electrical conductivity structure under the contiguous US constrains lateral variations in the upper mantle water content. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2023, 602, 117939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, G.A.; Alumbaugh, D.L. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion using non-linear conjugate gradients. Geophys. J. Int. 2000, 140, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, Y. Full 3-D inversion of electromagnetic data on PC. J. Appl. Geophys. 2001, 46, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, G.A.; Boggs, P.T. Solution accelerators for large-scale three-dimensional electromagnetic inverse problems. Inverse Probl. 2004, 20, S151–S170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S. Numerical Optimization; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Deng, J.Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.X.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Ye, Y.X.; Chen, S.N. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion under topographic relief based on the limited-memory quasi-Newton algorithm (L-BFGS). Chin. J. Geophys. 2019, 62, 3175–3188. [Google Scholar]
- Ledo, J. 2-D Versus 3-D Magnetotelluric Data Interpretation. Surv. Geophys. 2006, 27, 111–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.G. Parkinson’s pointers’ potential perfidy! Geophys. J. Int. 1986, 87, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.G. Distortion of magnetotelluric data: Its identification and removal. In The Magnetotelluric Method: Theory and Practice; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 219–302. [Google Scholar]



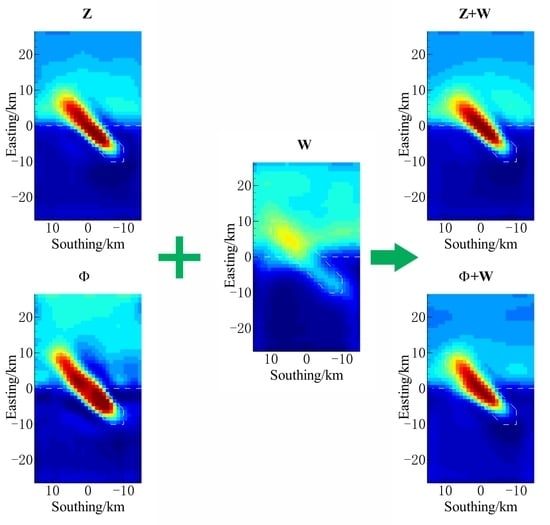
| Data Types | ρ + φ | Zo | Z | Φ | W | Zo + W | Z + W | Φ + W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ϕ initial | 187.07 | 806.22 | 407.49 | 77.95 | 11.42 | 408.82 | 275.37 | 44.69 |
| ϕ final | 2.16 | 0.77 | 0.89 | 0.43 | 0.55 | 0.83 | 1.61 | 2.08 |
| Iterations | 76 | 130 | 93 | 75 | 31 | 87 | 72 | 123 |
| Data Types | Zo | Z | Φ | Zo + W | Z + W | Φ + W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Difference | 0.127 | 0.139 | 0.124 | 0.119 | 0.132 | 0.172 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Tang, B.; Deng, J.; Chen, H.; Tang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhou, C. Appraisal of the Magnetotelluric and Magnetovariational Transfer Functions’ Selection in a 3-D Inversion. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133416
Yu H, Tang B, Deng J, Chen H, Tang W, Chen X, Zhou C. Appraisal of the Magnetotelluric and Magnetovariational Transfer Functions’ Selection in a 3-D Inversion. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(13):3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133416
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Hui, Bin Tang, Juzhi Deng, Hui Chen, Wenwu Tang, Xiao Chen, and Cong Zhou. 2023. "Appraisal of the Magnetotelluric and Magnetovariational Transfer Functions’ Selection in a 3-D Inversion" Remote Sensing 15, no. 13: 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133416
APA StyleYu, H., Tang, B., Deng, J., Chen, H., Tang, W., Chen, X., & Zhou, C. (2023). Appraisal of the Magnetotelluric and Magnetovariational Transfer Functions’ Selection in a 3-D Inversion. Remote Sensing, 15(13), 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133416