Temporal Changes in Mediterranean Pine Forest Biomass Using Synergy Models of ALOS PALSAR-Sentinel 1-Landsat 8 Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methodology Framework
2.3. Field Plot Measurement and Field Biomass Estimation
2.4. Remote Sensing Data
2.4.1. ALOS Data
2.4.2. Sentinel 1 Data
2.4.3. Landsat Data
2.4.4. Texture Analysis
2.4.5. ALS Data Processing and Biomass Modelling
2.5. Variable Selection
2.6. Biomass and Modeling of Structural Variables
2.7. Biomass and Structural Variables Maps
3. Results
3.1. Variable Selection
3.2. Biomass Models
3.2.1. Random Forest Variable Selection
3.2.2. Random Forest AGB Models
3.3. Biomass Maps and Temporal Change
4. Discussion
4.1. Forest Structural Variables
4.2. Forest Applications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Novo-Fernández, A.; Barrio-Anta, M.; Recondo, C.; Cámara-Obregón, A.; López-Sánchez, C.A. Integration of national forest inventory and nationwide airborne laser scanning data to improve forest yield predictions in north-western Spain. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, H.; Bastos, A.; Das, A.J.; Esquivel-Muelbert, A.; Hammond, W.M.; Martínez-Vilalta, J.; Allen, C.D. Climate change risks to global forest health: Emergence of unexpected events of elevated tree mortality worldwide. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2022, 73, 673–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderpour, E.; Mazzanti, P.; Mugnozza, G.S.; Bozzano, F. Coherency and phase delay analyses between land cover and climate across Italy via the least-squares wavelet software. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 118, 103241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y. Forest Aboveground Biomass Estimation and Response to Climate Change Based on Remote Sensing Data. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puliti, S.; Hauglin, M.; Breidenbach, J.; Montesano, P.; Neigh CS, R.; Rahlf, J.; Astrup, R. Modelling above-ground biomass stock over Norway using national forest inventory data with ArcticDEM and Sentinel-2 data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, A.J.; Andersen, H.; Frescino, T.; Gatziolis, D.; Healey, S.; Heath, L.S.; Wilson, B.T. Use of remote sensing data to improve the efficiency of national forest inventories: A case study from the United States national forest inventory. Forests 2020, 11, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardini, M.; Armston, J.; Qi, W.; Lee, S.K.; Tello, M.; Cazcarra Bes, V.; Fatoyinbo, L.E. Early lessons on combining lidar and multi-baseline SAR measurements for forest structure characterization. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 803–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.; Lundblad, M.; Petersson, H. Carbon accounting and the climate politics of forestry. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englhart, S.; Keuck, V.; Siegert, F. Modeling aboveground biomass in tropical forests using multi-frequency SAR data-A comparison of methods. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Toan, T.; Quegan, S.; Davidson, M.W.J.; Balzter, H.; Paillou, P.; Papathanassiou, K.; Plummer, S.; Rocca, F.; Saatchi, S.; Shugart, H.; et al. The BIOMASS mission: Mapping global forest biomass to better understand the terrestrial carbon cycle. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2850–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D. The potential and challenge of remote sensing-based biomass estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 1297–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, P.; Dubayah, R.; Peterson, B.; Blair, J.B.; Hofton, M.; Hunsaker, C. Mapping forest structure for wildlife habitat analysis using waveform lidar: Validation of montane ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Chen, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Li, G.; Moran, E. A survey of remote sensing-based aboveground biomass estimation methods in forest ecosystems. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 63–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashum, K.T.; Jayakumar, S. Methods to estimate above-ground biomass and carbon stock in natural forests—A review. J. Ecosyst. Ecography 2012, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.L.; Cohen, W.B.; Healey, S.P.; Kennedy, R.E.; Moisen, G.G.; Pierce, K.B.; Ohmann, J.L. Quantification of live aboveground forest biomass dynamics with Landsat time-series and field inventory data: A comparison of empirical modeling approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1053–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres-Mauricio, J.; Valdez-Lazalde, J.R.; George-Chacón, S.P.; Hernández-Stefanoni, J.L. Mapping structural attributes of tropical dry forests by combining Synthetic Aperture Radar and high-resolution satellite imagery data. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2021, 24, e12580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alappat, V.O.; Joshi, A.K.; Krishnamurthy, Y.V. Tropical Dry Deciduous Forest Stand Variable Estimation Using SAR Data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2011, 39, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Su, Z.; Chen, E.; Li, Z.; van der Tol, C.; Guo, J.; He, Q. Estimation of forest above-ground biomass using multi-parameter remote sensing data over a cold and arid area. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 14, 160–168. [Google Scholar]
- Santi, E.; Paloscia, S.; Pettinato, S.; Fontanelli, G.; Mura, M.; Zolli, C.; Maselli, F.; Chiesi, M.; Bottai, L.; Chirici, G. The potential of multifrequency SAR images for estimating forest biomass in Mediterranean areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 200, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Liao, J.; Shen, G. Combining spectral and texture features for estimating leaf area index and biomass of maize using sentinel-1/2, and landsat-8 data. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 53614–53626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.L.R.; Nichol, J.; Iz, H.B.; Ahmad, B.B.; Rahman, A.A. Forest biomass estimation using texture measurements of high-resolution dual-polarization C-band SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3371–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, I.; da Costa, J.-P.; Godineau, A.; Villard, L.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.; le Toan, T.; da Costa, J.P.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.; le Toan, T. Canopy structure effect on SAR image texture versus forest biomass relationships. EARSeL Eproc. 2013, 12, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Stefanoni, J.L.; Gallardo-Cruz, J.A.; Meave, J.A.; Rocchini, D.; Bello-Pineda, J.; López-Martínez, J.O. Modeling α-and β-diversity in a tropical forest from remotely sensed and spatial data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 19, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, J.; Fernández-Landa, A.; Tomé, J.L.; Gómez, C.; Marchamalo, M. Identification of Silvicultural Practices in Mediterranean Forests Integrating Landsat Time Series and a Single Coverage of ALS Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggisser, M.; Dorigo, W.; Dostálová, A.; Hollaus, M.; Navacchi, C.; Schlaffer, S.; Pfeifer, N. Potential of sentinel-1 c-band time series to derive structural parameters of temperate deciduous forests. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, S. Significance of dual polarimetric synthetic aperture radar in biomass retrieval: An attempt on Sentinel-1. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizalapur, V.; Jha, C.S.; Madugundu, R. Estimation of above ground biomass in erkel tropical forested area using multi frequency DLR ESAR data. Int. J. Geomat. Geosci. 2010, 1, 167–178. [Google Scholar]
- Forkuor, G.; Benewinde Zoungrana, J.B.; Dimobe, K.; Ouattara, B.; Vadrevu, K.P.; Tondoh, J.E. Above-ground biomass mapping in west erkele dryland forest using Sentinel-1 and 2 datasets—A case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potzschner, F.; Baumann, M.; Gasparri, N.I.; Conti, G.; Loto, D.; Piquer-Rodríguez, M.; Kuemmerle, T. Ecoregion-wide, multi-sensor biomass mapping highlights a major underestimation of dry forests carbon stocks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuthammachot, N.; Askar, A.; Stratoulias, D.; Wicaksono, P. Combined use of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data for improving above-ground biomass estimation. Geocarto Int. 2020, 37, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, D.; Planells, M.; Guyon, D.; Villard, L.; Mermoz, S.; Bouvet, A.; Thevenon, H.; Dejoux, J.F.; Le Toan, T.; Dedieu, G. Estimation and mapping of forest structure parameters from open access satellite images: Development of a generic method with a study case on coniferous plantation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ren, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Xi, Y. Estimation of forest above-ground biomass by geographically weighted regression and machine learning with sentinel imagery. Forests 2018, 9, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Cancio, A.F.; Navarro Cerrillo, R.M.; Sánchez-Salguero, R.; Fernández, R.F.; Menéndez, E.M. Viabilidad fitoclimática de las repoblaciones de pino silvestre (Pinus sylvestris L.) en la Sierra de los Filabres (Almería). Ecosistemas 2011, 20, 124–144. [Google Scholar]
- Navarrete-Poyatos, M.A.; Navarro-Cerrillo, R.M.; Lara-Gómez, M.A.; Duque-Lazo, J.; Varo, M.d.l.A.; Palacios Rodriguez, G. Assessment of the carbon stock in pine plantations in Southern Spain through ALS data and K-nearest neighbor algorithm-based models. Geosciences 2019, 9, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MITECO. Tercer Inventario Forestal Nacional (IFN3). 2007. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/es/biodiversidad/servicios/banco-datos-naturaleza/informacion-disponible/ifn3.aspx (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Guzmán Álvarez, J.R.; Venegas Troncoso, J.; Seseña Rengel, A.; Sillero Almazán, M.L.; Rodríguez Álvarez, J.A. Biomasa Forestal en Andalucía. 1. Modelo de Existencias, Crecimiento y Producción; Ediciones Mundi-Prensa: Madrid, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Peinado, R.; del Rio, M.; Montero, G. New models for estimating the carbon sink capacity of Spanish softwood species. For. Syst. 2011, 20, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Filho, R.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Rosenqvist, A.; Sánchez, G.A. Using dual-polarized ALOS PALSAR data for detecting new fronts of deforestation in the Brazilian Amazônia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 3735–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Du, H.; Han, N.; Li, X.; Zhu, D.; Mao, F.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, Z.; et al. Application of Convolutional Neural Network on Lei Bamboo Above-Ground-Biomass (AGB) Estimation Using Worldview-2. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvoleff, A. Package ‘glcm’, version 1.6.1. Available online: http://cran.uni-muenster.de/web/packages/glcm/glcm.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Haralick, R.M.; Dinstein, I.; Shanmugam, K. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaughey, R.J. FUSION/LDV: Software for LIDAR Data Analysis and Visualization; USDA Forest Service. PNW: Vancouver, WA, USA, 2007.
- Isenburg, M. LAStools; Rapidlasso GmbH: Gilching, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by Random Forest. 2002. Available online: http://www.stat.berkeley.edu/ (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Miranda, E.N.; Barbosa, B.H.G.; Silva, S.H.G.; Monti, C.A.U.; Tng, D.Y.P.; Gomide, L.R. Variable selection for estimating individual tree height using genetic algorithm and random forest. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2022, 504, 119828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. Model Assessment and Selection. In The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 219–259. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, M.; Wing, J.; Weston, S.; Williams, A.; Keefer, C.; Engelhardt, A.; Cooper, T.C.; Mayer, Z.; Kenkel, B.; Benesty, M.; et al. Package ‘Caret’—Classification and Regression Training version 6.0-93. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/caret/caret.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Crookston, N.L.; Finley, A.O. yaImpute: AR Package for Nearest Neighbor Imputation Routines, Variance Estimation, and Mapping. Available online: http://cran.r-project.org (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Guerra-Hernández, J.; Narine, L.L.; Pascual, A.; Gonzalez-Ferreiro, E.; Botequim, B.; Malambo, L.; Godinho, S. Aboveground biomass mapping by integrating ICESat-2, SENTINEL-1, SENTINEL-2, ALOS2/PALSAR2, and topographic information in Mediterranean forests. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1509–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, E.M.; Radeloff, V.C.; Martinuzzi, S.; Pastur, G.J.M.; Bono, J.; Politi, N.; Pidgeon, A.M. Nationwide native forest structure maps for Argentina based on forest inventory data, SAR Sentinel-1 and vegetation metrics from Sentinel-2 imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 285, 113391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quegan, S.; Le Toan, T.; Chave, J.; Dall, J.; Exbrayat, J.F.; Minh, D.H.T.; Williams, M. The European Space Agency BIOMASS mission: Measuring Forest above-ground biomass from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 227, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Hyyppä, J.; Karjalainen, M.; Nurminen, K.; Karila, K.; Vastaranta, M.; Katoh, M. Comparison of laser and stereo optical, SAR and InSAR point clouds from air-and space-borne sources in the retrieval of forest inventory attributes. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15933–15954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, Q.; White, J.C.; Coops, N.C. Comparing Airborne and Spaceborne Photon-Counting LiDAR Canopy Structural Estimates across Different Boreal Forest Types. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 262, 112510. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Li, C.; Liu, Z. Forest aboveground biomass estimation using Landsat 8 and Sentinel-1A data with machine learning algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Yan, M.; Ji, Y. Forest Above-Ground Biomass Inversion Using Optical and SAR Images Based on a Multi-Step Feature Optimized Inversion Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.L. Radar backscatter and biomass saturation: Ramifications for global biomass inventory. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesha, M.K.; Hussin, Y.A.; van Leeuwen, L.M.; Sulistioadi, Y.B. Modeling and mapping aboveground biomass of the restored mangroves using ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 in East Kalimantan, Indonesia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 91, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Mutanga, O. Remote Sensing of Above-Ground Biomass. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuplich, T.M.; Salvatori, V.; Curran, P.J. JERS-1/SAR backscatter and its relationship with biomass of regenerating forests. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 2513–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, T.; Mutanga, O. Investigating the robustness of the new Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager derived texture metrics in estimating plantation forest aboveground biomass in resource constrained areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 108, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearse, G.D.; Dash, J.P.; Persson, H.J.; Watt, M.S. Comparison of high-density LiDAR and satellite photogrammetry for forest inventory. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 142, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.L.; Mitchell, A.L.; Milne, A.K.; Danaher, T.; Horn, G. Addressing critical influences on L-band radar backscatter for improved estimates of basal area and change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 272, 112933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, G.; Ulander, L.M.; Fransson, J.E.; Holmgren, J.; Le Toan, T. L-and P-band backscatter intensity for biomass retrieval in hemiboreal forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2874–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zyl, J.J. The Effect of Topography on Radar Scattering from Vegetated Areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1993, 31, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réjou-Méchain, M.; Barbier, N.; Couteron, P.; Ploton, P.; Vincent, G.; Herold, M.; Pélissier, R. Upscaling Forest biomass from field to satellite measurements: Sources of errors and ways to reduce them. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 881–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Gong, P. Integration of multi-resource remotely sensed data and allometric models for forest aboveground biomass estimation in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurin, G.V.; Balling, J.; Corona, P.; Mattioli, W.; Papale, D.; Puletti, N.; Urban, M. Above-ground biomass prediction by Sentinel-1 multitemporal data in central Italy with integration of ALOS2 and Sentinel-2 data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 016008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, M.A.; Santoro, M.; De La Riva, J.; Fernando, P.; Le Toan, T. Sensitivity of X-, C-, and L-band SAR backscatter to burn severity in Mediterranean pine forests. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3663–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.T.; Awange, J.; Kuhn, M. Evaluation of Three Feature Dimension Reduction Techniques for Machine Learning-Based Crop Yield Prediction Models. Sensors 2022, 22, 6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, G.; Ruiz-Peinado, R.; Muñoz, M. Producción de Biomasa y Fijación de CO2 por los Bosques Españoles; Serie Forestal 13; Instituto Nacional de Investigación y Tecnología Agraria y Alimentaria, Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia: Madrid, Spain, 2005; 270p.
- Santoro, M.; Cartus, O.; Carvalhais, N.; Rozendaal, D.; Avitabile, V.; Araza, A.; Willcock, S. The global forest above-ground biomass pool for 2010 estimated from high-resolution satellite observations. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3927–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narine, L.L.; Popescu, S.C.; Malambo, L. Using ICESat-2 to estimate and map forest aboveground biomass: A first example. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Polarimetric Distortion Analysis of L-and S-Band Airborne SAR (LS-ASAR): A Precursor Study of the Spaceborne Dual-Frequency L-and S-Band NASA ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) Mission. Eng. Proc. 2022, 27, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Khati, U.; Lavalle, M.; Singh, G. The role of time-series L-band SAR and GEDI in mapping sub-tropical above-ground biomass. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 752254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araza, A.; De Bruin, S.; Herold, M.; Quegan, S.; Labriere, N.; Rodriguez-Veiga, P.; Avitabile, V.; Santoro, M.; Mitchard, E.T.A.; Ryan, C.M.; et al. A Comprehensive Framework for Assessing the Accuracy and Uncertainty of Global Above-Ground Biomass Maps. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 272, 112917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
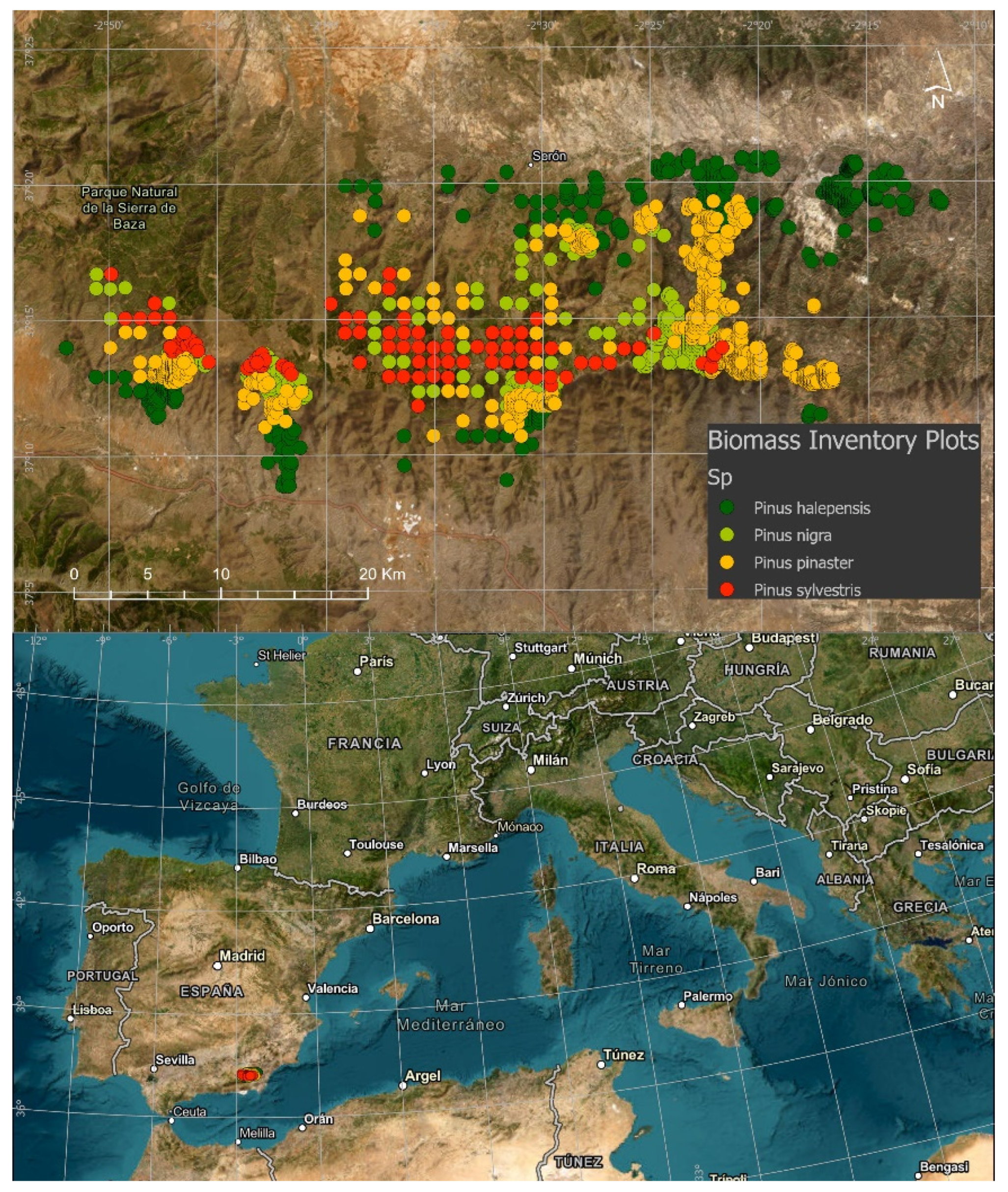
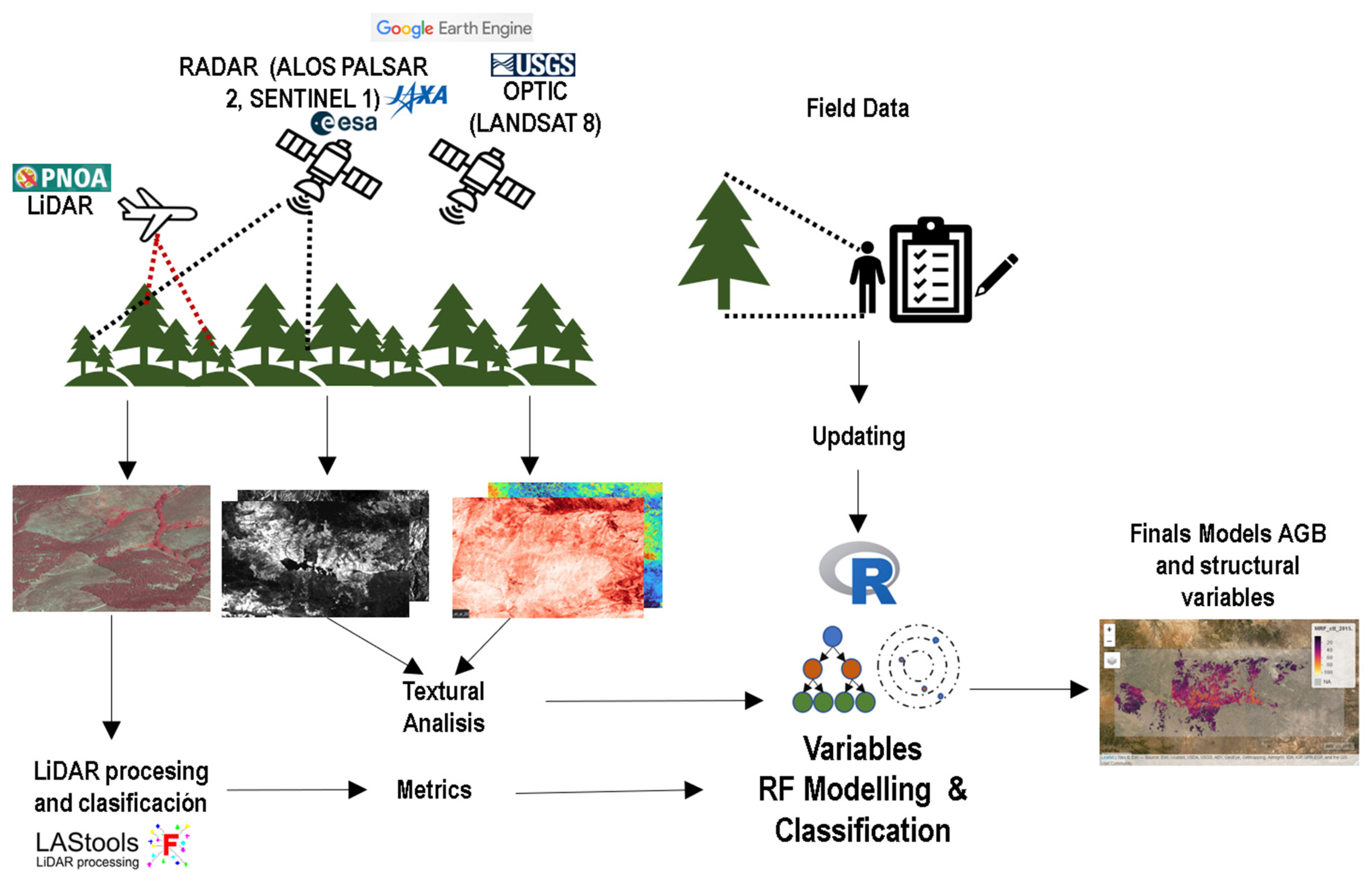





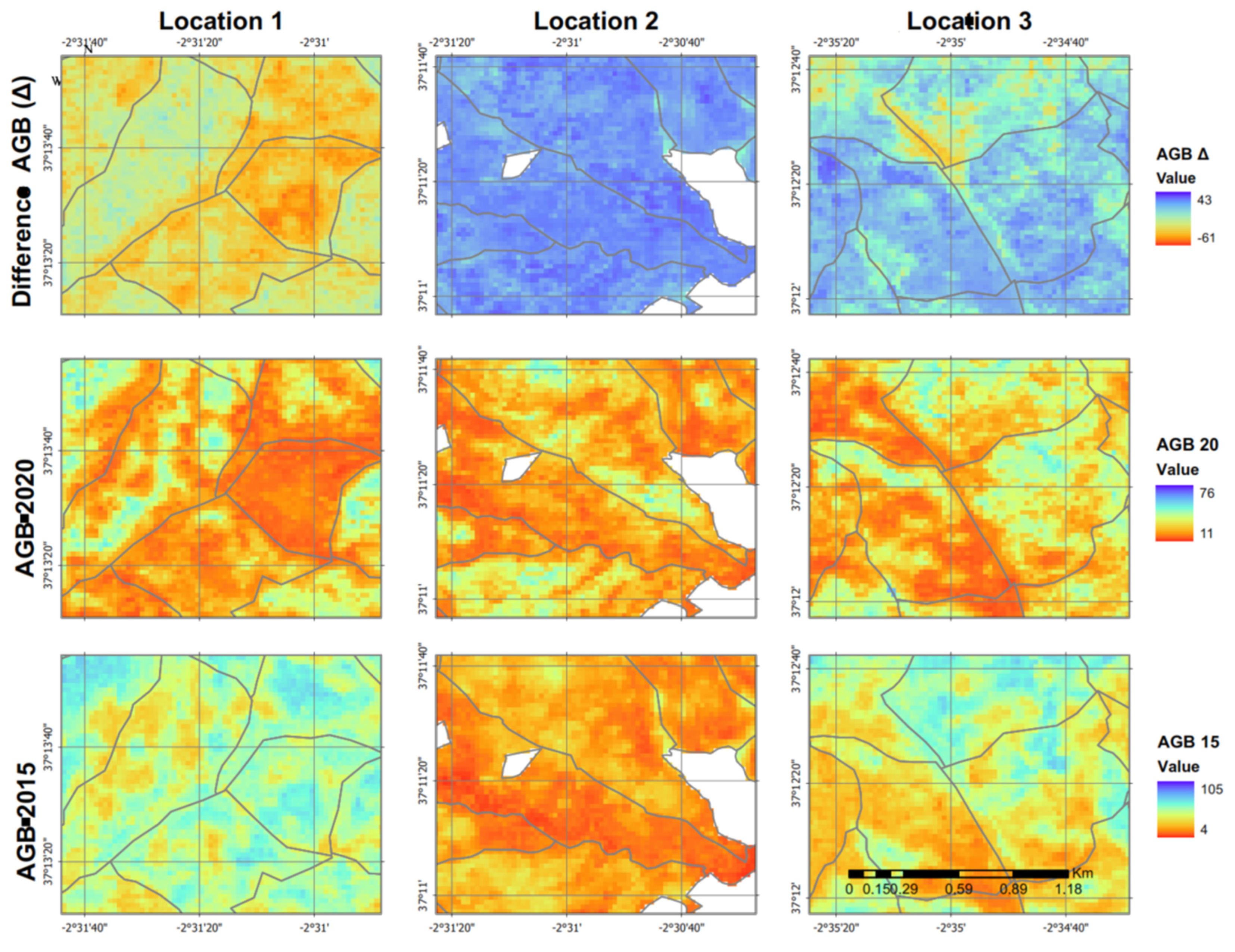
| Species | n. Plots | dbh | N | G | Ho | AGB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinus halepensis | 630 | 17.282 | 419.316 | 10.192 | 9.076 | 19.931 |
| Pinus nigra | 634 | 18.327 | 722.287 | 18.988 | 9.350 | 47.237 |
| Pinus pinaster | 718 | 23.387 | 534.441 | 23.790 | 11.281 | 42.986 |
| Pinus sylvestris | 104 | 17.774 | 605.043 | 14.410 | 8.743 | 35.235 |
| Average | 2086 | 19.726 | 560.284 | 17.756 | 9.902 | 36.929 |
| Data Source | Variable | Description | Season | Number of Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALOS PALSAR 2 | HH | Radar HH polarization | Year (2015, 2020) | 1 |
| HV | Radar HV polarization | Year (2015, 2020) | 1 | |
| NDBI | Normalized difference backscatter index of HH and HV polarizations | Year (2015, 2020) | 1 | |
| Texture HH, HV, and NDBI | Second-order texture measures (7) | Year (2015, 2020) | 21 | |
| DEM, slope and aspect | Derived of ALOS World 3D—30 m Dem Data | - | 3 | |
| Sentinel 1 | vhIwAscDes | Radar vh polarization | Year—(May–June) 2015, 2020 | 2 |
| vhIwAsc | Year—(May–June) 2015, 2020 | 2 | ||
| vhIwDesc | Year—(May–June) 2015, 2020 | 2 | ||
| vvIwAscDes | Radar vv polarization | Year—(May–June) 2015, 2020 | 2 | |
| vvIwAsc | Year—(May–June) 2015, 2020 | 2 | ||
| vvIwDesc | Year—(May–June) 2015, 2020 | 2 | ||
| Texture vhIwAscDes, vvIwAscDes | Second order texture measures (7) | Year—(May–June) 2015, 2020 | 24 | |
| Landsat 8 | reflectance | Red (SR_B4) an NIR (SR_B5) bands | Year—(May–June) 2015, 2020 | 6 |
| NDVI | Normalized difference vegetation index | Year—(May–June) 2015, 2020 | 2 | |
| Texture Red, NIR and NDVI | Second order texture measures (7) | Year—(May–June) 2015, 2020 | 42 | |
| ALS | P90, COV AND CHM | From PNOA 2014 and 2020 (0.5 p m−2) | - | 3 |
| Total | 116 | |||
| AGB | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Set | Model | R2 | RMSE | %RMSE | BIAS | rBias (%) |
| Calibration | ALOS2-SENTINEL1-LANDSAT 8 | 0.50 | 21.35 | 57.80% | 0.43 | −1.41 |
| LIDAR-ALOS2-SENTINEL1-LANDSAT 8 | 0.59 | 19.44 | 53.20% | 0.66 | −1.24 | |
| LIDAR | 0.56 | 20.04 | 54.10% | 0.86 | −1.28 | |
| LANDSAT 8_AGB | 0.47 | 21.96 | 59.10% | 0.47 | −1.53 | |
| ALOS2-SENTINEL1 | 0.49 | 21.54 | 58.30% | 0.43 | −1.51 | |
| SENTINEL 1-LANDSAT 8 | 0.49 | 21.61 | 59.20% | 0.55 | −1.42 | |
| SENTINEL 1 | 0.49 | 21.68 | 58.50% | 0.47 | −1.49 | |
| ALOS 2 | 0.36 | 24.13 | 64.80% | 0.50 | −1.74 | |
| Validation | ALOS2-SENTINEL1-LANDSAT 8 | 0.55 | 19.88 | 54.50% | −0.11 | −1.00 |
| LIDAR-ALOS2-SENTINEL1-LANDSAT 8 | 0.60 | 18.62 | 51.00% | −0.51 | −0.62 | |
| LIDAR | 0.56 | 19.59 | 53.70% | −0.57 | −0.69 | |
| LANDSAT 8_AGB | 0.52 | 20.54 | 56.30% | −0.23 | −0.77 | |
| ALOS2-SENTINEL1 | 0.48 | 21.17 | 58.00% | 0.56 | −0.94 | |
| SENTINEL 1-LANDSAT 8 | 0.53 | 20.22 | 55.40% | 0.14 | −0.77 | |
| SENTINEL 1 | 0.49 | 21.03 | 57.60% | 0.55 | −0.92 | |
| ALOS 2 | 0.35 | 23.89 | 65.50% | −0.02 | −1.25 | |
| Data Set | Forest Structure Variable | 2015 Model ALOS2-SENTINEL1-LANDSAT 8 | 2020 Model ALOS2-SENTINEL1-LANDSAT 8 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | %RMSE | BIAS | rBias% | R2 | RMSE | %RMSE | BIAS | rBias% | ||
| Calibration | AGB | 0.50 | 21.35 | 0.58 | 0.43 | −1.41 | 0.68 | 9.33 | 0.29 | 0.23 | −0.11 |
| BA | 0.47 | 10.12 | 0.57 | 0.21 | −1.29 | 0.50 | 9.78 | 0.56 | 0.18 | −1.27 | |
| N. Trees | 0.31 | 329.97 | 0.58 | 4.71 | −1.31 | 0.30 | 332.06 | 0.59 | 2.12 | −1.33 | |
| Dmc | 0.34 | 4.60 | 0.24 | −0.12 | −0.05 | 0.39 | 4.41 | 0.23 | −0.13 | −0.04 | |
| Ho_m | 0.31 | 2.11 | 0.21 | −0.01 | −0.01 | 0.35 | 2.04 | 0.21 | −0.02 | −0.04 | |
| Validation | AGB | 0.55 | 19.88 | 0.55 | −0.11 | −0.77 | 0.70 | 8.89 | 0.29 | 0.23 | −0.10 |
| BA | 0.55 | 9.33 | 0.53 | 0.02 | −0.64 | 0.55 | 9.27 | 0.53 | 0.36 | −0.60 | |
| N. Trees | 0.30 | 308.87 | 0.58 | −19.49 | −0.73 | 0.25 | 319.60 | 0.60 | −21.73 | −0.78 | |
| Dmc | 0.47 | 4.14 | 0.21 | 0.09 | −0.04 | 0.48 | 4.10 | 0.21 | 0.16 | −0.03 | |
| Ho_m | 0.46 | 1.98 | 0.20 | 0.10 | −0.03 | 0.44 | 2.01 | 0.20 | 0.16 | −0.02 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velasco Pereira, E.A.; Varo Martínez, M.A.; Ruiz Gómez, F.J.; Navarro-Cerrillo, R.M. Temporal Changes in Mediterranean Pine Forest Biomass Using Synergy Models of ALOS PALSAR-Sentinel 1-Landsat 8 Sensors. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133430
Velasco Pereira EA, Varo Martínez MA, Ruiz Gómez FJ, Navarro-Cerrillo RM. Temporal Changes in Mediterranean Pine Forest Biomass Using Synergy Models of ALOS PALSAR-Sentinel 1-Landsat 8 Sensors. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(13):3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133430
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelasco Pereira, Edward A., María A. Varo Martínez, Francisco J. Ruiz Gómez, and Rafael M. Navarro-Cerrillo. 2023. "Temporal Changes in Mediterranean Pine Forest Biomass Using Synergy Models of ALOS PALSAR-Sentinel 1-Landsat 8 Sensors" Remote Sensing 15, no. 13: 3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133430
APA StyleVelasco Pereira, E. A., Varo Martínez, M. A., Ruiz Gómez, F. J., & Navarro-Cerrillo, R. M. (2023). Temporal Changes in Mediterranean Pine Forest Biomass Using Synergy Models of ALOS PALSAR-Sentinel 1-Landsat 8 Sensors. Remote Sensing, 15(13), 3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133430







