Study of Atmospheric Aerosol in the Baikal Mountain Basin with Shipborne and Ground-Based Lidars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Equipment and Techniques
3. Results
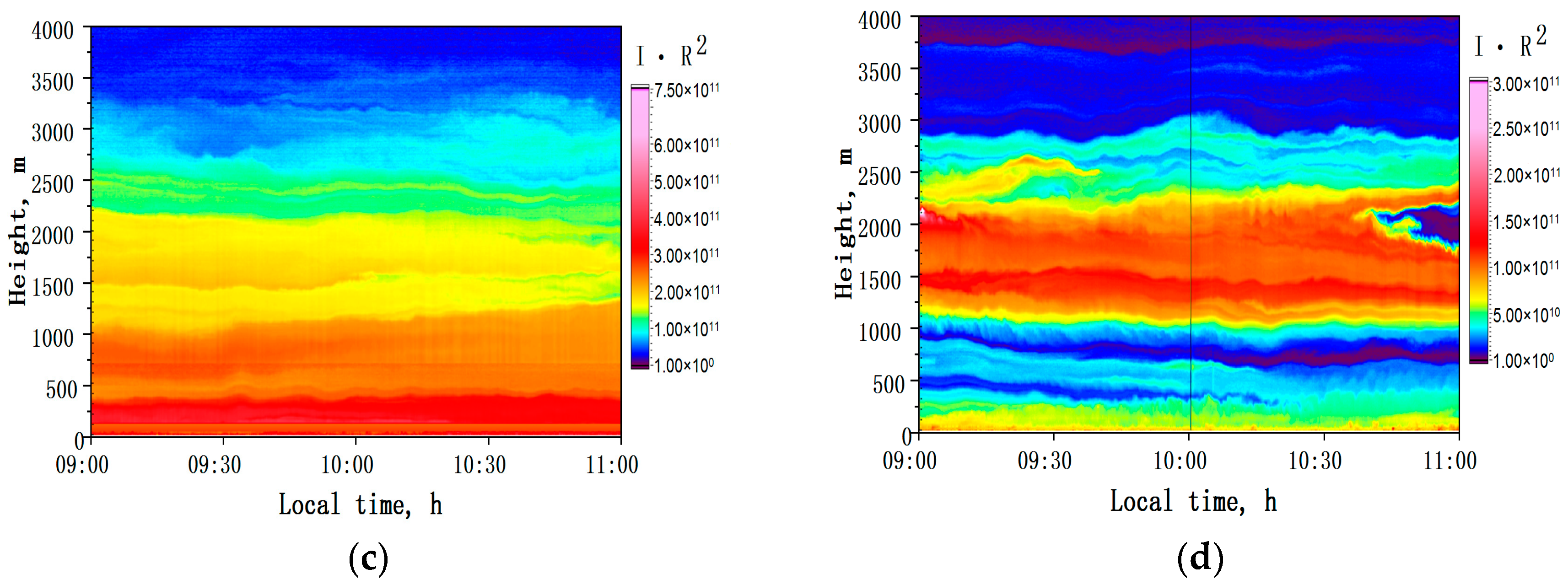
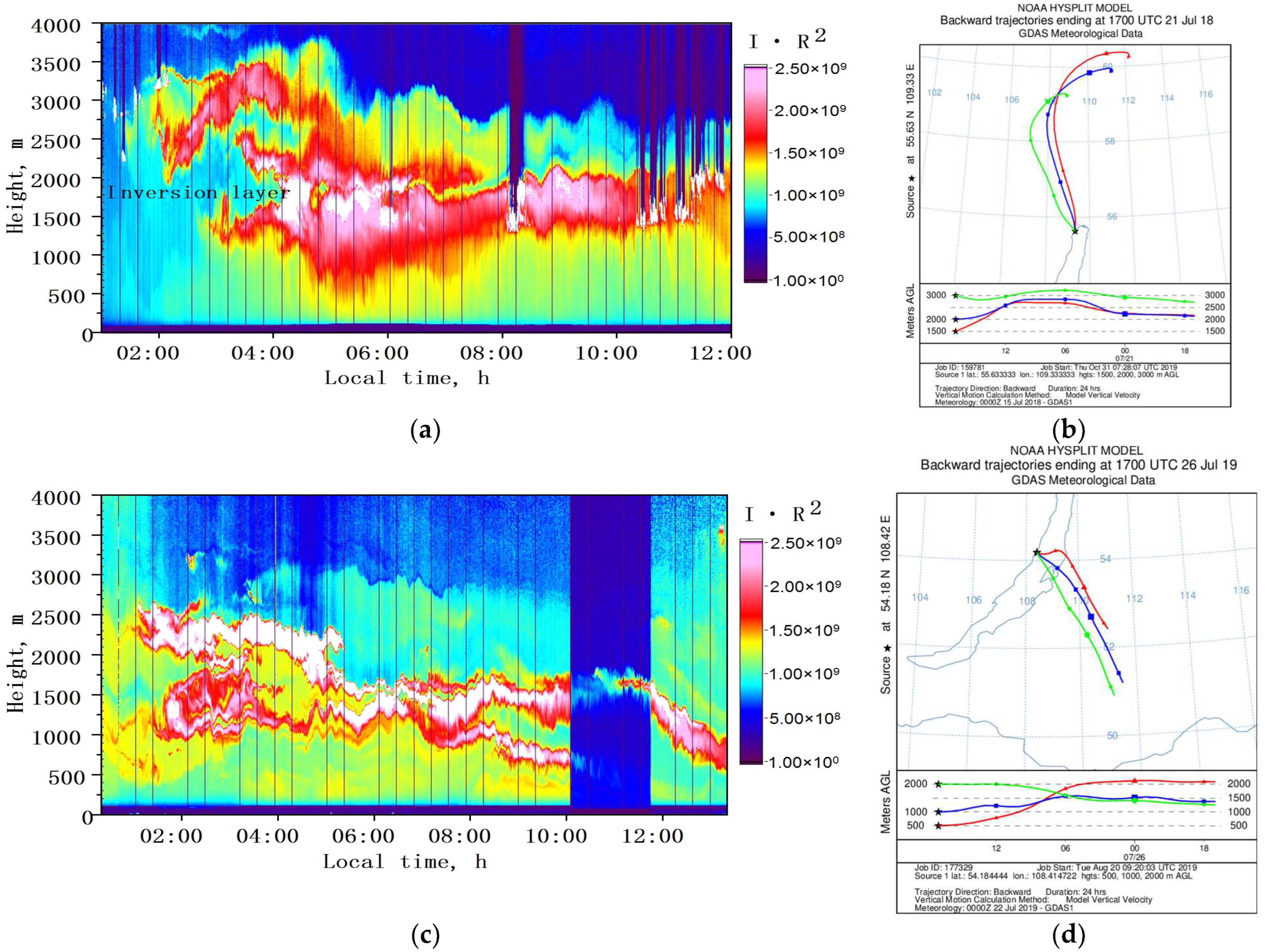
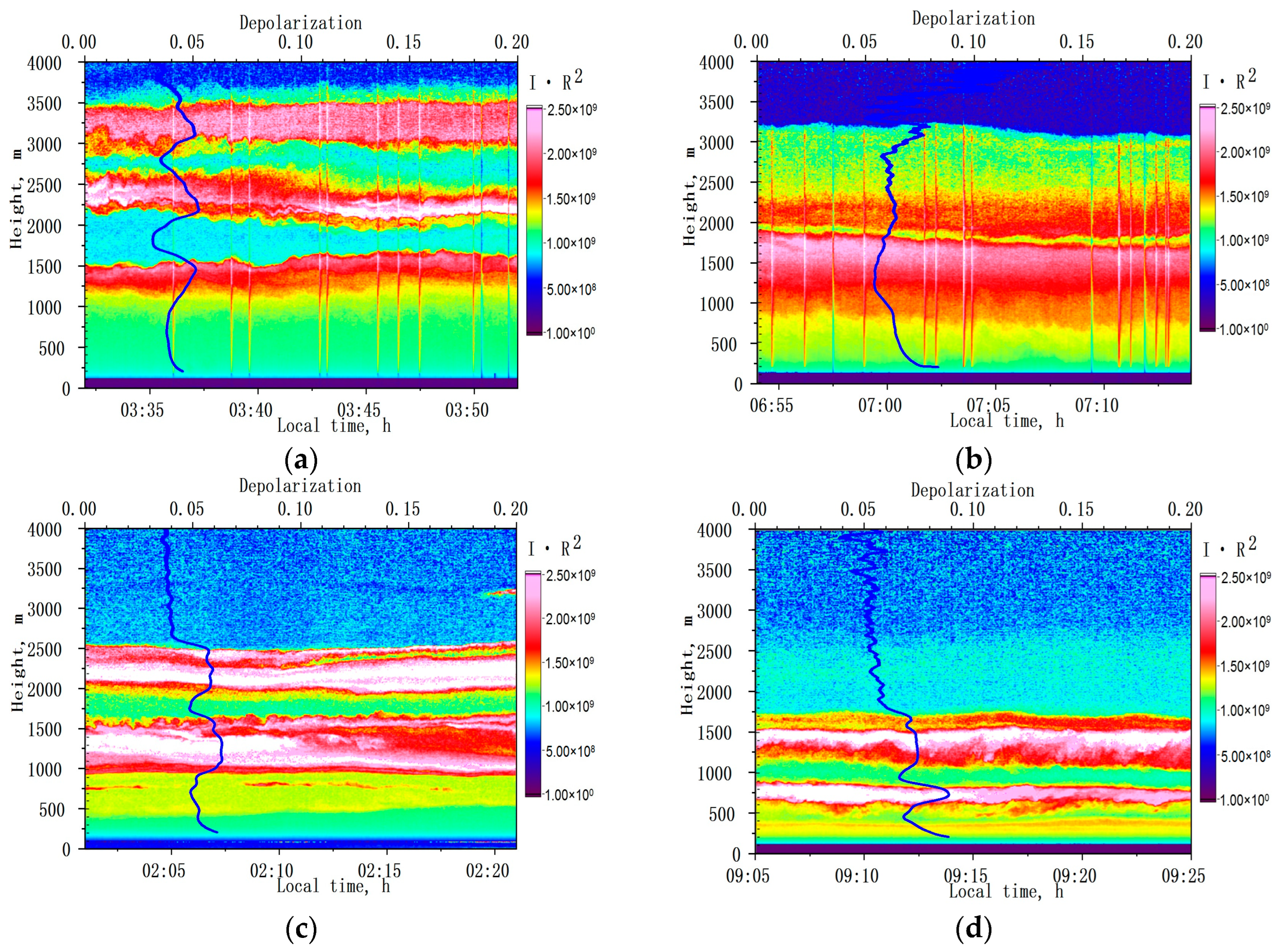
3.1. Observations in Background Conditions
- (1)
- 3 August 2015
- (2)
- 6 August 2016
- (3)
- 23 July 2018
- (4)
- 2 August 2019
- (1)
- 8 August 2016
- (2)
- 5 August 2017
- (3)
- 8 August 2017
- (4)
- 18 July 2018
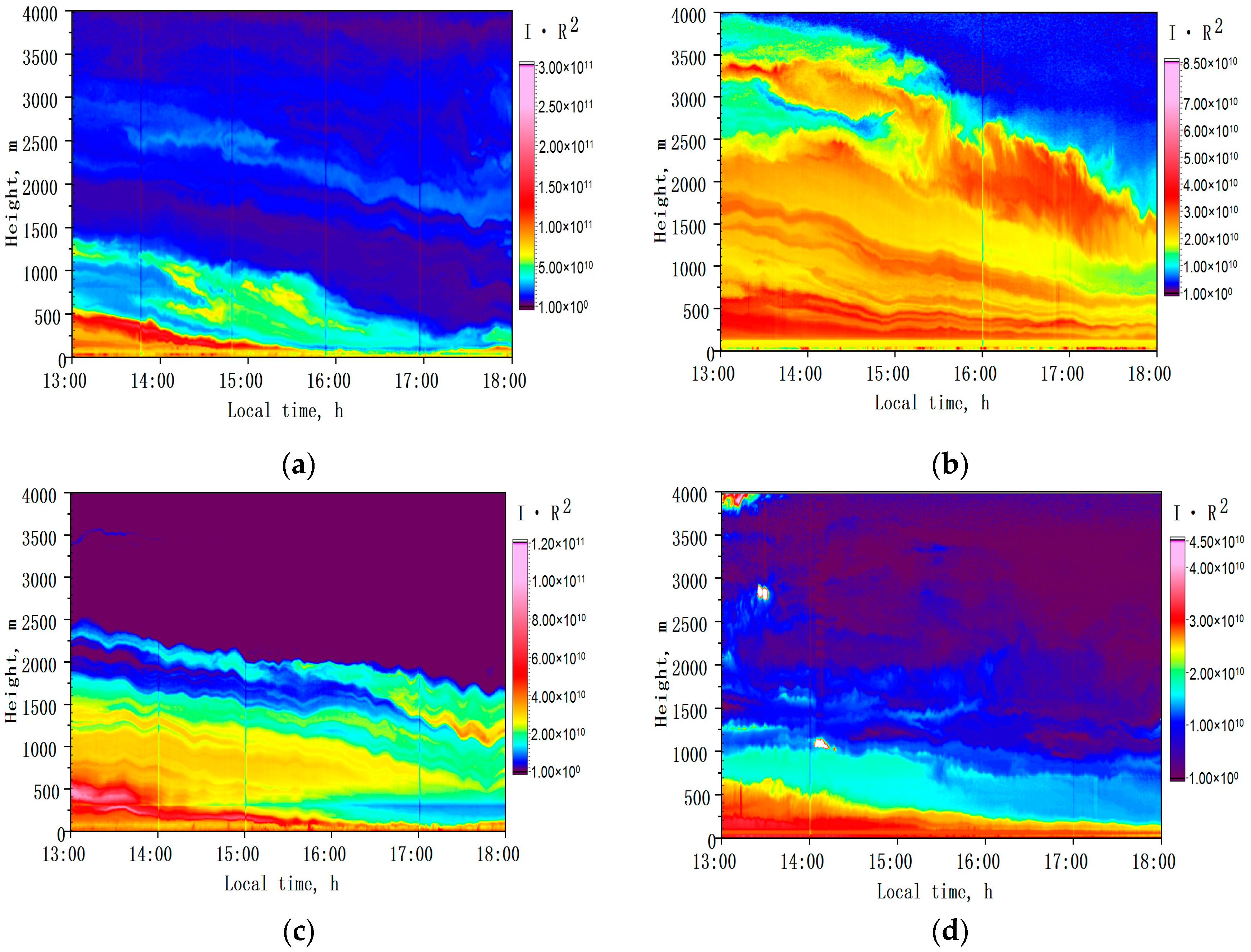
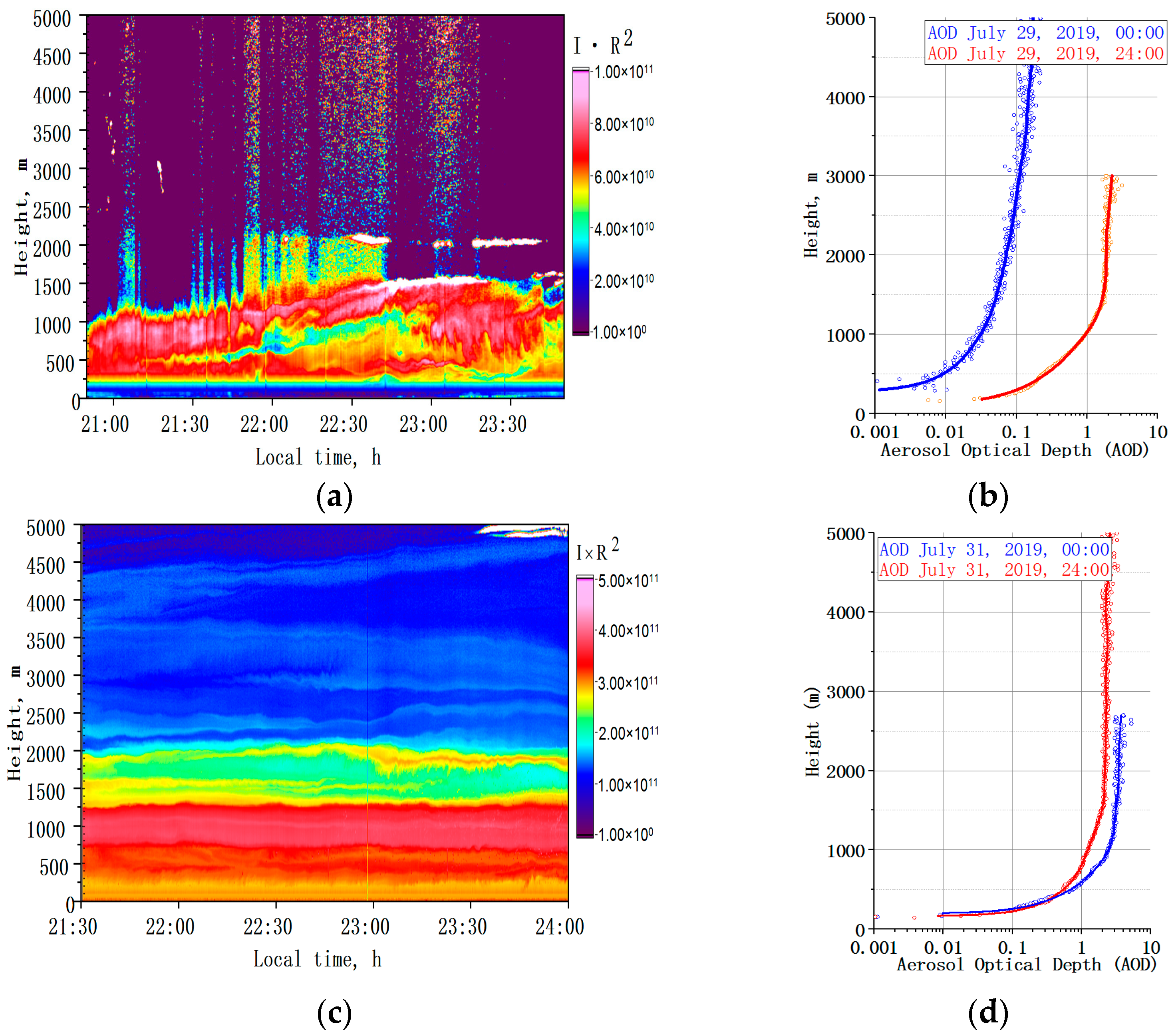
3.2. Observations under Wildfire Conditions
3.3. Calculations of AOD and Angström Parameter
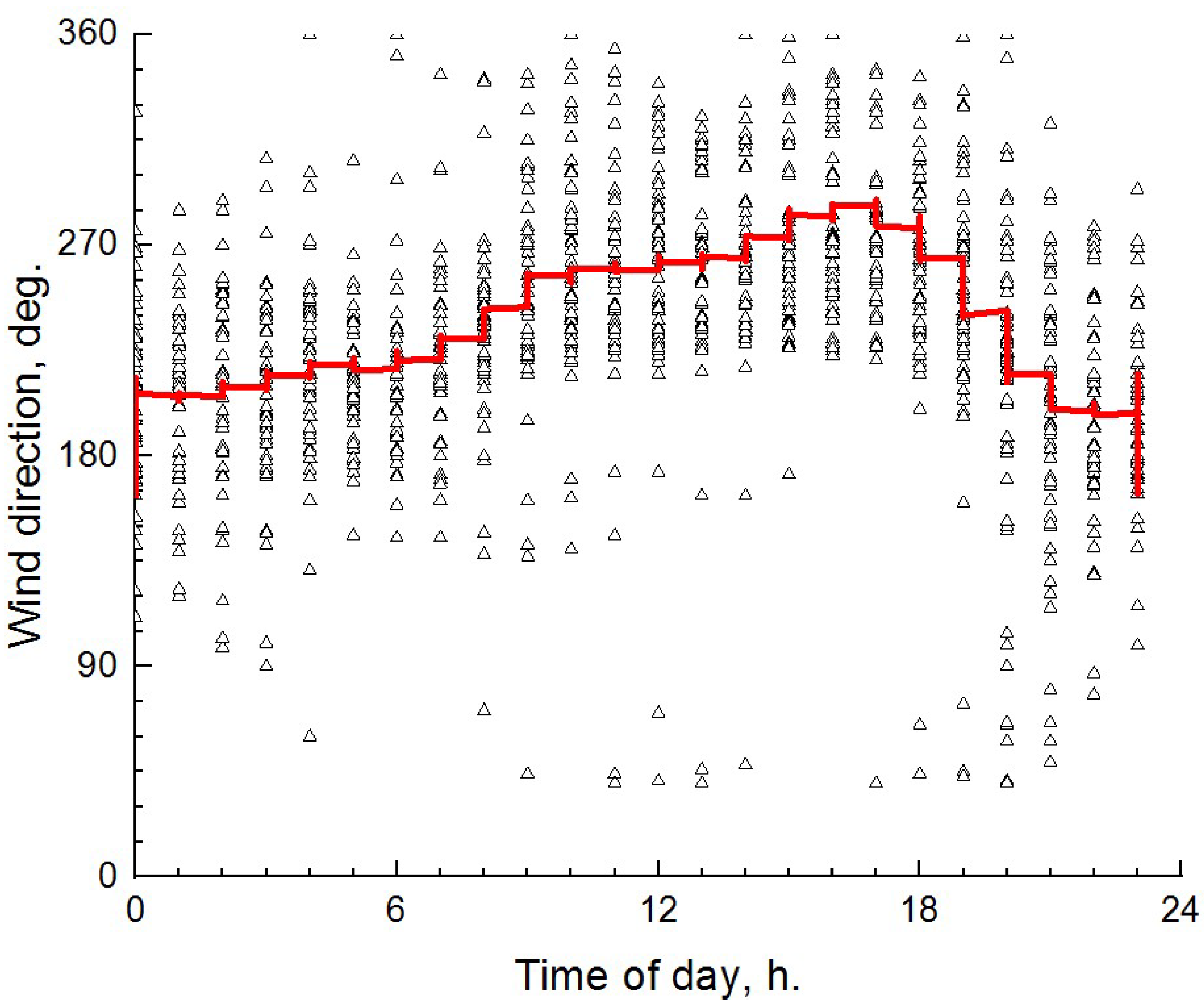
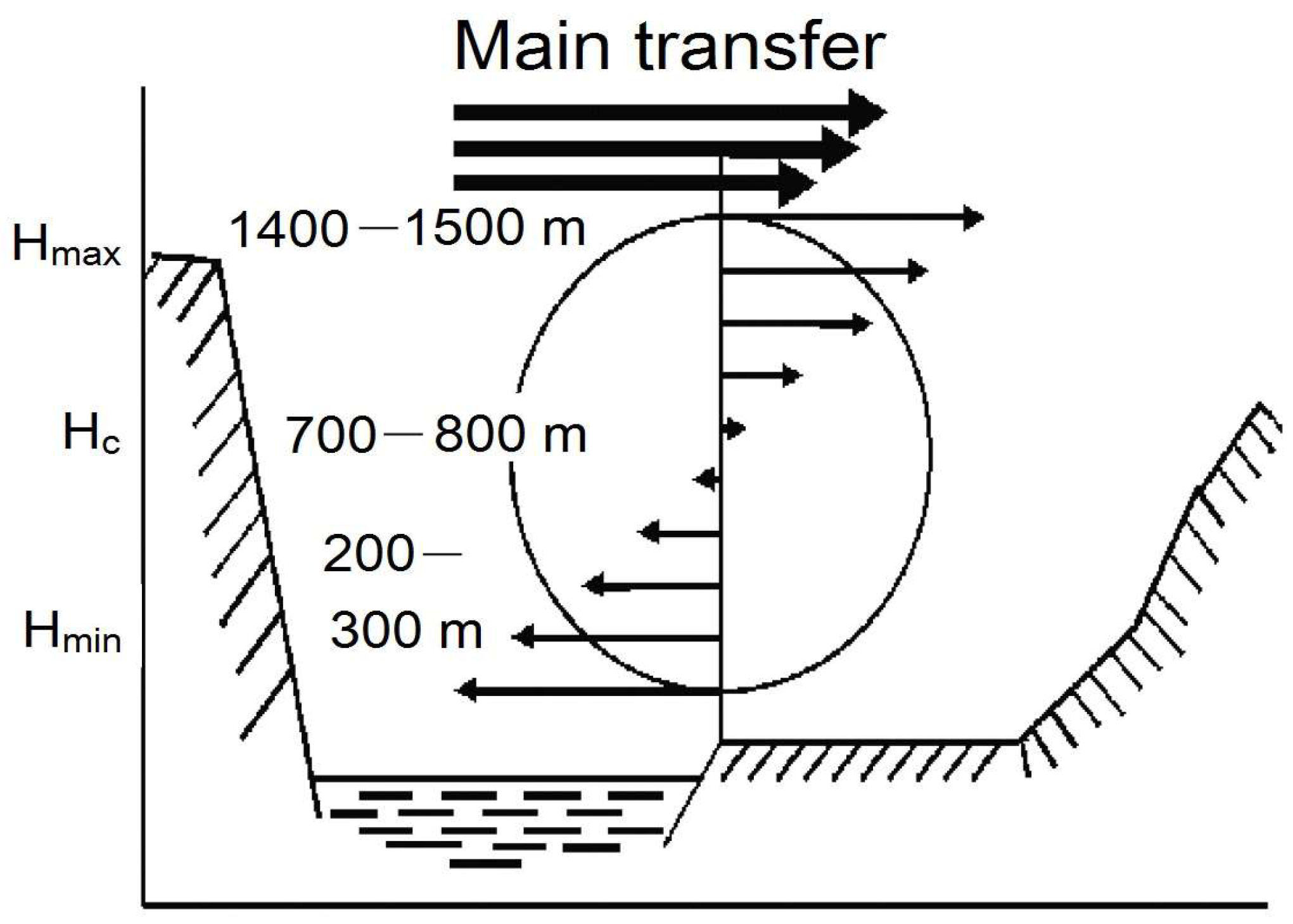
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Golobokova, L.; Khodzher, T.; Obolkin, V.; Potemkin, V.; Khuriganova, O.; Onischuk, N. Aerosol in the atmosphere of the Baikal region: History and contemporary researches. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 1, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchenko, M.V.; Domysheva, V.M.; Pestunov, D.A.; Sakirko, M.V.; Shamrin, A.M.; Shmargunov, V.P. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere-water system and biogenic elements in the littoral zone of Lake Baikal during period 2004–2018. J. Great Lakes Res. 2020, 46, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obolkin, V.A.; Potemkin, V.L.; Makukhin, V.L.; Khodzher, T.V.; Chipanina, E.V. Long-range transport of plumes of atmospheric emissions from regional coal power plants to the south Baikal water basin. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2017, 30, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banakh, V.A.; Smalikho, I.N. Lidar observations of atmospheric internal waves in the boundary layer of the atmosphere on the coast of Lake Baikal. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5239–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayakhanov, A.S.; Zhamsueva, G.S.; Sungrapova, I.P.; Tsydypov, V.V. Features of diurnal variability of ultrafine aerosol in the air of the Baikal coastal zone and arid zone of Mongolia. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2018, 31, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovicheva, O.; Molozhnikova, E.; Nasonov, S.; Potemkin, V.; Penner, I.; Klemasheva, M.; Marinaite, I.; Golobokova, L.; Vratolis, S.; Eleftheriadis, K.; et al. Industrial and wildfire aerosol pollution over world heritage Lake Baikal. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 107, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhamsueva, G.; Zayakhanov, A.; Tcydypov, V.; Dementeva, A.; Balzhanov, T. Spatial-temporal variability of small gas impurities over lake Baikal during the forest fires in the summer of 2019. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashchilin, M.; Yakovleva, I.; Sakerin, S.; Zorkaltseva, O.; Tatarnikov, A.; Scheglova, E. Spatiotemporal variations of aerosol optical depth in the atmosphere over Baikal region based on MODIS data. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domysheva, V.M.; Panchenko, M.V.; Pestunov, D.A.; Sakirko, M.V.; Shamrin, A.M. Estimation of primary production in the water of the coastal zone of Lake Baikal based on daily variations in CO2 concentration in different seasons of 2005–2021. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2023, 36, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyanova, E.A.; Penenko, V.V.; Gochakov, A.V.; Faleychik, L.M. Modeling the propagation of impurities from point sources in the winter atmosphere of the Baikal region. Proc. SPIE Intern. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2020, 11560, 1156071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsheva, T.V. Wind regime over Baikal. Collect. Irkutsk. GMO Name A.V. Voznesensk. 1967, 2, 52–80. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Berkin, N.S.; Makarov, A.A.; Rusinek, O.T. Baikal Studies; State University Press: Irkutsk, Russia, 2009; pp. 76–85. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Arshinov, M.Y.; Belan, B.D.; Ivlev, G.A.; Rasskazchikova, T.M. Spatiotemporal characteristics of air circulation in the hollow of Lake Baikal. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2001, 14, 263–266. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. World Heritage Convention. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/ru/list/754. (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Van Malderen, H.; Van Grieken, R.; Khodzher, T.; Obolkin, V.; Potemkin, V. Composition of individual aerosol particles above Lake Baikal, Siberia. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhamsueva, G.S.; Khodzher, T.V.; Balin, Y.S.; Zayakhanov, A.S.; Tsydypov, V.V.; Penner, I.E.; Nasonov, S.V.; Marinayte, I.I. Experimental studies of aerosol and gas admixtures in the near-water layer of the atmosphere of Lake Baikal (Ship-based expedition, September 2021). Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2022, 35, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izmest'eva, L.R.; Moore, M.V.; Hampton, S.E.; Ferwerda, C.J.; Gray, D.K.; Woo, K.H.; Pislegina, H.V.; Krashchuk, L.S.; Shimaraeva, S.V.; Silow, E.A. Lake-wide physical and biological trends associated with warming in Lake Baikal. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchenko, M.V.; Belan, B.D.; Shamanaev, V.S. Investigation of Lake Baikal environment with airplane-laboratory of the Institute of Atmospheric Optics SB RAS. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 1997, 10, 463–472. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dieudonné, E.; Chazette, P.; Marnas, F.; Totems, J.; Shang, X. Lidar profiling of aerosol optical properties from Paris to Lake Baikal (Siberia). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5007–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balin, Y.S.; Bairashin, G.S.; Kokhanenko, G.P.; Penner, I.E.; Samoilova, S.V. LOSA-M2 aerosol Raman lidar. Quantum Electron. 2011, 41, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasonov, S.; Balin, Y.; Klemasheva, M.; Kokhanenko, G.; Novoselov, M.; Penner, I.; Samoilova, S.; Khodzher, T. Mobile aerosol Raman polarizing lidar LOSA-A2 for atmospheric sounding. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.hamamatsu.com/eu/en/product/optical-sensors/pmt/pmt-module/current-output-type/H11526-20.html/ (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Slesar, A.S.; Chaikovsky, A.P.; Ivanov, A.P.; Denisov, S.V.; Korol, M.M.; Osipenko, F.P.; Balin, Y.S.; Kokhanenko, G.P.; Penner, I.E. Fotodetector modules for CIS-LiNet lidar network stations. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2013, 26, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.hamamatsu.com/eu/en/product/optical-sensors/pmt/pmt-module/current-output-type/H11706P-40.html. (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Samoilova, S.V.; Balin, Y.S.; Kokhanenko, G.P.; Penner, I.E. Investigations of the vertical distribution of troposphere aerosol layers based on the data of multifrequency raman lidar sensing. Part I. Method of optical parameter retrieval. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2009, 22, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilova, S.V. Simultaneous reconstruction of the complex refractive index and the particle size distribution function from lidar measurements: Testing the developed algorithms. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2019, 32, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. Circumsolar radiation as a measure of the turbidity of the atmosphere. Part 2. Appl. Opt. 1974, 13, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: http://meteosap.ru/catalog/amk-03/ (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D. HYbridSingle-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory Model (Dataset). Available online: http://www.arl.noaa.gov/ready/hysplit4.html (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Burman, E.A. Mestnye Vetry [Local Winds]; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1969; pp. 3–73. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nasonov, S.; Balin, Y.; Klemasheva, M.; Kokhanenko, G.; Novoselov, M.; Penner, I. Peculiarities of the vertical structure of atmospheric aerosol fields in the basin of Lake Baikal according to lidar observations. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Wyoming. Available online: http://weather.uwyo.edu/upperair/sounding.html (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Available online: http://fires-dv.kosmosnimki.ru/ (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- Dementeva, A.; Zhamsueva, G.; Zayakhanov, A.; Tcydypov, V. Interannual and seasonal variation of optical and microphysical properties of aerosol in the Baikal region. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute. Available online: http://old.aari.ru/odata/_d0010.php (accessed on 25 May 2023).
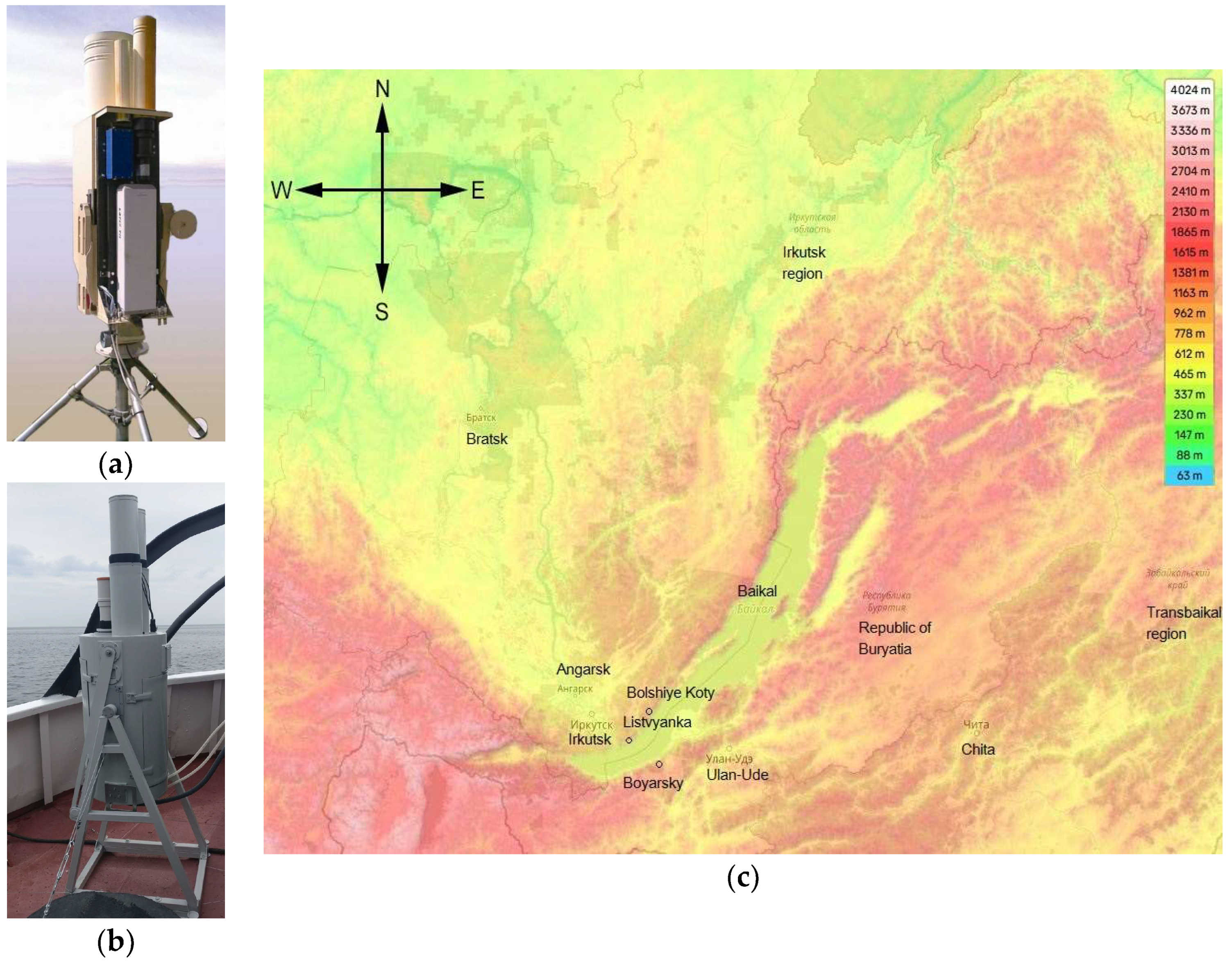


| Parameter | LOSA-A2 Lidar, Shipboard Version | LOSA-M2 Lidar, Stationary Version |
|---|---|---|
| Transmitter | ||
| Nd:YAG laser | LOTIS LS-2131M | LOTIS LS-2135 |
| (Belarus) | (Belarus) | |
| Energy, mJ, at a wavelength of | ||
| 1064 nm | 240 | 340 |
| 532 nm | 120 | 170 |
| Pulse duration, ns | 8 | 10–12 |
| Pulse repetition frequency, Hz | 1–20 | 10 |
| Collimator | ||
| Beam divergence, mrad | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| Beam diameter, mm | 50 | 60 |
| Output polarization | Linear | linear |
| Receiver | ||
| Receiving telescope | Two (for visible and IR regions) | Two (for near and far zones) |
| Telescope diameter, mm | 110 | 50 and 250 |
| Focal length, mm | 500 | 200 and 1000 |
| Field of view, mrad | 1–10 | 1 |
| Signal recording | ||
| 1. Receiving channel 532 nm | ||
| Receiving mode | analog (polarized, cross-polarized) | analog (without polarization) |
| Detector | H11526-20-NF Hammamatsu (Hamamatsu City, Japan) [22] | H11526-20-NF Hammamatsu (Hamamatsu City, Japan) [22] |
| 2. Receiving channel 1064 nm | ||
| Receiving mode | analog | analog |
| Detector | photo module based on a C30956E-TC avalanche photodetector (IAO, Tomsk, Russia) [23] | photo module based on a C30956E-TC avalanche photodetector (IAO, Tomsk, Russia) [23] |
| 3. Receiving channel 607 nm | ||
| Receiving mode | photon counting (nighttime) | photon counting (nighttime) |
| Detector | H11706P-40-MOD Hammamatsu (Hamamatsu City, Japan) [24] | H11706P-40-MOD Hammamatsu (Hamamatsu City, Japan) [24] |
| Mass of the system | 50 kg | 60 kg |
| Date | Altitude Range, m | Angström Parameter | AOD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clear air | |||
| 2 August 2015 | 150–2500 | 1.57 ± 0.16 | 0.09 |
| 9 September 2021 | 150–12,000 | 1.58 ± 0.15 | 0.10 |
| Short-range smoke transport | |||
| 3 August 2015 | 150–3000 | 1.05 ± 0.08 | 0.25 |
| Long-term smoke transport | |||
| 14 August 2015 | 150–3750 | 1.13 ± 0.12 | 0.26 |
| Far-range smoke transport | |||
| 7 August 2013 | 150–2250 | 1.41 ± 0.07 | 0.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasonov, S.; Balin, Y.; Klemasheva, M.; Kokhanenko, G.; Novoselov, M.; Penner, I. Study of Atmospheric Aerosol in the Baikal Mountain Basin with Shipborne and Ground-Based Lidars. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3816. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153816
Nasonov S, Balin Y, Klemasheva M, Kokhanenko G, Novoselov M, Penner I. Study of Atmospheric Aerosol in the Baikal Mountain Basin with Shipborne and Ground-Based Lidars. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(15):3816. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153816
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasonov, Sergei, Yurii Balin, Marina Klemasheva, Grigorii Kokhanenko, Mikhail Novoselov, and Ioganes Penner. 2023. "Study of Atmospheric Aerosol in the Baikal Mountain Basin with Shipborne and Ground-Based Lidars" Remote Sensing 15, no. 15: 3816. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153816
APA StyleNasonov, S., Balin, Y., Klemasheva, M., Kokhanenko, G., Novoselov, M., & Penner, I. (2023). Study of Atmospheric Aerosol in the Baikal Mountain Basin with Shipborne and Ground-Based Lidars. Remote Sensing, 15(15), 3816. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153816






