Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in the Tianshan Mountains Based on Machine Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
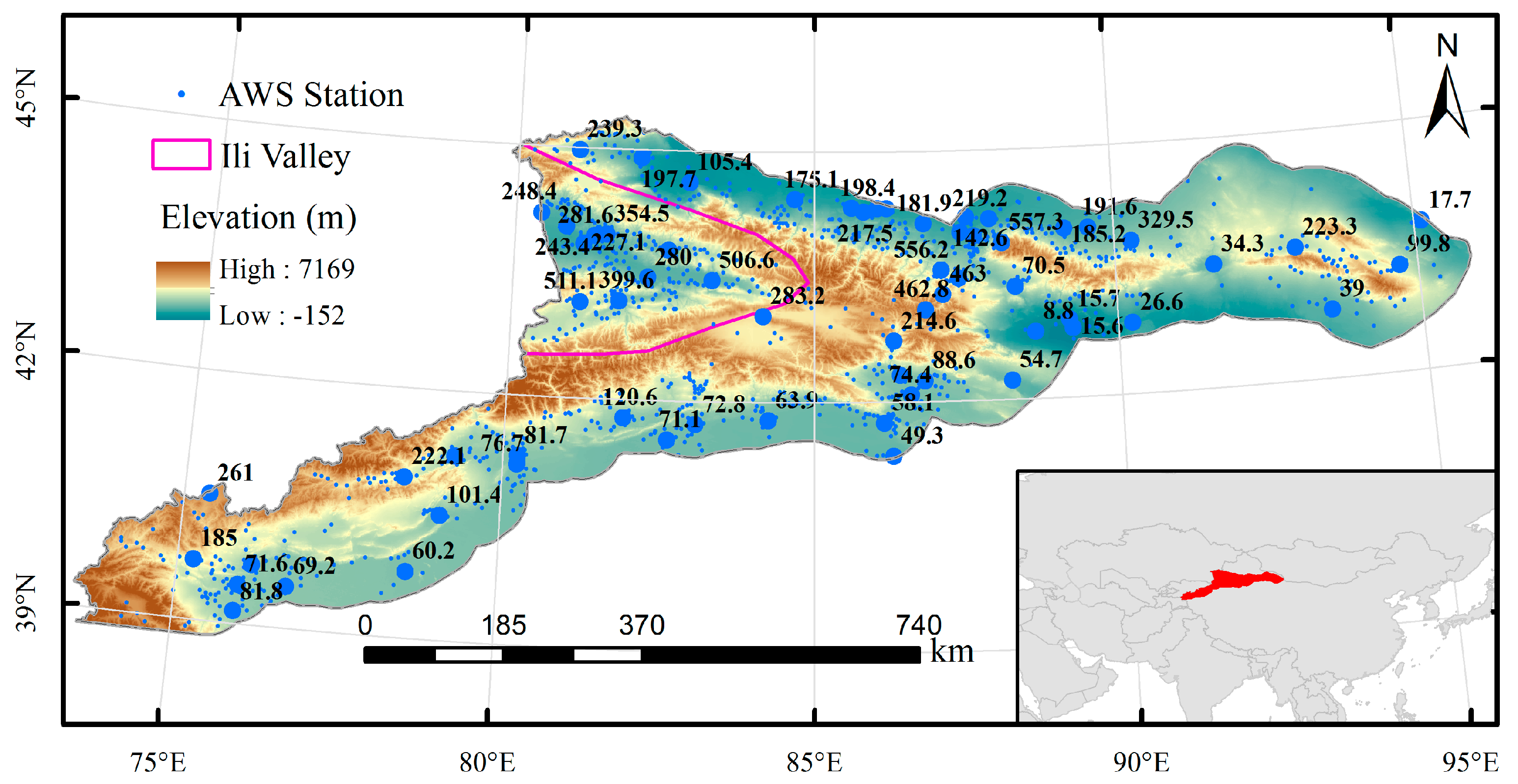
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Satellite Data Sets
- GPM IMERG
- 2.
- NDVI
- 3.
- DEM
2.2.2. Rain Gauge Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Stepwise Regression
2.3.2. GWR
2.3.3. Random Forest
2.3.4. Validation
3. Results
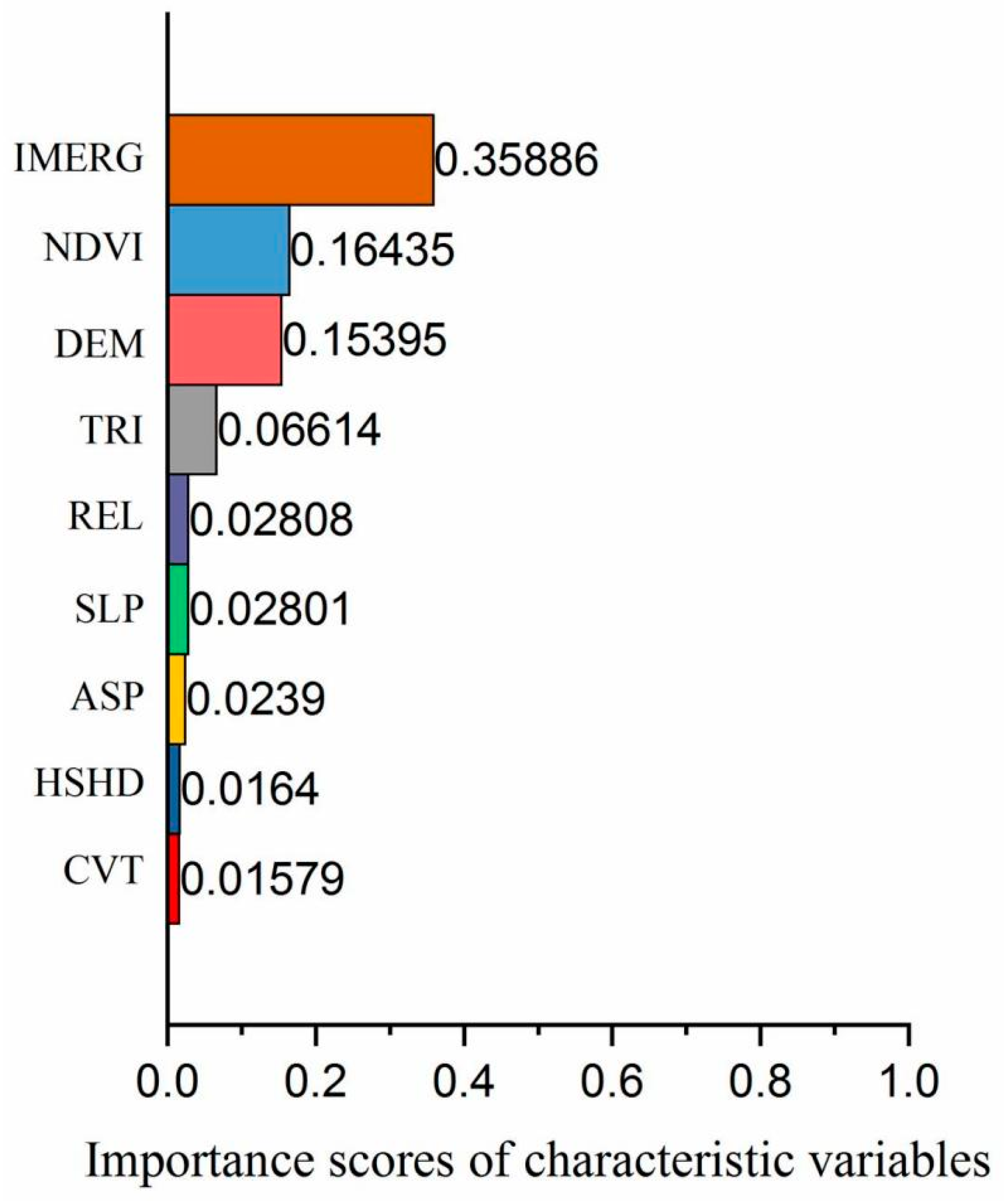
3.1. Importance Ranking of Predictive Factors
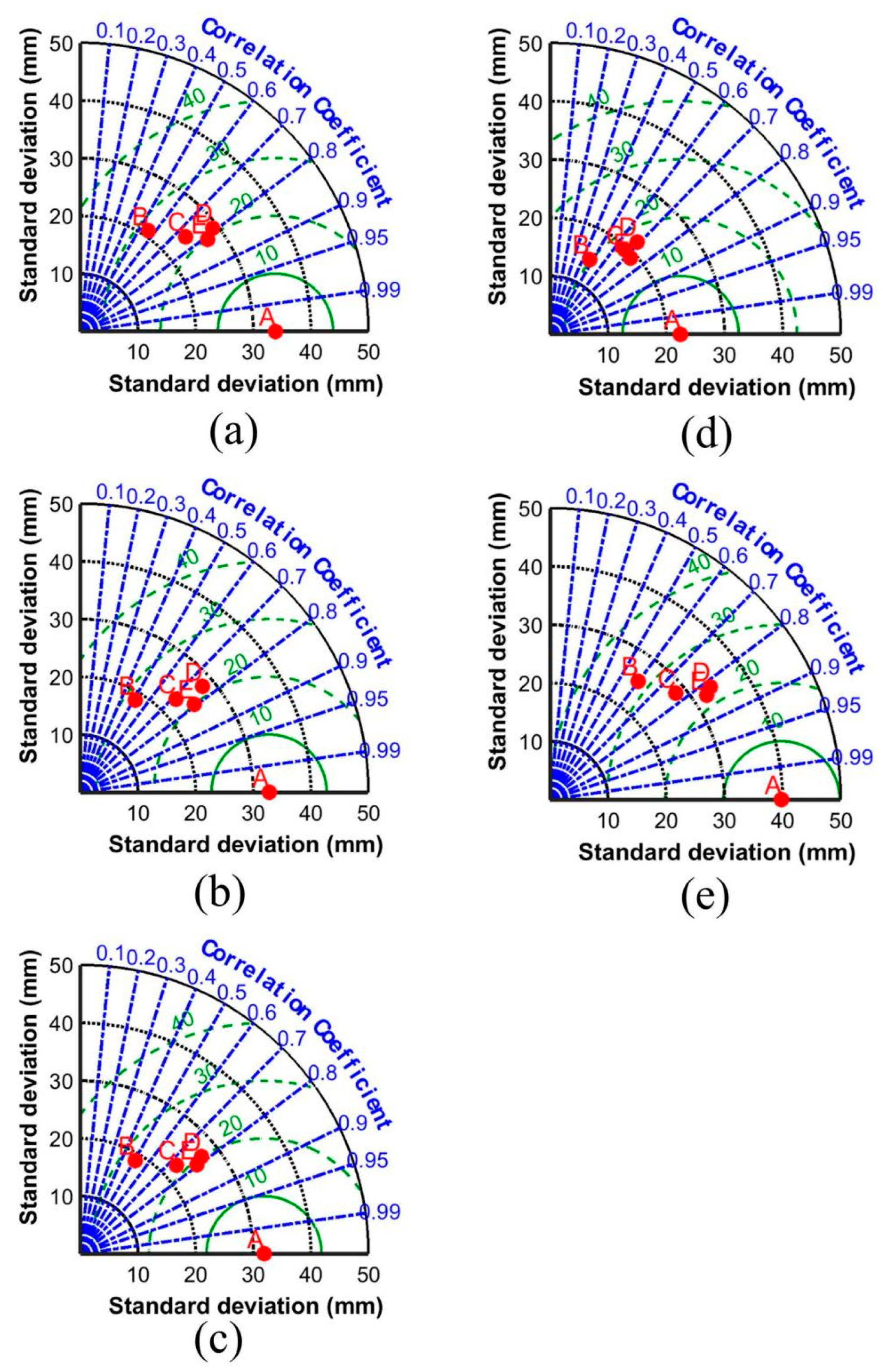
3.2. Overall Evaluation
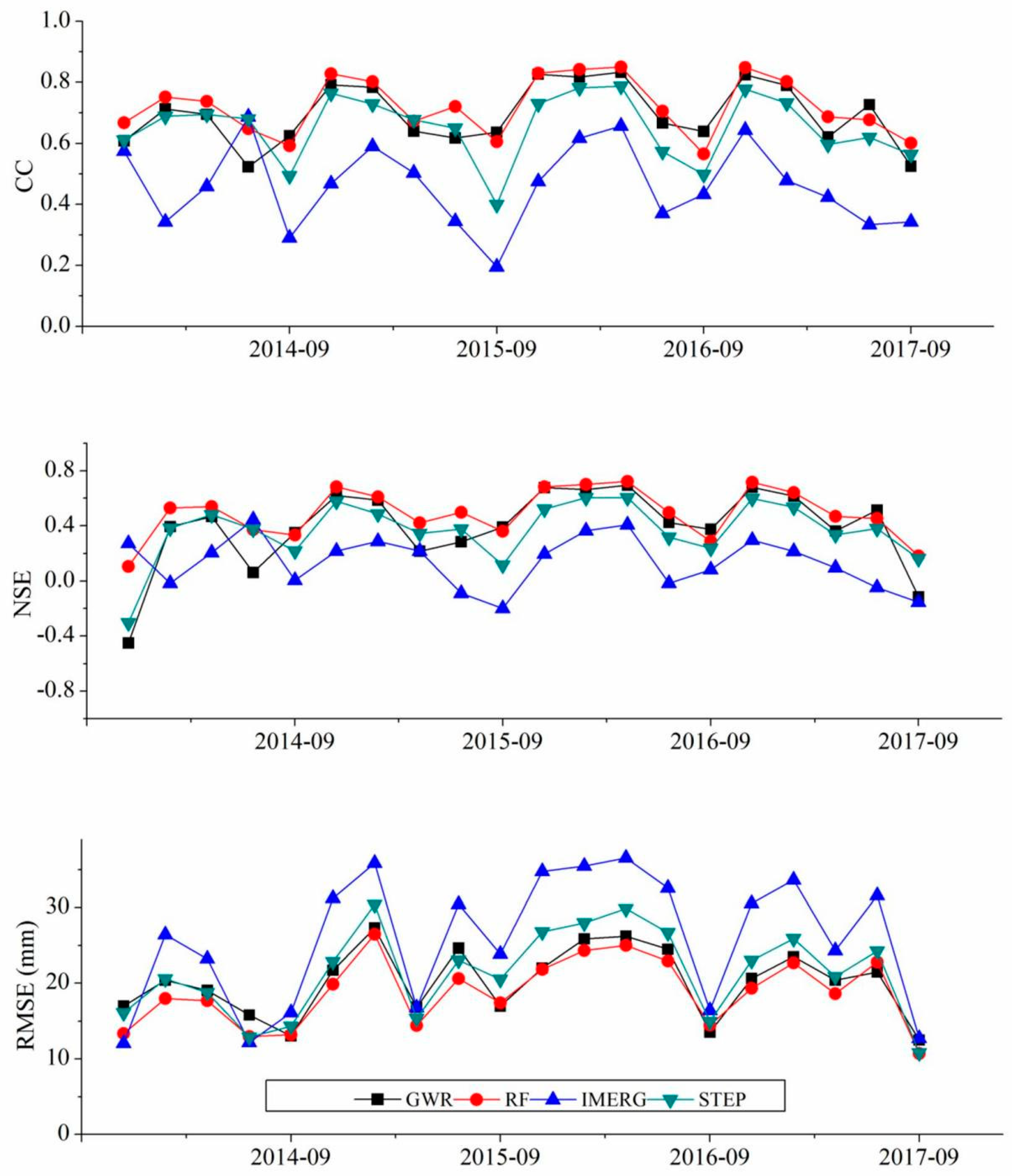
3.3. Evaluation at Different Time Scales
3.3.1. Annual Evaluation
3.3.2. Monthly Evaluation
3.4. Elevation Impact Analyses
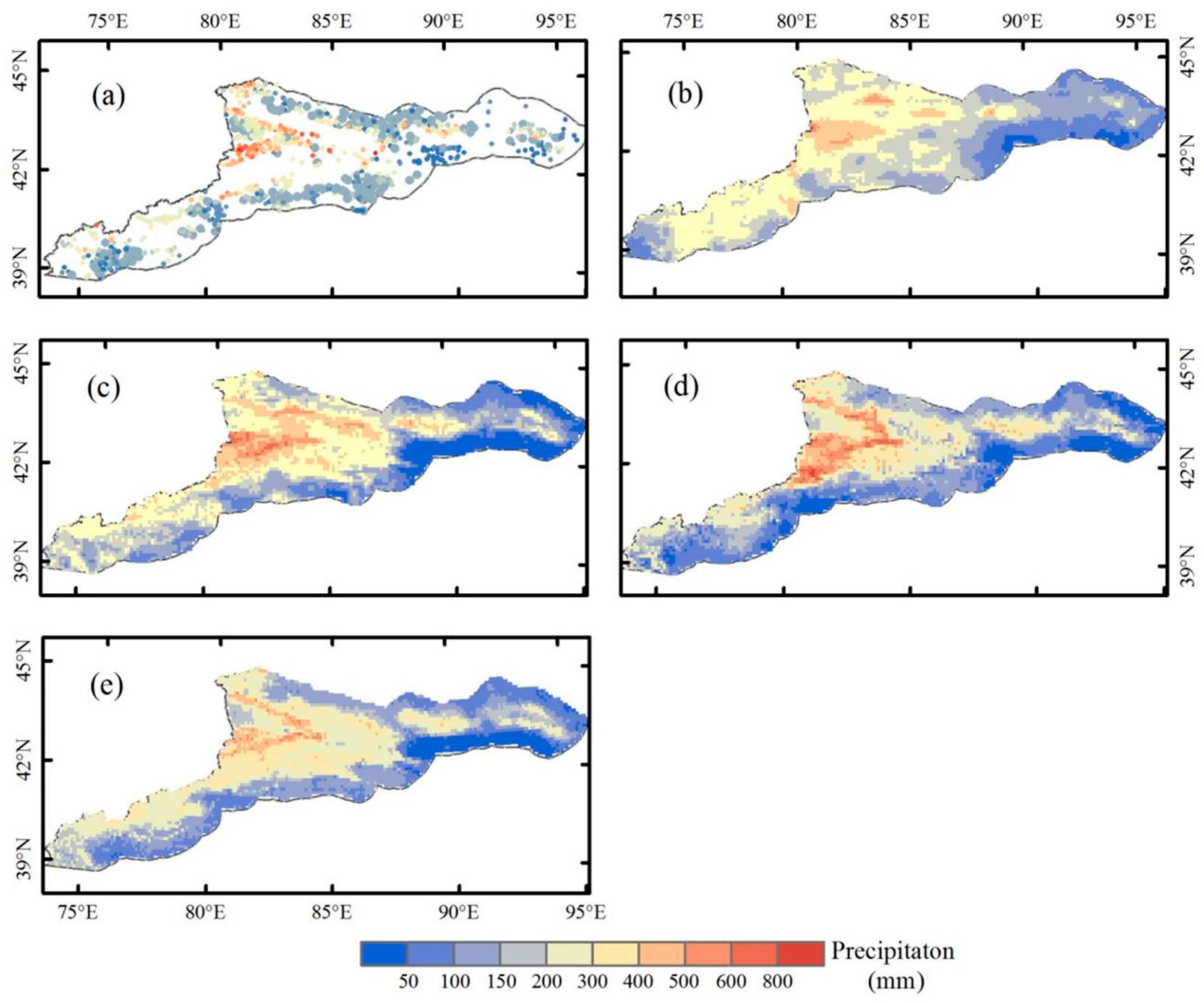
3.5. Actual Spatial Pattern of Precipitation Revealed by IMERG, STEP, GWR, and RF
4. Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yi, L.; Gao, Z.; Shen, Z.; Lin, H.; Liu, Z.; Ma, S.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Li, L. Precipitation Estimation Based on Infrared Data with a Spherical Convolutional Neural Network. J. Hydrometeor. 2023, 24, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Yan, S.; He, Y.; Lu, X.; Ma, Z. Spatio-temporal patterns of snow cover in the Tien Shan, China from 2000 to 2019 based on cloudfree data supported by Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 14, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Ma, Y.; Long, D.; Zhong, L.; Hong, Y. Evaluation of GPM Day-1 IMERG and TMPA Version-7 Legacy Products over Mainland China at Multiple Spatiotemporal Scales. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Tang, G.; Wei, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of multi-satellite precipitation products in Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 7437–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Xu, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, S.; He, K.; Zhang, S.; Ma, W.; Xu, X. AERA5-Asia: A Long-Term Asian Precipitation Dataset (0.1°, 1-Hourly, 1951–2015, Asia) Anchoring the ERA5-Land Under the Total Volume Control by APHRODITE. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 103, E1146–E1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yang, Q. Characteristics of area precipitation in Xinjiang region with its variations. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2008, 19, 326–332. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Fang, G.; Deng, H. Impact of climate change on water resources in the Tianshan Mountians, Central Asia. Acta Geo. Sin. 2017, 1, 18–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Xie, P. NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) Version 4.5. 2017. Available online: http://pmm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/document_files/IMERG_ATBD_V5.1b (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) Technical Documentation. 2017. Available online: http://pmm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/document_files/IMERG_doc_171117b.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Rutten, M.M.; Droogers, P. Spatial downscaling of TRMM precipitation using vegetation response on the Iberian Peninsula. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Zhu, W.; Lu, A.; Yan, T. A statistical spatial downscaling algorithm of TRMM precipitation based on NDVI and DEM in the Qaidam Basin of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3069–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Gonsamo, A.; Shen, Y.; Niu, Z. A new satellite-based monthly precipitation downscaling algorithm with non-stationary relationship between precipitation and land surface characteristics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, S.D.; Hohmann, M.G.; Auerswald, K.; Mitasova, H. An evaluation of methods to determine slope using digital elevation data. Catena 2004, 58, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Chung, C. Using a geographic information system to improve Special Sensor Microwave Imager precipitation estimates over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D03110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Cao, Q.; Gourley, J.J.; Kirstetter, P.E.; Yong, B. Similarity and difference of the two successive v6 and v7 TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis performance over China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 13060–13074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, R.; Seibert, J. Effects of DEM resolution on the calculation of topographical indices: TWI and its components. J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Colella, M.; Chen, X. An assessment of the biases of satellite rainfall estimates over the Tibetan Plateau and correction methods based on topographic analysis. J. Hydrometeor. 2008, 9, 301–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, Z. Quality assessment of hourly merged precipitation product over China. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 36, 37–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, T.; Frauenfeld, O.; Ye, B.; Yang, D.; Qin, D. Evaluation of precipitation from the ERA-40, NCEP-1, and NCEP-2 reanalysis and CMAP-1, CMAP-2, and GPCP-2 with ground-based measurements in China. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D09105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.; Buytaert, W.; Peaver, L.; Wheater, H. Evaluation of precipitation products over complex mountainous terrain: A water resources perspective. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacutt, L.; Herdies, D.; Goncalves, L.; Vila, D.; Andrade, M. Precipitation comparison for the CFSR, MERRA, TRMM3B42 and combined scheme datasets in Bolivia. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Li, Q. Evaluation of reanalysis, spatially-interpolated and satellite remotely-sensed precipitation datasets in Central Asia. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 5648–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beale, E.M.L.; Kendall, M.G.; Mann, D.W. The discarding of variables in multivariate analysis. Biometrika 1967, 54, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, R.G.; Spurrell, D.J. A development of multiple regression for the analysis of routine data. Appl. Stat. 1967, 16, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E. Geographically weighted regression: A method for exploring spatial nonstationarity. Geogr. Anal. 1996, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; 282p, ISBN 978-0-471-49616-8. [Google Scholar]
- Propastin, P.; Kappas, M.; Erasmi, S. Application of geographically weighted regression to investigate the impact of scale on prediction uncertainty by modelling relationship between vegetation and climate. Int. J. Spat. Data Infra. Res. 2008, 3, 73–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kalra, A.; Ahmad, S. Estimating annual precipitation for the Colorado River Basin using oceanic-atmospheric oscillations. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.A.; Tarboton, D.G. A tool for downscaling weather data from large-grid reanalysis products to finer spatial scales for distributed hydrological applications. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 84, 50–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, Y. Using the back propagation neural network approach to bias correct TMPA data in the arid region of North-west China. J. Hydrometeor. 2014, 15, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Tang, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Jia, L.; Xie, G.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Correcting GPM IMERG precipitation data over the Tianshan Mountains in China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 1239–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

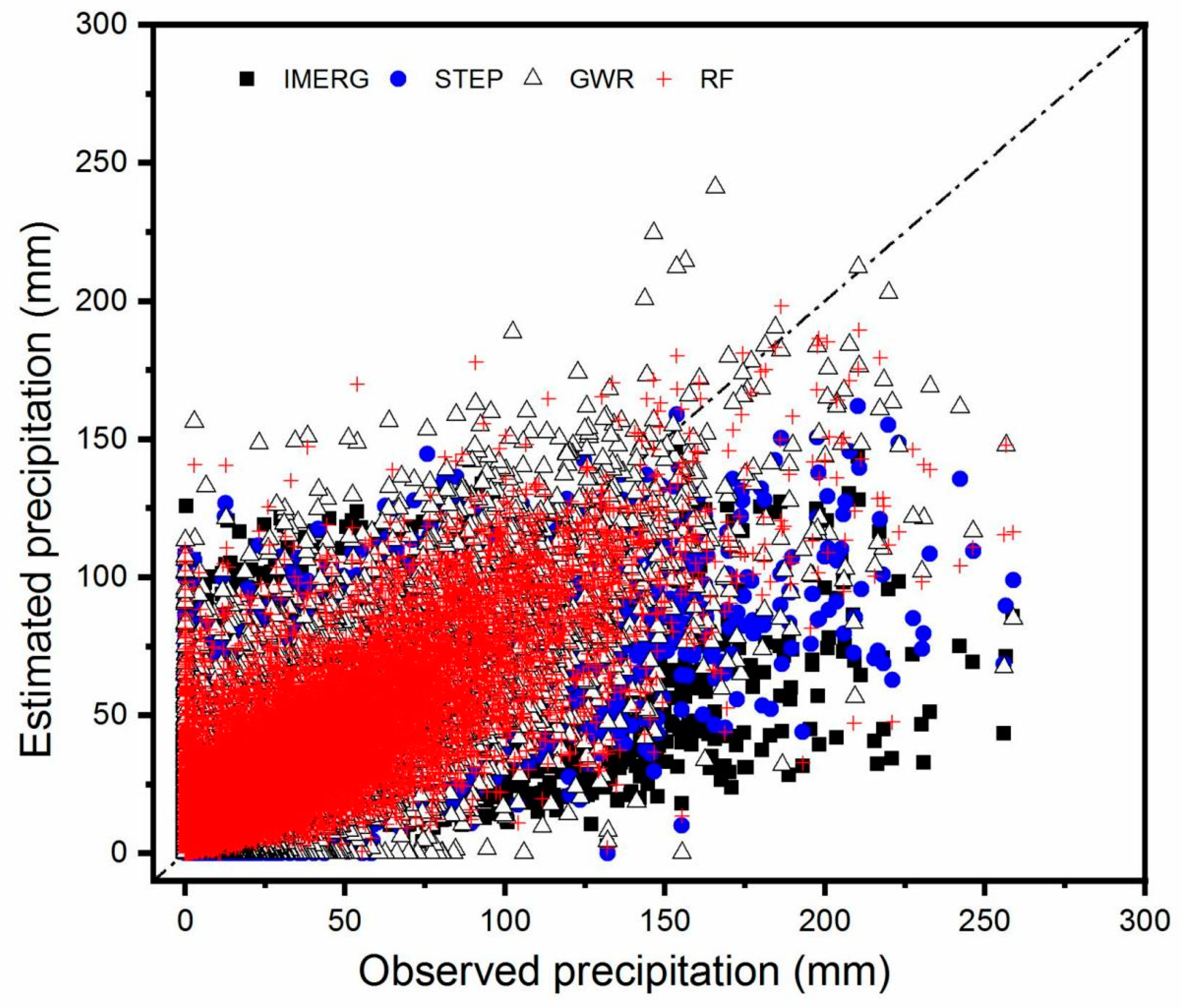
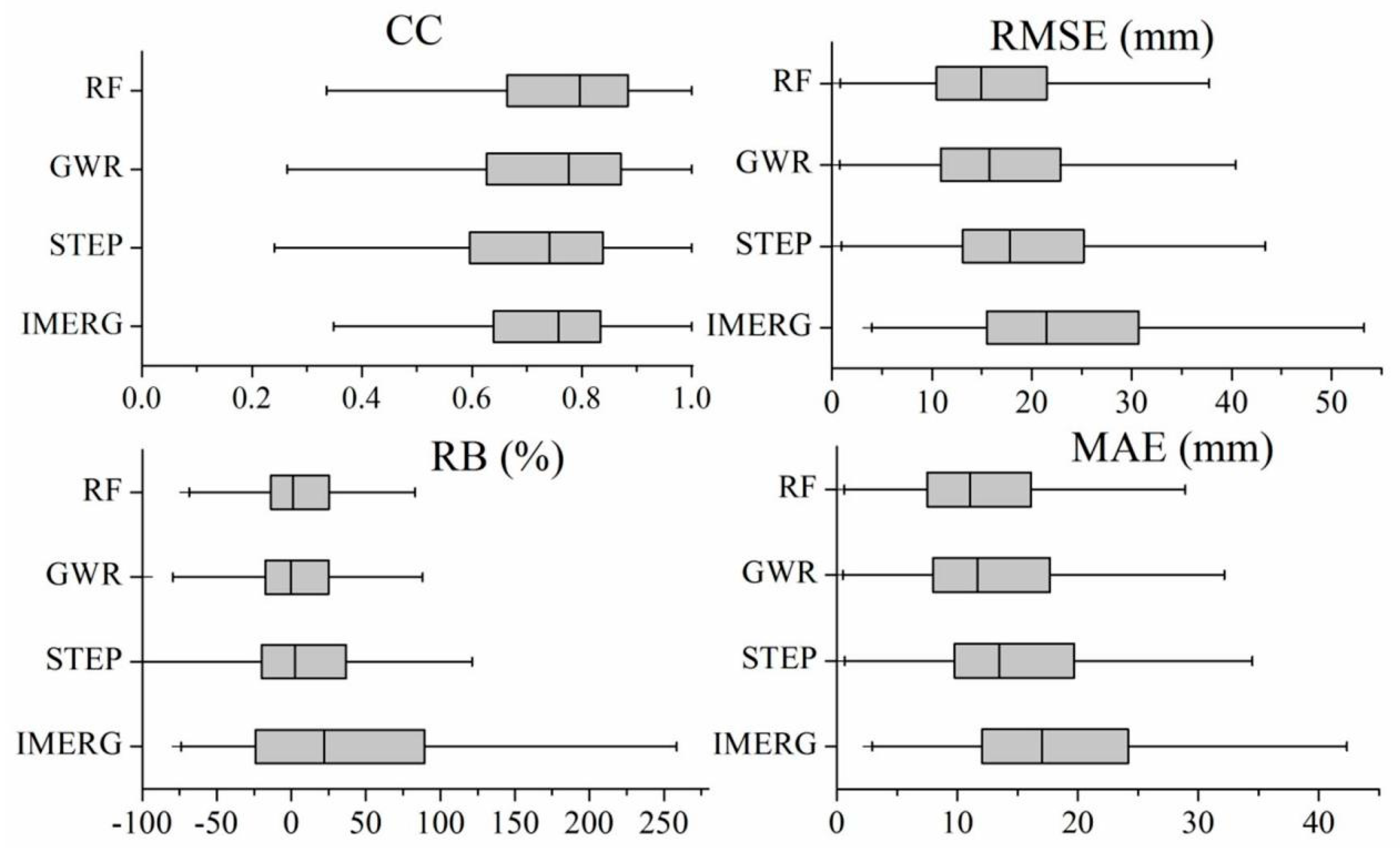
| Product | CC | NSE | RMSE (mm) | MAE (mm) | RB (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMERG | 0.56 | 0.31 | 28.11 | 19.43 | 7.10 |
| STEP | 0.74 | 0.55 | 22.63 | 15.42 | 1.32 |
| GWR | 0.79 | 0.62 | 20.94 | 13.80 | 1.12 |
| RF | 0.81 | 0.66 | 19.81 | 12.83 | 1.06 |
| Zone | ≤1000 m | 1000–2000 m | 2000–3000 m | >3000 m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of stations | 284 | 560 | 101 | 14 |
| CC | ||||
| IMERG | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.67 | 0.66 |
| STEP | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.67 | 0.74 |
| GWR | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.71 | 0.68 |
| RF | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.72 |
| NSE | ||||
| IMERG | 0.08 | −0.15 | −0.14 | −0.57 |
| STEP | 0.29 | 0.3 | 0.19 | −0.04 |
| GWR | 0.43 | 0.42 | 0.21 | −0.31 |
| RF | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.29 | −0.09 |
| RB (%) | ||||
| IMERG | 31.1 | 3.13 | −32.6 | −38.49 |
| STEP | 7.09 | −0.91 | 1.1 | 28.85 |
| GWR | 2.37 | 0.42 | −3.7 | −11.49 |
| RF | 0.91 | −0.15 | 0.73 | −13.4 |
| RMSE (mm) | ||||
| IMERG | 19.28 | 30.06 | 34.44 | 39.68 |
| STEP | 16.92 | 23.47 | 28.97 | 32.29 |
| GWR | 15.26 | 21.24 | 28.56 | 36.29 |
| RF | 14.5 | 20.09 | 27.15 | 33.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Huo, H. Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in the Tianshan Mountains Based on Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3962. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15163962
Lu X, Li J, Liu Y, Li Y, Huo H. Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in the Tianshan Mountains Based on Machine Learning. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(16):3962. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15163962
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Xinyu, Jing Li, Yan Liu, Yang Li, and Hong Huo. 2023. "Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in the Tianshan Mountains Based on Machine Learning" Remote Sensing 15, no. 16: 3962. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15163962
APA StyleLu, X., Li, J., Liu, Y., Li, Y., & Huo, H. (2023). Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in the Tianshan Mountains Based on Machine Learning. Remote Sensing, 15(16), 3962. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15163962






