Exploring the Spatial Relationship between the Ecological Topological Network and Carbon Sequestration Capacity of Coastal Urban Ecosystems: A Case Study of Yancheng City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
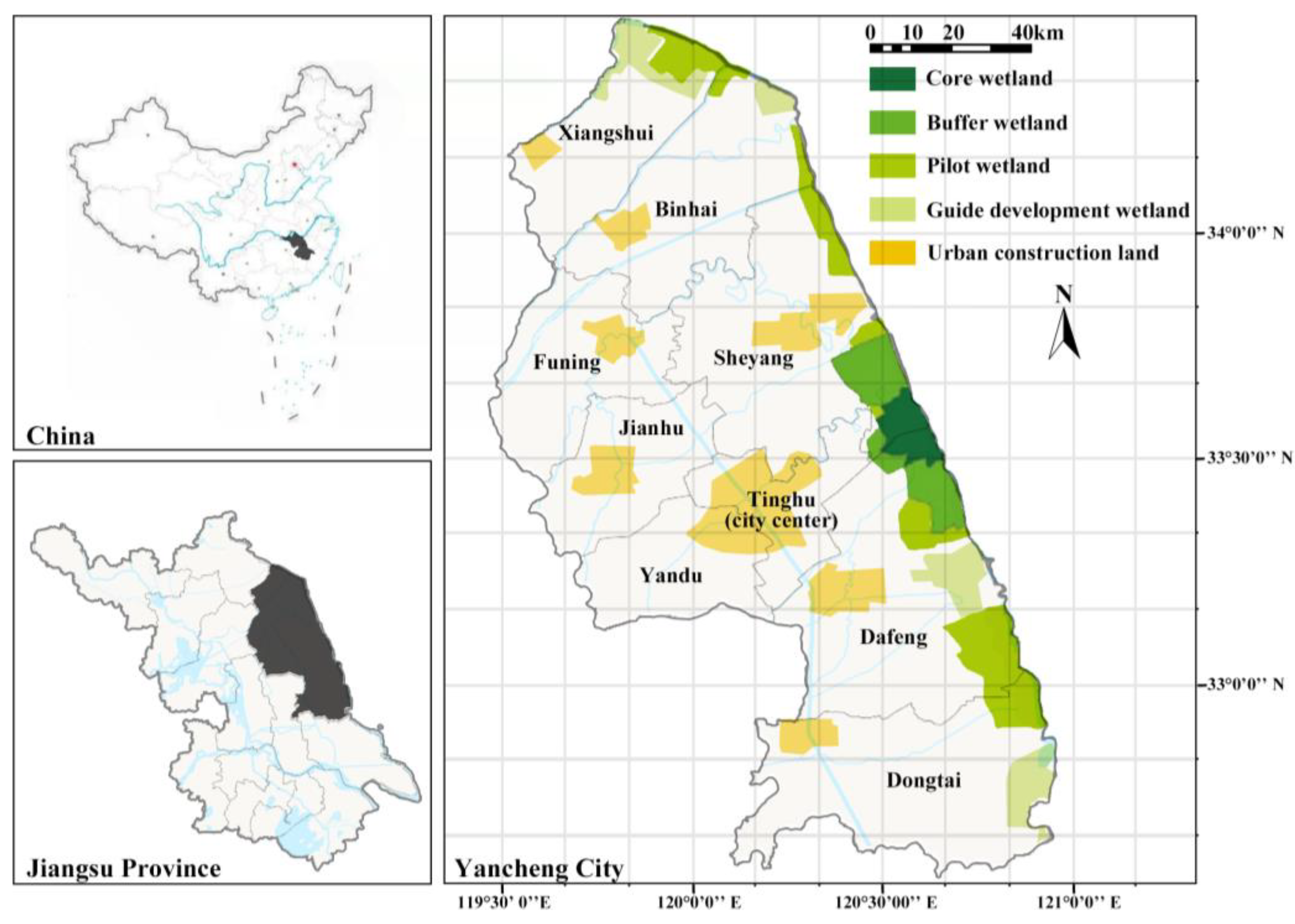
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
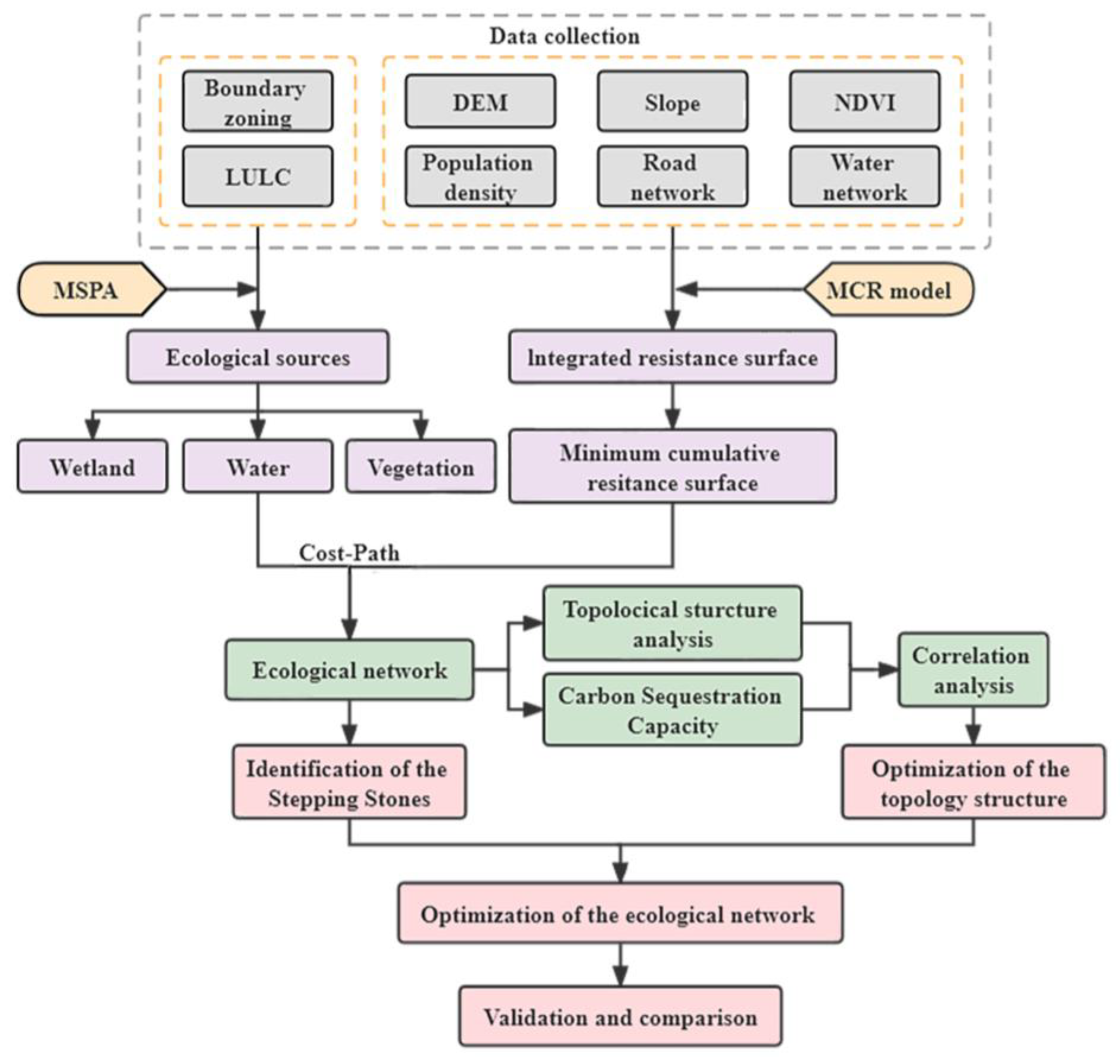
3. Methods
3.1. Construction of Ecological Network
3.1.1. Identification of Ecological Sources
3.1.2. Construction and Correction of Resistance Surface
3.1.3. Extraction of Ecological Corridors
3.1.4. Determination of Importance of Ecological Corridors
3.2. Topological Structure of Ecological Network
3.3. Estimation of CSA
| Land-Use Type | Carbon Sequestration Coefficient (Mg C ha−1) | Literature Sources | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetation * | Soil | Total | ||
| Forest | 159.0 | 124.9 | 283.9 | [47,48,49] |
| Shrub | 43.1 | 131.4 | 174.5 | [50] |
| grassland | 11.5 | 132.4 | 143.8 | [51,52,53] |
| wetland | 15.3 | 347.5 | 362.8 | [54,55] |
| Water area | / | 67.1 | 67.1 | [56,57] |
3.4. Verification of Robustness
4. Results
4.1. Construction and Analysis of Ecological Network
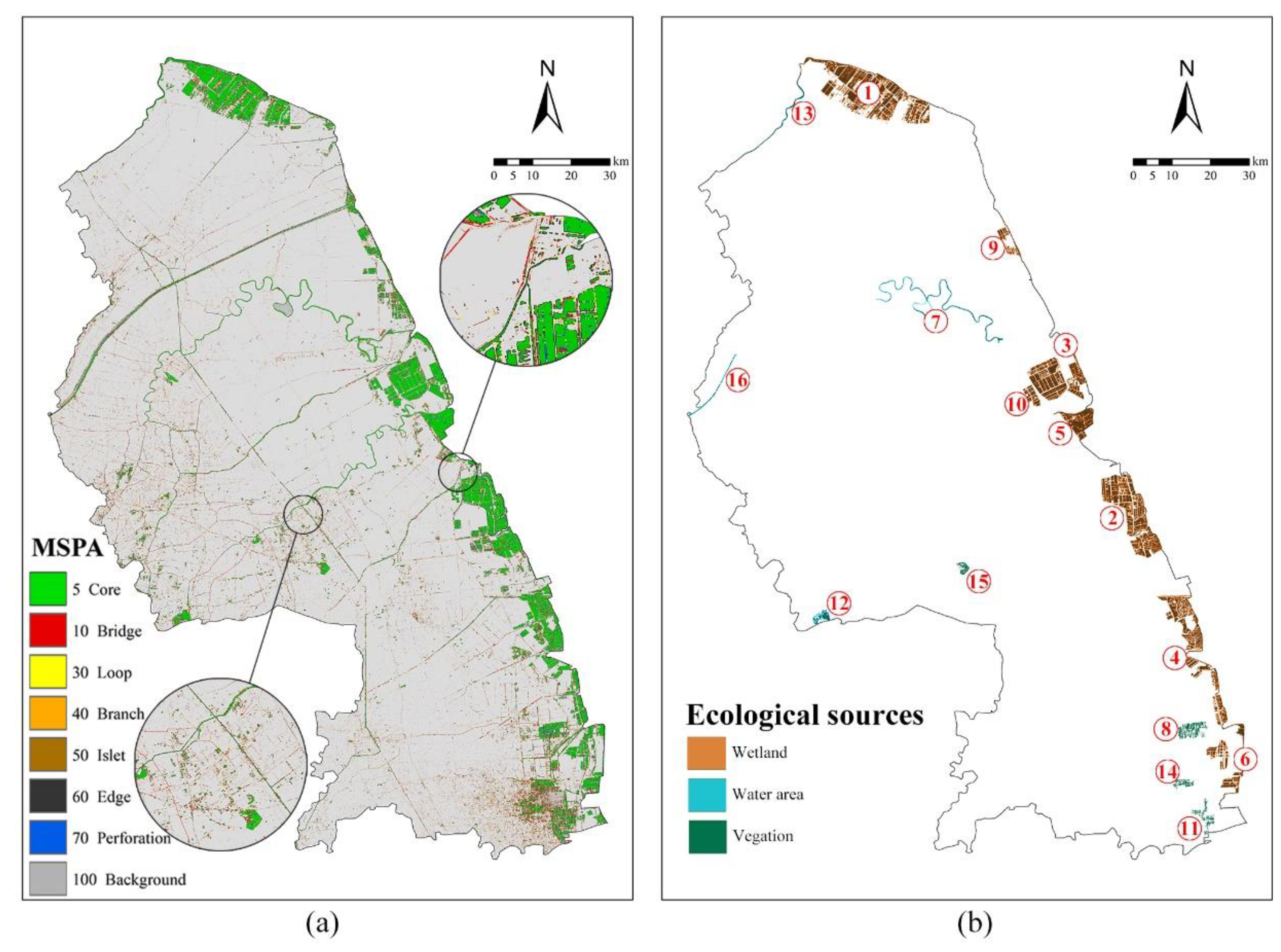
4.1.1. Identification of Ecological Sources
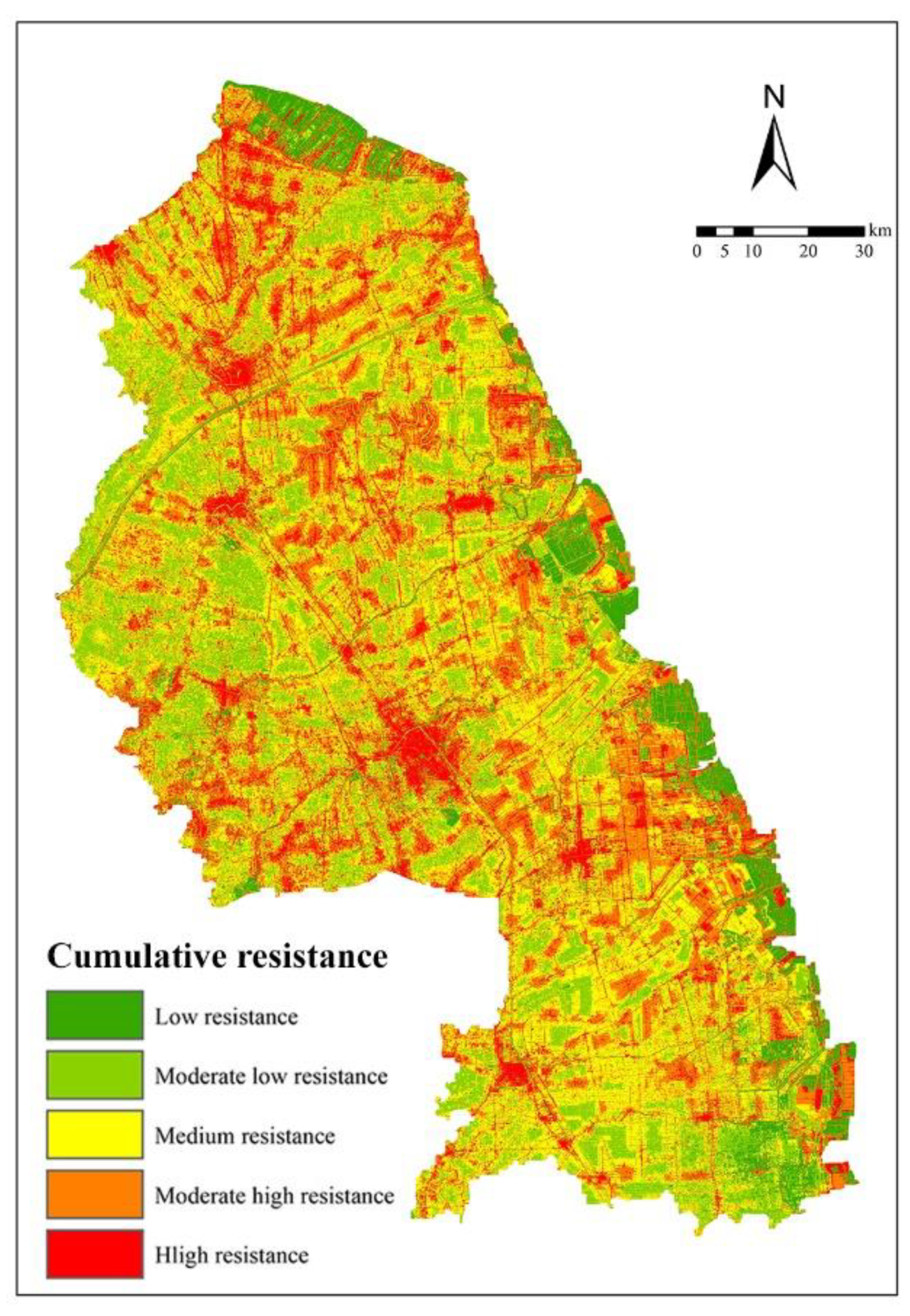
4.1.2. Results of MCR Surface
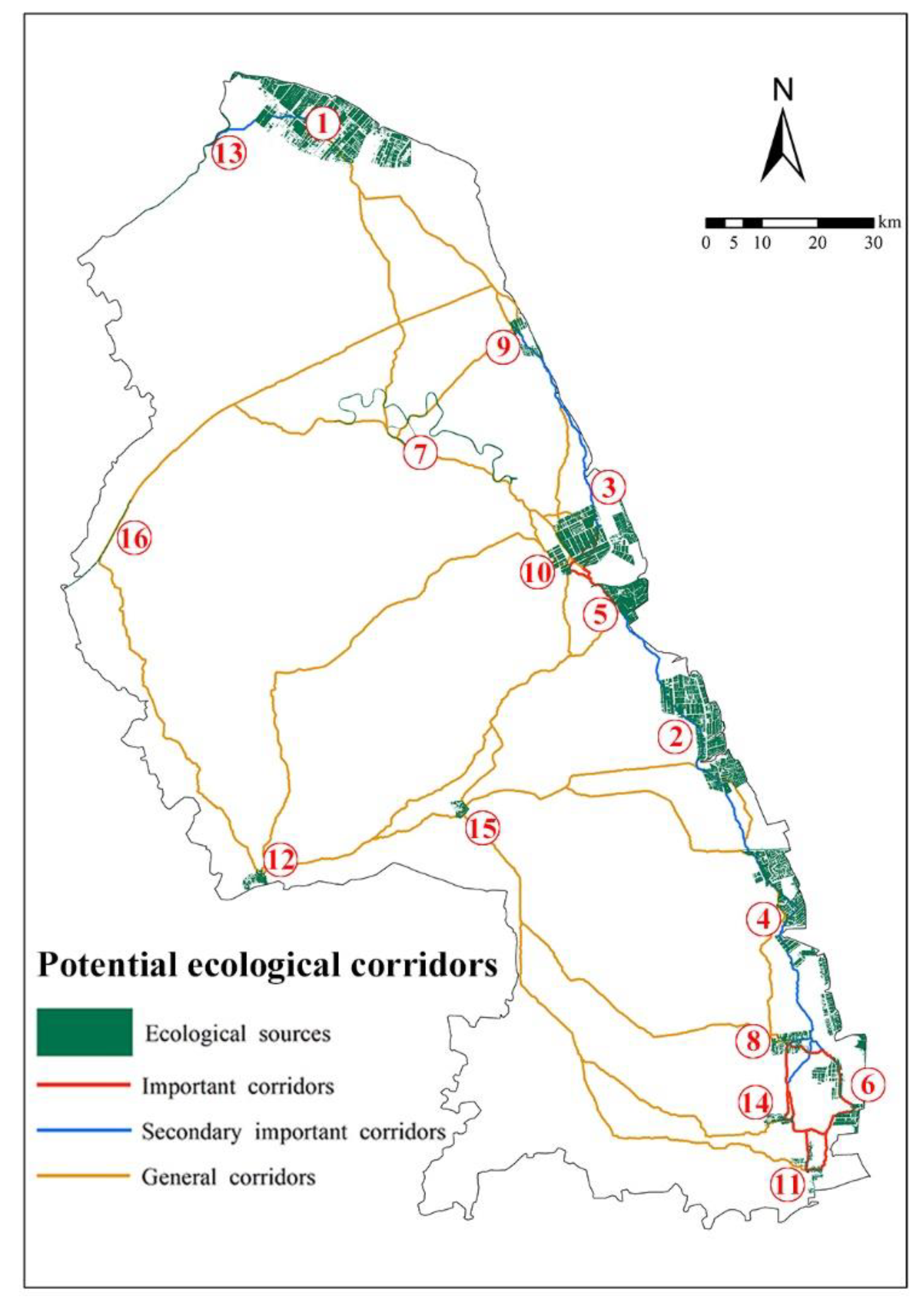
4.1.3. Analysis of Potential Ecological Corridors
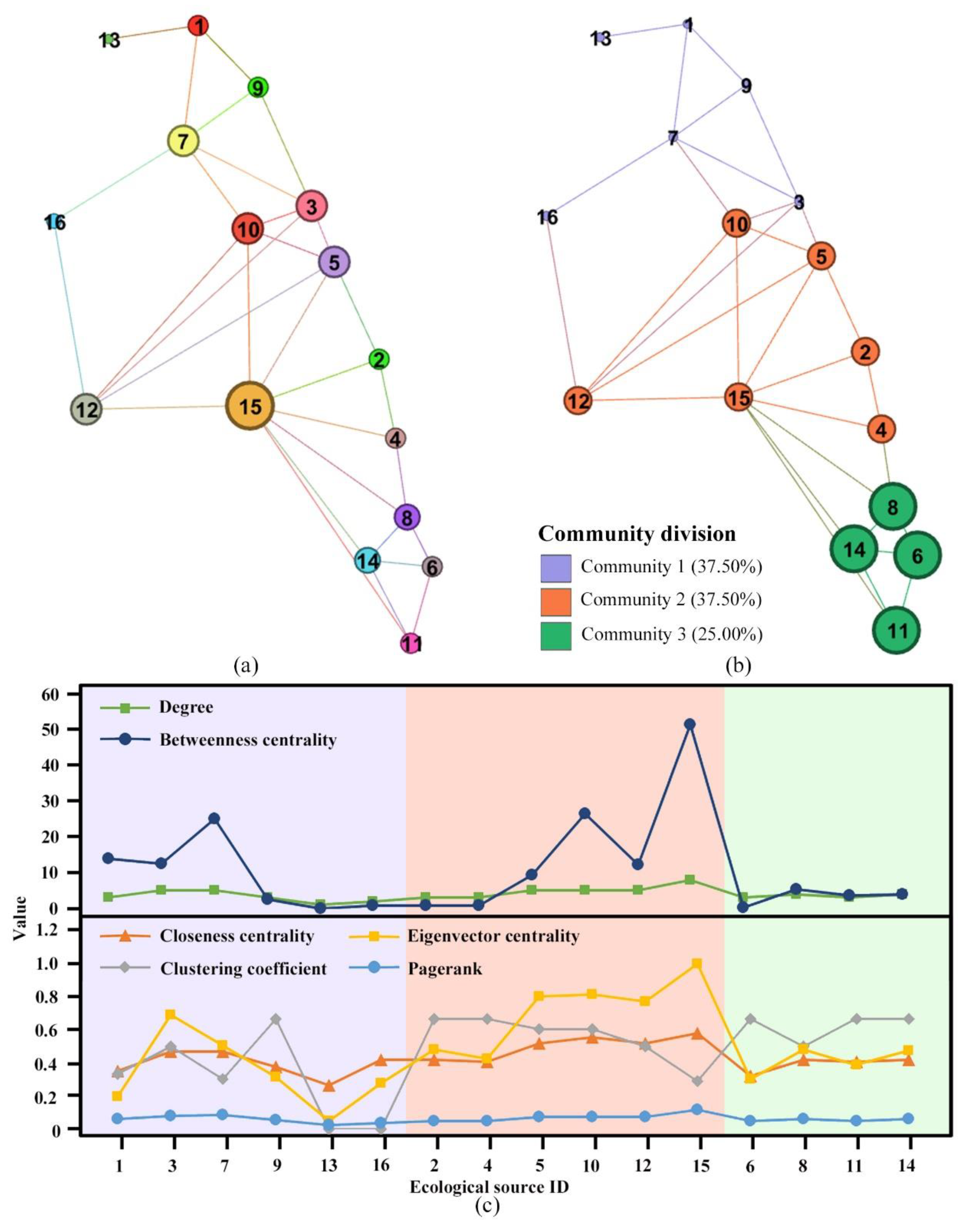
4.2. Analysis of Topological Structure
4.2.1. Evaluation of Overall Structure of Topological Network
4.2.2. Evaluation of Topological Nodes
4.3. Estimation and Validation of CSA
4.3.1. Estimation of CSA
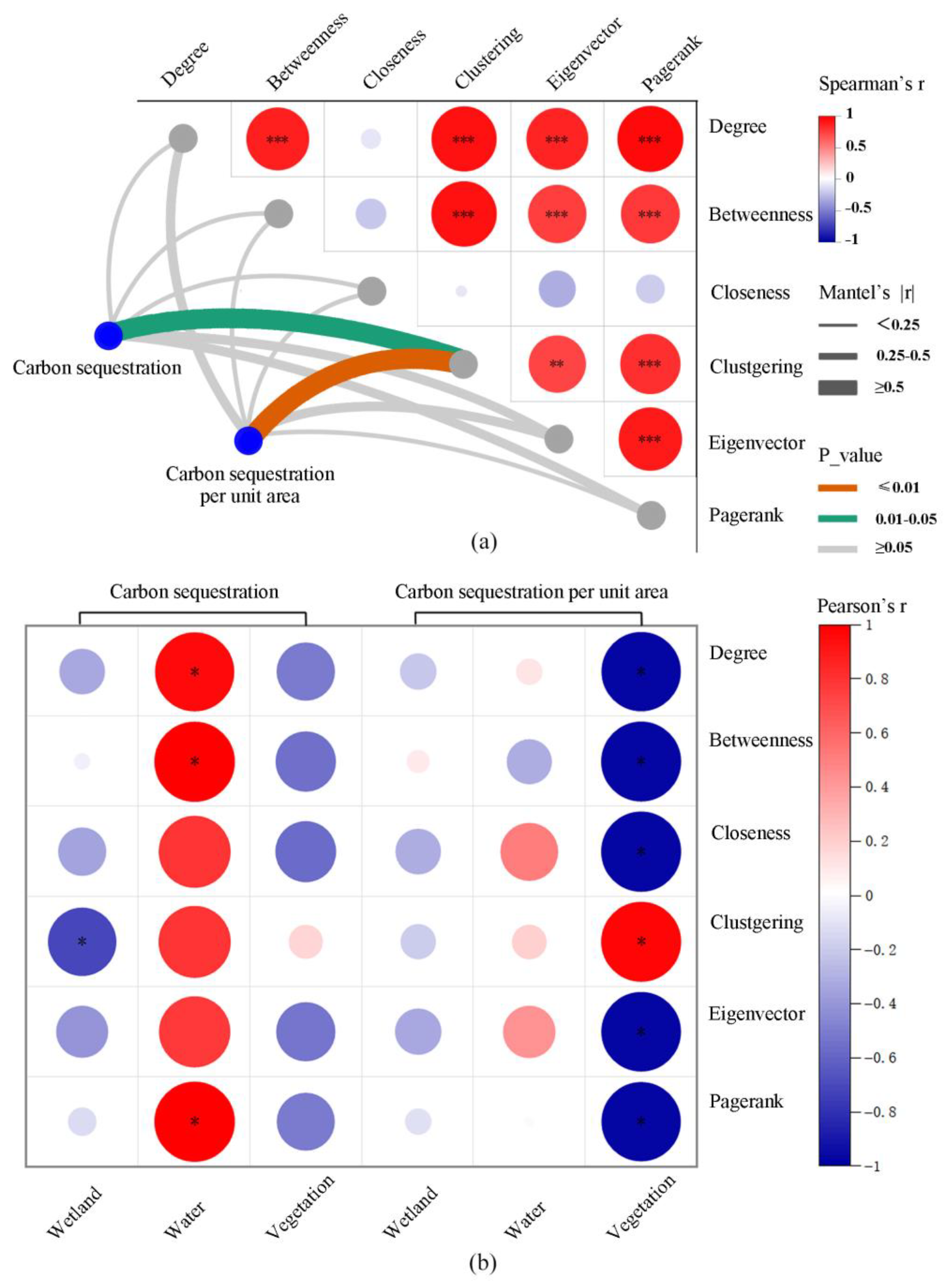
4.3.2. Correlation Analysis between Topological Indicators and CSC
5. Discussions
5.1. Spatial Distribution of Ecological Network
5.2. Optimization and Improvement of Ecological Network
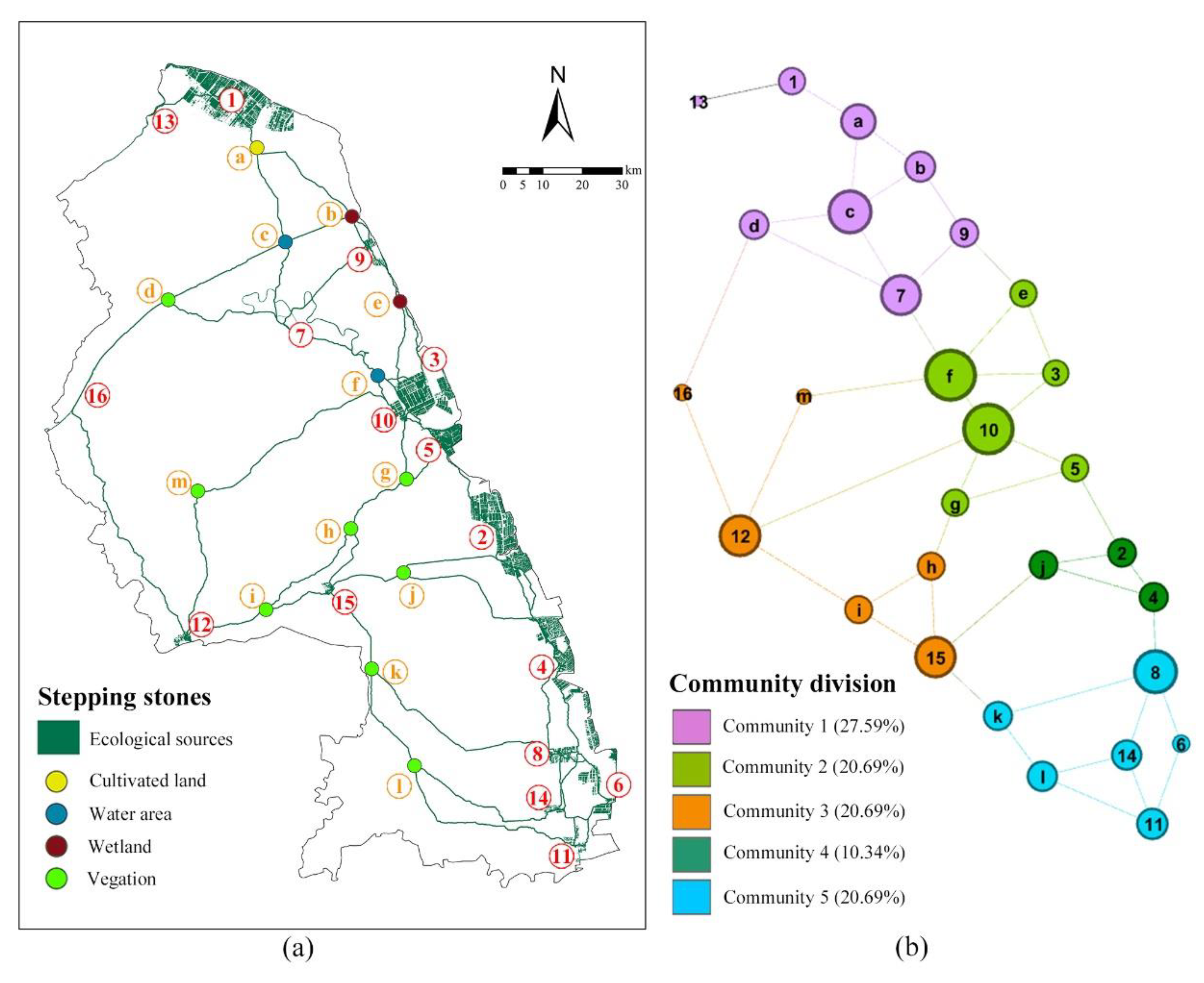
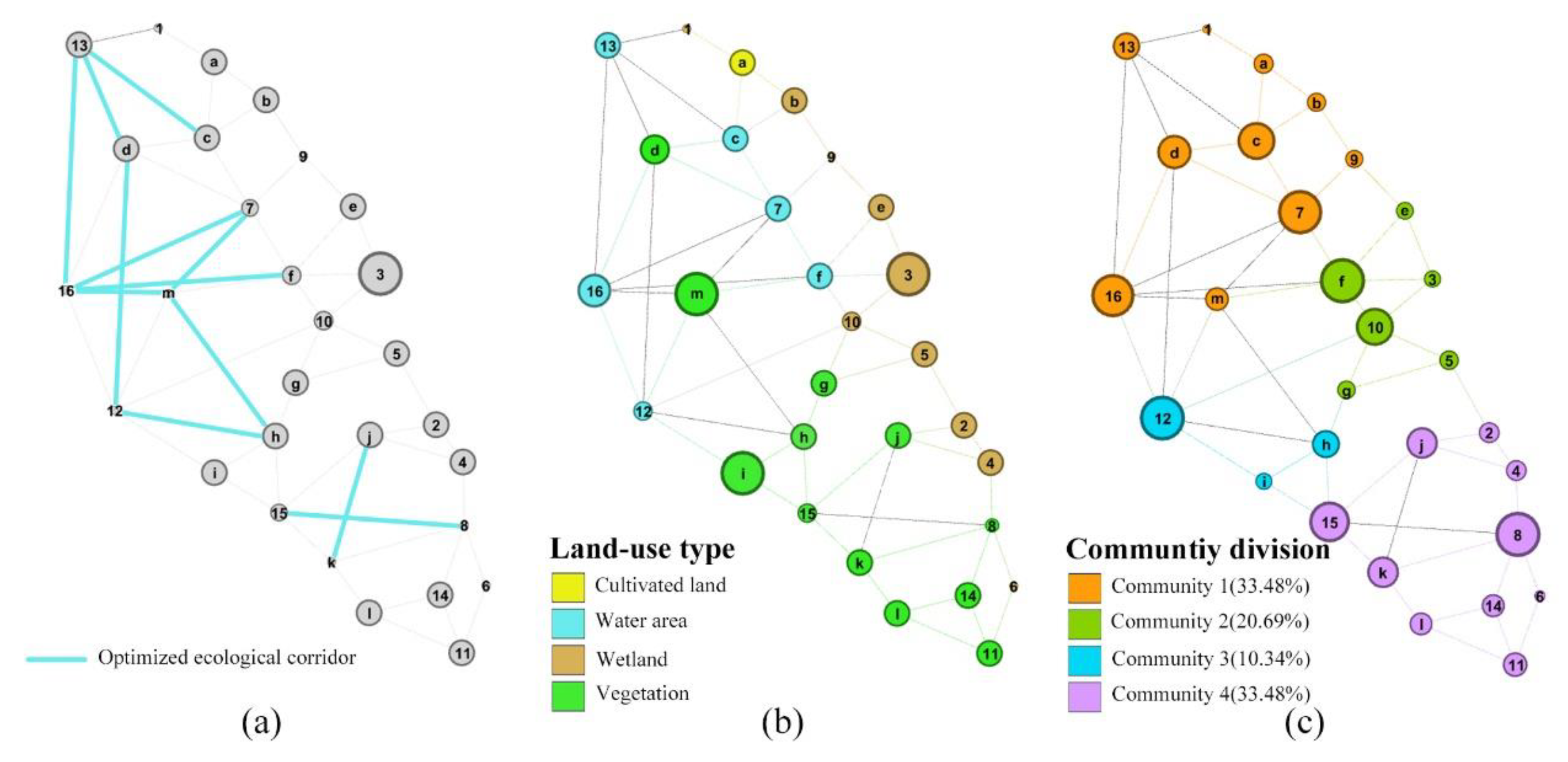
5.2.1. Identification of Stepping Stones
5.2.2. Optimization of Ecological Corridors
5.2.3. Enhancement of CSC
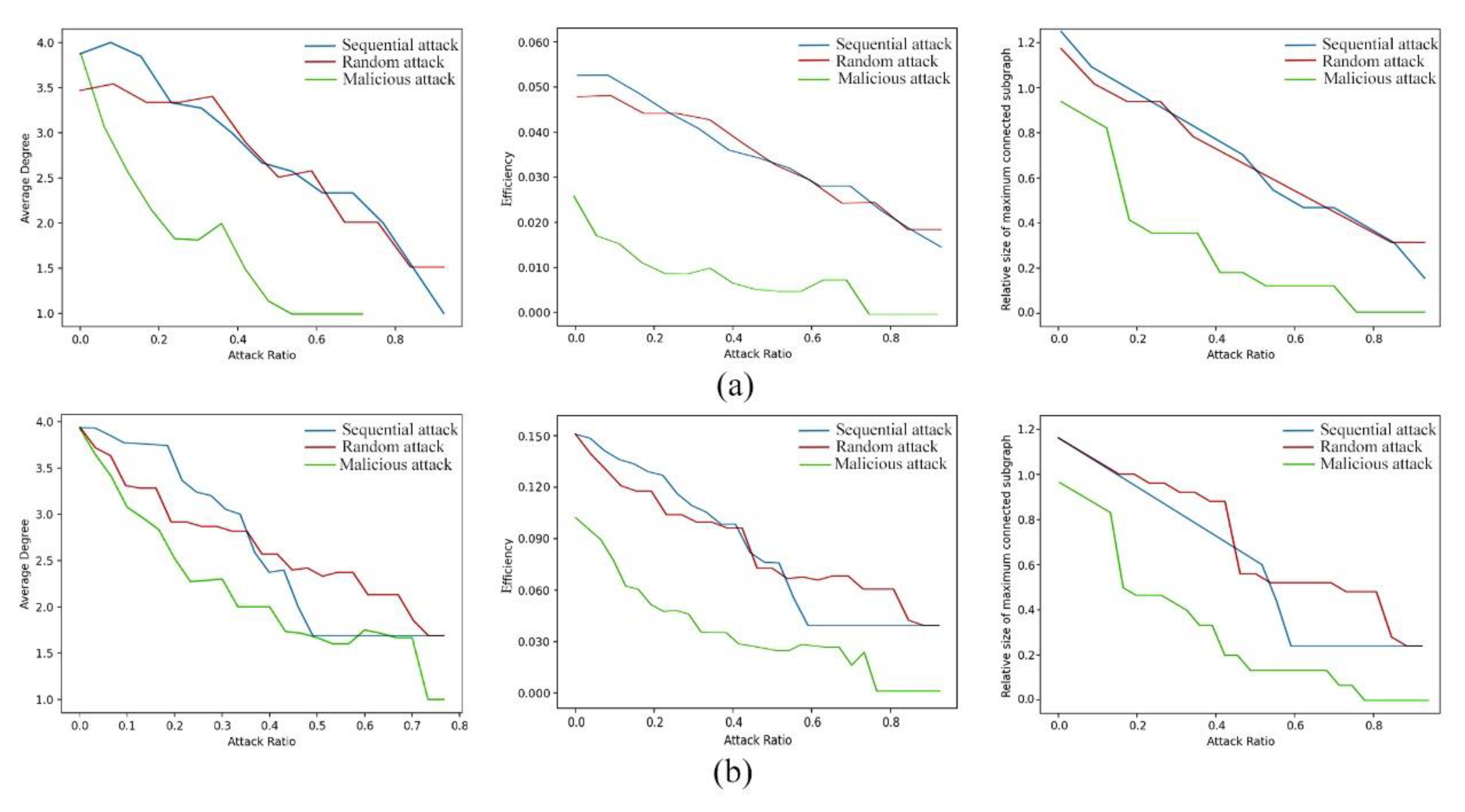
5.2.4. Comparison and Analysis of Robustness
5.3. Applicability and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drius, M.; Carranza, M.L.; Stanisci, A.; Jones, L. The role of Italian coastal dunes as carbon sinks and diversity sources. A multi-service perspective. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 75, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z. Construction of an ecological security pattern based on functional wetland theory: A case study in a landscape city. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 955230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.Y.; Pu, L.J.; Zhu, M.; Li, J.G.; Chen, X.J.; Wang, X.H.; Xie, X.F. Ecological security and ecosystem services in response to land use change in the coastal area of Jiangsu, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.T.; Li, M.; Xia, B.C. Spatio-temporal dynamics of ecological security pattern of the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration based on LUCC simulation. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Ju, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G. The construction of ecological security patterns in coastal areas based on landscape ecological risk assessment—A case study of Jiaodong peninsula, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Shen, W.; Du, X.; Li, S.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Z.J.; Feng, K.; Deng, Y. The large-scale spatial patterns of ecological networks between phytoplankton and zooplankton in coastal marine ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ye, Y.; Song, B.; Wang, R. Evaluation of urban suitable ecological land based on the minimum cumulative resistance model: A case study from Changzhou, China. Ecol. Model. 2015, 318, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Temporal and spatial changes in coupling and coordinating degree of new urbanization and ecological-environmental stress in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linehan, J.; Gross, M.; Finn, J. Greenway planning: Developing a landscape ecological network approach. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1995, 33, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Shi, F.; Beazley, R. Construction and optimization of an ecological network based on morphological spatial pattern analysis and circuit theory. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 36, 2059–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Montis, A.; Ganciu, A.; Cabras, M.; Bardi, A.; Peddio, V.; Caschili, S.; Massa, P.; Cocco, C.; Mulas, M. Resilient ecological networks: A comparative approach. Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongman, R.; Külvik, M.; Kristiansen, I. European ecological networks and greenways. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 68, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, Y.; Song, P.; Wang, Q. An optimized evaluation method of an urban ecological network: The case of the Minhang District of Shanghai. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 62, 127158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Guo, H.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Cui, X. Ecological network construction of a bational park based on MSPA and MCR models: An example of the proposed national parks of “Ailaoshan-Wuliangshan” in China. Land 2022, 11, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Yang, J.; Wu, F.; Sun, W.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.C. Regional thermal environment changes: Integration of satellite data and land use/land cover. iScience 2023, 26, 105820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Yang, J.; Sun, W.; He, B. Suitability of human settlements in mountainous areas from the perspective of ventilation: A case study of the main urban area of Chongqing. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Yue, D.; Wang, Y.; Kai, S.; Fang, M.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y. Optimization of ecological node layout and stability analysis of ecological network in desert oasis: A typical case study of ecological fragile zone located at Deng Kou County (Inner Mongolia). Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepcan, S.; Hepcan, C.C.; Bouwma, I.M.; Jongman, R.H.G.; Özkan, M.B. Ecological networks as a new approach for nature conservation in Turkey: A case study of İzmir Province. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 90, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, A.N.M.; Corstanje, R.; Harris, J.A.; Grafius, D.R.; Siriwardena, G.M. Ecological connectivity networks in rapidly expanding cities. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, S. Construction of landscape ecological network based on landscape ecological risk assessment in a large-scale opencast coal mine area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.D.F.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Travieso, G.; Boas, P.R.V. Characterization of complex networks: A survey of measurements. Adv. Phys. 2007, 56, 167–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhang, J. Combining MSPA-MCR model to evaluate the ecological network in Wuhan, China. Land 2022, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. Construction of ecological security pattern for plateau lake based on MSPA–MCR model: A case study of Dianchi lake area. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Lei, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. Optimization of landscape pattern in China Luojiang Xiaoxi basin based on landscape ecological risk assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Fang, M.; Yu, Q.; Niu, T.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Xu, C.; Ai, M.; Zhang, J. Study of spatialtemporal changes in Chinese forest eco-space and optimization strategies for enhancing carbon sequestration capacity through ecological spatial network theory. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; He, J.; Hong, X.; Zhang, W.; Qin, C.; Pang, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Carbon sources/sinks analysis of land use changes in China based on data envelopment analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, M.S.; Palmer, D.J.; Dungey, H.; Kimberley, M.O. Predicting the spatial distribution of Cupressus lusitanica productivity in New Zealand. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Li, F.; Sun, C. Robustness assessment of urban rail transit based on complex network theory: A Case study of the Beijing subway. Saf. Sci. 2015, 79, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Si, G.; Yu, Q.; Huang, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, W.; Guo, H. Study on the relationship between topological characteristics of vegetation ecospatial network and carbon sequestration capacity in the Yellow River basin, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Yu, Q.; Niu, T.; Fang, M.; Guo, H.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, J. Restoration and renewal of ecological spatial network in mining cities for the purpose of enhancing carbon Sinks: The case of Xuzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yu, G.; Liu, L.; Hu, S.; Chapin, F.S. Climate change, human impacts, and carbon sequestration in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4015–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Yu, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, W.; Ma, J.; Niu, T.; Yang, L. Study on the structural properties of an ecospatial network in inner Mongolia and its relationship with NPP. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhang, H.B.; Liu, Y.Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, C. Spatiotemporal change of landscape elasticity in Yancheng coastal wetland of China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2022, 20, 4935–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; Pu, R.; Shi, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, R.; Xu, H.; Tong, C.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Landscape grain effect in Yancheng coastal wetland and its response to landscape changes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; Pu, R.; Gong, H.; Li, C. Landscape characteristics and ecological risk assessment based on multi-scenario simulations: A case study of Yancheng coastal wetland, China. Sustainability 2020, 13, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soille, P.; Vogt, P. Morphological segmentation of binary patterns. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2009, 30, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Shi, X.; Sun, Y.; Cui, J.; Shao, S. Have China’s provinces achieved their targets of energy intensity reduction? Reassessment based on nighttime lighting data. Energy Policy 2019, 128, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, J.D.; Riitters, K.H.; Wade, T.G.; Vogt, P. A national assessment of green infrastructure and change for the conterminous United States using morphological image processing. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 94, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Hortal, L.; Saura, S. Comparison and development of new graph-based landscape connectivity indices: Towards the priorization of habitat patches and corridors for conservation. Landsc. Ecol. 2006, 21, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Pascual-Hortal, L. A new habitat availability index to integrate connectivity in landscape conservation planning: Comparison with existing indices and application to a case study. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 83, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaapen, J.P.; Scheffer, M.; Harms, B. Estimating habitat isolation in landscape planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1992, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Guo, C.X.; Zhao, M.Y.; Yang, Z.G.; Guo, M.Y.; Wu, B.Y.; Chen, Q.L. Integrating morphological spatial pattern analysis and the minimal cumulative resistance model to optimize urban ecological networks: A case study in Shenzhen City, China. Ecol. Process. 2021, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, C. Research on ecosystem security and restoration pattern of urban agglomeration in the Yellow River basin. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Pan, Y.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhao, H.J.; Wang, Y.L. Linking ecological degradation risk to identify ecological security patterns in a rapidly urbanizing landscape. Habitat Int. 2018, 71, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Yu, Q.; Yue, D.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.; Niu, T.; Sun, X. Simulation of a forest-grass ecological network in a typical desert oasis based on multiple scenes. Ecol. Model. 2019, 413, 108834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; Barabasi, A.L. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 47–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.R.; Chen, Z.; Piao, S.L.; Peng, C.H.; Ciais, P.; Wang, Q.F.; Li, X.R.; Zhu, X.J. High carbon dioxide uptake by subtropical forest ecosystems in the East Asian monsoon region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4910–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.D.; Birdsey, R.A.; Fang, J.; Houghton, R.; Kauppi, P.E.; Kurz, W.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Shvidenko, A.; Lewis, S.L.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’ s forests. Science 2011, 333, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.X.; Hu, H.F.; Tao, S.L.; Chi, X.L.; Li, P.; Jiang, L.; Ji, C.J.; Zhu, J.L.; Tang, Z.Y.; Pan, Y.D.; et al. Carbon stocks and changes of dead organic matter in China’ s forests. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Chen, B.Z.; van der Laan-Luijk, I.T.; Machida, T.; Matsueda, H.; Sawa, Y.; Fukuyama, Y.; Langenfelds, R.; van der Schoot, M.; Xu, G.; et al. Estimating Asian terrestrial carbon fluxes from CONTRAIL aircraft and surface CO2 observations for the period 2006–2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5807–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjes, N.H. Technologically achievable soil organic carbon sequestration in world croplands and grasslands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J. Carbon storage in terrestrial ecosystems of China: Estimates at different spatial resolutions and their responses to climate change. Clim. Chang. 2001, 49, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J. Carbon storage in grasslands of China. J. Arid. Environ. 2002, 50, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.R.; Deng, L.; Kim, D.G.; Huang, C.B.; Tian, K. Carbon budgets of wetland ecosystems in China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 2061–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.Z.; Xiao, J.F.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.A.; Lin, G.H. Contrasting ecosystem CO2 fluxes of inland and coastal wetlands: A meta-analysis of eddy covariance data. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 1180–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederman, J.A.; Scott, R.L.; Arnone, J.A.; Jasoni, R.L.; Litvak, M.E.; Moreo, M.T.; Papuga, S.A.; Ponce-Campos, G.E.; Schreiner-McGraw, A.P.; Vivoni, E.R. Shrubland carbon sink depends upon winter water availability in the warm deserts of North America. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 249, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J.; Prairie, Y.T.; Caraco, N.F.; McDowell, W.H.; Tranvik, L.J.; Striegl, R.G.; Duarte, C.M.; Kortelainen, P.; Downing, J.A.; Middelburg, J.J.; et al. Plumbing the global carbon cycle: Integrating inland waters into the terrestrial carbon budget. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Xu, D.; Hu, S.; Shi, M. Ecological network optimization in urban central district based on complex network theory: A case study with the urban central district of Harbin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Ding, F.; Wu, J.; Chang, I.S. Regional ecological security pattern construction based on ecological barriers: A case study of the Bohai bay terrestrial ecosystem. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Lu, Y.; He, T.; Wu, F.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, F.; Sun, Z.; Han, D. Spatial expansion paths of urban heat islands in chinese cities: Analysis from a dynamic topological perspective for the improvement of climate resilience. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 188, 106680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barot, S.; Yé, L.; Abbadie, L.; Blouin, M.; Frascaria-Lacoste, N. Ecosystem services must tackle anthropized ecosystems and ecological engineering. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Niu, T.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wu, H. Relationship between topological structure and ecosystem services of forest grass ecospatial network in China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podobnik, B.; Lipic, T.; Horvatic, D.; Majdandzic, A.; Bishop, S.R.; Stanley, H.E. Predicting the lifetime of dynamic networks experiencing persistent random attacks. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, M. Maintenance and optimization of ecological space in natural resource-Advantaged cities: A case study in Zhangzhou, Fujian Province. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Indicators | Sources (accessed on 10 March 2022) |
|---|---|---|
| Socioeconomic | Boundary zoning data | The Resource and Environment Science and Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn/) |
| Population density data | WorldPop (https://www.worldpop.org/) | |
| Land use and land cover (LULC) data | The Geographic Information Monitoring Cloud Global Land Cover (http://data.ess.tsinghua.edu.cn/) | |
| Road network data | OpenStreetMap (https://www.openstreetmap.org/) | |
| NPP and CO2 concentration data | Geographic Remote Sensing Ecological Network Platform (https://www.gisrs.cn) | |
| Geospatial | DEM and slope data | ASF Data Search (https://search.asf.alaska.edu/) |
| Water network data | OpenStreetMap (https://www.openstreetmap.org/) | |
| Mean annual precipitation data | Geographic Remote Sensing Ecological Network Platform (https://www.gisrs.cn) | |
| NDVI data | USGS (https://www.usgs.gov/) |
| Landscape Type | Area (km2) | Accounting for Area of Foreground (%) | Accounting for Area of Study Area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core | 781.46 | 48.40 | 5.04 |
| Bridge | 132.42 | 8.20 | 0.85 |
| Loop | 66.19 | 4.10 | 0.43 |
| Branch | 91.30 | 5.65 | 0.59 |
| Islet | 237.20 | 14.69 | 1.53 |
| Edge | 306.06 | 18.96 | 1.97 |
| Perforation | 28.79 | 1.78 | 0.19 |
| Total | 1614.63 | 100.00 | 10.41 |
| No. of Eco-Sources | Dominant Land-Use Type | Area (ha) | Accounting for Area of Total Eco-Sources (%) | CSA (Mg C) | Accounting for Total CSA (%) | CSA Per Unit Area (Mg C ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–6, 9, 10 | Wetland | 45,650 | 88.62 | 16,387,879 | 94.19 | 358.99 |
| 7, 12, 13, 16 | Water | 3074 | 5.97 | 2,734,780 | 1.57 | 88.96 |
| 8, 11, 14, 15 | Vegetation | 2785 | 5.41 | 738,028 | 4.24 | 264.96 |
| Total | 51,509 | 100 | 17,399,385 | 100 | 337.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, N.; Ai, J.; Zeng, Z.; Zhou, C. Exploring the Spatial Relationship between the Ecological Topological Network and Carbon Sequestration Capacity of Coastal Urban Ecosystems: A Case Study of Yancheng City, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4007. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164007
Zhu N, Ai J, Zeng Z, Zhou C. Exploring the Spatial Relationship between the Ecological Topological Network and Carbon Sequestration Capacity of Coastal Urban Ecosystems: A Case Study of Yancheng City, China. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(16):4007. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164007
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Nanyan, Jingwen Ai, Zhen Zeng, and Chunhua Zhou. 2023. "Exploring the Spatial Relationship between the Ecological Topological Network and Carbon Sequestration Capacity of Coastal Urban Ecosystems: A Case Study of Yancheng City, China" Remote Sensing 15, no. 16: 4007. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164007
APA StyleZhu, N., Ai, J., Zeng, Z., & Zhou, C. (2023). Exploring the Spatial Relationship between the Ecological Topological Network and Carbon Sequestration Capacity of Coastal Urban Ecosystems: A Case Study of Yancheng City, China. Remote Sensing, 15(16), 4007. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164007










