Analysis of Aerosol Optical Depth and Forward Scattering in an Ultraviolet Band Based on Sky Radiometer Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
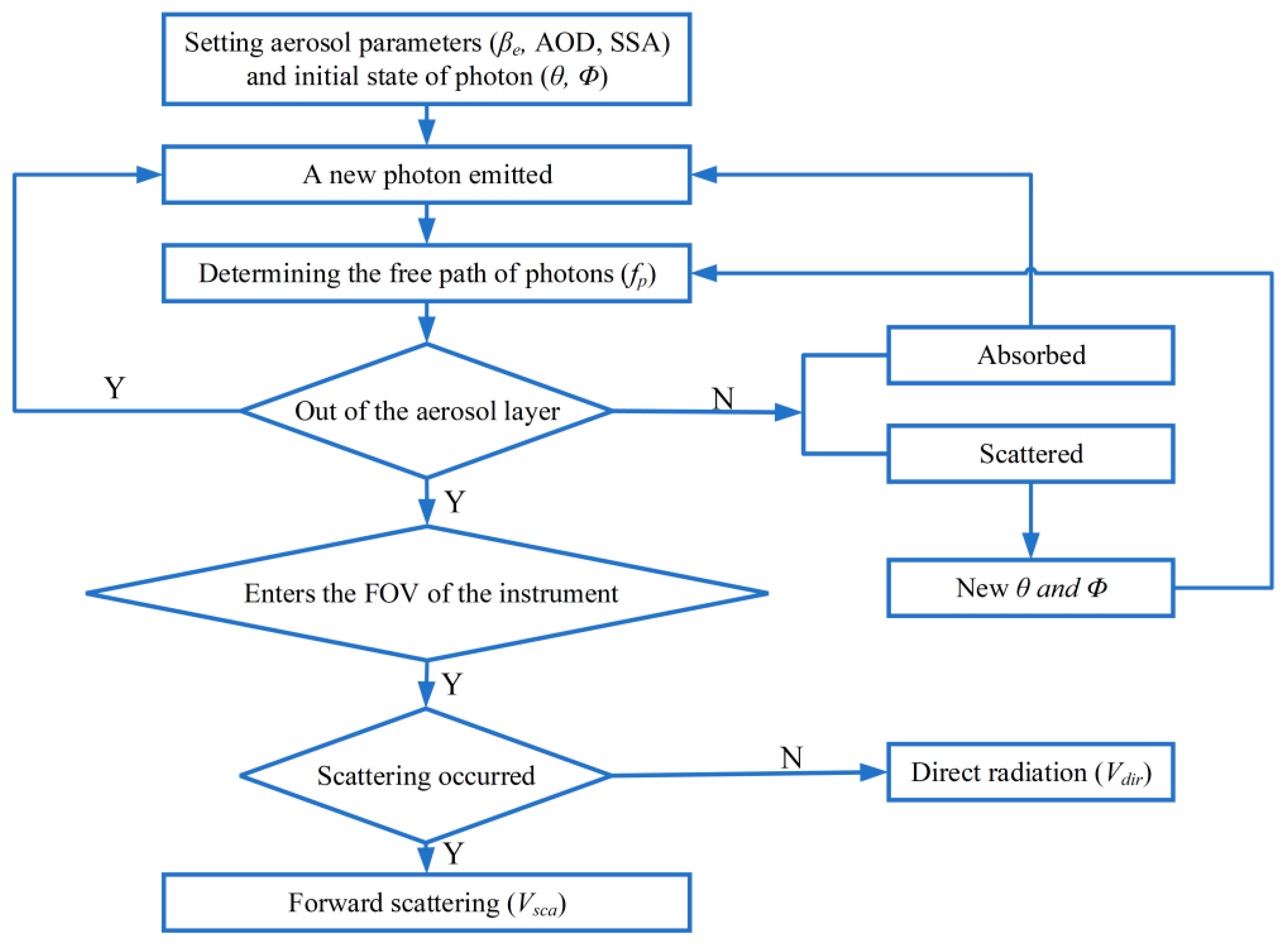
2.1. Monte Carlo Simulation
- (1)
- The initial position (x = 0, y = 0, z = 0) and initial state (SZA (θ), azimuth angle(ϕ)) of the simulated photon and AOPs, including the mean volume extinction coefficient (βe), single scattering albedo (SSA) and AOD, were given. The initial orientations of the photon are given by the following:
- (2)
- The free path length of photons then is calculated.
- (3)
- The position where photon interacts with aerosol is found.
- (4)
- Scattering direction of photons can be determined.
- (5)
- Termination condition is the final step.
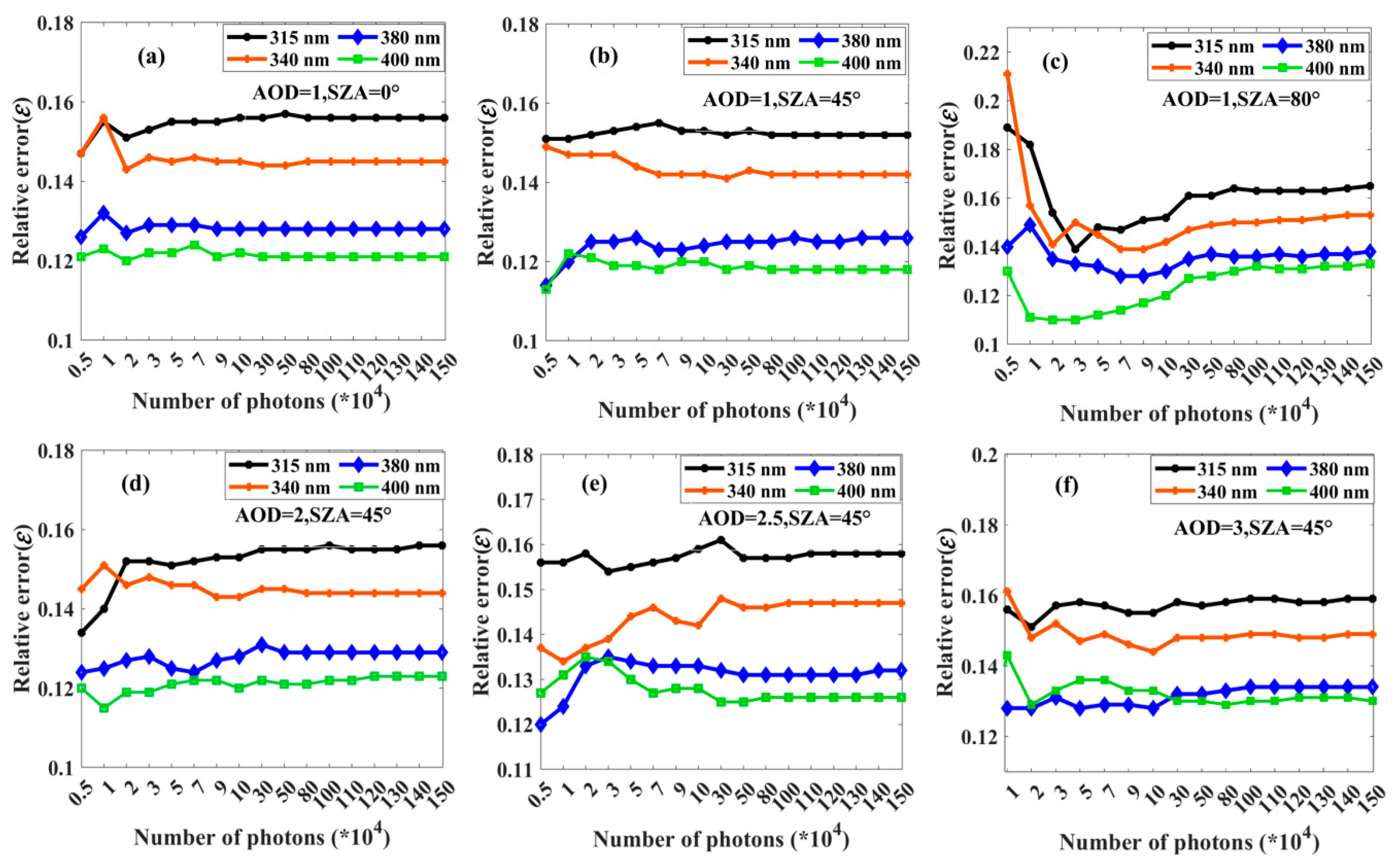
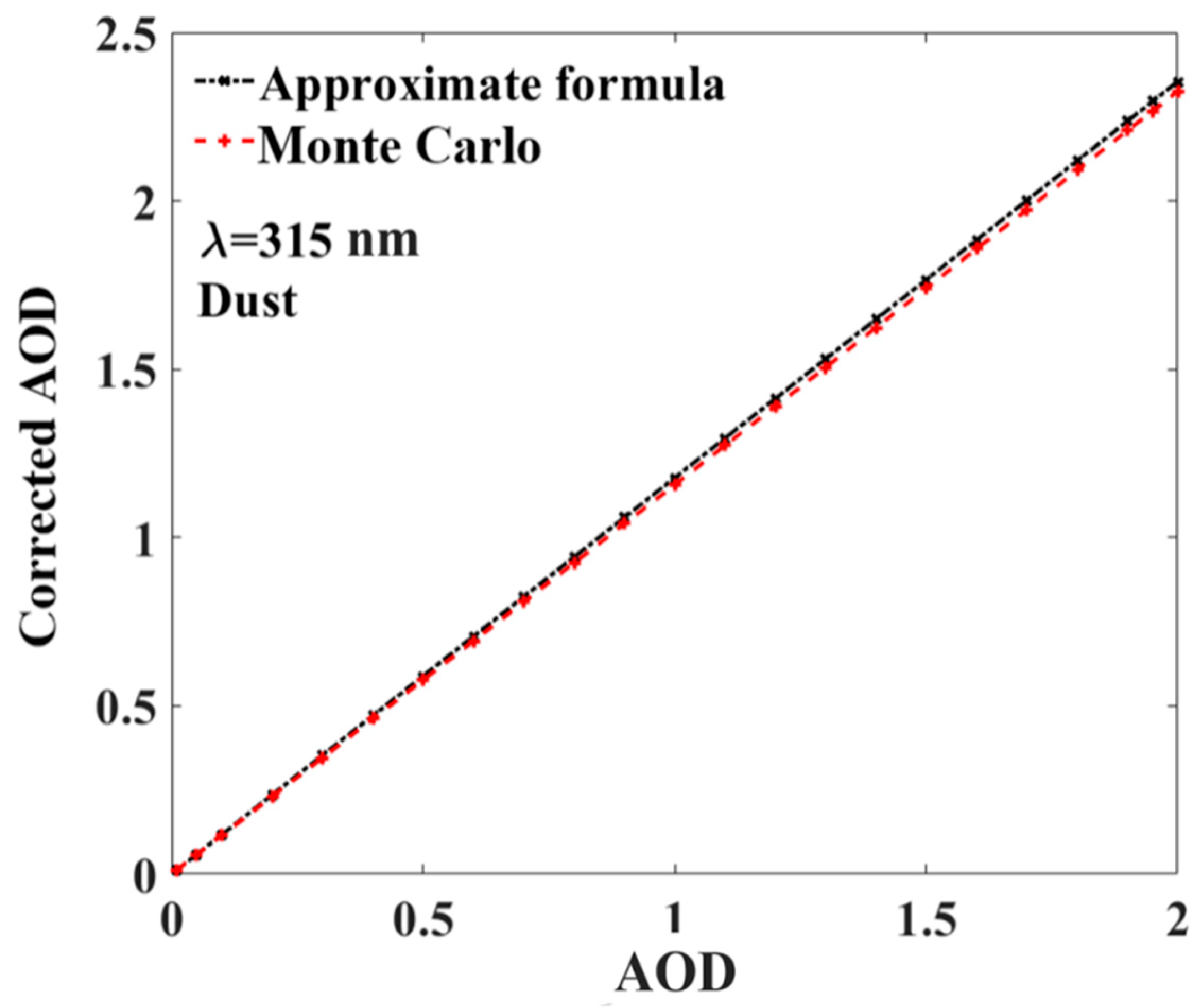
2.2. The Inversionand Relative Error of Sky-Radiometer AOD
3. Results
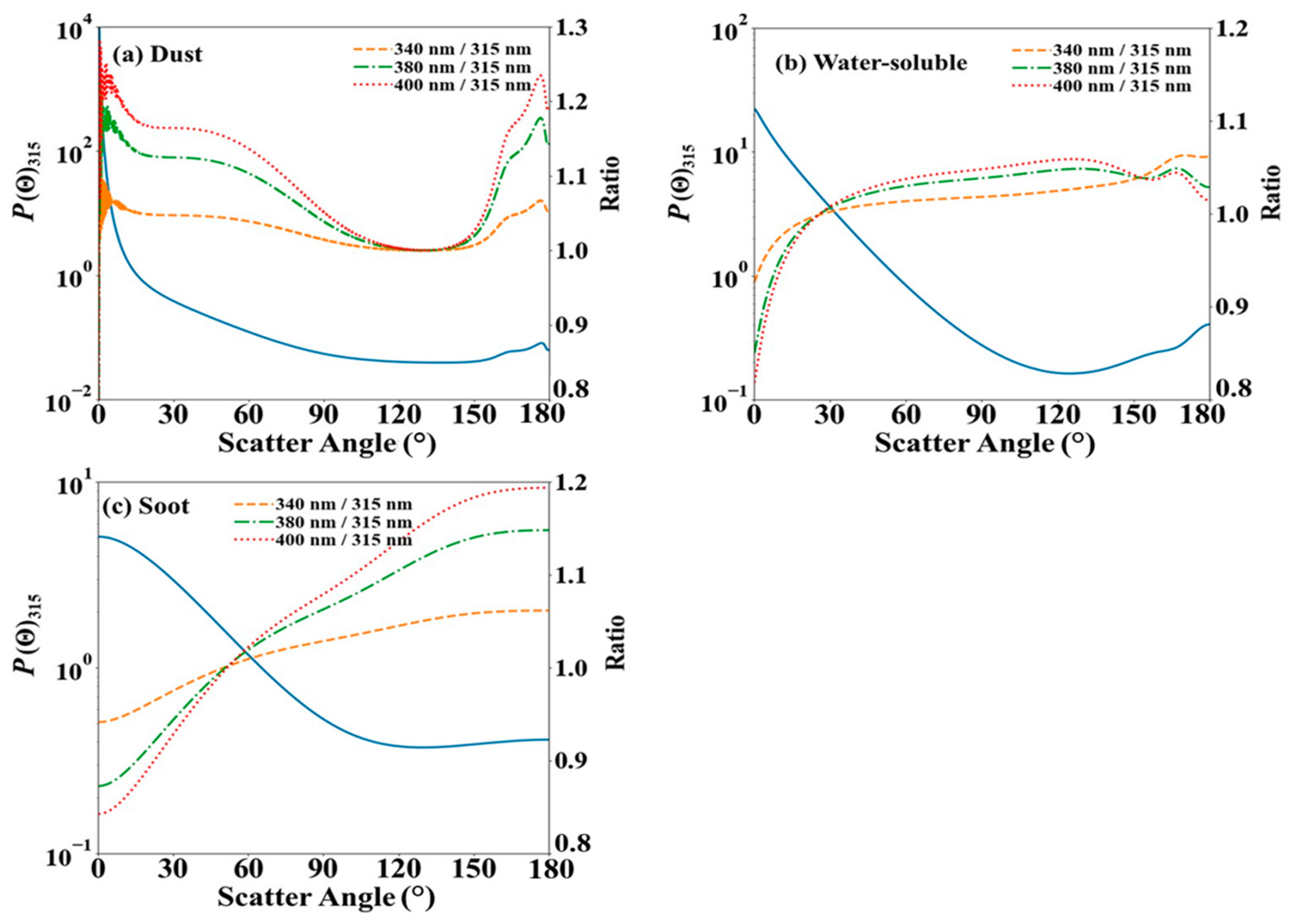
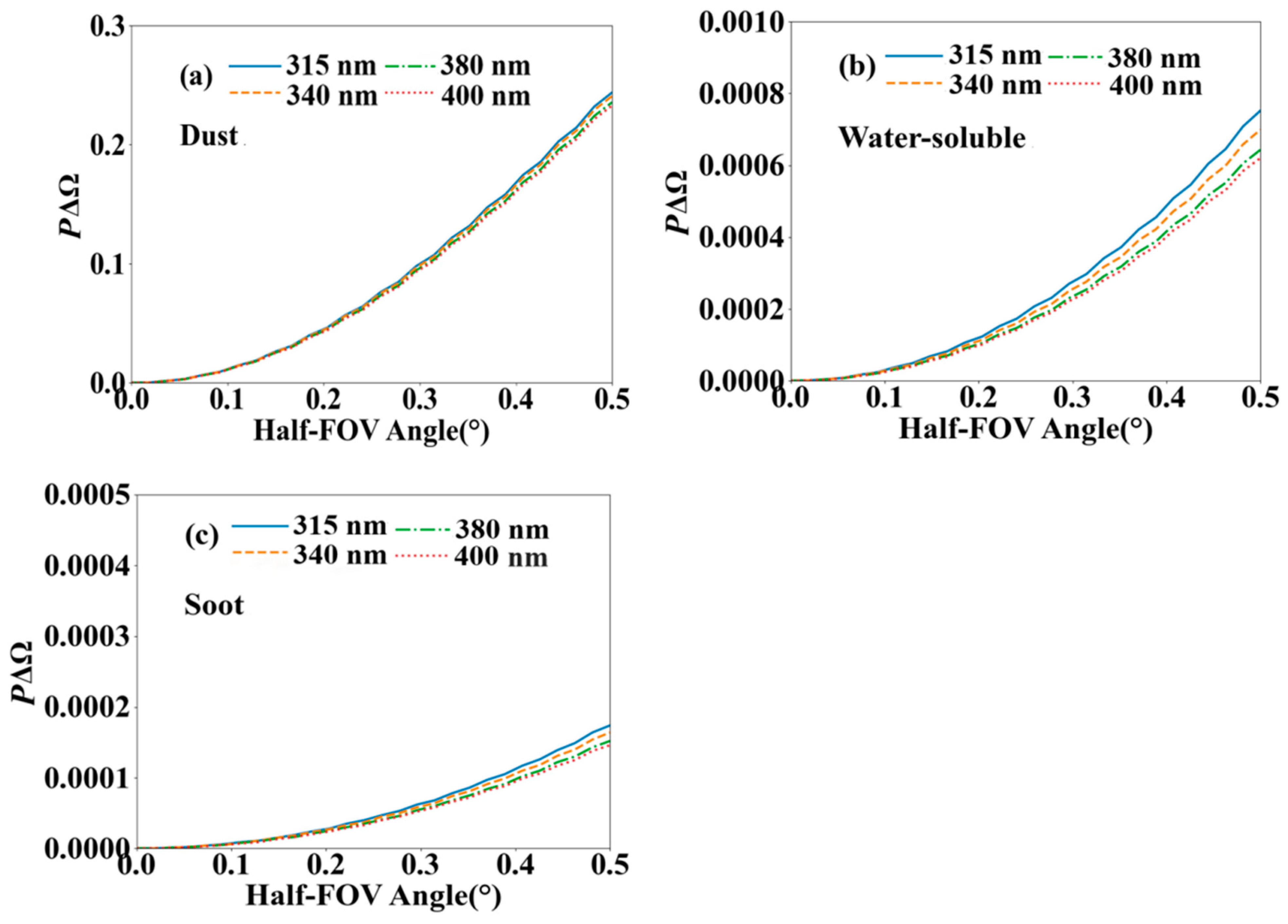
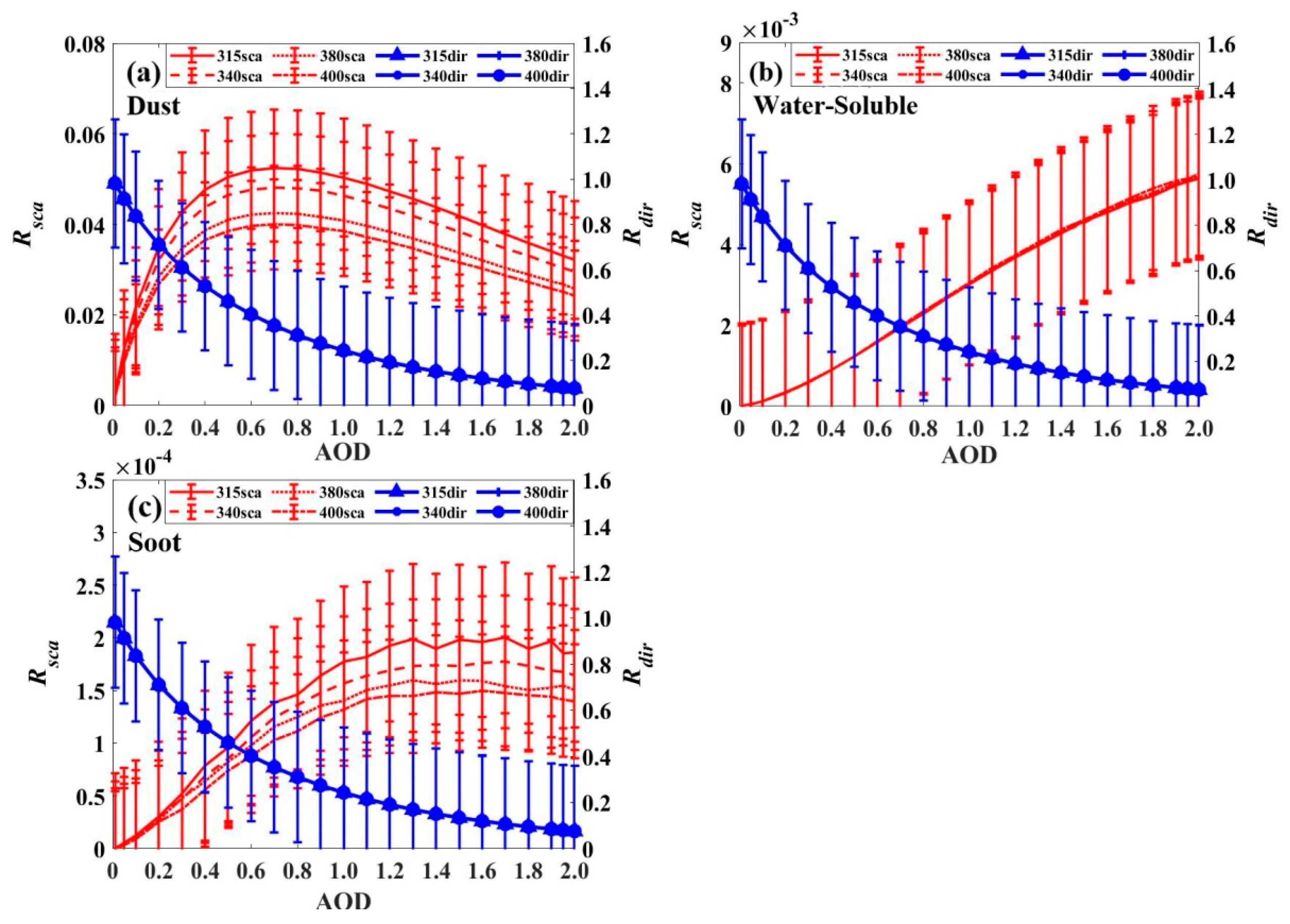
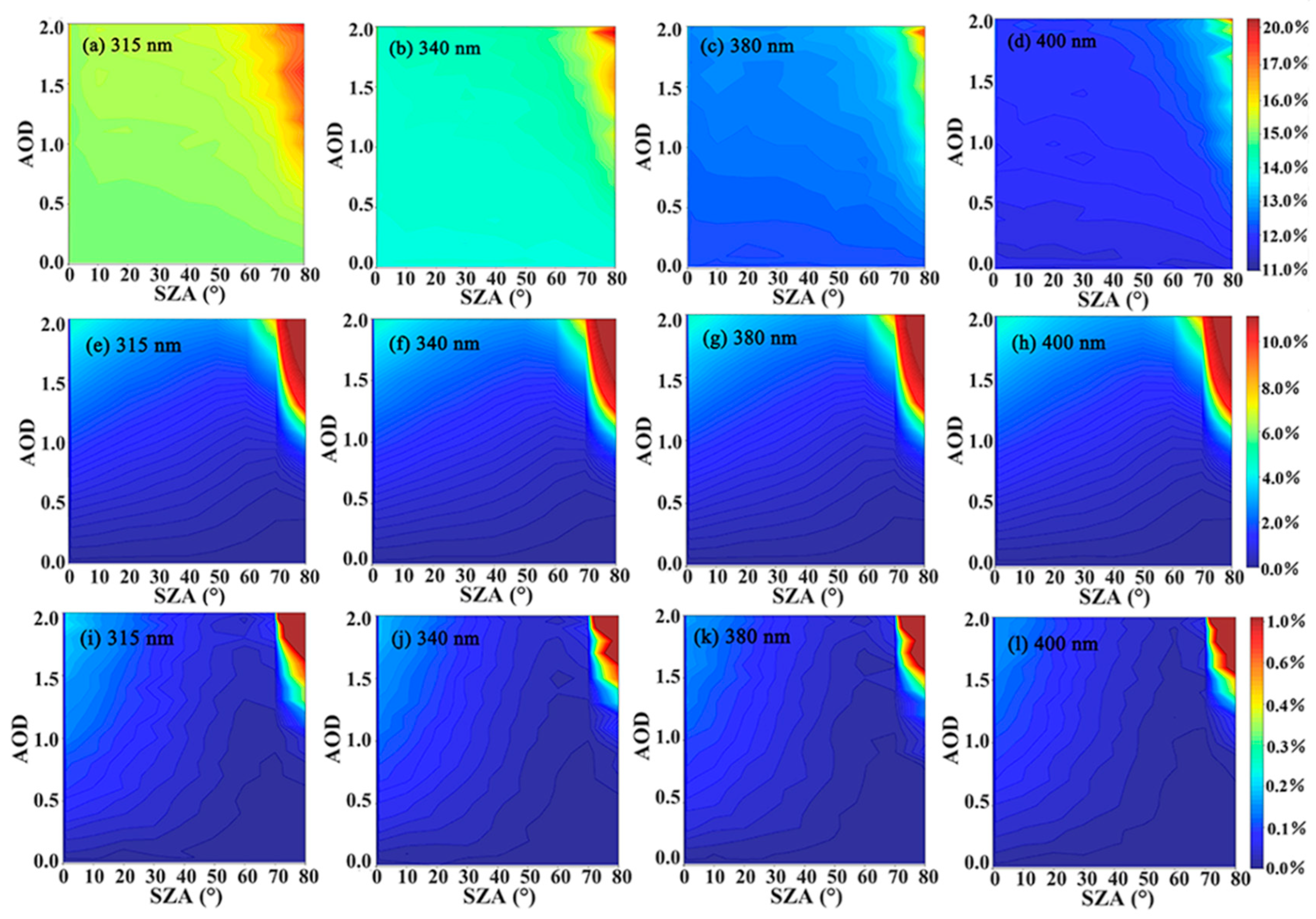
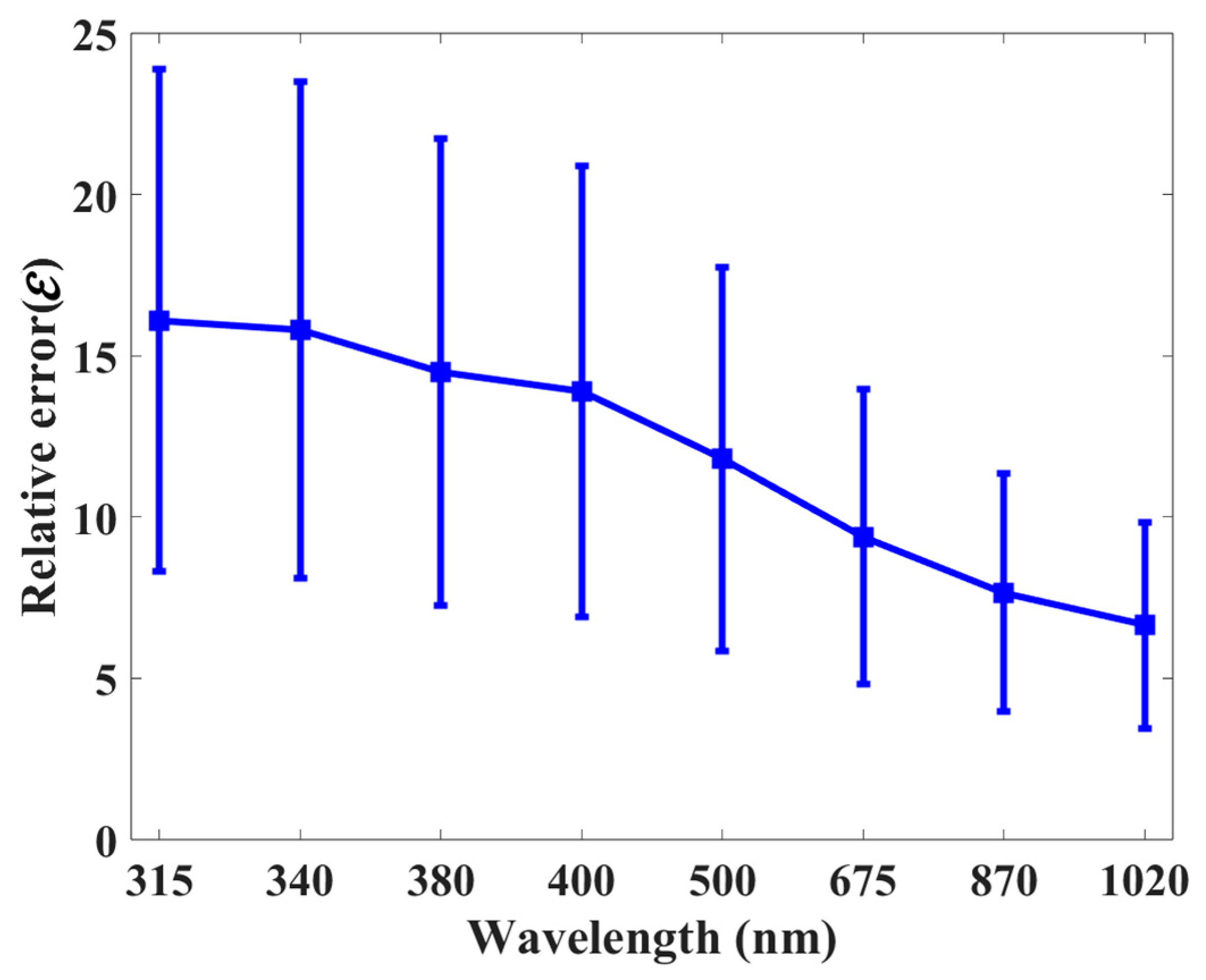
3.1. Analysis of the Forward Scattering Effect Using Simulated Data
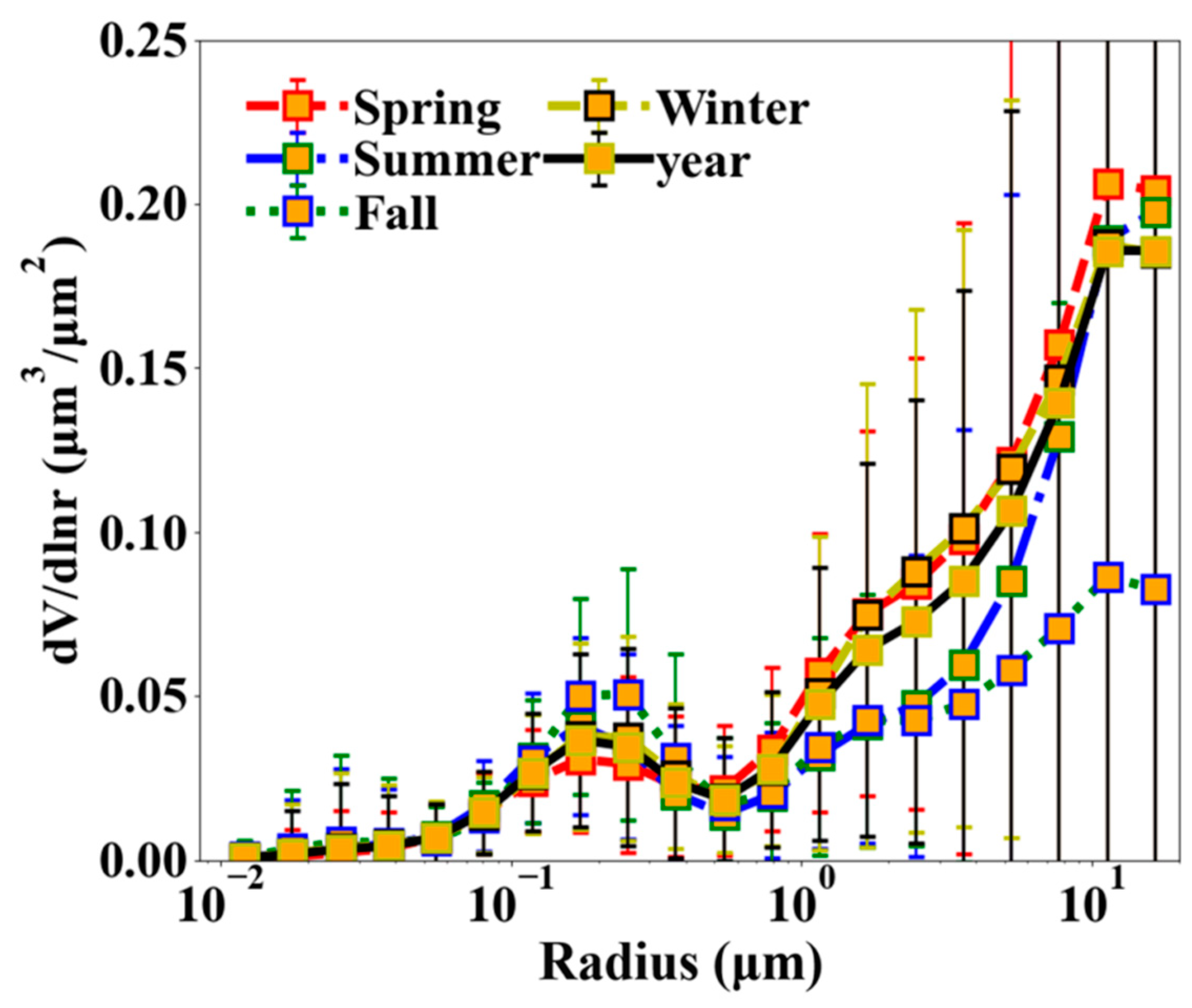
3.2. Analysis of Observed Data
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Boucher, O.; Tanré, D.; Chin, M.; Remer, L.A.; Takemura, T. Aerosol anthropogenic component estimated from satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L17804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, G.; di Sarra, A.; Meloni, D.; Piacentino, S.; Chamard, P. Aerosol optical properties at Lambeduca (central Mediterranean), 1. Influence of transport and identification of different aerosol types. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Chin, M.; Feingold, G.; Remer, L.; Anderson, T.L.; Balkanski, Y.; Bellouin, N.; Boucher, O.; Christopher, S.; et al. A review of measurement-based assessments of the aerosol direct radiative effect and forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 613–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.B.; Zhao, D.; Ruppel, M.J.; Laskina, O.; Grandquist, J.R.; Modini, R.; Stokes, M.D.; Russell, L.; Bertram, T.H.; Grassian, V.H.; et al. Direct aerosol chemical composition measurements to evaluate the physicochemical differences between controlled sea spray aerosol generation schemes. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 3667–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lü, R.; Liu, C.; Yuan, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, B.; Lei, L. Seasonal variation of columnar aerosol optical properties and radiative forcing over Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, P. Aerosol properties in a Chinese semiarid region. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4571–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Bhartia, P.K.; Herman, J.R.; Sinyuk, A.; Ginoux, P.; Holben, B. A long-term record of aerosol optical depth from TOMS observations and comparison to AERONET measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, J. Inversion of the haze aerosol sky columnar AVSD in central China by combining multiple ground observation equipment. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 8170–8185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Xia, X.; Goloub, P.; Holben, B.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Wang, H.; Blarel, L.; et al. Ground-based aerosol climatology of China: Aerosol optical depths from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) 2002–2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7619–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.; Estelles, V.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; et al. Column aerosol optical properties and aerosol radiative forcing during a serious haze-fog month over North China Plain in 2013 based on ground-based Sunphotometer measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 14, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, K.; Li, D.; Xie, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Zhao, W.; Tian, Q.; et al. Comprehensive study of optical, physical, chemical and radiative properties of total columnar atmospheric aerosols over China: An overview of Sun-sky radiometer Observation NETwork (SONET) measurements. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, Q.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Tie, X.; Shen, Z.; Wang, P.; An, Z. Impacts of aerosol compositions on visibility impairment in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; Li, L.; Arimoto, R.; Cheng, Y.; Huebert, B.; Wang, D. Characterization of atmospheric aerosol over Xi’an in the south margin of the Loess Plateau, China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4189–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Shi, J.S.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Takamura, T.; Khatri, P. Dust aerosol characteristics and shortwave radiative impact at a Gobi Desert of Northwest China during the spring of 2012. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 92A, 33–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Huang, J.P.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, B. Toward characterization of the aerosol optical properties over Loess Plateau of Northwestern China. J. Quant. Spectroc. Radiat. Transf. 2011, 112, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, T.H.; Tan, R.; Tang, J.; Wang, C.; He, S.; Dong, Y.; Huang, Z.; Bi, J. CALIOP-Based Quantification of Central Asian Dust Transport. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Han, Y.; Hua, W.; Tang, J.; Huang, J.; Zhou, T.; Huang, Z.; Bi, J.; Xie, H. Profiling dust mass concentration in Northwest China using a joint lidar and sun-photometer setting. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunjobi, K.O.; Kim, Y.J. Ultraviolet (0.280–0.400 μm) and broadband solar hourly radiation at Kwangju, South Korea: Analysis of their correlation with aerosol optical depth and clearness index. Atmos. Res. 2004, 71, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenny, B.N.; Saxena, V.K.; Frederick, J.E. Aerosol optical depth measurements and their impact on surface levels of ultraviolet-B radiation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 17311–17319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellitto, P.; di Sarra, A.; Siani, A.M. An improved algorithm for the determination of aerosol optical depth in the ultraviolet spectral range from Brewer spectrophotometer observations. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2006, 8, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madronich, S.; McKenzie, R.L.; Björn, L.O.; Caldwell, M.M. Changes in biologically active ultraviolet radiation reaching the Earth’s surface. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1998, 46, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haigh, J.D. The role of stratospheric ozone in modulating the solar radiative forcing of climate. Nature 1994, 370, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, S.; Guruprasad, K.N. Solar UV-B and UV-A/B exclusion effects on intraspecific variations in crop growth and yield of wheat varieties. Field Crops Res. 2011, 125, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; McKeen, S.A.; Madronich, S. Effect of anthropogenic aerosols on biologically active Ultraviolet radiation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1991, 18, 2265–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanhill, G.; Ianetz, A. Long-term trends in, and the spatial variation of, global irradiance in Israel. Tellus B 1997, 49, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, C.C.; Mao, J.T. Evaluation of atmospheric aerosol optical depth products at Ultraviolet bands derived from MODIS Products. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Tan, Y.; Li, Z.; Gai, C. The effect and correction of aerosol forward scattering on retrieval of aerosol optical depth from Sun photometer measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L14805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Q.; Wei, H. The treatment of scattering phase function in the multi-scattering radiative transfer calculation. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer. 2007, 19, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.M.; Su, J.; Fu, Q.; Ackerman, T.; Huang, J. Dust aerosol forward scattering effects on ground-based aerosol optical depth retrievals. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer. 2011, 112, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinyuk, A.; Holben, B.N.; Smirnov, A.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Schafer, J.S.; Giles, D.M.; Sorokin, M. Assessment of error in aerosol optical depth measured by AERONET due to aerosol forward scattering. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 23806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, P.B.; Livingston, J.M.; Dubovik, O.; Ramirez, S.A.; Wang, J.; Redemann, J.; Schmid, B.; Box, M.; Holben, B.N. Sunlight transmission through desert dust and marine aerosols: Diffuse light corrections to Sun photometry and pyrheliometry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D08207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Shen, J. Multiple scattering characteristics of unpolarized light in dustlike aerosol. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2010, 47, 82901. [Google Scholar]
- Kinne, S.; Akerman, T.; Shiobara, M.; Uchiyama, A.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Miloshevich, L.M.; Wendell, J.; Eloranta, E.W.; Purgold, C.; Bergstrom, R.W. Cirrus Cloud Radiative and Microphysical Properties from Ground Observations and In Situ Measurements During FIRE 1991 and Their Application to Exhibit Problems in Cirrus Solar Radiative Transfer Modeling. J. Atmos. Sci. 1997, 54, 2320–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, A.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamazaki, A. The instrument constant of sky radiometers (POM-02)–Part 2: Solid view angle. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5389–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiobara, M.; Asano, S. Estimation of cirrus optical thickness from sun photometer measurements. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 1994, 33, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, K.N. An Introduction to Atmospheric Radiation; Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2004; p. 343. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Thorsen, T.J.; Su, J.; Ge, J.M.; Huang, J.P. Test of Mie-based single-scattering properties of non-spherical dust aerosols in radiative flux calculations. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2009, 110, 1640–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, M.; Nakajima, T.; Olivieri, B. Determination of the Solar Calibration Constant for a Sun-Sky Radiometer: Proposal of an In-Situ Procedure. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, M.; Estellés, V.; Tomasi, C.; Nakajima, T.; Malvestuto, V.; Martínez-Lozano, J.A. Application of the SKYRAD Improved Langley plot method for the in situ calibration of CIMEL Sun-sky photometers. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 2688–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodhaine, B.A.; Wood, N.B.; Dutton, E.G.; Slusser, J.R. On rayleigh optical depth calculations. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y. Fundamentals of Atmospheric Radiation; Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 1993; pp. 30–192. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G. Atmospheric Radiation; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 367–370. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.L.; Cao, J.J.; Li, Z.Q.; Li, K.T.; Xu, H.; Liu, S.X.; Fan, X.H. Multi-Year Analyses of Columnar Aerosol Optical and Microphysical Properties in Xi’an, a Megacity in Northwestern China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Tonna, G.; Rao, R.; Boi, P.; Kaufman, Y.; Holben, B. Use of sky brightness measurements from ground for remote sensing of particulate polydispersions. Appl. Optics 1996, 35, 2672–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Dubovik, O.; Slutsker, I. Cloud-screening and quality control algorithms for the AERONET data-base. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, P.; Takamura, T. An algorithm to screen cloud-affected data for sky radiometer data analysis. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 87, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Gobbi, G.P.; Koren, I. Aerosol climatology using a tunable spectral variability, cloud screening of AERONET data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.Z.; Shi, G.Y.; Uchiyama, A.; Yamazaki, A.; Chen, H.; Goloub, P. Intercomparison between aerosol optical properties by a PREDE skyradiometer and CIMEL sunphotometer over Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 3199–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Campanelli, M.; Che, H.Z.; Estellés, V.; Irie, H.; Kim, S.W. An overview of and issues with sky radiometer technology and SKYNET. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 4195–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; King, M.D. Variability of absorption and optical properties of key aerosol types observed in worldwide locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.E.; Wang, Y.J.; Khatri, P.; Zhou, J. Seasonal characteristics of aerosol optical properties at the SKYNET Hefei site (31.90° N, 117.17° E) from 2007 to 2013: First long-term AOP over Hefei. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 6128–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Typical Aerosols | rm/μm | ln (σ) | re /μm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dust | 0.5000 | 1.0953 | 7.2 |
| Soot | 0.0118 | 0.6931 | 0.1 |
| Water-soluble | 0.0050 | 1.0953 | 0.04 |
| Wavelength /nm | Dust | Water-Soluble | Soot | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real | Imaginary | SSA | Real | Imaginary | SSA | Real | Imaginary | SSA | |
| 315 | 1.53 | 0.008 | 0.6111 | 1.53 | 0.008 | 0.9616 | 1.74 | 0.47 | 0.3044 |
| 340 | 1.53 | 0.008 | 0.6167 | 1.53 | 0.005 | 0.9621 | 1.75 | 0.47 | 0.2943 |
| 380 | 1.53 | 0.008 | 0.6254 | 1.53 | 0.005 | 0.9628 | 1.75 | 0.46 | 0.2768 |
| 400 | 1.53 | 0.008 | 0.6296 | 1.53 | 0.005 | 0.9630 | 1.75 | 0.46 | 0.2671 |
| Months | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | 106 | 1926 | 1462 | 2023 | 2469 | 995 | 42 | 374 | 645 | 214 | 219 | 311 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Li, M.; Zhou, L.; Ge, J.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, Q.; Hua, D. Analysis of Aerosol Optical Depth and Forward Scattering in an Ultraviolet Band Based on Sky Radiometer Measurements. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4342. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174342
Liu J, Li M, Zhou L, Ge J, Liu J, Guo Z, Liu Y, Wang J, Yan Q, Hua D. Analysis of Aerosol Optical Depth and Forward Scattering in an Ultraviolet Band Based on Sky Radiometer Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(17):4342. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174342
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jingjing, Mengping Li, Luyao Zhou, Jinming Ge, Jingtao Liu, Zhuqi Guo, Yangyang Liu, Jun Wang, Qing Yan, and Dengxin Hua. 2023. "Analysis of Aerosol Optical Depth and Forward Scattering in an Ultraviolet Band Based on Sky Radiometer Measurements" Remote Sensing 15, no. 17: 4342. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174342
APA StyleLiu, J., Li, M., Zhou, L., Ge, J., Liu, J., Guo, Z., Liu, Y., Wang, J., Yan, Q., & Hua, D. (2023). Analysis of Aerosol Optical Depth and Forward Scattering in an Ultraviolet Band Based on Sky Radiometer Measurements. Remote Sensing, 15(17), 4342. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174342






