Accumulation and Cross-Shelf Transport of Coastal Waters by Submesoscale Cyclones in the Black Sea
Abstract
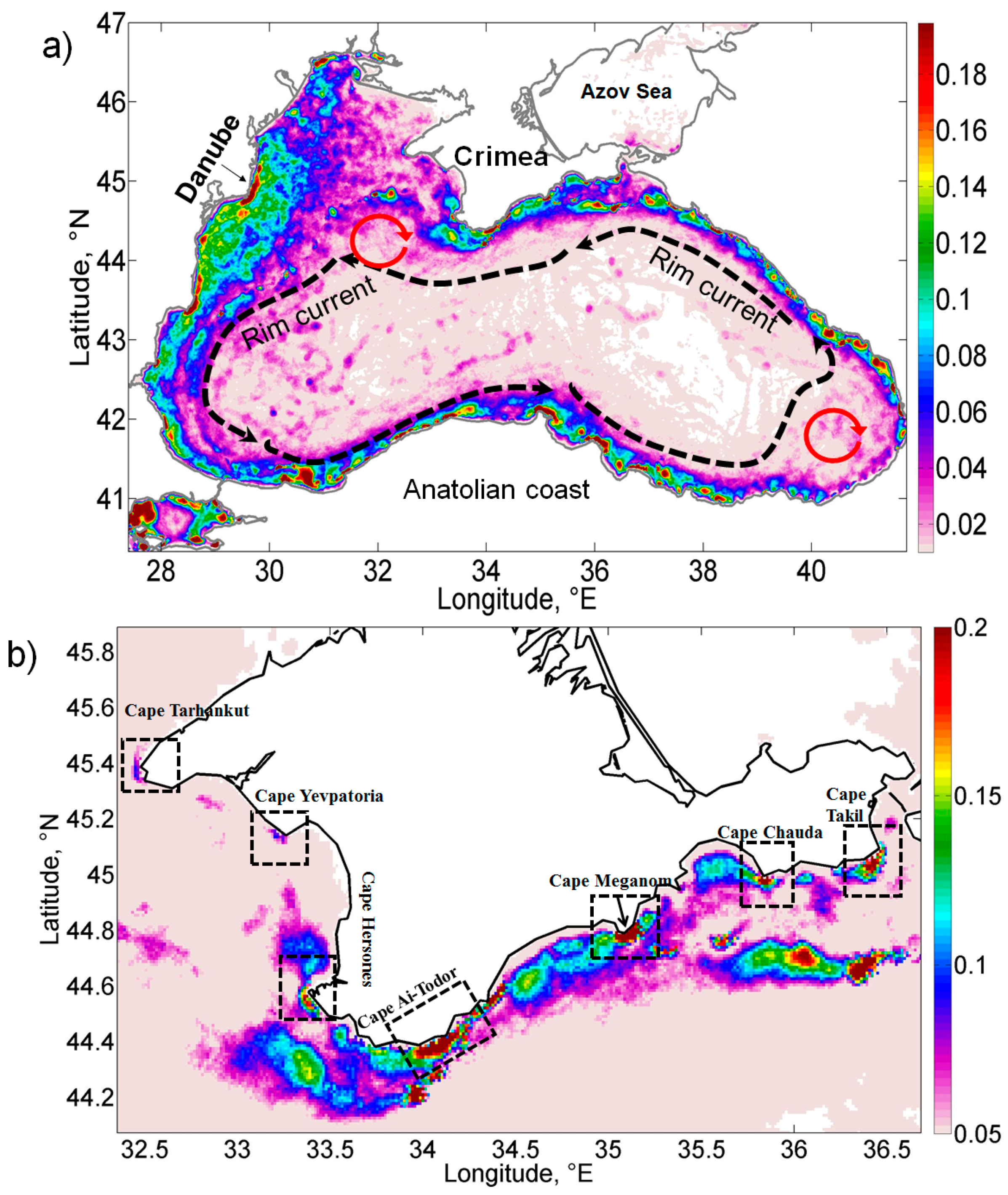
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Accumulation of Suspended Matter in Submesoscale Cyclones
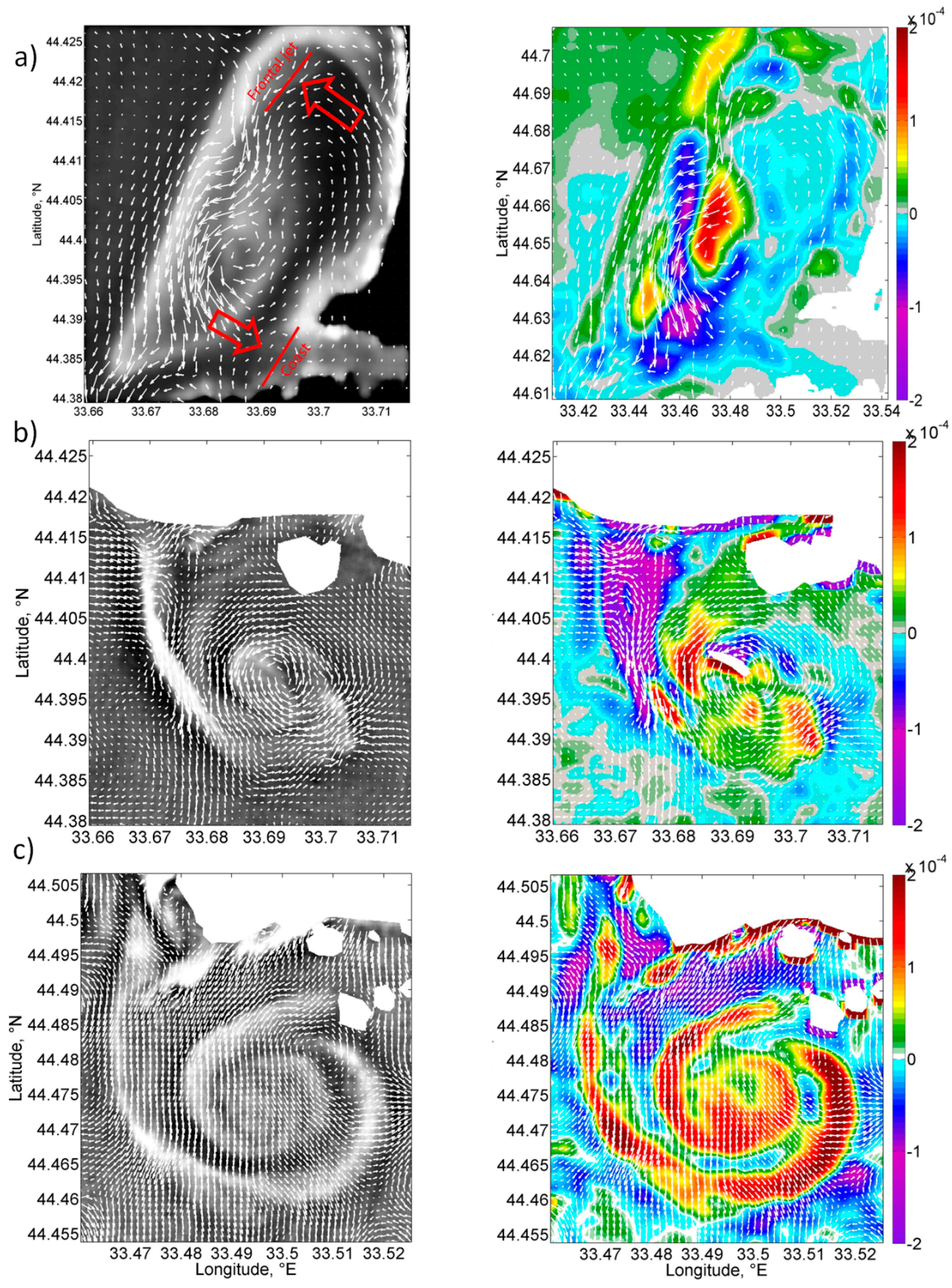
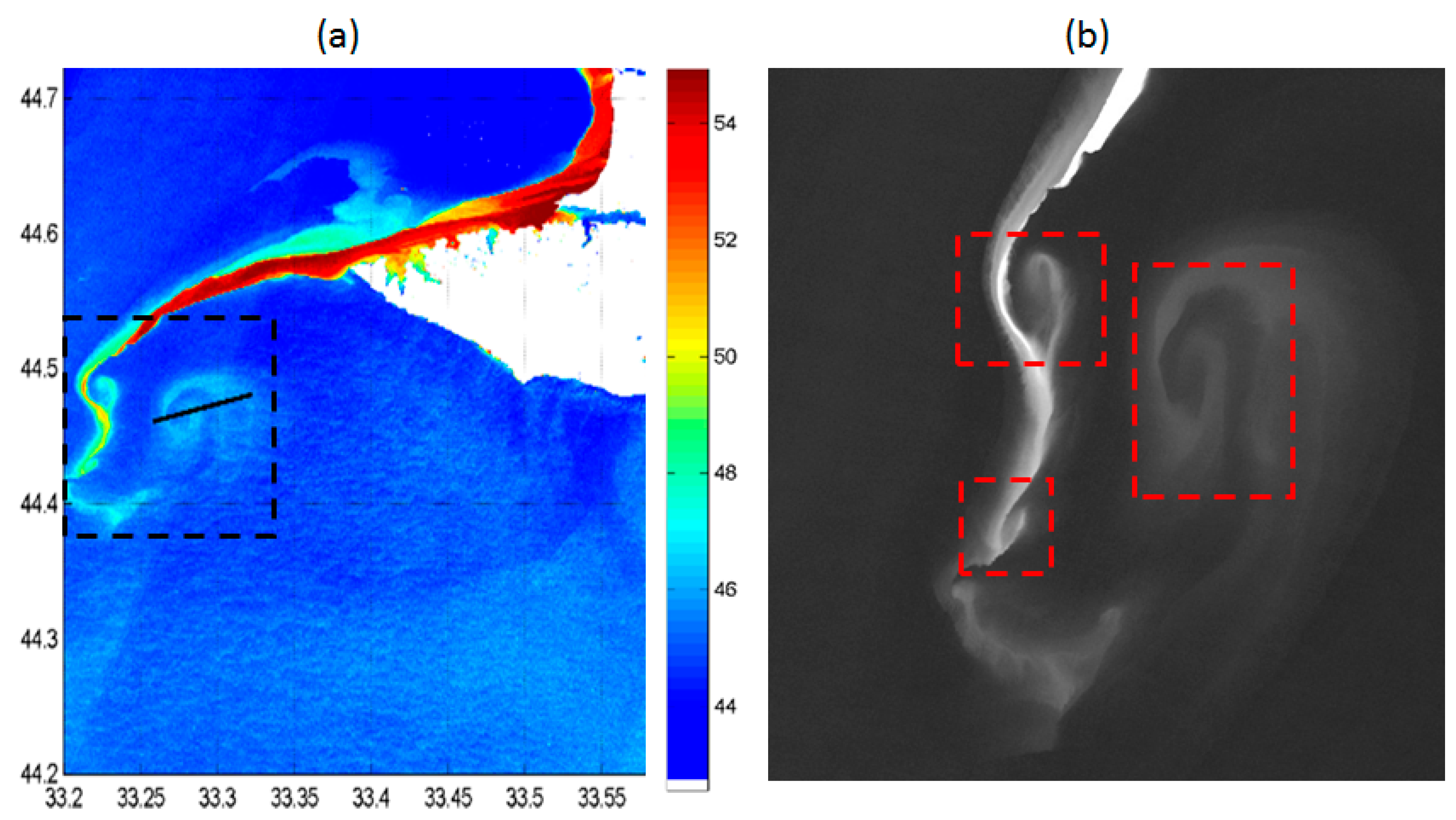
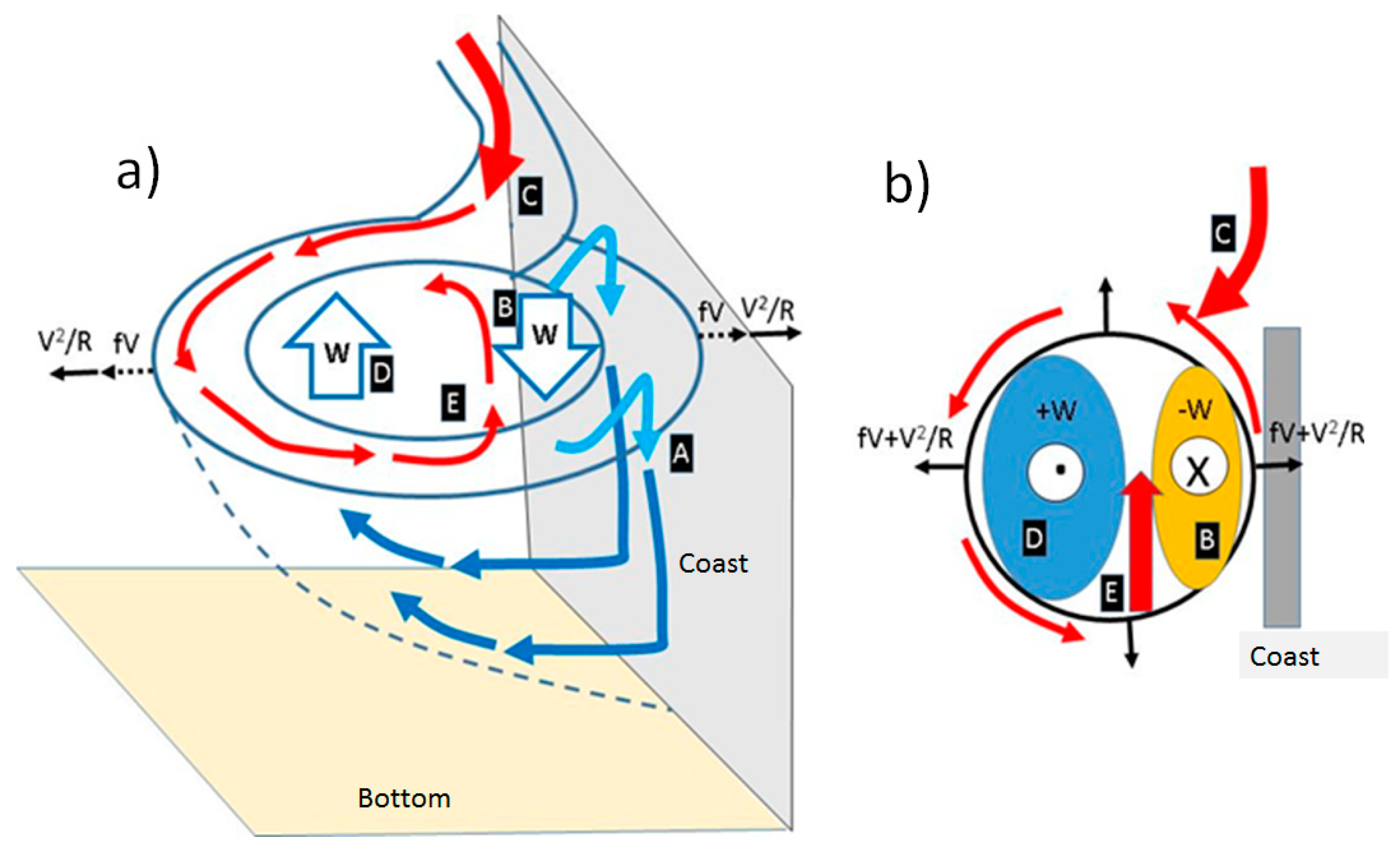
3.2. Convergence in the Coastal Part of Submesoscale Cyclones
3.3. Transport by Submesoscale Eddies from Satellite Data
3.3.1. Case 1. August 2020
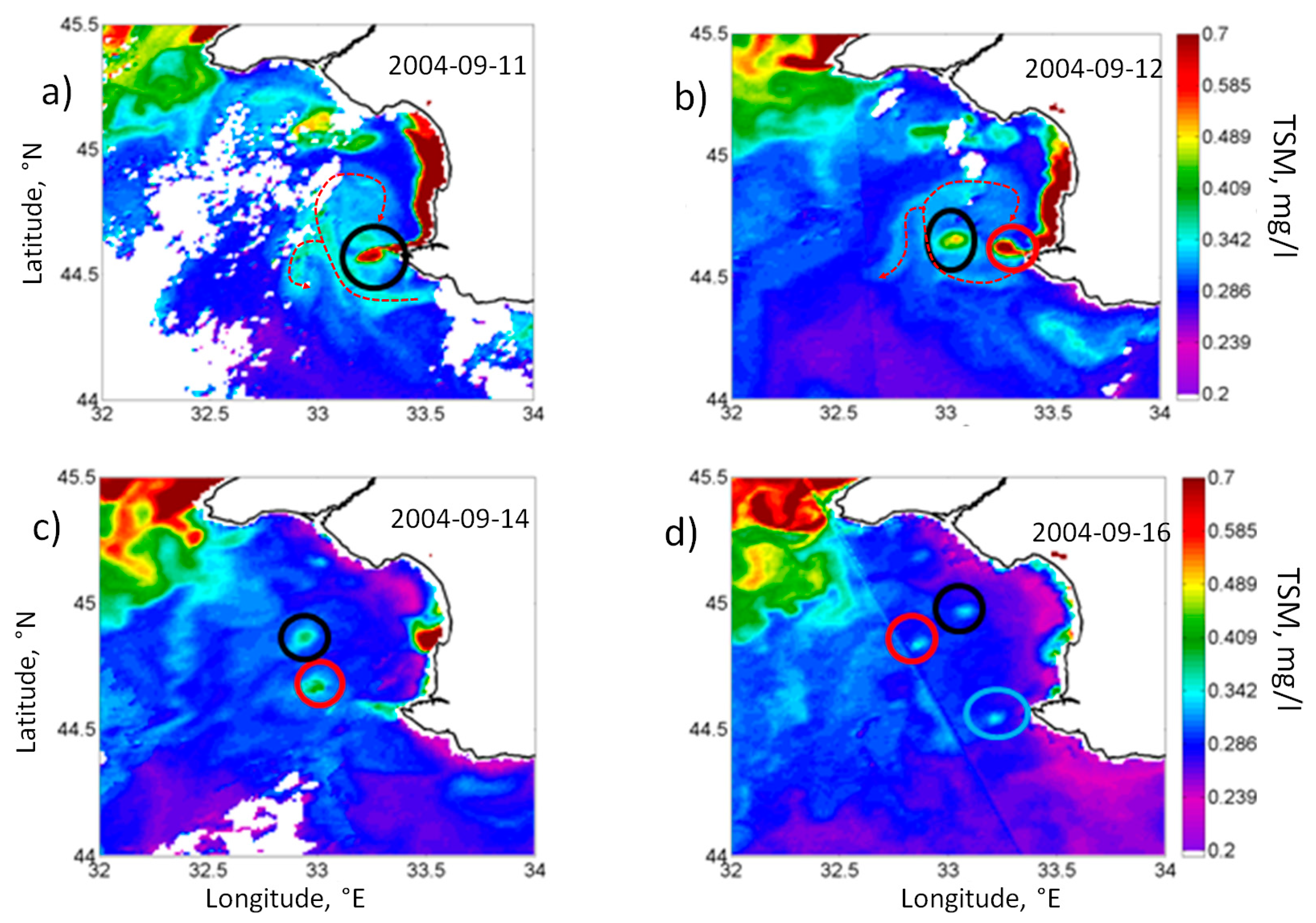
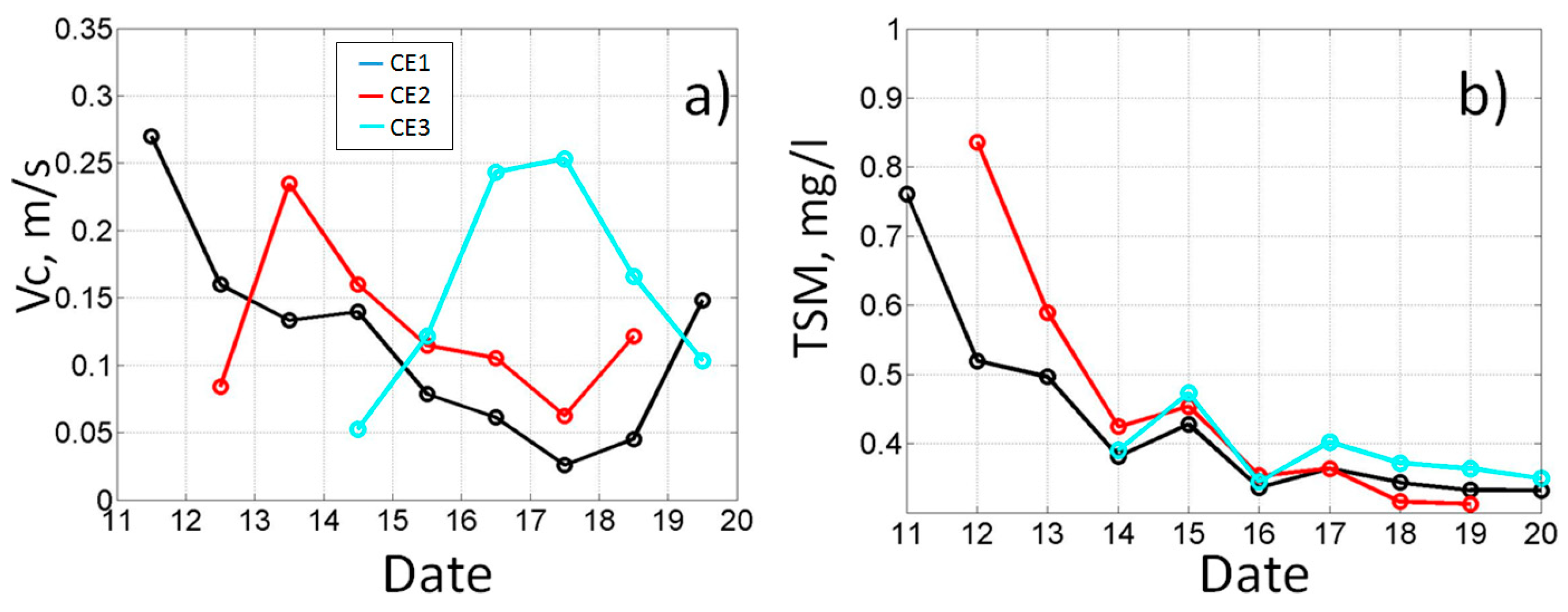
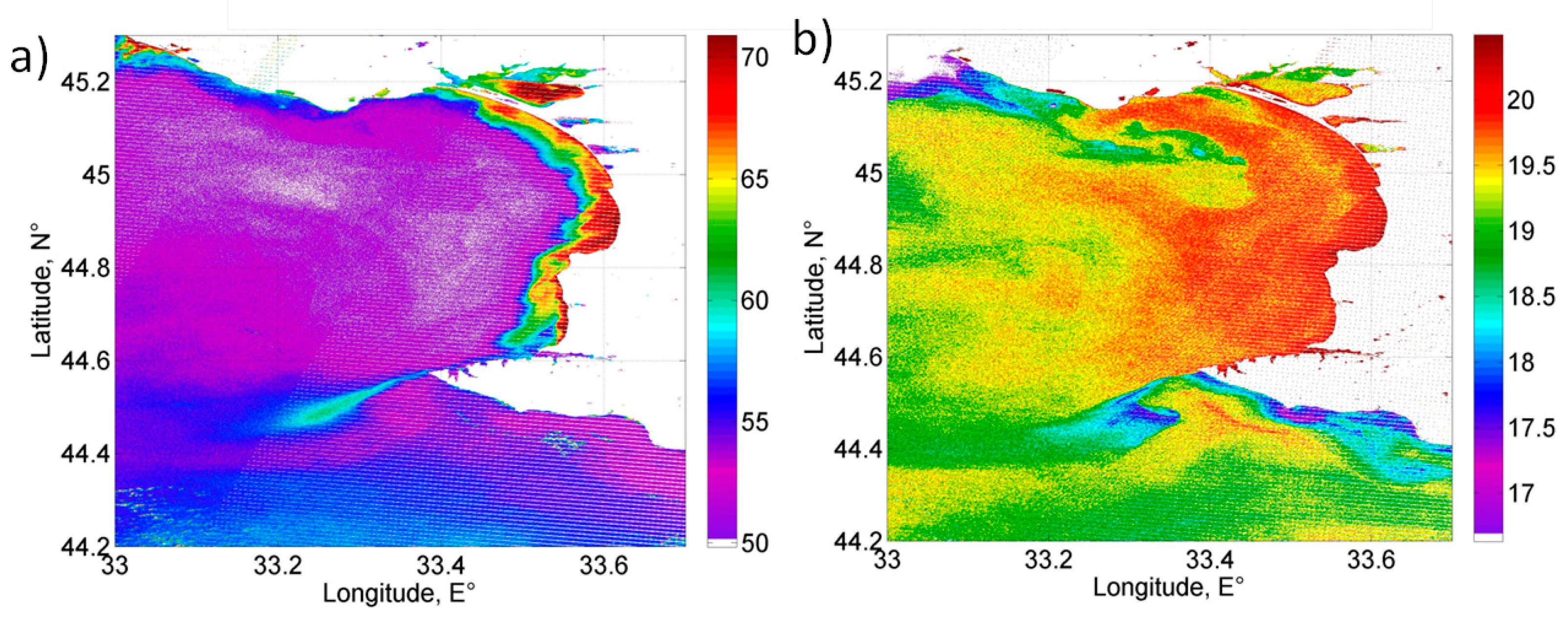
3.3.2. Case 2. September 2004
3.3.3. Case 3. August 2003
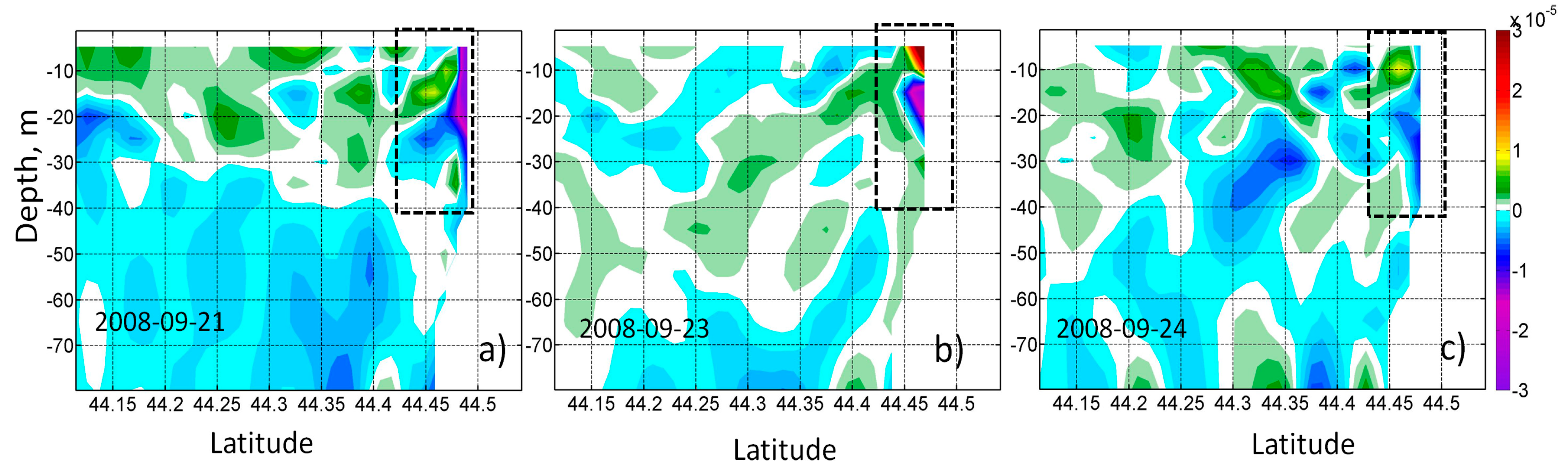
3.4. Transport of Coastal Waters in SCE from NEMO Model Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Submesoscale cyclones accumulate coastal waters in their core and transport them offshore. Detailed analysis of their structure from satellite data shows that they represent a spiral, which spins inward in the core of SCEs. This indicates that SCEs are characterized by convergence and downwelling in the coastal part of their core, which contradicts the expected divergence and uplift observed in the cyclonic eddies. This contradiction can be explained by the impact of the “wall”, which blocks the outward motion on the coastal periphery of the SCE and turn the water back to the core of the eddy. The hypothesis is confirmed through the analysis of the dynamic structure of SCEs from satellite and modeling data, which show the presence of the convergence pattern in the coastal part of SCEs and divergence in their offshore part;
- SCEs can transport suspended matter to a large distance away from the coast (~100 km). Often, series of SCEs are formed on the periphery of the mesoscale anticyclone or upwelling. Their separation from the coast cause a short-period entrainment of the coastal matter in the open ocean and the appearance of local anomalies in TSM and other optical properties. Such SCEs rapidly propagate offshore with a translational velocity of ~0.1–0.3 m/s due to the impact of background currents. The local anomalies of chlorophyll concentration, TSM and temperature in such SCEs gradually decrease during eddy’s evolution but still can be observed for more than 1 week. The estimated transport of TSM in SCEs as per satellite data is about 50 tonn/s;
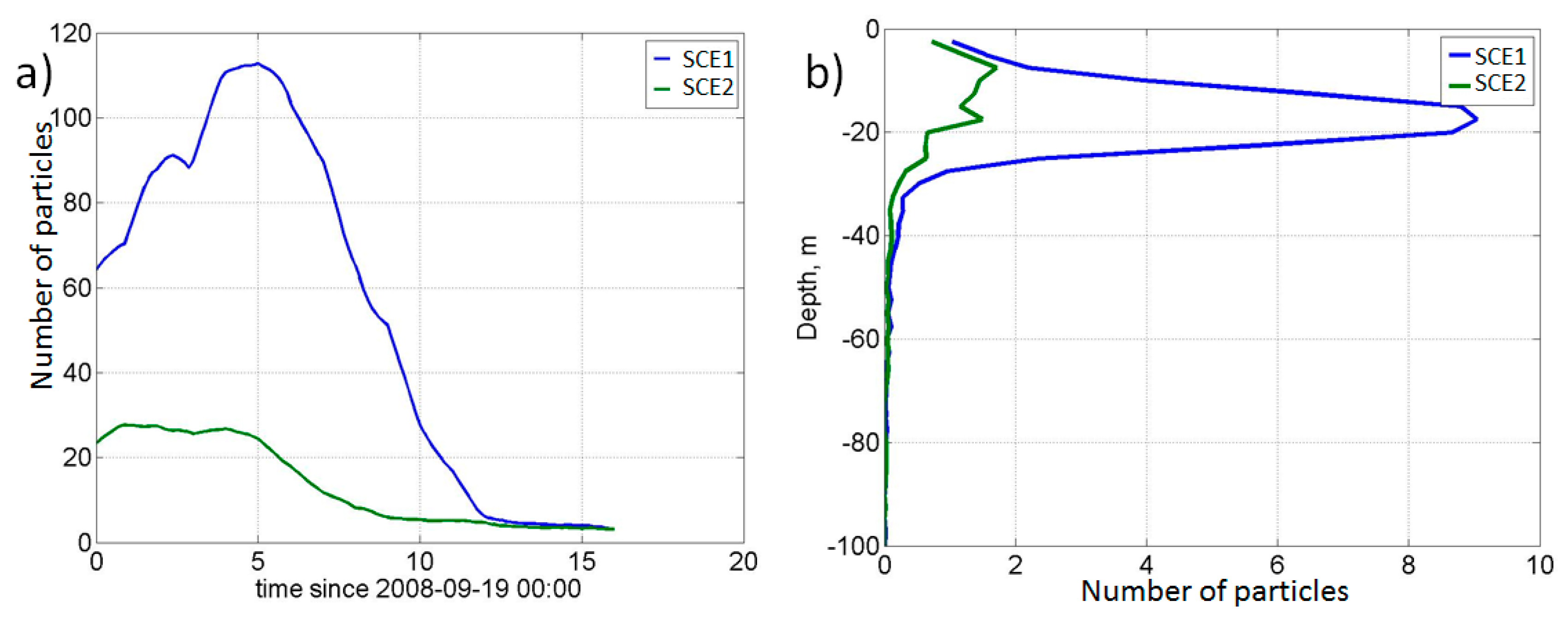
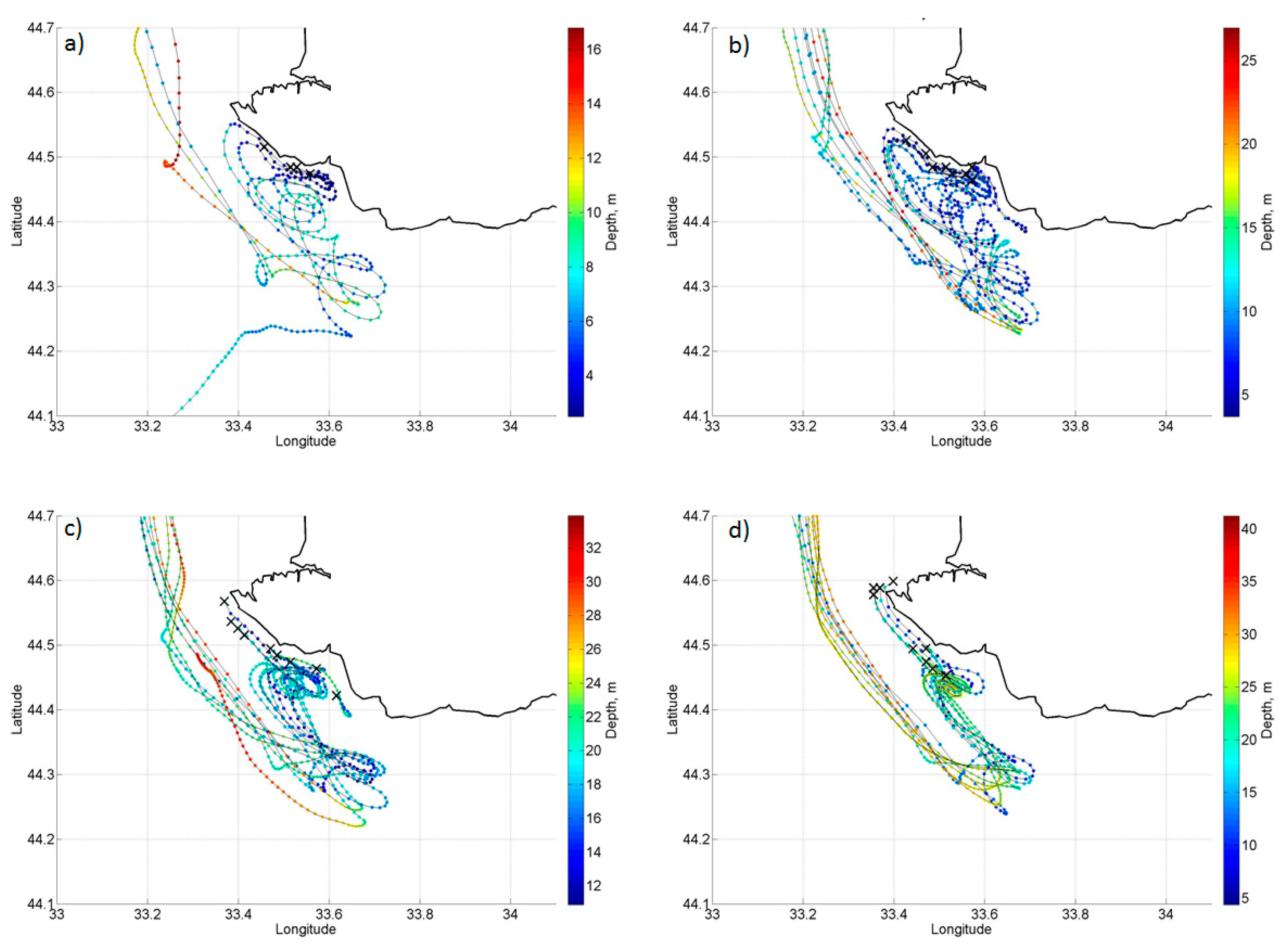
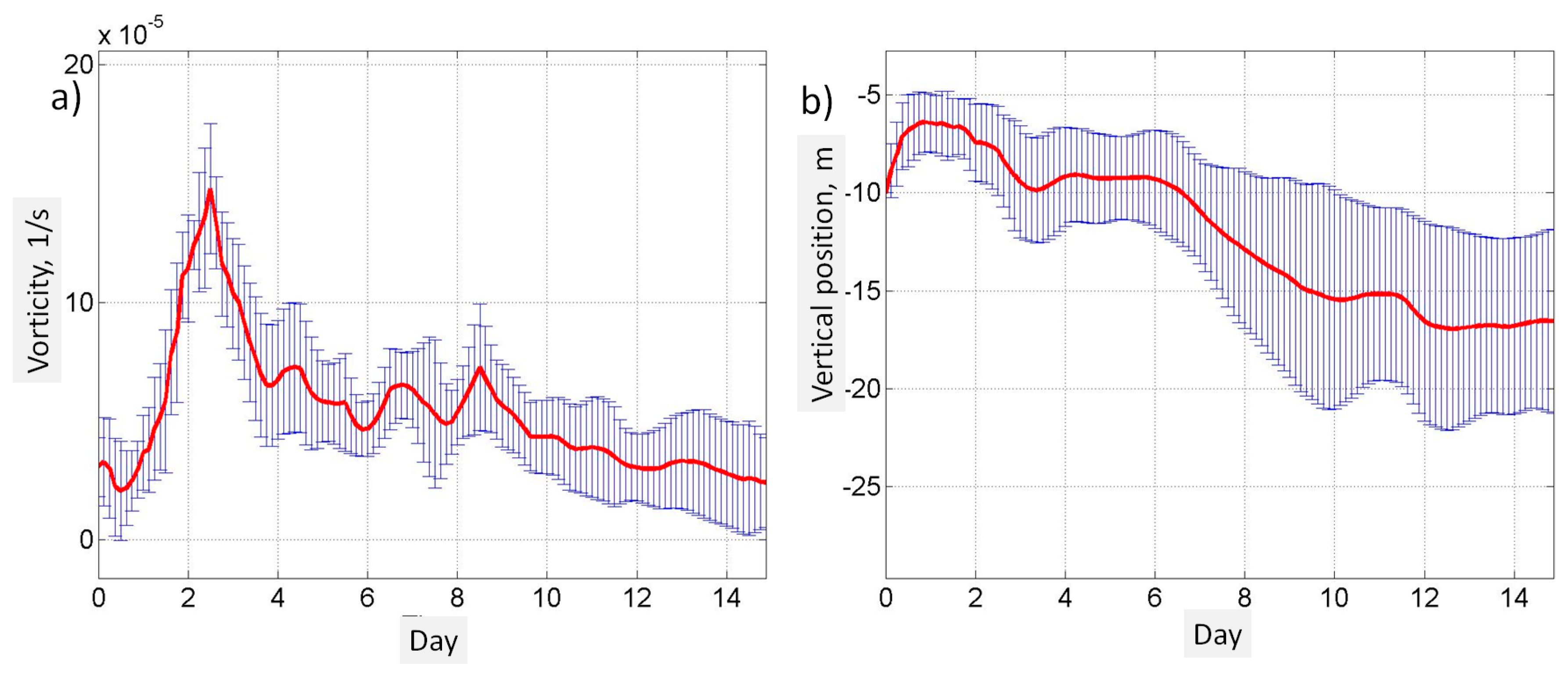
- Lagrangian analysis of high-resolution model data allows us to conduct an in-depth investigation of the transport of the coastal waters in the SCEs, which were formed in the area of coastal upwelling. The most intense entrainment of the particles is observed in the core of SCEs at the depth of the seasonal thermocline (15–25 m). This process intensifies when cold SCEs were separated from the coast and were surrounded by warm waters of the open sea. Then, the eddy began to gradually weaken. The particles made 2–3 rotations around its own center before the SCEs dissipated after ~10 days. Model data show that the decrease in SCEs’ vorticity after the separation is accompanied by the flattening of initially risen isopycnals. Therefore, the coastal particles trapped in the SCEs rapidly deepen with time to 10–20 m, i.e., SCEs cause their downward transport. The total estimated volume of the trapped coastal waters from the Lagrangian analysis in one of these SCEs is 0.25 km3.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flierl, G.R. Isolated eddy models in geophysics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1987, 19, 493–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzale, A. Transport by coherent barotropic vortices. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1999, 31, 55–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehahn, Y.; d’Ovidio, F.; Lévy, M.; Amitai, Y.; Heifetz, E. Long range transport of a quasi isolated chlorophyll patch by an Agulhas ring. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatsepin, A.G.; Baranov, V.I.; Kondrashov, A.A.; Korzh, A.O.; Kremenetskiy, V.V.; Ostrovskii, A.G.; Soloviev, D.M. Submesoscale eddies at the Caucasus Black Sea shelf and the mechanisms of their generation. Oceanology 2011, 51, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, A.; Tandon, A. An analysis of mechanisms for submesoscale vertical motion at ocean fronts. Ocean Model. 2006, 14, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurovsky, Y.Y.; Kubryakov, A.A.; Plotnikov, E.V.; Lishaev, P.N. Submesoscale Currents from UAV: An Experiment over Small-Scale Eddies in the Coastal Black Sea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosse, A.; Testor, P.; Mayot, N.; Prieur, L.; d’Ortenzio, F.; Mortier, L.; Le Goff, H.; Gourcuff, C.; Coppola, L.; Lavigne, H.; et al. A submesoscale coherent vortex in the L igurian S ea: From dynamical barriers to biological implications. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 6196–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W.; Armi, L.; Fischer, K.; Zachariasen, F. Spirals on the sea. Procedings R. Soc. Lond. A 2000, 456, 1217–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostianoy, A.G.; Ginzburg, A.I.; Lavrova, O.Y.; Mityagina, M.I. Satellite Remote Sensing of Submesoscale Eddies in the Russian Seas. In The Ocean in Motion: Circulation, Waves, Polar Oceanography; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleskerova, A.; Kubryakov, A.; Stanichny, S.; Medvedeva, A.; Plotnikov, E.; Mizyuk, A.; Verzhevskaia, L. Characteristics of topographic submesoscale eddies off the Crimea coast from high-resolution satellite optical measurements. Ocean Dyn. 2021, 71, 655–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roullet, G.; Klein, P. Cyclone-anticyclone asymmetry in geophysical turbulence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 218501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloosterziel, R.C.; Van Heijst, G.J.F. An experimental study of unstable barotropic vortices in a rotating fluid. J. Fluid Mech. 1991, 223, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Hou, Y.; Chu, X. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea: Mean properties, spatiotemporal variability, and impact on thermohaline structure. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubryakov, A.A.; Stanichny, S.V. Mesoscale eddies in the Black Sea from satellite altimetry dat. Oceanology 2015, 55, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubryakov, A.A.; Lishaev, P.N.; Chepyzhenko, A.I.; Aleskerova, A.A.; Kubryakova, E.A.; Medvedeva, A.V.; Stanichny, S.V. Impact of Submesoscale Eddies on the Transport of Suspended Matter in the Coastal Zone of Crimea Based on Drone, Satellite, and In Situ Measurement Data. Oceanology 2021, 61, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatsepin, A.; Kubryakov, A.; Aleskerova, A.; Elkin, D.; Kukleva, O. Physical mechanisms of submesoscale eddies generation: Evidences from laboratory modeling and satellite data in the Black Sea. Ocean Dyn. 2019, 69, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrova, O.; Bocharova, T. Satellite SAR observations of atmospheric and oceanic vortex structures in the Black Sea coastal zone. Adv. Space Res. 2006, 38, 2162–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrova, O.; Serebryany, A.; Bocharova, T.; Mityagina, M. Investigation of fine spatial structure of currents and submesoscale eddies based on satellite radar data and concurrent acoustic measurements. In Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, Coastal Waters, and Large Water Regions 2012; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 8532, p. 85320L. [Google Scholar]
- Mityagina, M.I.; Lavrova, O.Y.; Karimova, S.S. Multi-sensor survey of seasonal variability in coastal eddy and internal wave signatures in the north-eastern Black Sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 4779–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimova, S. Eddy statistics for the Black Sea by visible and infrared remote sensing. In Remote Sensing of the Changing Oceans; Tang, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 61–75. [Google Scholar]
- Zatsepin, A.G.; Ostrovskii, A.G.; Kremenetskiy, V.V.; Piotukh, V.B.; Kuklev, S.B.; Moskalenko, L.V.; Podymov, O.I.; Baranov, V.I.; Korzh, A.O.; Stanichny, S.V. On the nature of short-period oscillations of the main Black Sea pycnocline, submesoscale eddies, and response of the marine environment to the catastrophic shower of 2012. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2013, 49, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demyshev, S.G.; Evstigneeva, N.A. Modeling meso-and sub-mesoscale circulation along the eastern Crimean coast using numerical calculations. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2016, 52, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzina, O.S.; Kubryakov, A.A.; Mizyuk, A.I. Seasonal and Vertical Variability of Currents Energy in the Sub-Mesoscale Range on the Black Sea Shelf and in its Central Part. Phys. Oceanogr. 2021, 28, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubryakov, A.A.; Puzina, O.S.; Mizyuk, A.I. Cross-Slope Buoyancy Fluxes Cause Intense Asymmetric Generation of Submesoscale Eddies on the Periphery of the Black Sea Mesoscale Anticyclones. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2022, 127, e2021JC018189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiev, A.; Barymova, A.; Sedakov, R.; Zhiba, R.; Dbar, R. Spatial structure, short-temporal variability, and dynamical features of small river plumes as observed by aerial drones: Case study of the Kodor and Bzyp river plumes. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayman, P.; Ostrovskii, A.; Lobanov, V.; Park, J.H.; Park, Y.G.; Sergeev, A. Submesoscale eddies in Peter the Great Bay of the Japan/East Sea in winter. Ocean Dyn. 2019, 69, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, I.E.; Plotnikov, E.V.; Manucharyan, G.E. Brief Communication: Mesoscale and submesoscale dynamics in the marginal ice zone from sequential synthetic aperture radar observations. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 2941–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichs, D.M.; McInerney, J.B.; Oldroyd, H.J.; Lee, W.S.; Yun, S.; Yoon, S.T.; Stevens, C.L.; Zappa, C.J.; Dow, C.F.; Mueller, D.; et al. Observations of submesoscale eddy-driven heat transport at an ice shelf calving front. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubryakov, A.A.; Aleskerova, A.A.; Goryachkin, Y.N.; Stanichny, S.V.; Latushkin, A.A.; Fedirko, A.V. Propagation of the Azov Sea waters in the Black sea under impact of variable winds, geostrophic currents and exchange in the Kerch Strait. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 176, 102119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpınar, A.; Sadighrad, E.; Fach, B.A.; Arkın, S. Eddy induced cross-shelf exchanges in the Black Sea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, G.I.; Stanichny, S.V.; Stanychna, R.R. Anatomy of shelf–deep sea exchanges by a mesoscale eddy in the North West Black Sea as derived from remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubryakov, A.A.; Stanichny, S.V.; Zatsepin, A.G. Interannual variability of Danube waters propagation in summer period of 1992–2015 and its influence on the Black Sea ecosystem. J. Mar. Syst. 2018, 179, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotaev, G.K.; Huot, E.; Le Dimet, F.X.; Herlin, I.; Stanichny, S.V.; Solovyev, D.M.; Wu, L. Retrieving ocean surface current by 4-D variational assimilation of sea surface temperature images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubryakov, A.; Plotnikov, E.; Stanichny, S. Reconstructing large-and mesoscale dynamics in the Black Sea region from satellite imagery and altimetry data—a comparison of two methods. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremenchutskiy, D.A.; Kubryakov, A.A.; Zav’yalov, P.O.; Konovalov, B.V.; Stanichniy, S.V.; Aleskerova, A.A. Determination of the Suspended Matter Concentration in the Black Sea Using to the Satellite MODIS Data. Ecol. Saf. Coast. Shelf Zones Compr. Use Shelf Resour. 2014, 29, 5–9. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zavialov, P.O.; Makkaveev, P.N.; Konovalov, B.V.; Osadchiev, A.A.; Khlebopashev, P.V.; Pelevin, V.V.; Grabovskiy, A.B.; Izhitskiy, A.S.; Goncharenko, I.V.; Soloviev, D.M.; et al. Hydrophysical and hydrochemical characteristics of the sea areas adjacent to the estuaries of small rivers of the Russian coast of the Black Sea. Oceanology 2014, 54, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizyuk, A.I.; Puzina, O.S. Dynamics of the Azov-Black Sea basin by means of parallel ocean circulation modeling. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1359, 012083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizyuk, A.I.; Korotaev, G.K. Black Sea Intrapycnocline Lenses according to the Results of a Numerical Simulation of Basin Circulation. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2020, 56, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodi, W. Examples of calculation methods for flow and mixing in stratified fluids. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1987, 92, 5305–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalesak, S.T. Fully multidimensional flux-corrected transport algorithms for fluids. J. Comput. Phys. 1979, 31, 335–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkin, D.N.; Zatsepin, A.G. Laboratory study of a shear instability of an alongshore sea current. Oceanology 2014, 54, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannigan, L.; Marshall, D.P.; Naveira Garabato, A.C.; Nurser, A.G.; Kaiser, J. Submesoscale instabilities in mesoscale eddies. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2017, 47, 3061–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atadzhanova, O.A.; Zimin, A.V.; Romanenkov, D.A.; Kozlov, I.E. Satellite radar observations of small eddies in the White, Barents and Kara Seas. Phys. Oceanogr. 2017, 2, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg, A.I.; Bulycheva, E.V.; Kostianoy, A.G.; Solovyov, D.M. Vortex dynamics in the Southeastern Baltic Sea from satellite radar data. Oceanology 2015, 55, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleskerova, A.A.; Kubryakov, A.A.; Goryachkin, Y.N.; Stanichny, S.V.; Garmashov, A.V. Suspended-matter distribution near the western coast of Crimea under the impact of strong winds of various directions. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2019, 55, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largier, J.L. Upwelling bays: How coastal upwelling controls circulation, habitat, and productivity in bays. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2020, 12, 415–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gula, J.; Molemaker, M.J.; McWilliams, J.C. Topographic vorticity generation, submesoscale instability and vortex street formation in the Gulf Stream. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 4054–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.A.; Peterson, P.; McGillicuddy, D.J., Jr.; Maritorena, S.; Nelson, N.B. Bio-optical footprints created by mesoscale eddies in the Sargasso Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanichny, S.V.; Kubryakova, E.A.; Kubryakov, A.A. Quasi-tropical cyclone caused anomalous autumn coccolithophore bloom in the Black Sea. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 3173–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazyulya, S.; Deryagin, D.; Glukhovets, D.; Silkin, V.; Pautova, L. Regional Algorithm for Estimating High Coccolithophore Concentration in the Northeastern Part of the Black Sea. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, K.H. Cross-Shelf Exchange. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2016, 8, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubryakov, A.; Aleskerova, A.; Plotnikov, E.; Mizyuk, A.; Medvedeva, A.; Stanichny, S. Accumulation and Cross-Shelf Transport of Coastal Waters by Submesoscale Cyclones in the Black Sea. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4386. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184386
Kubryakov A, Aleskerova A, Plotnikov E, Mizyuk A, Medvedeva A, Stanichny S. Accumulation and Cross-Shelf Transport of Coastal Waters by Submesoscale Cyclones in the Black Sea. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(18):4386. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184386
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubryakov, Arseny, Anna Aleskerova, Evgeniy Plotnikov, Artem Mizyuk, Alesya Medvedeva, and Sergey Stanichny. 2023. "Accumulation and Cross-Shelf Transport of Coastal Waters by Submesoscale Cyclones in the Black Sea" Remote Sensing 15, no. 18: 4386. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184386
APA StyleKubryakov, A., Aleskerova, A., Plotnikov, E., Mizyuk, A., Medvedeva, A., & Stanichny, S. (2023). Accumulation and Cross-Shelf Transport of Coastal Waters by Submesoscale Cyclones in the Black Sea. Remote Sensing, 15(18), 4386. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184386





