Spatiotemporal Projections of Precipitation in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin Based on CMIP6 Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
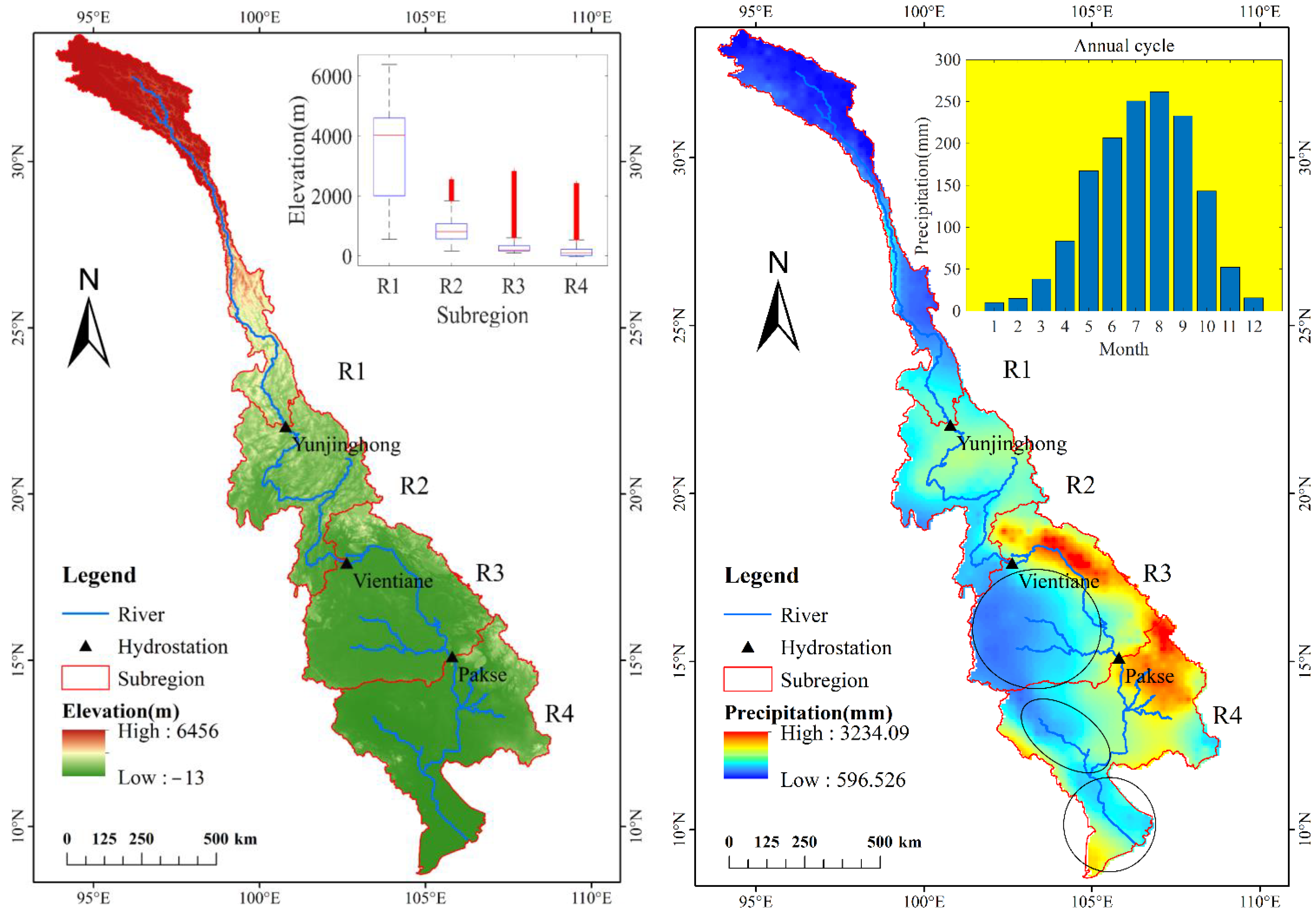
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Description
3. Methodology
3.1. Bias Correction
3.2. Trend Analysis
3.3. Evaluation Metrics for Performance
4. Results
4.1. Evaluation of Simulation Deviation
4.2. Trends in Future Precipitation
4.3. Annual Cycle of Average Seasonal Precipitation
4.4. Changes in Daily Precipitation Composition
4.5. Changes in the Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Future Precipitation
5. Discussion: Reliability of Future Projections
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schneider, U.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Rustemeier, E.; Ziese, M.; Becker, A. Evaluating the Hydrological Cycle over Land Using the Newly-Corrected Precipitation Climatology from the Global Precipitation Climatology Centre (GPCC). Atmosphere 2017, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Miao, C.; Duan, Q.; Ashouri, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.-L. A review of global precipitation data sets: Data sources, estimation, and intercomparisons. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassen, C.; Dietmar, D.; Chadwick, R. Conceptual deconstruction of the simulated precipitation response to climate change. Clim. Dynam. 2020, 55, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.L.; Hu, Y. Are climate-related changes to the character of global-mean precipitation predictable? Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 025209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalexiou, S.M.; Montanari, A. Global and regional increase of precipitation extremes under global warming. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 4901–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, K. Global precipitation system scale increased from 2001 to 2020. J. Hydrol. 2023, 616, 128768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhai, G.; Gao, S.; Shen, X. Decadal trends of global precipitation in the recent 30 years. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2015, 16, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, K. Global precipitation system size. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 054005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contractor, S.; Donat, M.G.; Alexander, L.V. Changes in Observed Daily Precipitation over Global Land Areas since 1950. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Y.; Chen, D.; Qin, D.; Zhai, P. Understanding human influence on climate change in China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwab113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.F.; Sapiano, M.R.P.; Huffman, G.J.; Wang, J.-J.; Gu, G.; Bolvin, D.; Chiu, L.; Schneider, U.; Becker, A.; Nelkin, E. The Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) Monthly Analysis (New Version 2.3) and a Review of 2017 Global Precipitation. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’gorman, P.A.; Allan, R.P.; Byrne, M.P.; Previdi, M. Energetic constraints on precipitation under climate change. Surv. Geophys. 2012, 33, 585–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassl, H. Climate change challenges. Surv. Geophys. 2011, 32, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Jacob, D.; Taylor, M.; Bolaños, T.G.; Bindi, M.; Brown, S.; Camilloni, I.A.; Diedhiou, A.; Djalante, R.; Ebi, K.; et al. The human imperative of stabilizing global climate change at 1.5 °C. Science 2019, 365, eaaw6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, T.; Huang, Y.; Peng, J.; Ling, Y. Evaluation of the CMIP6 precipitation simulations over global land. Earths. Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.K.-M.; Wu, H.-T.; Kim, K.-M. A canonical response of precipitation characteristics to global warming from CMIP5 models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 3163–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Pan, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Q.; Ciais, P.; Penuelas, J. Global socioeconomic risk of precipitation extremes under climate change. Earths. Future 2020, 8, e2019EF001331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, T. Increasing impacts from extreme precipitation on population over China with global warming. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billi, P.; Fazzini, M. Global change and river flow in Italy. Global Planet. Chang. 2017, 155, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.J.; Foster, P.N.; Prentice, I.C. Future global water resources with respect to climate change and water withdrawals as estimated by a dynamic global vegetation model. J. Hydrol. 2012, 448–449, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzadilla, A.; Rehdanz, K.; Betts, R.; Falloon, P.; Wiltshire, A.; Tol, R.S.J. Climate change impacts on global agriculture. Clim. Chang. 2013, 120, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloat, L.L.; Gerber, J.S.; Samberg, L.H.; Smith, W.K.; Herrero, M.; Ferreira, L.G.; Godde, C.M.; West, P.C. Increasing importance of precipitation variability on global livestock grazing lands. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray-Tortarolo, G.N.; Jaramillo, V.J. Precipitation extremes in recent decades impact cattle populations at the global and national scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, Y. Asymmetric responses of leaf litter decomposition to precipitation changes in global terrestrial ecosystem. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 387, 135898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, L.A.; Sala, O.E. Effect of interannual precipitation variability on dryland productivity: A global synthesis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Liu, P.; Xia, J.; Ming, B.; Cheng, L.; Chen, J.; Xie, K.; Liu, Z.; Li, X. Contribution of complementary operation in adapting to climate change impacts on a large-scale wind–solar–hydro system: A case study in the Yalong River Basin, China. Appl. Energy 2022, 325, 119809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamududu, B.; Killingtveit, A. Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Global Hydropower. Energies 2012, 5, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeland, K.; Borga, M.; Creutin, J.-D.; François, B.; Ramos, M.-H.; Vidal, J.-P. Space-time variability of climate variables and intermittent renewable electricity production—A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2017, 79, 600–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobiet, A.; Kotlarski, S.; Beniston, M.; Heinrich, G.; Rajczak, J.; Stoffel, M. 21st century climate change in the European Alps—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 1138–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, T. Detectable anthropogenic forcing on the long-term changes of summer precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 59, 1939–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Huete, A.; Cleverly, J.; Phinn, S.; McDonald-Madden, E.; Cao, Y.; Qin, F. Multi-climate mode interactions drive hydrological and vegetation responses to hydroclimatic extremes in Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.; Dai, A.; Trenberth, K.E. Hydroclimatic Trends in the Mississippi River Basin from 1948 to 2004. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 4599–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, J.A.; El-Askary, H.M.; Allali, M.; Sayed, E.; Sweliem, H.; Piechota, T.C.; Struppa, D.C. Characterizing El Niño-Southern Oscillation Effects on the Blue Nile Yield and the Nile River Basin Precipitation using Empirical Mode Decomposition. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 4, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Gruber, A. Validation of the abrupt change in GPCP precipitation in the Congo River Basin. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghtalab, N.; Moore, N.; Heerspink, B.P.; Hyndman, D.W. Evaluating spatial patterns in precipitation trends across the Amazon basin driven by land cover and global scale forcings. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 140, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, X.; Qian, C.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Variations and changes of annual precipitation in Central Asia over the last century. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Huang, W.; Jin, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal precipitation variations in the arid Central Asia in the context of global warming. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irannezhad, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, D. Influential climate teleconnections for spatiotemporal precipitation variability in the Lancang-Mekong River basin from 1952 to 2015. J. Geophys. Res-Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD033331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Peng, J.; Xu, C.Y.; Singh, V.P. Spatiotemporal variations of precipitation regimes across Yangtze River Basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Milliman, J.D.; Xu, H. Temporal trend of precipitation and runoff in major Chinese Rivers since 1951. Global Planet. Chang. 2010, 73, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zeng, T.; Chen, Q.; Han, X.; Weng, X.; He, P.; Zhou, Z.; Du, Y. Spatio-temporal changes in daily extreme precipitation for the Lancang–Mekong River Basin. Nat. Hazards 2023, 115, 641–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Mao, G.; Irannezhad, M.; Pokhrel, Y. Past and Future Changes in Climate and Water Resources in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin: Current Understanding and Future Research Directions. Engineering 2022, 13, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Bolch, T.; Chen, D.; Gao, J.; Immerzeel, W.; Piao, S.; Su, F.; Thompson, L.; Wada, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. The imbalance of the Asian water tower. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, T.J.; Zhang, W.X.; Li, J. Change in precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau projected by weighted CMIP6 models. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 1133–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.-L.; Li, F.-F.; Gong, T.-L.; Gao, Y.-H.; Li, J.-F.; Qiu, J. Reasons behind seasonal and monthly precipitation variability in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its surrounding areas during 1979∼2017. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Duan, K.; Shang, W.; Shi, P.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, Z. Increase in seasonal precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau in the 21st century projected using CMIP6 models. Atmos. Res. 2022, 277, 106306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Zhao, T.; He, Y.; Chen, X. Hydropower change of the water tower of Asia in 21st century: A case of the Lancang River hydropower base, upper Mekong. Energy 2019, 179, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shen, L. A Collaborative Framework for Hydropower Development and Sustainable Livelihood of Farmers in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin: A Review with the Perspective of Energy-Water-Food Nexus. Water 2022, 14, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Luo, X. Precipitation and Flow Variations in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin and the Implications of Monsoon Fluctuation and Regional Topography. Water 2019, 11, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, H.; Leung, L.R.; Li, H.-Y.; Zhao, J.; Tian, F.; Yang, K.; Sothea, K. Dam construction in Lancang-Mekong River Basin could mitigate future flood risk from warming-induced intensified rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 10378–10386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Zhao, X.; Yao, L.; Jiang, H.; Xu, J.; Yang, J.; Li, Y. Variations in terrestrial water storage in the Lancang-Mekong river basin from GRACE solutions and land surface model. J. Hydrol. 2020, 580, 124258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Castelletti, A.; Burlado, P.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J. Soft-cooperation via data sharing eases transboundary conflicts in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2022, 606, 12746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, J.; ASCE, M.; Wang, H. Dam-Impacted Water–Energy–Food Nexus in Lancang-Mekong River Basin. J. Water Res. Pl-ASCE 2021, 147, 04021010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, P.; Tian, F.; Zhu, T.; Zohidov, B.; Ni, G.; Lu, H.; Liu, H. Exploring synergies in the water-food-energy nexus by using an integrated hydro-economic optimization model for the Lancang-Mekong River basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 137996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayiranga, A.; Chen, B.; Guo, L.; Measho, S.; Hirwa, H.; Liu, S.; Bofana, J.; Sun, S.; Wang, F.; Karamage, F.; et al. Spatiotemporal variations of forest ecohydrological characteristics in the Lancang-Mekong region during 1992-2016 and 2020-2099 under different climate scenarios. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 2021, 310, 108662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission 2010. State of the Basin Report 2010; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Tian, F.; Guo, L.; Borzì, I.; Patil, R.; Wei, J.; Liu, D.; Wei, Y.; Yu, D.J.; Sivapalan, M. Socio-hydrologic modeling of the dynamics of cooperation in the transboundary Lancang–Mekong River. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 1883–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, W.; Suman, D.; Yu, S.; He, D. Water Cooperation Priorities in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin Based on Cooperative Events Since the Mekong River Commission Establishment. Chinese Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wei, Y.; Tian, F.; Nott, N.; Wit, C.; Guo, L.; Lu, Y. News media coverage of conflict and cooperation dynamics of water events in the Lancang–Mekong River basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 1603–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Cao, H. Drought and flood occurrences in the Lancang River Basin during the last 60 years: Their variations and teleconnections with monsoons. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2020, 11, 1798–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Yao, Z. Climate change and its impact on water availability of large international rivers over the mainland Southeast Asia. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 3966–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, B.; Narasimhan, B.; Paul, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Wangpimool, W.; Sith, R.; Sayasane, R. Development and propagation of hydrologic drought from meteorological and agricultural drought in the Mekong River Basin. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e14935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.M.; Merz, B.; Apel, H. A climate-flood link for the lower Mekong River. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irannezhad, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, D. Extreme precipitation variability across the Lancang-Mekong River Basin during 1952–2015 in relation to teleconnections and summer monsoons. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 2614–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Mei, Y.; Di, C. Air temperature and precipitation variation trends of the Lancang river upstream from 1957 to 2011. Therm. Sci. 2013, 17, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, G.; Wu, F.; Li, C. Analysis of temporal-spatial precipitation variations during the crop growth period in the Lancang River basin, southwestern China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 76, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapuarachchi, H.A.P.; Takeuchi, K.; Zhou, M.; Kiem, A.S.; Georgievski, M.; Magome, J.; Ishidaira, H. Investigation of the Mekong River basin hydrology for 1980–2000 using the YHyM. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Le, M.-H.; Lakshmi, V. Land use, climate, and water change in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta (VMD) using earth observation and hydrological modeling. J. Hydrol-Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Try, S.; Tanaka, S.; Tanaka, K.; Sayama, T.; Khujanazarov, T.; Oeurng, C. Comparison of CMIP5 and CMIP6 GCM performance for flood projections in the Mekong River Basin. J. Hydrol-Reg. Stud. 2022, 40, 101035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, T.D.; Hoang, P.L.; Bui, D.M.; Rutschmann, P. Modelling seasonal flows alteration in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta under upstream discharge changes, rainfall changes and sea level rise. Int. J. River Basin Ma. 2019, 17, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.I.; Bell, A.R.; Anchukaitis, K.J.; Buckley, B.M. Snow cover and precipitation impacts on dry season streamflow in the Lower Mekong Basin. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D16116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Try, S.; Tanaka, S.; Tanaka, K.; Sayama, T.; Lee, G.; Oeurng, C. Assessing the effects of climate change on flood inundation in the lower Mekong Basin using high-resolution AGCM outputs. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2020, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Xiao, Z.-N.; Nguyen, M. Projection on precipitation frequency of different intensities and precipitation amount in the Lancang-Mekong River basin in the 21st century. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2021, 12, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; She, D.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Q. Future projections of flooding characteristics in the lancang-mekong river basin under climate change. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Yang, K.; Wang, W.; Tang, Q.; Khem, S.; Huang, Y. Meteorological and hydrological droughts in mekong river basin and surrounding areas under climate change. J. Hydrol. 2021, 36, 100873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, J.; Yu, E. Projection of temperature change and extreme temperature events in the Lancang–Mekong River basin. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2020, 13, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Barradas, A.; Nigam, S. Hydroclimate variability and change over the mekong river basin: Modeling and predictability and policy implications. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018, 19, 849–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Cai, T. Multi-model ensemble simulation and projection in the climate change in the mekong river basin. Part I: Temperature. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 7513–7523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Shahid, S.; Ahmed, K.; Ismail, T.; Ziarh, G.F.; Chung, E.; Wang, X. Evaluation of CMIP6 GCM rainfall in mainland Southeast Asia. Atmos. Res. 2021, 254, 105525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, S. Evaluation of CMIP6 for historical temperature and precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau and its comparison with CMIP5. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2020, 11, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, Y.; Liu, L.; Cheng, L.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Xu, Z. Assessment of GCMs simulation performance for precipitation and temperature from CMIP5 to CMIP6 over the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 3994–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Wood, E.F.; Pan, M.; Fisher, C.K.; Miralles, D.G.; Dijk, A.I.J.M.; McVicar, T.R.; Adler, R.F. MSWEP V2 global 3-hourly 0.1° precipitation: Methodology and quantitative assessment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 473–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Levizzani, V.; Schellekens, J.; Miralles, D.G.; Martens, B.; Roo, A.D. MSWEP: 3-hourly 0.25° global gridded precipitation (1979–2015) by merging gauge, satellite, and reanalysis data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 589–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Vergopolan, N.; Pan, M.; Levizzani, V.; Dijk, A.I.J.M.V.; Weedon, G.P.; Brocca, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Huffman, G.J.; Wood, E.F. Global-scale evaluation of 22 precipitation datasets using gauge observations and hydrological modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 6201–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shangguan, D.; Liu, S.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Evaluation and comparison of CHIRPS and MSWEP daily-precipitation products in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during the period of 1981–2015. Atmos. Res. 2019, 230, 104634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Li, L.; Li, C. Spatio-temporal accuracy evaluation of MSWEP daily precipitation over the Huaihe River Basin, China: A comparison study with representative satellite- and reanalysis-based products. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 2271–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S. Performance assessment of CHIRPS, MSWEP, SM2RAIN-CCI, and TMPA precipitation products across India. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Chen, Y.; Azmat, M.; Patient, M.K.; Ahmed, Z.; Richard, M.; Tariq, A. Long-term performance evaluation of the latest multi-source weighted-ensemble precipitation (MSWEP) over the highlands of indo-pak (1981–2009). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Ruben, G.B.; Bao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Jin, J. Error Correction of Multi-Source Weighted-Ensemble Precipitation (MSWEP) over the Lancang-Mekong River Basin. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, J.; Gao, C.; Ruben, G.; Wang, G. Assessing the Uncertainties of Four Precipitation Products for Swat Modeling in Mekong River Basin. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Bai, P.; Liang, K.; Liu, C. Evaluation of six precipitation products in the Mekong River Basin. Atmos. Res. 2021, 255, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Brissette, F.P.; Chaumont, D.; Braun, M. Performance and uncertainty evaluation of empirical downscaling methods in quantifying the climate change impacts on hydrology over two North American River Basins. J. Hydrol. 2013, 479, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Guo, S.; He, S.; Guo, J.; Hong, X.; Liu, Z. A copula-based analysis of projected climate changes to bivariate flood quantiles. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Ajami, N.K.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S. Multi-model ensemble hydrologic prediction using Bayesian model averagin. Adv. Water Res. 2007, 30, 1371–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Jiang, S.; Dong, J.; Ren, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Duan, Z. Fusion of gauge-based, reanalysis, and satellite precipitation products using Bayesian model averaging approach: Determination of the influence of different input sources. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftery, A.E.; Gneiting, T.; Balabdaoui, F.; Polakowski, M. Using Bayesian model averaging to calibrate forecast ensembles. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2005, 113, 1155–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloughter, J.M.L.; Raftery, A.E.; Gneiting, T.; Fraley, C. Probabilistic quantitative precipitation forecasting using Bayesian model averaging. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2007, 135, 3209–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.; Gibbons, J.D. Rank Correlation Methods, 5th ed.; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.D. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraglia, G.; Brattich, E.; Carbone, G. Precipitation trends in North and South Carolina, USA. J. Hydrol-Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 101201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; You, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Bhatti, A.S.; Ullah, W.; Hagan, D.F.T.; Ali, A.; Ali, G.; Jan, M.A.; Khan, S.N.; et al. Evaluation of CMIP5 models and projected changes in temperatures over South Asia under global warming of 1.5 °C, 2 °C, and 3 °C. Atmos. Res. 2020, 246, 105122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimonsree, S.; Kamworapan, S.; Gheewala, S.H.; Thongbhakdi, A.; Prueksakorn, K. Evaluation of CMIP6 GCMs performance to simulate precipitation over Southeast Asia. Atmos. Res. 2023, 282, 106522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Guo, H.; Huth, J.; Leinenkugel, P.; Li, X.; Dech, S. Flood mapping and flood dynamics of the mekong delta: ENVISAT-ASAR-WSM based time series analyses. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 687–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raesaenen, T.A.; Kummu, M. Spatiotemporal influences of ENSO on precipitation and flood pulse in the mekong river basin. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Try, S.; Tanaka, S.; Tanaka, K.; Sayama, T.; Hu, M.; Sok, T.; Oeurng, C. Projection of extreme flood inundation in the mekong river basin under 4K increasing scenario using large ensemble climate data. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 4350–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, D.Y.; Li, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Ji, M. Spatiotemporal variation of precipitation on a global scale from 1960 to 2016 in a new normalized daily precipitation dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 3648–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, G.; Jin, J.; Bao, Z.; Qi, W. A Framework to Identify the Uncertainty and Credibility of GCMs for Projected Future Precipitation: A Case Study in the Yellow River Basin, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 863575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Li, L.; Hu, J.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, K. Accuracy validation of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis daily precipitation products in the Lancang River Basin of China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 112, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lei, Y. Multiscale Flood Disaster Risk Assessment in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin: A Focus on Watershed and Community Levels. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission. Assessment of Basin-Wide Development Scenarios-Main Report; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Shu, Z.; Guan, T.; Wang, G.; Jin, J.; Bao, Z.; Liu, C. Deterministic and probabilistic projections and their credibility in analyzing future precipitation variations in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2022, 13, 1806–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Number | Model (Abbreviation) | Resolution (lon × lat) | Country or Institution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ACCESS-CM2 (ACC) | 1.875° × 1.25° | Australia |
| 2 | ACCESS-ESM1-5 (ACE) | 1.875° × 1.25° | Australia |
| 3 | CanESM5 (Can) | 2.8125° × 2.8125° | Canada |
| 4 | CMCC-ESM2 (CMC) | 1.25° × 0.9375° | Italy |
| 5 | EC-Earth3 (EC) | 0.703125° × 0.679245° | European Union |
| 6 | EC-Earth3-Veg (ECV) | 0.703125° × 0.679245° | European Union |
| 7 | EC-Earth3-Veg-LR (ECL) | 1.125° × 1.125° | European Union |
| 8 | FGOALS-g3 (FGO) | 2° × 2.25° | China |
| 9 | GFDL-ESM4 (GFD) | 1.25° × 1° | the United States |
| 10 | INM-CM4-8 (INM4) | 2° × 1.5° | Russia |
| 11 | INM-CM5-0 (INM5) | 2° × 1.5° | Russia |
| 12 | IPSL-CM6A-LR (IPS) | 2.5° ×1.25° | France |
| 13 | MIROC6 (MIR) | 1.40625° × 1.40625° | Japan |
| 14 | MPI-ESM1-2-HR (MPH) | 0.9375° × 0.9375° | Germany |
| 15 | MPI-ESM1-2-LR (MPL) | 1.875° × 1.875° | Germany |
| 16 | MRI-ESM2-0 (MRI) | 1.125° × 1.125° | Japan |
| 17 | NorESM2-LM (NoL) | 2.5° × 1.89474° | Norway |
| 18 | NorESM2-MM (NoM) | 1.25° × 0.9375° | Norway |
| 19 | TaiESM1 (Tai) | 1.25° × 0.9375° | China |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, G.; Tang, L. Spatiotemporal Projections of Precipitation in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin Based on CMIP6 Models. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184502
Sun Z, Liu Y, Zhang J, Chen H, Jin J, Liu C, Wang G, Tang L. Spatiotemporal Projections of Precipitation in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin Based on CMIP6 Models. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(18):4502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184502
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhouliang, Yanli Liu, Jianyun Zhang, Hua Chen, Junliang Jin, Cuishan Liu, Guoqing Wang, and Liushan Tang. 2023. "Spatiotemporal Projections of Precipitation in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin Based on CMIP6 Models" Remote Sensing 15, no. 18: 4502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184502
APA StyleSun, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, J., Chen, H., Jin, J., Liu, C., Wang, G., & Tang, L. (2023). Spatiotemporal Projections of Precipitation in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin Based on CMIP6 Models. Remote Sensing, 15(18), 4502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184502








