Nocturnal Boundary Layer Height Uncertainty in Particulate Matter Simulations during the KORUS-AQ Campaign
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Model, Domain, Configurations, and Emissions
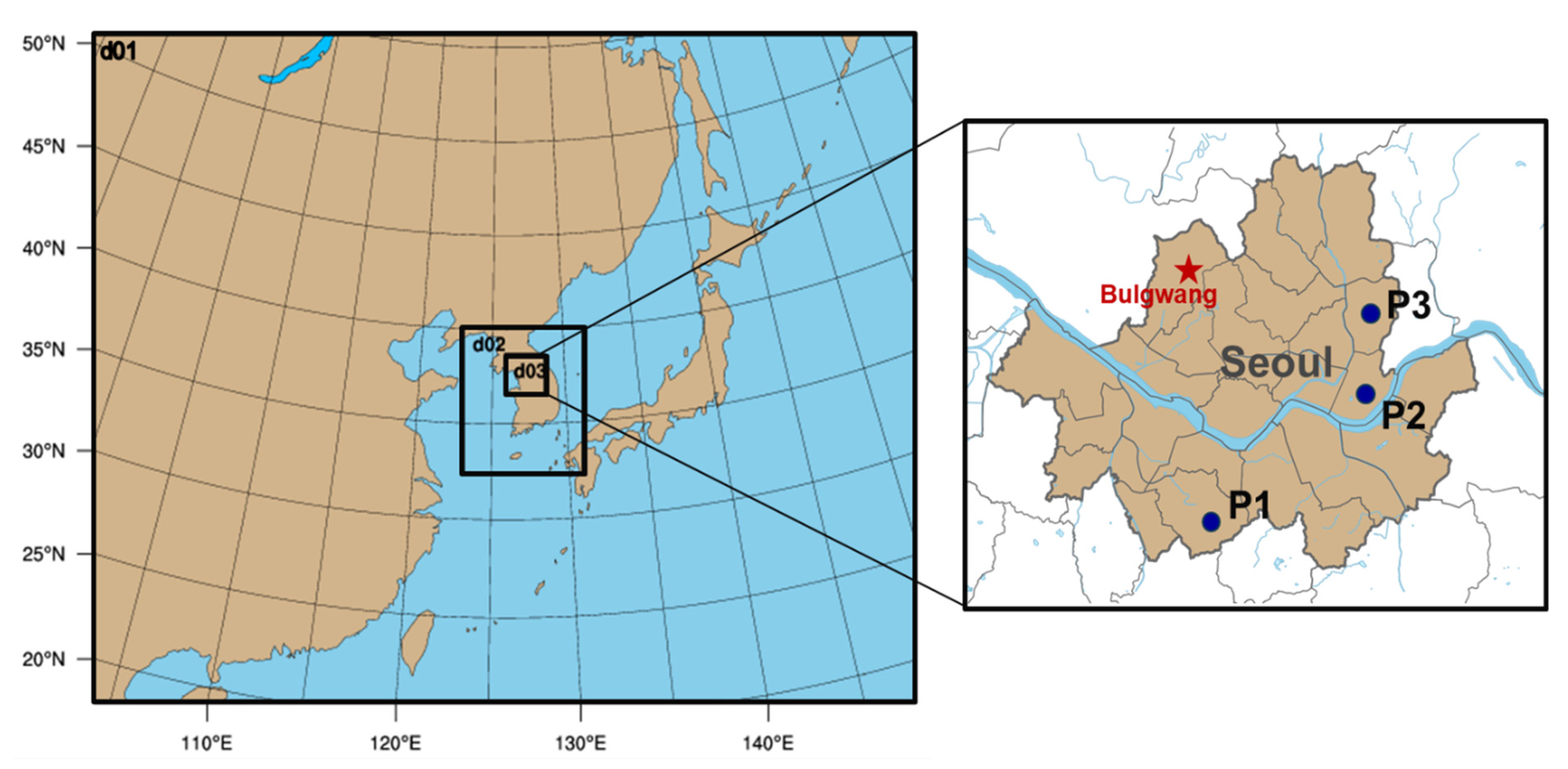
2.2. PBLH and Ground PM2.5 Measurements during the KORUS-AQ Campaign
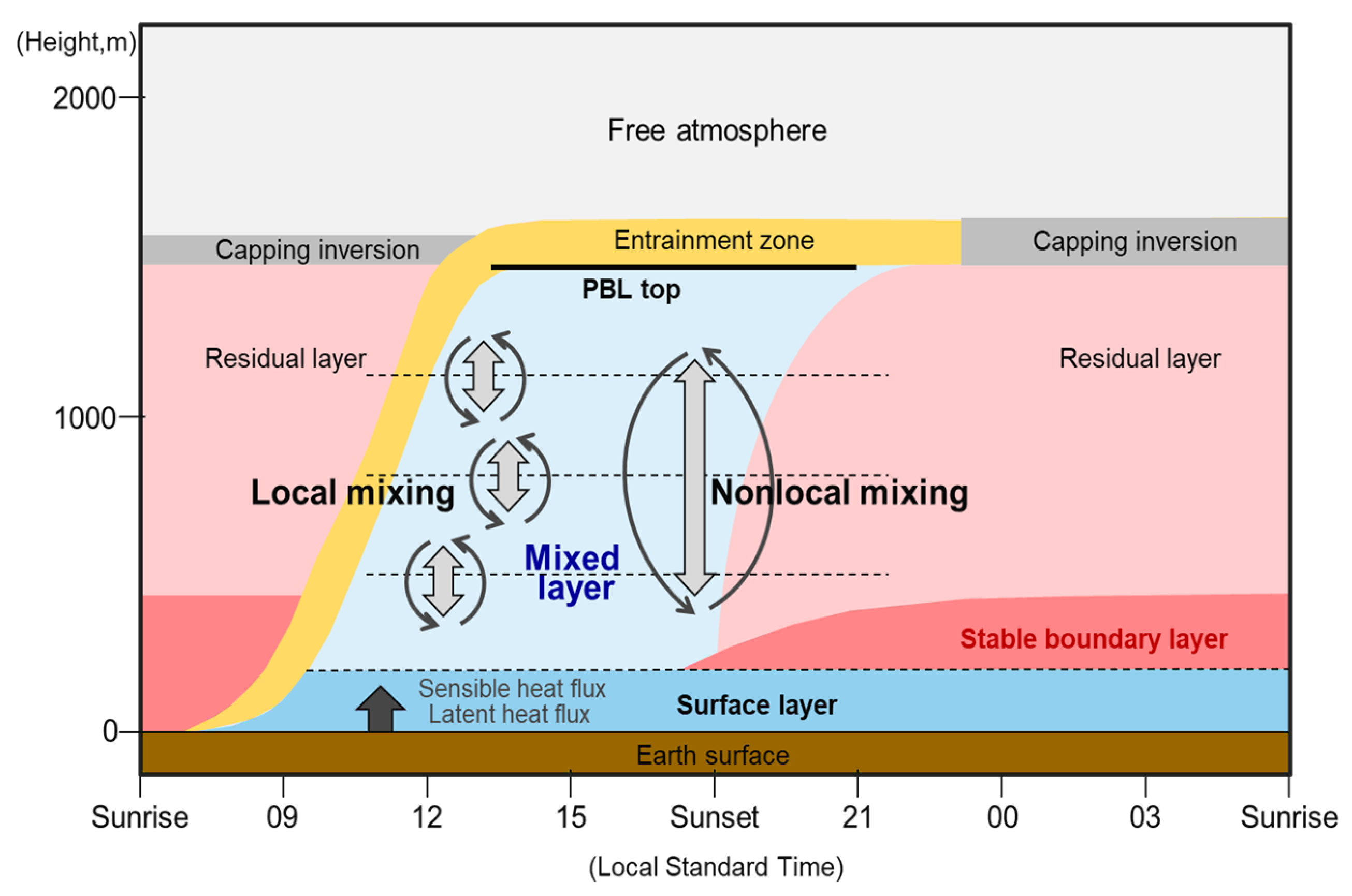
2.3. PBL Parameterizations and Sensitivity Experiment Setup
3. Results
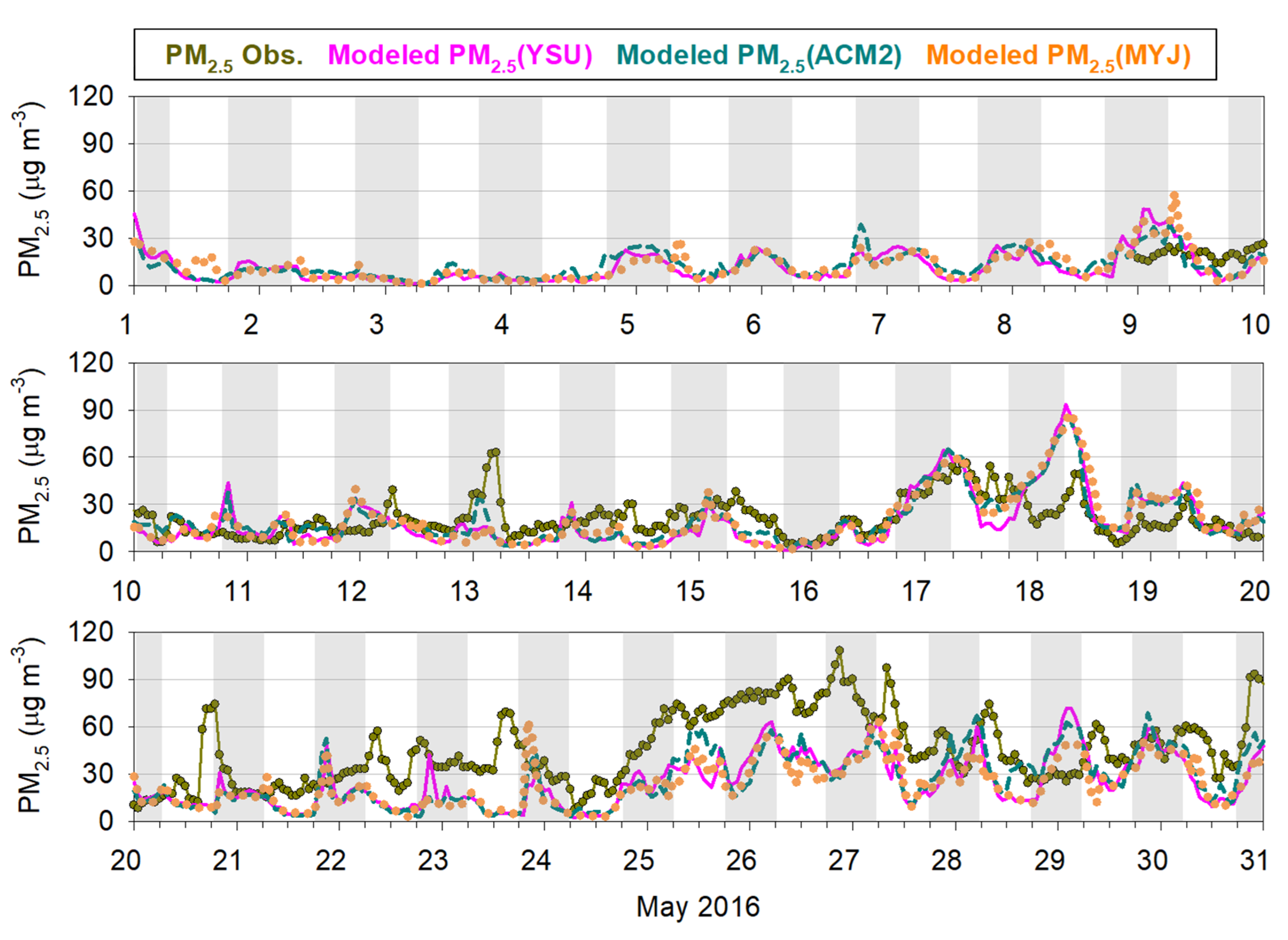
3.1. Comparison of PM2.5 Simulation Results with Observations
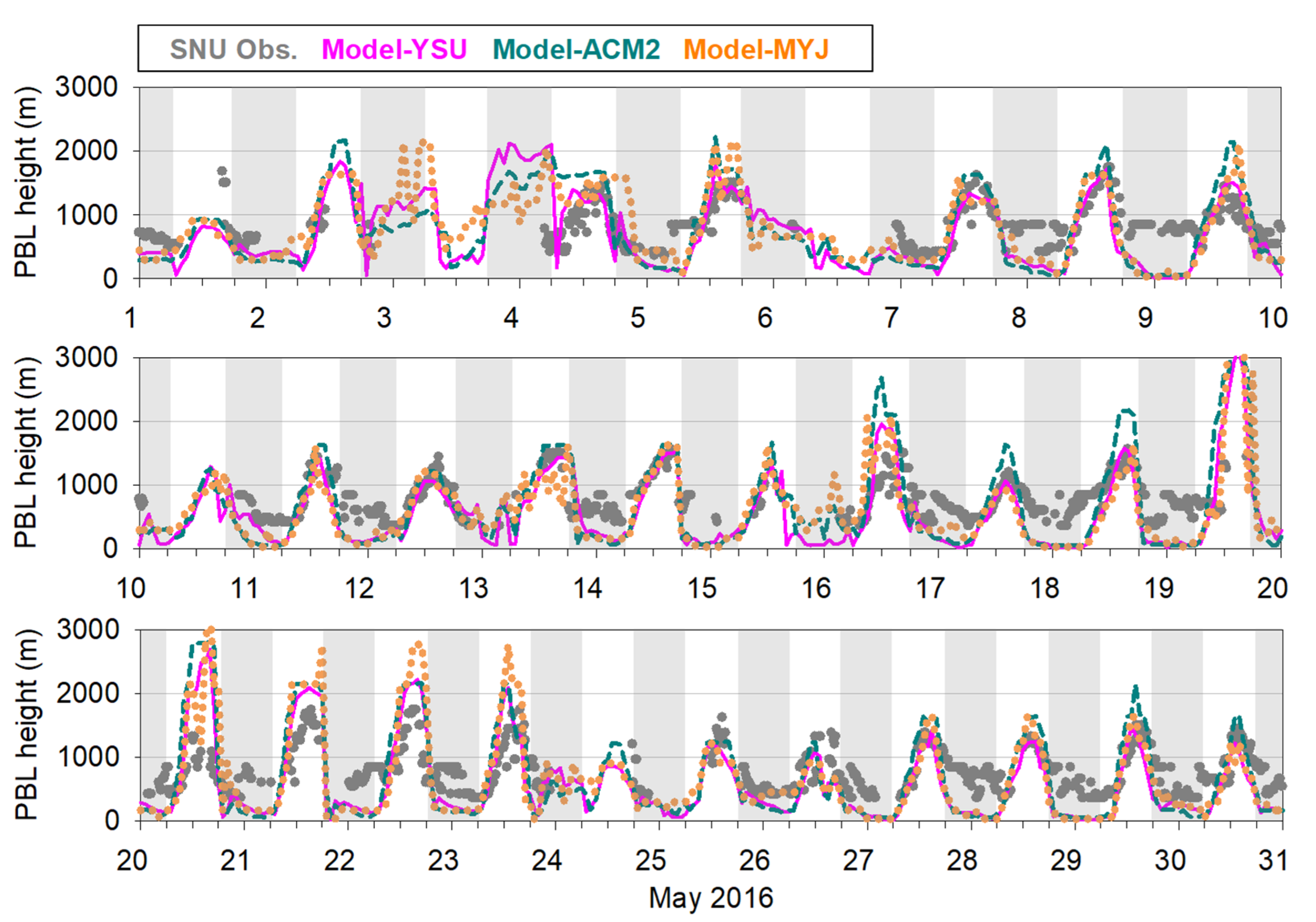
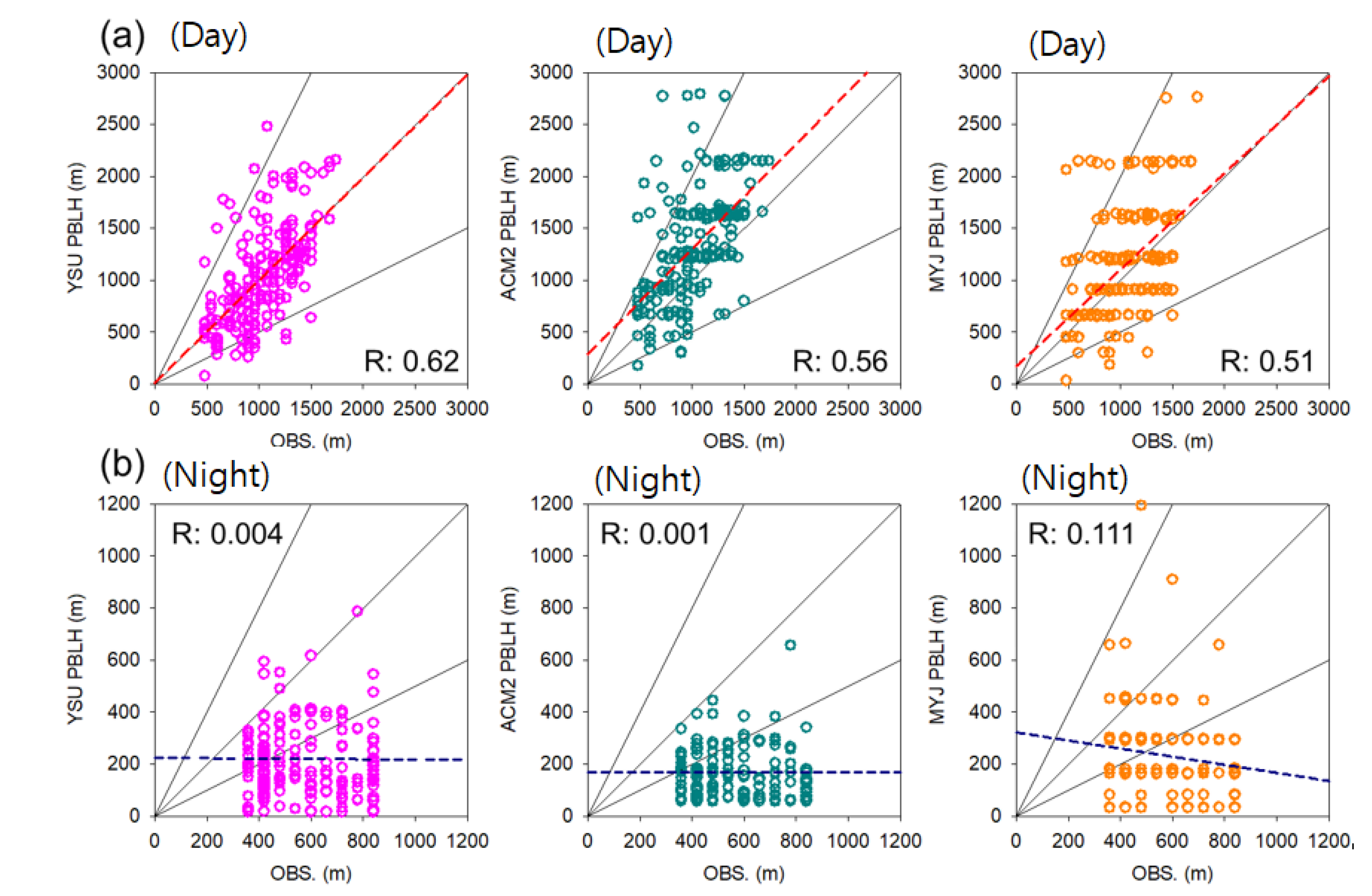
3.2. Comparison of PBLH Simulated Results with Observations
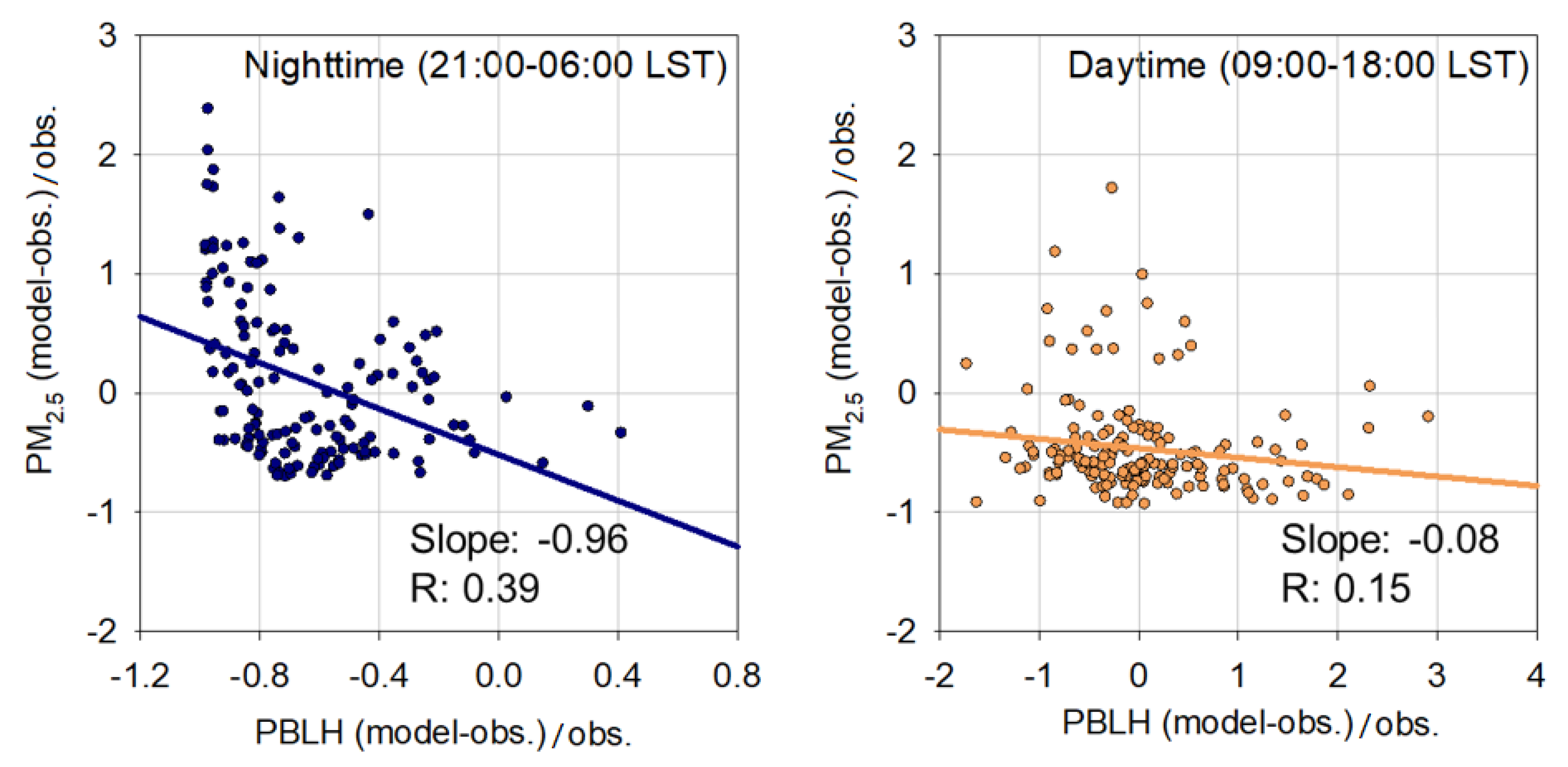
3.3. Uncertainties in Nocturnal PBLH Simulations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marcazzan, G.M.; Vaccaro, S.; Valli, G.; Vecchi, R. Characterisation of PM10 and PM2.5 particulate matter in the ambient air of Milan (Italy). Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4639–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuzzi, S.; Baltensperger, U.; Carslaw, K.; Decesari, S.; Denier van der Gon, H.; Facchini, M.C.; Fowler, D.; Koren, I.; Langford, B.; Lohmann, U.; et al. Particulate matter, air quality and climate: Lessons learned and future needs. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8217–8299. [Google Scholar]
- Chiashi, A.; Lee, S.; Pollitt, H.; Chewpreecha, U.; Vercoulen, P.; He, Y.; Xu, B. Transboundary PM Air Pollution and Its Impact on Health in East Asia. In Energy, Environmental and Economic Sustainability in East Asia: Policies and Institutional Reforms; Lee, S., Pollitt, H., Fujikawa, K., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, M. Transboundary Air Pollution in Northeast Asia: The Political Economy of Yellow Dust, Particulate Matter, and PM2.5. In KEI Academic Paper Series; Korea Economic Institute of America: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- McConnell, R.; Berhane, K.; Gilliland, F.; Molitor, J.; Thomas, D.; Lurmann, F. Prospective study of air pollution and bronchitic symptoms in children with asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, M.; Ichinose, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Arashidani, K.; Yoshida, S.; Takano, H.; Sun, G.; Shibamoto, T. Urban PM2.5 exacerbates allergic inflammation in the murine lung via a TLR2/TLR4/MyD88-signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, M.C.; Cohen, A.; Burnett, R.T.; Jerrett, M.; Diver, W.R.; Gapstur, S.M.; Krewski, D.; Samet, J.M.; Pope, C.A. Interactions between cigarette smoking and ambient PM2.5 for cardiovascular mortality. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, S.; Chen, D.; Guo, X.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Xing, X.; Wang, H. Trends of PM2.5 and chemical composition in Beijing, 2000~2015. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, Y.-H.; You, S.; Bae, M.; Kim, E.; Son, K.; Bae, C.; Kim, Y.; Kim, B.-U.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, S. The impacts of COVID-19, meteorology, and emission control policies on PM2.5 drops in Northeast Asia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Li, J.; Miao, S.; Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, R.; Liu, S. Interaction between Planetary Boundary Layer and PM2.5 Pollution in Megacities in China: A Review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2019, 5, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, R.K.; Wu, W.S.; Wang, T. Summertime PM2.5 ionic species in four major cities of China: Nitrate formation in an ammonia-deficient atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.S.; Ryerson, T.B.; Wollny, A.G.; Brock, C.A.; Peltier, R.; Sullivan, A.P.; Weber, R.J.; Dube, W.P.; Trainer, M.; Meagher, J.F.; et al. Variability in nocturnal nitrogen oxide processing and its role in regional air quality. Science 2006, 311, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.-Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Jo, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-J.; Ban, S.; Lee, J.-J.; Chang, L.-S.; Heo, G.; Kim, C.-H. Nocturnal fine particulate nitrate formation by N2O5 heterogeneous chemistry in Seoul Metropolitan Area, Korea. Atmos. Res. 2019, 225, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.-Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Jo, Y.-J.; Heo, G.; Lee, M.; Kim, J.-A.; Park, M.-S.; Lee, T.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, Y.-H.; et al. A case study of heavy PM2.5 secondary formation by N2O5 nocturnal chemistry in Seoul, Korea in January 2018: Model performance and error analysis. Atmos. Res. 2022, 266, 105951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeneveld, G.J.; Mauritsen, T.; DeBruijn, E.I.F.; De Arellano, J.V.G.; Svensson, G.; Holtslag, A.A.M. Evaluation of limited-area models for the representation of the diurnal cycle and contrasting nights in CASES-99. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 869–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storm, B.; Dudhia, J.; Basu, S.; Swift, A.; Giammanco, I. Evaluation of the Weather Research and Forecasting model on forecasting low-level jets: Implications for wind energy. Wind Energy 2009, 12, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-M.; Doughty, D.C.; Sanchez, K.J.; Joseph, E.; Fuentes, J.D. Ozone variability in the atmospheric boundary layer in Maryland and its implications for vertical transport model. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Diez, M.; Fernández, J.; Fitaand, L.; Yague, C. Seasonal dependence of WRF model biases and sensitivity to PBL schemes over Europe. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 139, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boadh, R.; Satyanarayana, A.N.V.; Rama Krishna, T.V.B.P.S.; Madala, S. Sensitivity of PBL schemes of the WRF-ARW model in simulating the boundary layer flow parameters for their application to air pollution dispersion modeling over a tropical station. Atmósfera 2016, 29, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Du, A.; Lei, L.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Tang, G.; Song, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Vertically Resolved Aerosol Chemistry in the Low Boundary Layer of Beijing in Summer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 9312–9324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.H.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Al-Saadi, J.; Chang, L.; Emmons, L.K.; Kim, J.; Lee, G.; Park, J.-H.; Park, R.J.; Woo, J.H.; et al. The Korea–United States Air Quality (KORUS-AQ) field study. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2021, 9, 00163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Kang, J.-E.; Jo, H.-Y.; Park, S.-Y.; Jo, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-J.; Yang, G.-H.; Park, T.; Lee, T. Meteorological Overview and Signatures of Long-range Transport Processes during the MAPS-Seoul 2015 Campaign. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2173–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, R.J.; Oak, Y.J.; Emmons, L.K.; Kim, C.-H.; Pfister, G.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; Saide, P.E.; Cho, S.-Y.; Kim, S.; Woo, J.-H.; et al. Multi-model intercomparisons of air quality simulations for the KORUS-AQ campaign. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2021, 9, 00139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, J.; Ohara, T.; Morikawa, T.; Hanayama, S.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Fukui, T.; Kawashima, K.; Akimoto, H. Emissions of air pollutants and greenhouse gases over Asian regions during 2000–2008: Regional Emission inventory in ASia (REAS) version 2. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 11019–11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.-G.; Lee, Y.-M.; Jang, K.-W.; Yoo, C.; Kang, K.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Jung, S.-W.; Park, J.-M.; Lee, S.-B.; Han, J.-S.; et al. Korean National Emissions Inventory System and 2007 Air Pollutant Emissions. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 5, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, J.-H.; Choi, K.-C.; Kim, H.K.; Baek, B.H.; Jang, M.; Eum, J.-H.; Song, C.H.; Ma, Y.-L.; Sunwoo, Y.; Chang, L.-S.; et al. Development of an anthropogenic emissions processing system for Asia using SMOKE. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 58, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.-H.; Jo, Y.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Song, C.-K.; Kim, C.-H. Numerical Sensitivity Tests of Volatile Organic Compounds Emission to PM2.5 Formation during Heat Wave Period in 2018 in Two Southeast Korean Cities. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.-J.; Jo, H.-Y.; Song, C.-K.; Jo, Y.-J.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, C.-H. Sensitivity of Simulated PM2.5 Concentrations over Northeast Asia to Different Secondary Organic Aerosol Modules during the KORUS-AQ Campaign. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Jo, H.-Y.; Park, S.-Y.; Jo, Y.-J.; Jeon, W.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Kim, C.-H. A Case Study of the Transport/Transformation of Air Pollutants Over the Yellow Sea During the MAPS 2015 Campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 6532–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, J.T.; Leard, D.C.; Zhang, X.; Davidovits, P.; Smith, K.A.; Kolb, C.E.; Worsnop, D.R. Development of an Aerosol Mass Spectrometer for Size and Composition Analysis of Submicron Particles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2000, 33, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jimenez, J.L.; Jayne, J.T.; Shi, Q.; Kolb, C.E.; Worsnop, D.R.; Yourshaw, I.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Flagan, R.C.; Zhang, X.; Smith, K.A.; et al. Ambient aerosol sampling using the Aerodyne Aerosol Mass Spectrometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 8425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drewnick, F.; Hings, S.S.; DeCarlo, P.; Jayne, J.T.; Gonin, M.; Fuhrer, K.; Weimer, S.; Jimenez, J.L.; Demerjian, K.L.; Borrmann, S.; et al. A New Time-of-Flight Aerosol Mass Spectrometer (TOF-AMS)—Instrument Description and First Field Deployment. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCarlo, P.F.; Kimmel, J.R.; Trimborn, A.; Northway, M.J.; Jayne, J.T.; Aiken, A.C.; Gonin, M.; Fuhrer, K.; Horvath, T.; Docherty, K.S.; et al. Field-Deployable, High-Resolution, Time-of-Flight Aerosol Mass Spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 8281–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canagaratna, M.R.; Jayne, J.T.; Jimenez, J.L.; Allan, J.D.; Alfarra, M.R.; Zhang, Q.; Onasch, T.B.; Drewnick, F.; Coe, H.; Middlebrook, A.; et al. Chemical and microphysical characterization of ambient aerosols with the aerodyne aerosol mass spectrometer. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2007, 26, 185–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, I.M. Finding Boundary Layer Top: Application of a Wavelet Covariance Transform to Lidar Backscatter Profiles. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo, V.; Rappenglück, B.; Lefer, B.; Morris, G.; Toledo, D.; Delgado, R. Comparison of aerosol lidar retrieval methods for boundary layer height detection using ceilometer aerosol backscatter data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, M.-S.; Song, C.-K. Measurements of planetary boundary layer winds with scanning Doppler lidar. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tucker, S.C.; Brewer, W.A.; Banta, R.M.; Senff, C.J.; Sandberg, S.P.; Law, D.C.; Weickmann, A.M.; Hardesty, R.M. Doppler lidar estimation of mixing height using turbulence, shear, and aerosol profiles. J. Atmos. Oceanic Tech. 2009, 26, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C. Doppler Wind Lidar. In Lidar: Range-Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere; Weitkamp, C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 325–354. ISBN 978-0-387-25101-1. [Google Scholar]
- Schween, J.H.; Hirsikko, A.; Lohnert, U.; Crewell, S. Mixing-layer height retrieval with ceilometer and Doppler lidar: From case studies to long-term assessment. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 3685–3704. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.-H.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, M.-H.; Yeo, H.; Park, S.S.; Nishizawa, T.; Shimizu, A.; Kim, C.-H. Impacts of local versus long-range transported aerosols on PM10 concentrations in Seoul, Korea: An estimate based on 11-year PM10 and lidar observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, M.-H.; Yeo, H.; Shim, K.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, C.-H.; Song, C.-K.; Park, M.-S.; Shimizu, A.; Nishizawa, T.; et al. Determination of mixing layer height from co-located lidar, ceilometer and wind Doppler lidar measurements: Intercomparison and implications for PM2.5 simulations. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Lim, J.-O.; Dudhia, J. The WRF single–moment 6–class microphysics scheme (WSM6). J. Korean Meteor. Soc. 2006, 42, 129–151. [Google Scholar]
- Ahasan, M.N.; Chowdhury, M.A.M.; Quadir, D.A. Sensitivity Test of Parameterization Schemes of MM5 Model for Prediction of the High Impact Rainfall Events over Bangladesh. J. Mech. Eng. 2014, 44, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emery, C.; Liu, Z.; Russell, A.G.; Odman, M.T.; Yarwood, G.; Kumar, N. Recommendations on statistics and benchmarks to assess photochemical model performance. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.-W.; Lee, J.-H.; Woo, J.-W.; Kim, C.-H.; Lee, S.-H. Comparison of PM2.5 Chemical Components over East Asia Simulated by the WRF-Chem and WRF/CMAQ Models: On the Models’ Prediction Inconsistency. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.Y.; Kim, C.H. Bias Analysis of WRF-CMAQ Simulated PM2.5 Concentration Caused by Different PBL Parameterizations: Application to the Haze period of March in 2019 over the Seoul Metropolitan Area. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 37, 835–852, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Jo, H.-Y.; Woo, J.-H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, T.; Heo, G.; Park, S.-M.; Jung, D.; Park, J. Changes in inorganic aerosol compositions over the Yellow Sea area from impact of Chinese emissions mitigation. Atmos. Res. 2020, 240, 104948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Jo, H.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Park, M.S.; Kim, C.H. Impacts of Atmospheric Vertical Structures on Transboundary Aerosol Transport from China to South Korea. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.G.; Roberts, P.T.; McCarthy, M.C.; Lurmann, F.W. Wintertime vertical variations in particulate matter (PM) and precursor concentrations in the San Joaquin valley during the California regional coarse PM/Fine PM air quality study. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 2006, 56, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prabhakar, G.; Parworth, C.L.; Zhang, X.; Kim, H.; Young, D.E.; Beyersdorf, A.J.; Ziemba, L.D.; Nowak, J.B.; Bertram, T.H.; Faloona, I.C.; et al. Observational assessment of the role of nocturnal residual-layer chemistry in determining daytime surface particulate nitrate concentrations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 14747–14770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Physics Option | Adopted Scheme |
| Microphysics | Lin et al. scheme |
| Longwave radiation | Rapid radiative transfer model (RRTM) |
| Shortwave radiation | Goddard |
| Surface layer | Monin–Obukhov similarity |
| Land surface | Noah Land Surface Model |
| Planetary boundary layer | Yonsei University scheme (YSU)/Mellor-Yamada-Janjic (MYJ)/Asymmetric Convective Model, version 2 (ACM2) |
| Cumulus parameterizations | Grell 3-D |
| Chemistry option | Adopted scheme |
| Photolysis | Madronich photolysis (TUV) |
| Gas phase chemistry | NOAA/ESRL Regional Atmospheric Chemistry (RACM) |
| Aerosols | Modal Approach Dynamics model for Europe/Volatility Basis Set (MADE/VBS) |
| Anthropogenic emissions | KORUS v2 |
| Biogenic emissions | Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature (MEGAN) v2.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.-J.; Jo, H.-Y.; Kim, J.-M.; Bak, J.; Park, M.-S.; Kim, J.-K.; Jo, Y.-J.; Kim, C.-H. Nocturnal Boundary Layer Height Uncertainty in Particulate Matter Simulations during the KORUS-AQ Campaign. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020300
Lee H-J, Jo H-Y, Kim J-M, Bak J, Park M-S, Kim J-K, Jo Y-J, Kim C-H. Nocturnal Boundary Layer Height Uncertainty in Particulate Matter Simulations during the KORUS-AQ Campaign. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(2):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020300
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyo-Jung, Hyun-Young Jo, Jong-Min Kim, Juseon Bak, Moon-Soo Park, Jung-Kwon Kim, Yu-Jin Jo, and Cheol-Hee Kim. 2023. "Nocturnal Boundary Layer Height Uncertainty in Particulate Matter Simulations during the KORUS-AQ Campaign" Remote Sensing 15, no. 2: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020300
APA StyleLee, H.-J., Jo, H.-Y., Kim, J.-M., Bak, J., Park, M.-S., Kim, J.-K., Jo, Y.-J., & Kim, C.-H. (2023). Nocturnal Boundary Layer Height Uncertainty in Particulate Matter Simulations during the KORUS-AQ Campaign. Remote Sensing, 15(2), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020300








