Automatic Inspection of Bridge Bolts Using Unmanned Aerial Vision and Adaptive Scale Unification-Based Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
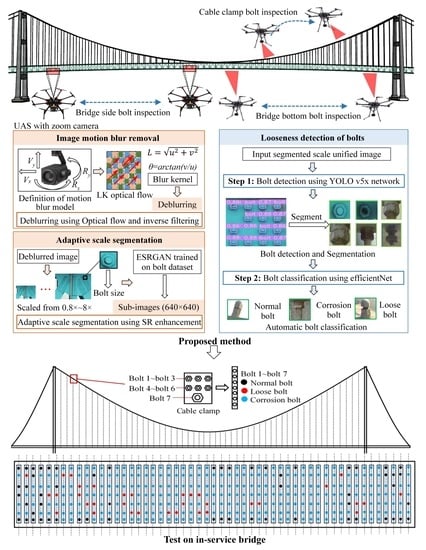
2. Framework of the Proposed Method
3. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
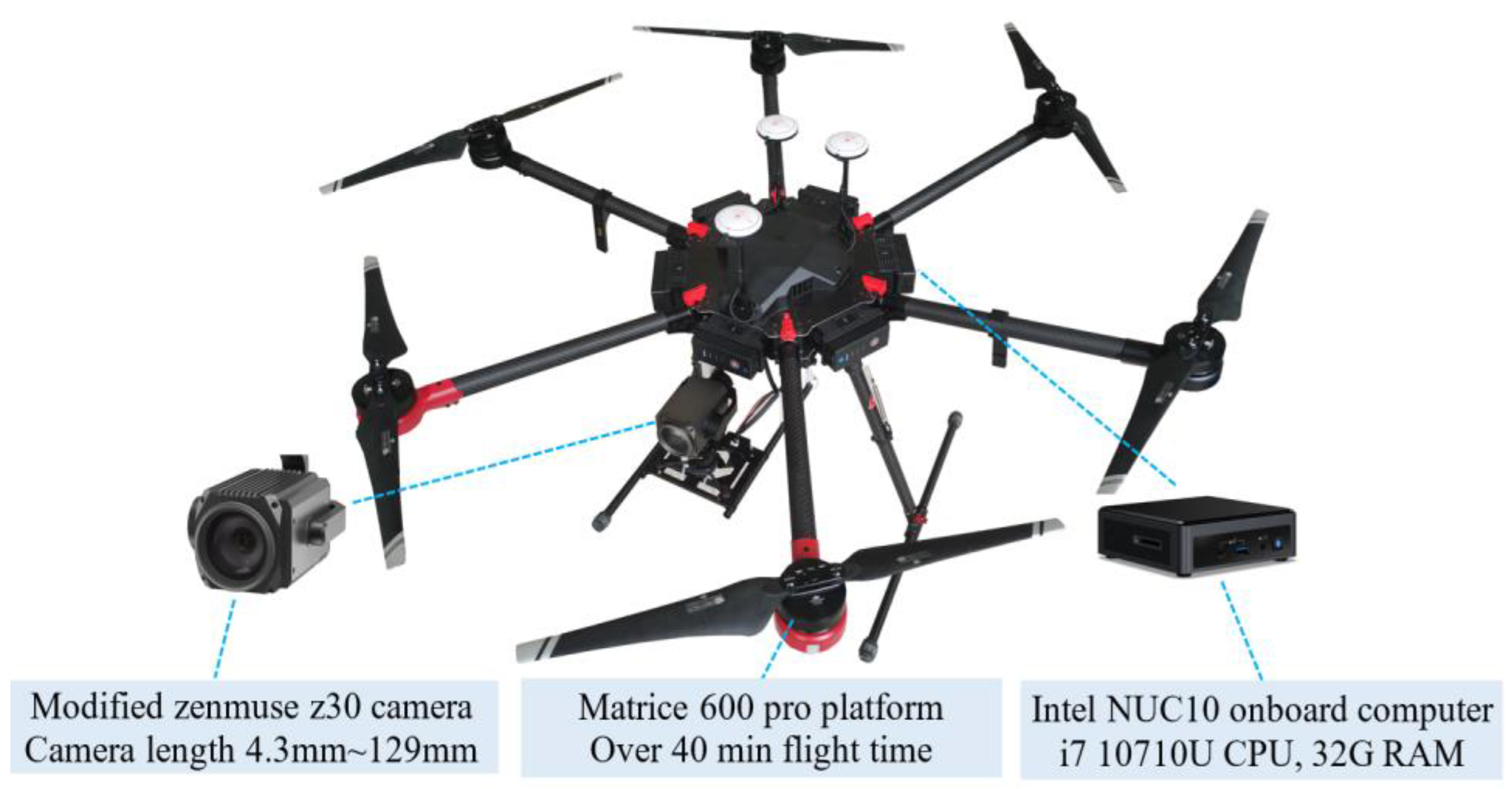
3.1. Design of the UAS
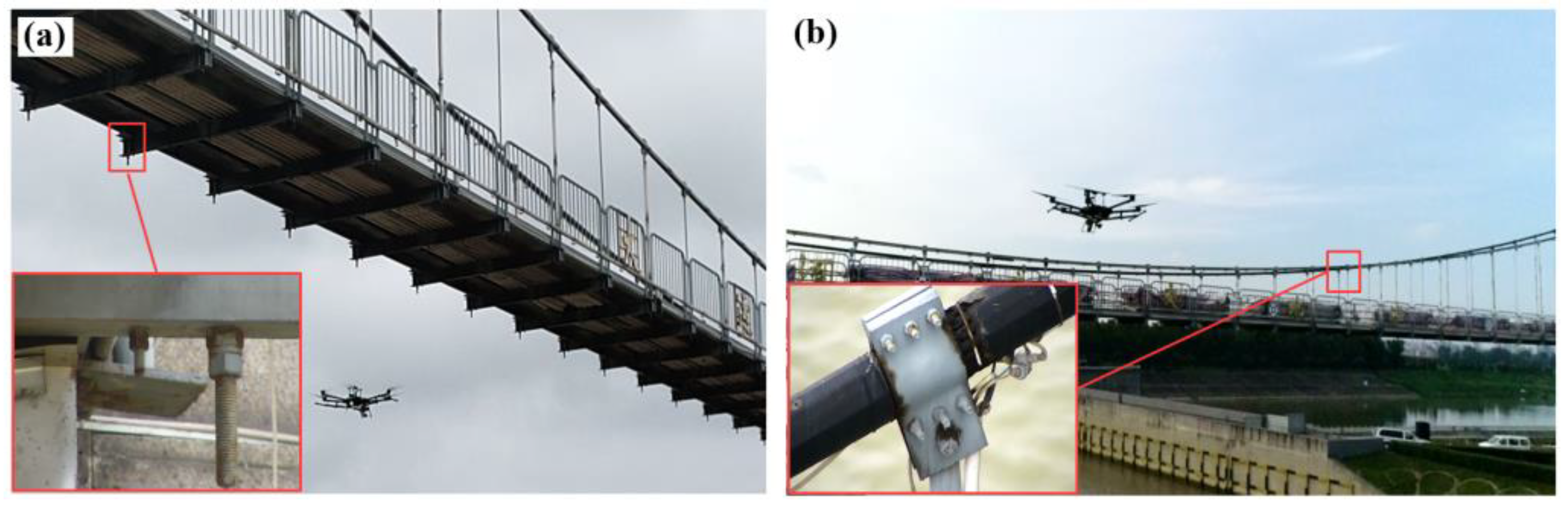
3.2. Strategy for Bridge Bolt Data Acquisition Using UAS
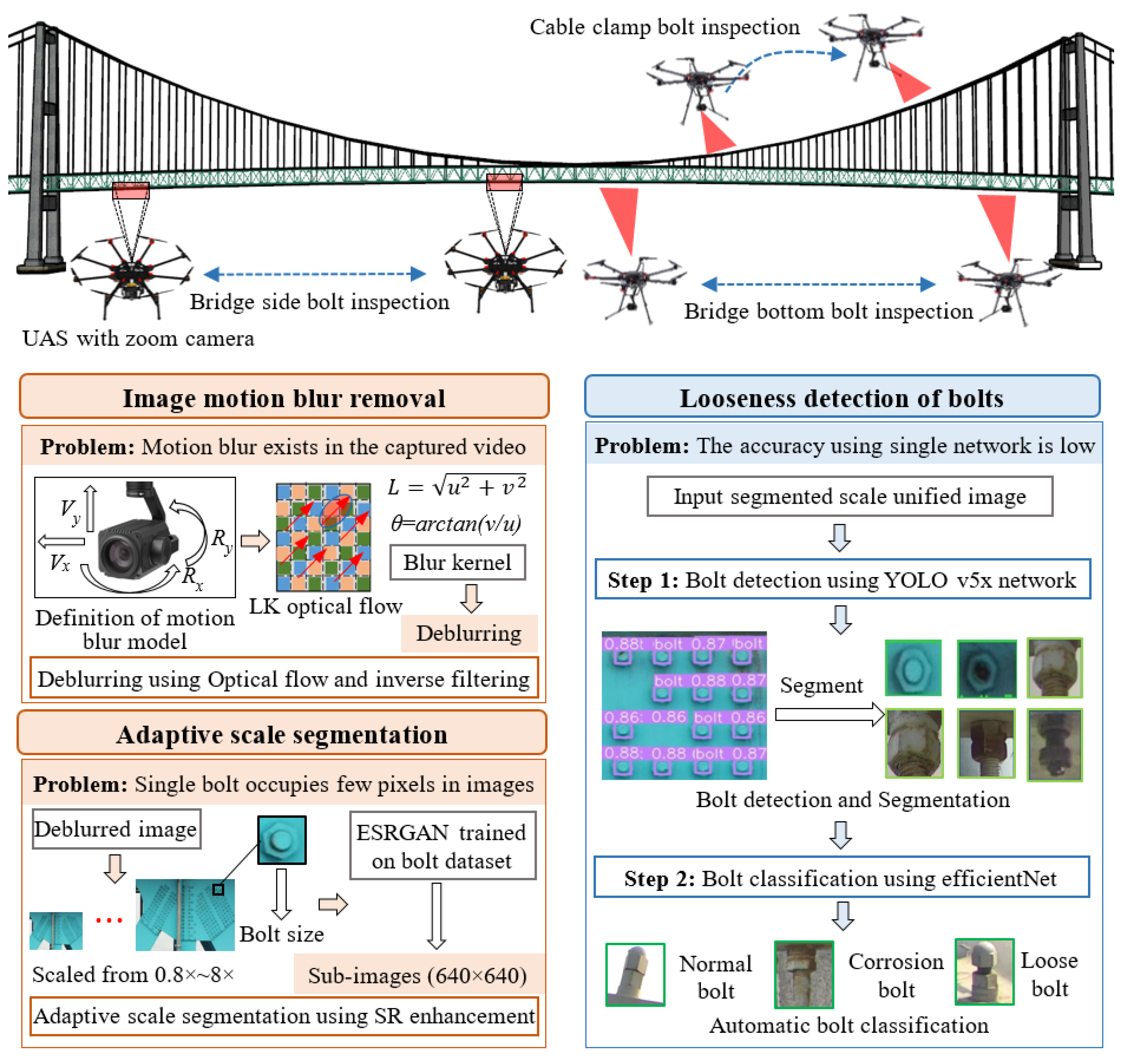
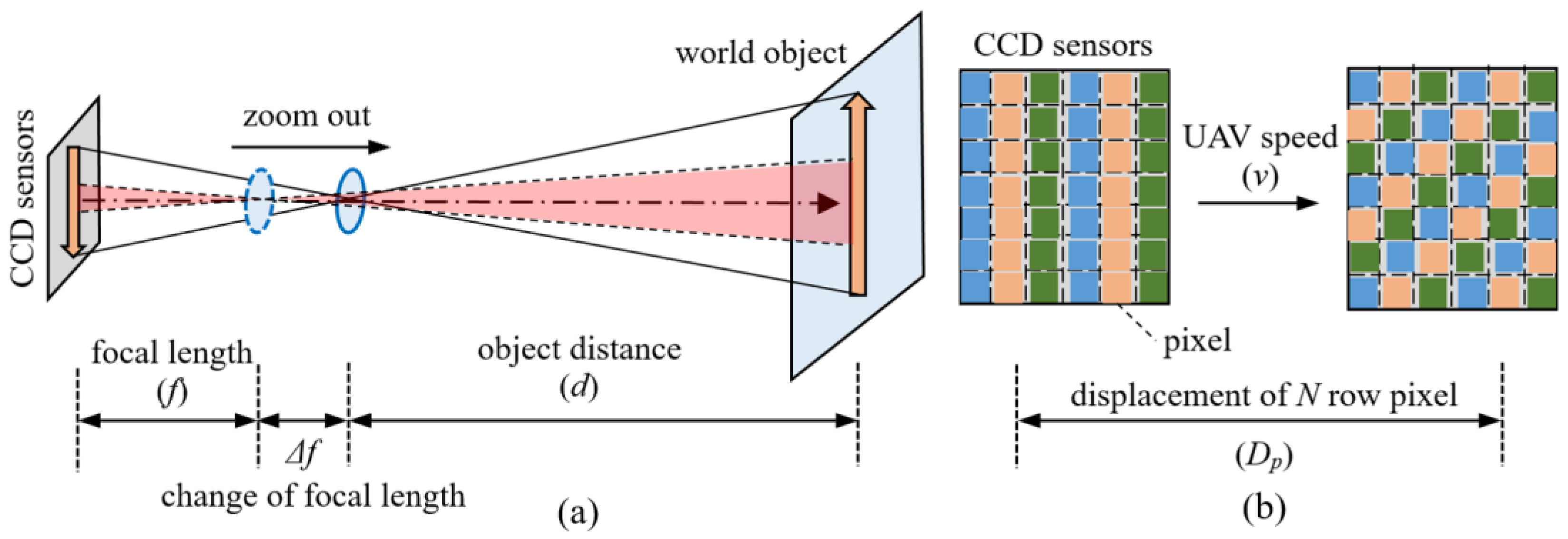
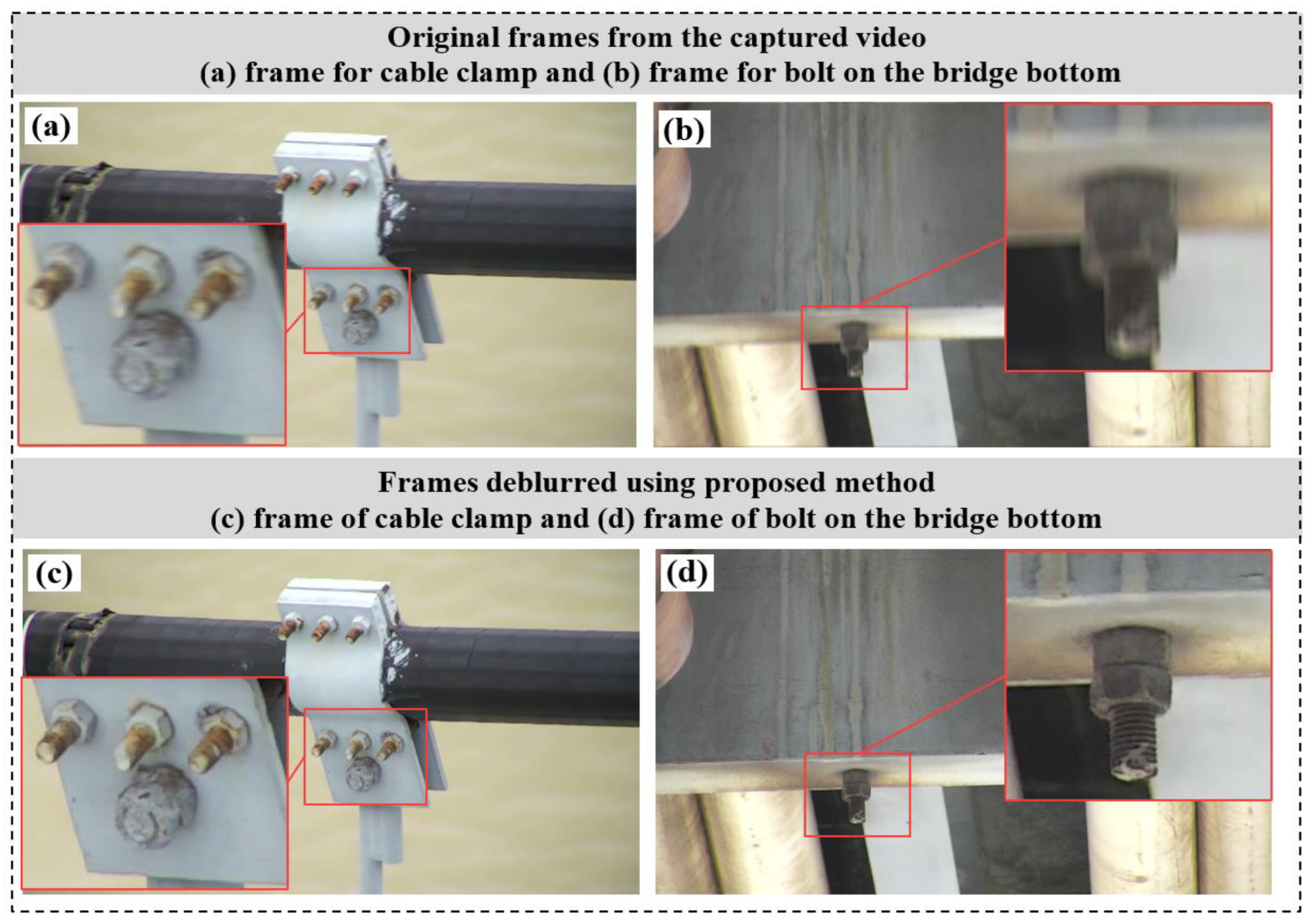
3.3. Zoom Camera Model and Motion Deblurring
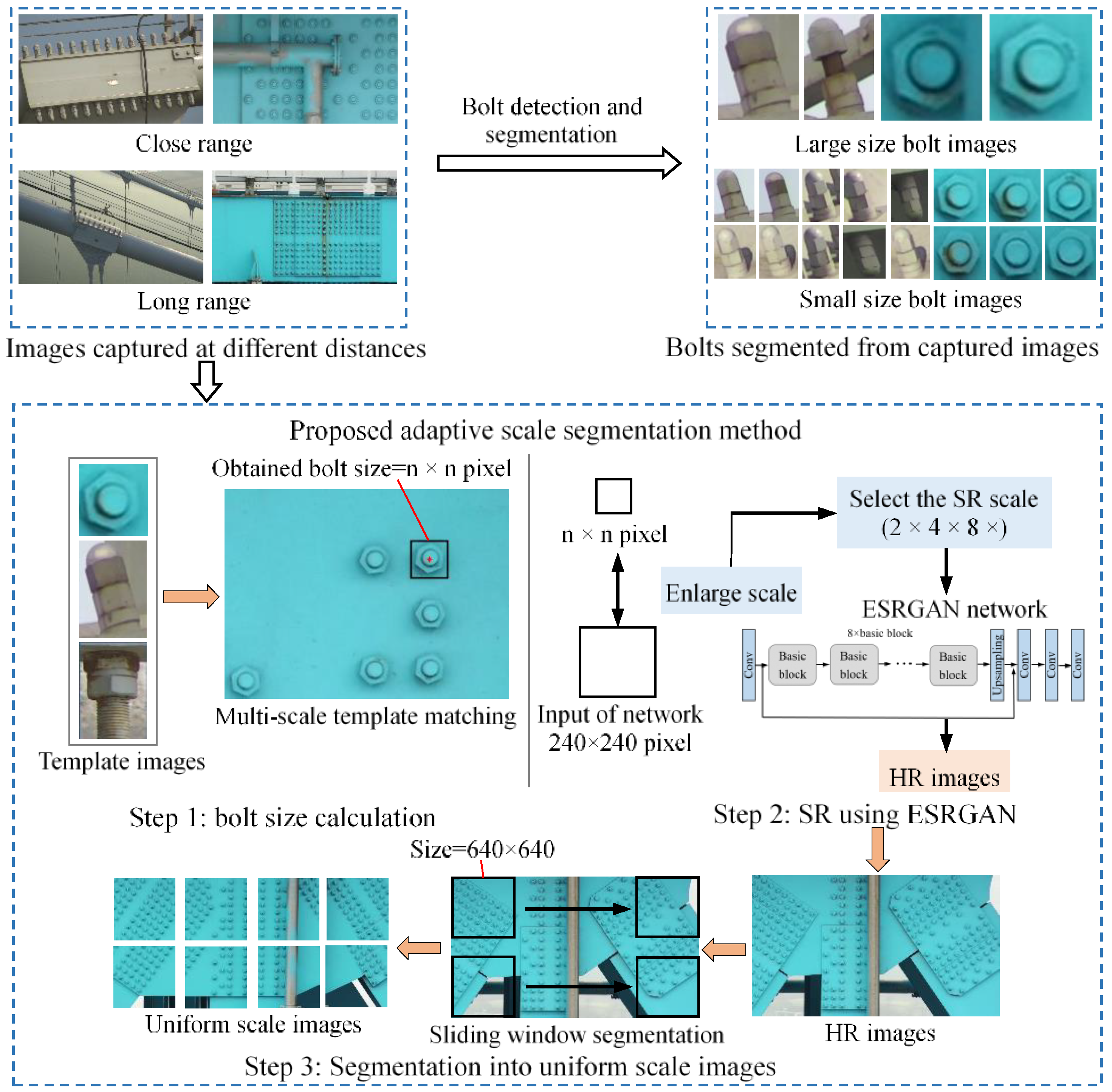
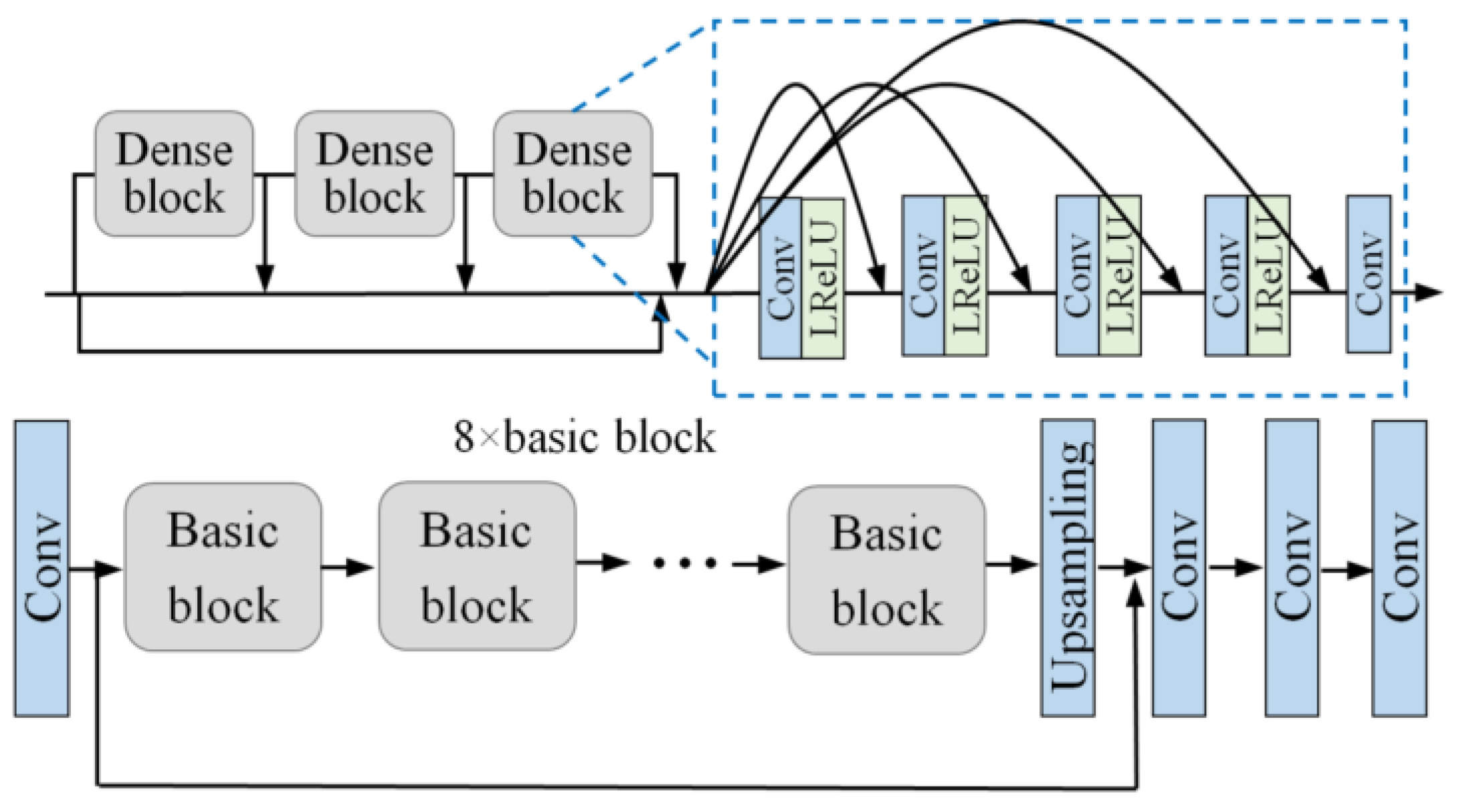
3.4. Adaptive Scale Segmentation Based on ESRGAN
4. Two-Stage Bolt Inspection Based on Deep Learning
4.1. Establishment of Bridge Bolt Dataset
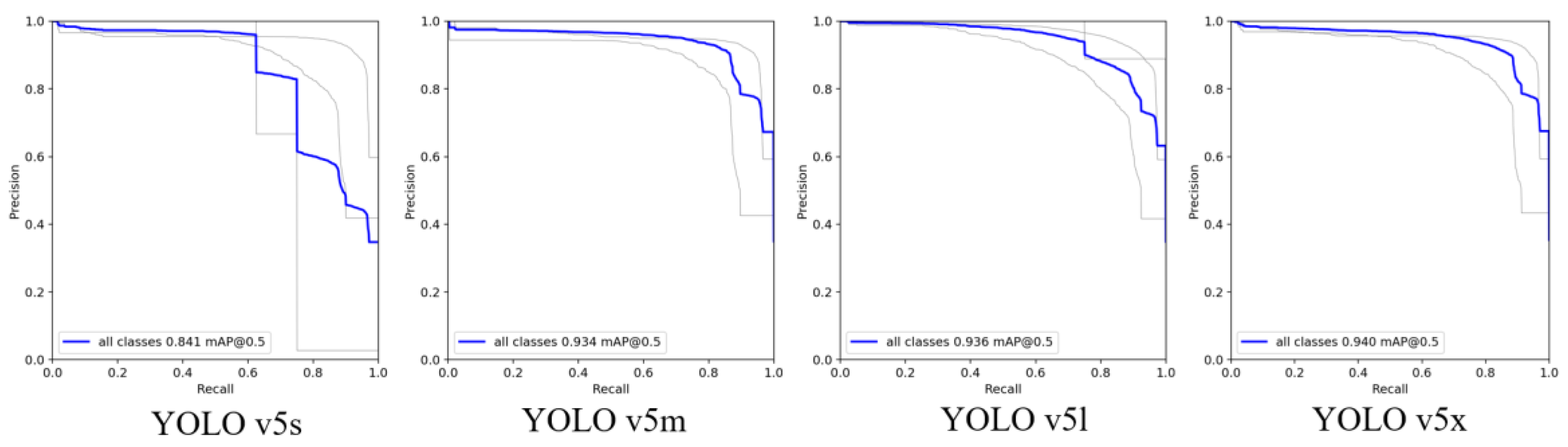
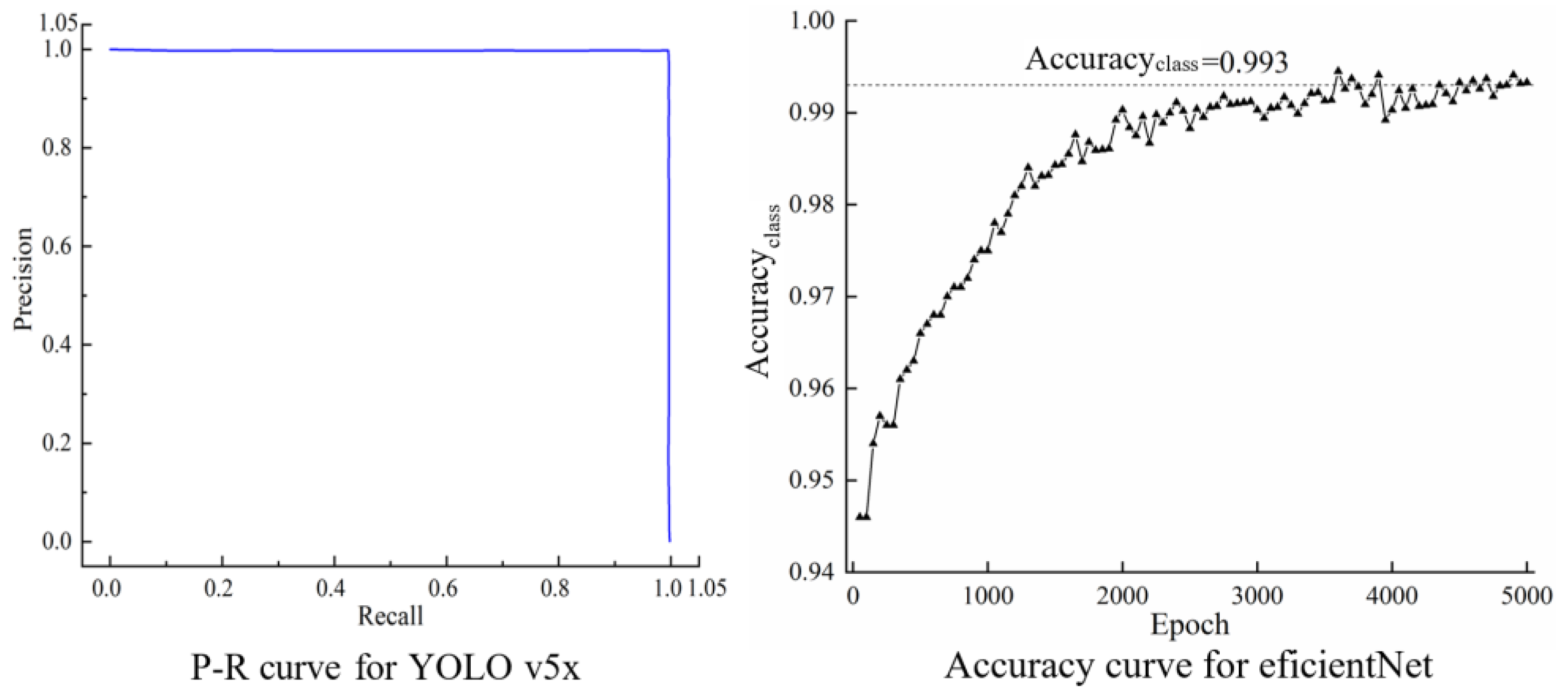
4.2. Test Using a Single Object Detection Network
4.3. Test Using a Two-Stage Inspection Method
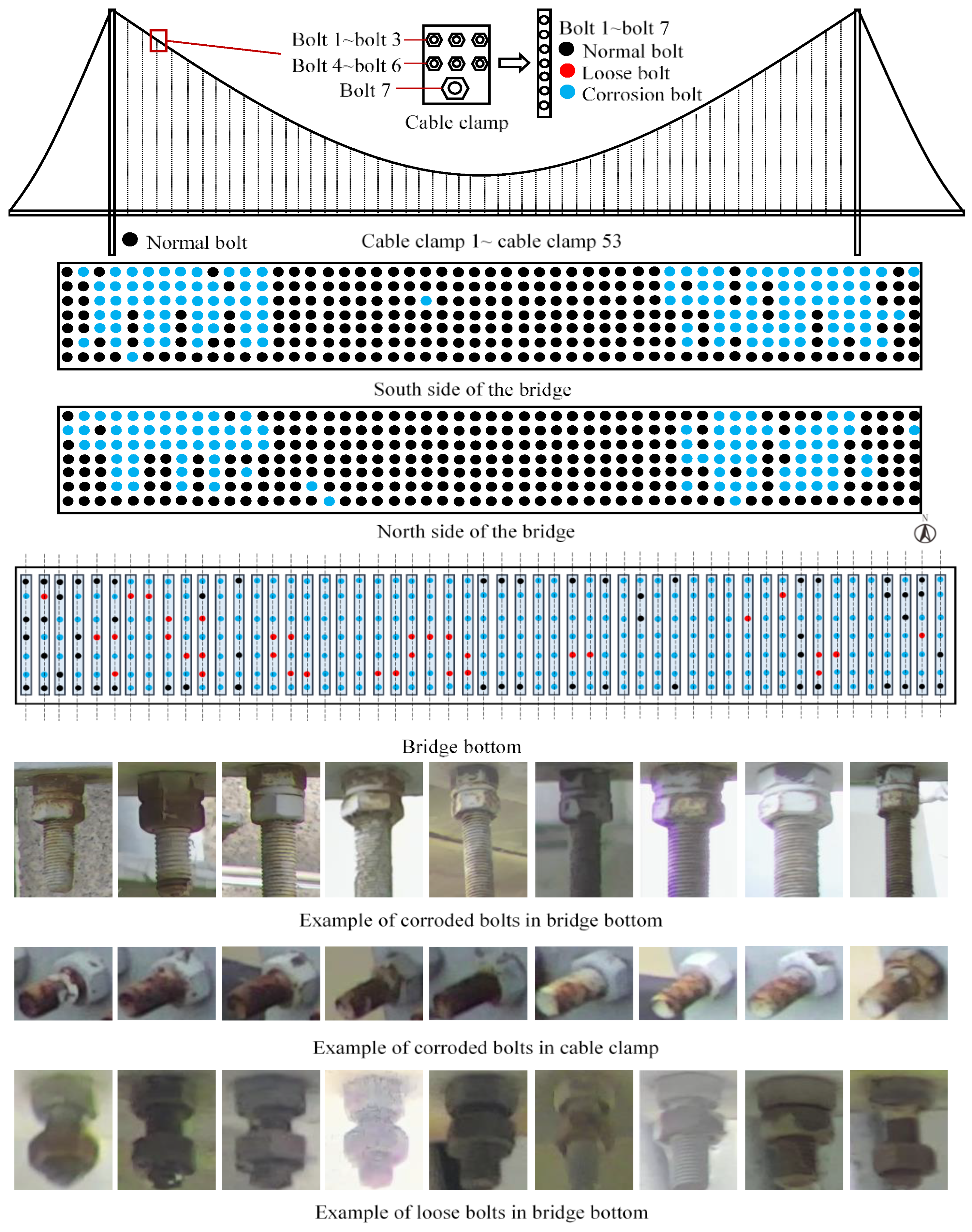
5. Filed Test on a Suspension Bridge
5.1. Establishment of Bridge Bolt Dataset
5.2. Data Preprocessing
5.3. Bolt Inspection Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amerini, F.; Meo, M. Structural health monitoring of bolted joints using linear and nonlinear acoustic/ultrasound methods. Struct. Health Monit. 2010, 10, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, J.; Hamilton, R.; Fischer, W. Acoustic detection of bolt detorquing in structures. In Proceedings of the Meetings on Acoustics 157ASA; Acoustical Society of America: Melville, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 6, p. 065002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Song, G. Bolt early looseness monitoring using modified vibro-acoustic modulation by time-reversal. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 130, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Song, G. Monitoring of multi-bolt connection looseness using entropy-based active sensing and genetic algorithm-based least square support vector machine. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 136, 106507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, T.; Kim, J. Image-based bolt-loosening detection technique of bolt joint in steel bridges. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Advances in Experimental Structural Engineering, University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, Chicago, IL, USA, 1–2 August 2015; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, Y.J.; You, K.; Choi, W. Vision-based detection of loosened bolts using the Hough transform and support vector machines. Autom. Constr. 2016, 71, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, L.; Choi, W.; Cha, Y.J. Fully automated vision-based loosened bolt detection using the Viola-Jones algorithm. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 18, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xie, Y.; Cheng, X. A fast bolt-loosening detection method of running train’s key components based on binocular vision. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 32227–32239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qin, H.; Miao, F. A Multi-Path Encoder Network for GPR Data Inversion to Improve Defect Detection in Reinforced Concrete. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Z.; Guo, H.; Leng, B.; He, Z.; Yang, J.; Xing, S. SegDetector: A Deep Learning Model for Detecting Small and Overlapping Damaged Buildings in Satellite Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, P.; Shahbazi, M.; Nielsen, J. Semantic Segmentation and 3D Reconstruction of Concrete Cracks. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhen, L.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, G. Automated building extraction using satellite remote sensing imagery. Autom. Constr. 2021, 123, 103509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Shen, C. A real-time detection approach for bridge cracks based on YOLOv4-FPM. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.; Aziz, F.; Newaz, M.T.; Sher, W.; Simon, L. The classification of construction waste material using a deep convolutional neural network. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.Z.; Catbas, F.N. A review of computer vision-based structural health monitoring at local and global levels. Struct. Health Monit. 2020, 20, 692–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z. Zernike-moment measurement of thin-crack width in images enabled by dual-scale deep learning. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2019, 34, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z. Pixel-level crack delineation in images with convolutional feature fusion. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N. Bolt loosening angle detection technology using deep learning. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, H.C.; Ta, Q.B.; Kim, J.T.; Ho, D.D.; Tran, X.L.; Huynh, T.C. Bolt-loosening monitoring framework using an image-based deep learning and graphical model. Sensors 2020, 20, 3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.C.; Park, J.H.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, J.T. Quasi-autonomous bolt-loosening detection method using vision-based deep learning and image processing. Autom. Constr. 2019, 105, 102844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Loh, K.J.; Su, W.; Xue, Z.; Zhao, X. Autonomous bolt loosening detection using deep learning. Struct. Health Monit. 2020, 19, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Chen, W.; Hao, H. Near real-time bolt-loosening detection using mask and region-based convolutional neural network. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2021, 28, e2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.; Kim, N.; An, Y.K. Deep learning-based autonomous concrete crack evaluation through hybrid image scanning. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 18, 1722–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; He, C.; Zou, C.; Wang, A. Displacement Measurement Based on UAV Images Using SURF-Enhanced Camera Calibration Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Cha, Y.J. Autonomous UAVs for structural health monitoring using deep learning and an ultrasonic beacon system with geo-tagging. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 33, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Nie, X.; Fan, J.S.; Liu, X.G. Image-based crack assessment of bridge piers using unmanned aerial vehicles and three-dimensional scene reconstruction. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 35, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liang, Q.; Zhong, W.; Gao, X.; Cui, F. Homography-based measurement of bridge vibration using UAV and DIC method. Measurement 2021, 170, 108683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, J. Real-time crack assessment using deep neural networks with wall-climbing unmanned aerial system. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 35, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, J.; Duan, W. Non-contact cable force estimation with unmanned aerial vehicle and computer vision. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2021, 36, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; Matthews, I. Lucas-kanade 20 years on: A unifying framework. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 56, 221–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Huang, H. Super-resolution method for multiview face recognition from a single image per person using nonlinear mappings on coherent features. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2012, 19, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, K.M. Deeply-Recursive Convolutional Network for Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, W.; Caballero, J.; Huszár, F.; Totz, J.; Aitken, A.P.; Bishop, R.; Rueckert, D.; Wang, Z. Real-Time Single Image and Video Super-Resolution Using an Efficient Sub-Pixel Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1874–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszar, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Wu, S.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Tang, X. ESRGAN: Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2018 Workshops, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; volume 11133, pp. 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.W.; Ding, Y.L.; Li, A.Q.; Chen, B.; Wang, K.P. Digital modeling approach of distributional mapping from structural temperature field to temperature-induced strain field for bridges. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2022, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.W.; Du, Y.L.; Yi, T.H.; Yang, D.H. Influence lines-based model updating of suspension bridges considering boundary conditions. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2022, 26, 13694332221126374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6517–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Evaluating Indicator | Times | Bicubic Interpolation | VDSR | ESRGAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | 2× | 36.03 | 38.00 | 38.83 |
| 4× | 31.21 | 33.30 | 33.93 | |
| 8× | 27.63 | 29.13 | 29.70 | |
| SSIM | 2× | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| 4× | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.94 | |
| 8× | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.91 | |
| Laplace gradient sum | 2× | 20.30 | 50.73 | 52.75 |
| 4× | 4.71 | 15.51 | 51.47 | |
| 8× | 2.91 | 9.83 | 24.49 |
| Method | Time | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed method (image preprocessing and two-stage inspection) | Step1: Image preprocessing | Deblurring | 611.6 s |
| Uniform scale | 592.7 s | ||
| Step 2: Two-stage bolt inspection | 11.5 s | ||
| Traditional method | One-stage bolt inspection | 6.9 s | |
| Method | Group | TP | TN | FP | FN | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Proposed method (preprocessing and two-stage method) | Blurred | 102 | 36 | 2 | 0 | 0.986 |
| Non-blurred | 169 | 96 | 1 | 0 | 0.996 | |
| 2. Preprocessing and single network | Blurred | 91 | 25 | 15 | 9 | 0.829 |
| Non-blurred | 150 | 86 | 19 | 11 | 0.884 | |
| 3. Using single network | Blurred | 79 | 18 | 29 | 22 | 0.655 |
| Non-blurred | 143 | 79 | 27 | 17 | 0.835 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Automatic Inspection of Bridge Bolts Using Unmanned Aerial Vision and Adaptive Scale Unification-Based Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020328
Jiang S, Zhang J, Wang W, Wang Y. Automatic Inspection of Bridge Bolts Using Unmanned Aerial Vision and Adaptive Scale Unification-Based Deep Learning. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(2):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020328
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shang, Jian Zhang, Weiguo Wang, and Yingjun Wang. 2023. "Automatic Inspection of Bridge Bolts Using Unmanned Aerial Vision and Adaptive Scale Unification-Based Deep Learning" Remote Sensing 15, no. 2: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020328
APA StyleJiang, S., Zhang, J., Wang, W., & Wang, Y. (2023). Automatic Inspection of Bridge Bolts Using Unmanned Aerial Vision and Adaptive Scale Unification-Based Deep Learning. Remote Sensing, 15(2), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020328