High-Resolution PM2.5 Concentrations Estimation Based on Stacked Ensemble Learning Model Using Multi-Source Satellite TOA Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data
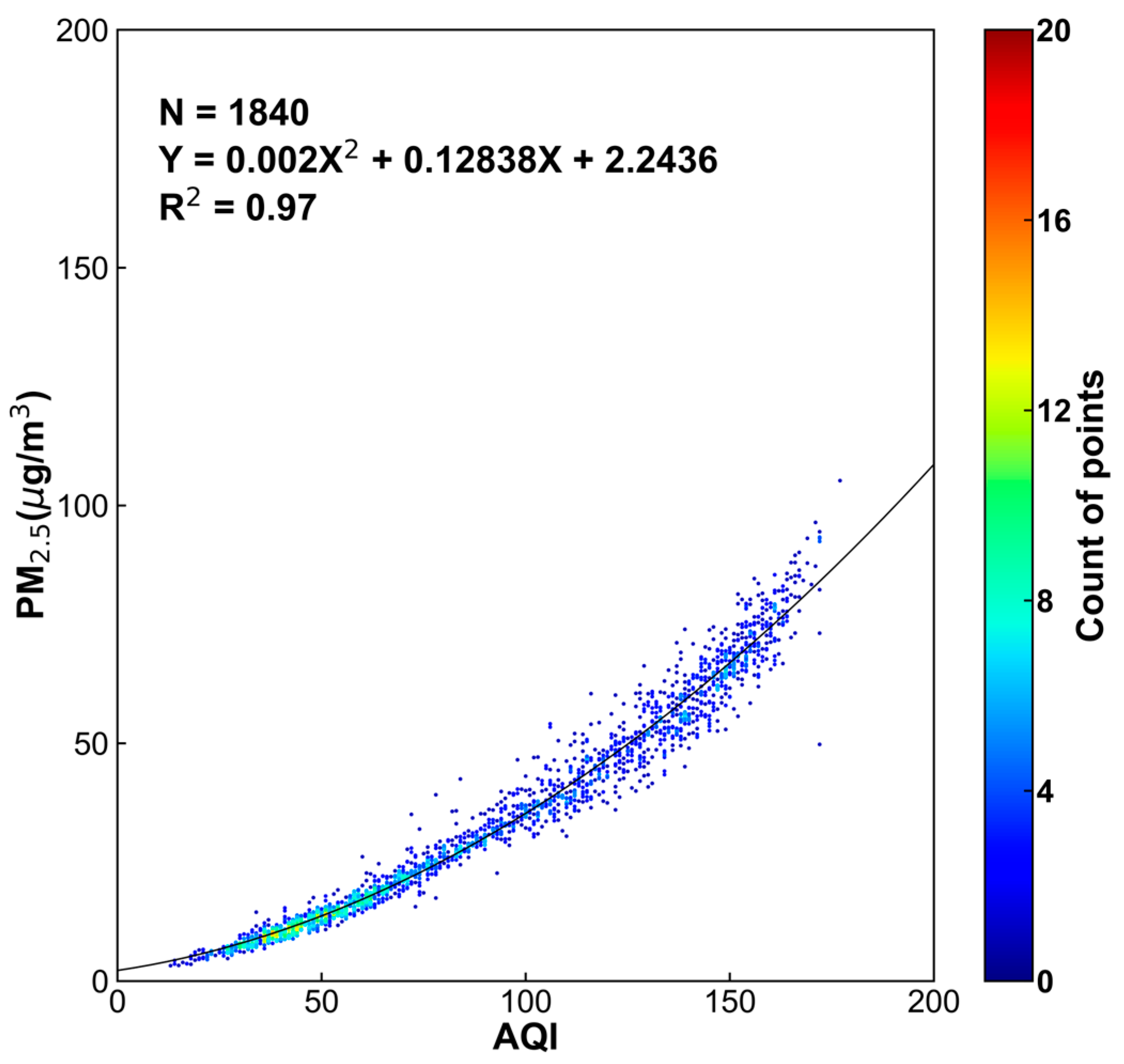
2.1. PM2.5 Measurements
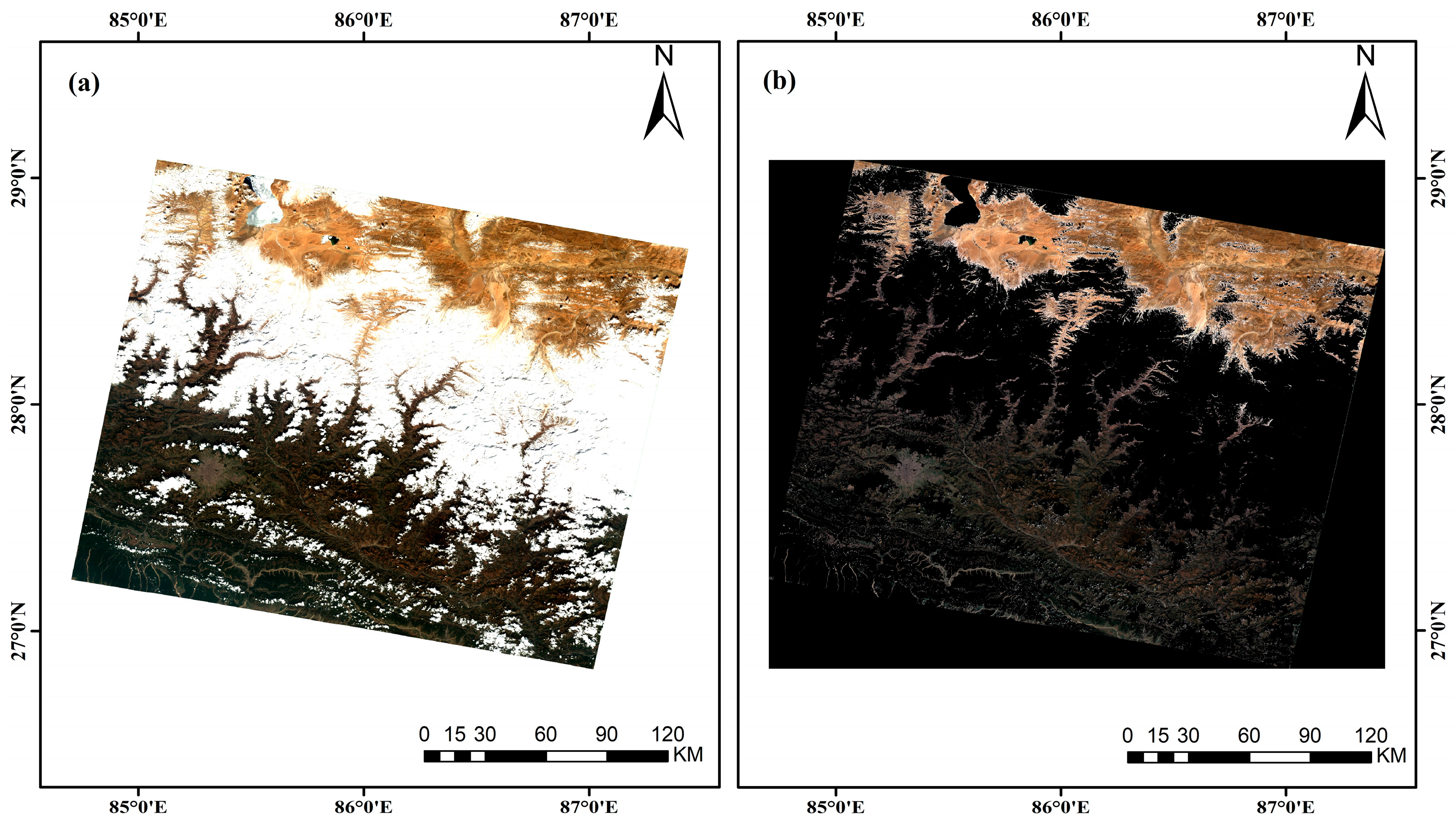
2.2. TOA Data
2.3. Auxiliary Data
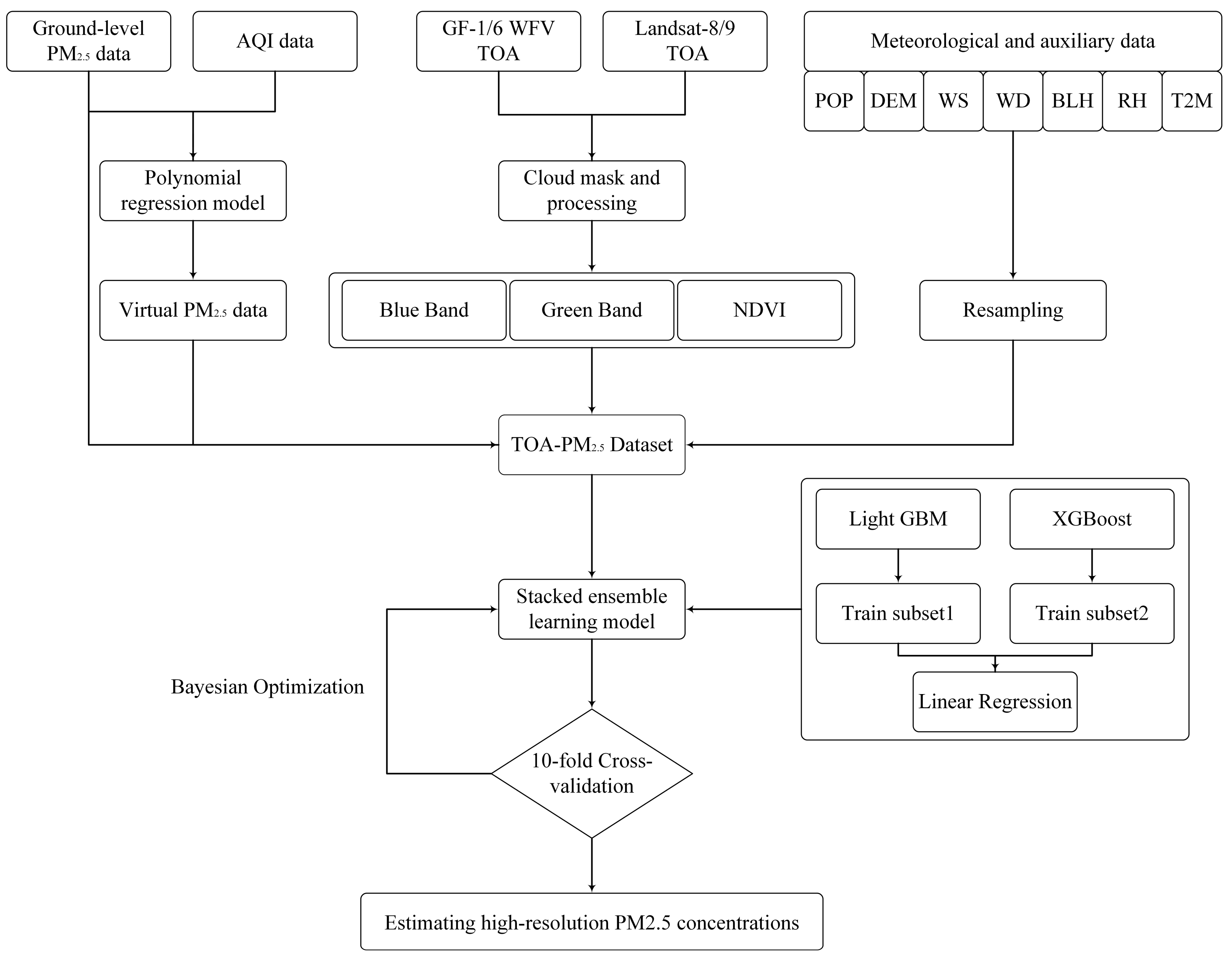
3. Methodology
3.1. Machine Learning Model
3.2. Bayesian Optimization Algorithm
3.3. Ensemble Stacking Model
4. Results and Analysis
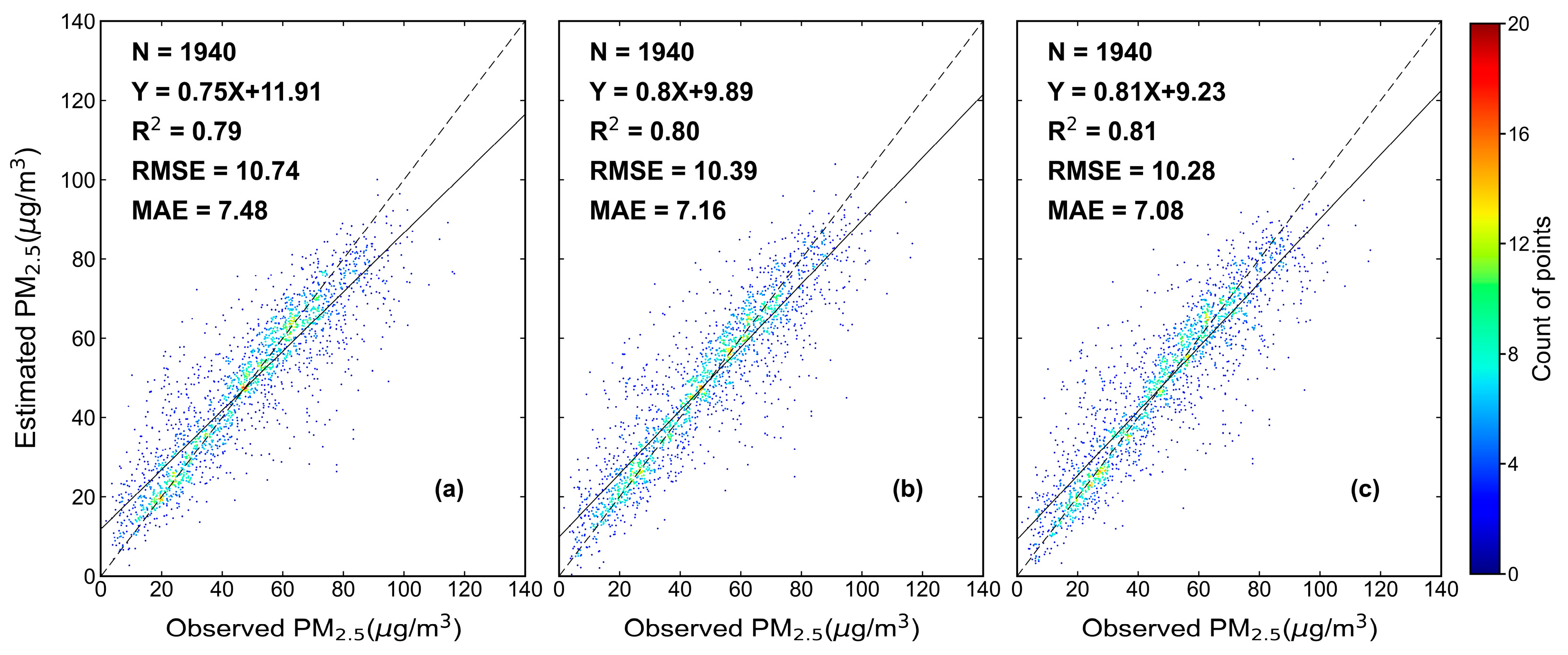
4.1. Evaluation of the XGBLL model
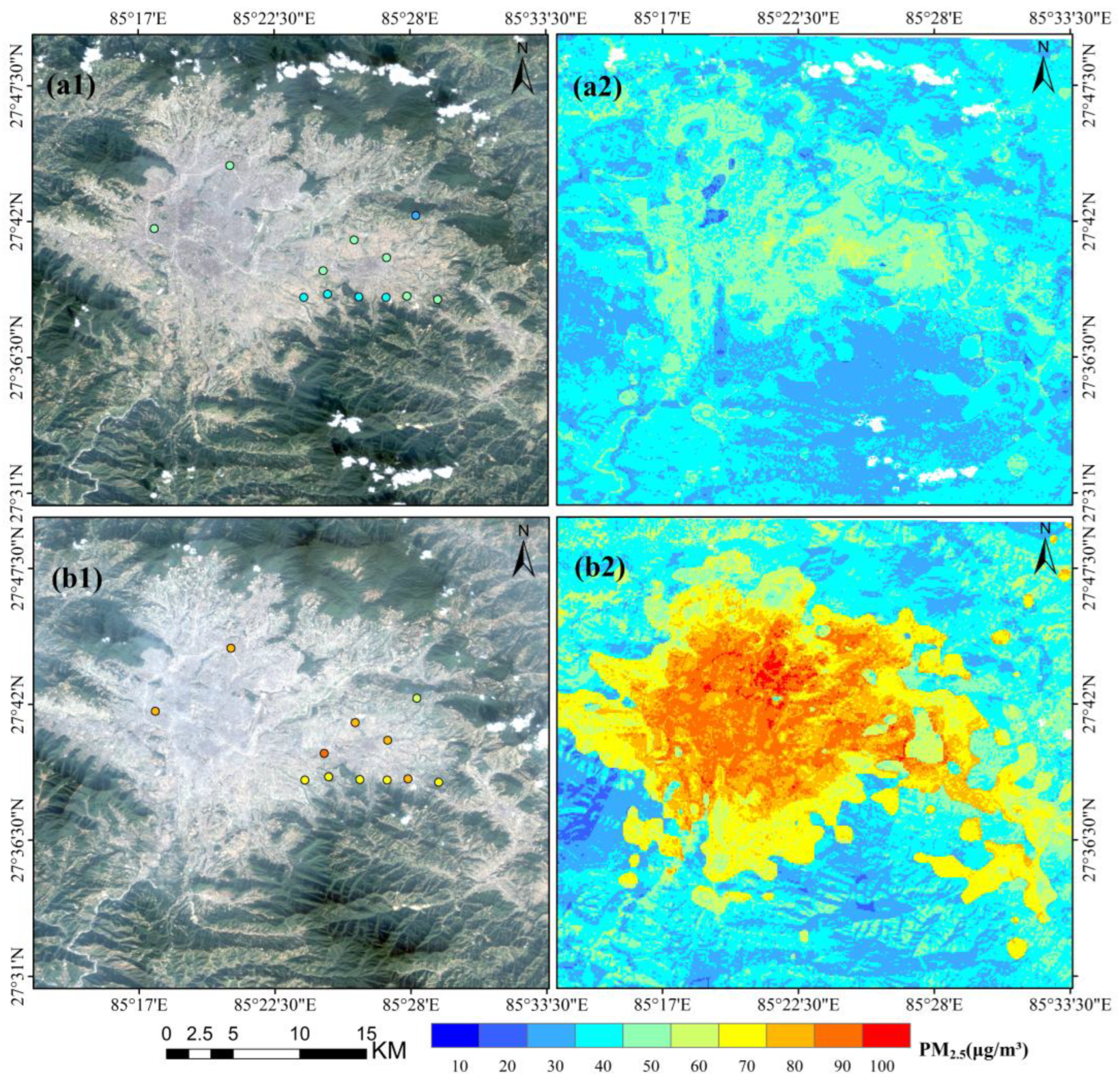
4.2. High-Resolution PM2.5 Concentration Monitoring Application
4.3. Fusion of the Nepal PM2.5 Dataset
4.4. Nepal PM2.5 Dataset Evaluation
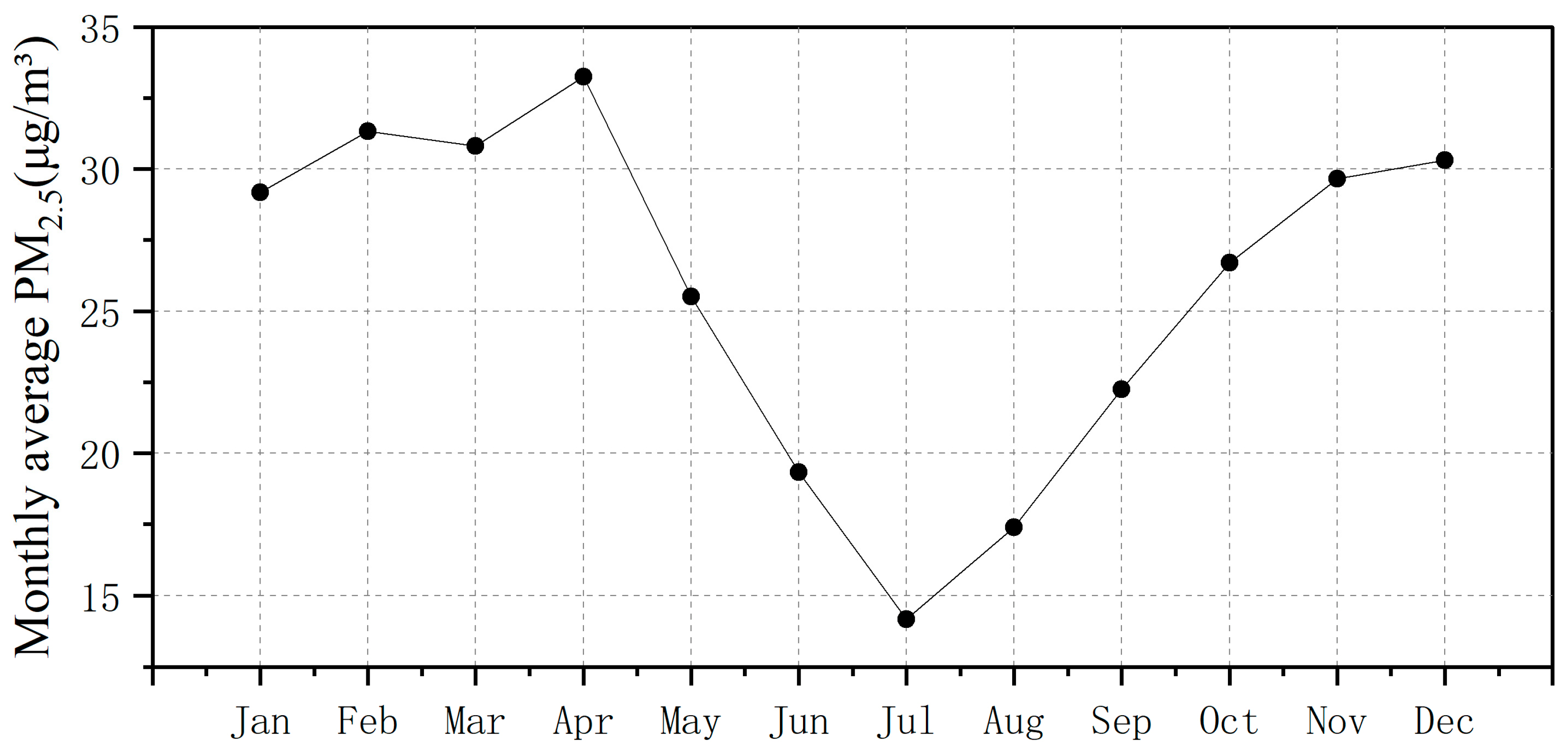
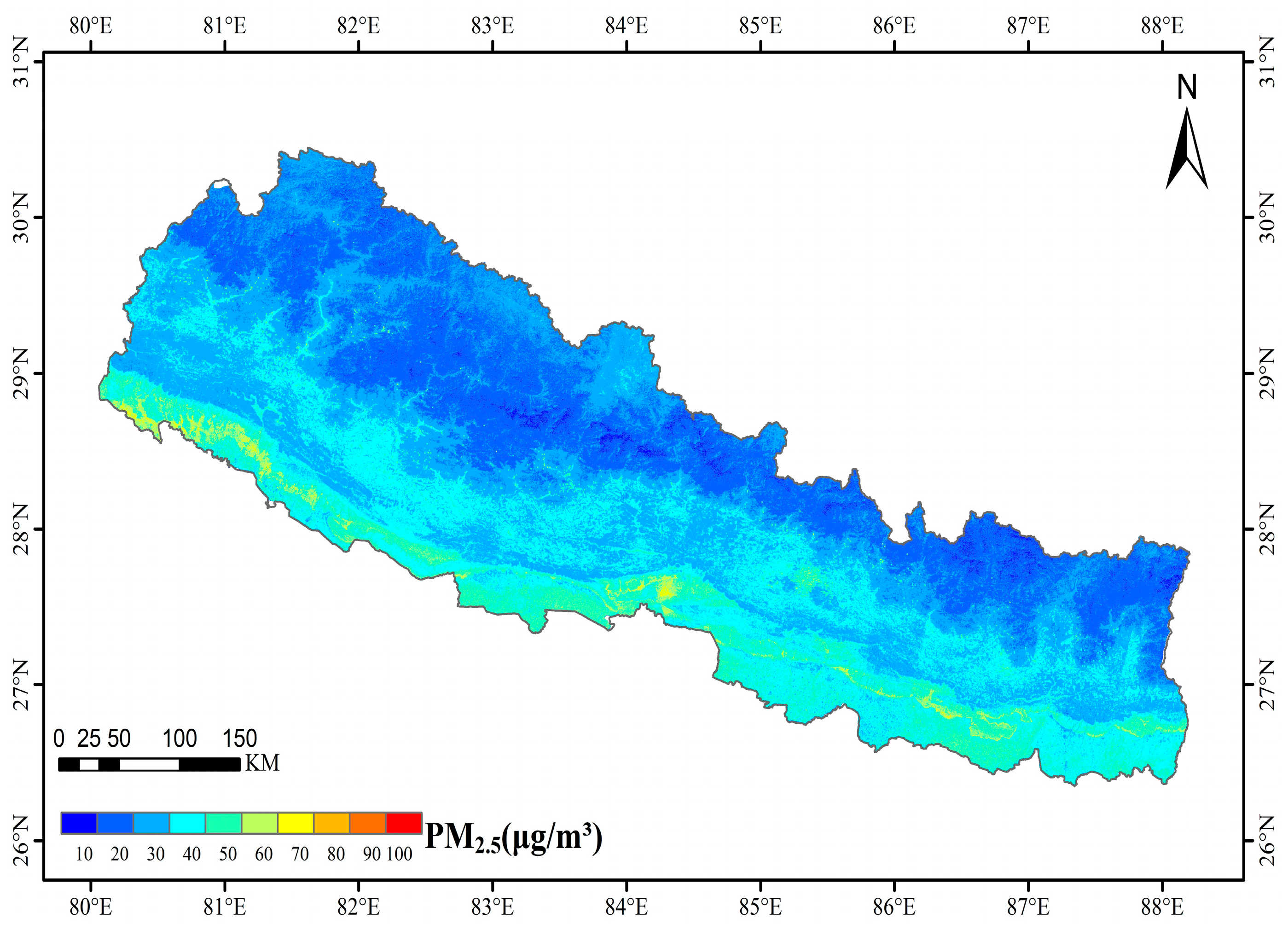
4.5. Spatiotemporal Distribution of PM2.5 Values in Nepal
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IQAir. 2020 World Air Quality Report. Available online: www.iqair.com/world-most-polluted-cities/world-air-quality-report-2020-en.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- IQAir. 2021 World Air Quality Report. Available online: www.iqair.com/world-most-polluted-cities/world-air-quality-report-2021-en.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- IQAir. 2022 World Air Quality Report. Available online: www.iqair.com/world-most-polluted-cities/world-air-quality-report-2022-en.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Yang, L.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; He, X.; Liu, P.; Xu, N.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, P. Preliminary test of quantitative capability in aerosol retrieval over land from MERSI-II onboard FY-3D. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 923–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, L. Comparison of Satellite-Based PM2.5 Estimation from Aerosol Optical Depth and Top-of-Atmosphere Reflectance. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, T.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, L. Estimating regional ground-level PM2.5 directly from satellite top-of-atmosphere reflectance using deep belief networks. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 13–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Mao, F.; Zang, L.; Chen, J.; Lu, X.; Hong, J. Retrieving PM2.5 with high spatio-temporal coverage by TOA reflectance of Himawari-8. Atmospheric Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, W.; Guo, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, C.; Husi, L. A Spatial-Temporal Interpretable Deep Learning Model for improving interpretability and predictive accuracy of satellite-based PM2.5. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Deng, R.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Cao, B.; Liu, Y.; Hua, Z.; Yu, J. Estimating high-spatial-resolution daily PM2.5 mass concentration from satellite top-of-atmosphere reflectance based on an improved random forest model. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 302, 119724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Li, T.; Zhang, L. Estimate hourly PM2.5 concentrations from Himawari-8 TOA reflectance directly using geo-intelligent long short-term memory network. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zeng, C.; Li, T.; Shen, H. Performance comparison of Fengyun-4A and Himawari-8 in PM2.5 estimation in China. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 271, 118898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Shi, Z.; Shi, W.; Zhang, A. Estimation of On-Road PM2.5 Distributions by Combining Satellite Top-of-Atmosphere with Microscale Geographic Predictors for Healthy Route Planning. GeoHealth 2022, 6, e2022GH000669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, H.; Yu, S. Estimating PM2.5 concentrations in Yangtze River Delta region of China using random forest model and the Top-of-Atmosphere reflectance. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 272, 111061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Hong, J.; Min, Q.; Gong, W.; Zang, L.; Yin, J. Estimating hourly full-coverage PM2.5 over China based on TOA reflectance data from the Fengyun-4A satellite. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Weng, F.; Li, Z. Satellite-based PM2.5 estimation directly from reflectance at the top of the atmosphere using a machine learning algorithm. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 208, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zuo, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.W.; Jiang, Y.; He, B.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Shi, W. Cooperative simultaneous inversion of satellite-based real-time PM2.5 and ozone levels using an improved deep learning model with attention mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T. Ultrahigh-resolution PM2.5 estimation from top-of-atmosphere reflectance with machine learning: Theories, methods, and applications. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, K.; Li, K.; Sun, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, N.-B.; Li, Z. Global synthesis of two-decade of research on improving PM2.5 estimation models: From remote sensing and data science perspectives. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2023, 241, 104461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hao, J.; Xu, W. PM2.5 and PM10 Concentration Estimation Based on the Top-of-Atmosphere Reflectance. In Wireless Algorithms, Systems, and Applications; Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Algorithms, Systems, and Applications, Nanjing, China, 25–27 June 2021; Liu, Z., Wu, F., Das, S.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 574–581. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Li, Z. Hourly PM2.5 concentration forecasting based on feature extraction and stacking-driven ensemble model for the winter of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei area. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Zou, X.; Tan, J.; Li, J.; Karimian, H. Short-Term PM2.5 Concentration Changes Prediction: A Comparison of Meteorological and Historical Data. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, Q. Estimating hourly and continuous ground-level PM2.5 concentrations using an ensemble learning algorithm: The ST-stacking model. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, F. Cloud detection based on band operation texture feature for GF-1 multispectral data. Remote Sens. Inf. 2018, 33, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Haralick, R.M. Statistical and structural approaches to texture. Proc. IEEE 1979, 67, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, B.; Bright, E.; Coleman, P.; Dobson, J. LandScan. Geoinformatics 2002, 5, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Danielson, J.J.; Gesch, D.B. Global Multi-Resolution Terrain Elevation Data 2010 (GMTED2010); U.S. Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Yu, Z.; Qu, Y.; Xu, J.; Cao, Y. Application of the XGBoost Machine Learning Method in PM2.5 Prediction: A Case Study of Shanghai. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B. Application of XGBoost algorithm in hourly PM2.5 concentration prediction. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advances in Energy Resources and Environment Engineering, Harbin, China, 8–10 December 2017; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 113, p. 012127. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Cheng, J.C.; Xu, Z.; Chen, K.; Lin, C.; Jiang, F. Identification of the most influential areas for air pollution control using XGBoost and Grid Importance Rank. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 122835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.-Y.; Lee, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Zeng, Y.-T.; Chern, Y.-R.; Chen, N.-T.; Lung, S.-C.C.; Su, H.-J.; Wu, C.-D. Using a land use regression model with machine learning to estimate ground level PM2.5. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. Lightgbm: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, R.; Xu, J.; Yu, Z. MERRA-2 PM2.5 mass concentration reconstruction in China mainland based on LightGBM machine learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y. Prediction of air quality based on Gradient Boosting Machine Method. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Big Data and Informatization Education (ICBDIE), Zhangjiajie, China, 23–25 April 2020; pp. 395–397. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.; Gui, K.; Wang, Z.; Luo, M.; Geng, H.; Ge, E.; An, J.; Song, X.; Ning, G.; Zhai, S.; et al. Estimating hourly surface PM2.5 concentrations across China from high-density meteorological observations by machine learning. Atmos. Res. 2021, 254, 105516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, R.; Wu, P. Spatiotemporally Continuous Reconstruction of Retrieved PM2.5 Data Using an Autogeoi-Stacking Model in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelikan, M.; Goldberg, D.E.; Cantú-Paz, E. BOA: The Bayesian optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference GECCO-99, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–17 July 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Li, N. Ensemble learning models with a Bayesian optimization algorithm for mineral prospectivity mapping. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 145, 104916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jin, Y.; Schmitt, S.; Olhofer, M. Recent Advances in Bayesian Optimization. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, L.-D.; Lei, H.; Deng, S.-H. Hyperparameter optimization for machine learning models based on Bayesian optimization. J. Electron. Sci. Technol. 2019, 17, 26–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, C.F.; Lobo, F.G.; Pelikan, M.; Goldberg, D.E. Model accuracy in the Bayesian optimization algorithm. Soft Comput. 2011, 15, 1351–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H. Stacked generalization. Neural Netw. 1992, 5, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlyshenko, B. Using stacking approaches for machine learning models. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Second International Conference on Data Stream Mining & Processing (DSMP), Lviv, Ukraine, 21–25 August 2018; pp. 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Du, N.; Wang, L.; Cai, H.; Zhou, B. Analysis of the Gridded Influencing Factors of the PM2.5 Concentration in Sichuan Province Based on a Stacked Machine Learning Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2023, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Hammer, M.S.; Bindle, L.; Brauer, M.; Brook, J.R.; Garay, M.J.; Hsu, N.C.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Kahn, R.A.; Lee, C.; et al. Monthly Global Estimates of Fine Particulate Matter and Their Uncertainty. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15287–15300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Satellites | Bands | Wavelength (μm) | Spatial Resolution (m) | Temporal Resolution (Day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat-8/9 | Band 2 | 0.45–0.51 | 30 | 16 |
| Band 3 | 0.53–0.59 | 30 | ||
| Band 4 | 0.64–0.67 | 30 | ||
| Band 5 | 0.85–0.88 | 30 | ||
| Gaofen-1/6 WFV | Band 1 | 0.45–0.52 | 16 | 4 |
| Band 2 | 0.52–0.59 | 16 | ||
| Band 3 | 0.63–0.69 | 16 | ||
| Band 4 | 0.77–0.89 | 16 |
| Abbreviations | Data Sources | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| BLH | ERA5 hourly data on single levels | 0.25° | 1 h |
| RH | ERA5 hourly data on pressure levels | 0.25° | 1 h |
| T2M | ERA5-Land hourly data | 0.1° | 1 h |
| WS | ERA5-Land hourly data | 0.1° | 1 h |
| WD | ERA5-Land hourly data | 0.1° | 1 h |
| SP | ERA5-Land hourly data | 0.1° | 1 h |
| NDVI | Calculation of TOA data | 0.001° | / |
| POP | LandScan | 1 km | 1 year |
| DEM | GMTED2010 | 0.1° | / |
| Models | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|
| XGBoost | n_estimators | 673 |
| max_depth | 9 | |
| min_child_weigth | 3 | |
| gamma | 0.3 | |
| subsample | 0.87 | |
| colsample_bytree | 0.81 | |
| learning_rate | 0.01 | |
| LightGBM | n_estimators | 840 |
| max_depth | 4 | |
| min_child_samples | 20 | |
| min_child_weight | 0.001 | |
| num_leaves | 31 | |
| colsample_bytree | 1 |
| Dataset | R2 | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|
| V5GL03 | 0.75 | 18.00 | 14.06 |
| This study | 0.80 | 12.56 | 8.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Q.; Guo, H.; Gu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Mi, X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, D. High-Resolution PM2.5 Concentrations Estimation Based on Stacked Ensemble Learning Model Using Multi-Source Satellite TOA Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5489. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235489
Fu Q, Guo H, Gu X, Li J, Zhang W, Mi X, Zhao Q, Chen D. High-Resolution PM2.5 Concentrations Estimation Based on Stacked Ensemble Learning Model Using Multi-Source Satellite TOA Data. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(23):5489. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235489
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Qiming, Hong Guo, Xingfa Gu, Juan Li, Wenhao Zhang, Xiaofei Mi, Qichao Zhao, and Debao Chen. 2023. "High-Resolution PM2.5 Concentrations Estimation Based on Stacked Ensemble Learning Model Using Multi-Source Satellite TOA Data" Remote Sensing 15, no. 23: 5489. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235489
APA StyleFu, Q., Guo, H., Gu, X., Li, J., Zhang, W., Mi, X., Zhao, Q., & Chen, D. (2023). High-Resolution PM2.5 Concentrations Estimation Based on Stacked Ensemble Learning Model Using Multi-Source Satellite TOA Data. Remote Sensing, 15(23), 5489. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235489









