Detection of Aquatic Invasive Plants in Wetlands of the Upper Mississippi River from UAV Imagery Using Transfer Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (i)
- Evaluate and implement suitable DL model to accurately detect purple loosestrife patches;
- (ii)
- Analyze the relationship between spatial morphology of purple loosestrife patches and model performance;
- (iii)
- Explore repeat implementation strategies to evaluate model reusability.
2. Vegetation Specie Mapping and Deep Learning Models
3. Transfer Learning
4. Data and Methodology
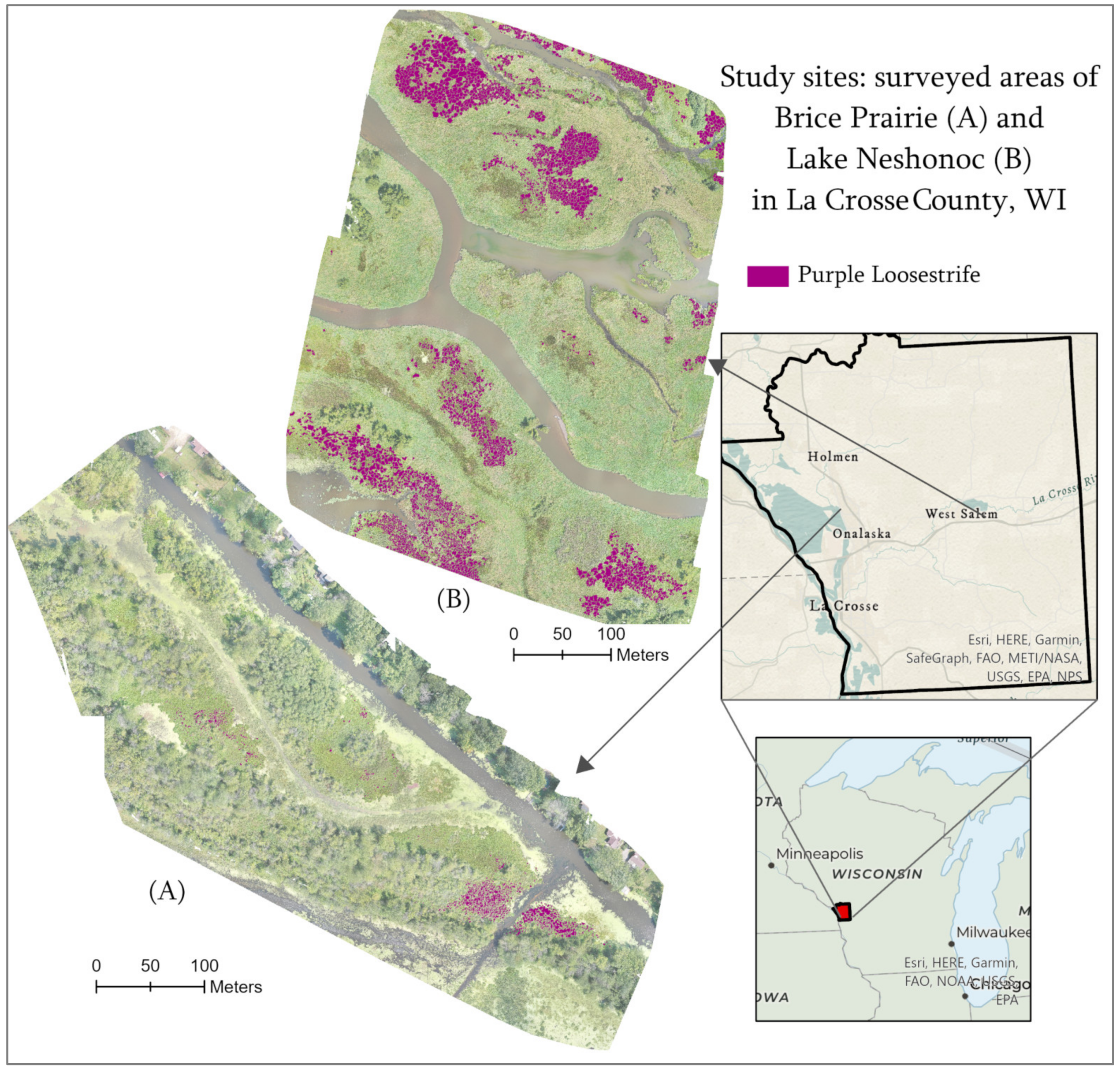
4.1. Study Area
4.2. UAV Data Acquisition and Post-Processing
4.3. Image Data and Reference Data Preparation
4.4. U-Net and LinkNet Models
4.5. Experiment # 1
4.6. Experiment # 2
4.7. Accuracy Assessment
4.8. Patch Morphology with Spatial Metrics
5. Results
5.1. Model Training and Testing—Experiment # 1
5.2. Spatial Metrics
5.3. Model Training and Testing—Experiment # 2
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prentis, P.J.; Wilson, J.R.U.; Dormontt, E.E.; Richardson, D.M.; Lowe, A.J. Adaptive Evolution in Invasive Species. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Early, R.; Bradley, B.A.; Dukes, J.S.; Lawler, J.J.; Olden, J.D.; Blumenthal, D.M.; Gonzalez, P.; Grosholz, E.D.; Ibañez, I.; Miller, L.P.; et al. Global Threats from Invasive Alien Species in the Twenty-First Century and National Response Capacities. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Havel, J.E.; Kovalenko, K.E.; Thomaz, S.M.; Amalfitano, S.; Kats, L.B. Aquatic Invasive Species: Challenges for the Future. Hydrobiologia 2015, 750, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyšek, P.; Richardson, D.M. Invasive Species, Environmental Change and Management, and Health. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 25–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walsh, J.R.; Carpenter, S.R.; Van Der Zanden, M.J. Invasive Species Triggers a Massive Loss of Ecosystem Services through a Trophic Cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4081–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olden, J.D.; Tamayo, M. Incentivizing the Public to Support Invasive Species Management: Eurasian Milfoil Reduces Lakefront Property Values. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, M.; Meder, M.E. Effects of Aquatic Invasive Species on Home Prices. 2013. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2316911 (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Connelly, N.A.; Lauber, T.B.; Stedman, R.C.; Knuth, B.A. The Role of Anglers in Preventing the Spread of Aquatic Invasive Species in the Great Lakes Region. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fantle-Lepczyk, J.E.; Haubrock, P.J.; Kramer, A.M.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Turbelin, A.J.; Crystal-Ornelas, R.; Diagne, C.; Courchamp, F. Economic Costs of Biological Invasions in the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, C.J.A.; Leroy, B.; Bellard, C.; Roiz, D.; Albert, C.; Fournier, A.; Barbet-Massin, M.; Salles, J.M.; Simard, F.; Courchamp, F. Massive yet Grossly Underestimated Global Costs of Invasive Insects. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisbee, G.; Blumer, D.; Burbach, D.; Iverson, B.; Kemp, D.; Richter, L.; Sklavos, S.; Strohl, D.; Thompson, B.; Welch, R.J.; et al. Purple Loosestrife Biological Control Activities for Educators; Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, Wisconsin Wetland Association: Madison, WI, USA, 2016; PUBL-SS-981 REV2016. [Google Scholar]
- University of Wisconsin Sea Grant and Water resource Institute. Wisconsin Aquatic Invasive Species Management Plan; Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources: Madison, WI, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wisconsin DNR. Wisconsin Invasive Species Program Report; Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources: Madison, WI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- US Dept of the Interior. Safeguarding America’s Lands and Waters from Invasive Species: A National Framework for Early Detection and Rapid Response Contents; US Dept of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Kattenborn, T.; Eichel, J.; Fassnacht, F.E. Convolutional Neural Networks Enable Efficient, Accurate and Fine-Grained Segmentation of Plant Species and Communities from High-Resolution UAV Imagery. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grenzdörffer, G.J.; Engel, A.; Teichert, B. The Photogrammetric Potential of Low-Cost Uavs in Forestry and Agriculture. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.-ISPRS Arch. 2008, 31, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Raparelli, E.; Bajocco, S. A Bibliometric Analysis on the Use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Agricultural and Forestry Studies. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 9070–9083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Shao, G. Drone Remote Sensing for Forestry Research and Practices. J. Res. 2015, 26, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentsch, S.; Caceres, M.L.L.; Serrano, D.; Roure, F.; Diez, Y. Computer Vision and Deep Learning Techniques for the Analysis of Drone-Acquired Forest Images, a Transfer Learning Study. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gambella, F.; Sistu, L.; Piccirilli, D.; Corposanto, S.; Caria, M.; Arcangeletti, E.; Proto, A.R.; Chessa, G.; Pazzona, A. Forest and UAV: A Bibliometric Review. Contemp. Eng. Sci. 2016, 9, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natesan, S.; Armenakis, C.; Vepakomma, U. Resnet-Based Tree Species Classification Using Uav Images. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.-ISPRS Arch. 2019, XLII-2/W13, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabezas, M.; Kentsch, S.; Tomhave, L.; Gross, J.; Larry, M.; Caceres, L.; Diez, Y. Remote Sensing Detection of Invasive Species in Wetlands: Practical DL with Heavily Imbalanced Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, I.; Chen, Z.; Popovic, M.; Khanna, R.; Liebisch, F.; Nieto, J.; Siegwart, R. WeedNet: Dense Semantic Weed Classification Using Multispectral Images and MAV for Smart Farming. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, F.H.; Sanchez, A.; Tarabalka, Y.; Lotte, R.G.; Ferreira, M.P.; Aidar, M.P.M.; Gloor, E.; Phillips, O.L.; Aragão, L.E.O.C. Using the U-Net Convolutional Network to Map Forest Types and Disturbance in the Atlantic Rainforest with Very High Resolution Images. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 5, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiferaw, H.; Bewket, W.; Eckert, S. Performances of Machine Learning Algorithms for Mapping Fractional Cover of an Invasive Plant Species in a Dryland Ecosystem. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 2562–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Gill, L.; Ghosh, B. Drone Image Segmentation Using Machine and Deep Learning for Mapping Raised Bog Vegetation Communities. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2015, 9351, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Brodrick, P.G.; Davies, A.B.; Asner, G.P. Uncovering Ecological Patterns with Convolutional Neural Networks. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasia, A.; Culurciello, E. LinkNet: Exploiting Encoder Representations for Efficient Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 10–13 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learnin. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q. A Survey on Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2010, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015—Conference Track Proceedings, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Deep Learning with Python, 2nd ed.; Manning: Shelter Island, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Behbood, V.; Hao, P.; Zuo, H.; Xue, S.; Zhang, G. Transfer Learning Using Computational Intelligence: A Survey. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 80, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, A.; Cassey, P.; Segaran, R.R.; Koh, L.P. Deep Learning for Environmental Conservation. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R977–R982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, N.; Yoshinaga, I.; Sekijima, K.; Azechi, I.; Baba, D. Convolutional Neural Network Coupled with a Transfer-Learning Approach for Time-Series Flood Predictions. Water 2019, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavoie, C. Should We Care about Purple Loosestrife? The History of an Invasive Plant in North America. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 1967–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Lu, K.; Audebert, N.; Khalel, A.; Tarabalka, Y.; Malof, J.; Boulch, A.; Le Saux, B.; Collins, L.; Bradbury, K.; et al. Large-Scale Semantic Classification: Outcome of the First Year of Inria Aerial Image Labeling Benchmark. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Jin, Y.; Brown, P. An Enhanced Bloom Index for Quantifying Floral Phenology Using Multi-Scale Remote Sensing Observations. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 156, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F.; TensorFlower Gardener. Keras. 2015. Available online: https://github.com/fchollet/keras (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1603.04467. [Google Scholar]
- Yakubovskiy, P.; Segmentation Models. GitHub Repos. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/qubvel/segmentation_models (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS v4: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical and Continuous Maps; Computer Software Program Produced by the Authors at the University of Massachusetts: Amherst, MA, USA, 2012; Available online: http://www.umass.edu/landeco/research/fragstats/fragstats.html (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Li, H.; Reynolds, J.F. A New Contagion Index to Quantify Spatial Patterns of Landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 1993, 8, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.C.; Roth, H.R.; Gao, M.; Lu, L.; Xu, Z.; Nogues, I.; Yao, J.; Mollura, D.; Summers, R.M. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Computer-Aided Detection: CNN Architectures, Dataset Characteristics and Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.; Yin, G.; Johnson, B.A. Deep Learning in Remote Sensing Applications: A Meta-Analysis and Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Img | Training | Testing | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoU | F1-Score | IoU | F1-Score | |||||
| U-Net | LinkNet | U-Net | LinkNet | U-Net | LinkNet | U-Net | LinkNet | |
| LK0 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 0.63 | 0.60 |
| LK1 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| LK2 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.82 | 0.81 |
| LK3 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.54 | 0.57 | 0.66 | 0.72 |
| LK4 | 0.68 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.65 | 0.62 | 0.68 | 0.75 |
| LK5 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.59 | 0.58 |
| LK6 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.66 | 0.71 | 0.77 | 0.73 |
| BP1 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.68 | 0.70 | 0.74 | 0.75 |
| BP2 | 0.75 | 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.76 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Img | Time (mm.ss) | Chips # | Total Area (ha) | Class Area (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | LinkNet | ||||
| LK0 | 26:09 | 23:15 | 1040 | 1.81 | 6.20 |
| LK1 | 24:27 | 22:27 | 930 | 1.60 | 25.22 |
| LK2 | 39:35 | 36:47 | 1550 | 2.67 | 11.41 |
| LK3 | 27:38 | 27:03 | 1092 | 1.88 | 10.68 |
| LK4 | 32:32 | 30:03 | 1274 | 2.16 | 2.07 |
| LK5 | 39:31 | 36:39 | 1550 | 2.64 | 11.36 |
| LK6 | 32:29 | 30:11 | 1275 | 2.16 | 16.41 |
| BP1 | 37:57 | 35:09 | 1476 | 1.48 | 7.30 |
| BP2 | 20:44 | 23:58 | 1023 | 1.04 | 0.57 |
| Img | Epochs | Training | Testing | Time (h:mm:ss) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoU | F1-Score | IoU | F1-Score | ||||||||
| U-Net | LinkNet | U-Net | LinkNet | U-Net | LinkNet | U-Net | LinkNet | U-Net | LinkNet | ||
| LK | 100 | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 3:40:07 | 3:25:15 |
| BP1 | 20 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.72 | 0.70 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0:07:45 | 0:07:55 |
| 40 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.85 | 0:15:08 | 0:15:12 | |
| 60 | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.70 | 0.83 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 0:22:40 | 0:22:51 | |
| 80 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.73 | 0.81 | 0.89 | 0.78 | 0:30:13 | 0:30:20 | |
| 100 | 0.90 | 0.83 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.79 | 0.71 | 0.85 | 0.76 | 0:37:39 | 0:37:55 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaudhuri, G.; Mishra, N.B. Detection of Aquatic Invasive Plants in Wetlands of the Upper Mississippi River from UAV Imagery Using Transfer Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030734
Chaudhuri G, Mishra NB. Detection of Aquatic Invasive Plants in Wetlands of the Upper Mississippi River from UAV Imagery Using Transfer Learning. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(3):734. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030734
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaudhuri, Gargi, and Niti B. Mishra. 2023. "Detection of Aquatic Invasive Plants in Wetlands of the Upper Mississippi River from UAV Imagery Using Transfer Learning" Remote Sensing 15, no. 3: 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030734
APA StyleChaudhuri, G., & Mishra, N. B. (2023). Detection of Aquatic Invasive Plants in Wetlands of the Upper Mississippi River from UAV Imagery Using Transfer Learning. Remote Sensing, 15(3), 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030734





