Monitoring Land Subsidence along the Subways in Shanghai on the Basis of Time-Series InSAR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
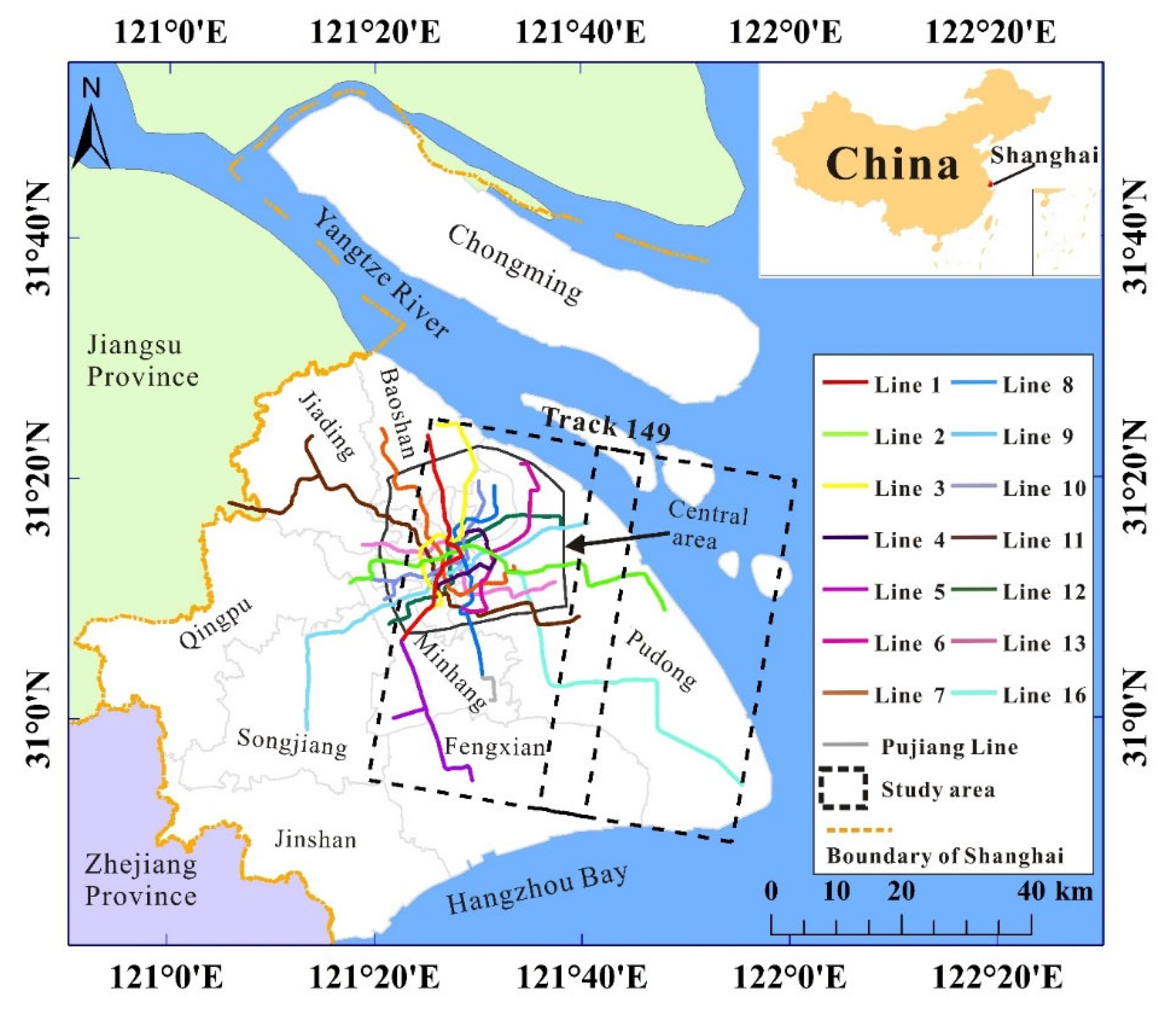
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. TerraSAR-X Images
2.2.2. Geological Environment Data
2.2.3. Optical Images
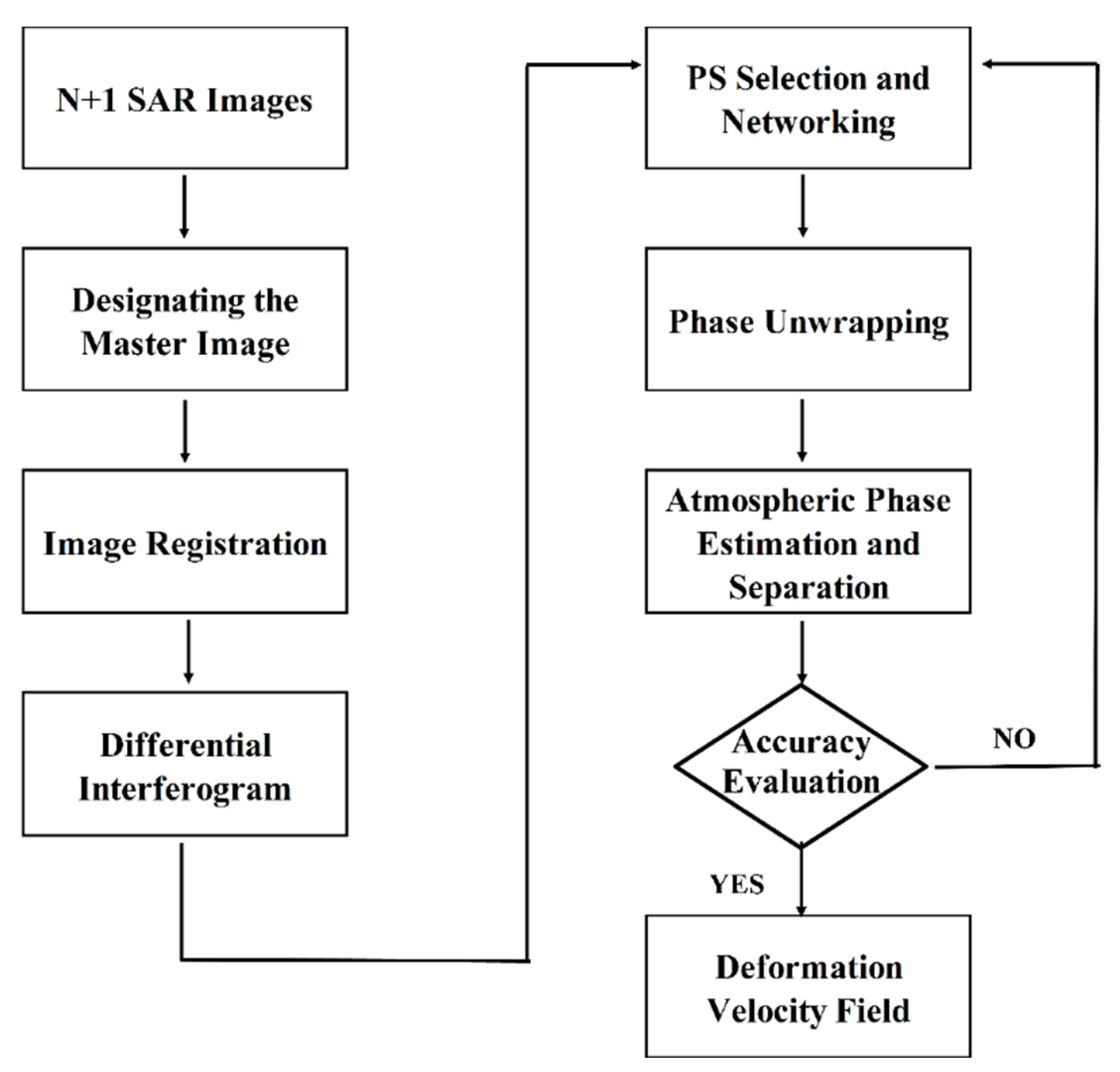
3. Methodology
3.1. Principle of Time-Series PS-InSAR
3.2. Data Processing
4. Results
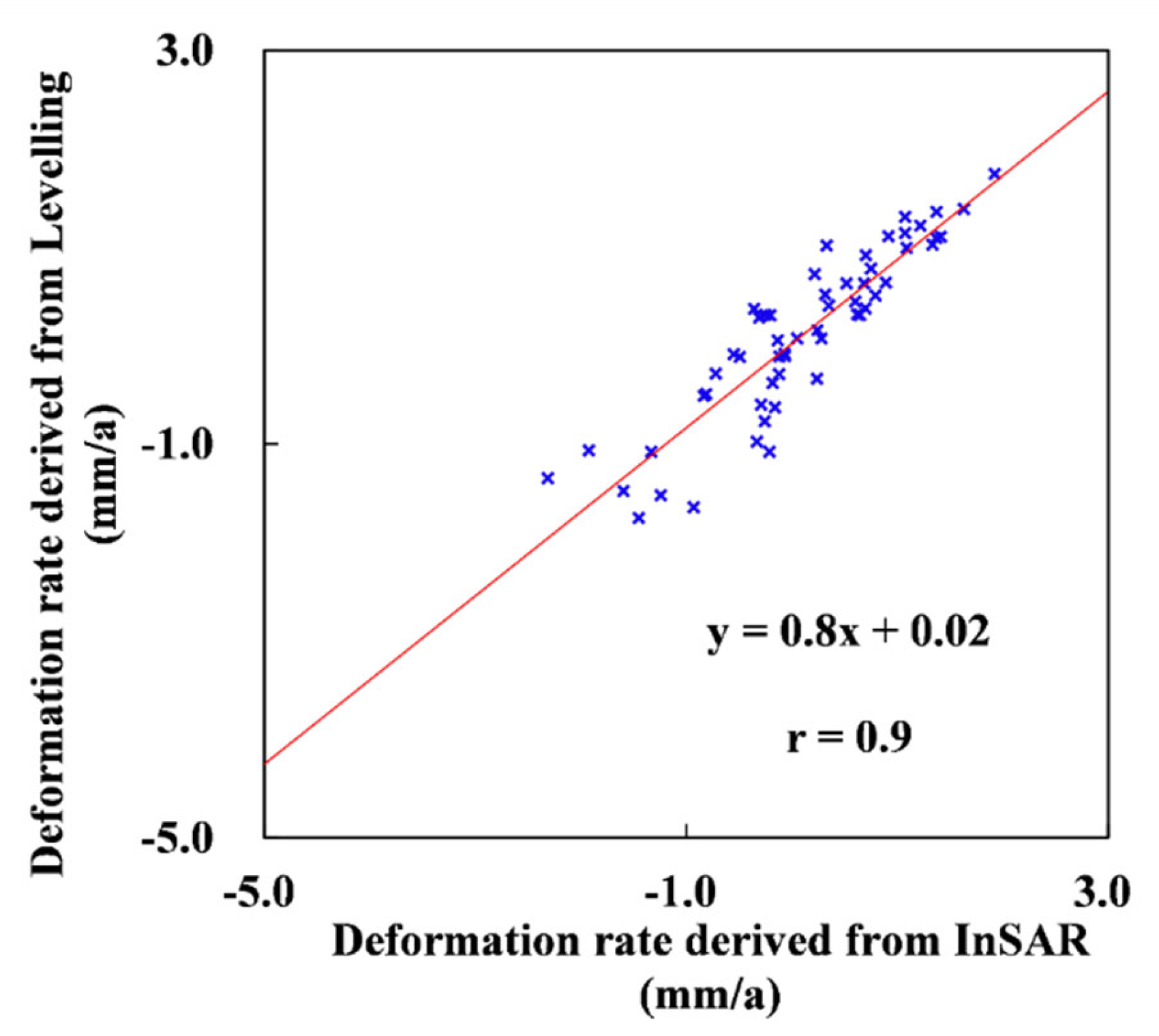
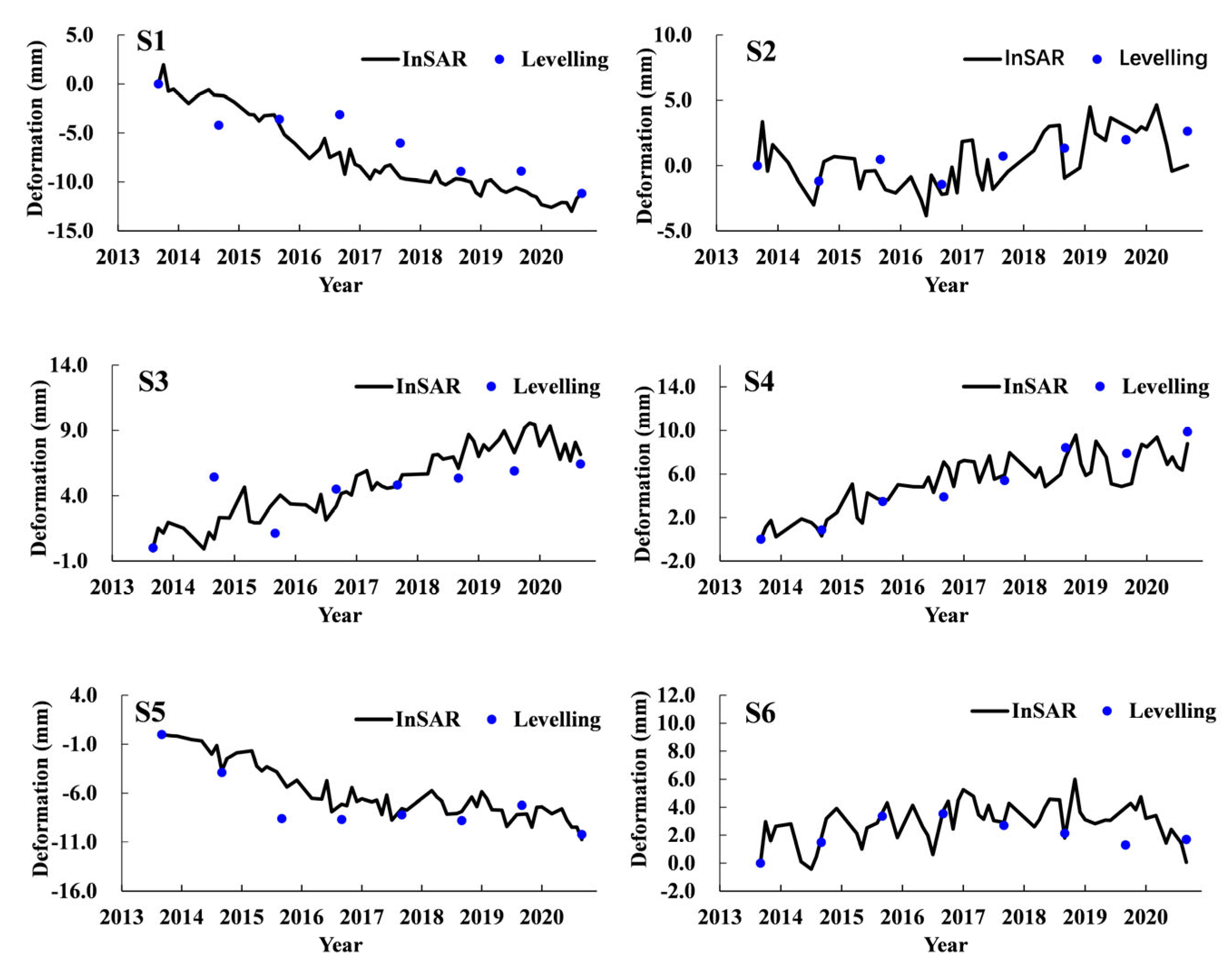
4.1. Verification
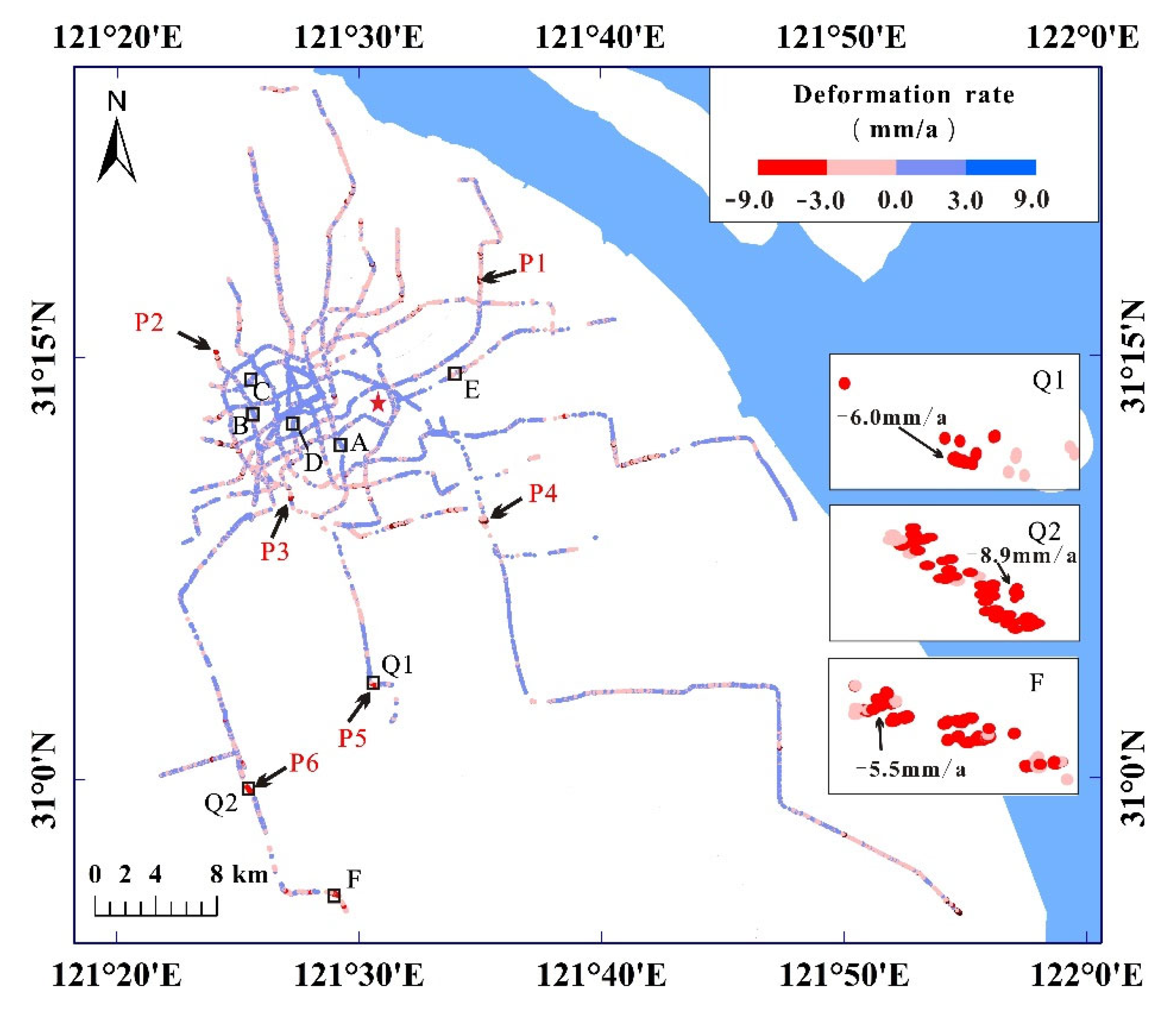
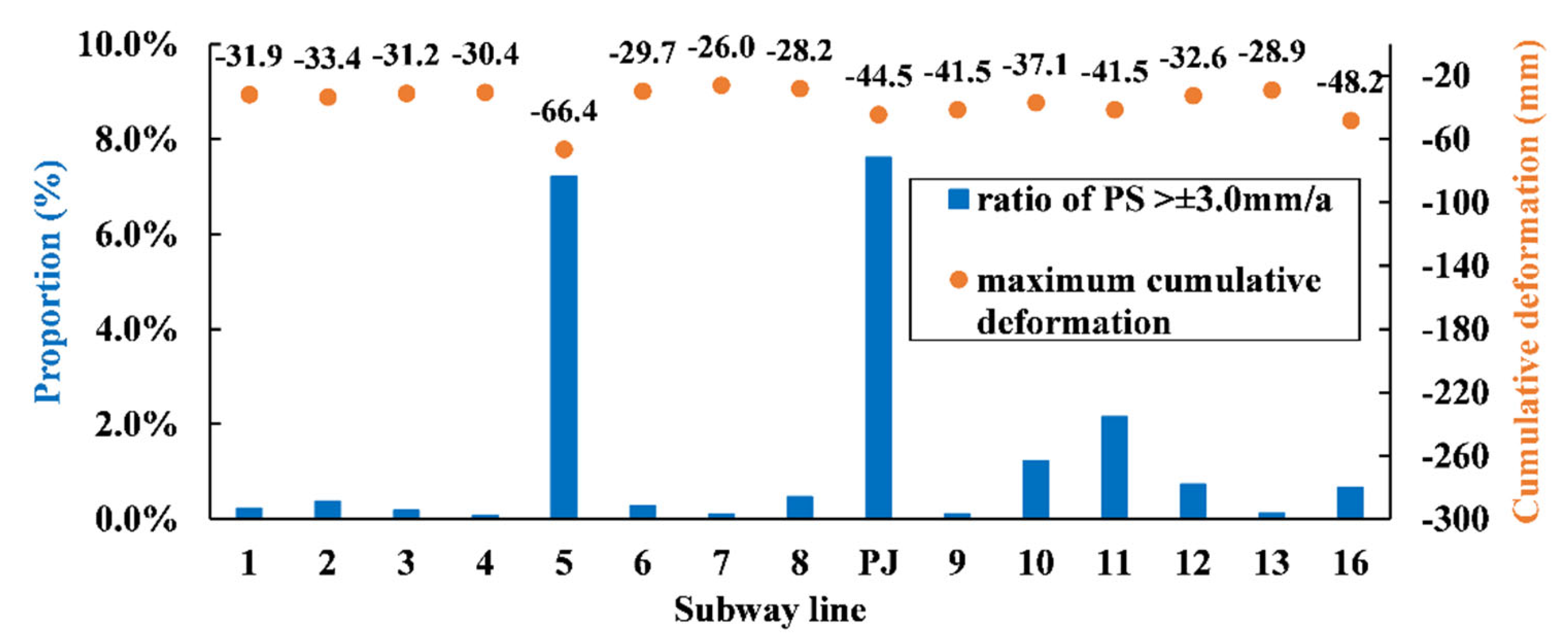
4.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Ground Deformation
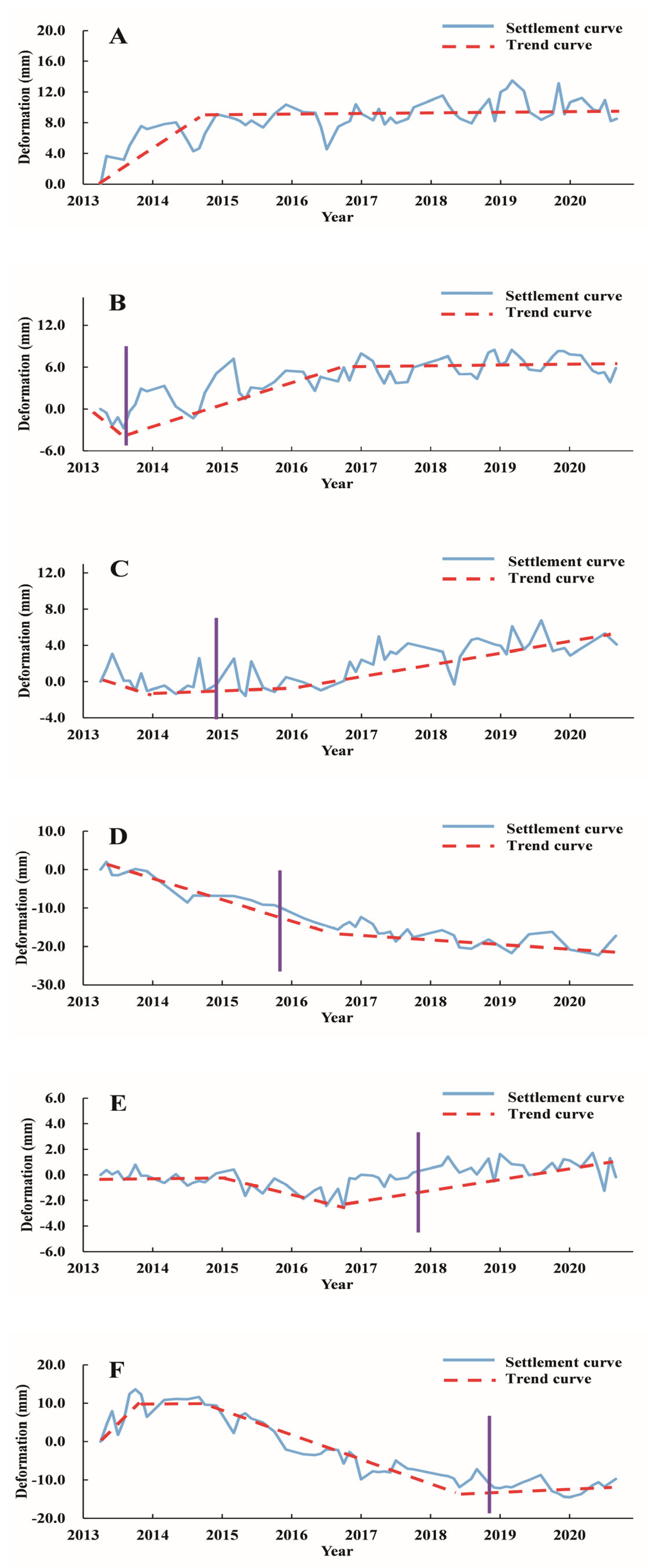
4.3. Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Land Subsidence
5. Discussion
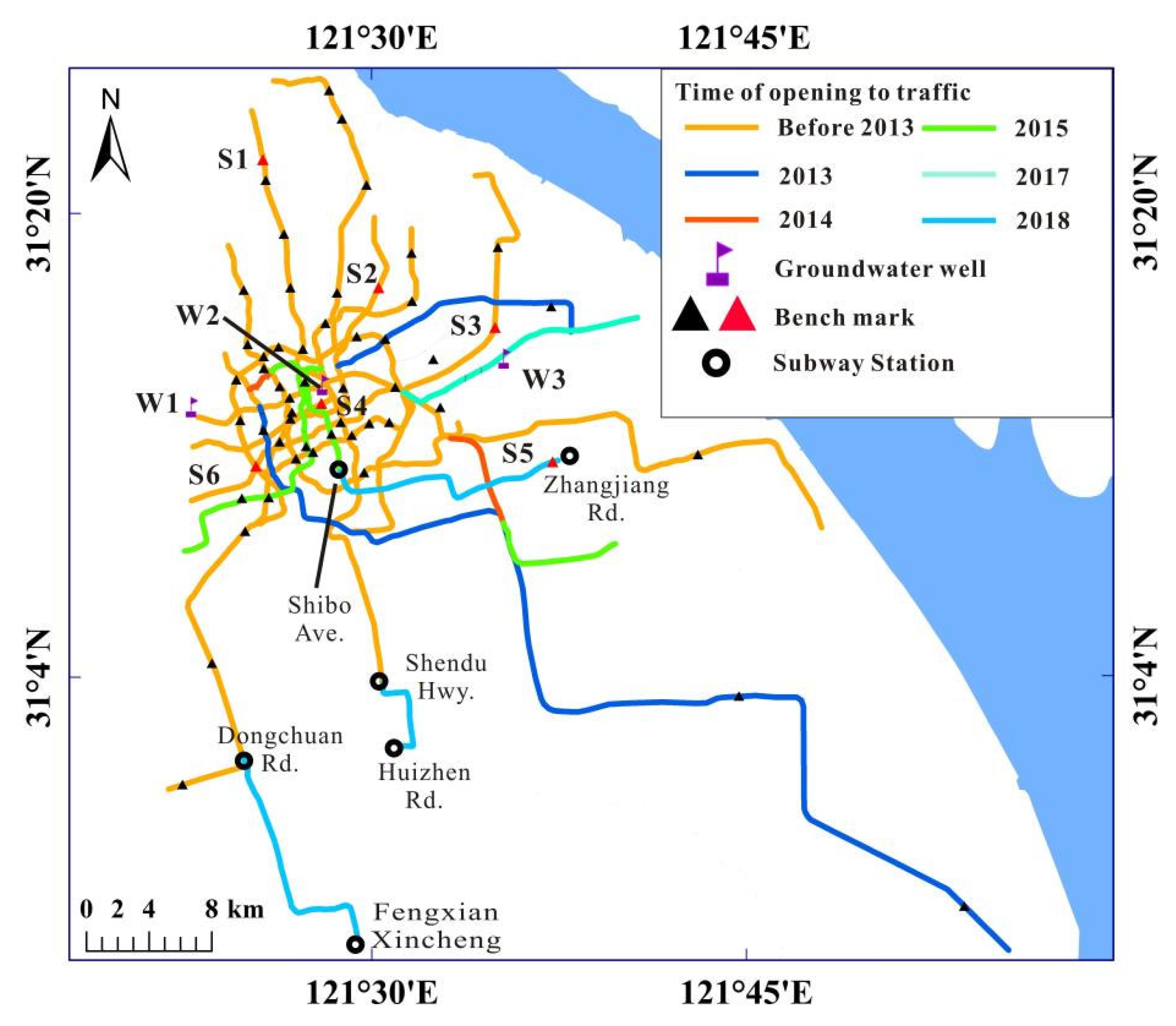
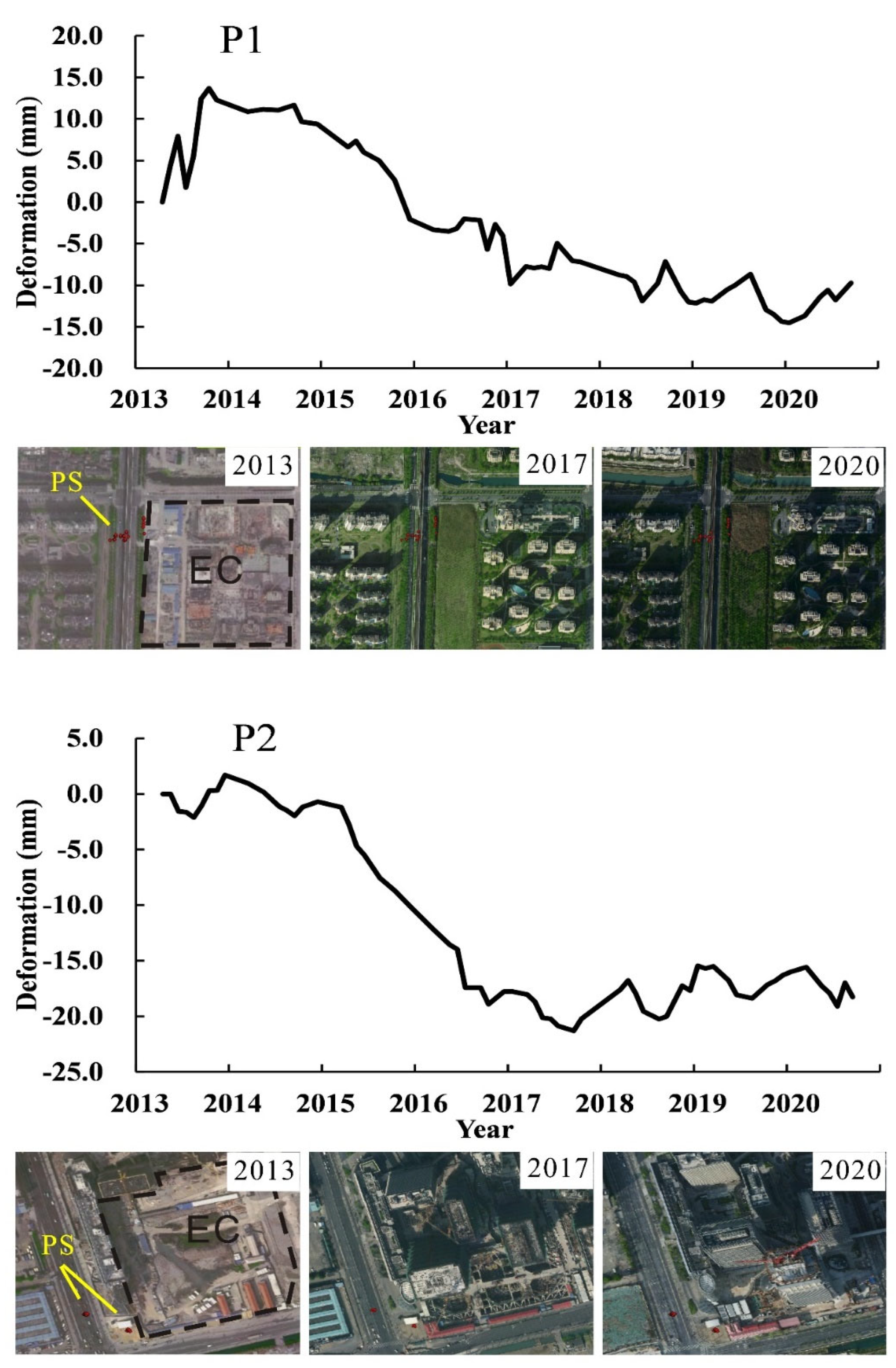
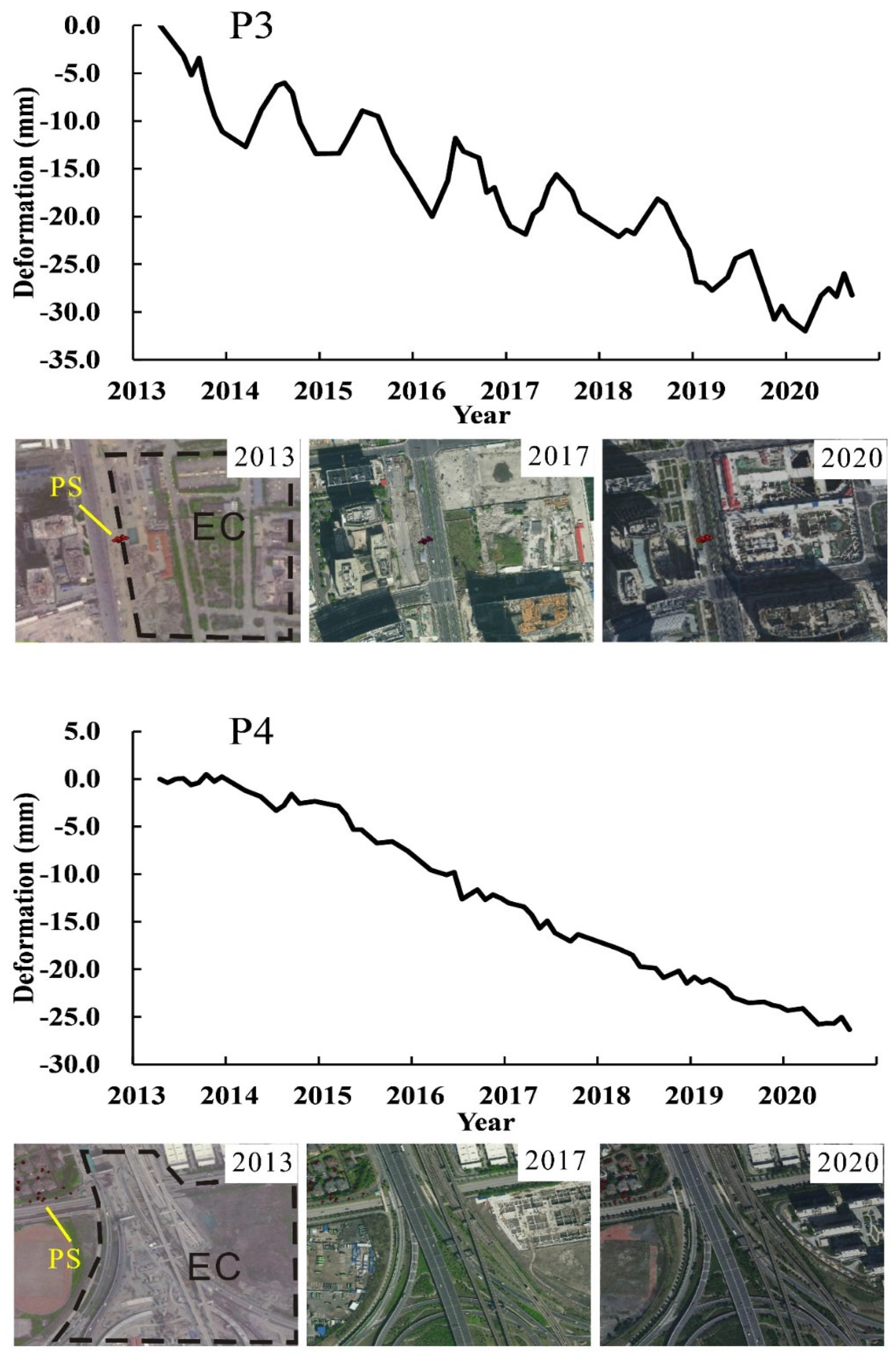
5.1. Impact of Engineering Construction
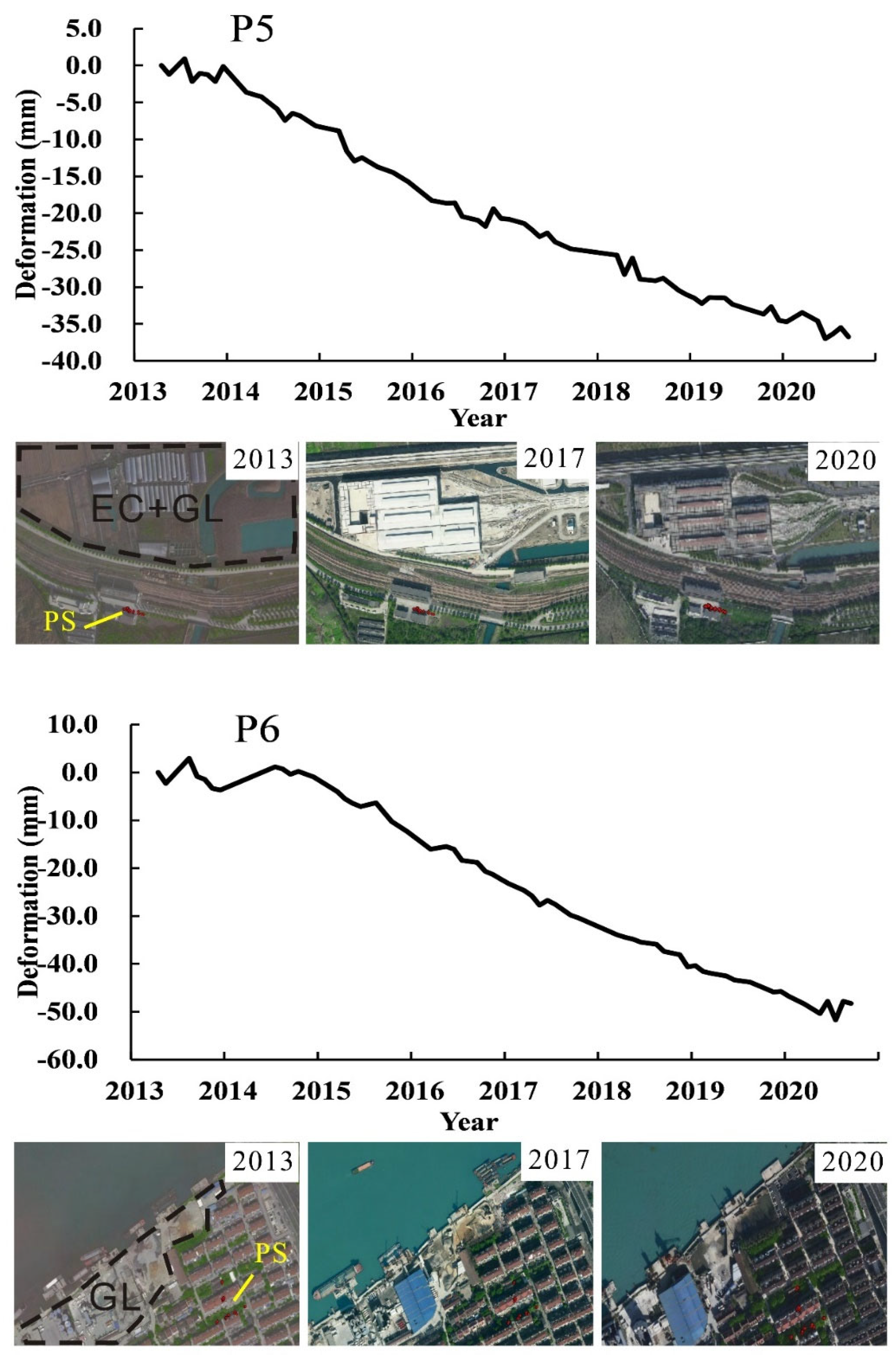
In the process of engineering constructions, it is often accompanied by soil disturbance and foundation pit dewatering, which are the main reasons for inducing the surrounding land subsidence. In addition, the constructed buildingsand roads, the parked subway trains, and concrete materials (P6) mentioned aboveincreased the surface load, leading to soil consolidation and contributing to land subsidence.
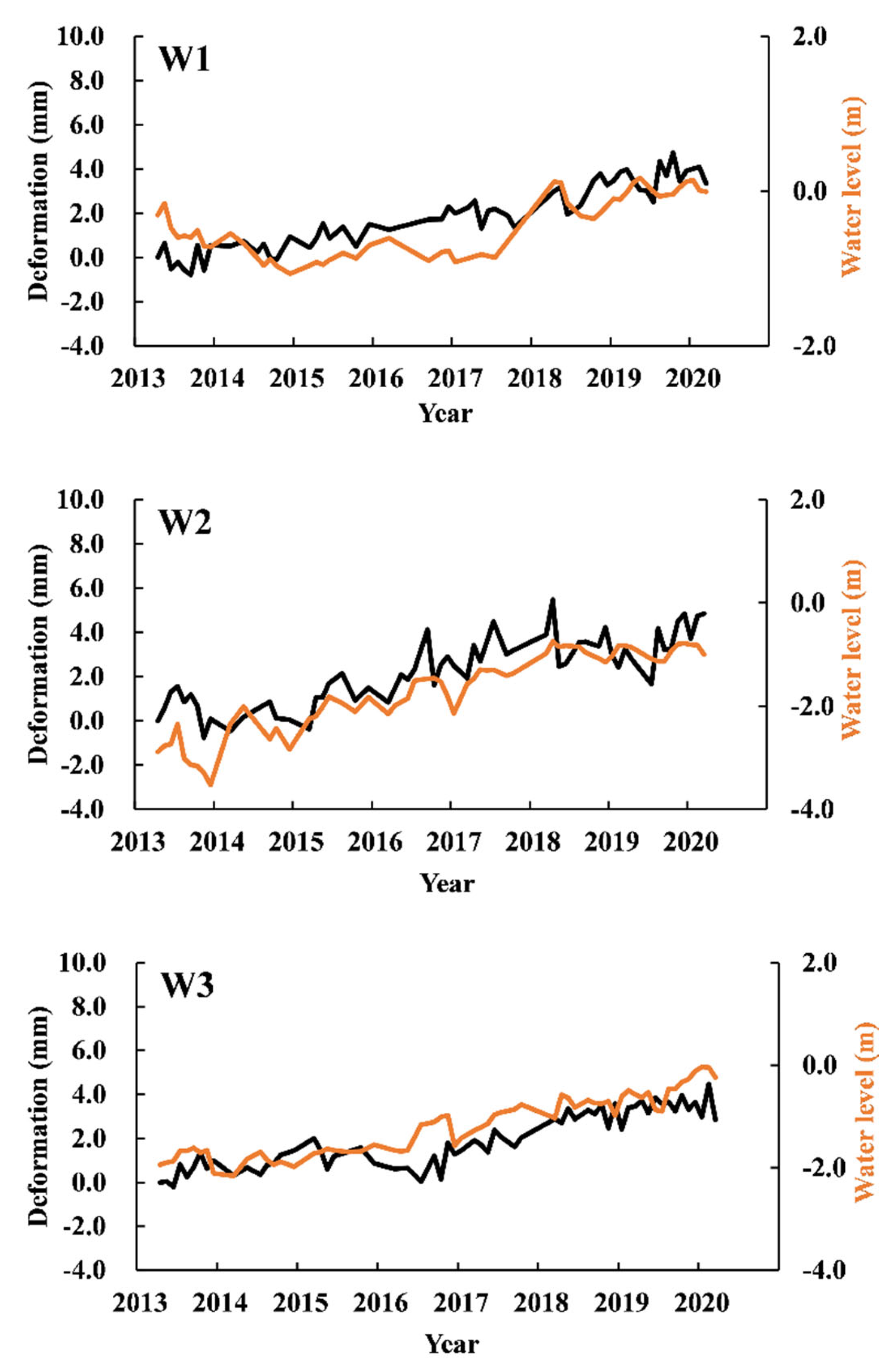
5.2. Impact of the Groundwater Level
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bagheri-Gavkosh, M.; Bagheri, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Sohani, Y.; Homa Ebrahimian, H.; Morovat, F.; Ashrafi, S. Land Subsidence: A Global Challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faunt, C.C.; Sneed, M.; Traum, J.; Brandt, J.T. Water Availability and Land Subsidence in the Central Valley, California, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.X.; Yang, T.L. Suggestions for a Strategy on Land Subsidence Prevention and Control in Shanghai Under the New Situation. Shanghai Land Resour. 2020, 41, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, D.Q. Research on the Key Techniques of SAR Interferometry for Regional Land Subsidence Monitoring; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.X. Comparative Study on Development Background of Land Subsidence Between Shanghai, China and Hanoi, Vietnam. Shanghai Land Resour. 2022, 43, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.K.; Ye, S.J.; Yan, X.X.; Yang, T.L.; Huang, X.L. Subsidence Characteristics, Groundwater Pumping, and Recharge of Land Subsidence Prevention and Control Zone in Shanghai. Shanghai Land Resour. 2021, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gezgin, C. The Influence of Ggroundwater Levels on Land Subsidence in Karaman (Turkey) Using the PS-InSAR Technique. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 70, 3568–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, O.; Golkarian, A.; Biggs, T.; Keesstra, S.; Mohammadi, F.; Daliakopoulos, I.N. Land Subsidence Hazard Modeling: Machine Learning to Identify Predictors and the Role of Human Activities. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.H.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, K.Y.; Chen, W.L.; Wang, X.C.; Li, H.J.; Liu, J.L.; Kou, P.L. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Surface Response of Land Subsidence over a Large-scale Land Creation Area on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 111, 102835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.T. The Main Causes of Land Subsidence in Ho Chi Minh City. Procedia Eng. 2016, 142, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, G.; Vilardo, G.; Terranova, C. Multiple Causes of Ground Deformation in the Napoli Metropolitan Area (Italy) from Integrated Persistent Scatterers DinSAR, Geological, Hydrological, and Urban Infrastructure Data. Earth-Sci. Rev. Int. Geol. J. Bridg. Gap Res. Artic. Textb. 2015, 146, 105–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, P.P.; Jia, C.; Di, S.T.; Wu, J.; Wei, R.C. Analysis and Evaluation of Land Subsidence along Linear Engineering Based on InSAR Data. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 3477–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.Y.; Yang, C.S.; Sun, Q.F.; Chen, W.R. Monitoring Land Subsidence in the Southern Part of the Lower Liaohe Plain, China with a Multi-track PS-InSAR Technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 188, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.L.; Xu, Y. Research Ttrends in internationnal Land Subsidence and Urban Security: An Overview of the First International Symposium on Urban Geology. Shanghai Land Resour. 2017, 38, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.G.; Wei, Z.X. Past, Present and Future Research on Land Subsidence in Shanghai City. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2002, 5, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, S.L. Review on Land Subsidence Research of Shanghai. Shanghai Geogloy 2006, 27, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, X.; Wang, H.M.; Yang, T.L.; Fang, Z.; Lin, J.X.; Zhang, H. Regionalization of Land Subsidence Prevention Based on the Consideration of Uncontrollable Factors. Shanghai Land Resour. 2017, 38, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Li, J.H.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Zhu, Z.L.; Lv, J.J. Analysis of Time-series InSAR-based Subsidence Monitoring along the 2018-2020 Metro Line in Shanghai Area. Geod. Geodyn. 2021, 41, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.J.; Li, Z.W.; Hu, J. Research Progress and Methods of InSAR for Ddeformation Monitoring. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1717–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, M.S.; Wang, R.; Yang, S.M.; Wang, N.; Qin, X.Q.; Yang, T.L. Techniques and Applications of Spaceborne Time-series InSAR in Urban Dynamic Monitoring. J. Radars 2020, 9, 409–424. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, G.H.; Ke, C.Q.; Zhang, J.H.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhao, J.M.; Lee, H. Surface Deformation Monitoring of Shanghai Based on ENVISAT ASAR and Sentinel-1A Data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.S.; Wang, R.; Li, M.H.; Liao, M.S. A PSI Targets Characterization Approach to Interpreting Surface Displacement Signals: A Case Study of the Shanghai Metro Tunnels. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Ma, P.F.; Wang, W.X. Urban Infrastructure Health Monitoring with Spaceborne Multi-temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1421–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.H.; Bie, W.P.; Bo, Z.Y.; Li, C.Q.; Zheng, K.; Lang, B. Urban Underground Rail Transit Subsidence and Disaster Monitoring Based on InSAR. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2020, 2, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Barla, G.; Tamburini, A.; Conte, S.D.; Giannico, C. InSAR Monitoring of Tunnel Induced Ground Movements. Geomech. Tunn. 2016, 9, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.L.; Wang, H.M.; Wu, J.Z.; Lu, L.J.; Wang, Y. Application Research on Monitoring Land Subsidence Research in Shanghai Using InSAR Technology. Shanghai Geogloy 2009, 2, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Yang, M.S.; Dong, J.; Liao, M.S. Investigating Deformation Along Metro Lines in Coastal Cities Considering Dfferent Structures With InSAR and SBM Analyses. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 115, 103099. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.S.; Zhu, J.J.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.W. Study on Two Pass D-InSAR Using SRTM Data for Urban Land Subsidence Measurement. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2009, 34, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Liao, M.S.; Li, D.R.; Wei, Z.X.; Fang, Z. Subsidence Velocity Retrieval from Long-term Coherent Targets in Radar Interferometric Stacks. Chin. J. Geophys. 2007, 50, 598–604. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.S.; Jiang, Y.N.; Liao, M.S.; Wang, H.M. The Analysis of the Subsidence Patterns in Lingang New City (Shanghai) Using High-resolution SAR images. Shanghai Land Resour. 2013, 34, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.Q.; Yang, M.S.; Wang, H.M.; Yang, T.L.; Lin, J.X.; Liao, M.S. Exploring Temporal-Spatial Characteristics of Shanghai Road Networks Subsidence with Multi-temporal PS-InSAR Technique. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2016, 45, 713–721. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H. Persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar for crustal deformation analysis, with application to Volcán Alcedo. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.Q.; Yang, T.L.; Yang, M.S.; Zhang, L.; Liao, M.S. Health Diagnosis of Major Transportation Infrastructures in Shanghai Metropolis Using High-Resolution Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Sensors 2017, 17, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Li, T.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Singleton, A. Extracting Vertical Displacement Rates in Shanghai (China) with Multi-Platform SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9542–9562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, G.; Wang, Q.; Yang, T.L.; Liu, M.; Gao, W.; Falabella, F.; Mastro, P.; Pepe, A. Generation of Long-term InSAR Ground Displacement Time-series Through a Novel Multi-sensor Data Merging Technique: The Case Study of the Shanghai Coastal Area. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 154, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.X.; Zhai, G.Y.; Yan, X.X. Shanghai Urban Geology; Geology Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Zi, H.B. Explorations and Practices of Rail Transit Multi-level network Integration Planning in Shanghai. J. Transp. Eng. 2020, 5, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, W.P.; Bian, H.; Yan, W.D.; Zheng, G.; Lv, Y. System Characteristics and Application Analysis of TerraSAR-X Radar Satellite. Radar Sci. Technol. 2009, 7, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent Scatterers in SAR Interferometry. J. Traps. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.S.; Wang, T. Time-Series InSAR Technology and Application; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.Y. Research on Regional Subsidence Monitoring along High-Speed Railway Using MT-InSAR Technique; Beijing Jiaotong University: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, Z.; Qin, J.; Xian, L.; Zhang, D.; Huang, L. Surface Deformation Mechanism Analysis in Shanghai Areas Based on TS-InSAR Technology. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liao, M.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Xiong, F.; Liu, S.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X. Elastic and Inelastic Ground Deformation in Shanghai Lingang Area Revealed by Sentinel-1, Leveling, and Groundwater Level Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.L.; Li, L.Z.; Zhu, H.F.; Kong, Y.; Hu, X.F. Shanghai Water Resources Bulletin in 2020; Shanghai Water Authority: Shanghai China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
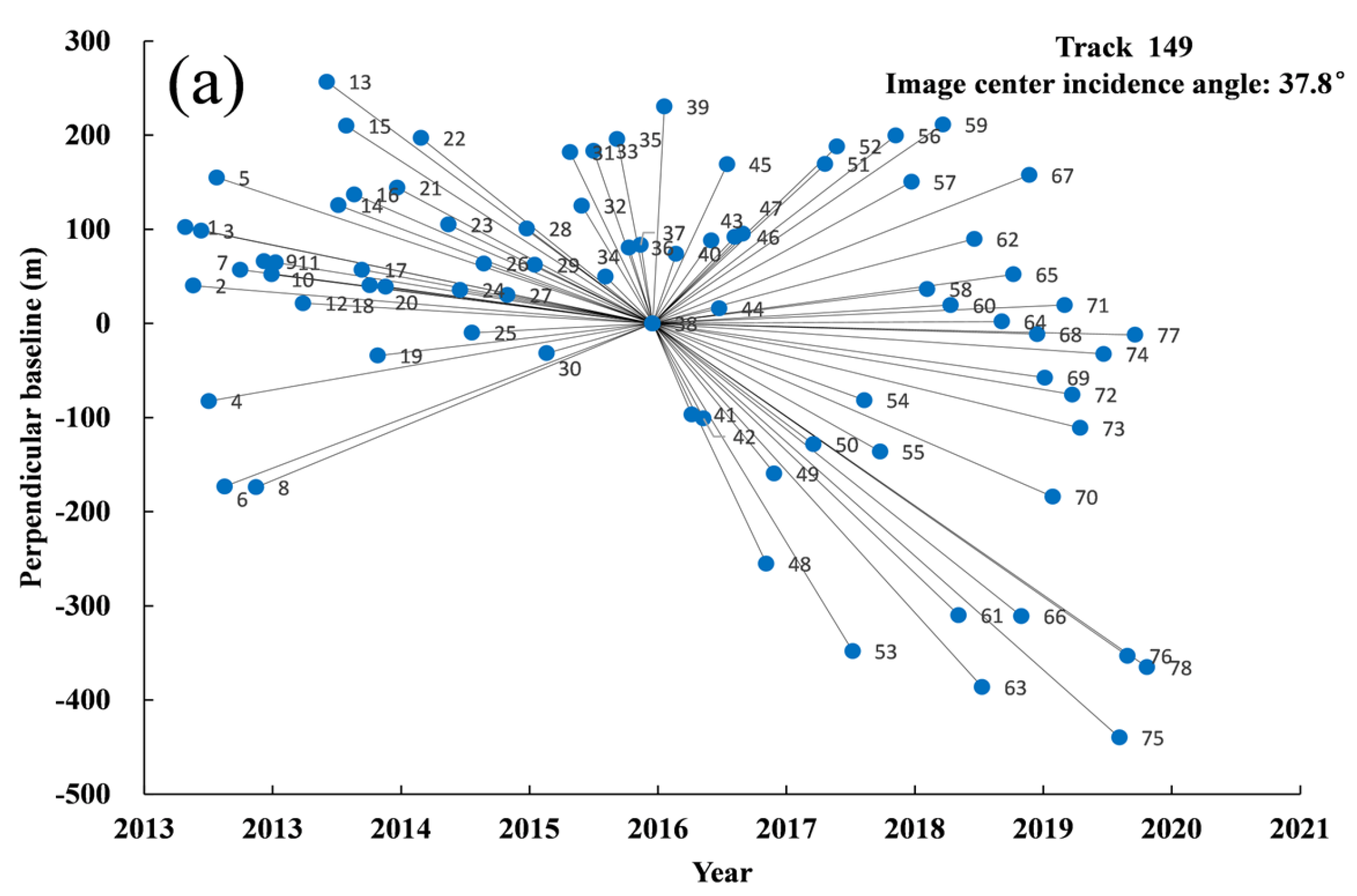
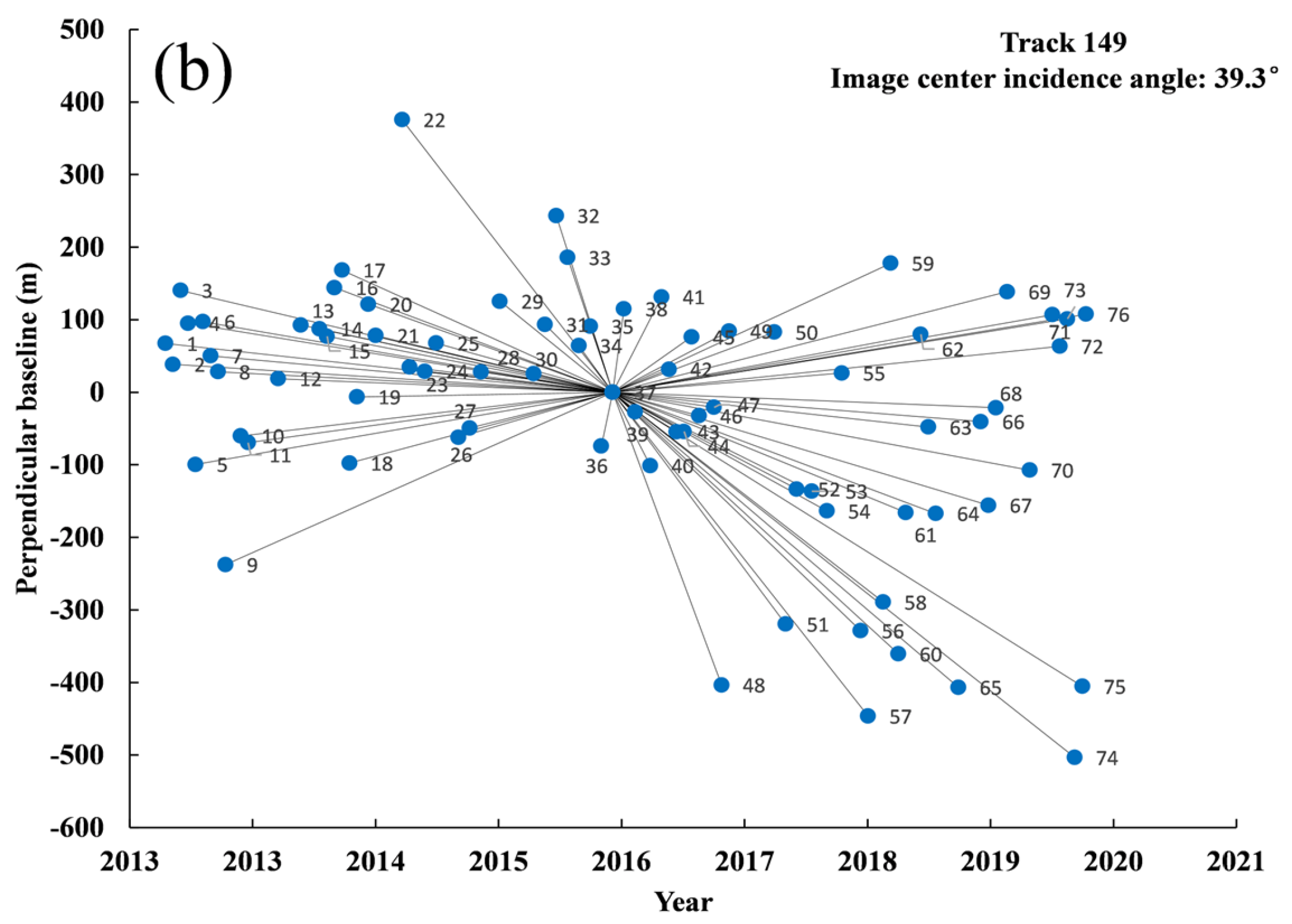
| Track 149 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Image Center Incidence Angle: 39.3°) | (Image Center Incidence Angle: 37.8°) | ||||||
| No. | Acquisition Time | Time Baseline | Perpendicular Baseline | No. | Acquisition Time | Time Baseline | Perpendicular Baseline |
| 1 | 20130416 | −1309 | 67.3 | 1 | 20130427 | −1309 | 102.4 |
| 2 | 20130508 | −1287 | 38.4 | 2 | 20130519 | −1287 | 40.2 |
| 3 | 20130530 | −1265 | 140.4 | 3 | 20130610 | −1265 | 98.6 |
| 4 | 20130621 | −1243 | 95.0 | 4 | 20130702 | −1243 | −82.5 |
| 5 | 20130713 | −1221 | −99.6 | 5 | 20130724 | −1221 | 155.0 |
| 6 | 20130804 | −1199 | 97.3 | 6 | 20130815 | −1199 | −173.3 |
| 7 | 20130826 | −1177 | 50.2 | 7 | 20130928 | −1155 | 57.1 |
| 8 | 20130917 | −1155 | 28.2 | 8 | 20131111 | −1111 | −174.0 |
| 9 | 20131009 | −1133 | −237.5 | 9 | 20131203 | −1089 | 66.1 |
| 10 | 20131122 | −1089 | −60.2 | 10 | 20131225 | −1067 | 52.2 |
| 11 | 20131214 | −1067 | −69.4 | 11 | 20140105 | −1056 | 64.8 |
| 12 | 20140312 | −979 | 18.6 | 12 | 20140323 | −979 | 21.5 |
| 13 | 20140517 | −913 | 92.6 | 13 | 20140528 | −913 | 256.8 |
| 14 | 20140711 | −858 | 87.4 | 14 | 20140630 | −880 | 125.6 |
| 15 | 20140802 | −836 | 77.0 | 15 | 20140722 | −858 | 210.0 |
| 16 | 20140824 | −814 | 144.1 | 16 | 20140813 | −836 | 137.0 |
| 17 | 20140915 | −792 | 168.3 | 17 | 20140904 | −814 | 57.1 |
| 18 | 20141007 | −770 | −97.6 | 18 | 20140926 | −792 | 40.6 |
| 19 | 20141029 | −748 | −6.4 | 19 | 20141018 | −770 | −34.2 |
| 20 | 20141201 | −715 | 121.4 | 20 | 20141109 | −748 | 39.0 |
| 21 | 20141223 | −693 | 78.1 | 21 | 20141212 | −715 | 144.1 |
| 22 | 20150310 | −616 | 375.6 | 22 | 20150216 | −649 | 197.0 |
| 23 | 20150401 | −594 | 34.6 | 23 | 20150504 | −572 | 105.0 |
| 24 | 20150515 | −550 | 28.8 | 24 | 20150606 | −539 | 35.5 |
| 25 | 20150617 | −517 | 67.7 | 25 | 20150709 | −506 | −9.9 |
| 26 | 20150822 | −451 | −62.0 | 26 | 20150811 | −473 | 63.7 |
| 27 | 20150924 | −418 | −49.3 | 27 | 20151016 | −407 | 30.2 |
| 28 | 20151027 | −385 | 28.1 | 28 | 20151210 | −352 | 100.7 |
| 29 | 20151221 | −330 | 125.3 | 29 | 20160101 | −330 | 62.2 |
| 30 | 20160329 | −231 | 25.4 | 30 | 20160203 | −297 | −31.6 |
| 31 | 20160501 | −198 | 93.5 | 31 | 20160409 | −231 | 181.9 |
| 32 | 20160603 | −165 | 243.3 | 32 | 20160512 | −198 | 124.9 |
| 33 | 20160706 | −132 | 185.7 | 33 | 20160614 | −165 | 183.3 |
| 34 | 20160808 | −99 | 64.1 | 34 | 20160717 | −132 | 49.8 |
| 35 | 20160910 | −66 | 91.0 | 35 | 20160819 | −99 | 195.8 |
| 36 | 20161013 | −33 | −74.0 | 36 | 20160921 | −66 | 80.6 |
| 37 | 20161115 | 0 | 0.0 | 37 | 20161024 | −33 | 83.3 |
| 38 | 20161218 | 33 | 115.0 | 38 | 20161126 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 39 | 20170120 | 66 | −27.2 | 39 | 20161229 | 33 | 230.5 |
| 40 | 20170305 | 110 | −101.2 | 40 | 20170131 | 66 | 74.1 |
| 41 | 20170407 | 143 | 131.3 | 41 | 20170316 | 110 | −96.8 |
| 42 | 20170429 | 165 | 31.7 | 42 | 20170418 | 143 | −101.0 |
| 43 | 20170521 | 187 | −54.5 | 43 | 20170510 | 165 | 88.0 |
| 44 | 20170612 | 209 | −54.1 | 44 | 20170601 | 187 | 15.9 |
| 45 | 20170704 | 231 | 76.3 | 45 | 20170623 | 209 | 169.0 |
| 46 | 20170726 | 253 | −32.4 | 46 | 20170715 | 231 | 92.0 |
| 47 | 20170908 | 297 | −20.8 | 47 | 20170806 | 253 | 95.5 |
| 48 | 20170930 | 319 | −403.4 | 48 | 20171011 | 319 | −255.3 |
| 49 | 20171022 | 341 | 84.3 | 49 | 20171102 | 341 | −159.4 |
| 50 | 20180303 | 473 | 82.8 | 50 | 20180220 | 451 | −128.3 |
| 51 | 20180405 | 506 | −319.6 | 51 | 20180325 | 484 | 169.3 |
| 52 | 20180508 | 539 | −133.5 | 52 | 20180427 | 517 | 188.1 |
| 53 | 20180621 | 583 | −136.5 | 53 | 20180610 | 561 | −348.2 |
| 54 | 20180804 | 627 | −163.6 | 54 | 20180713 | 594 | −81.5 |
| 55 | 20180917 | 671 | 26.4 | 55 | 20180826 | 638 | −136.1 |
| 56 | 20181111 | 726 | −328.7 | 56 | 20181009 | 682 | 199.7 |
| 57 | 20181203 | 748 | −446.3 | 57 | 20181122 | 726 | 150.4 |
| 58 | 20190116 | 792 | −289.3 | 58 | 20190105 | 770 | 36.5 |
| 59 | 20190207 | 814 | 177.8 | 59 | 20190218 | 814 | 211.4 |
| 60 | 20190301 | 836 | −360.5 | 60 | 20190312 | 836 | 19.5 |
| 61 | 20190323 | 858 | −165.8 | 61 | 20190403 | 858 | −310.0 |
| 62 | 20190506 | 902 | 79.9 | 62 | 20190517 | 902 | 89.8 |
| 63 | 20190528 | 924 | −48.0 | 63 | 20190608 | 924 | −386.4 |
| 64 | 20190619 | 946 | −167.2 | 64 | 20190802 | 979 | 2.0 |
| 65 | 20190824 | 1012 | −406.7 | 65 | 20190904 | 1012 | 52.1 |
| 66 | 20191029 | 1078 | −40.5 | 66 | 20190926 | 1034 | −311.0 |
| 67 | 20191120 | 1100 | −155.8 | 67 | 20191018 | 1056 | 157.6 |
| 68 | 20191212 | 1122 | −21.4 | 68 | 20191109 | 1078 | −11.3 |
| 69 | 20200114 | 1155 | 138.5 | 69 | 20191201 | 1100 | −57.6 |
| 70 | 20200320 | 1221 | −107.4 | 70 | 20191223 | 1122 | −184.1 |
| 71 | 20200525 | 1287 | 106.9 | 71 | 20200125 | 1155 | 19.6 |
| 72 | 20200616 | 1309 | 63.3 | 72 | 20200216 | 1177 | −75.6 |
| 73 | 20200708 | 1331 | 101.1 | 73 | 20200309 | 1199 | −111.1 |
| 74 | 20200730 | 1353 | −503.3 | 74 | 20200514 | 1265 | −32.4 |
| 75 | 20200821 | 1375 | −405.3 | 75 | 20200627 | 1309 | −439.9 |
| 76 | 20200901 | 1386 | 107.5 | 76 | 20200719 | 1331 | −353.1 |
| 77 | 20200810 | 1353 | −12.1 | ||||
| 78 | 20200912 | 1386 | −365.3 | ||||
| Parameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Amplitude dispersion index | 0.3 |
| Weed_max_noise | 1.5 |
| Weed_standard_dev | 1.2 |
| Unwrap_method | ‘3D_quick’ |
| Unwrap_grid_size | 60 |
| Max_topo_err | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Ke, C.; Shen, X.; Lin, J.; Wang, R. Monitoring Land Subsidence along the Subways in Shanghai on the Basis of Time-Series InSAR. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15040908
Zhang J, Ke C, Shen X, Lin J, Wang R. Monitoring Land Subsidence along the Subways in Shanghai on the Basis of Time-Series InSAR. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(4):908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15040908
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jinhua, Changqing Ke, Xiaoyi Shen, Jinxin Lin, and Ru Wang. 2023. "Monitoring Land Subsidence along the Subways in Shanghai on the Basis of Time-Series InSAR" Remote Sensing 15, no. 4: 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15040908
APA StyleZhang, J., Ke, C., Shen, X., Lin, J., & Wang, R. (2023). Monitoring Land Subsidence along the Subways in Shanghai on the Basis of Time-Series InSAR. Remote Sensing, 15(4), 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15040908






