Spatiotemporal and Vertical Distribution of Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer Using Long-Term Multi-Source Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CALIPSO
2.2. SAGEII
2.3. MERRA-2
3. Results
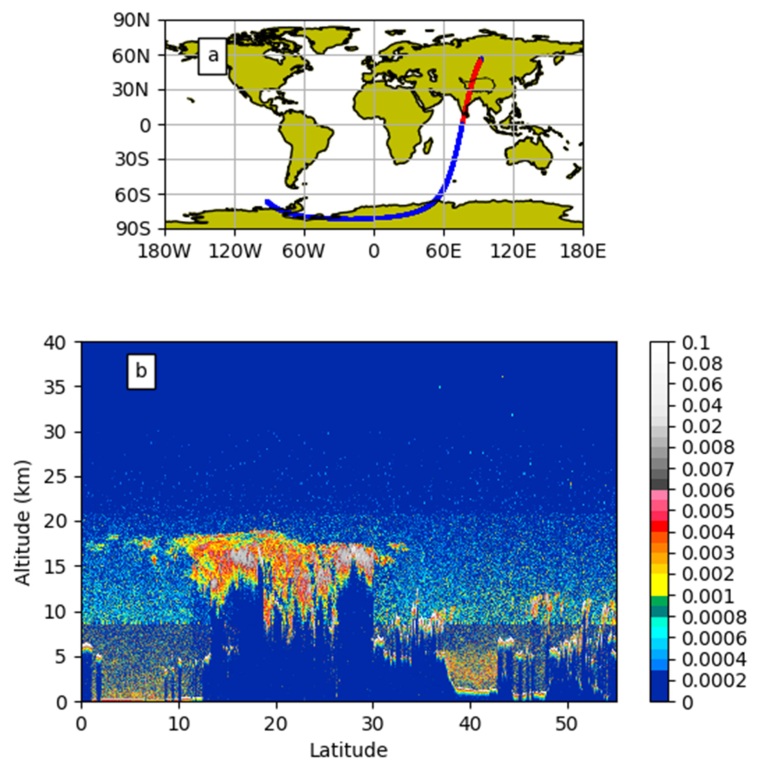
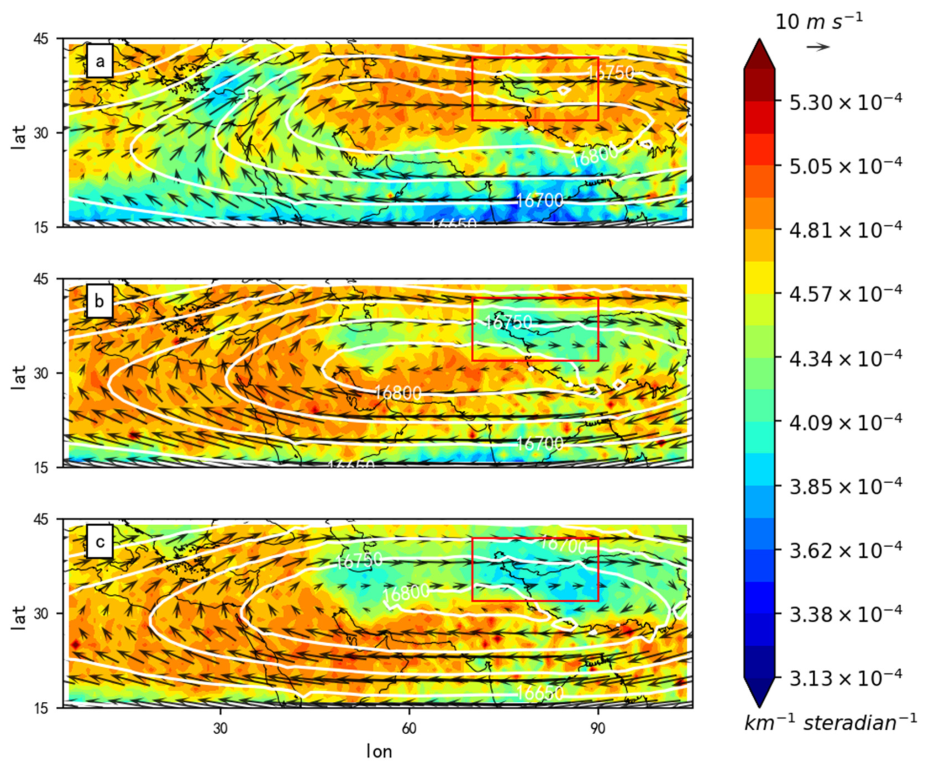
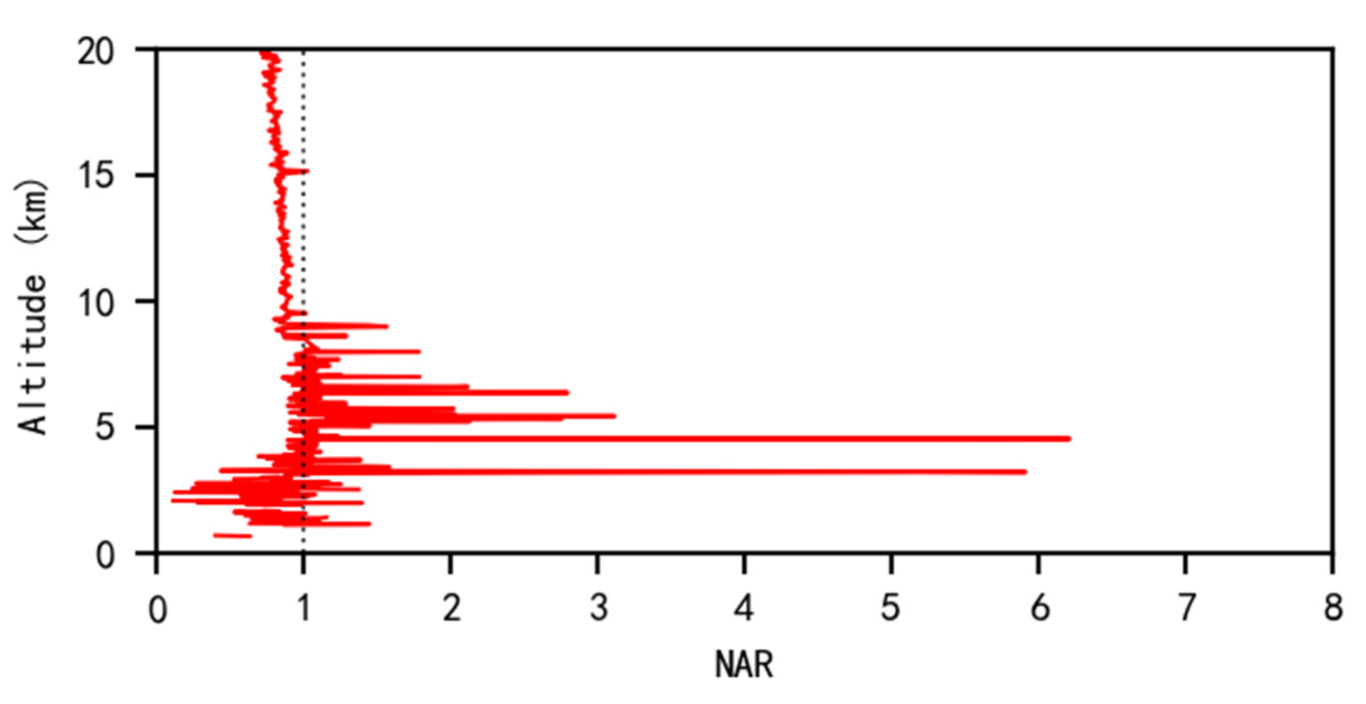
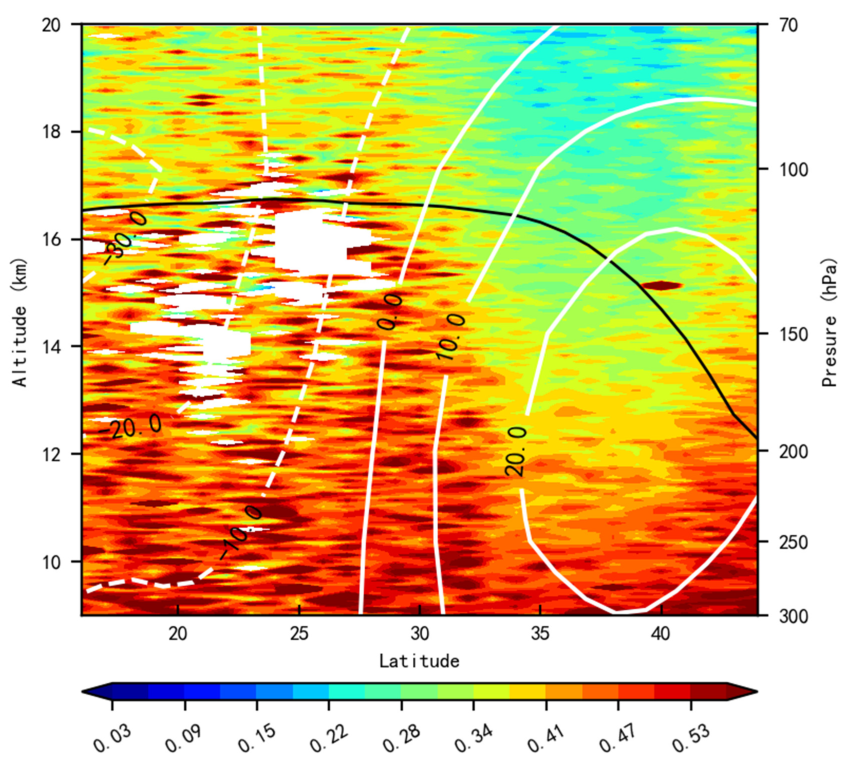
3.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of ATAL
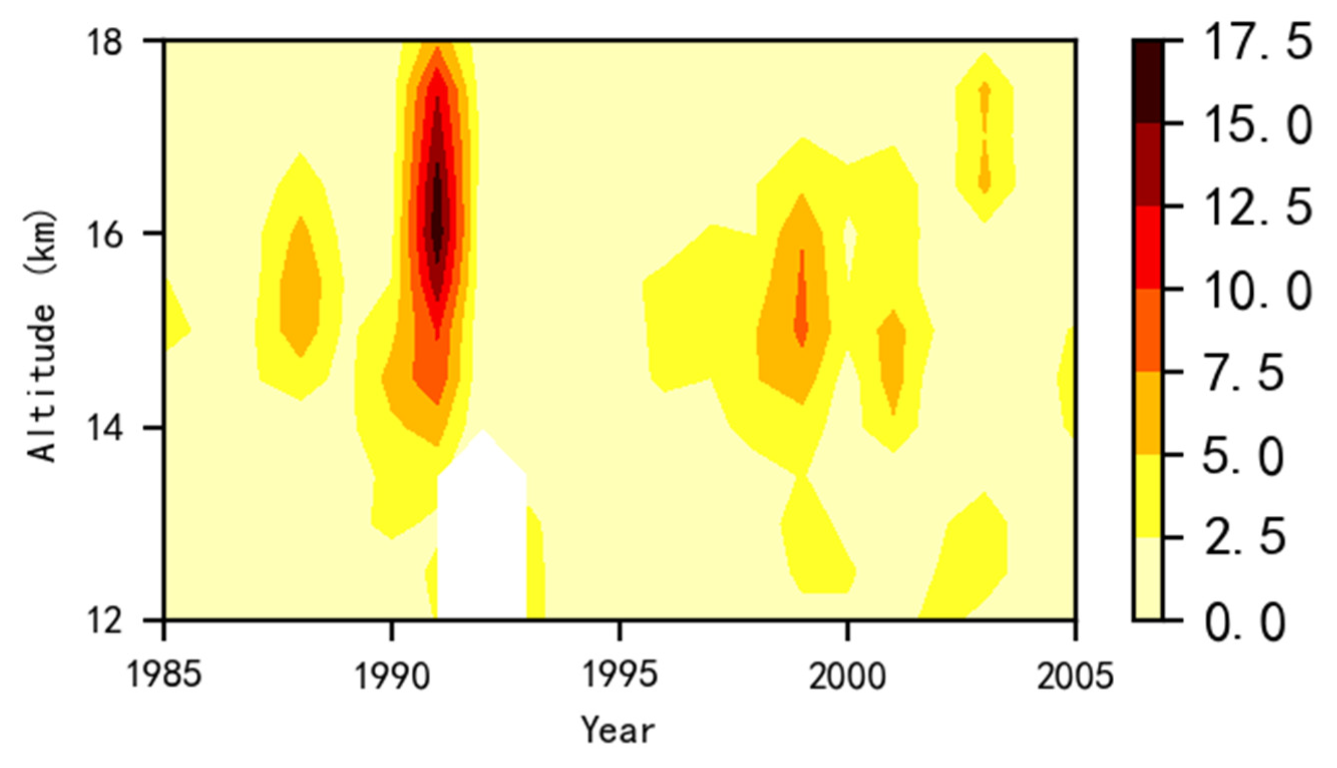
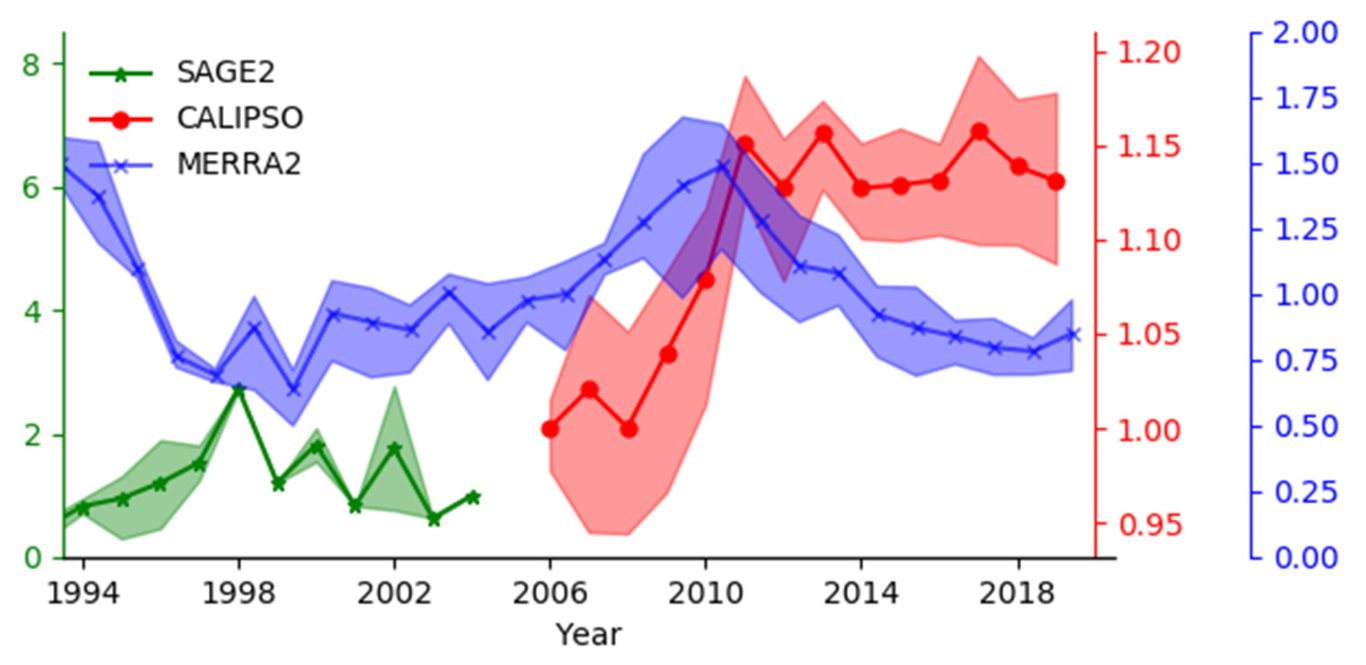
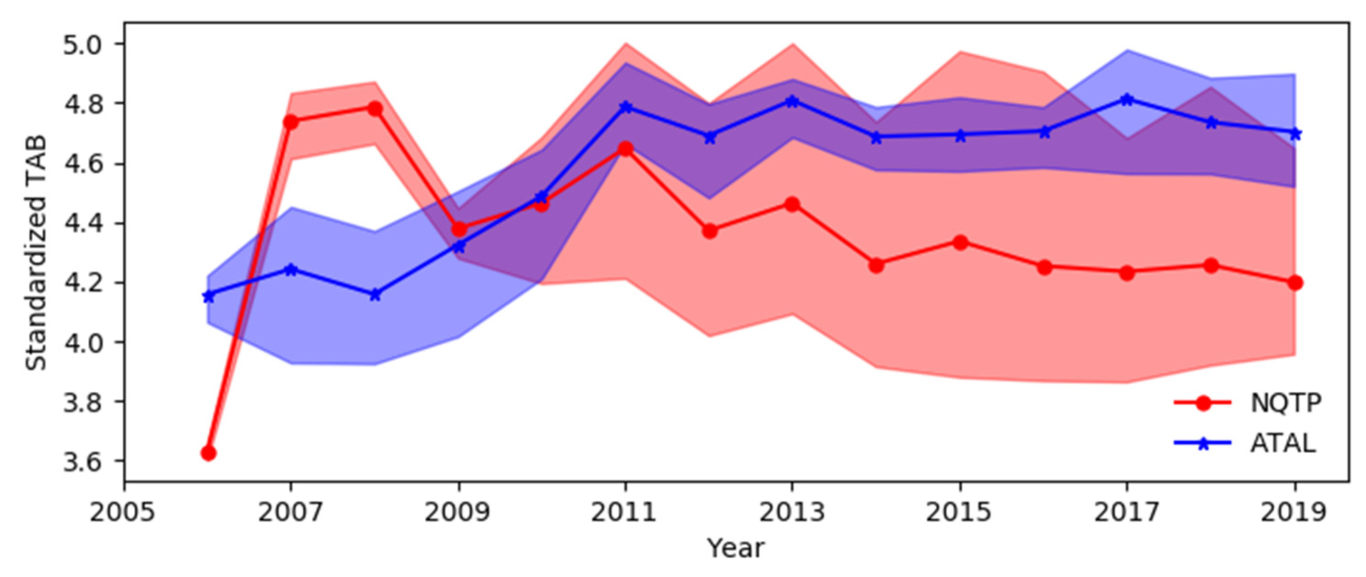
3.2. Temporal Trend of ATAL
4. Discussion
4.1. The North–South Differences (NSDs)
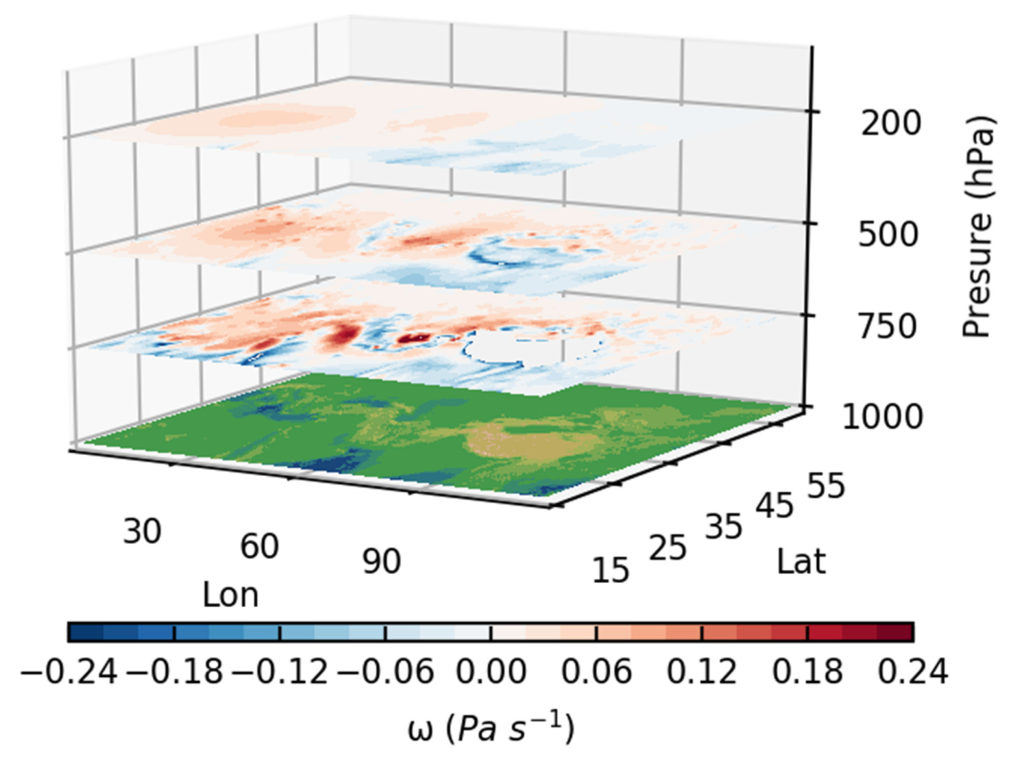
4.2. Causes of NSDs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bucci, S.; Legras, B.; Sellitto, P.; d’Amato, F.; Viciani, S.; Montori, A.; Chiarugi, A.; Ravegnani, F.; Ulanovsky, A.; Cairo, F. Deep-convective influence on the upper troposphere–lower stratosphere composition in the Asian monsoon anticyclone region: 2017 StratoClim campaign results. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12193–12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, W.J.; Park, M.; Emmons, L.; Kinnison, D.; Bernath, P.; Walker, K.A.; Boone, C.; Pumphrey, H. Asian monsoon transport of pollution to the stratosphere. Science 2010, 328, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Agrawal, M. Acid rain and its ecological consequences. J. Environ. Biol. 2007, 29, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Morakinyo, O.M.; Mokgobu, M.I.; Mukhola, M.S.; Hunter, R.P. Health Outcomes of Exposure to Biological and Chemical Components of Inhalable and Respirable Particulate Matter. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Kang, S.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Paudyal, R. Vertical distribution of the Asian tropopause aerosols detected by CALIPSO. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S. Demographic Changes and Economic Growth: Empirical Evidence from Asia. 2013. Available online: https://digitalcommons.iwu.edu/econ_honproj/121 (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Chen, S. Environmental pollution emissions, regional productivity growth and ecological economic development in China. China Econ. Rev. 2015, 35, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, G.; Yang, P. Study on the Sensitivity of Summer Ozone Density to the Enhanced Aerosol Loading over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettelman, A.; Kinnison, D.E.; Dunkerton, T.J.; Brasseur, G.P. Impact of monsoon circulations on the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holton, J.R.; Haynes, P.H.; McIntyre, M.E.; Douglass, A.R.; Rood, R.B.; Pfister, L. Stratosphere-troposphere exchange. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 403–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S. Stratospheric ozone depletion: A review of concepts and history. Rev. Geophys. 1999, 37, 275–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernier, J.P.; Thomason, L.; Kar, J. CALIPSO detection of an Asian tropopause aerosol layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernier, J.P.; Fairlie, T.D.; Natarajan, M.; Wienhold, F.G.; Bian, J.; Martinsson, B.G.; Crumeyrolle, S.; Thomason, L.W.; Bedka, K.M. Increase in upper tropospheric and lower stratospheric aerosol levels and its potential connection with Asian pollution. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 1608–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.S.; Moorthy, K.K.; Manchanda, R.K.; Sinha, P.R.; Satheesh, S.; Vajja, D.P.; Srinivasan, S.; Kumar, V.A. Free tropospheric black carbon aerosol measurements using high altitude balloon: Do BC layers build “their own homes” up in the atmosphere? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.; Ramachandran, S.; Bhavani Kumar, Y.; Narayana Rao, D.; Krishnaiah, M. Features of upper troposphere and lower stratosphere aerosols observed by lidar over Gadanki, a tropical Indian station. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobo, Y.; Iwasaka, Y.; Shi, G.-Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Ohashi, T.; Tamura, K.; Zhang, D. Balloon-borne observations of high aerosol concentrations near the summertime tropopause over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2007, 84, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettelman, A.; Hoor, P.; Pan, L.; Randel, W.; Hegglin, M.I.; Birner, T. The extratropical upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. Rev. Geophys. 2011, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Rosenlof, K.H.; Portmann, R.W.; Daniel, J.S.; Davis, S.M.; Sanford, T.J.; Plattner, G.K. Contributions of stratospheric water vapor to decadal changes in the rate of global warming. Science 2010, 327, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riese, M.; Ploeger, F.; Rap, A.; Vogel, B.; Konopka, P.; Dameris, M.; Forster, P. Impact of uncertainties in atmospheric mixing on simulated UTLS composition and related radiative effects. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossaini, R.; Chipperfield, M.; Montzka, S.; Rap, A.; Dhomse, S.; Feng, W. Efficiency of short-lived halogens at influencing climate through depletion of stratospheric ozone. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckendorn, P.; Weisenstein, D.; Fueglistaler, S.; Luo, B.P.; Rozanov, E.; Schraner, M.; Thomason, L.W.; Peter, T. The impact of geoengineering aerosols on stratospheric temperature and ozone. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 045108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, B.; Robock, A.; Shindell, D.T.; Miller, M.A. Sensitivity of stratospheric geoengineering with black carbon to aerosol size and altitude of injection. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, J.H.; Wu, D.L.; Read, W.G.; Livesey, N.J.; Waters, J.W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Filipiak, M.J.; Davis, C.P. Trapping of Asian pollution by the Tibetan anticyclone: A global CTM simulation compared with EOS MLS observations. Geophys. Res. Lett 2005, 32, L14826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, W.J.; Park, M. Deep convective influence on the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone and associated tracer variability observed with Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Randel, W.J.; Emmons, L.K.; Bernath, P.F.; Walker, K.A.; Boone, C.D. Chemical isolation in the Asian monsoon anticyclone observed in Atmospheric Chemistry Experiment (ACE-FTS) data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernier, J.-P.; Fairlie, T.; Deshler, T.; Ratnam, M.V.; Gadhavi, H.; Kumar, B.; Natarajan, M.; Pandit, A.; Raj, S.A.; Kumar, A.H. BATAL: The balloon measurement campaigns of the Asian tropopause aerosol layer. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 955–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höpfner, M.; Ungermann, J.; Borrmann, S.; Wagner, R.; Spang, R.; Riese, M.; Stiller, G.; Appel, O.; Batenburg, A.M.; Bucci, S. Ammonium nitrate particles formed in upper troposphere from ground ammonia sources during Asian monsoons. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadnavis, S.; Semeniuk, K.; Pozzoli, L.; Schultz, M.; Ghude, S.; Das, S.; Kakatkar, R. Transport of aerosols into the UTLS and their impact on the Asian monsoon region as seen in a global model simulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8771–8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Toon, O.B.; Neely, R.R.; Martinsson, B.G.; Brenninkmeijer, C.A. Composition and physical properties of the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer and the North American Tropospheric Aerosol Layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 2540–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadnavis, S.; Kalita, G.; Kumar, K.R.; Gasparini, B.; Li, J.-L.F. Potential impact of carbonaceous aerosol on the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) and precipitation during Asian summer monsoon in a global model simulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 11637–11654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairlie, T.D.; Liu, H.; Vernier, J.P.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Jimenez, J.L.; Jo, D.S.; Zhang, B.; Natarajan, M.; Avery, M.A.; Huey, G. Estimates of regional source contributions to the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer using a chemical transport model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Liao, H.; Bian, J. Summertime nitrate aerosol in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere over the Tibetan Plateau and the South Asian summer monsoon region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 6641–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Ratnam, M.V.; Madhavan, B.; Prasad, P.; Narayanamurthy, C. Vertical and spatial distribution of elevated aerosol layers obtained using long-term ground-based and space-borne lidar observations. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xia, X.; Che, H.; Wang, J.; Cong, Z.; Zhao, T.; Kang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y. Spatiotemporal variation of aerosol and potential long-range transport impact over the Tibetan Plateau, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 14637–14656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, H.A. ATMOS version 3 water vapor measurements: Comparisons with observations from two ER-2 Lyman-α hygrometers, MkIV, HALOE, SAGE II, MAS, and MLS. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, ACH-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, G.; Thomason, L.W.; Burton, S.P. Comparison of Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE) II version 6.2 water vapor with balloon-borne and space-based instruments. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, M.; Poole, L.; McCormick, M. SAGE II observations of polar stratospheric clouds near 50°N January 31–February 2, 1989. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Mohnen, V.A.; Yue, G.K.; Jäger, H. Intercomparison of multiplatform stratospheric aerosol and ozone observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16127–16136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunnold, D.; Wang, H.; Thomason, L.; Zawodny, J.; Logan, J.; Megretskaia, I. SAGE (version 5.96) ozone trends in the lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 4445–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labitzke, K.; McCormick, M. Stratospheric temperature increases due to Pinatubo aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Genio, A.D.; Kovari, W., Jr.; Yao, M.S. Climatic implications of the seasonal variation of upper troposphere water vapor. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 2701–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, L.; Vernier, J.-P. Improved SAGE II cloud/aerosol categorization and observations of the Asian tropopause aerosol layer: 1989–2005. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4605–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, P.; Mejia, J.F. Impact of transported dust aerosols on precipitation over the Nepal Himalayas using convection-permitting WRF-Chem simulation. Atmos. Environ. X 2022, 15, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchard, V.; Randles, C.; Da Silva, A.; Darmenov, A.; Colarco, P.; Govindaraju, R.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; Beyersdorf, A.; Ziemba, L. The MERRA-2 aerosol reanalysis, 1980 onward. Part II: Evaluation and case studies. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6851–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichle, R.H.; Liu, Q.; Koster, R.D.; Draper, C.S.; Mahanama, S.P.; Partyka, G.S. Land surface precipitation in MERRA-2. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 1643–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R. The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provençal, S.; Buchard, V.; da Silva, A.M.; Leduc, R.; Barrette, N. Evaluation of PM surface concentrations simulated by Version 1 of NASA’s MERRA Aerosol Reanalysis over Europe. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, G.; Ratnam, M.V.; Kishore, P. Asian summer monsoon anticyclone: Trends and variability. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6789–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manney, G.L.; Santee, M.L.; Lawrence, Z.D.; Wargan, K.; Schwartz, M.J. A moments view of climatology and variability of the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 7821–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Smolik, J.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Kulmala, M. Modeling dry deposition of aerosol particles onto rough surfaces. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knote, C.; Hodzic, A.; Jimenez, J. The effect of dry and wet deposition of condensable vapors on secondary organic aerosols concentrations over the continental US. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, B.; Lohmann, U.; Martin, R.V.; Stier, P.; Wurzler, S.; Feichter, J.; Hoose, C.; Heikkilä, U.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Ferrachat, S. Influences of in-cloud aerosol scavenging parameterizations on aerosol concentrations and wet deposition in ECHAM5-HAM. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 1511–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.K.M.; Yuan, C.; Li, Z. Origin, Maintenance and Variability of the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer (ATAL): The Roles of Monsoon Dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.; Noel, V.; Chepfer, H. Properties of cirrus and subvisible cirrus from nighttime Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization (CALIOP), related to atmospheric dynamics and water vapor. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adcock, K.E.; Fraser, P.J.; Hall, B.D.; Langenfelds, R.L.; Lee, G.; Montzka, S.A.; Oram, D.E.; Röckmann, T.; Stroh, F.; Sturges, W.T. Aircraft-based observations of ozone-depleting substances in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere in and above the Asian summer monsoon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, G.; Kumar, S. Vertical structure of cumulonimbus towers and intense convective clouds over the South Asian region during the summer monsoon season. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 1710–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnis, P.; Harrison, E.F.; Stowe, L.L.; Gibson, G.G.; Denn, F.M.; Doelling, D.R.; Smith, W.L., Jr. Radiative climate forcing by the mount pinatubo eruption. Science 1993, 259, 1411–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soden, B.J.; Wetherald, R.T.; Stenchikov, G.L.; Robock, A. Global cooling after the eruption of Mount Pinatubo: A test of climate feedback by water vapor. Science 2002, 296, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossolasco, A.; Jegou, F.; Sellitto, P.; Berthet, G.; Kloss, C.; Legras, B. Global modeling studies of composition and decadal trends of the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 2745–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Lau, W.K.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M. Relationship between Asian monsoon strength and transport of surface aerosols to the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer (ATAL): Interannual variability and decadal changes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1901–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; Fan, H.; Huang, J.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kang, S.; Cong, Z.; Letu, H.; Menenti, M. Aerosol characteristics and impacts on weather and climate over the Tibetan Plateau. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.; Kim, M.; Kim, K. Asian summer monsoon anomalies induced by aerosol direct forcing: The role of the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2006, 26, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, R.; Liu, H.; Huang, Z.; Wu, T.; Hu, G.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Du, Y.; Yang, S. The Surface Energy Budget and Its Impact on the Freeze-thaw Processes of Active Layer in Permafrost Regions of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, R.; Huang, Z.; Wu, T.; Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, H.; Hu, G.; Xiao, Y.; Du, Y. Evaluation and spatio-temporal analysis of surface energy flux in permafrost regions over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and Arctic using CMIP6 models. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 1948–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.; Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, P. Weather and climate effects of the Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; He, B.; Bao, Q.; Duan, A.; Jin, F.-F. Thermal controls on the Asian summer monsoon. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Hu, Y.; Wright, J.S.; Jiang, J.H.; Dickinson, R.E.; Chen, M.; Filipiak, M.; Read, W.G.; Waters, J.W.; Wu, D.L. Short circuit of water vapor and polluted air to the global stratosphere by convective transport over the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5664–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissier, A.-S.; Legras, B. Convective sources of trajectories traversing the tropical tropopause layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3383–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Randel, W.J.; Emmons, L.K.; Livesey, N.J. Transport pathways of carbon monoxide in the Asian summer monsoon diagnosed from Model of Ozone and Related Tracers (MOZART). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Bai, Z.; Xia, X.; Chen, B.; Zong, X.; Bian, J. In situ measurements and backward-trajectory analysis of high-concentration, fine-mode aerosols in the UTLS over the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 124068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. China: The third pole. Nature 2008, 454, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Li, D.; Bai, Z.; Li, Q.; Lyu, D.; Zhou, X. Transport of Asian surface pollutants to the global stratosphere from the Tibetan Plateau region during the Asian summer monsoon. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Ma, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mu, H.; Cheng, T.; He, R.; Huang, G.; Liu, D. Formation and dissipation dynamics of the Asian tropopause aerosol layer. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 16, 014015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khain, A.; Rosenfeld, D.; Pokrovsky, A. Aerosol impact on the dynamics and microphysics of deep convective clouds. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. A J. Atmos. Sci. Appl. Meteorol. Phys. Oceanogr. 2005, 131, 2639–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.K.; Chen, J.P.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C. Impact of aerosols on convective clouds and precipitation. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, M.; Croci Maspoli, M.; Wernli, H. Tropopause folds and cross-tropopause exchange: A global investigation based upon ECMWF analyses for the time period March 2000 to February 2001. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, M. Turbulent mixing within tropopause folds as a mechanism for the exchange of chemical constituents between the stratosphere and troposphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Li, R.; Ma, J. Spatiotemporal and Vertical Distribution of Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer Using Long-Term Multi-Source Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051315
Liu H, Li R, Ma J. Spatiotemporal and Vertical Distribution of Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer Using Long-Term Multi-Source Data. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(5):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051315
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hongchao, Ren Li, and Junjie Ma. 2023. "Spatiotemporal and Vertical Distribution of Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer Using Long-Term Multi-Source Data" Remote Sensing 15, no. 5: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051315
APA StyleLiu, H., Li, R., & Ma, J. (2023). Spatiotemporal and Vertical Distribution of Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer Using Long-Term Multi-Source Data. Remote Sensing, 15(5), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051315






