MAFF-HRNet: Multi-Attention Feature Fusion HRNet for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
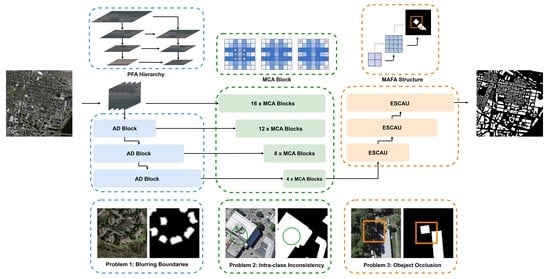
- We propose a high-resolution network (HRNet) [34] based on a pyramidal feature attention (PFA) hierarchy. Our model can retain more spatial feature information and achieve more accurate semantic segmentation, thus effectively solving the problem of the blurring of segmented object boundaries in remote sensing images.
- We introduce a novel mixed convolution attention (MCA) block that can improve the capture range of receptive fields [35] and improve the ability to recognize object contours, thus mitigating segmentation errors caused by intra-class inconsistency.
- We develop a novel multiscale attention feature aggregation (MAFA) block to boost the semantic representation in the feature map and better retain fine contextual details, thereby addressing the problem of inaccurate segmentation caused by object occlusion.
- Without the use of additional datasets, data augmentation [36], or postprocessing, MAFF-HRNet achieves the best accuracy among a set of comparable models on two building segmentation datasets, and the practicability of our model was verified on the Gaofen 16 m dataset. Our code is available at https://github.com/ZhihaoChe/MAFF-HRNet (accessed on 17 January 2023).
2. Methods
2.1. Architecture of the Proposed Framework
2.2. Pyramidal Feature Attention (PFA) Hierarchy
2.3. Mixed Convolution Attention (MCA) Block
2.4. Multiscale Attention Feature Aggregation (MAFA) Block
3. Experiment
3.1. Public Datasets
3.2. Experimental Setup
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
3.4. Results on Public Datasets
3.5. Ablation Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tong, X.; Lin, X.; Feng, T.; Xie, H.; Liu, S.; Hong, Z.; Chen, P. Use of shadows for detection of earthquake-induced collapsed buildings in high-resolution satellite imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 79, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R.; Cowen, D.C. Remote sensing of urban/suburban infrastructure and socio-economic attributes. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1999, 65, 611–622. [Google Scholar]
- Neupane, B.; Horanont, T.; Aryal, J. Deep Learning-Based Semantic Segmentation of Urban Features in Satellite Images: A Review and Meta-Analysis. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, A.O. Automated detection of buildings from single VHR multispectral images using shadow information and graph cuts. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 86, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Tang, Y.; Jing, L.; Li, H.; Ding, H. A novel unsupervised segmentation quality evaluation method for remote sensing images. Sensors 2017, 17, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Zoej, M.V.; Ebadi, H.; Moghaddam, H.A.; Mohammadzadeh, A. Automatic urban building boundary extraction from high resolution aerial images using an innovative model of active contours. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2010, 12, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cui, S.; Yan, Q. Building extraction from high resolution satellite imagery based on multi-scale image segmentation and model matching. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications, Beijing, China, 30 June–2 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanea, M.; Moallem, P.; Momeni, M. Building extraction from high-resolution satellite images in urban areas: Recent methods and strategies against significant challenges. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 5234–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G. Urban Area Extraction by Regional and Line Segment Feature Fusion and Urban Morphology Analysis. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, J.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y. An improved snake model for building detection from urban aerial images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2005, 26, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X. Semantic classification of urban buildings combining VHR image and GIS data: An improved random forest approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aptoula, E. Remote sensing image retrieval with global morphological texture descriptors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 3023–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, P.; Shankar, B.U.; Pal, S.K. Segmentation of multispectral remote sensing images using active support vector machines. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2004, 25, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.N.; Yang, J.G.; Zhong, Y.W.; Deng, C. (2004) Multi-class svm based remote sensing image classification and its semi-supervised improvement scheme. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (IEEE Cat. No. 04EX826), Shanghai, China, 26–29 August 2004; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 5, pp. 3146–3151. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Du, P.; He, X.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification based on rotation forest. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 11, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, B.; Al-Huda, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wu, X. Multi-scale region composition of hierarchical image segmentation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 32833–32855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. Research on Remote Sensing Image Matching with Special Texture Background. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1380. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xin, Q.; Sun, Y.; Cao, M. A Deep Learning-Based Framework for Automated Extraction of Building Footprint Polygons from Very High-Resolution Aerial Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y. Convolutional networks for images, speech, and time series. In Handbook of Brain Theory & Neural Networks; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Li, D.; Fan, M.; Zhao, L. Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images Using Multiscale Decoding Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1492–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, S.; Xiong, D.; Fang, P.; Liao, M. Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation Based on Edge Information Guidance. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Bi, F.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Feng, S. A Multi-Attention UNet for Semantic Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images. Symmetry 2022, 14, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghalles, K.; Li, H.-C.; Alazeb, A. Weakly Supervised Building Semantic Segmentation Based on Spot-Seeds and Refinement Process. Entropy 2022, 24, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Liu, S.; Jin, K.; Cheng, H. CT-UNet: An Improved Neural Network Based on U-Net for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Peng, C.; Xue, X.; Sun, J. Exfuse: Enhancing feature fusion for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. Learning a discriminative feature network for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1857–1866. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Shi, J.; Change, L.C.; Lin, D.; Jia, J. Psanet: Point-wise spatial attention network for scene parsing. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 267–283. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. (2021) Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Abdollahi, A.; Pradhan, B.; Shukla, N.; Chakraborty, S.; Alamri, A. Multi-Object Segmentation in Complex Urban Scenes from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; arXiv e-prints. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, F.H.; Wei, S.Z. Multi-Scale Receptive Field Detection Network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 138825–138832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, M.; Guo, S.; Zhao, J.; Shen, F. Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning: A Survey. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.08610. [Google Scholar]
- Sindagi, V.; Patel, V. Multi-Level Bottom-Top and Top-Bottom Feature Fusion for Crowd Counting. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Milan, A.; Shen, C.; Reid, I. RefineNet: Multi-path Refinement Networks for High-Resolution Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderrer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In ICLR (2021). arXiv 2021, arXiv:2010.11929. preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X. Cascaded Multi-scale Structure with Self-smoothing Atrous Convolution for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Song, Y. A multiple-channel and atrous convolution network for ultrasound image segmentation. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 6270–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jia, W.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; He, X. See More Than Once—Kernel-Sharing Atrous Convolution for Semantic Segmentation. Neurocomputing 2021, 443, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; He, T.; Shen, C.; Yan, Y. Decoders matter for semantic segmentation: Data-dependent decoding enables flexible feature aggregation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3126–3135. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.; Wei, S.; Lu, M. Fully convolutional networks for multisource building extraction from an open aerial and satellite imagery data set. IEEE Tran. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V. Machine Learning for Aerial Image Labeling. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 9 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- He, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J.; Li, M. Bag of tricks for image classification with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 558–567. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, P.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R.; Noordhuis, P.; Wesolowski, L.; Kyrola, A.; Tulloch, A.; Jia, Y.; He, K. Accurate, large minibatch SGD: Training imagenet in 1 hour. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.02677. preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder–decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), 11211 LNCS; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 833–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Shi, Q.; Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y. Building Footprint Extraction from High-Resolution Images via Spatial Residual Inception Convolutional Neural Network. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Shen, L.; Wang, J.; Deng, X.; Li, Z. MSG-SR-Net: A Weakly Supervised Network Integrating Multiscale Generation and Superpixel Refinement for Building Extraction From High-Resolution Remotely Sensed Imageries. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. Comput. Sci. 2014. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980 (accessed on 23 December 2021).











| Method | IoU (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SegNet | 56.57 | 69.82 | 75.21 | 72.08 |
| U-Net | 63.67 | 78.10 | 77.51 | 77.80 |
| DeepLabv3 | 58.20 | 73.37 | 73.80 | 73.58 |
| FPN | 62.24 | 77.89 | 75.51 | 76.68 |
| HRNet | 66.60 | 81.31 | 78.23 | 79.74 |
| MAFF-HRNet | 68.32 | 83.15 | 79.29 | 81.17 |
| Method | IoU (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLabv3+ (fully) | 89.19 | 94.95 | 93.64 | 94.29 |
| U-Net++ (fully) | 89.36 | 95.34 | 93.44 | 94.38 |
| PSPNet (fully) | 88.17 | 94.16 | 93.27 | 93.71 |
| SRINet (fully) | 89.09 | 95.21 | 93.27 | 94.23 |
| MSG-SR-Net (weakly) | 52.64 | - | - | 68.98 |
| SSRP (weakly) | 82.34 | 87.02 | 86.75 | 85.45 |
| MAFF-HRNet | 91.69 | 95.90 | 95.43 | 95.66 |
| Index | Baseline | MCA | MAFA | PFA | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ✓ | 75.41 | |||
| 2 | ✓ | ✓ | 76.83 | ||
| 3 | ✓ | ✓ | 77.25 | ||
| 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 79.58 | |
| 5 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 80.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Che, Z.; Shen, L.; Huo, L.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Bi, F. MAFF-HRNet: Multi-Attention Feature Fusion HRNet for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051382
Che Z, Shen L, Huo L, Hu C, Wang Y, Lu Y, Bi F. MAFF-HRNet: Multi-Attention Feature Fusion HRNet for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(5):1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051382
Chicago/Turabian StyleChe, Zhihao, Li Shen, Lianzhi Huo, Changmiao Hu, Yanping Wang, Yao Lu, and Fukun Bi. 2023. "MAFF-HRNet: Multi-Attention Feature Fusion HRNet for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images" Remote Sensing 15, no. 5: 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051382
APA StyleChe, Z., Shen, L., Huo, L., Hu, C., Wang, Y., Lu, Y., & Bi, F. (2023). MAFF-HRNet: Multi-Attention Feature Fusion HRNet for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing, 15(5), 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051382