Spatial Diffusion Waves of Human Activities: Evidence from Harmonized Nighttime Light Data during 1992–2018 in 234 Cities of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
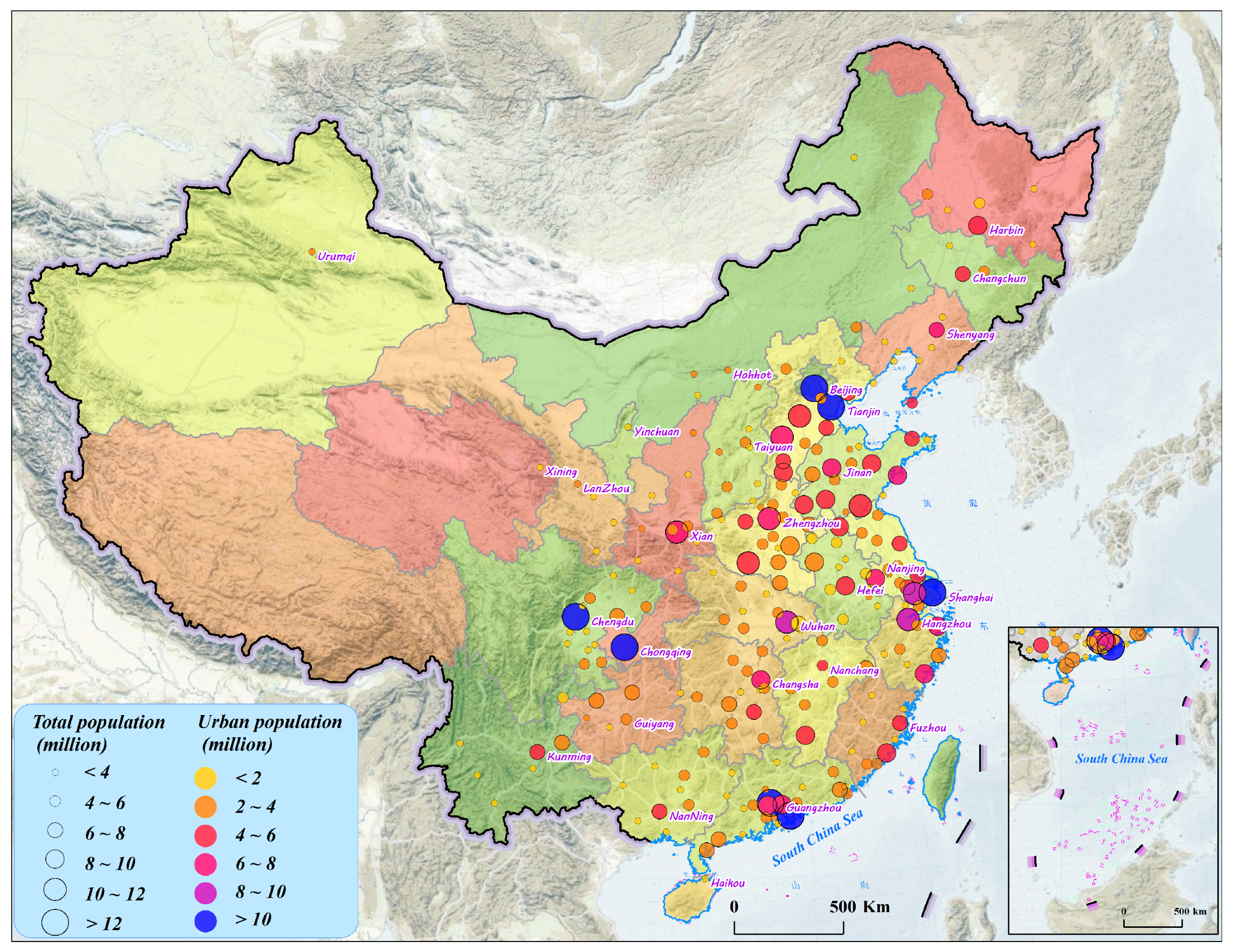
2.1. Sample Cities
2.2. Data and Preprocessing
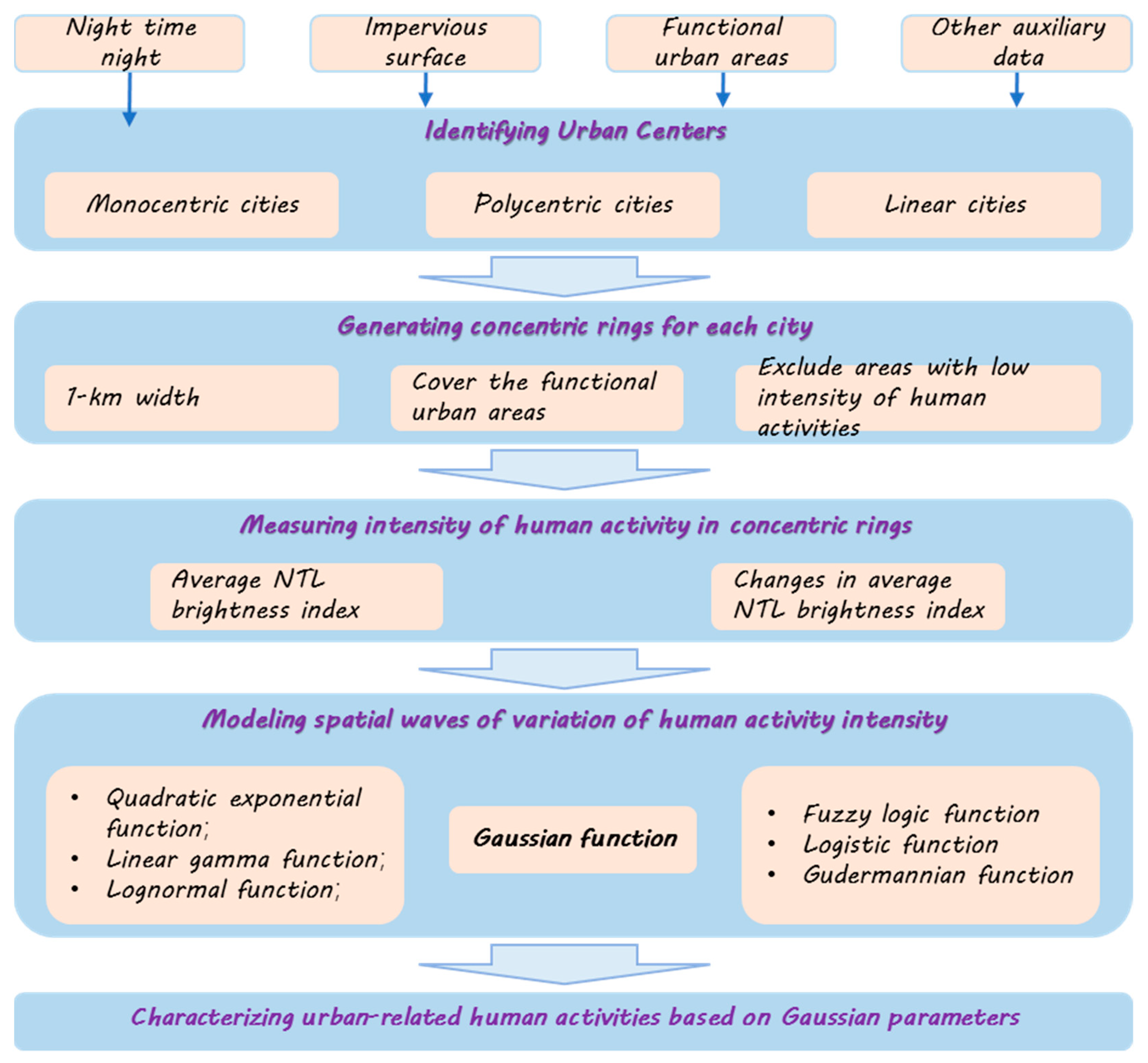
2.3. Methodologies
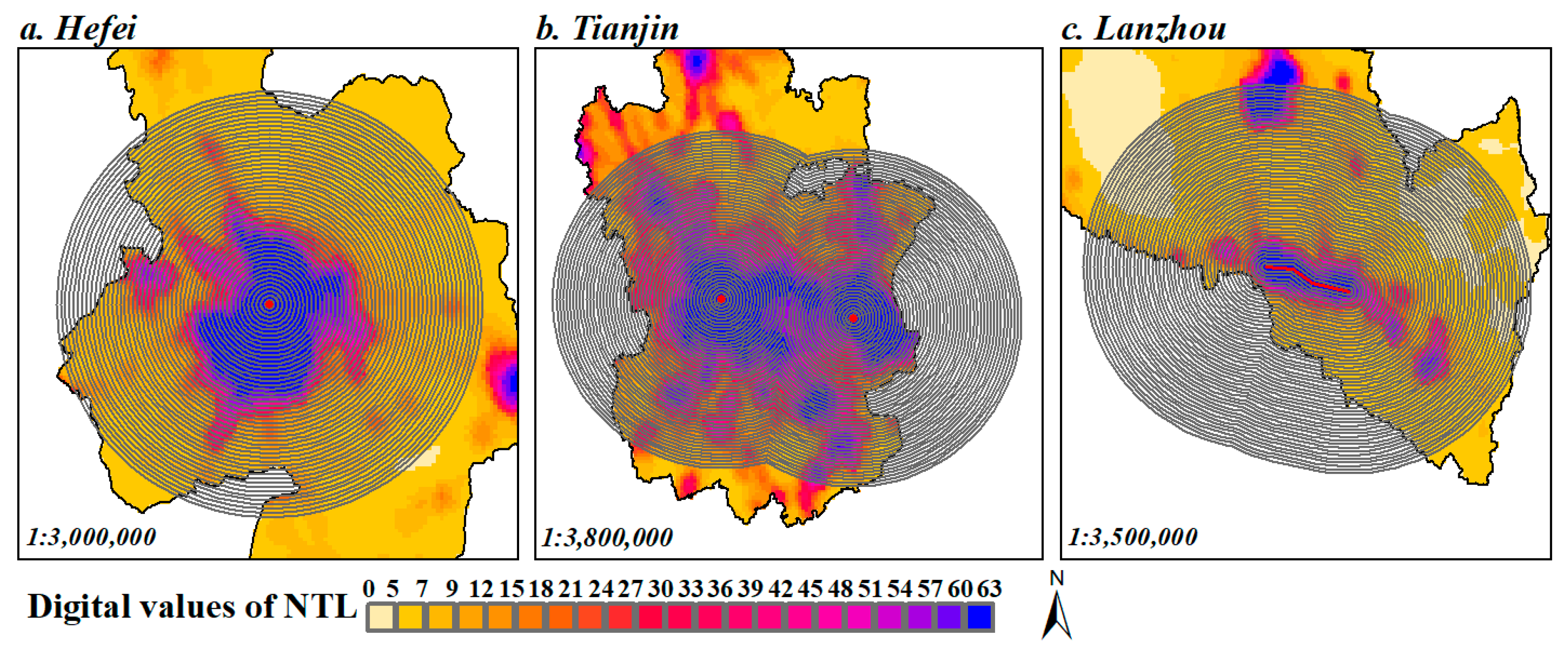
2.3.1. Identifying Urban Centers for Each City
2.3.2. Generating Concentric Rings for Each City
2.3.3. Measuring Intensity of Human Activity in Concentric Rings
2.3.4. A Gaussian Function for Simulating Spatial Variations of Human Activity Intensity
3. Results
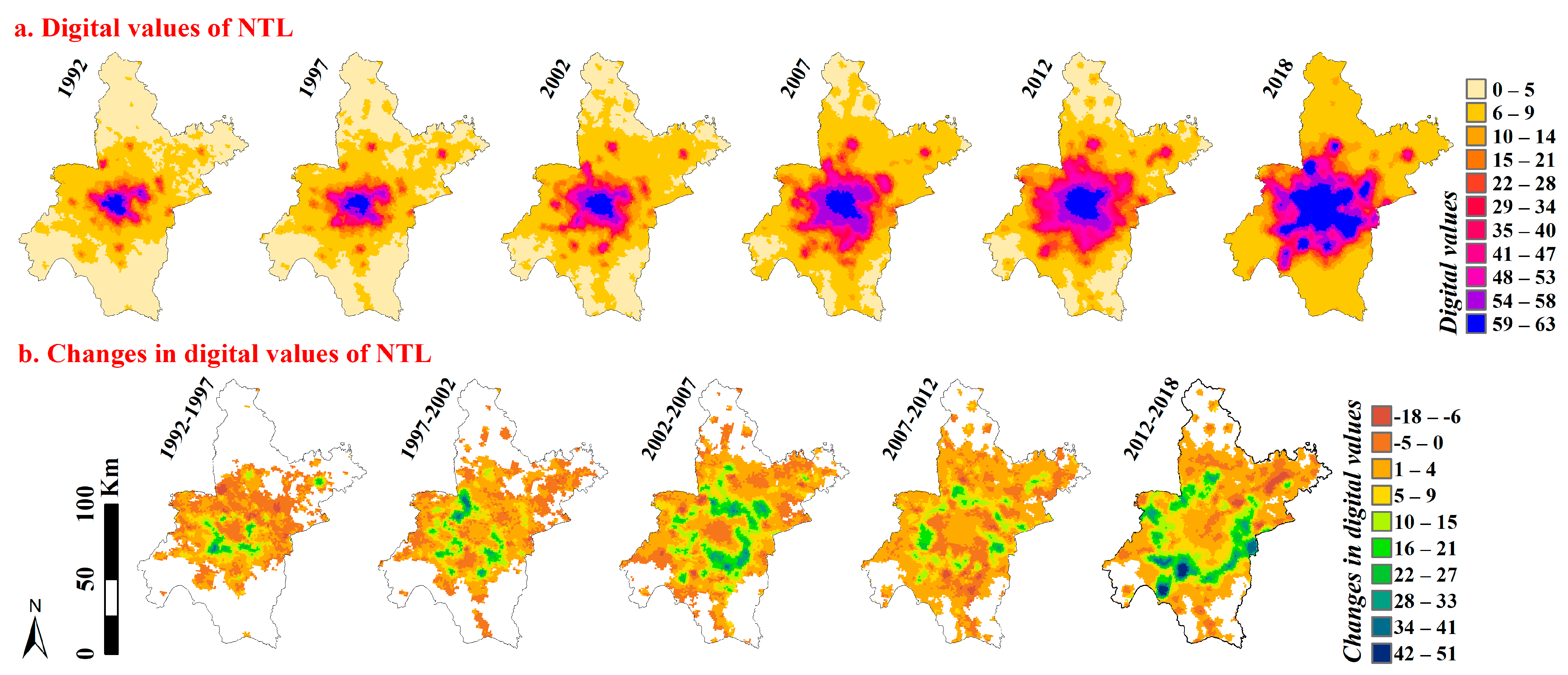
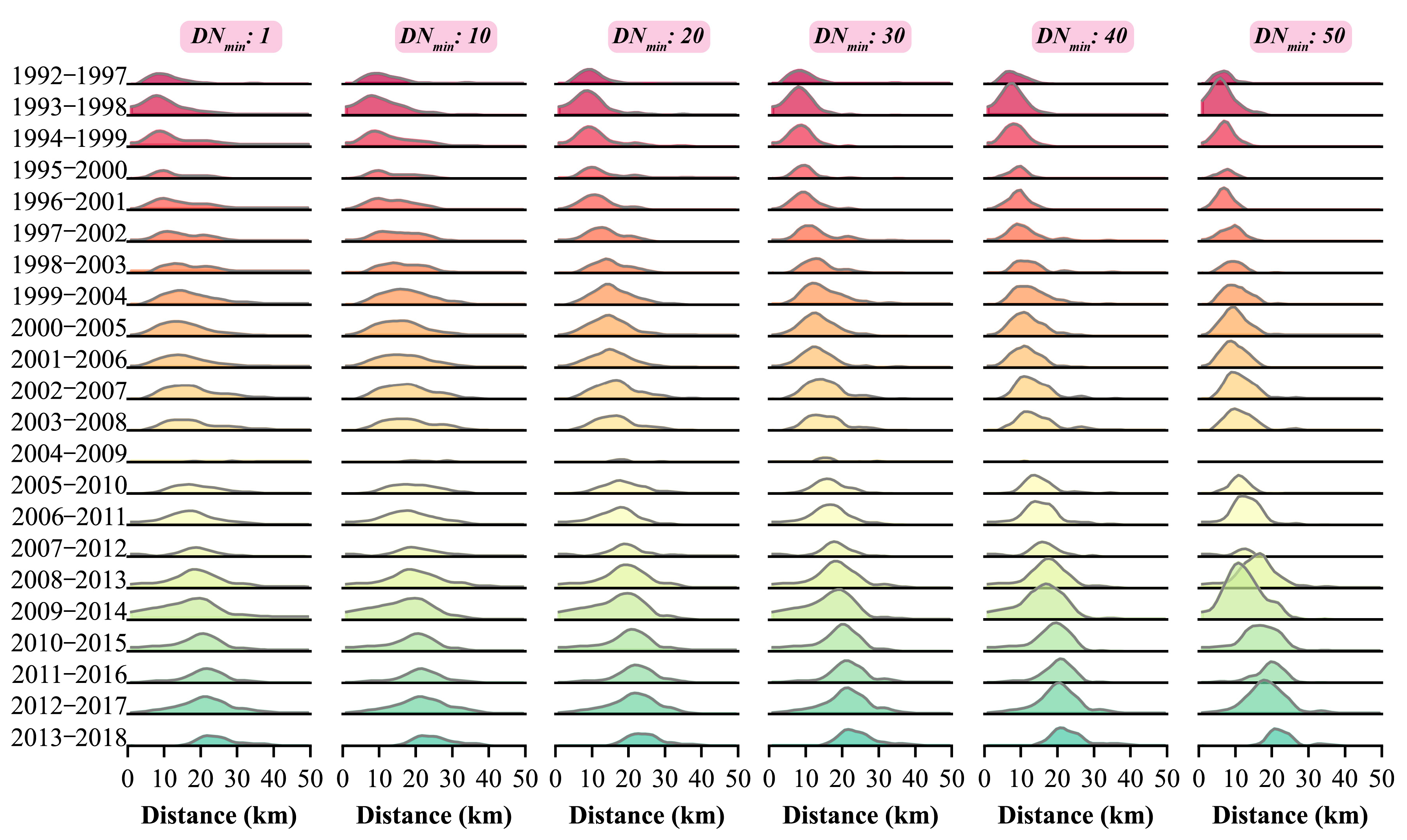
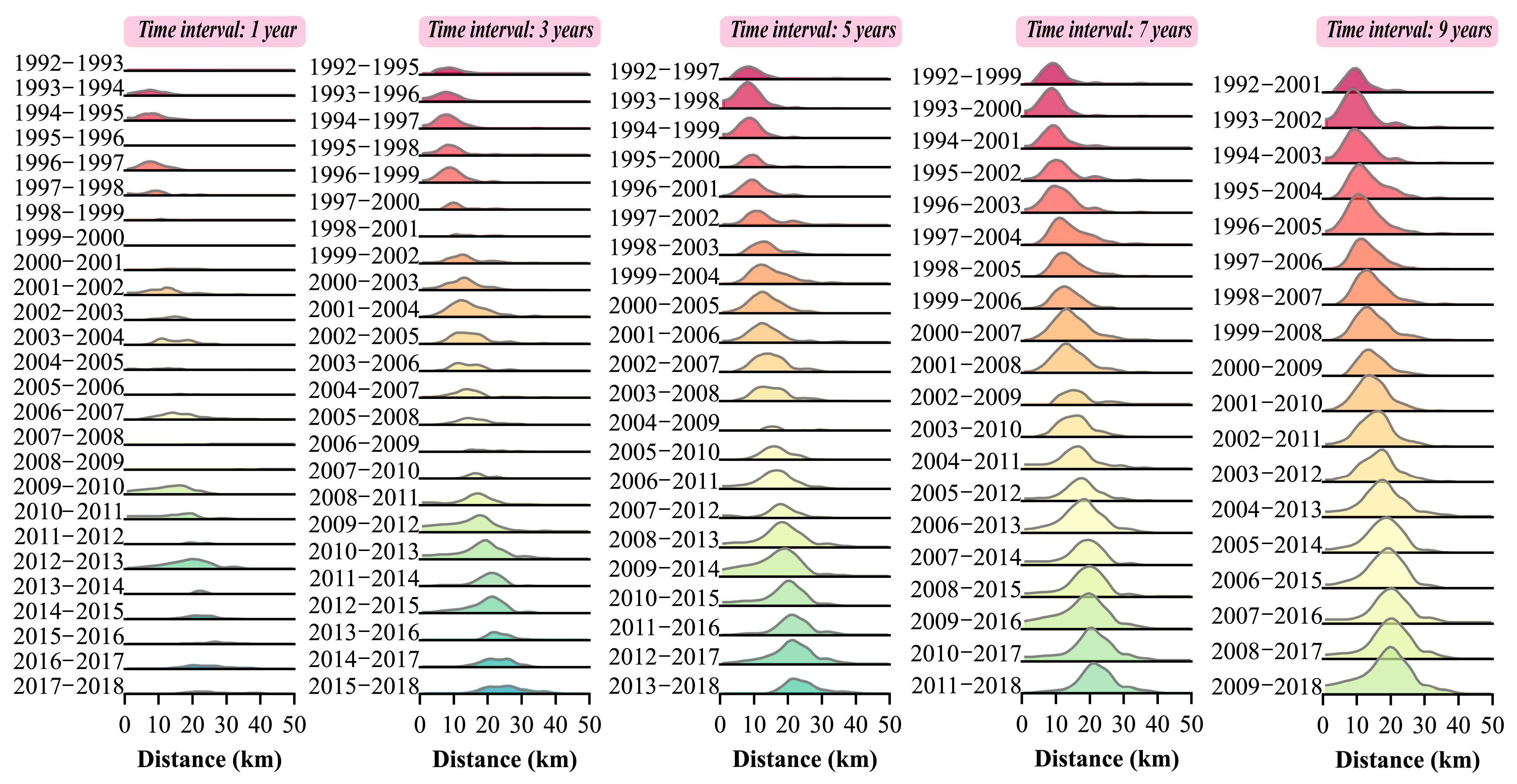
3.1. Space–Time Pattern of Observed Intensity of Human Activities
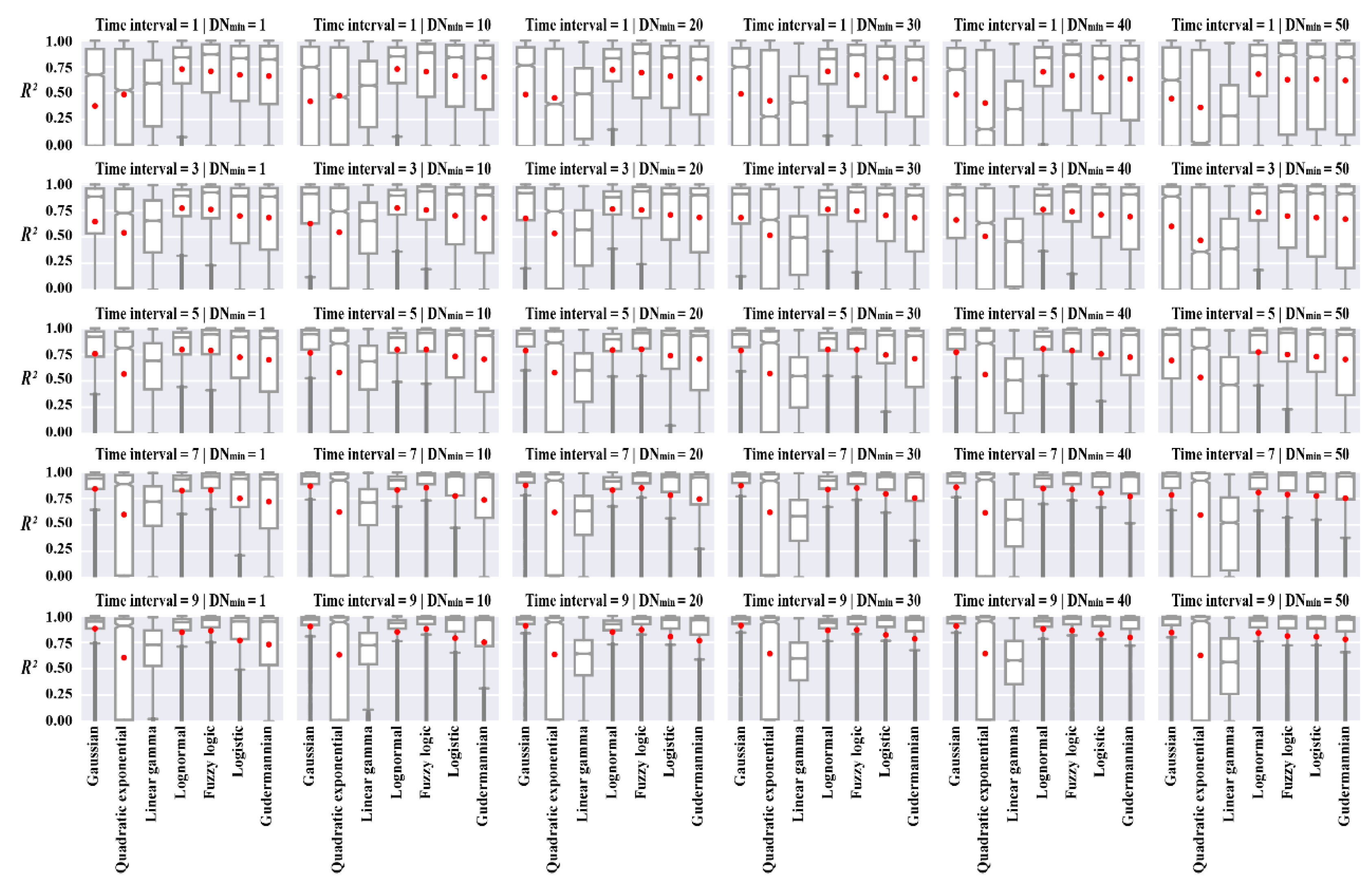
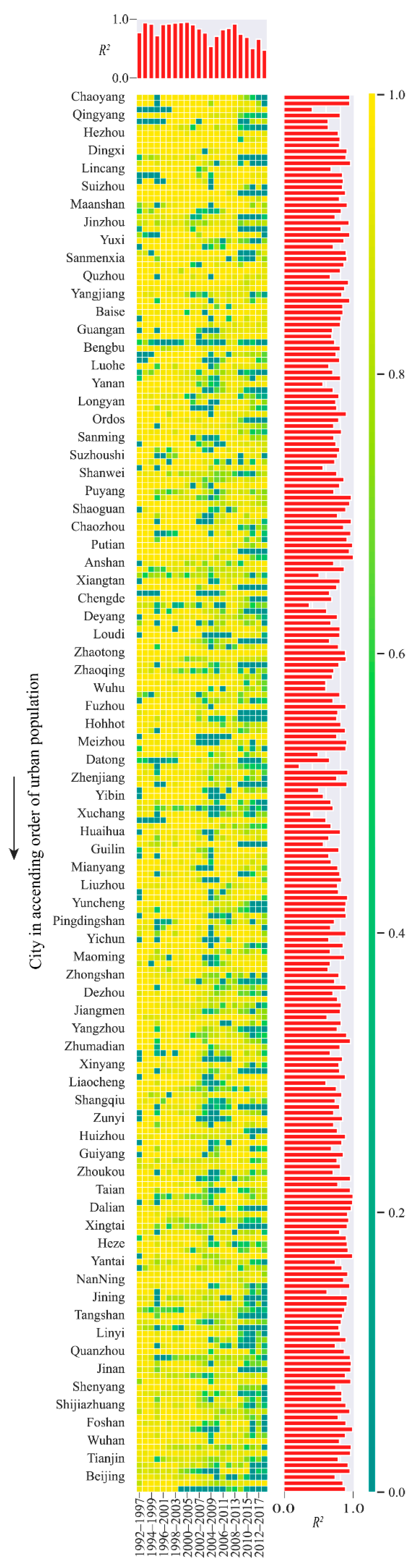
3.2. Model Performance for Simulating Variations of Human Activity Intensity
3.3. Characterizing Urban-Related Human Activities Based on Gaussian Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Process-Pattern Linkage of Human Activities
4.2. A Prediction Model for Dynamics of Human Activity
4.3. Wave-Shaped Phenomenon Manifested during Urbanization
4.4. Major Contributions of This Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, G.; Jiao, L.; Yuan, M.; Dong, T.; Zhang, B.; Du, C. How does urban population density decline over time? An exponential model for Chinese cities with international comparisons. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 183, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, X. Analyzing Parcel-Level Relationships between Urban Land Expansion and Activity Changes by Integrating Landsat and Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, F.; Valenzuela, L.M.; Botequilha-Leitao, A. Landscape metrics in the analysis of urban land use patterns: A case study in a Spanish metropolitan area. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 99, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Wang, X.D.; Zhou, Z.X.; Li, M.W.; Jing, C.F. Spatial Quantitative Model of Human Activity Disturbance Intensity and Land Use Intensity Based on GF-6 Image, Empirical Study in Southwest Mountainous County, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, K. Experimental analysis of eleven models of urban population density. Environ. Plan. A 1979, 11, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L. Urban land density function: A new method to characterize urban expansion. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 139, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linard, C.; Tatem, A.J.; Gilbert, M. Modelling spatial patterns of urban growth in Africa. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 44, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meentemeyer, R.K.; Tang, W.; Dorning, M.A.; Vogler, J.B.; Cunniffe, N.J.; Shoemaker, D.A. FUTURES: Multilevel Simulations of Emerging Urban-Rural Landscape Structure Using a Stochastic Patch-Growing Algorithm. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2013, 103, 785–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, I.; Frankhauser, P.; Biernacki, C. The morphology of built-up landscapes in Wallonia (Belgium): A classification using fractal indices. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2008, 84, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Woodcock, C.E. Compact, Dispersed, Fragmented, Extensive? A Comparison of Urban Growth in Twenty-five Global Cities using Remotely Sensed Data, Pattern Metrics and Census Information. Urban Stud. 2008, 45, 659–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gober, P.; Burns, E.K. The Size and Shape of Phoenix’s Urban Fringe. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2002, 21, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzel, C.; Oguz, H.; Hemphill, J.J.; Clarke, K.C.; Gazulis, N. Diffusion and Coalescence of the Houston Metropolitan Area: Evidence Supporting a New Urban Theory. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2016, 32, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzel, C.; Herold, M.; Hemphill, J.J.; Clarke, K.C. Spatio-temporal dynamics in California’s central valley: Empirical links to urban theory. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2005, 19, 175–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, M.; Ferrara, C.; Rontos, K.; Zambon, I.; Salvati, L. The long breadth of cities: Revisiting worldwide urbanization patterns, 1950–2030. Appl. Econ. 2020, 52, 4162–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenfeld, H. The Tidal Wave of Metropolitan Expansion. J. Am. Inst. Plan. 1954, 20, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newling, B.E. The spatial variation of urban population densities. Geogr. Rev. 1969, 59, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; An, S.; Yu, W.; Chen, J.M. The spatiotemporal dynamics of rapid urban growth in the Nanjing metropolitan region of China. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrill, R.L. Waves of Spatial Diffusion. J. Reg. Sci. 2010, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koreclli, P. A wave-like model of metropolitan spatial growth. Pap. Reg. Sci. Assoc. 2010, 24, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, J.F. The Perimetropolitan Bow Wave. Geogr. Rev. 1991, 81, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, J.B. The form of the regional density function. Reg. Stud. 2007, 19, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.C.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.Q.; Cheng, B.; Hu, T.Y.; Liu, X.P.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Annual maps of global artificial impervious area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Fang, L.; Feng, S.; et al. Mapping essential urban land use categories in China (EULUC-China): Preliminary results for 2018. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.-H. Quantifying Urban Form: Compactness versus ‘Sprawl’. Urban Stud. 2005, 42, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, S.; Parent, J.; Civco, D. Urban sprawl metrics: An analysis of global urban expansion using GIS. In Proceedings of the ASPRS 2007 Annual Conference, Tampa, FL, USA, 7–11 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, L.; Dong, T.; Xu, G.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. Geographic micro-process model: Understanding global urban expansion from a process-oriented view. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 87, 101603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, J.; Xu, F.; Li, S.; Zheng, M.; Gong, J. Urban development wave: Understanding physical spatial processes of urban expansion from density gradient of new urban land. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 97, 101867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Ma, Q. Dynamics of Urbanization Levels in China from 1992 to 2012: Perspective from DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1721–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.S.; Xu, Z.J. Functional Coupling Degree and Human Activity Intensity of Production-Living-Ecological Space in Underdeveloped Regions in China: Case Study of Guizhou Province. Land 2021, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Li, X.C.; Cao, W.T.; He, C.Y.; Yu, B.L.; Li, X.; Elvidge, C.D.; Cheng, W.M.; Zhou, C.H. Applications of Satellite Remote Sensing of Nighttime Light Observations: Advances, Challenges, and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T. Multi-Level Relationships between Satellite-Derived Nighttime Lighting Signals and Social Media-Derived Human Population Dynamics. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.F.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.Y. Remotely sensed nighttime lights reveal increasing human activities in protected areas of China mainland. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Gong, X.Y.; Da, H.L.; Wen, H.Z. How do population inflow and social infrastructure affect urban vitality? Evidence from 35 large- and medium-sized cities in China. Cities 2020, 100, 102454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keola, S.; Andersson, M.; Hall, O. Monitoring Economic Development from Space: Using Nighttime Light and Land Cover Data to Measure Economic Growth. World Devel. 2015, 66, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Xu, D.Y.; Ali, S.H.; Ma, R.Y.; Cheng, J.H. Can Nighttime Light Data Be Used to Estimate Electric Power Consumption? New Evidence from Causal-Effect Inference. Energies 2019, 12, 3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, W.M.; Zhou, C.H.; Li, M.C.; Huang, K.; Wang, N. Assessing Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Urbanization Dynamics in Southeast Asia Using Time Series of DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T. An Estimate of the Pixel-Level Connection between Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Day/Night Band (VIIRS DNB) Nighttime Lights and Land Features across China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Kong, X.S.; Wang, R.; Chen, L. Identifying the relationship between urban land expansion and human activities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 94, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, Z.; Guo, H.; Tian, Z.; Wang, X. Analysing the consistency between built-up areas and human activities and the impacts on the urbanization process: A case study of Zhengzhou, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 6008–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, X. A harmonized global nighttime light dataset 1992–2018. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.C.; Zhou, Y.Y. A Stepwise Calibration of Global DMSP/OLS Stable Nighttime Light Data (1992–2013). Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Song, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Ren, H.; Dong, M.; Feng, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, J. Toward accurate mapping of 30-m time-series global impervious surface area (GISA). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 109, 102787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gong, P.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; et al. Mapping global urban boundaries from the global artificial impervious area (GAIA) data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 094044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, C.D.; Silverman, B.W. Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Jiao, L.; Liu, J.; Shi, Z.; Zeng, C.; Liu, Y. Understanding urban expansion combining macro patterns and micro dynamics in three Southeast Asian megacities. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Jiao, L.; Xu, G.; Yang, L.; Liu, J. Towards sustainability? Analyzing changing urban form patterns in the United States, Europe, and China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xu, G.; de Jong, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, P. Examining the Density and Diversity of Human Activity in the Built Environment: The Case of the Pearl River Delta, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.X.; Liu, W.D.; Lu, D.D.; Chen, H.; Ye, C. Progress of China’s new-type urbanization construction since 2014: A preliminary assessment. Cities 2018, 78, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.L. Land consolidation: An indispensable way of spatial restructuring in rural China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.L.; Wang, Z.B. Quantitative Diagnoses and Comprehensive Evaluations of the Rationality of Chinese Urban Development Patterns. Sustainability 2015, 7, 3859–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.N.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, Y. The Random Forest-Based Method of Fine-Resolution Population Spatialization by Using the International Space Station Nighttime Photography and Social Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tang, W.; Gong, J.; Shi, R.; Zheng, M.; Dai, Y. Simulating urban expansion using cellular automata model with spatiotemporally explicit representation of urban demand. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2023, 231, 104640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jiao, L.; Dong, T.; Xu, Z.; Xu, G. Simulating urban dynamics by coupling top-down and bottom-up strategies. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2019, 33, 2259–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


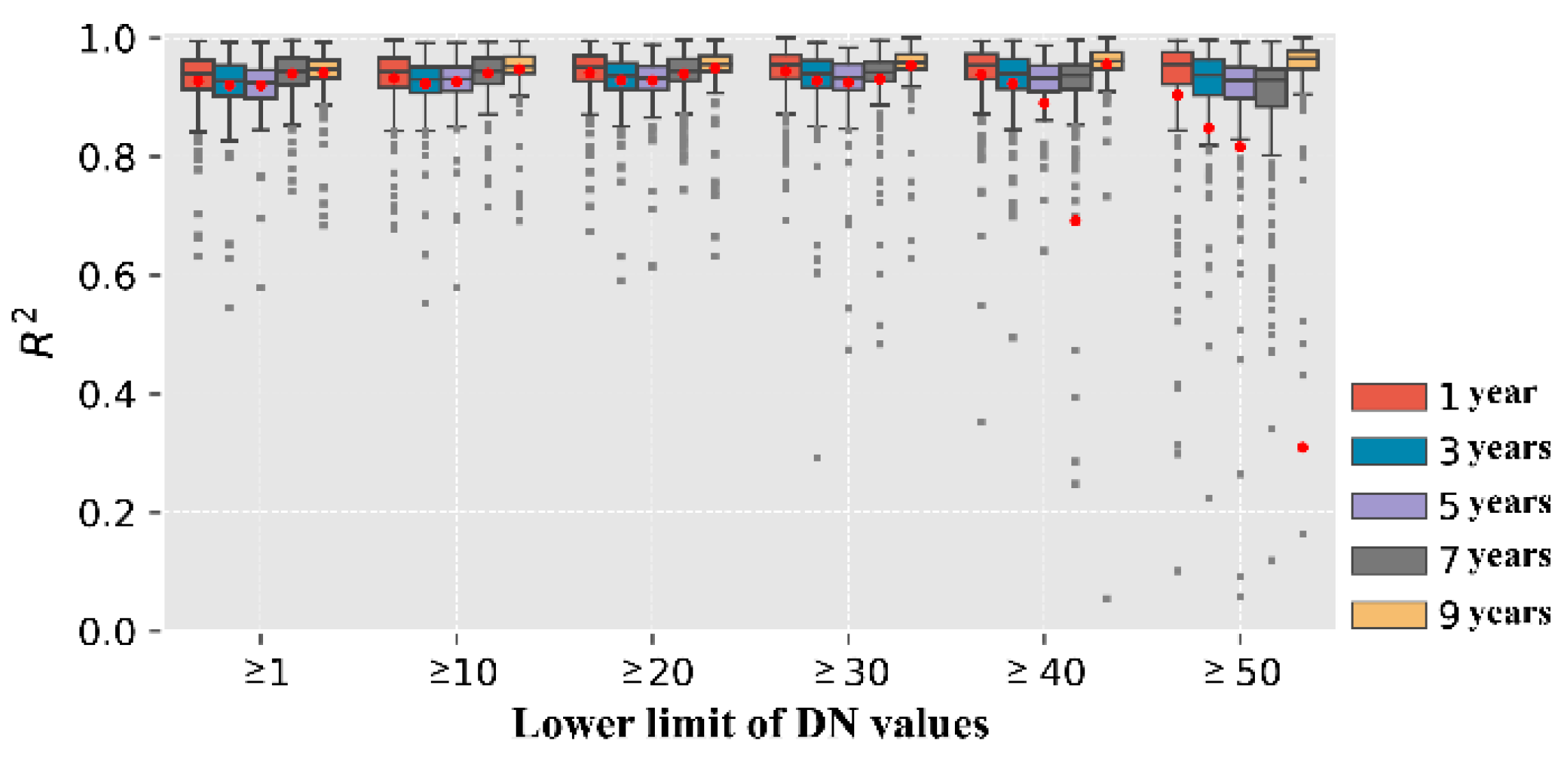
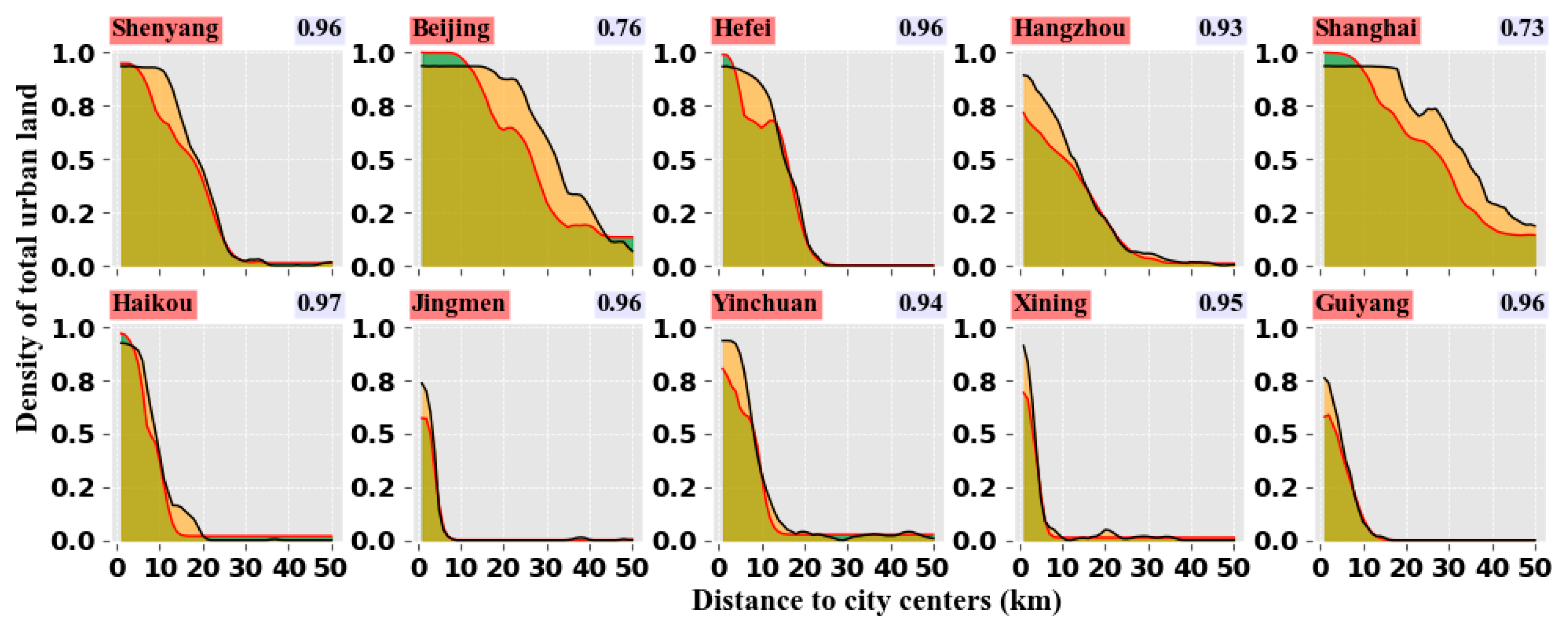
| Data | Source | Space-Time Resolution | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nighttime night | A harmonized global nighttime light dataset produced by Li et al. [40] which can be downloaded from https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.9828827.v2 on 19 September 2022 | Spatial resolution: 30 arc-seconds (about 1 km near the equator) Time resolution: 1 year Time span: 1992–2018 | These NTL data record the DN values, ranging from 0 to 63, to indicate the intensity of city light at night. |
| Impervious surface | A global-scale impervious surface dataset mapped in 30 m resolution by Huang et al. [42] which is freely available at irsip.whu.edu.cn/resources/resources_en_v2.php on 17 September 2022 | Spatial resolution: 30 m Time resolution: 1 year Time span: 1972–2019 | We use impervious surface data from 2018 to help identify urban centers. |
| Extent of functional urban areas | A global urban boundaries dataset mapped from the global artificial impervious area (GAIA) data by Li et al. [43], accessed at http://data.ess.tsinghua.edu.cn on 15 September 2022 | Spatial resolution: vector Time resolution: 1 year Time span: 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2018 | We use urban boundaries of each city in 2018 as auxiliary data to locate urban centers. |
| Total and urban population | Statistical yearbook | Time resolution: 1 year Time span: 2019 | The population dataset was used to select and group the sample cities. |
| Urban planning maps | Official websites of the Bureau of Natural Resources | —— | Auxiliary data was used to locate urban centers. |
| Name of Function | Basic Form in Literature | Derivative Form Used in This Study | Description of Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gaussian function | Parameter a is the amplitude of the Gaussian function; b and c are the mean and standard deviation, respectively. d is a constant parameter that offsets the function along the y-axis (). | ||
| Quadratic exponential function | Parameter a impacts the height of the function curve. Parameter b and c determine the central location (i.e., ) and the width of the function curve, respectively. Parameter d offsets the function along the y-axis (). | ||
| Linear gamma function | Parameter a impacts the height of function curve. Parameter b and k determine the central location (i.e., ) of the function curve. Parameter d offsets the function along the y-axis (). | ||
| Lognormal function | Parameter a is the amplitude of the lognormal function; b and c are the mean and standard deviation, respectively. d is a constant parameter that offsets the lognormal function along the y-axis (). | ||
| Fuzzy logic function | Parameter a is the height of fuzzy logic function; b and c determine the center and width of the function, respectively; k (together with c) determines the slope () of the curve. d is a constant parameter that offsets the function along the y-axis (). | ||
| Logistic function | Parameter a impacts the amplitude of the function; b and c determine the central location and the width of the function curve, respectively. Parameter d offsets the function along the y-axis (). | ||
| Gudermannian function |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Yuan, M.; Yang, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Song, D.; Dai, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gong, J. Spatial Diffusion Waves of Human Activities: Evidence from Harmonized Nighttime Light Data during 1992–2018 in 234 Cities of China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051426
Yang J, Yuan M, Yang S, Zhang D, Wang Y, Song D, Dai Y, Gao Y, Gong J. Spatial Diffusion Waves of Human Activities: Evidence from Harmonized Nighttime Light Data during 1992–2018 in 234 Cities of China. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(5):1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051426
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jianxin, Man Yuan, Shengbing Yang, Danxia Zhang, Yingge Wang, Daiyi Song, Yunze Dai, Yan Gao, and Jian Gong. 2023. "Spatial Diffusion Waves of Human Activities: Evidence from Harmonized Nighttime Light Data during 1992–2018 in 234 Cities of China" Remote Sensing 15, no. 5: 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051426
APA StyleYang, J., Yuan, M., Yang, S., Zhang, D., Wang, Y., Song, D., Dai, Y., Gao, Y., & Gong, J. (2023). Spatial Diffusion Waves of Human Activities: Evidence from Harmonized Nighttime Light Data during 1992–2018 in 234 Cities of China. Remote Sensing, 15(5), 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051426






