Landscape Patterns and Topographic Features Affect Seasonal River Water Quality at Catchment and Buffer Scales
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Quality Monitoring and Analysis
2.3. Spatial Data and Landscape Metrics Data Acquisition and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
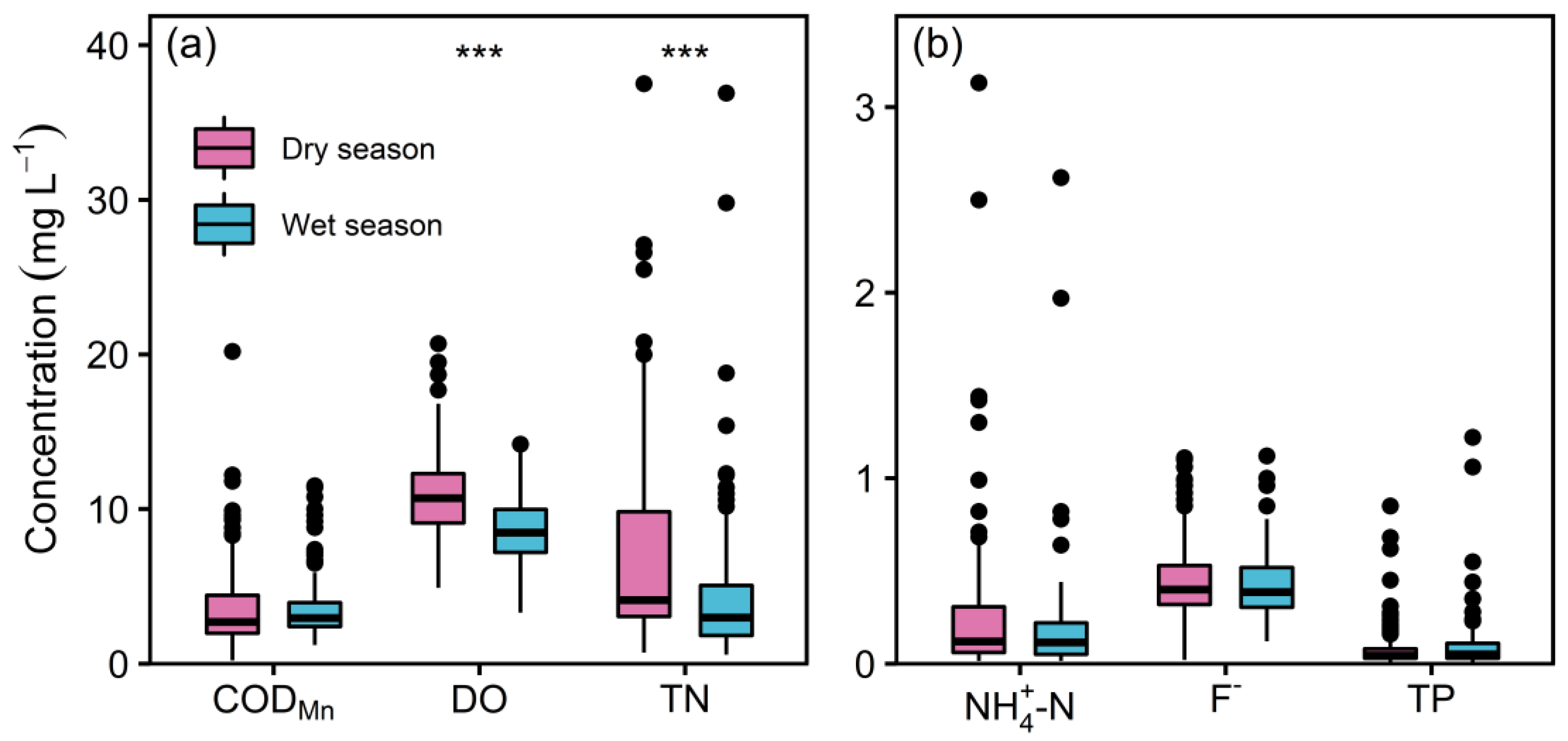
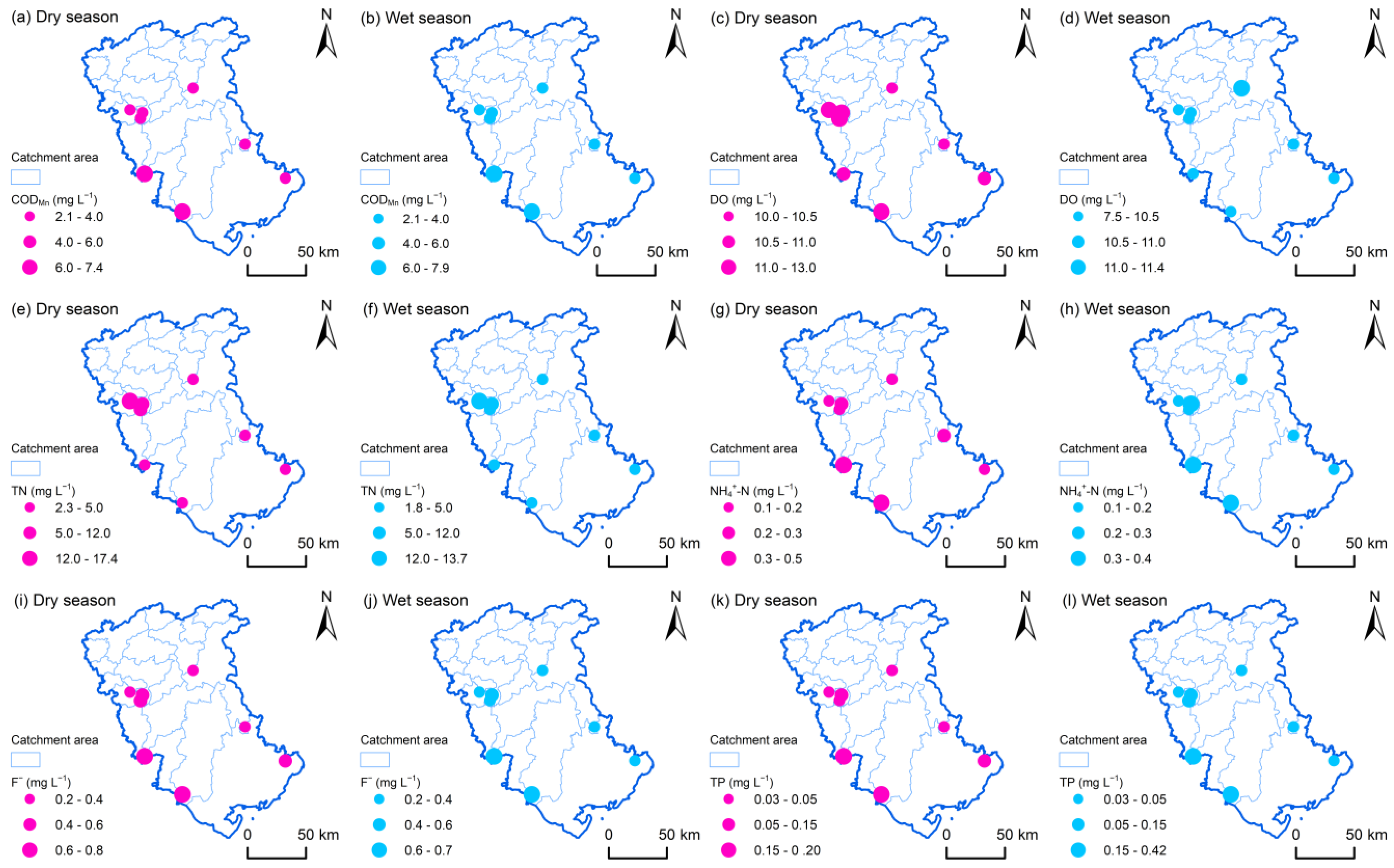
3.1. Seasonal and Spatial Differentiation of River Water Environment
3.2. Changes in Landscape Metrics at Multiple Scales
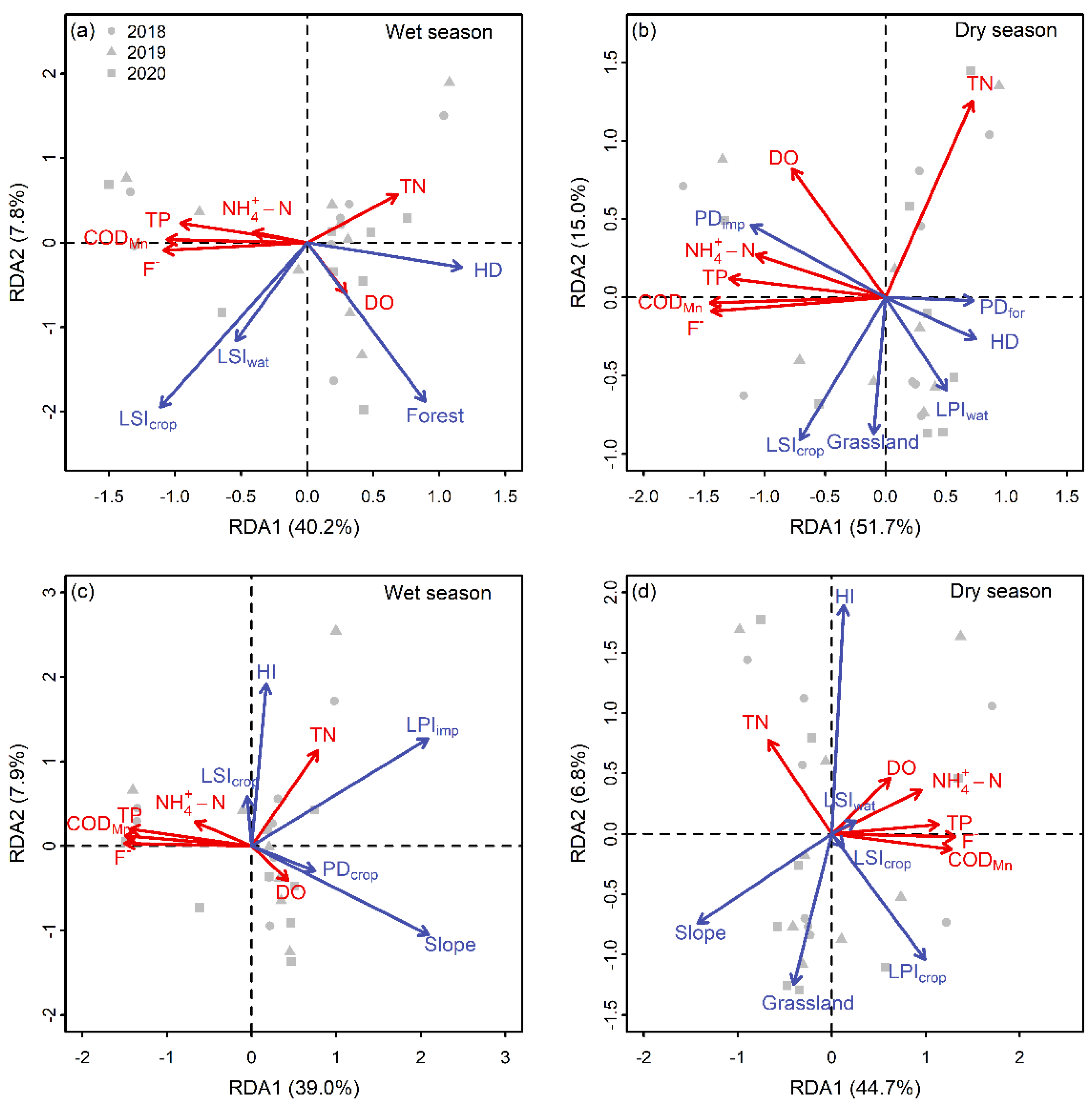
3.3. Associations between Landscape Metrics and Aquatic Environment
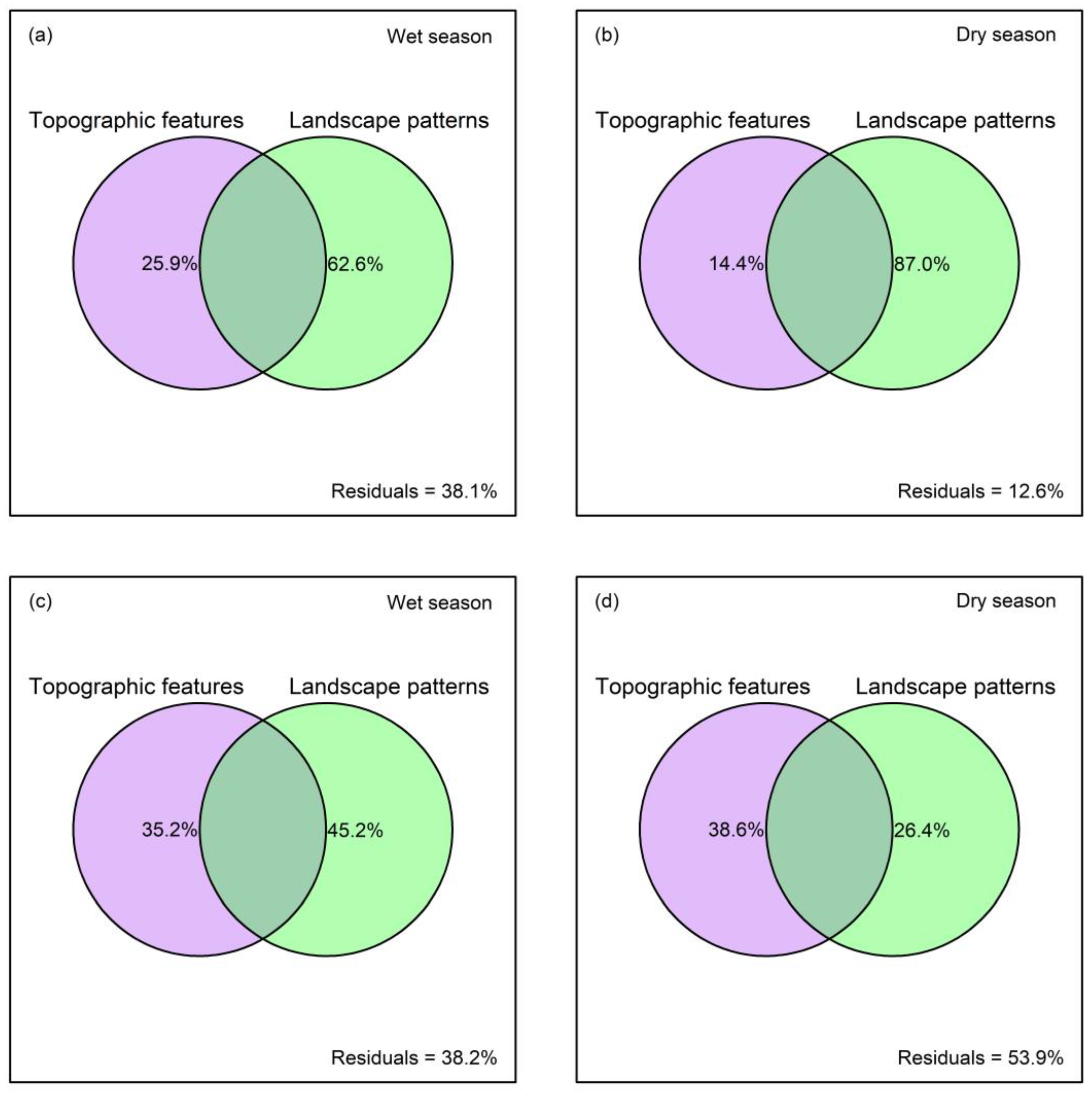
3.4. Variation Partitioning of Landscape Metrics
4. Discussion
4.1. Impacts of Topographic Features and Landscape Patterns on Water Environment
4.2. Impacts of Temporal and Spatial Scales
4.3. Limitations and Inspirations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chai, N.; Yi, X.; Xiao, J.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Deng, L.; Jin, Z. Spatiotemporal Variations, Sources, Water Quality and Health Risk Assessment of Trace Elements in the Fen River. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global Threats to Human Water Security and River Biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Y.; Deng, J. Assessing River Water Quality Using Water Quality Index in Lake Taihu Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Lv, G.; Chai, N.; Hu, J.; Jin, Z. Hydrochemistry and Source Apportionment of Boron, Sulfate, and Nitrate in the Fen River, a Typical Loess Covered Area in the Eastern Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Shan, B.; Sun, B.; Guo, X.; Li, Z. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Suspended Particulate Matter in a Typical Urban River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 46649–46664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Han, M.Y.; Yao, Y.X.; Chen, G.Q. Multi-Scale Water Use Balance for a Typical Coastal City in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shan, B.; Qin, J.; Zhang, H. The impact of socioeconomic development on the river water quality in the Haihe River Basin (in Chinese). Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2015, 35, 2354–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Shao, J.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Lu, J. Changes in the Soil Erosion Status in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River Basin from 2001 to 2014 and the Impacts of Erosion on the Water Quality of Lakes and Reservoirs. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 3175–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Chan, N.W.; Rahman, H.A.; Yang, S.; Tan, M.L. Assessing the Factors Influencing Water Quality Using Environment Water Quality Index and Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Model in the Ebinur Lake Watershed, Xinjiang, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 29033–29048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puczko, K.; Jekatierynczuk-Rudczyk, E. Analysis of Urban Land Cover Influence to Organic Carbon and Nutrients in Surface Water via Impacted Groundwater. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryberg, K.R.; Chanat, J.G. Climate Extremes as Drivers of Surface-Water-Quality Trends in the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 152165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornevi, A.; Bergstedt, O.; Forsberg, B. Precipitation Effects on Microbial Pollution in a River: Lag Structures and Seasonal Effect Modification. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, A.S.; Atkinson, S.; Santini, T.; Falinski, K.; Hutley, N.; Albert, S.; Horning, N.; Watson, J.E.M.; Mumby, P.J.; Jupiter, S.D. Predicting the Impact of Logging Activities on Soil Erosion and Water Quality in Steep, Forested Tropical Islands. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 044035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, S.-L.; Zhong, J.; Li, C. Spatial Scale Effects of the Variable Relationships between Landscape Pattern and Water Quality: Example from an Agricultural Karst River Basin, Southwestern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 300, 106999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Cai, Y. Impacts of Rainfall Spatial and Temporal Variabilities on Runoff Quality and Quantity at the Watershed Scale. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S. Landscape Pattern, Perception and Visualisation in the Visual Management of Forests. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 54, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Xu, Q.; Yi, J.; Jin, L. Study on the Threshold Relationship between Landscape Pattern and Water Quality Considering Spatial Scale Effect—A Case Study of Dianchi Lake Basin in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 44103–44118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W.; Hwang, S.-J.; Lee, S.-B.; Hwang, H.-S.; Sung, H.-C. Landscape Ecological Approach to the Relationships of Land Use Patterns in Watersheds to Water Quality Characteristics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Jin, R.; Zhu, W.; Tian, L.; Lv, X. Effects of Multi-Scale Landscape Pattern Changes on Seasonal Water Quality: A Case Study of the Tumen River Basin in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 76847–76863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, F.; Ruiz, J.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Blais, D.; Campeau, S. Landscape Diversity and Forest Edge Density Regulate Stream Water Quality in Agricultural Catchments. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Li, S. Scale Relationship between Landscape Pattern and Water Quality in Different Pollution Source Areas: A Case Study of the Fuxian Lake Watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G. Influence of Land Use and Land Cover Patterns on Seasonal Water Quality at Multi-Spatial Scales. CATENA 2017, 151, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gu, S.; Liu, W.; Han, H.; Zhang, Q. Water Quality in Relation to Land Use and Land Cover in the Upper Han River Basin, China. CATENA 2008, 75, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jin, Y.; Hao, Y.; Lu, J. Identification of the Control Factors Affecting Water Quality Variation at Multi-Spatial Scales in a Headwater Watershed. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 11129–11141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliva, L.; Dudley Williams, D. Buffer Zone versus Whole Catchment Approaches to Studying Land Use Impact on River Water Quality. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3462–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Hou, X.; Li, W.; Aini, G.; Chen, L.; Gong, Y. Impact of Landscape Pattern at Multiple Spatial Scales on Water Quality: A Case Study in a Typical Urbanised Watershed in China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hou, Z.; Liao, J.; Fu, L.; Peng, Q. Influences of the Land Use Pattern on Water Quality in Low-Order Streams of the Dongjiang River Basin, China: A Multi-Scale Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, J. Spatial Scale Effects of Landscape Metrics on Stream Water Quality and Their Seasonal Changes. Water Res. 2021, 191, 116811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, H.; Meng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, J. Relationships between Land Use Patterns and Water Quality in the Taizi River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 41, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, X.; Liang, T.; Song, H.; Bolan, N.; Shaheen, S.M.; White, J.R.; et al. Impacts of Land Uses on Spatio-Temporal Variations of Seasonal Water Quality in a Regulated River Basin, Huai River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Shi, Z.H.; Yin, W.; Huang, X. Spatial and Seasonal Patterns in Stream Water Contamination across Mountainous Watersheds: Linkage with Landscape Characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Sarker, S.; Sarker, T.; Leta, O.T. Analyzing the Critical Locations in Response of Constructed and Planned Dams on the Mekong River Basin for Environmental Integrity. Environ. Res. Commun. 2022, 4, 101001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Jim, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, M.L.; Liu, C.; Chan, N.W.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; et al. Impact of Land-Use/Land-Cover and Landscape Pattern on Seasonal in-Stream Water Quality in Small Watersheds. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 357, 131907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangshan Government. Available online: http://www.tangshan.gov.cn/zhuzhan/tsgl/20200910/1072598.html (accessed on 2 July 2022).
- Wei, M.; Huang, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Akram, W.; Khatoon, Z.; Renaud, F.G. Evolution of Water Quality and Biota in the Panjiakou Reservoir, China as a Consequence of Social and Economic Development: Implications for Synergies and Trade-Offs between Sustainable Development Goals. Sustain. Sci. 2021, 17, 1385–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y. Coupling Coordination Analysis of Ecosystem Services and Urban Development of Resource-Based Cities: A Case Study of Tangshan City. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Han, Y.; Jia, D. Impact of Climate Change on the Blue Water Footprint of Agriculture on a Regional Scale. Water Supply 2018, 19, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, H. The Spatial Variations of Water Quality and Effects of Water Landscape in Baiyangdian Lake, North China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 16716–16726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m Annual Land Cover Dataset and Its Dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESRI. ArcGIS Desktop: Release 10.2; ESRI: Redlands, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS v4: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical and Continuous Maps; University of Massachusetts: Amherst, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Yang, N.; Zhao, J.; Shaaban, M.; Hu, R. Crop Straw Incorporation Mediates the Impacts of Soil Aggregate Size on Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Geoderma 2021, 401, 115342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres-Neto, P.R.; Legendre, P.; Dray, S.; Borcard, D. Variation Partitioning of Species Data Matrices: Estimation and Comparison of Fractions. Ecology 2006, 87, 2614–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-7. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- Yu, S.; Xu, Z.; Wu, W.; Zuo, D. Effect of Land Use Types on Stream Water Quality under Seasonal Variation and Topographic Characteristics in the Wei River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.X.; Xu, J.F.; Yin, W.; Chen, Q.Z.; Wang, J.; Shi, Z.H. Effect of Local Watershed Landscapes on the Nitrogen and Phosphorus Concentrations in the Waterbodies of Reservoir Bays. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, C.; Johnson, L.B.; Host, G.E. Landscape-Scale Influences on Stream Habitats and Biota. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1996, 53, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Cueva, P.; Fries, A.; Montesinos, P.; Rodriguez-Diaz, J.A.; Boll, J. Spatial Estimation of Soil Erosion Risk by Land-Cover Change in the Andes OF Southern Ecuador. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yu, Z. Land Use Pattern Optimization Based on CLUE-S and SWAT Models for Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution Control. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 58, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Hong, S.; Zhan, F.B.; Zhang, L. Influencing Factor Analysis of Phosphorus Loads from Non-Point Source: A Case Study in Central China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xia, J.; Liang, T. Non-Point Source Pollution Modelling Using Soil and Water Assessment Tool and Its Parameter Sensitivity Analysis in Xin’anjiang Catchment, China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuda, Y.; Ito, S. A Review of Spatial-Explicit Factors Determining Spatial Distribution of Land Use/Land-Use Change. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 7, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Xiang, A.; Xiao, S.; Lin, D.; Lin, Y.; Lu, Y. Terrain Gradient Response of Landscape Ecological Environment to Land Use and Land Cover Change in the Hilly Watershed in South China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Rousseau, A.N. Landscape Influences on Water Quality in Riparian Buffer Zone of Drinking Water Source Area, Northern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Dong, R.; Jiang, C.; Ni, M. Influences of Land Use Metrics at Multi-Spatial Scales on Seasonal Water Quality: A Case Study of River Systems in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, C.; Mao, J.; Li, Z.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B. Effects of Driving Factors at Multi-Spatial Scales on Seasonal Runoff and Sediment Changes. CATENA 2023, 222, 106867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Coupled Effects of Natural and Anthropogenic Controls on Seasonal and Spatial Variations of River Water Quality during Baseflow in a Coastal Watershed of Southeast China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carey, R.O.; Migliaccio, K.W.; Li, Y.; Schaffer, B.; Kiker, G.A.; Brown, M.T. Land Use Disturbance Indicators and Water Quality Variability in the Biscayne Bay Watershed, Florida. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, T.; Mazumder, A. Spatial Scale of Land-Use Impacts on Riverine Drinking Source Water Quality. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Song, J.; Yan, J. Influences of Landscape Pattern on Water Quality at Multiple Scales in an Agricultural Basin of Western China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 319, 120986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, S.; Wu, Q.; Li, F.; Wu, P.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Zeng, J. Buffer Zone-Based Trace Elements Indicating the Impact of Human Activities on Karst Urban Groundwater. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urgeghe, A.M.; Mayor, Á.G.; Turrión, D.; Rodríguez, F.; Bautista, S. Disentangling the Independent Effects of Vegetation Cover and Pattern on Runoff and Sediment Yield in Dryland Systems—Uncovering Processes through Mimicked Plant Patches. J. Arid Environ. 2021, 193, 104585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, L.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Landscape Patterns and Topographic Features Affect Seasonal River Water Quality at Catchment and Buffer Scales. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051438
Deng L, Li W, Liu X, Wang Y, Wang L. Landscape Patterns and Topographic Features Affect Seasonal River Water Quality at Catchment and Buffer Scales. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(5):1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051438
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Li, Wanshu Li, Xiaojie Liu, Yazhu Wang, and Lingqing Wang. 2023. "Landscape Patterns and Topographic Features Affect Seasonal River Water Quality at Catchment and Buffer Scales" Remote Sensing 15, no. 5: 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051438
APA StyleDeng, L., Li, W., Liu, X., Wang, Y., & Wang, L. (2023). Landscape Patterns and Topographic Features Affect Seasonal River Water Quality at Catchment and Buffer Scales. Remote Sensing, 15(5), 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051438







