Spatial Correlations of Land Use Carbon Emissions in Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration: A Perspective from City Level Using Remote Sensing Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
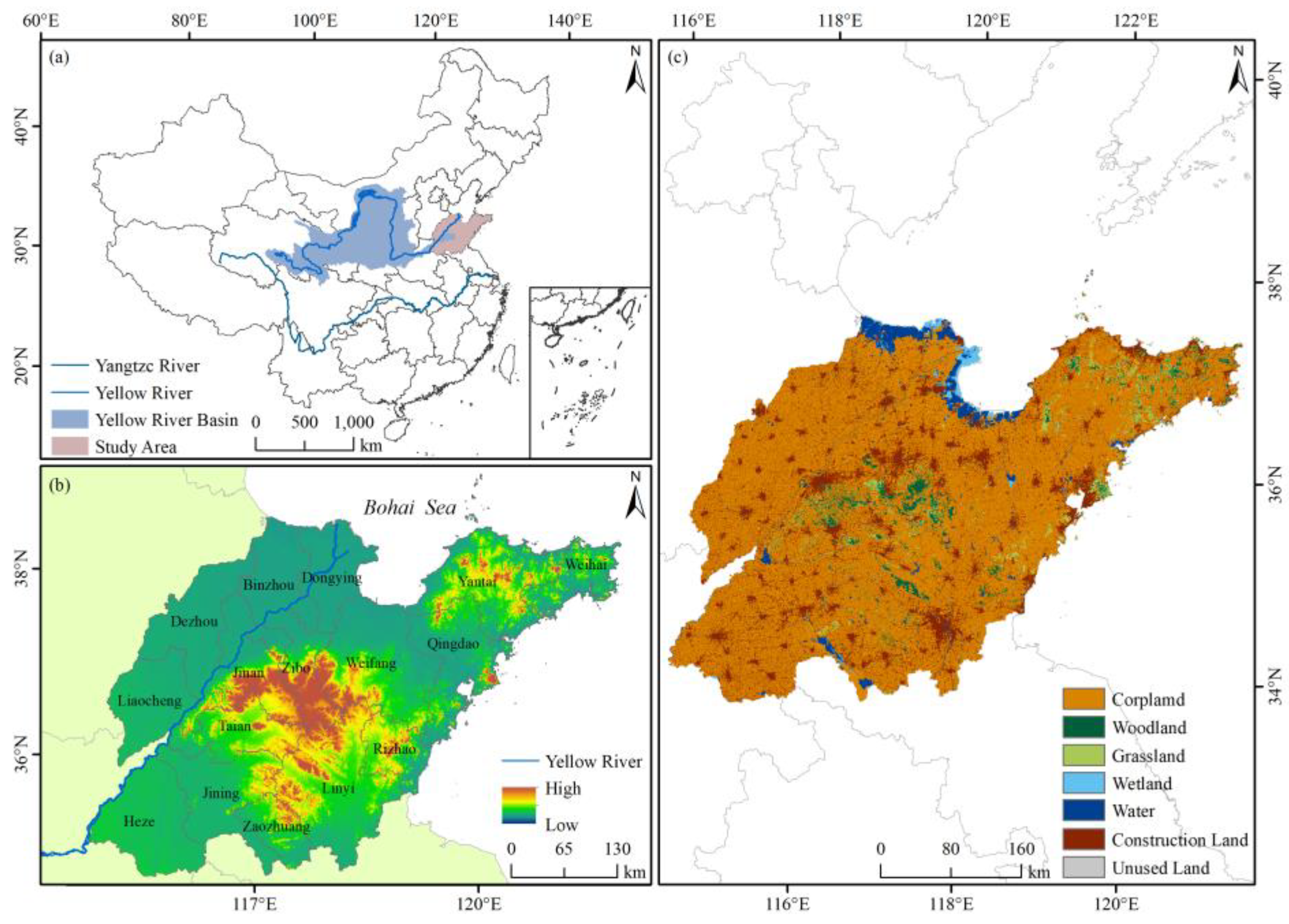
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.3. Research Methodology
2.3.1. Carbon Emissions Calculation Method
- Direct Carbon Emissions
- 2.
- Indirect Carbon Emissions
2.3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Models
3. Results
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Land Use Change
3.1.1. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Land Use Change in the Urban Agglomeration
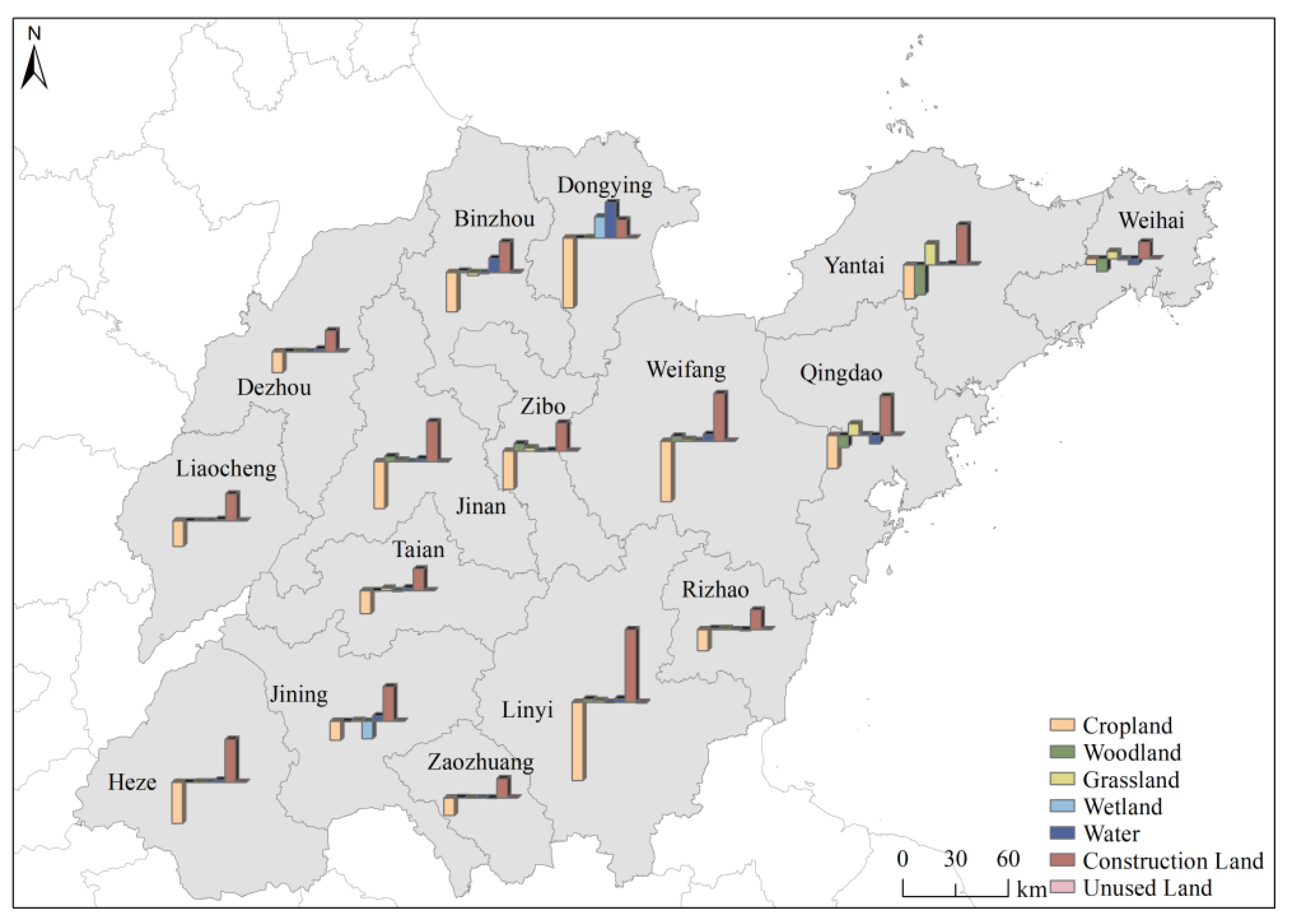
3.1.2. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Land Use Change at the City Level
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Carbon Emissions at the City Level
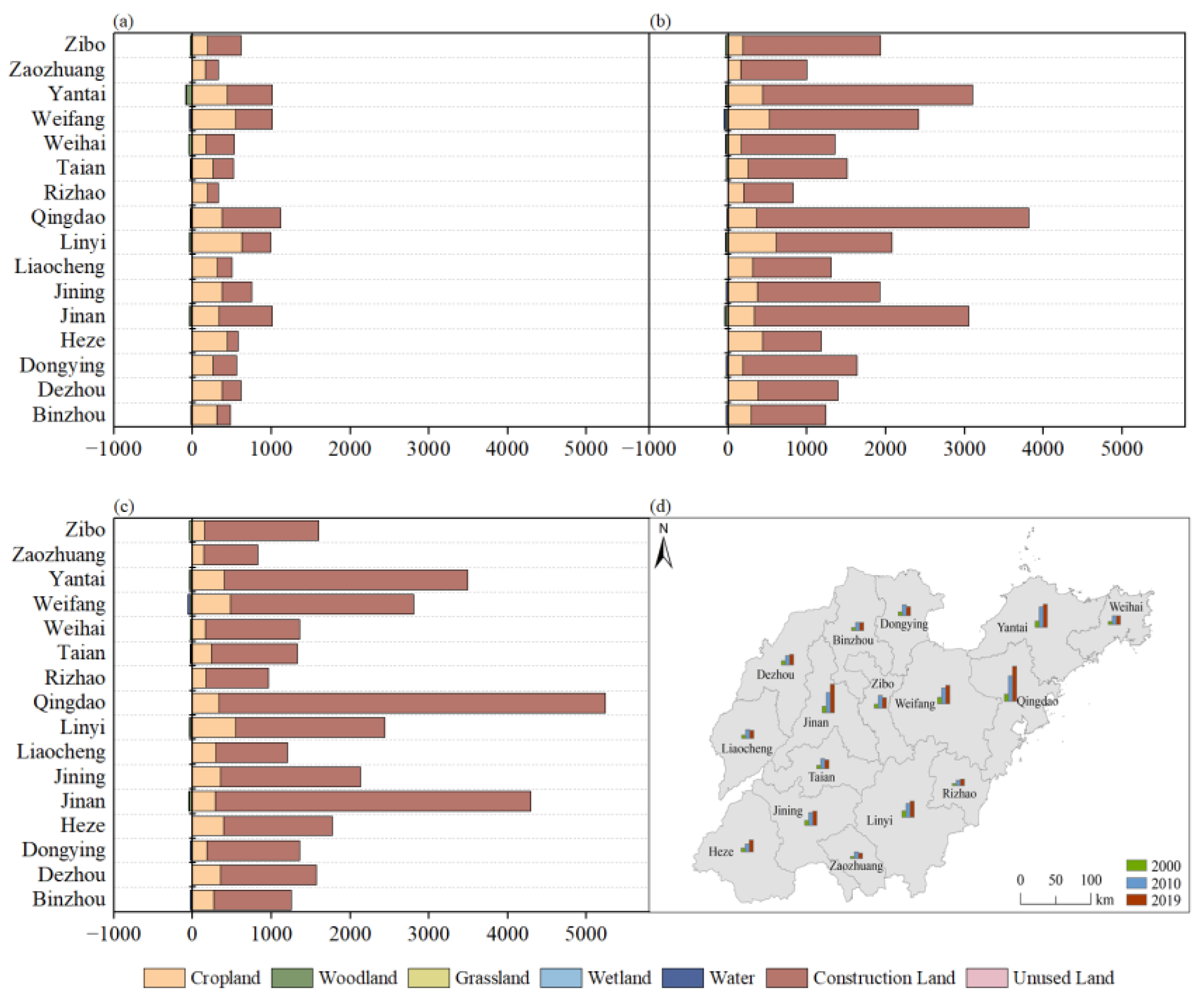
3.2.1. Characteristics of Carbon Emissions from Different Land Use Types
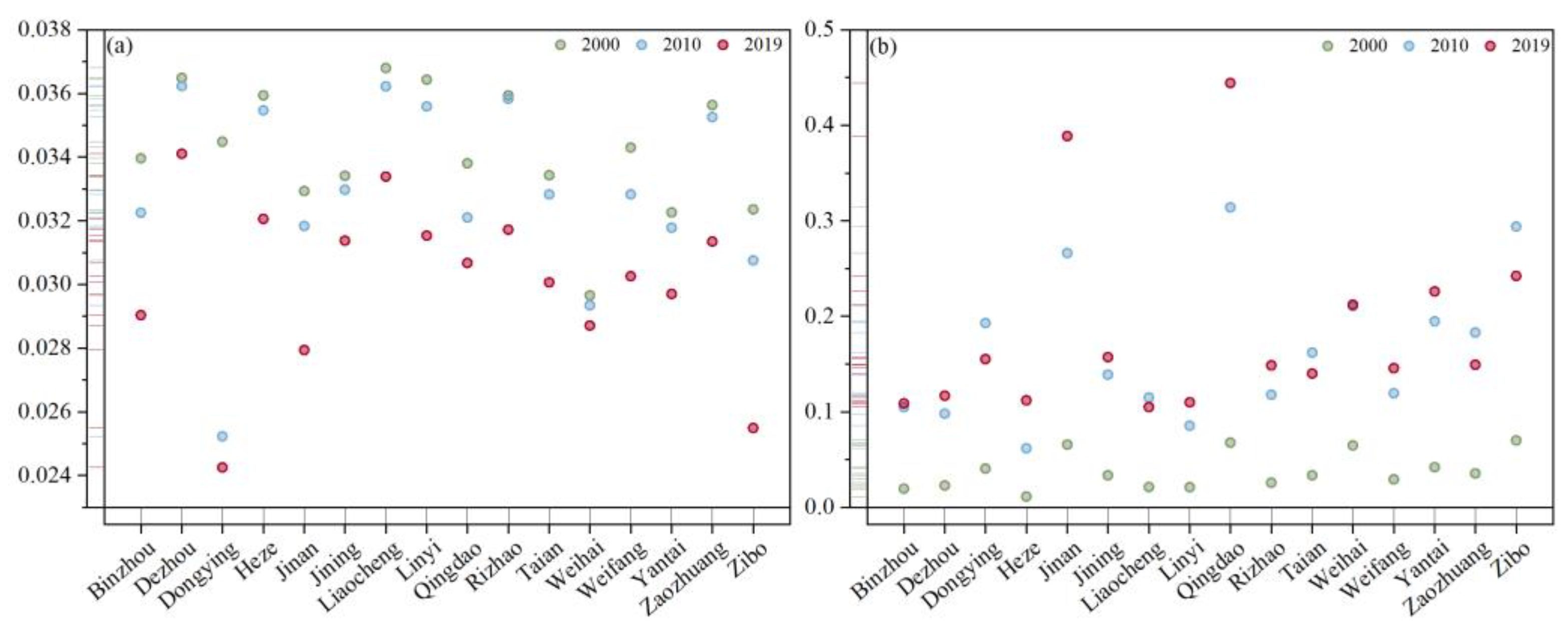
3.2.2. Characteristics of Land-Average Carbon Emissions and Carbon Emissions per Capita at the City Level
3.2.3. Characteristics of Land-Average Carbon Emissions and Carbon Emissions per Capita of Major Carbon Sources
3.3. Spatial Characteristics of Carbon Emissions in the Urban Agglomeration
3.3.1. Global Spatial Autocorrelation Characteristics at the City Level
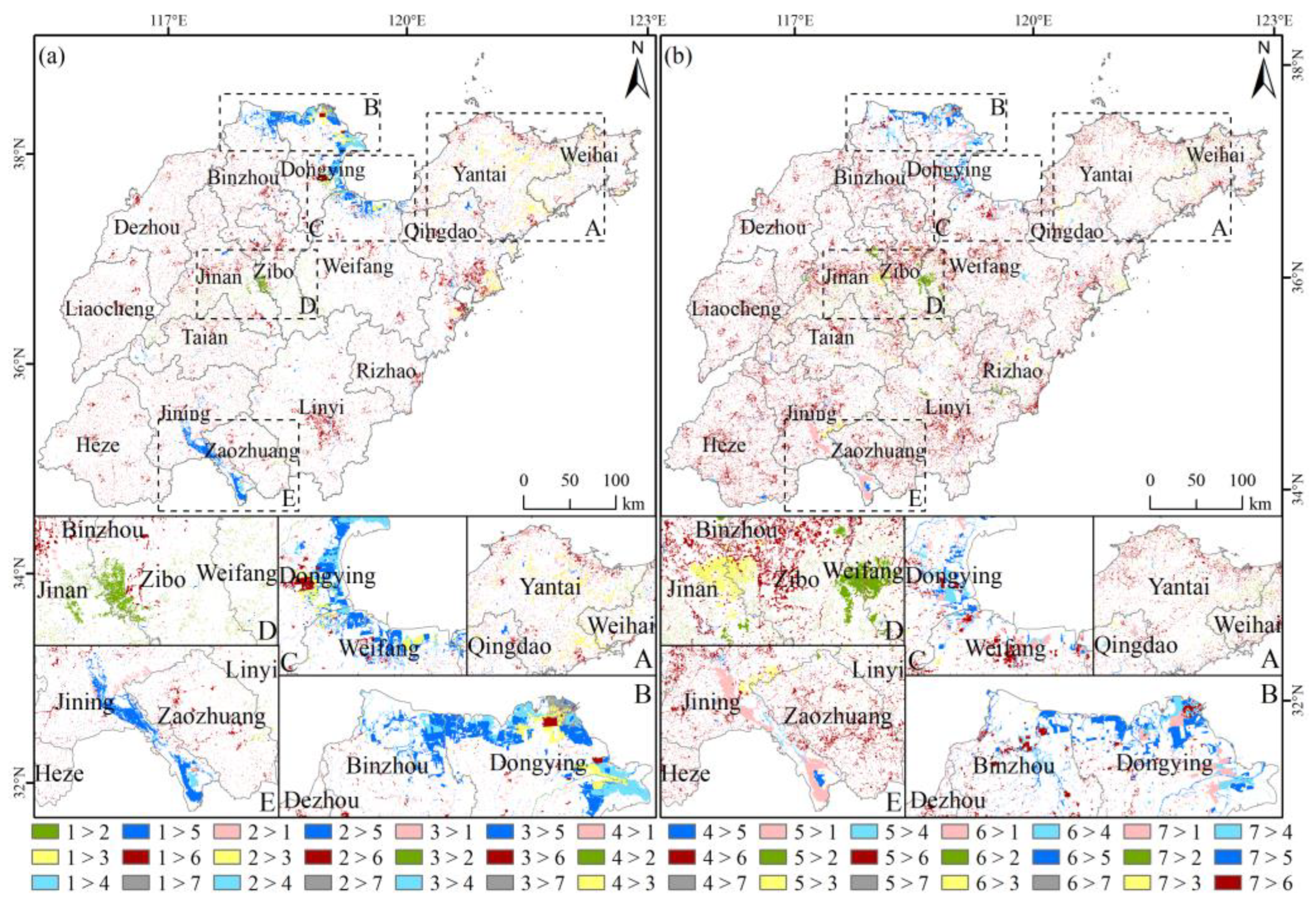
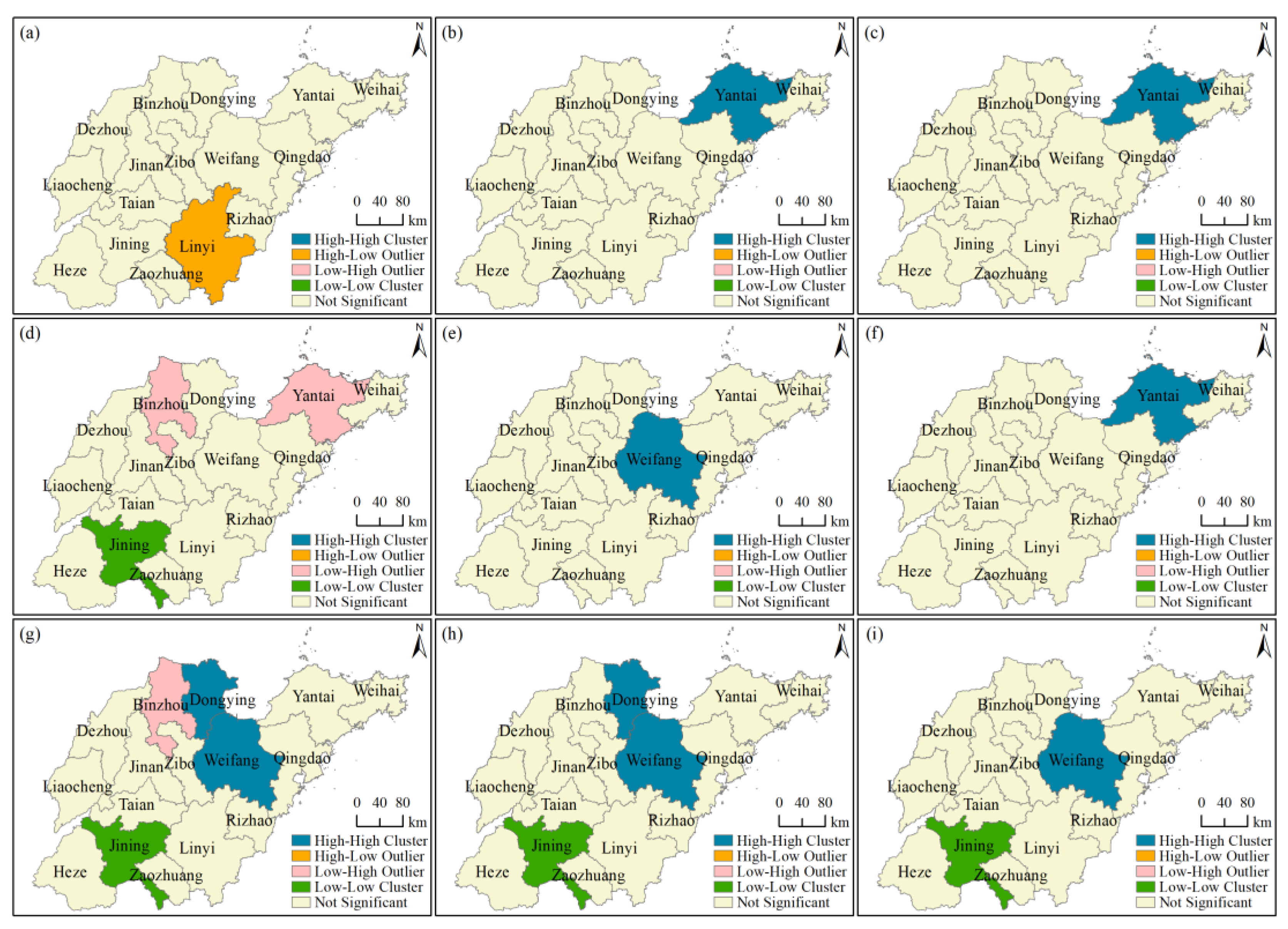
3.3.2. Local Spatial Autocorrelation Characteristics at the City Level
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Land Use Change
4.2. Analysis of Carbon Emissions at the City Level
4.3. Analysis the Spatial Agglomeration of Carbon Emissions at the City Level
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; Kafy, A.A.; Xiao, P.; Han, S.; Zou, S.; Saha, M.; Zhang, C.; Tan, S. Impact of urban expansion on land surface temperature and carbon emissions using machine learning algorithms in Wuhan, China. Urban Clim. 2023, 47, 101347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranagalage, M.; Morimoto, T.; Simwanda, M.; Murayama, Y. Spatial Analysis of Urbanization Patterns in Four Rapidly Growing South Asian Cities Using Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabous, S.A.; Shanableh, A.; AlRuzouq, R.; Hosny, F.; Khalil, M.A. A spatio-temporal framework for sustainable planning of buildings based on carbon emissions at the city scale. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liang, X.; Leng, J.; Xu, X.; Liao, W.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, Q.; et al. Global projections of future urban land expansion under shared socioeconomic pathways. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Liao, H.; Wei, Y. Impacts of urbanization on carbon emissions: An empirical analysis from OECD countries. Energy Policy 2021, 151, 112171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Wei, D.; Lin, W. Influencing factors and spatial patterns of energy-related carbon emissions at the city-scale in Fujian province, Southeastern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Tang, J.; Nguyen, M.; Cui, S. Identifying the trade-offs between climate change mitigation and adaptation in urban land use planning: An empirical study in a coastal city. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpio, A.; Ponce-Lopez, R.; Lozano-García, D.F. Urban form, land use, and cover change and their impact on carbon emissions in the Monterrey Metropolitan area, Mexico. Urban Clim. 2021, 39, 100947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.S.; Yi, L. Evaluating the nexus between ongoing and increasing urbanization and carbon emission: A study of ARDL-bound testing approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 27548–27559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Li, X.; Tan, W.; Xiao, R. Decoupling relationship analysis between urbanization and carbon emissions in 33 African countries. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Andlib, Z.; Genie, M.G. How do renewable energy and urbanization cause carbon emissions? Evidence from advanced panel estimation techniques. Renew. Energy 2022, 185, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Z.; Wang, L.; Che, M.; Hou, S. Effects of Different Urbanization Levels on Land Surface Temperature Change: Taking Tokyo and Shanghai for Example. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, L.; Wang, Q. The impact of energy efficiency on carbon emissions: Evidence from the transportation sector in Chinese 30 provinces. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cai, Y.; Liu, L. Research on the Effect of Urbanization on China’s Carbon Emission Efficiency. Sustainability 2019, 12, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, B.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, Q.; Yu, X.; Chen, Y. Spatial heterogeneity of urban–rural integration and its influencing factors in Shandong province of China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; Fang, R.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q. Spatial-temporal characteristics of carbon emissions from land use change in Yellow River Delta region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Jiang, F. Spatial and temporal distribution of population in urban agglomerations changes in China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, T.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Spatial correlation evolution and prediction scenario of land use carbon emissions in China. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 71, 101802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, S.; Tong, X.; Lei, Z.; Gao, C.; Wang, J. Modeling changes in China’s 2000–2030 carbon stock caused by land use change. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Bai, L.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, J.; Li, Z.; Min, Z.; Cui, L.; Li, P. Vegetation position impacts soil carbon losses on the slope of the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2023, 222, 106875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Yang, C.; Yuan, J.; Xie, M. Seasonal freeze-thaw characteristics of soil carbon pools under different vegetation restoration types on the Longzhong Loess Plateau. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Kafy, A.; Ren, B.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, S.; Li, J. Application of the Optimal Parameter Geographic Detector Model in the Identification of Influencing Factors of Ecological Quality in Guangzhou, China. Land 2022, 11, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Wang, W.; Cai, W.; Chen, N.; Hu, S.; Luo, X.; Li, J.; Zhan, C. Remote sensing inversion and prediction of land use land cover in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatappa, M.; Sasaki, N.; Anantsuksomsri, S.; Smith, B. Applications of the Google Earth Engine and Phenology-Based Threshold Classification Method for Mapping Forest Cover and Carbon Stock Changes in Siem Reap Province, Cambodia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liang, H.; Chang, X.; Cui, Q.; Tao, Y. Land Use Patterns on Carbon Emission and Spatial Association in China. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 35, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Seto, K.C. Projecting global urban land expansion and heat island intensification through 2050. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 114037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, M.; Tang, Z.; Mei, Z. Urbanization, land use change, and carbon emissions: Quantitative assessments for city-level carbon emissions in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xing, H.; Hou, D. Analysis of carbon emissions from land cover change during 2000 to 2020 in Shandong Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Ma, Q.; Chen, L.; Ma, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, C. Research on peak prediction of urban differentiated carbon emissions-a case study of Shandong Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 134050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C. Decoupling analysis and peak prediction of carbon emission based on decoupling theory. Sustain. Comput.Inform. Sys. 2020, 28, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhan, Z.; Shi, J. Research on the temporal and spatial characteristics, spatial clustering and governance strategies of carbon emissions in cities of Shandong. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, D. Transportation carbon emission reduction potential and mitigation strategy in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Chatalova, L.; Gao, X.; Zhang, A. Reduction of carbon emissions through resource-saving and environment-friendly regional economic integration: Evidence from Wuhan metropolitan area, China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 166, 120590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Li, S.; Kang, Q.; Wang, N.; Guo, K.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J. Spatial Spillover Effects of Renewable Energy on Carbon Emissions in Less-developed Areas of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 19019–19032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Lu, X.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, Y. Evaluating urban agglomeration resilience to disaster in the Yangtze Delta city group in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wood, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, X.; Long, X. CO2 emission in transportation sector across 51 countries along the Belt and Road from 2000 to 2014. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 122000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X. Carbon Emission, air and water pollution in coastal China: Financial and trade effects with application of CRS-SBM-DEA model. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, X.; Sun, D. The Influencing Effects of Industrial Eco-Efficiency on Carbon Emissions in the Yangtze River Delta. Energies 2021, 14, 8169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Tong, B.; Ren, B.; Zhang, L.; Lin, X. Analysis of the coupling characteristics of land transfer and carbon emissions and its influencing factors: A case study of China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Woodcock, C.E.; Olofsson, P.; Hutyra, L.R. Spatiotemporal assessment of land use/land cover change and associated carbon emissions and uptake in the Mekong River Basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J. How China will protect one-quarter of its land. Nature 2019, 569, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Zuo, L.; Wen, Q.; Yi, L.; Xu, J.; Hu, S.; Liu, B. Chinese cropland losses due to urban expansion in the past four decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, W. Study on the spatial and temporal differentiation and influencing factors of carbon emissions in Shandong province. Nat. Hazards 2017, 87, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Woods, M.; Zou, J. Accelerated restructuring in rural China fueled by ‘increasing vs. decreasing balance’ land-use policy for dealing with hollowed villages. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, W. Decoupling between Economic Development and Carbon Emissions and Its Driving Factors: Evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 15, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Land Type | Factor of Carbon Emissions |
|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.0422 |
| Woodland | −0.0644 |
| Grassland | −0.0021 |
| Wetland | −0.00006132 |
| Water | −0.0253 |
| Unused land | −0.0005 |
| Energy Type | Standard Coal Conversion Factors (kgce·kg−1) | Carbon Emissions Factors (kg·kgce−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Coal | 0.7143 | 0.7559 |
| Coke | 0.9714 | 0.855 |
| Gasoline | 1.4714 | 0.59 |
| Kerosene | 1.4714 | 0.57 |
| Fuel oil | 1.4286 | 0.62 |
| Moran’s I Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Emissions | Land-Average Carbon Emissions | Carbon Emissions per Capita | |
| 2000 | −0.164 | −0.052 | 0.269 |
| 2010 | −0.037 | −0.018 | 0.290 |
| 2019 | −0.066 | −0.049 | 0.289 |
| 2000 | −0.164 | −0.052 | 0.269 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Yang, C.-h.; Zhao, Y.-c.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.-p. Spatial Correlations of Land Use Carbon Emissions in Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration: A Perspective from City Level Using Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061488
Zhao L, Yang C-h, Zhao Y-c, Wang Q, Zhang Q-p. Spatial Correlations of Land Use Carbon Emissions in Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration: A Perspective from City Level Using Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(6):1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061488
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Lin, Chuan-hao Yang, Yu-chen Zhao, Qian Wang, and Qi-peng Zhang. 2023. "Spatial Correlations of Land Use Carbon Emissions in Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration: A Perspective from City Level Using Remote Sensing Data" Remote Sensing 15, no. 6: 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061488
APA StyleZhao, L., Yang, C.-h., Zhao, Y.-c., Wang, Q., & Zhang, Q.-p. (2023). Spatial Correlations of Land Use Carbon Emissions in Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration: A Perspective from City Level Using Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing, 15(6), 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061488






