Abstract
Object tracking using Hyperspectral Images (HSIs) obtains satisfactory result in distinguishing objects with similar colors. Yet, the tracking algorithm tends to fail when the target undergoes deformation. In this paper, a SiamRPN based hyperspectral tracker is proposed to deal with this problem. Firstly, a band selection method based on a genetic optimization method is designed for rapidly reducing the redundancy of information in HSIs. Specifically, three bands with highest joint entropy are selected. To solve the problem that the information of the template in the SiamRPN model decays over time, an update network is trained on the dataset from general objective tracking benchmark, which can obtain effective cumulative templates. The use of cumulative templates with spectral information makes it easier to track the deformed target. In addition, transfer learning of the pre-trained SiamRPN is designed to obtain a better model for HSIs. The experimental results show that the proposed tracker can obtain good tracking results over the entire public dataset, and that it is better than the other popular trackers when the target’s deformation is qualitatively and quantitatively compared, achieving an overall success rate of 57.5% and a deformation challenge success rate of 70.8%.
1. Introduction
Hyperspectral Object Tracking (HOT) tries to predict the position of targets continuously over Hyperspectral Videos (HSVs), using only information on the state of the targets at the initial time. For popular visual target tracking methods, it is limited in describing physical characteristics of the image, which leads to tracking failure, as the target is deformed [1,2]. Most HOT algorithms extract the spatial and spectral information for objects of interest [3], which makes it easy to distinguish objects with similar colors. In spite of the potential of hyperspectral trackers, their robustness can be negatively affected by the presence of redundant information in the HSVs [4]. Thus, there is a pressing need for further research to enhance the accuracy of tracking targets in HSVs.
Currently, there are two main tracking methods, including methods based on Deep Learning (DL) [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13] and methods based on Discriminative Correlation Filtering (DCF) [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21]. The former leverages neural networks to obtain more sophisticated depth features, which have proven to be effective for subsequent tracking. The Deep Learning Tracker (DLT) [5] was the first tracker to utilize deep learning techniques, completing the tracking process through a particle filtering framework. The feature extraction method is based on a stacked auto-encoder network. Yet, DLT tends to lose targets with partial multi-target overlap. The first application [7] of the siamese network-based tracker made by Bertinetto performs a convolution operation on the feature space of the candidate template and corresponding search region, and then determines the location of the target by finding the maximum response. The Siamese Region Proposal Network (SiamRPN) algorithm [22] draws inspiration from the principle of generating candidate regions for target detection, ultimately refining these areas to achieve a more precise bounding box. However, the algorithm’s performance can be negatively impacted when the background is mistakenly identified as the semantic object, as the SiamRPN algorithm considers the semantic background as a source of interference. Furthermore, the Distractor-aware Siamese Networks (DaSiamRPN), introduced by Zhu [23], improves the discriminatory power of the tracker by incorporating difficult negative samples in the training model. Besides, Li et al. applied the ResNet network into a SiamRPN++ visual tracker [24], which achieves good tracking results. Yet, the SiamRPN-based tracker is susceptible to drift towards regions that are similar to the target, due to the absence of model updates.
The DCF method [25,26] has demonstrated notable efficiency in training the frequency domain filter. The pioneer Minimum Output Sum of Squared Error (MOSSE) algorithm [14] adopts the gray-scale feature to complete target tracking with high execution efficiency. Yet, this algorithm does not take the background information and scale updating into consideration. Moreover, additional features, such as color name features [27], Histogram of Gradient (HOG) [15], and deep features [8], have proven to be valuable in advancing the development of tracking. To be more specific, the HOG representation is obtained by the Kernel Correlation Filter (KCF) algorithm [15]. Furthermore, a multi-feature of Visual Geometry Group (VGG) and HOG are fused with multi-cue correlation by Wang et al. [28]. However, the above DCF algorithms are sensitive to the situation of occlusion [29] during tracking. Besides, another issue that arises in visual tracking is when the target is similar in color features to its surrounding background.
From the above analysis, tracking methods based on DL and DCF have been widely applied to tracking visible targets [24,30,31]. The similarity in color between the target and background often results in tracking drift for most trackers to some extent. The spatial and spectral characteristics of hyperspectral data can effectively distinguish objects from the background, which is widely used in the field of image classification [32,33]. Specifically, Ding et al. [32] proposed a novel multi-feature fusion network, which extracts multi-scale pixel-level local features for HSI classification. Zhang et al. [33] proposed a graph neural framework based on multiple adaptive receptive fields, which addresses issues such as insufficient labeled training samples and high spectral mixing between materials. Benefiting from spectral properties, a number of effective algorithms [3,34,35,36,37] have been developed in the field of HOT. Qian et al. [4] introduced a HOT method utilizing the convolutional network without a training strategy. The DCF framework obtains a high execution efficiency, yet the elimination of redundancy in the spectral information is not considered. Uzkent et al. [38] introduced a Deep Kernelized Correlation Filter-based method (DeepHKCF) for object tracking, which did not consider the valuable spectral information. In their work, HOG feature channels were concatenated with pure hyperspectral channels for tracking aerial objects. Zhang et al. [39] proposed an HSV tracking method based on multi-feature integration(MFI-HVT), which generates feature maps by a Histogram of Gradients (HOG) and a pre-trained VGG-19 network, and then detects targets on high-speed aircraft by using a kernelized correlation filter framework. The Material-based Hyperspectral Tracking (MHT) [3] method, developed by Xiong, embeds spectral-spatial information into multi-dimensional gradient histograms. In addition, the Band Attention Aware Ensemble Network (BAENet) [34] method, introduced by Li, utilizes a band selection network combined with the VITAL [40] tracking framework. Liu et al. [41] proposed an anchor-free siamese network (called HA-Net), including RGB classification, a regression network, and a hyperspectral network. Furthermore, HA-Net performs online updates by selecting the image with the highest confidence every ten frames. However, the limited number of HSVs may result in insufficient training for the model.
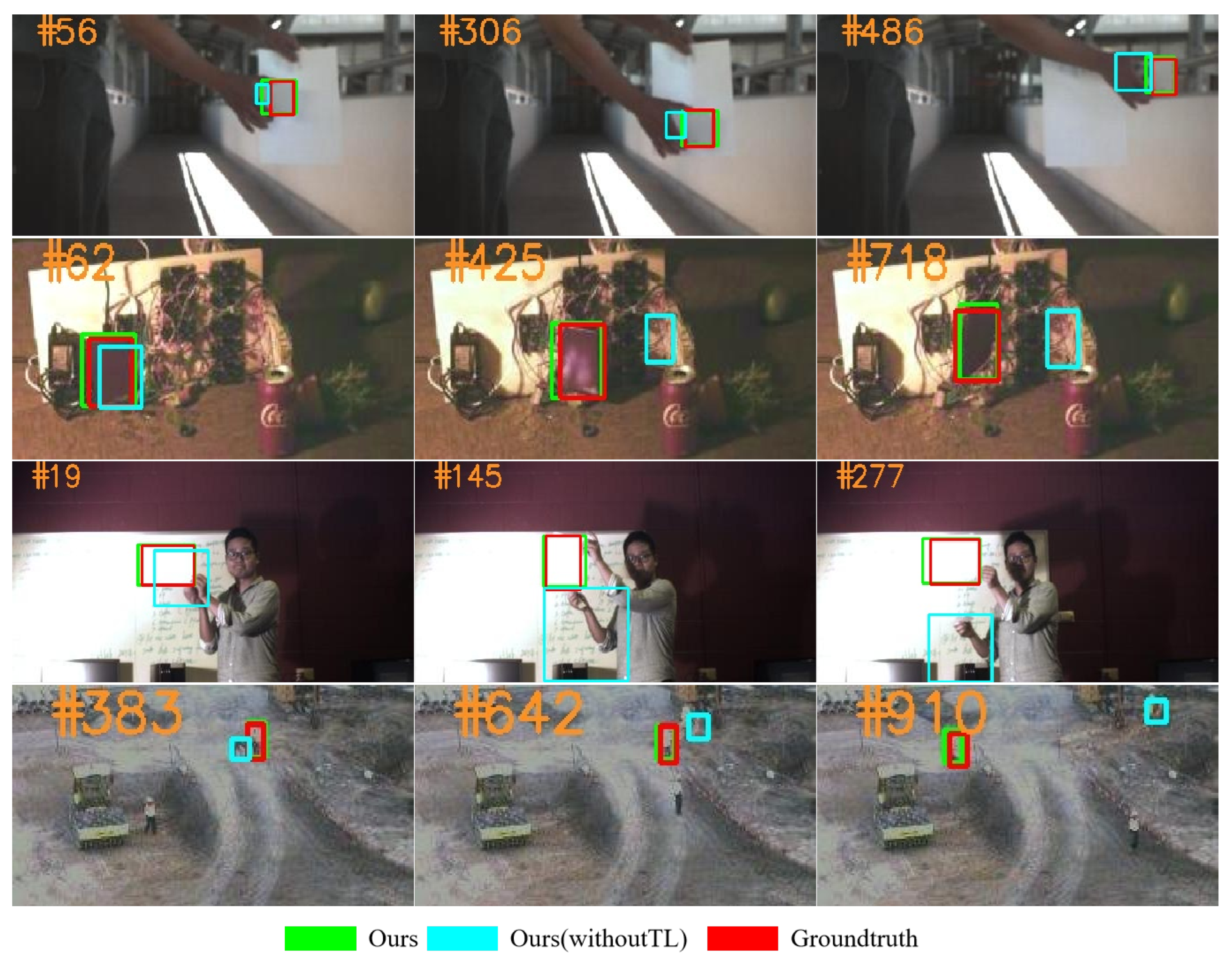
In general, tracking algorithms that utilize HSVs encounter limitations related to the size of the dataset, which can make it challenging to effectively leverage the semantic information of Hyperspectral images (HSIs). In this paper, with the siamese network as the backbone model in our tracker, the overall framework also includes band selection [42], model training, feature transfer, and the template updating mechanism. Specifically, the three valuable bands are first obtained via a genetic algorithm [43] with the joint entropy or the optimal index factor. Besides, our model is pre-trained on datasets from the General Objective Tracking (GOT) benchmark [44], and the semantic information in the HSV is known to benefit from Transfer Learning (TL) [45]. In addition, a convolutional neural network named Hyperspectral template Update Network (HSUpdateNet) has been developed, inspired by the UpdateNet [46]. This method not only replaces the template manual update function, but also utilizes the spectral information for tracking. For the reason that the UpdateNet [46] is successfully applied into the Fully Convolutional Siamese Networks (SiamFC [47]) and the SiamRPN++ [24], the HSUpdateNet designed by us is applied into our previous work named BS-SiamRPN [36]. Subsequently, the material composition provided by the rich spectral information improves the ability of feature identification. Finally, the selected bands are input into the backbone network, which extracts spectral features of HSVs. The effect of the TL strategy on the proposed model can be seen in Figure 1, which proves that a tracking algorithm without the TL strategy is very susceptible to the representation of the target.
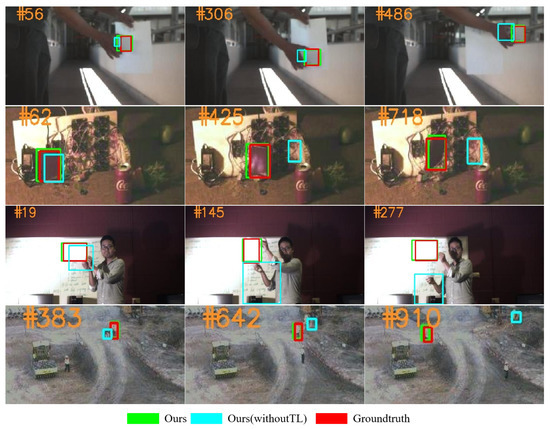
Figure 1.
Comparison of trackers with and without TL.
The main contributions are listed as follows.
- •
- The SiamRPN model is applied into the field of HOT, which verifies its applicability in processing HSVs.
- •
- To reduce redundancy in HSVs, bands are determined by an intelligent optimization algorithm based on maximum joint entropy.
- •
- TL has been effectively applied into the domain of HOT, which effectively solves the limitation of lacking labeled data in hyperspectral datasets referring to learning deep models.
- •
- The proposed HSUpdateNet with an effective template update strategy, which exploits rich spectral information, helps to obtain a more accurate cumulative template, and deals with the problem of deformation.
The following is the relevant content of this paper. In Section 1, the current state of development of the HSV tracking is given in detail. Then, the proposed framework is described in Section 2. In Section 3, experimental results are analyzed. In Section 4, the direction of future research is discussed. Finally, Section 5 draws several conclusions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SiamRPN
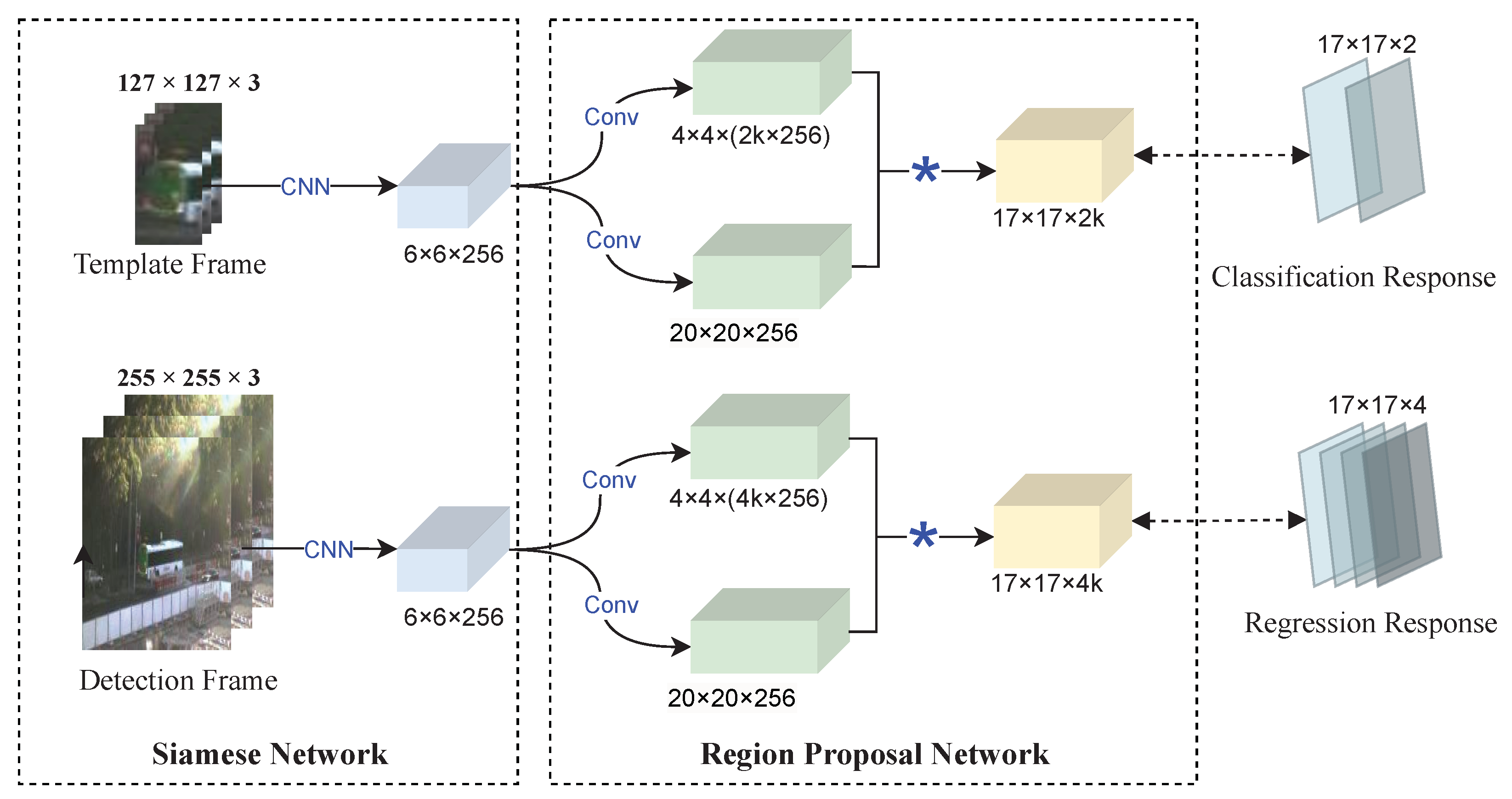
The SiamRPN model converts the initial similarity calculation problem into a regression or classification problem using a large-scale offline training network, which is shown in Figure 2. The SiamRPN extracts features using a siamese network, which is in line with the architecture of the SiamFC [47] model. The region proposal network also includes a classification branch and a regression one. The former is specifically used to calculate the Intersection Over Union (IOU) of the output box with the real target. Besides, a fixed threshold is set to distinguish the target from the background. The regression branch of the proposed method is responsible for both accurately matching the predicted bounding box for the target with its actual state, as well as compensating for any potential scale variations during the initial stages of the tracking process.
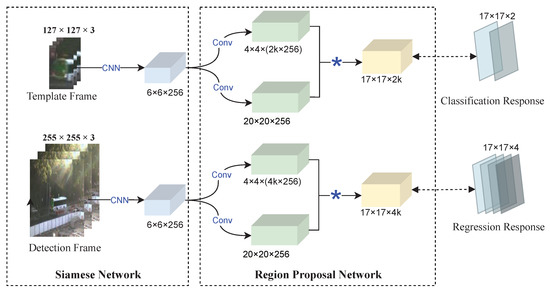
Figure 2.
The framework of SiamRPN.
The accuracy and speed of several trackers, including the CFNet tracker [48], the DaSiamRPN tracker [49], and the SiamRPN++ tracker [24], are balanced, yet several problems still need to be solved. First of all, most siamese trackers only utilize characteristics that can differentiate between foreground and non-semantic contexts. It is challenging to ensure the performance in complex environments. Secondly, siamese trackers lack an online update paradigm, which can cause the tracker to lose the target if it undergoes abrupt changes in appearance. Thirdly, the local search technique of the siamese tracker is sensitive to partially occluded targets. However, HSVs help to make up for the disadvantage of visible data in tracking.
Here, the feature of the detection frame is subjected to convolution operations by the classification branch, and the feature of the template frame refers to the regression branch.
where ∗ denotes the convolution operation and softmax is utilized in calculating the classification loss. consist of channels, indicating positive and negative excitation. Each point in the channels of is represented as and . This is the distance between the anchor and ground truth. and denote the output feature in the detection branch. Both the template feature maps and are kernels.
The definition of the loss function is as follows:
where the center point is denoted by and and the shape of anchor boxes is represented by and , respectively. Moreover, the ground truth boxes are described by , and , respectively. can control the error range of using mean square error or mean absolute error. In Equation (3), the loss is formulated as follows:
Finally, the total loss function is as follows:
where describes the cross entropy loss and is a hyperparameter of the two losses ( = 1.2).
2.2. Hyperspectral Band Selection
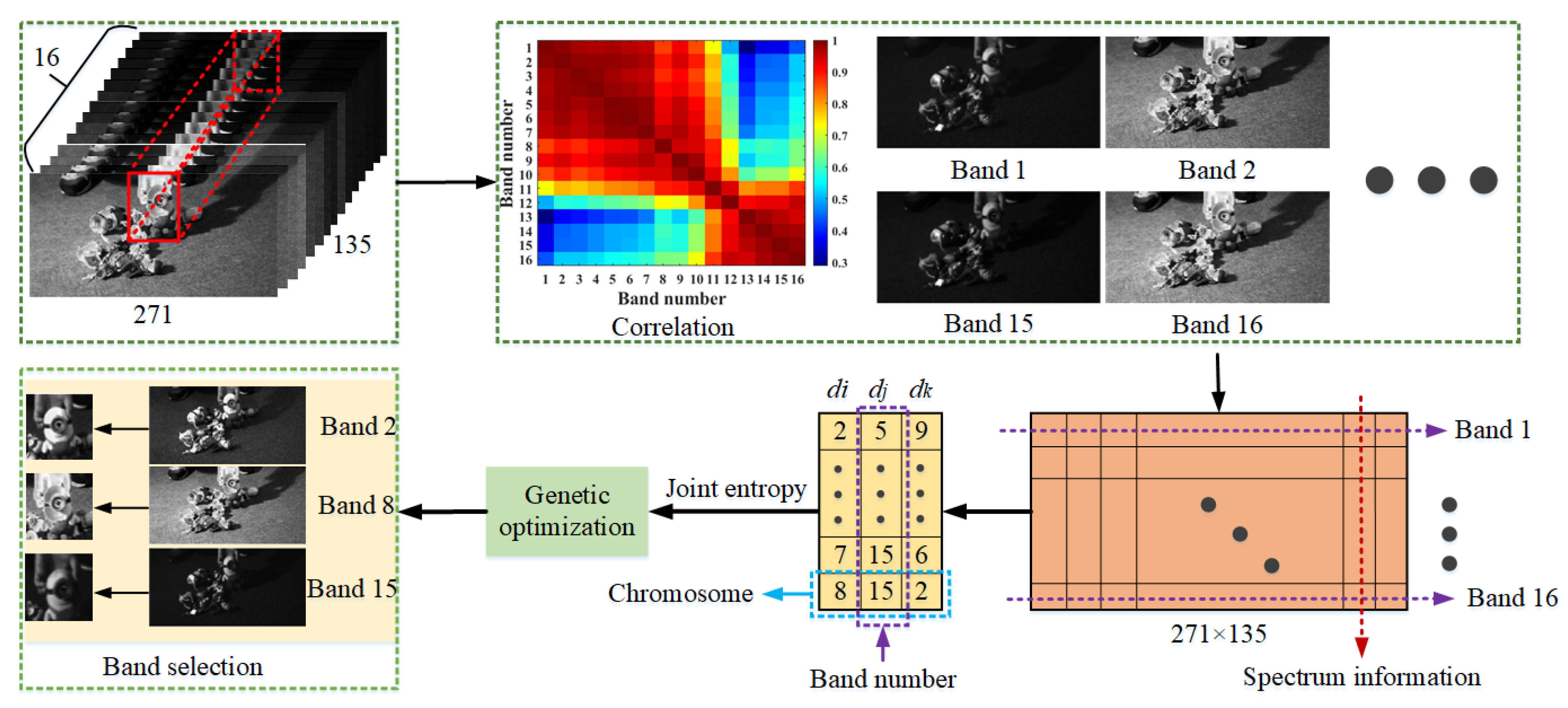
In order to simplify the tracking process and reduce the redundant information of HSVs, the valuable features of HSVs are obtained by feature dimension reduction, such as feature extraction [16] and feature selection [50]. The former contains some popular methods, such as singular value decomposition and principal component analysis, which are utilized to extract features in a reduced dimensional space. However, these algorithms need to provide a new definition of feature attributes. The latter focuses on choosing features with a strong performance of classification, such as band selection on HSIs. In order to preserve the majority of the hyperspectral information, the genetic algorithm [51] is employed. As a result, the correlation value between the retained bands is usually low. Figure 3 displays the procedure of band selection.
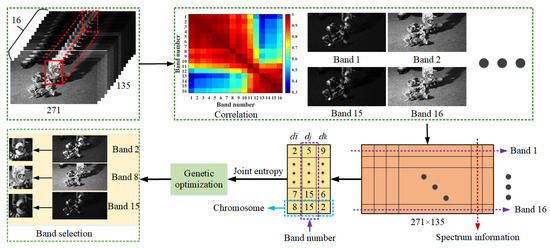
Figure 3.
Band selection for the first toy1 picture.
In Figure 3, the matrix diagram of the correlation coefficient shows that the initial images can be separated into numerous groups. In addition, images belonging to the same group exhibit high correlation coefficients, and those not belonging to the same group exhibit low correlation coefficients. Therefore, it is imperative to decrease the redundancy of the original information.
With HSVs, it is time consuming to calculate the information entropy during tracking tasks. Therefore, a genetic optimization approach [52,53] is designed to swiftly identify selected bands with the highest entropy values. Given the initial image , the joint information entropy H is described as
where represents the joint probability between pixel intensity value J in band , pixel intensity value I in band , and pixel intensity value K in band .
Therefore, the entropy H can be defined as a fitness function in the optimization method. Subsequently, banded arrays are used as chromosomes in the genetic algorithm, as depicted in Figure 3. Iterations of selection, crossover, and variation are carried out to determine the appropriate band. Based on correlation analysis and the genetic method, three bands (band 2, band 5, and band 8 for the initial image of the toy1 video) are obtained. Additionally, a three-spectra input is required by the fundamental deep network.
In conclusion, band selection based on joint entropy takes into account both implementation effectiveness and information parsimony. Specifically, the inclusion of additional bands may lead to redundant information within a particular spectral dataset.
2.3. Transfer Learning
Transfer Learning (TL) is widely used in machine learning areas, such as item recognition, medical diagnosis, and speech recognition [54,55,56]. This is because training DL models in specific application contexts sometimes exhibits various contradictions, such as too few training samples and the high cost of data labeling.
TL can be divided into four categories based on its processing, sample instance based, feature based, parameter sharing based, and relationship based. We use a TL based on parameter sharing, where certain parameters are shared between the model in the source domain of normal RGB data and the target domain of hyperspectral video data from the perspective of the model. The goal of migration learning is to find the prediction function F, formulated as:
where X is the test set of hyperspectral data and Y is the tracking results.
The normal RGB data are pre-trained first and then the model is fine-tuned using the hyperspectral video data. Pre-trained models that employ frequently employed RGB data source domains, encompassing vast datasets, have the potential to augment model robustness and foster superior generalization, such as ImageNet [49], COCO [57], and GOT-10K [44].
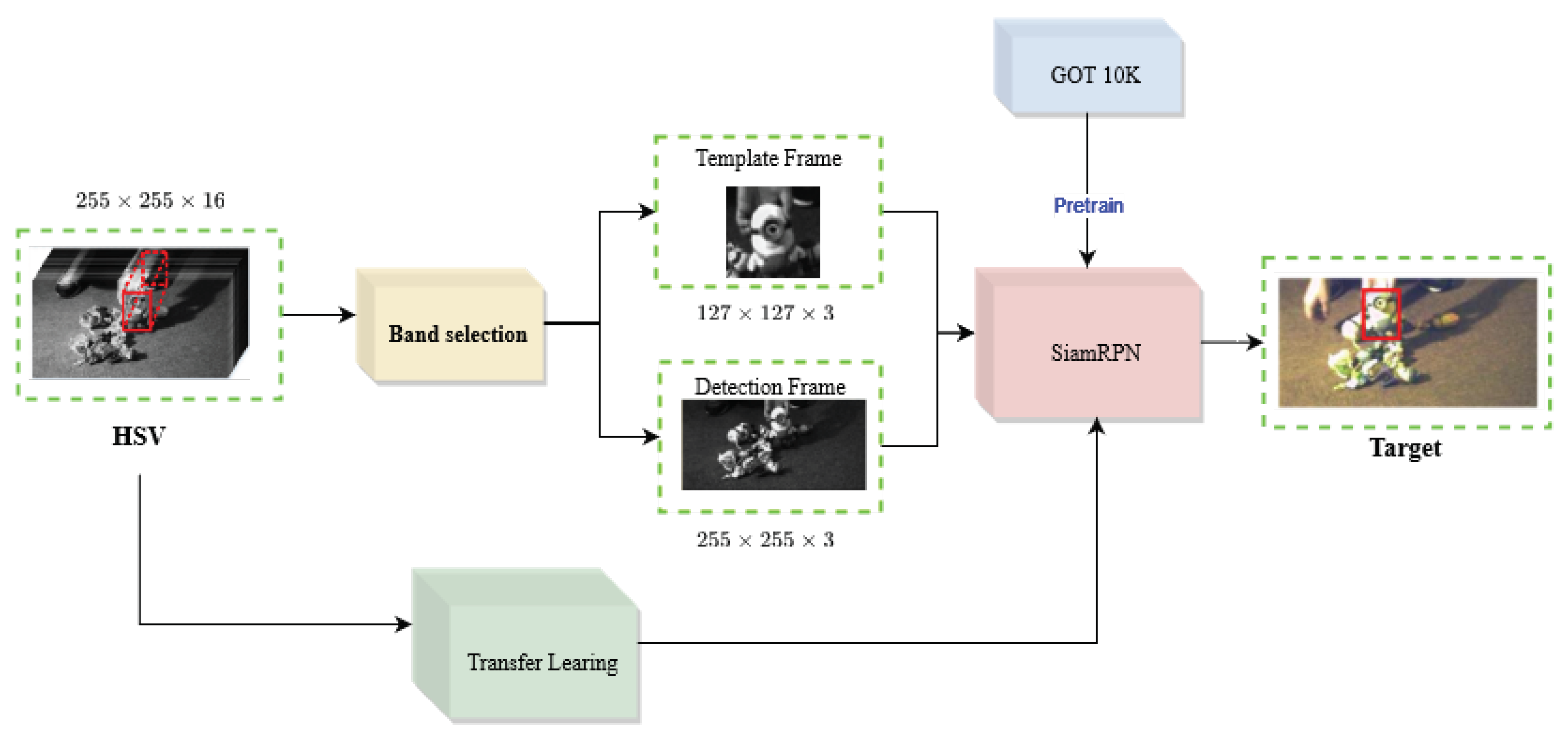
The HSIs contain spectral information, which can be lost during pre-training with RGB data. Furthermore, the TL strategy cannot be used directly with hyperspectral data, due to of its multichannel information. Thus, the band selection module is required. Finally, Figure 4 shows the flowchart of the proposed algorithm.
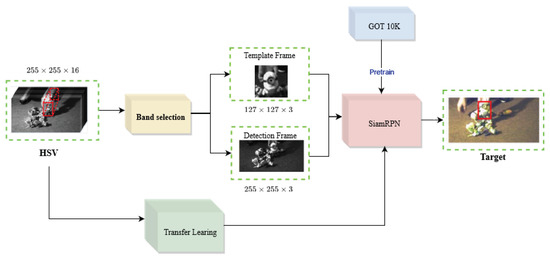
Figure 4.
The flowchart of the proposed method.
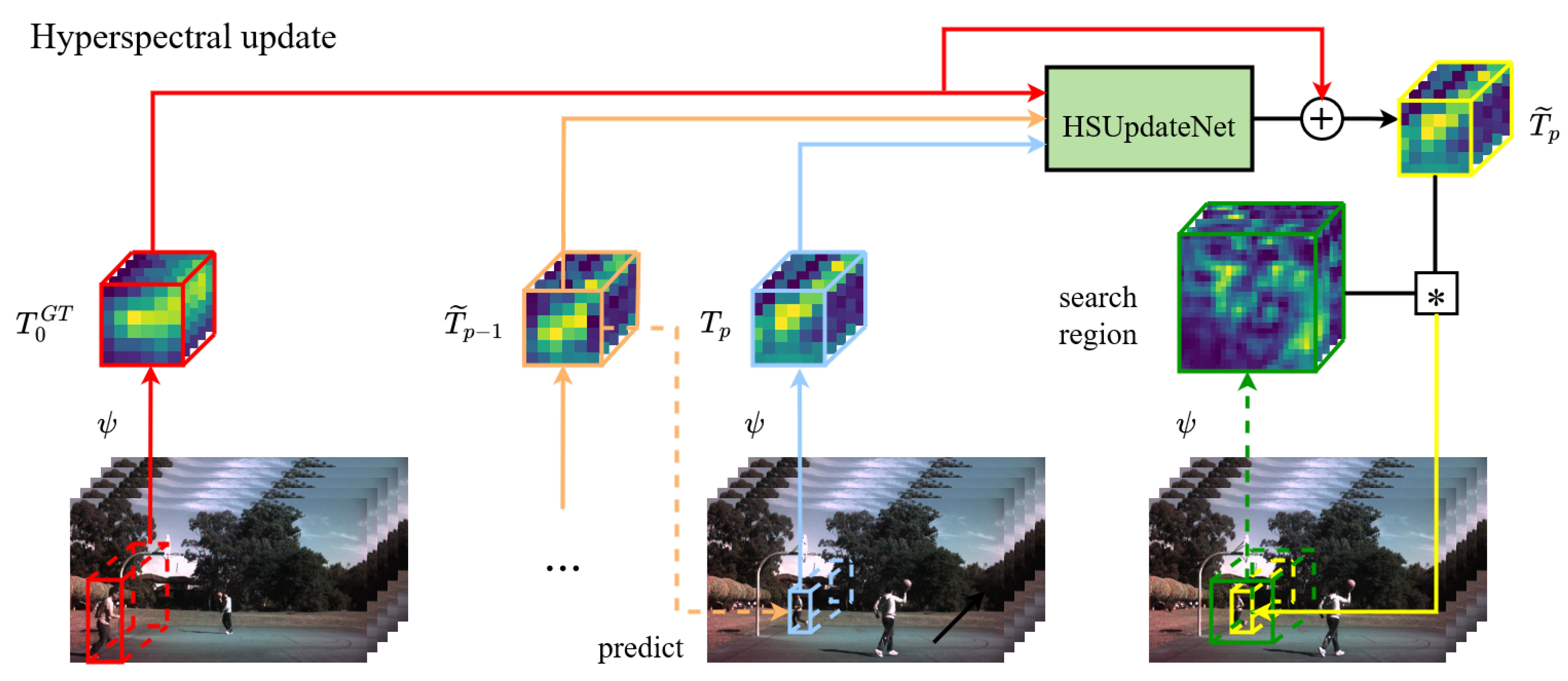
2.4. Hyperspectral Update Learning
For long-term tracking tasks, such as long sequences in hyperspectral datasets, hyperspectral video tracking has difficulty coping with the fact that the appearance of targets changes dramatically. The SiamRPN model updates targets’ template with the linear fusion of the current and the cumulative template, which causes information to decay exponentially over time. Its simplicity limits the potential benefits that can be obtained from learning updates, despite the fact that it can enhance tracking performance. Moreover, this linear combination method cannot utilize the potential spectral information for HOT. Therefore, a learned updating method is adopted to replace the linear mechanism. Inspired by UpdateNet [46], a convolutional neural network named HSUpdateNet is designed to obtain the optimal template for HSVs. It replaces the template manual update function and takes advantage of the spectral information. The template in SiamRPN is updated to an an exponentially decaying moving average value over time. Specifically, the recursive formula for the template update is represented as follows:
where denotes the new template sample at frame p, and denotes the accumulated template. Besides, is the update factor, which means that the appearance of objects changes smoothly over the subsequent images.
To exploit the spectral information of HSIs, a universal function is learned to overcome the limitations of simple template averaging.
The learning function HSUpdateNet is based on the initial true template, the last accumulated one, and the template referring to the predicted object position at frame p. represents the initial frame of each HSV, which is shown in Figure 5. The HSUpdateNet is trained to obtain a prediction of the target template. The predict template should match the template , referring to the true position at frame . To accomplish this, HSUpdateNet is trained by minimizing the Euclidean distance between real templates and updated templates at the next frame, which is defined as follows:
where represents the Euclidean distance and n represents the length of test HSVs.
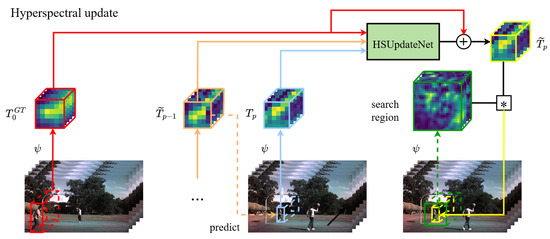
Figure 5.
An overview of the tracking framework using HSUpdateNet.
Meanwhile, the multi-stage training strategy is utilized to avoid repeated training, which makes the procedure simple and efficient. It is not reasonable to use real values for and during the first training, because real templates are rarely used in real tracking. In the first phase, the original tracker with the linear updating strategy is executed on HSVs to generate the cumulative template and the actual predicted position for each frame.
The update factor corresponds to the first approximation value of HSUpdateNet. In each subsequent training phase , the HSUpdateNet model is trained to obtain the cumulative template and object location prediction.
The network takes the initial template at each frame into account, which provides highly reliable information. Moreover, spectral information is learned, which helps to improve the tracker’s performance.
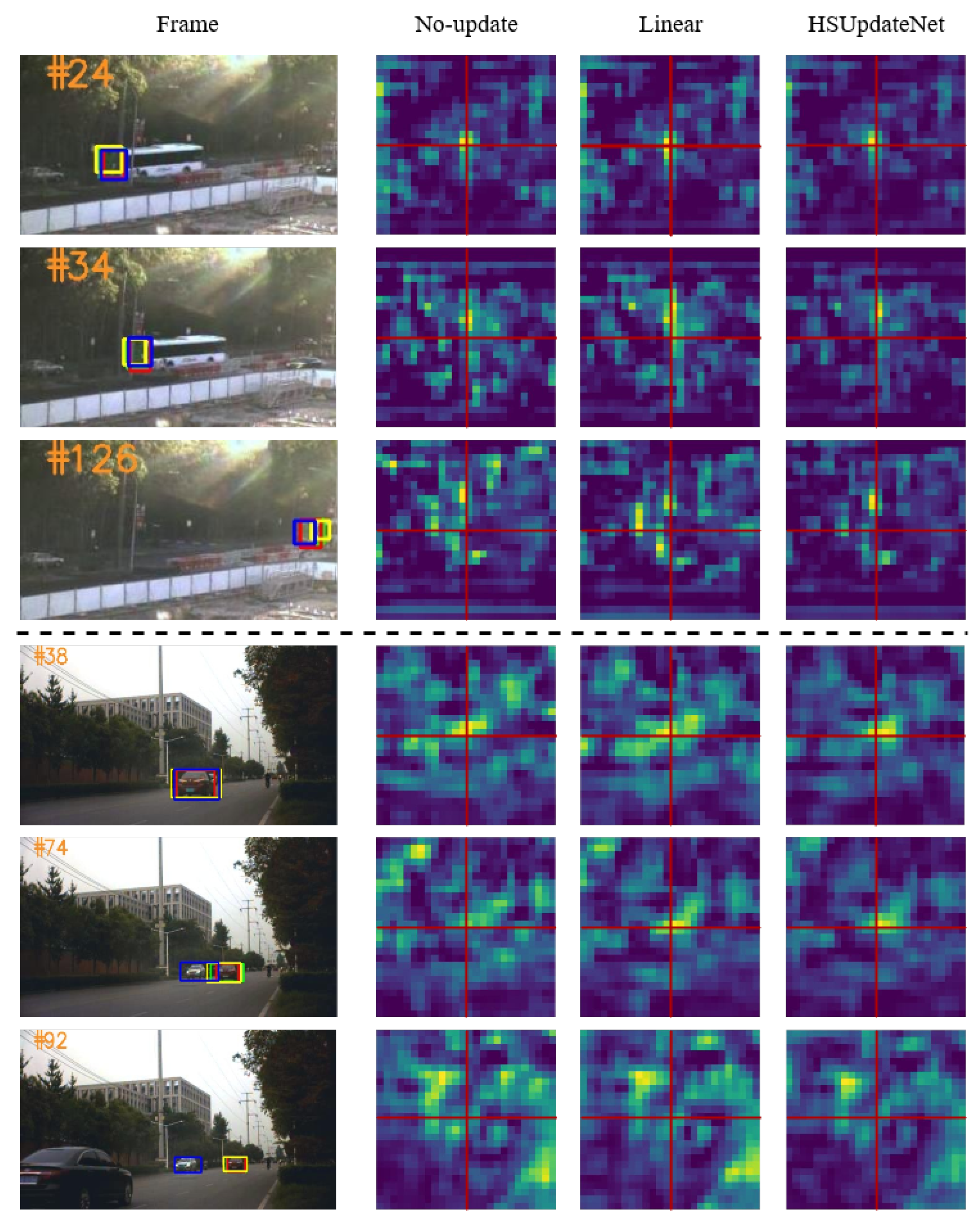
Furthermore, the linearly updated cumulative templates and HSUpdateNet are visualized in Figure 6. The cumulative template approach utilized by the HSUpdateNet model more closely reflects real-world situations when compared to the linear update strategy. However, the linearly updated cumulative template changes at an exceptionally slow rate, making it difficult to track objects with significantly altered appearances, thus presenting a significant limitation.
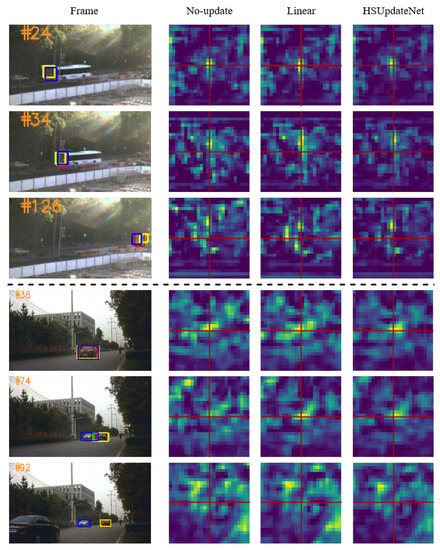
Figure 6.
Response maps generated on the search area for different template update strategies. HSUpdate is shown in green, Linear in blue, No-Update in yellow, and ground truth in red.
This is despite the fact that the UpdateNet [46] update strategy suffers from a self-learning problem, meaning that by updating with mislabeled samples, the tracker may permanently degrade and drift. However, HSUpdateNet is trained using hyperspectral datasets and more spectral information is retained during template accumulation, which enhances the tracker’s ability to identify erroneous samples.
3. Results
The experimental setup is detailed in Section 3.1, and the ablation study is given to prove the importance of several components in the proposed tracker in Section 3.2. Section 3.4 shows the quantitative comparison of deformation. In addition, qualitative and quantitative comparisons with existing trackers on the whole dataset are given in Section 3.3 and Section 3.5, respectively.
3.1. Experiment Setup
Dataset: The GOT10K dataset, which was introduced by Huang et al. [44], serves as a valuable resource for obtaining pre-trained parameters. With over 10,000 video clips and more than one million labeled bounding boxes, the dataset consists of five subcategories: animals, motor vehicles, people, assisting objects, and partially moving objects. We performed transfer learning using the HOT2022 dataset [3], which is provided by the 2022 Hyperspectral Object Tracking (HOT2022) challenge on https://www.hsitracking.com/contest/, (accessed on 13 September 2022). The HOT2022 dataset contains 40 training video sets and 35 test sets with RGB videos, HSVs, and false-color videos. The dataset authors applied weight to each band in HSVs to generate channels of color images. This method [58] generates images(false-color videos) with similar color intensity to the color images, ensuring a fair comparison with color trackers. The HSVs are acquired by a hyperspectral camera with 16 bands of wavelengths ranging from 470 nm to 620 nm, which was modeled as a snapshot VIS produced by interuniversity microelectronics center with a bandwidth of about 10 nm per band. Each video is also labeled with relevant challenge factors, which include Deformation (DEF), Scale Variation (SV), Occlusion (OCC), Illumination Variation (IV), Background Clutters (BC), Fast Motion (FM), Out-of-view (OV), Out-of-plane Rotation (OPR), In-plane Rotation (IPR), Motion Blur (MB), and Low Resolution (LR). Ablation experiments and tracking experiments are performed using all videos. Deformation experiments are performed using videos with target deformation properties.
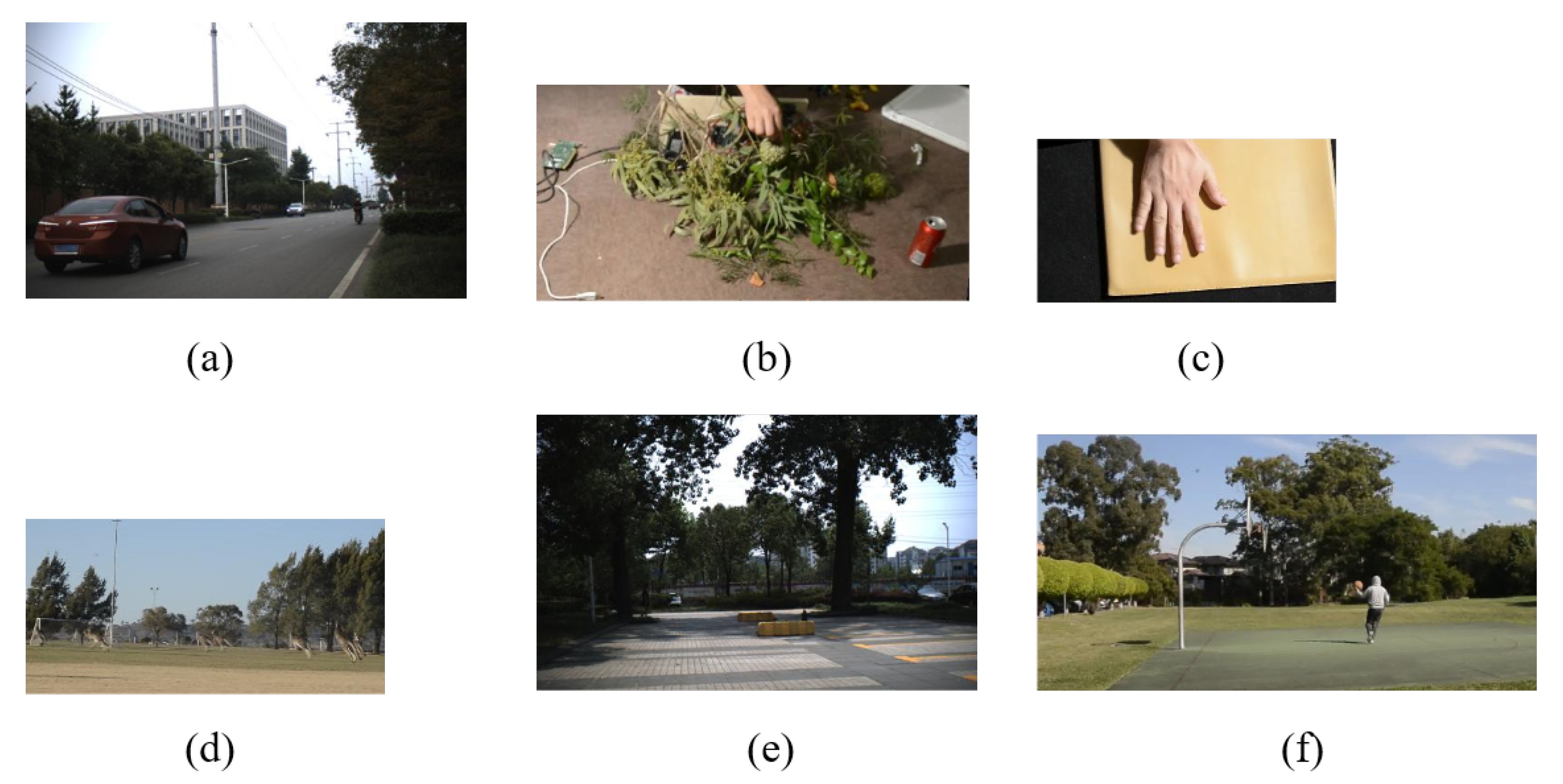
Table 1 presents details regarding our experimental videos, while Figure 7 depicts the corresponding RGB videos. The series for Figure 7a consists of 331 frames of 512 × 256 pixels. The tracking target is a black automobile traveling from near to far on the highway. The vehicle ranges in size from 188 × 84 pixels to 13 × 9 pixels. There are concurrent SV, LR, OCC, and IV challenges in the sequence.

Table 1.
The details of the experimental videos.

Figure 7.
RGB videos for six experiments. (a) Car3; (b) Fruit; (c) Hand; (d) Kangaroo; (e) Pedestrian2; (f) Player.
Table 1 has comparable details for the other five sequences. In Figure 7b, the tracked target is a green fruit with sizes ranging from 32 × 37 pixels to 26 × 25 pixels. The video shows green fruit moving randomly in front of a cluttered branch. In addition, the target tracking in Figure 7c is a palm moving back and forth in front of a yellow background and undergoing constant changes in shape and size, ranging from 103 × 108 pixels to 87 × 98 pixels. In Figure 7d, our tracking target is a kangaroo running in front of the woods, surrounded by many similar kangaroos, and its size is from 22 × 41 pixels to 19 × 33 pixels.
In Figure 7e, the object of attention is a person walking in the shadows, who is obscured by a tree during their movement, with sizes ranging from 13 × 44 pixels to 15 × 39. Finally, in Figure 7f, the tracking target is a basketball player who keeps moving and turning around. The size of the target range from 23 × 69 pixels to 34 × 101 pixels.
Evaluation Metrics: The four most popular target tracking assessment metrics [59], i.e., precision plot, success plot, average Distance Precision at a threshold of 20 Pixels (DP@20P), and Area Under the Curve (AUC), are introduced to give the performance comparison.
The success plot represents the proportion of successful frames, where the predicted tracking box overlaps the ground truth with a fixed threshold (from zero to one). Besides, the precision plot shows the proportion of frames, where the centroid difference referring to the estimated target position and the real target position is not more than a specified threshold. In addition, the curve is determined by the varying percentages that arise from different thresholds. With the initial target state, all compared trackers execute on the full test HSVs, and all results are obtained with One-Pass Evaluation (OPE).
Implementation details: The SiamRPN model [22] is pre-trained with GOT10K [44]. The learning rate is between and . In the training model, the batch size is 128, and the epoch parameter is fixed as 50 (Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) for optimization). For transfer learning, the learning rate is set from to . The first three convolutional layers are fixed for the first five training epochs and then unfreeze. A batch size of 128 and an epoch of 20 were employed during training. In the first training phase of HSUpdateNet, a linear update with an update rate of 0.0102 is used in the template generation part. Three bands of the hyperspectral dataset are considered as training samples. Furthermore, weights are initialized by the model generated in the previous stage, while the learning rate is reduced from to in each epoch.
3.2. Ablation Study
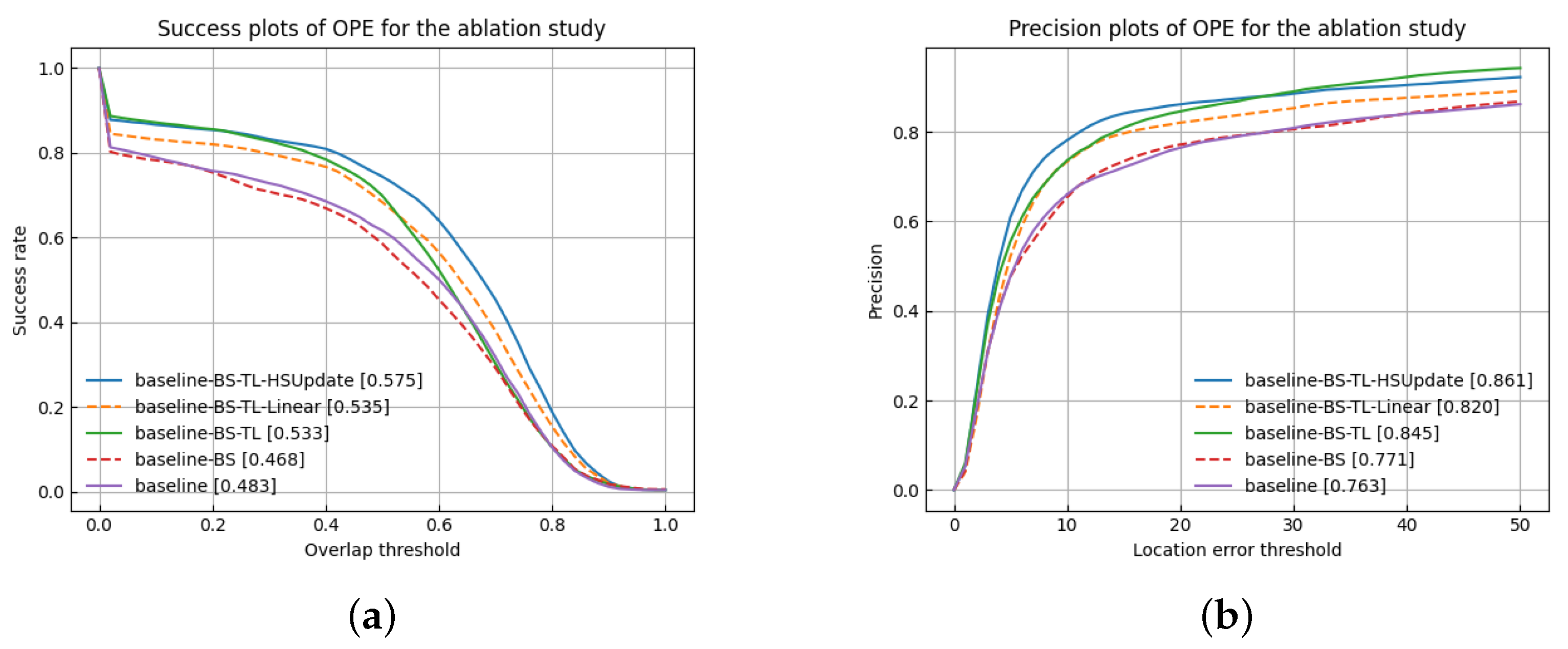
To verify the algorithm’s effectiveness, a baseline algorithm is first implemented by adopting only the pre-trained model without enabling the band selection module, transfer learning module, and online update module. Based on the baseline algorithm, two alternative algorithms are also implemented. First, the band selection and transfer learning modules are utilized. Secondly, based on the second method, linear template update, and HSUpdateNet template update are executed, respectively. Results on the HOT2022 dataset are shown in Figure 8. Both the second and third two algorithms perform better than the baseline. In Table 2, the AUC value of the baseline algorithm reaches 0.483. Besides, the algorithm with only the band selection module does not perform well in objective indicators. This is because hyperspectral data are different from RGB data in feature extraction, and the baseline algorithm does not understand the spectral features well. In contrast, by enabling the band selection module and transfer learning module, which effectively utilizes the informative spectral features, the tracker performance is improved by 5%. Both the strategies of linear template update and the HSUpdateNet template update improve the tracker’s performance. In general, the former is typically used by the siamese tracker, which runs fast but with limited improvement. Compare with the strategy of no template update, the performance is only improved by 0.2%. The HSUpdateNet model not only avoids the exponential decay of information arising from a linear update but also obtains spectral information that is effective for tracking, resulting in a 4.2% improvement in performance.
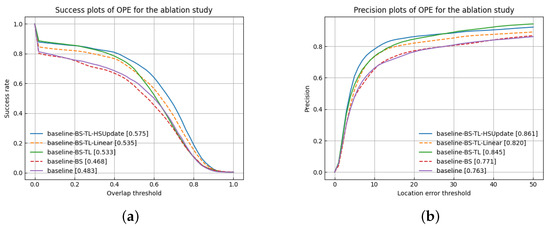
Figure 8.
Success and precision plots for the ablation study over all the test HSVs. (a) Success plots; (b) Precision plots.

Table 2.
Ablation study over all the test HSVs.
3.3. Qualitative Comparison
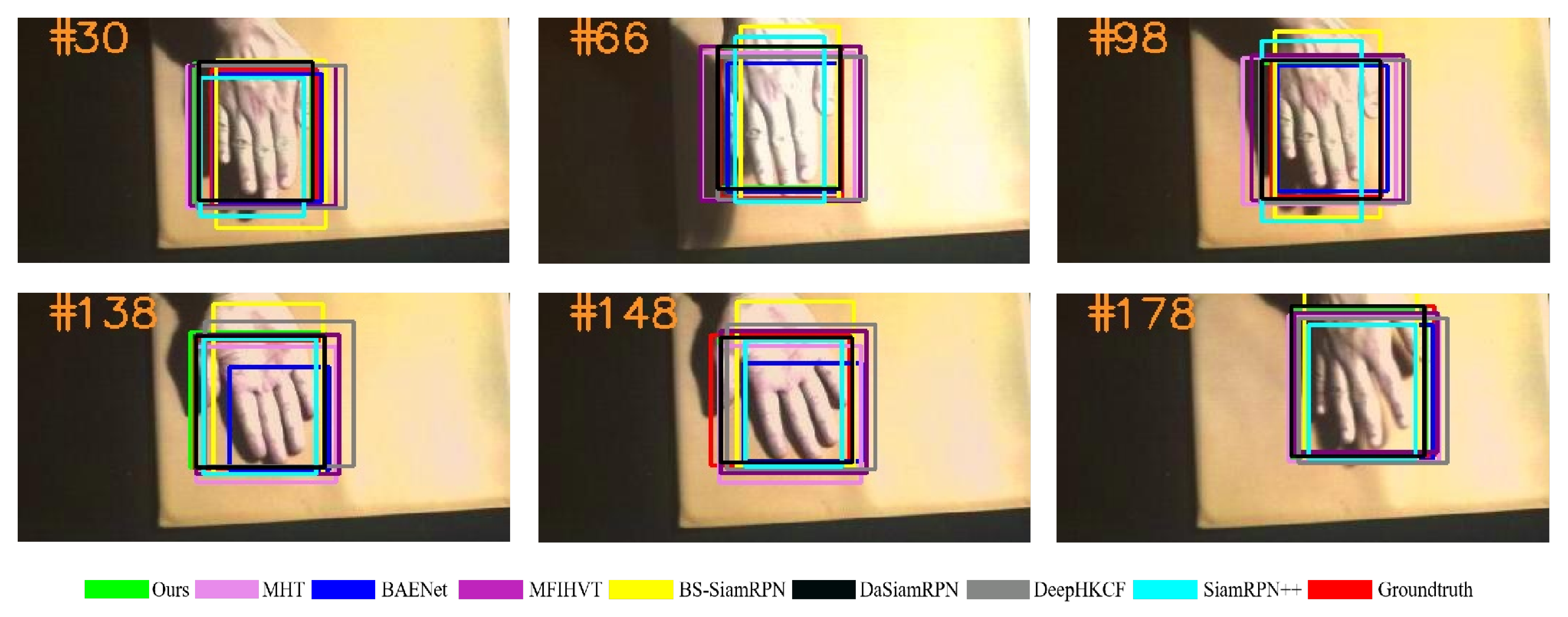
In this section, our method is compared against seven other trackers, namely MHT, MFIHVT, BAENet, DeepHKCF, BS-SiamRPN, DaSiamRPN, and SiamRPN++. Among them, DaSiamRPN and SiamRPN++ are color trackers, and the rest are the latest HS trackers. The MHT model introduces hand-crafted features, which extracts material information, to improve the tracker performance. BAENet transforms HSVs into a group of three-channel images. These altered images are run through a number of VITAL trackers to produce several weak trackers. Furthermore, an ensemble learning process is adopted to track targets. The MFIHVT algorithm generates feature maps by HOG and the pre-trained VGG19 feature, and the DCF framework is adopted to estimate the location of objects. The DeepHKCF tracker converts HSV into a three-channel image sequence, which is fed into the VGGNet for extracting features. The BS-SiamRPN algorithm lacks a template update strategy. The DaSiamRPN algorithm utilizes data augmentation to increase its performance. The SiamRPN++ algorithm completes feature extraction using a deeper network. In this paper, the false-color videos are utilized as the input of the color tracker to compare with the HS tracker.
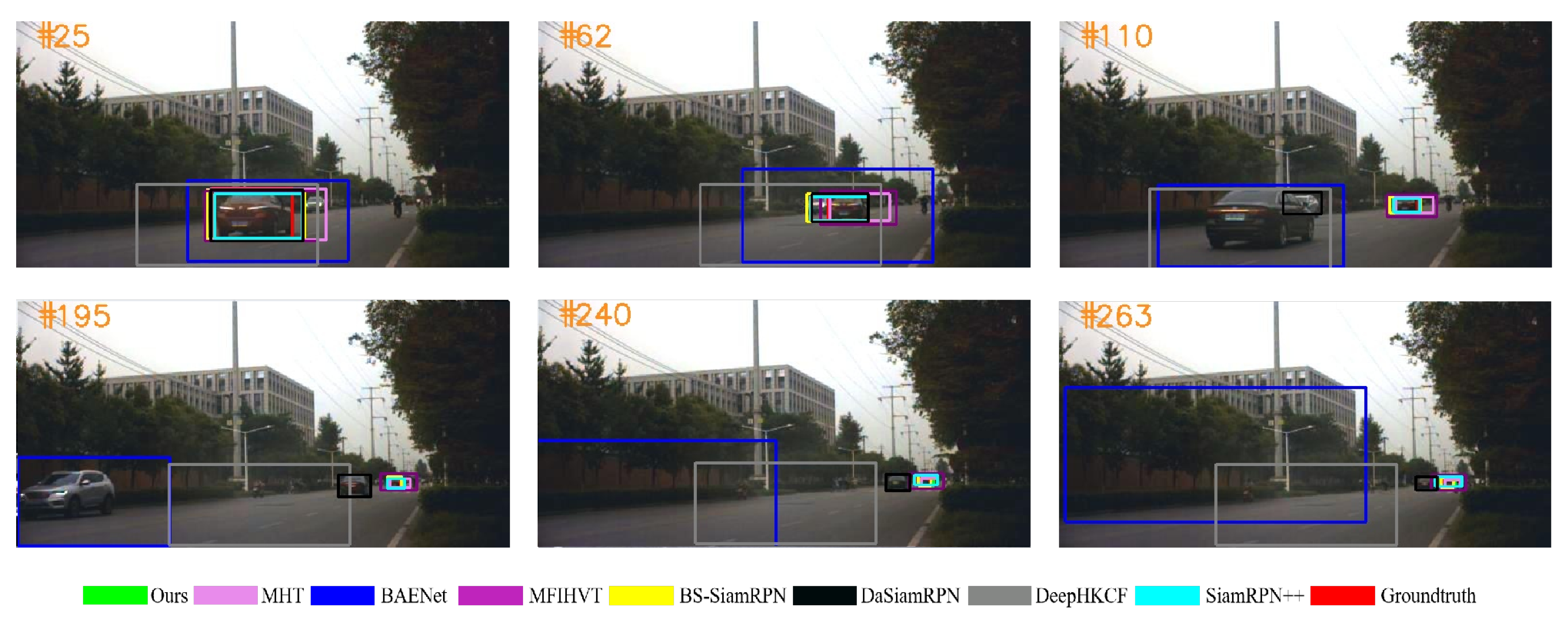
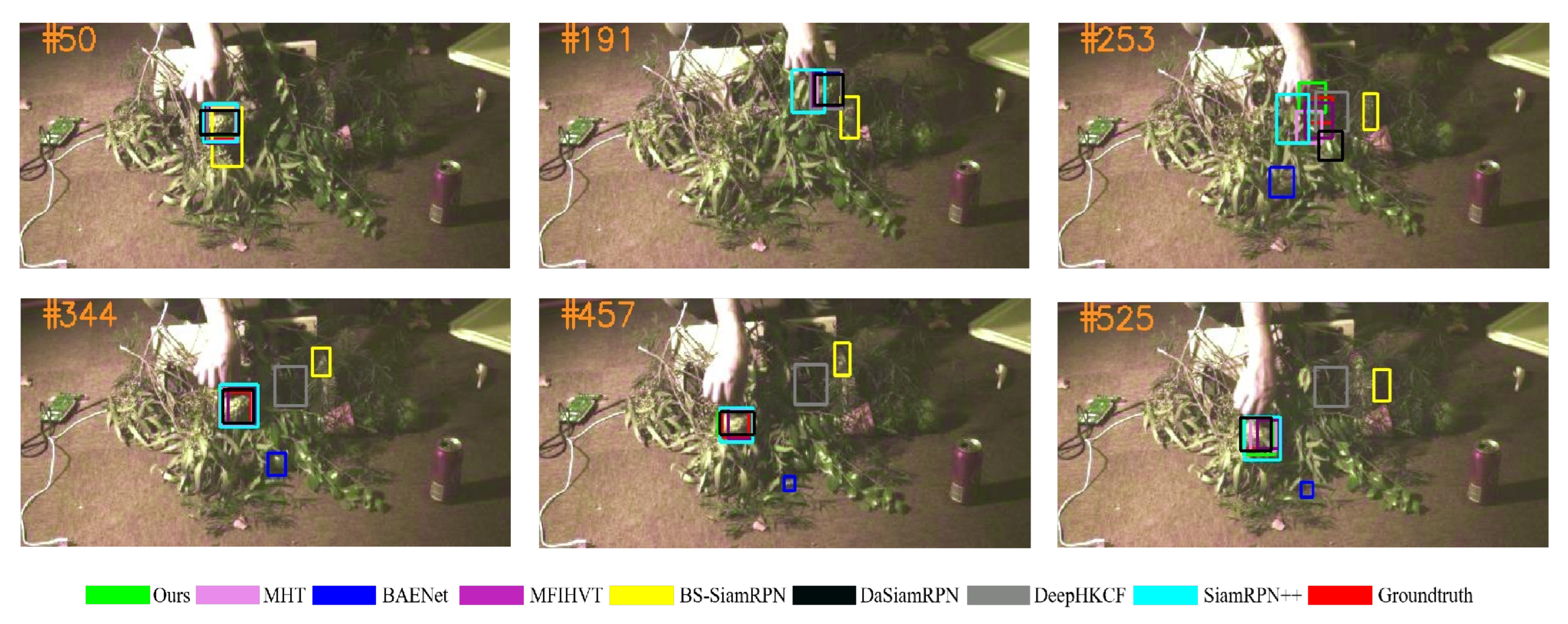
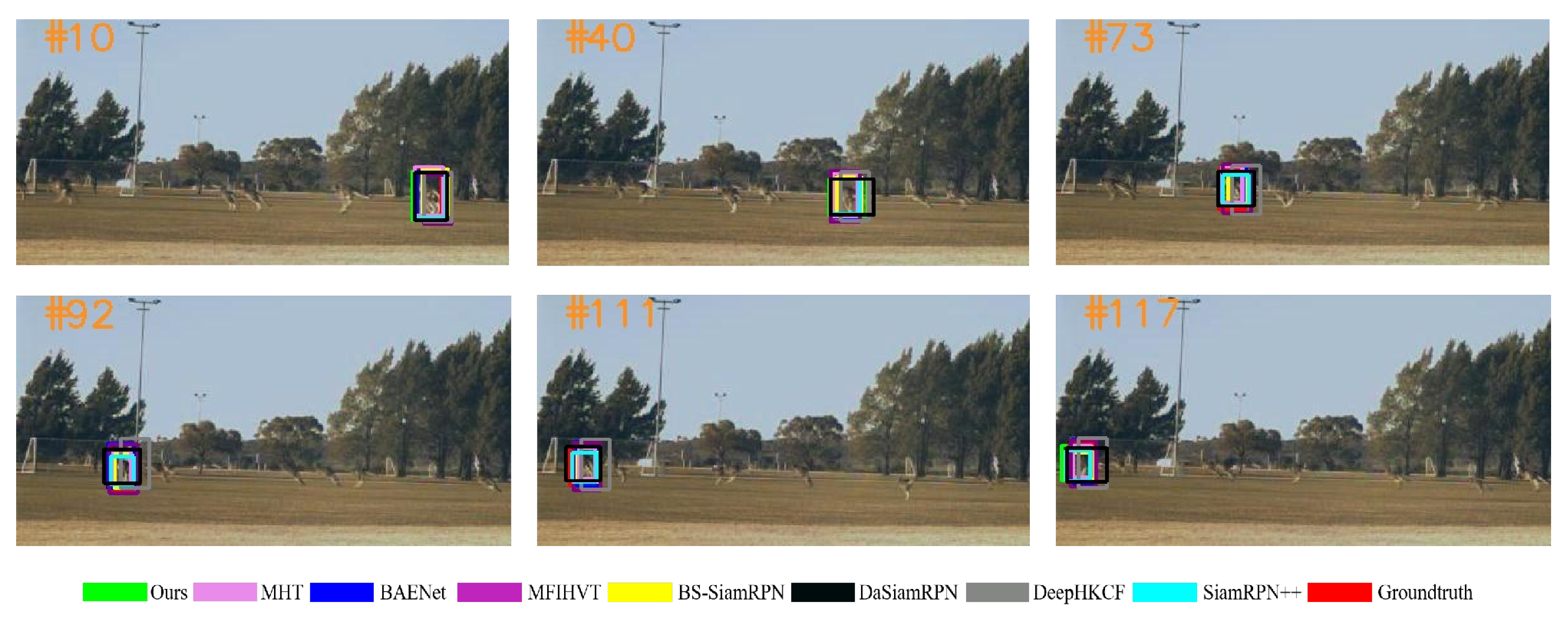
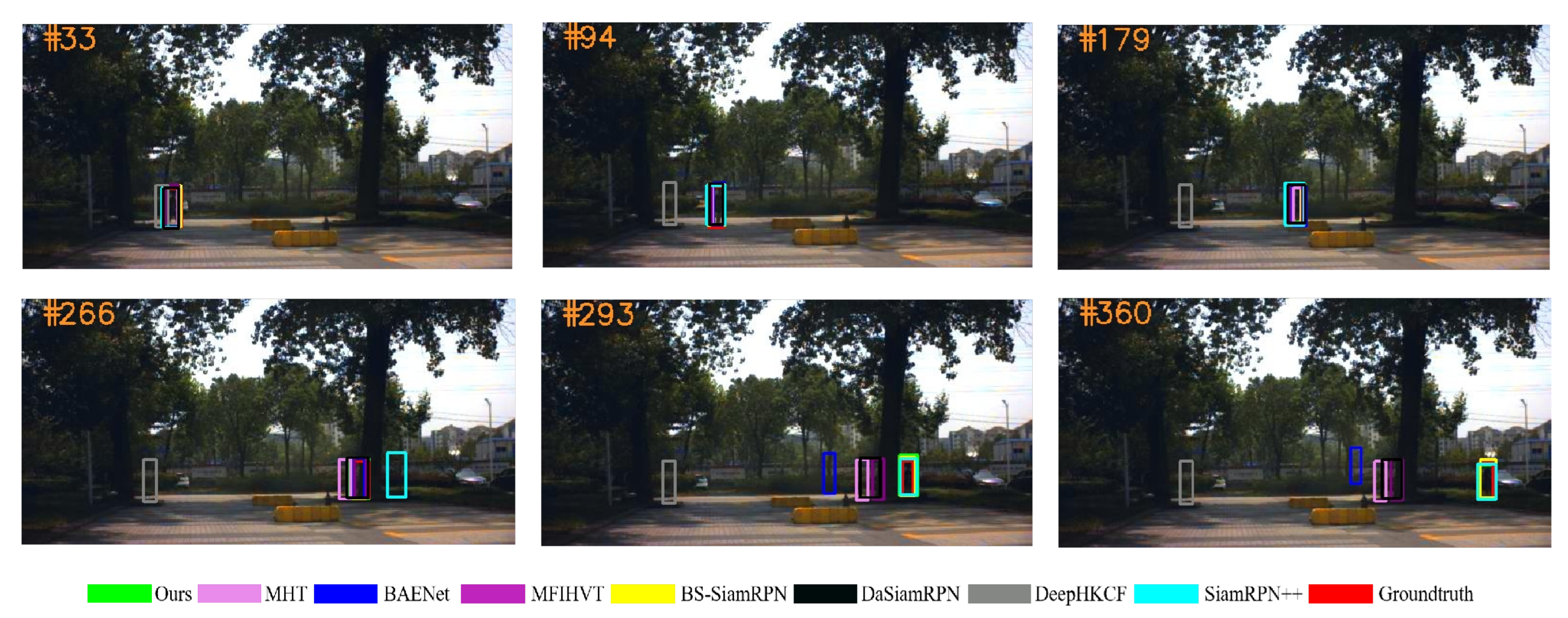
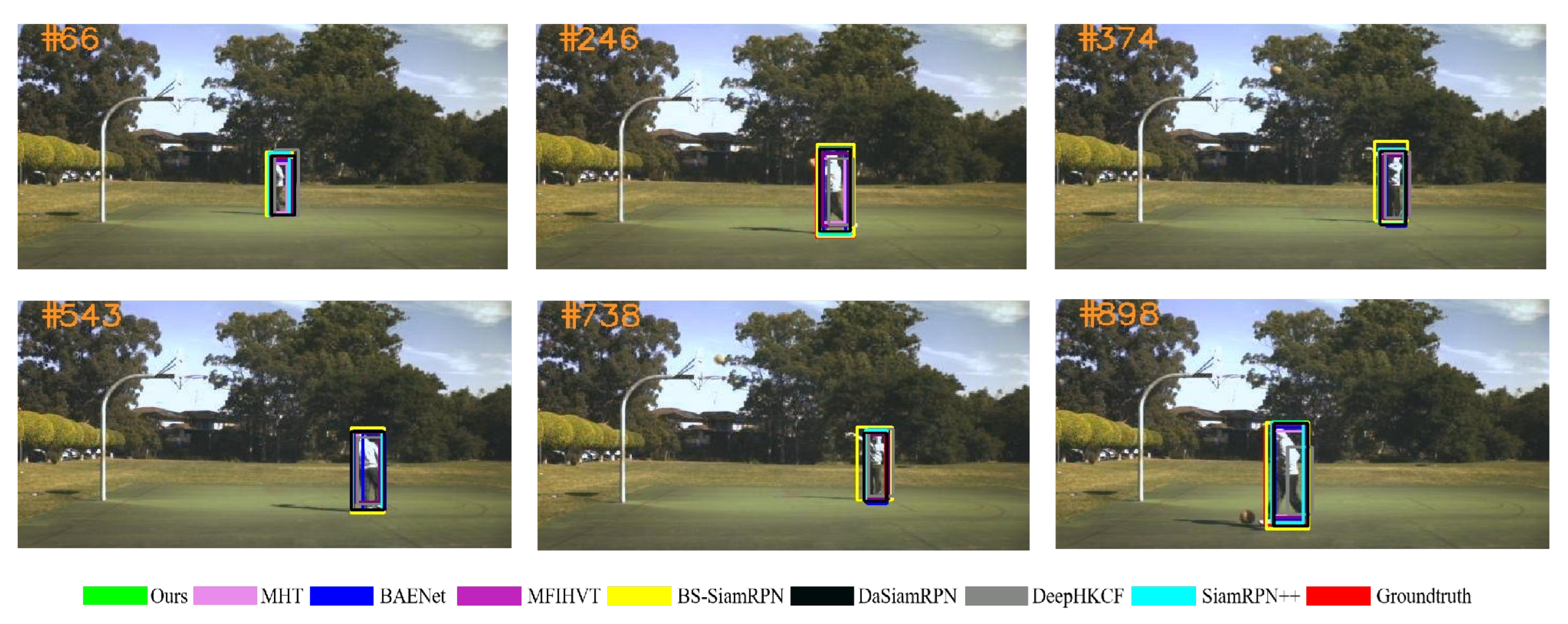
Experimental results of all the trackers on all six experimental sequences are shown in Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14. The image contains several various colored rectangular boxes, as shown below, and the varied colors represent different algorithms, i.e., green denotes ours, blue denotes BANet, black denotes DaSiamRPN, yellow denotes BS-SiamRPN, cyan denotes SiamRPN++, and red denotes the ground truth.
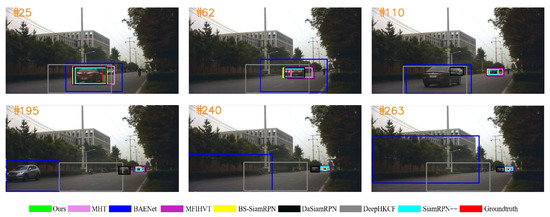
Figure 9.
Qualitative results on the car3 sequence.

Figure 10.
Qualitative results on the fruit sequence.
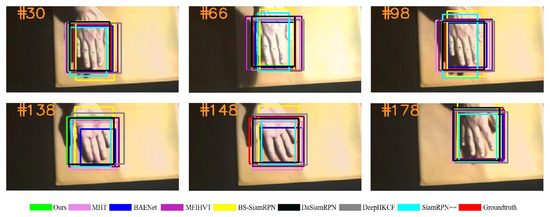
Figure 11.
Qualitative results on the hand sequence.

Figure 12.
Qualitative results on the kangaroo sequence.
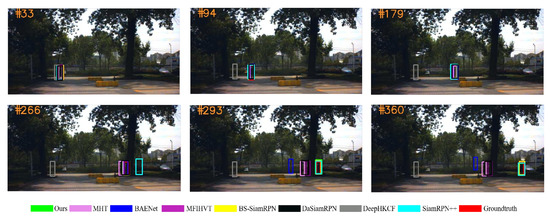
Figure 13.
Qualitative results on the pedestrian2 sequence.

Figure 14.
Qualitative results on the player sequence.
In Figure 9, the black car begins at the beginning of the road, and gradually shrinks as it travels further and further. Furthermore, when the black car is traveling down the center of the road, a white car is driving in the other direction. When the target vehicle reaches the end of the road, another vehicle is close behind it. During this time, the two vehicles gradually shrink. The BAENet algorithm is unable to accurately surround the target due to the changing aspect ratio of the black car. At frame 263, it can be found that only the BS-SiamRPN and ours get a high overlap value with true results.
As can be seen in Figure 10, the fruit moves above the leaf, resulting in size changes that are difficult to track. Because of the blockage of leaves during the subsequent target movement, all of the trackers addressed in this paper are unable to precisely obtain the target state. Therefore, BAENet and DeepHKCF can only see a portion of the target. This problem becomes more serious as targets are frequently occluded by leaves. At frame 253, it is evident that our tracker is capable of reliably locating the target, and adapting to changes in targets. It is worth mentioning that only our tracker has a decent overlap with the true result.
The palm in Figure 11 moves over a background with similar colors, causing the palm to deform due to constant flipping. During the tracking process, the target varies frequently, yet most trackers cannot react adequately to the target changes. Nevertheless, our tracker uses HSUpdate to retrieve the best-accumulated template at frame 148, making the tracker perfectly overlap with the ground truth.
Figure 12 illustrates the challenges of tracking the kangaroo, as its fast jumps cause variations in appearance and scale, making tracking difficult. Furthermore, with a similar representation feature to that of the tracking target, other kangaroos create a significant amount of background interference for object tracking. It is difficult for the DeepHKCF to completely coincide with the real target box.
Figure 13 depicts a pedestrian walking from a well-lit area to a darker region amid a background of trees. During subsequent target motion, the pedestrian becomes occluded by trees, resulting in temporary loss of the target on the screen, posing a significant challenge for the trackers. The DeepHKCF algorithm fails to obtain the target state at frame 40. At frame 266, SiamRPN++ also loses the target due to the occurrence of occlusion. At frame 360, the BS-SiamRPN algorithm and our algorithm correctly detect the target, due to the fact of that the spectral information is preserved with band selection.
Figure 14 shows an athlete dressed in white playing basketball on a court, with movements such as shooting and running leading to variations in the shape of the target. BS-SiamRPN does not perform well in the tracking task, and because of that, the tracker does not utilize the strategy of template updating. The DeepHKCF model only adopts one deep feature, which makes the target drift to the background.
3.4. Quantitative Comparison of Adversarial Deformation
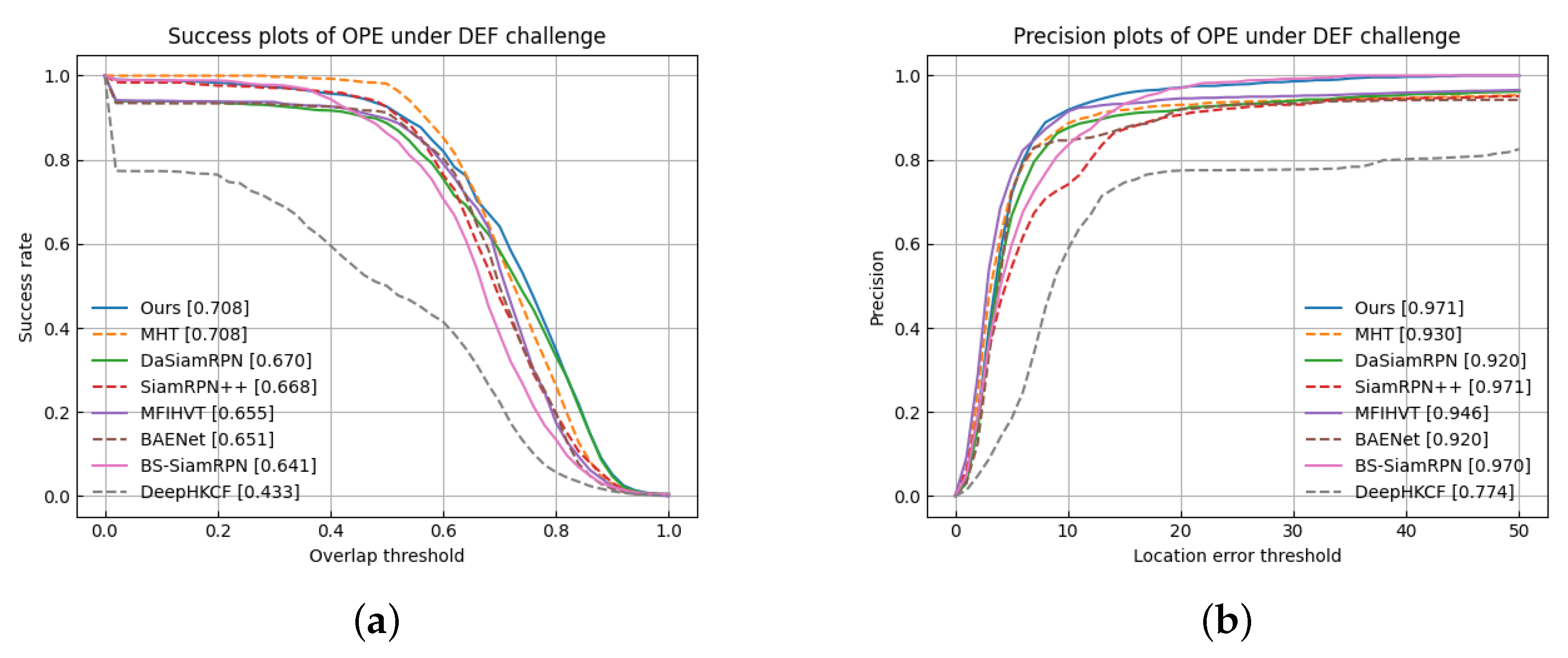
Sequentially, the performance is represented in Table 3, in terms of deformation challenges. Specifically, our algorithm almost reaches the top two performances in terms of evaluation metrics. Figure 15 displays the success and precision curves of the algorithm on videos with a deformation challenge, where the area covered by the curve represents the value. The specific results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Performance comparison with other trackers in terms of deformation challenge.
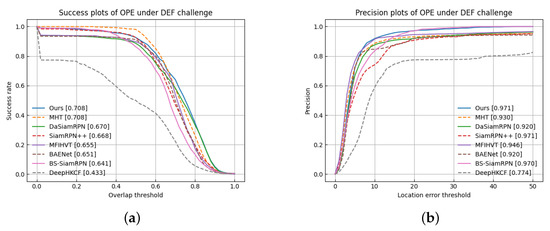
Figure 15.
Comparison of performance curves in terms of deformation. (a) Success plots; (b) Precision plots.
Overall, the MHT achieved a success rate of 0.708 and a precision value of 0.930. Besides, our proposed algorithm has the same success rate, and the precision is improved by 4.1%. It is worth noting that the MHT is the state of the art. Our tracker produced better results than other algorithms in the DEF challenge, which is shown in Figure 15 and Table 3. Specifically, the precision value of the proposed algorithm is 0.708 and the success rate is 0.971, which is a significant improvement over MHT and BS-SiamRPN, referring to the DEF challenge. Compared to BS-SiamRPN, the success rate of our algorithm is 0.1% higher and the precision rate is 6.7% higher, which is because the BS-SiamRPN algorithm lacks a template update strategy. In addition, both SiamRPN++ and our algorithm achieve the highest precision, but our algorithm’s success rate is 3.9% higher. This is because our algorithm utilizes the spectral information of HSVs. Numerical results confirm that AD-SiamRPN can make good use of HSUpdateNet to obtain the best cumulative template, which helps the tracker cope with the deformation challenge.
3.5. Quantitative Comparison
Here, the quantitative result for all seven trackers is represented by the precision and the success plots. The AUC comparison of several hyperspectral trackers and visual DL trackers is shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Performance comparison with other trackers.
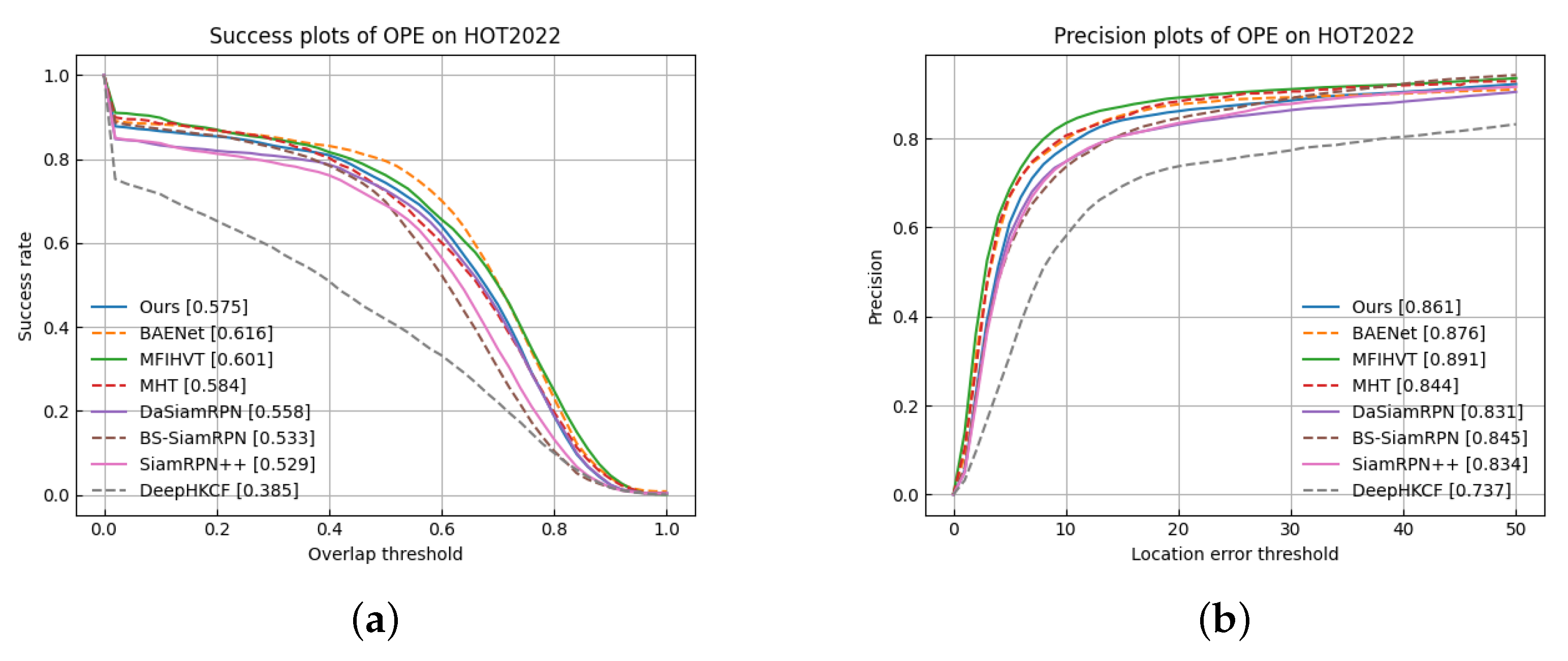
Figure 16 shows the comparative results of the trackers over the entire dataset. It can be found that our algorithm achieves high AUC scores (0.575 in the success plot and 0.861 in the precision plot). Facing difficulties such as fast motion, occlusion, same backdrop, and low resolution, the SiamRPN++ and the DaSiamRPN easily fail to detect targets. The false-color video, which loses spectral information, does not enhance the two-color trackers very well. Moreover, the complexity of HSIs necessitates the use of transfer learning techniques for effective understanding. Our tracker, which utilizes transfer learning to capture the semantic aspects of multispectral data, achieves robust performance. The MHT algorithm leverages both spectral and spatial information to effectively distinguish the target from the background by adding material features, leading to good performance. The BAENet model performs best, for the reason that it sent the band group into the VITAL tracker via the band selection network. The spectral information is retained well, which is instructive for us for future research. The DeepHKCF algorithm does not perform well, because it only extracts one type of feature. It introduces a multi-feature fusion tracking algorithm, which retains more spectral information and has good robustness to the complex background. Compared with BS-SiamRPN, a template update module, which makes full use of spectral information, helps to deal with occlusion challenges and other aspects. As a matter of fact, the overall performance is improved, the AUC score in the success plot is from 0.533 to 0.575, and the AUC score in the precision plot is from 0.845 to 0.861.
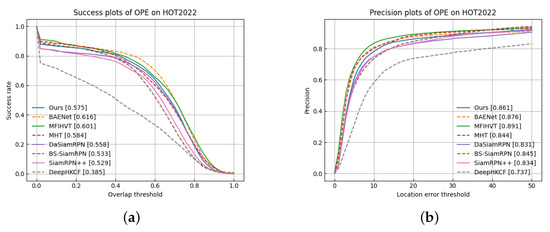
Figure 16.
Success rate and precision rate referring to overall sequences. (a) Success plots; (b) Precision plots.
4. Discussion
While the comprehensive experiments and analyses have established the effectiveness of the proposed AD-SiamRPN, there remains a need for further discussion regarding potential avenues for future research.
- •
- The dearth of high-quality datasets with annotations is a major drawback of hyperspectral target tracking, potentially hindering the learning of valuable information and resulting in overfitting. To address this limitation, our future efforts will focus on enhancing the feature extraction capabilities of the tracker, perhaps by employing self-supervised approaches, such as contrast learning.
- •
- The band selection module eliminates the information redundancy of HSVs and retaines the physical information. It obtains high tracking speed, but the improvement in performance was not quantified. In the future, we will compare this with other feature reduction approaches to validate the effectiveness of our band selection module.
- •
- Experiments have demonstrated that the spectral information helps to distinguish the target from the background information, and from this, future work can proceed to design a rational network that uses the raw 16-dimensional data as input to the network to extract valid hyperspectral features.
5. Conclusions
A tracking algorithm on hyperspectral videos in this paper benefits from band selection and an improved siamese network. From the above experiments and analysis, some conclusions are given as follows.
- •
- Hyperspectral information helps trackers detect an object with similar color attributes from its neighborhood.
- •
- The high quality of the training set in the GOT database provides the basis for the generalizability of our tracking algorithm (AD-SiamPRN).
- •
- The band selection module retains the spectral significance of the spectral channel, and the intelligent optimization algorithm speeds up the tracking task.
- •
- The transfer model aids in the extraction of semantic information from HSV, hence enhancing the tracker’s performance. The template update module (HSUpdateNet) performs well with respect to issues such as deformation.
- •
- Future work proceeds to design a rational network that uses the raw 16-dimensional data as input to the network to extract valid hyperspectral features. Besides, the effective attention mechanism should be applied into the field of HOT.
In addition, experimental results validate that the AD-SiamPRN method performs well in HOT (with an overall success rate of 0.575 and a deformation challenge success rate of 0.708), which lays the foundation for moving target recognition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.W. and K.Q.; Methodology, S.W. and K.Q.; Software, S.W.; Validation, K.Q. and J.S.; Formal analysis, K.Q.; Investigation, P.C.; Resources, K.Q.; Data curation, K.Q. and J.S.; Writing—original draft, S.W.; Writing—review & editing, K.Q., J.S., H.M. and P.C.; Visualization, J.S.; Supervision, P.C.; Funding acquisition, K.Q. and H.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is partially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JUSRP121072), the International Science and Technology Cooperation Project of Jiangsu Province (BZ2020069), and the Major Program of University Natural Science Research of Jiangsu Province (21KJA520001).
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, S.; Zhang, T.; Cao, X.; Xu, C. Structural correlation filter for robust visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4312–4320. [Google Scholar]
- Lukezic, A.; Vojir, T.; Cehovin Zajc, L.; Matas, J.; Kristan, M. Discriminative correlation filter with channel and spatial reliability. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6309–6318. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, F.; Zhou, J.; Qian, Y. Material based object tracking in hyperspectral videos. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 3719–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Zhou, J.; Xiong, F.; Zhou, H.; Du, J. Object tracking in hyperspectral videos with convolutional features and kernelized correlation filter. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Multimedia, Toulon, France, 24–26 August 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 308–319. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Yeung, D.Y. Learning a deep compact image representation for visual tracking. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X.; Lu, H. Visual tracking with fully convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Boston, MA, USA, 11–18 December 2015; pp. 3119–3127. [Google Scholar]
- Bertinetto, L.; Valmadre, J.; Henriques, J.F.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P.H. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 850–865. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, H.; Han, B. Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4293–4302. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Fan, N.; He, Z.; Wang, H. Hierarchical spatial-aware siamese network for thermal infrared object tracking. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2019, 166, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, B.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Lu, H. Gradnet: Gradient-guided network for visual object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6162–6171. [Google Scholar]
- Xiu, C.; Chai, Z. Target tracking based on the cognitive associative network. IET Image Process. 2019, 13, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Quan, S.; Yang, Z.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Gan, H. A two-stage method for ship detection using PolSAR image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5236918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Gan, H.; Ning, C.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, T. TransCS: A Transformer-Based Hybrid Architecture for Image Compressed Sensing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 6991–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolme, D.S.; Beveridge, J.R.; Draper, B.A.; Lui, Y.M. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 2544–2550. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, J.F.; Caseiro, R.; Martins, P.; Batista, J. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 37, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Yang, M.H. Fast visual tracking via dense spatio-temporal context learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 127–141. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Hager, G.; Shahbaz Khan, F.; Felsberg, M. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4310–4318. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Suganthan, P.N. Robust visual tracking via co-trained kernelized correlation filters. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 69, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani Galoogahi, H.; Fagg, A.; Lucey, S. Learning background-aware correlation filters for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1135–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, B. Target tracker with masked discriminative correlation filter. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 2227–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yuen, P.C. Spatial-temporal Regularized Multi-modality Correlation Filters for Tracking with Re-detection. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 2021, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yan, J.; Wu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Hu, X. High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8971–8980. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Wu, W.; Yan, J.; Hu, W. Distractor-aware siamese networks for visual object tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 17–24 May 2018; pp. 101–117. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Xing, J.; Yan, J. Siamrpn++: Evolution of siamese visual tracking with very deep networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4282–4291. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Li, J.; He, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, H. Distracter-aware tracking via correlation filter. Neurocomputing 2019, 348, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, S.; Choi, J.Y.; Joo, Y.H. Gaussian-response correlation filter for robust visual object tracking. Neurocomputing 2020, 411, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danelljan, M.; Shahbaz Khan, F.; Felsberg, M.; Van de Weijer, J. Adaptive color attributes for real-time visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1090–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, W.; Tian, Q.; Hong, R.; Wang, M.; Li, H. Multi-cue correlation filters for robust visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4844–4853. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, J.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, M.; Li, S. Collaborative model tracking with robust occlusion handling. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S. SiamCAR: Siamese fully convolutional classification and regression for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6269–6277. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, H.; Fu, J.; Li, B.; Hu, W. Ocean: Object-aware anchor-free tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 771–787. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Hong, D.; Cai, W.; Yu, C.; Yang, N.; Cai, W. Multi-feature fusion: Graph neural network and CNN combining for hyperspectral image classification. Neurocomputing 2022, 501, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, X.; Siye, L.; Yang, N.; Cai, Y.; Zhan, Y. Multireceptive field: An adaptive path aggregation graph neural framework for hyperspectral image classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 217, 119508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xiong, F.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Qian, Y. BAE-Net: A band attention aware ensemble network for hyperspectral object tracking. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Online, 6–8 March 2020; pp. 2106–2110. [Google Scholar]
- Van Nguyen, H.; Banerjee, A.; Chellappa, R. Tracking via object reflectance using a hyperspectral video camera. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition-Workshops, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Qian, K.; Chen, P. BS-SiamRPN: Hyperspectral Video Tracking based on Band Selection and the Siamese Region Proposal Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 12th Workshop on Hyperspectral Imaging and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Rome, Italy, 13–16 September 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, D.; Arun, P.V.; Zhou, H.; Qian, K.; Hu, J. Hyperspectral Video Target Tracking Based on Deep Features with Spectral Matching Reduction and Adaptive Scale 3D Hog Features. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzkent, B.; Rangnekar, A.; Hoffman, M.J. Tracking in aerial hyperspectral videos using deep kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qian, K.; Juan, D.; Zhou, H. Multi-Features Integration Based Hyperspectral Videos Tracker. In Proceedings of the 2021 11th Workshop on Hyperspectral Imaging and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–26 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Ma, C.; Wu, X.; Gong, L.; Bao, L.; Zuo, W.; Shen, C.; Lau, R.W.; Yang, M.H. Vital: Visual tracking via adversarial learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8990–8999. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Shu, M.; Li, G.; Sun, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, Y. An anchor-free Siamese target tracking network for hyperspectral video. In Proceedings of the 2021 11th Workshop on Hyperspectral Imaging and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–26 March 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Du, Q. Hyperspectral band selection: A review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2019, 7, 118–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Chen, P.; Zhao, D. GOMT: Multispectral video tracking based on genetic optimization and multi-features integration. In Proceedings of the IET Image Processing; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA; 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhao, X.; Huang, K. Got-10k: A large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 1562–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Hu, W. Robust visual tracking via transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 2011 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 11–14 September 2011; pp. 485–488. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Gonzalez-Garcia, A.; Joost, V.; Danelljan, M.; Khan, F.S. Learning the Model Update for Siamese Trackers. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Valmadre, J.; Bertinetto, L.; Henriques, J.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P.H. End-to-end representation learning for correlation filter based tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2805–2813. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Feng, W.; Zhou, C.; Huang, R.; Wan, L.; Wang, S. Learning dynamic siamese network for visual object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1763–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xijun, L.; Jun, L. An adaptive band selection algorithm for dimension reduction of hyperspectral images. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Image Analysis and Signal Processing, Wuhan, China, 21–23 October 2009; pp. 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Bruzzone, L.; Guan, R.; Zhou, F.; Yang, C. Spectral-Spatial Genetic Algorithm-Based Unsupervised Band Selection for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 9616–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, D. Improved neural network classification of hyperspectral imagery using weighted genetic algorithm and hierarchical segmentation. IET Image Process. 2019, 13, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeline, P.J.; Saunders, G.M.; Pollack, J.B. An evolutionary algorithm that constructs recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994, 5, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawaz, H.I.; Forestier, G.; Weber, J.; Idoumghar, L.; Muller, P.A. Transfer learning for time series classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Seattle, WA, USA, 10–13 December 2018; pp. 1367–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.J.; Tsang, I.W.; Kwok, J.T.; Yang, Q. Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2010, 22, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, M.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jordan, M. Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Pitié, F.; Kokaram, A. The linear Monge-Kantorovitch linear colour mapping for example-based colour transfer. In Proceedings of the 4th European Conference on Visual Media Production, London, UK, 27–28 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Lim, J.; Yang, M.H. Online object tracking: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2411–2418. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).