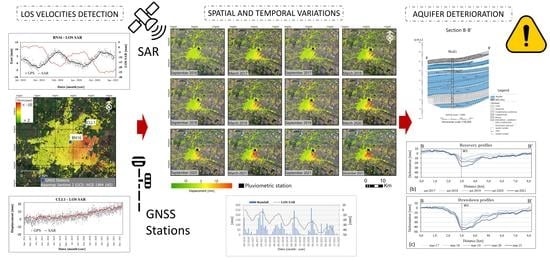
InSAR-Based Early Warning Monitoring Framework to Assess Aquifer Deterioration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study area and Hydrogeological Context
Hydrogeological Context
3. Materials and Method
3.1. InSAR Approach
3.2. Data Set
3.3. P-SBAS Processing
4. Results and Discussions
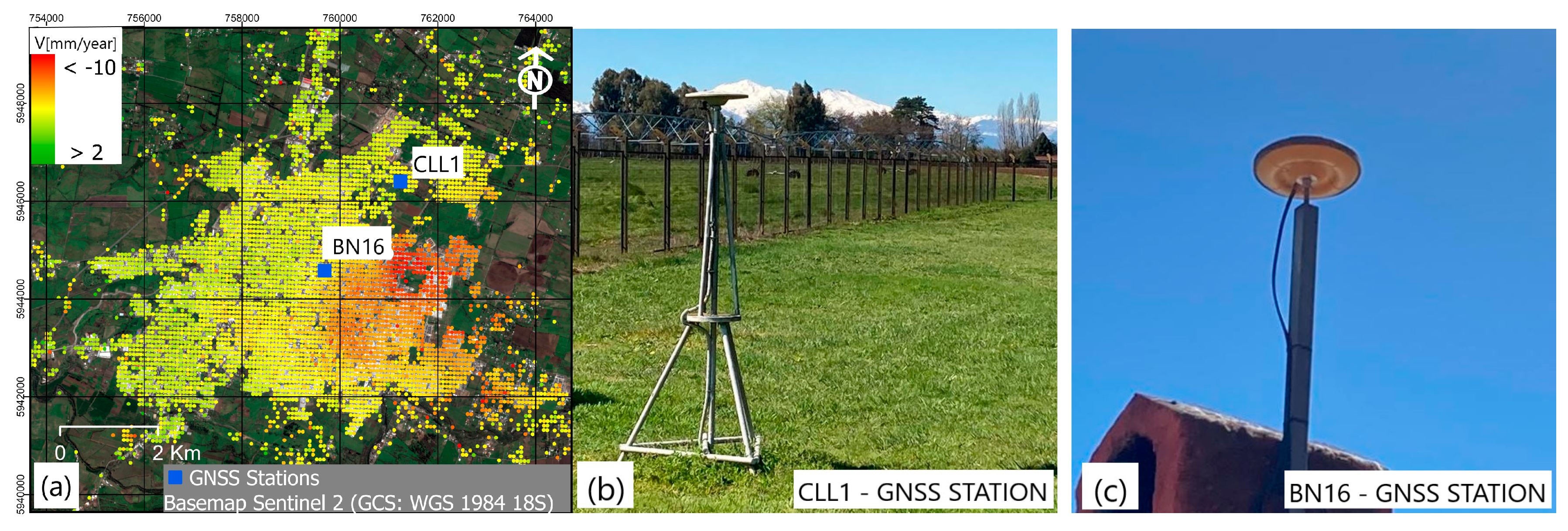
4.1. Measurement and Classifications
InSAR Measurement Verification
4.2. Ground Deformation and Time-Series
4.3. Spatial and Temporal Variations
4.4. Geological and Hydrogeological Interpretations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.-W.; Lin, C.-W.; Yang, C.-Y.; Ding, C.-F.; Hwung, H.-H.; Hsiao, S.-C. Assessment of Land Subsidence and Climate Change Impacts on Inundation Hazard in Southwestern Taiwan. Irrig. Drain. 2018, 67, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinar, A.; Esteban, E.; Calvo, E.; Herrera, G.; Teatini, P.; Tomás, R.; Li, Y.; Ezquerro, P.; Albiac, J. We lose ground: Global assessment of land subsidence impact extent. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minderhoud, P.S.J.; Erkens, G.; Pham, V.H.; Bui, V.T.; Erban, L.; Kooi, H.; Stouthamer, E. Impacts of 25 years of groundwater extraction on subsidence in the Mekong delta, Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 064006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.S.; Seifollahi-Aghmiuni, S.; Destouni, G.; Ghajarnia, N.; Kalantari, Z. Soil degradation in the European Mediterranean region: Processes, status and consequences. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, L.; Dai, Z.; Gong, H.; Guo, T.; Guo, G.; Wang, J.; Teatini, P. Spatiotemporal modeling of land subsidence using a geographically weighted deep learning method based on PS-InSAR. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.G.; Majumdar, S. Groundwater Storage Loss Associated with Land Subsidence in Western US Mapped Using Machine Learning. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, G.; Wang, Q.; Ma, M.; Li, E.; Deng, H. Threat of land subsidence to the groundwater supply capacity of a multi-layer aquifer system. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 101240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Gumilar, I.; Sidiq, T.P.; Gamal, M. Environmental impacts of land subsidence in urban areas of Indonesia. In FIG Working Week; TS 3—Positioning and Measurement: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2015; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.Y.; Lo, M.H.; Wada, Y.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Reager, J.T.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Ducharne, A.; Yang, Z.L. Divergent effects of climate change on future groundwater availability in key mid-latitude aquifers. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Vigna, F. Review: Urban groundwater issues and resource management, and their roles in the resilience of cities. Hydrogeol. J. 2022, 30, 1657–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzy, A.; Malinowska, A.A. State of the Art and Recent Advancements in the Modelling of Land Subsidence Induced by Groundwater Withdrawal. Water 2020, 12, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccatelli, M.; Del Soldato, M.; Solari, L.; Fanti, R.; Mannori, G.; Castelli, F. Numerical modelling of land subsidence related to groundwater withdrawal in the Firenze-Prato-Pistoia basin (central Italy). Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 629–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.J. Review: Regional Land Subsidence Accompanying Groundwater Extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arangio, S.; Bontempi, F.; Ciampoli, M. Structural integrity monitoring for dependability. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2011, 71, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas, M.; Crippa, B. Spaceborne Differential SAR Interferometry: Data Analysis Tools for Deformation Measurement. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manunta, M.; Marsella, M.; Zeni, G.; Sciotti, M.; Atzori, S.; Lanari, R. Two-scale surface deformation analysis using the SBAS-DInSAR technique: A case study of the city of Rome, Italy. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1665–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzano, F.; Esposito, C.; Mazzanti, P.; Patti, M.; Scancella, S. Imaging Multi-Age Construction Settlement Behaviour by Advanced SAR Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, F.; Hormazábal, J.; Montalva, G.; Moreno, M. Measuring Coastal Subsidence after Recent Earthquakes in Chile Central Using SAR Interferometry and GNSS Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foumelis, M.; Papageorgiou, E.; Stamatopoulos, C. Episodic ground deformation signals in Thessaly Plain (Greece) revealed by data mining of SAR interferometry time series. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 3696–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ding, X.L.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.W.; Zhu, J.J. Slope deformation prior to Zhouqu, China landslide from InSAR time series analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunori, C.A.; Norini, G.; Stramondo, S.; Capra, L.; Zucca, F.; Groppelli, G.; Bignami, C.; Chini, M.; Manea, M.; Manea, V. Crustal deformation induced by volcanic activity measured by InSAR time series analysis (Volcan de Colima-Mexico). In EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts; 2010; p. 6958. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2010EGUGA..12.6958B/abstract (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Orellana, F.; Delgado Blasco, J.M.; Foumelis, M.; D’Aranno, P.J.V.; Marsella, M.A.; Di Mascio, P.D. Dinsar for road infrastructure monitoring: Case study highway network of Rome metropolitan (Italy). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, D.; Di Martire, D.; Confuorto, P.; Tessitore, S.; Ramondini, M.; Calcaterra, D. Differential Sar Interferometry Technique for Control of Linear Infrastructures Affected by Ground Instability Phenomena. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 3, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Tapete, D. Urban growth and land subsidence: Multi-decadal investigation using human settlement data and satellite InSAR in Morelia, Mexico. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 152211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezquerro, P.; Tomás, R.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Fernández-Merodo, J.A.; Guardiola-Albert, C.; Staller, A.; Sánchez-Sobrino, J.A.; Herrera, G. Improving multi-technique monitoring using Sentinel-1 and Cosmo-SkyMed data and upgrading groundwater model capabilities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Lei, K.; Zhu, L.; Duan, L.; Zhao, X. Land subsidence and its relation with groundwater aquifers in Beijing Plain of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, S.; Jain, K.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Gupta, V.; Varade, D.; Singh, H.; Narayan, A.B.; Budillon, A. Analyzing urbanization induced groundwater stress and land deformation using time-series Sentinel-1 datasets applying PSInSAR approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, F.; Moreno, M.; Yáñez, G. High-Resolution Deformation Monitoring from DInSAR: Implications for Geohazards and Ground Stability in the Metropolitan Area of Santiago, Chile. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitrano, D.; Di Martino, G.; Iodice, A.; Mitidieri, F.; Papa, M.N.; Riccio, D.; Ruello, G. Sentinel-1 for Monitoring Reservoirs: A Performance Analysis. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10676–10693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzano, F.; Esposito, C.; Franchi, S.; Mazzanti, P.; Perissin, D.; Rocca, A.; Romano, E. Understanding the Subsidence Process of a Quaternary Plain by Combining Geological and Hydrogeological Modelling with Satellite InSAR Data: The Acque Albule Plain Case Study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquerro, P.; Herrera, G.; Marchamalo, M.; Tomás, R.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Martínez, R. A Quasi-Elastic Aquifer Deformational Behavior: Madrid Aquifer Case Study. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquerro, P.; Guardiola-Albert, C.; Herrera, G.; Fernández-Merodo, J.A.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Bonì, R. Groundwater and Subsidence Modeling Combining Geological and Multi-Satellite SAR Data over the Alto Guadalentín Aquifer (SE Spain). Geofluids 2017, 2017, 1359325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry: A Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A New Algorithm for Processing Interferometric Data-Stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.J. A Multi-Temporal InSAR Method Incorporating Both Persistent Scatterer and Small Baseline Approaches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, F.; Elefante, E.; Imperatore, P.; Zinno, I.; Manunta, M.; De Luca, C.; Lanari, R. SBAS-DInSAR Parallel Processing for Deformation Time Series Computation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manunta, M.; De Luca, C.; Zinno, I.; Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Bonano, M.; Fusco, A.; Pepe, A.; Onorato, G.; Berardino, P.; et al. The Parallel SBAS Approach for Sentinel-1 Interferometric Wide Swath Deformation Time-Series Generation: Algorithm Description and Products Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6259–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manunta, M.; Casu, F.; Zinno, I.; de Luca, C.; Pacini, F.; Brito, F.; Blanco, P.; Iglesias, R.; Lopez, A.; Briole, P.; et al. The Geohazards Exploitation Platform: An advanced cloud-based environment for the Earth Science community. In Proceedings of the19th EGU General Assembly, EGU2017, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2017; p. 14911. [Google Scholar]
- Foumelis, M.; Papadopoulou, T.; Bally, P.; Pacini, F.; Provost, F.; Patruno, J. Monitoring Geohazards Using On-Demand and Systematic Services on Esa’s Geohazards Exploitation Platform. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019, IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 5457–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galve, J.P.; Pérez-Peña, J.V.; Azañón, J.M.; Closon, D.; Calò, F.; Reyes-Carmona, C.; Jabaloy, A.; Ruano, P.; Mateos, R.M.; Notti, D.; et al. Evaluation of the SBAS InSAR Service of the European Space Agency’s Geohazard Exploitation Platform (GEP). Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Carmona, C.; Galve, J.P.; Barra, A.; Monserrat, O.; Maria Mateos, R.; Azañón, J.M.; Perez-Pena, J.V.; Ruano, P. The Sentinel-1 CNR-IREA SBAS service of the European Space Agency’s Geohazard Exploitation Platform (GEP) as a powerful tool for landslide activity detection and monitoring. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 3–8 May 2020; p. 19410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, F. Hydrogeological characterization of the Chillán sheet (36°30′–36°45′South Latitude and 72°00′–72°15′ West Longitude), VIII Region of Bíobío, Chile; Report to qualify for the title of Geologist; University of Concepción: Concepcion, Chile, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zinno, I.; Casu, F.; De Luca, C.; Elefante, S.; Lanari, R.; Manunta, M. A cloud computing solution for the efficient implementation of the P-SBAS DInSAR approach. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 802–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperatore, P.; Pepe, A.; Sansosti, E. High performance computing in satellite SAR interferometry: A critical perspective. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Samsonov, S.; Yin, H.; Ye, S.; Cao, Y. Time-series analysis of subsidence associated with rapid urbanization in Shanghai, China measured with SBAS InSAR method. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yague-Martinez, N.; DeZan, F.; Prats-Iraola, P. Coregistration of Interferometric Stacks of Sentinel-1 TOPS Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumí, J.L.; Rivera, D.; Muñoz, E.; Billib, M. Interactions between surface and groundwater in the Bío Bío region of Chile. Work. Proj. 2012, 12, 4–13. [Google Scholar]
- Blewitt, G.; Hammond, W.C.; Kreemer, C. Harnessing the GPS data explosion for interdisciplinary science. Eos 2018, 99, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.F.; Brumby, S.P.; Guzder-Williams, B.; Birch, T.; Hyde, S.B.; Mazzariello, J.; Czerwinski, W.; Pasquarella, V.J.; Haertel, R.; Ilyushchenko, S.; et al. Dynamic World, Near real-time global 10 m land use land cover mapping. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Hoffmann, J. The application of satellite differential SAR interferometry-derived ground displacements in hydrogeology. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 15, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, P.J.; Tiampo, K.F.; Palano, M.; Cannavó, F.; Fernández, J. The 2011 Lorca earthquake slip distribution controlled by groundwater crustal unloading. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonì, R.; Herrera, G.; Meisina, C.; Notti, D.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Zucca, F.; González, P.J.; Palano, M.; Tomás, R.; Fernández, J.; et al. Twenty-year advanced DInSAR analysis of severe land subsidence: The Alto Guadalentín Basin (Spain) case study. Eng. Geol. 2015, 198, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taftazani, R.; Kazama, S.; Takizawa, S. Spatial Analysis of Groundwater Abstraction and Land Subsidence for Planning the Piped Water Supply in Jakarta, Indonesia. Toilet 2022, 14, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, S. Physical Geology. Victoria, BC: BCcampus. 2015. Available online: https://opentextbc.ca/geology/ (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Terzaghi, K. Principles of soil mechanics: IV. Settlement and consolidation of clay. Erdbaummechanic 1925, 95, 874–878. [Google Scholar]
- Biot, M. General theory of three-dimensional consolidation. J. Appl. Phys. 1941, 12, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Tapete, D. Land Subsidence and Aquifer-System Storage Loss in Central Mexico: A Quasi-Continental Investigation with Sentinel-1 InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Orbit | Descending |
|---|---|
| Sensor | Sentinel 1B |
| N° acquisitions | 145 |
| Date of measurement start | 10 September 2016 |
| Date of measurement end | 30 December 2021 |
| Relative orbit | 156 |
| Polarization | VV |
| Swath | IW-2 |
| Bursts | 2–3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orellana, F.; Rivera, D.; Montalva, G.; Arumi, J.L. InSAR-Based Early Warning Monitoring Framework to Assess Aquifer Deterioration. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071786
Orellana F, Rivera D, Montalva G, Arumi JL. InSAR-Based Early Warning Monitoring Framework to Assess Aquifer Deterioration. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(7):1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071786
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrellana, Felipe, Daniela Rivera, Gonzalo Montalva, and José Luis Arumi. 2023. "InSAR-Based Early Warning Monitoring Framework to Assess Aquifer Deterioration" Remote Sensing 15, no. 7: 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071786
APA StyleOrellana, F., Rivera, D., Montalva, G., & Arumi, J. L. (2023). InSAR-Based Early Warning Monitoring Framework to Assess Aquifer Deterioration. Remote Sensing, 15(7), 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071786