Study on the Vertical Structure and the Evolution of Precipitation Particle Spectrum Parameters of Stratocumulus Clouds over North China Based on Aircraft Observation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. Introduction of the Observation Data
2.2. Introduction of the Instrumentation
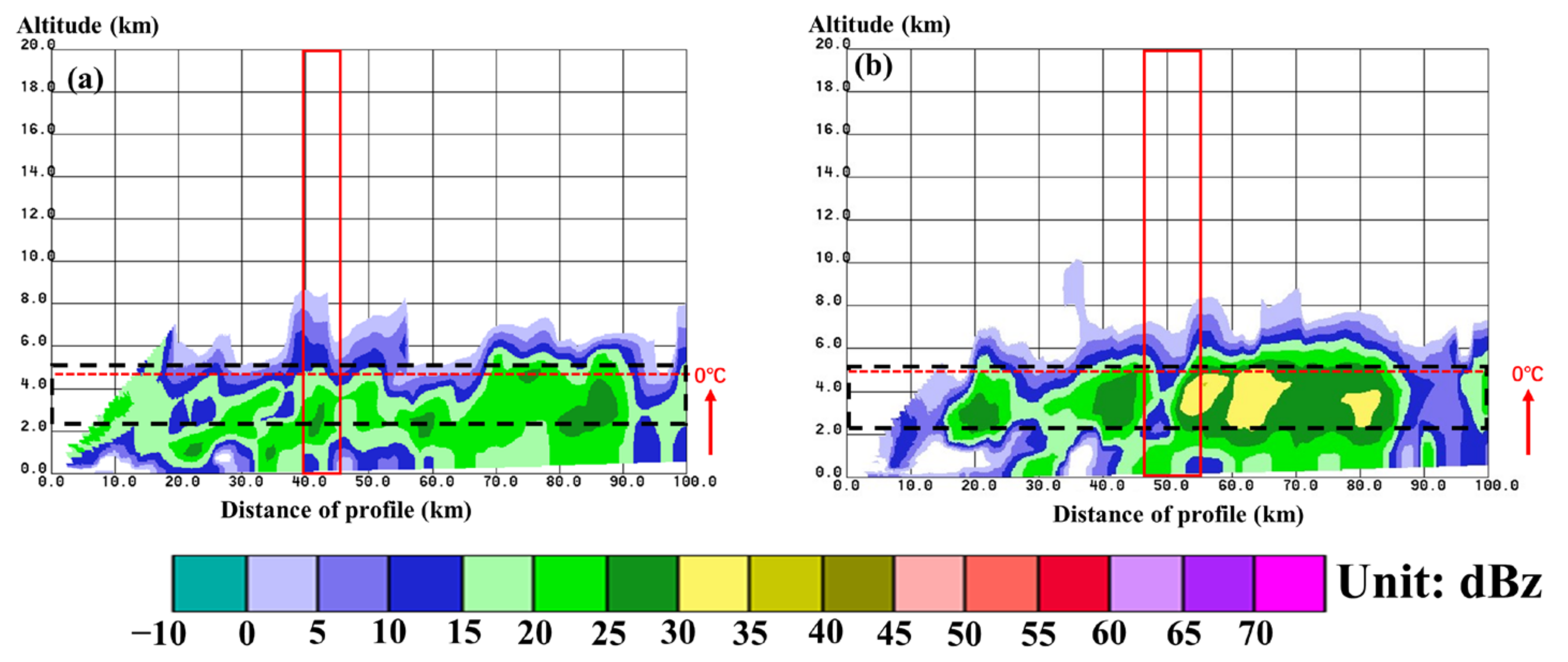
2.3. Precipitation and Radar Data
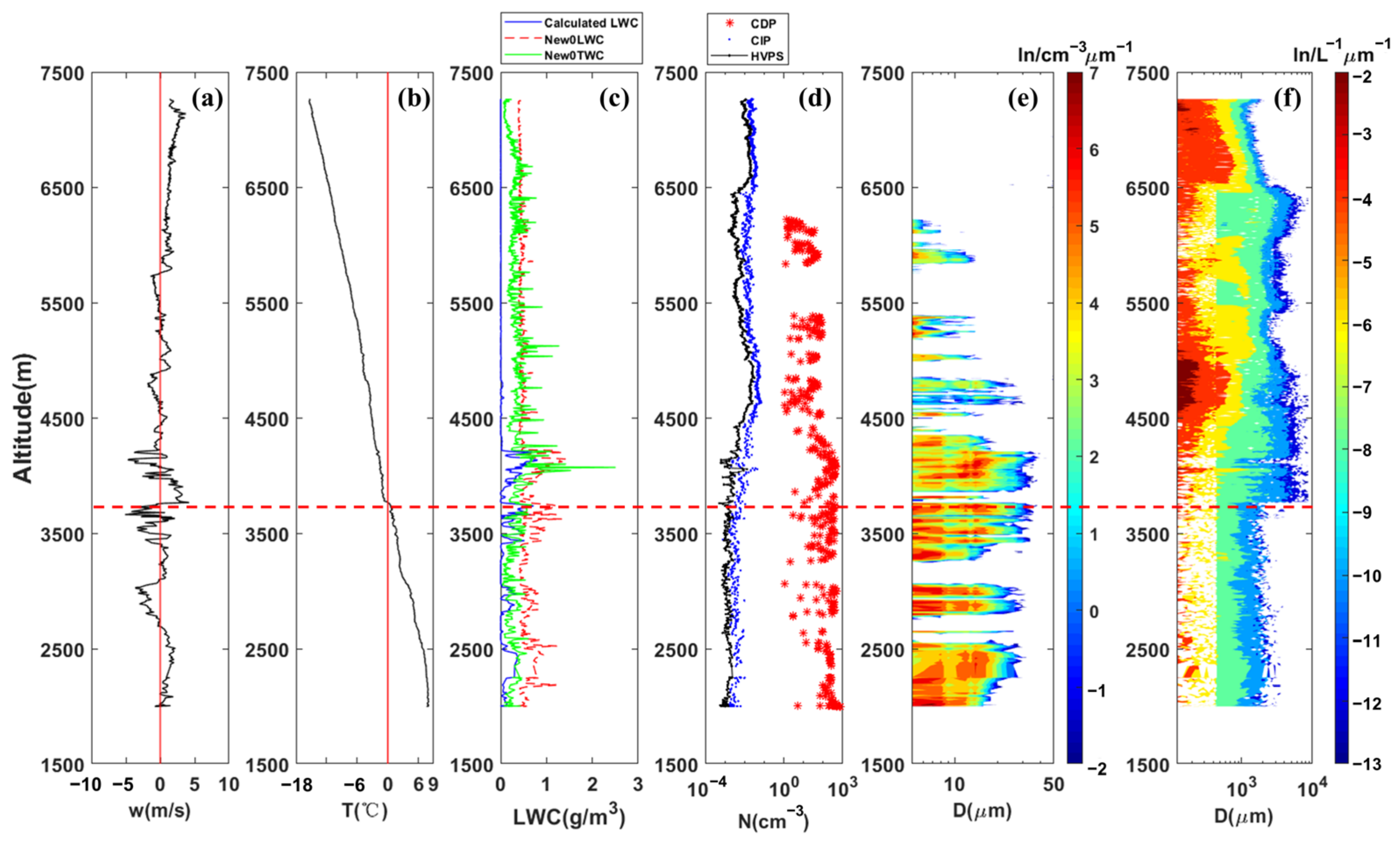
3. Result
3.1. Vertical Distribution of Microphysical Characteristics in Clouds
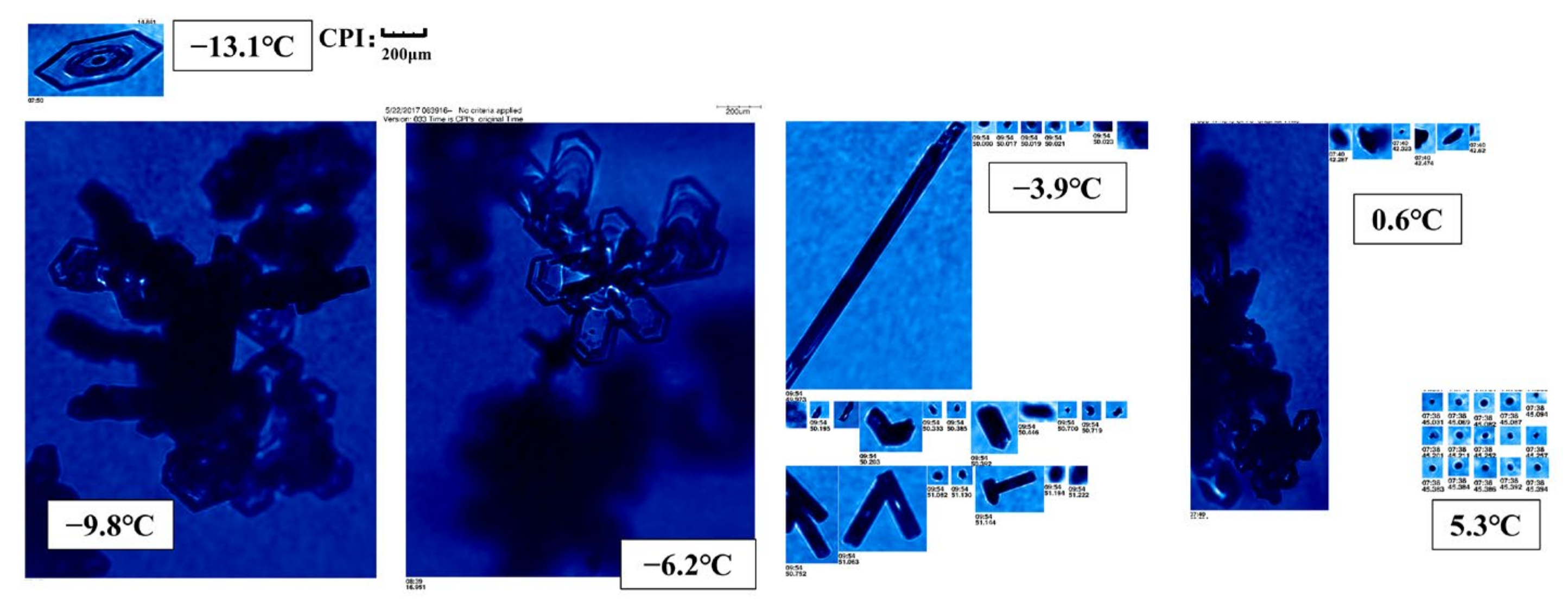
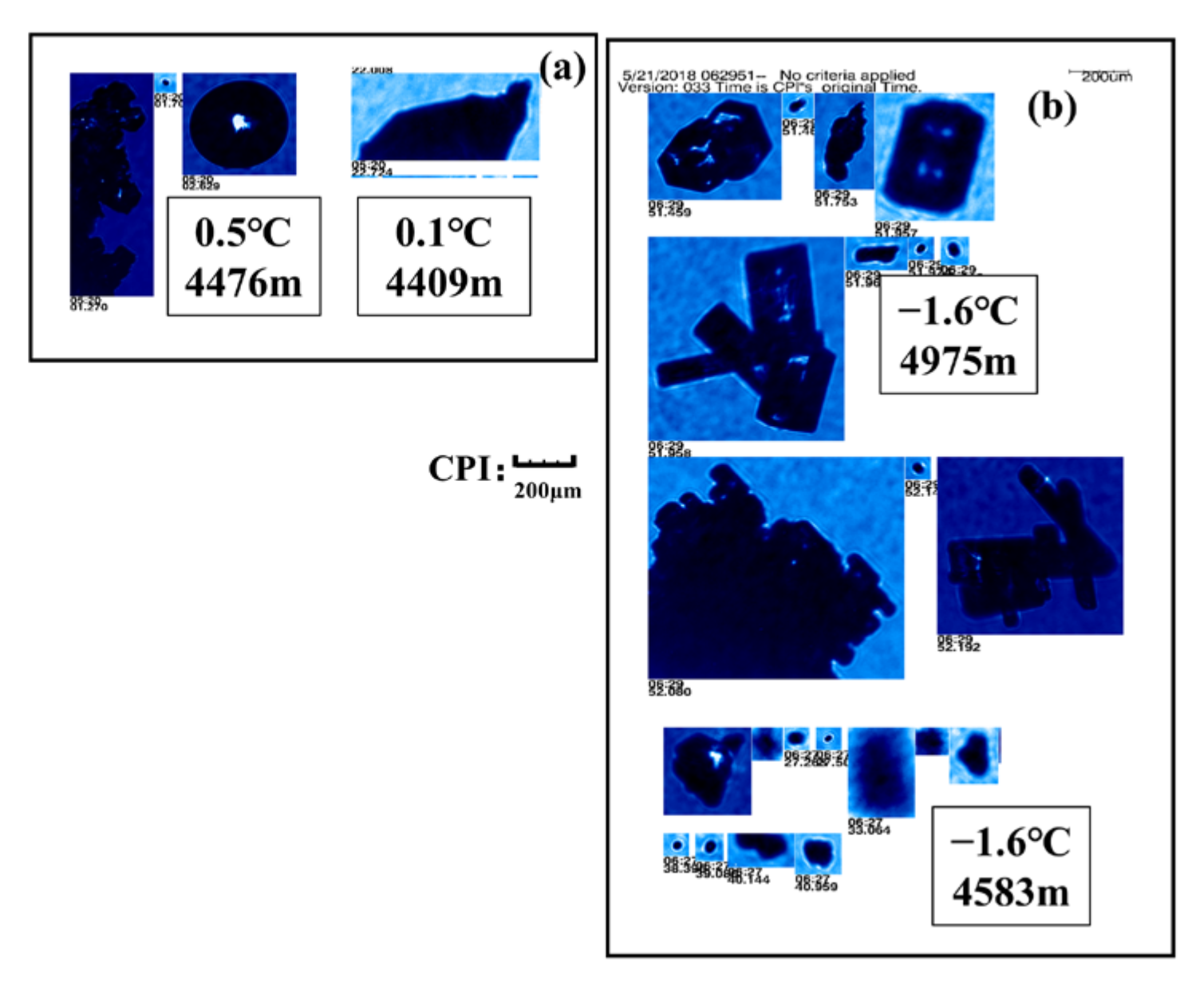
3.2. The Image of Ice Particles
3.3. Particle Size Distribution (PSD)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, T.J.; Lei, H.C.; He, Y.J.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, Z.X. Aircraft Measurements of the Microphysical Properties of Stratiform Clouds with Embedded Convection. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 966–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.C.; Guo, X.L. Ice crystal habits, distribution and growth process in stratiform clouds with embedded convection in North China: Aircraft measurement. Acta Meteor. Sinica. 2014, 72, 366–389. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, P.; Guo, X.L.; Lu, G.X.; Duan, Y.; Li, B.D.; Wu, Z.H.; Dong, X.B.; Hu, X.F.; Yang, Y.S.; Fan, H.; et al. Aircraft Measurements of a Stable Stratiform Cloud with Embedded Convection in Eastern Taihang Mountain of North China: Characteristics of Embedded Convection and Melting Layer Structure. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 43, 1365–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.M.; Li, Z.L.; Liu, W.; Dong, X.B.; Mai, R.; Sun, Y.W. Aircraft observations on physical properties of precipitation clouds in Hebei province. J. Meteor. Environ. 2019, 35, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.F.; Hu, X.F.; Lei, H.C.; Duan, Y.; Lv, F.; Zhao, L.W. Airborne Observations of Microphysical Characteristics of Stratiform Cloud Over Eastern Side of Taihang Mountains. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 45, 88–106. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Guo, X.L.; He, H.; Liu, X.E.; Huang, M.Y.; Ma, X.C. Numerical Simulation Study on the Microphysical Characteristics of Stratiform Clouds with Embedded Convections in Northern China based on Aircraft Measurements. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 44, 899–912. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.F.; Xiao, H.X.; Cui, Y.; Lv, F.; Zhao, L.W.; Ji, X.S. Microphysical characteristics of precipitating stratiform clouds in north China revealed by joint observations of an aircraft and a polarimetric radar. J. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 79, 2799–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Lei, H.; Hu, W.; Huang, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Hou, T.; Lv, Y. An Analysis of the Microstructure of the Melting Layer of a Precipitating Stratiform Cloud at the Dissipation Stage. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.S.; Lei, H.C. Ice particle habit distribution in stratiform clouds at different precioitation stages. Trans. Amos. Sci. 2022, 45, 247–256. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Lei, H. Observed microphysical structure of nimbostratus in northeast cold vortex over China. Atmos. Res. 2014, 142, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.J.; Niu, S.J.; Hou, T.J.; Fan, X.P.; Shen, D.D.; Yang, J.M. Aircraft-Based Observation of the Physical Characteristics of Snowfall Cloud in Shanxi Province. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 45, 1146–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher, S.A.; Pal, J.S.; Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Benedetti, M.M. Future changes in snowmelt-driven runoff timing over the western US. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L16703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.S.; Ghosh, S.C.; Kao, S.C.; Bowling, L.C.; Mote, P.; Touma, D.; Rauscher, S.A.; Diffenbaugh, N.S. Nearterm acceleration of hydroclimatic change in the western U.S. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 10676–10693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, C.; Tilg, A.M.; Jonas, T. Recent evidence of largescale receding snow water equivalents in the European Alps. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mote, P.W.; Li, S.H.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Xiao, M.; Engel, R. Dramatic declines in snowpack in the western US. Npj. Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, S.K.; Ebtehaj, A.M.; Prein, A.F.; Heymsfield, A.J. Linking global changes of snowfall and wet-bulb temperature. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S.; Goss, S.M.; Baldwin, M.E. The melting effect as a factor in precipitation-type forecasting. Weather. Forecast. 2000, 15, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraltay, R.G.; Hallett, J. Evaporation and melting of ice crystals: A laboratory study. Atmos. Res. 1989, 24, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Sasyo, Y. Empirical formula for the melting rate of snowflakes. J. Meteorol. Soc. JPN. Ser. II 1981, 59, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.K.; Vohl, O.; Ahr, M.; Pruppacher, H.R. A wind tunnel and theoretical study of the melting behavior of atmospheric ice particles. IV: Experiment and theory for snow flakes. J. Atmos. Sci. 1990, 47, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.J.; Bansemer, A.; Field, P.R.; Durden, S.L.; Stith, J.; Dye, J.E.; Hall, W.; Grainger, T. Observations and parameterizations of particle size distributions in deep tropical cirrus and stratiform precipitating clouds: Results from in situ observations in TRMM field campaigns. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 72, 2902–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.J.; Bansemer, A.; Poellot, M.R.; Wood, N. Observations of ice microphysics through the melting layer. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 2902–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Zhao, C.F.; Zhou, Y.Q. SPEC airborne cloud detection system and its cloud physics research progress. Torrential Rain Disaster 2021, 40, 280–286. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.L.; Fu, D.H.; Guo, X.; Fang, C.G. Study on physical plane observation of cloud precipitation in China. JAM 2021, 32, 641–645. [Google Scholar]
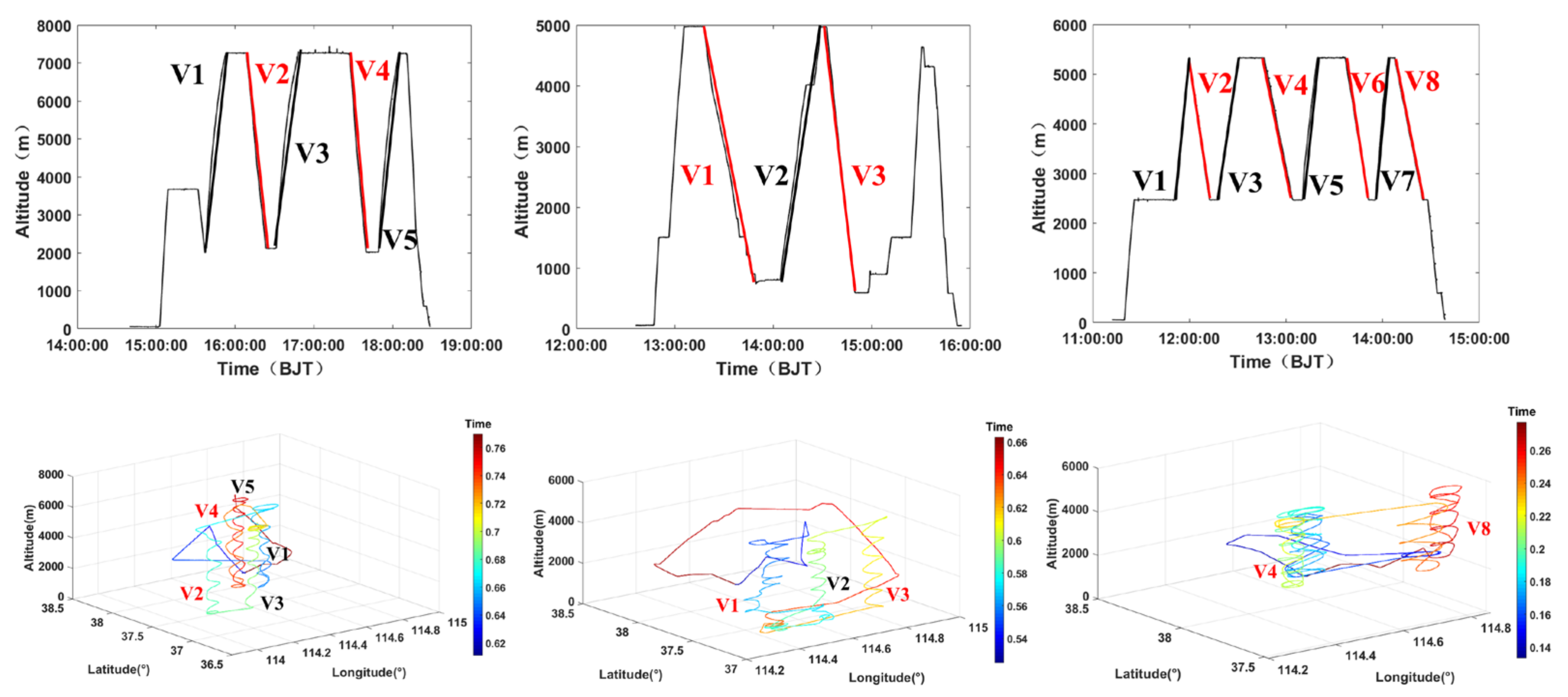
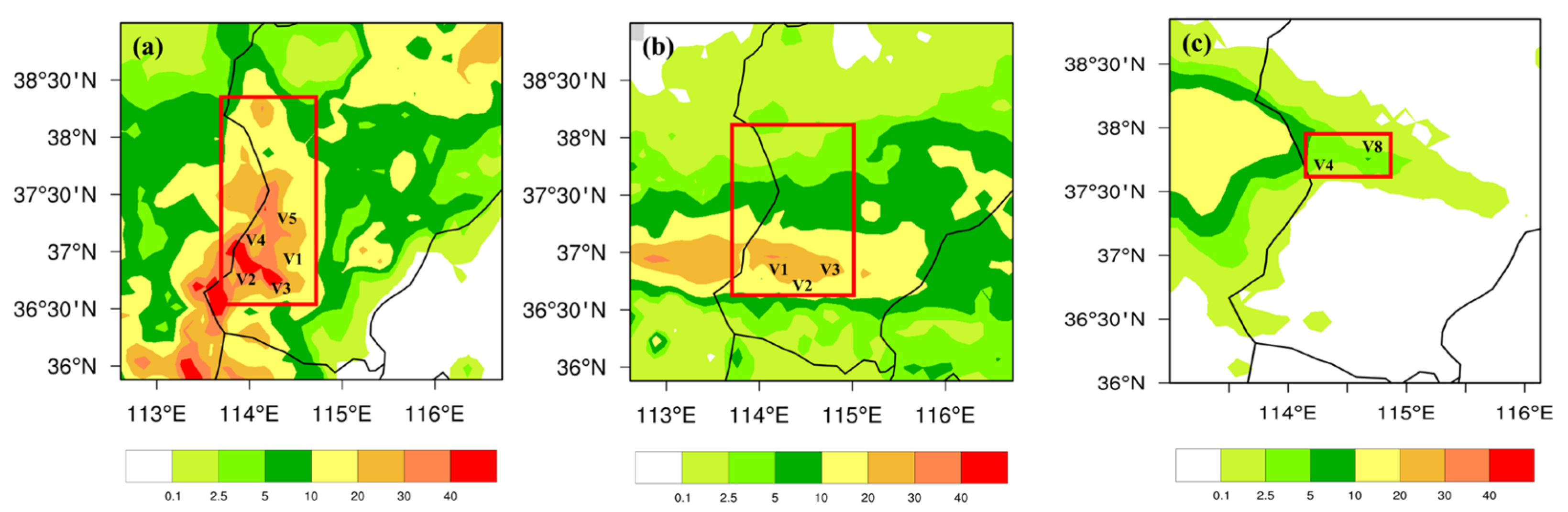


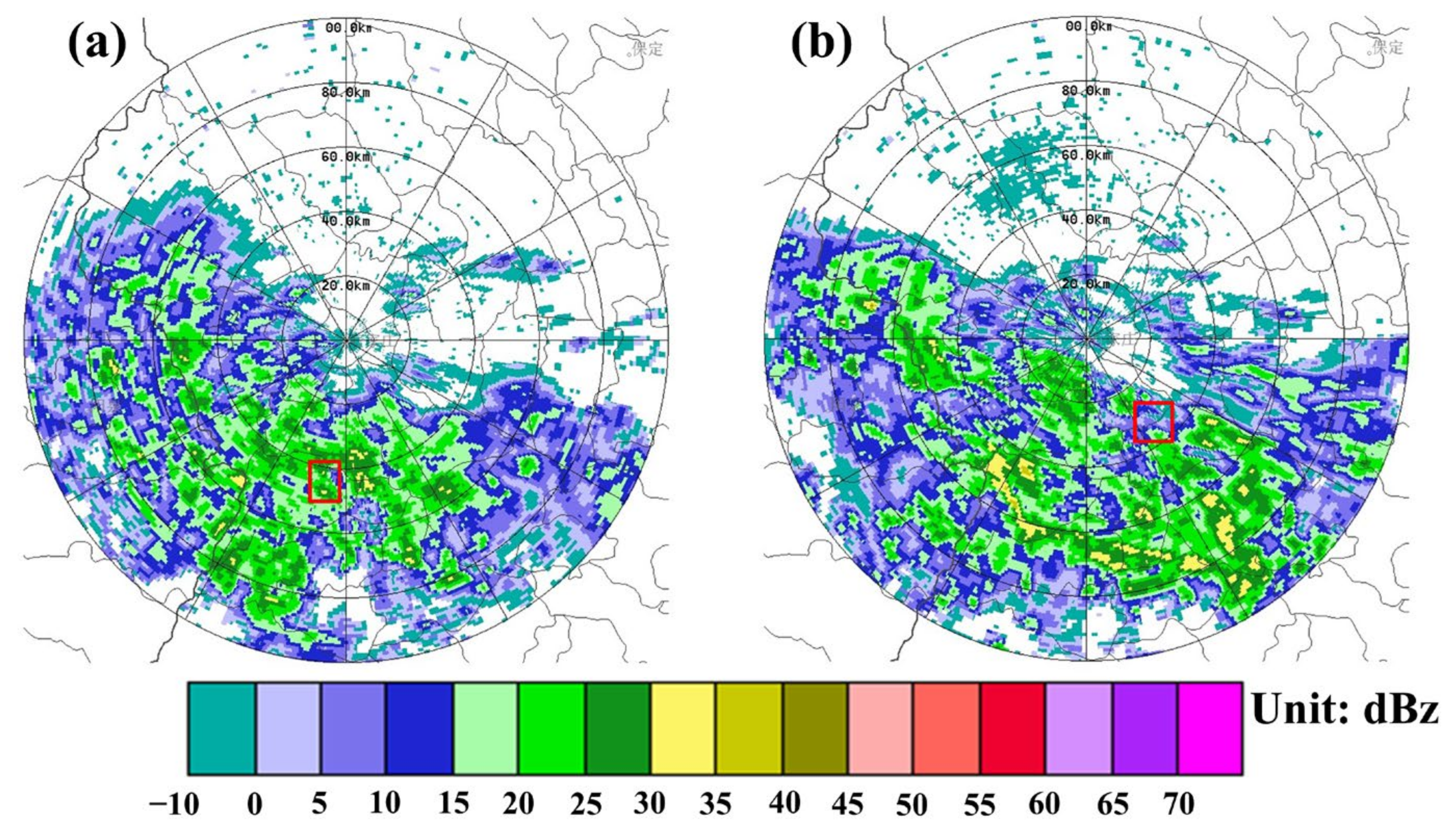

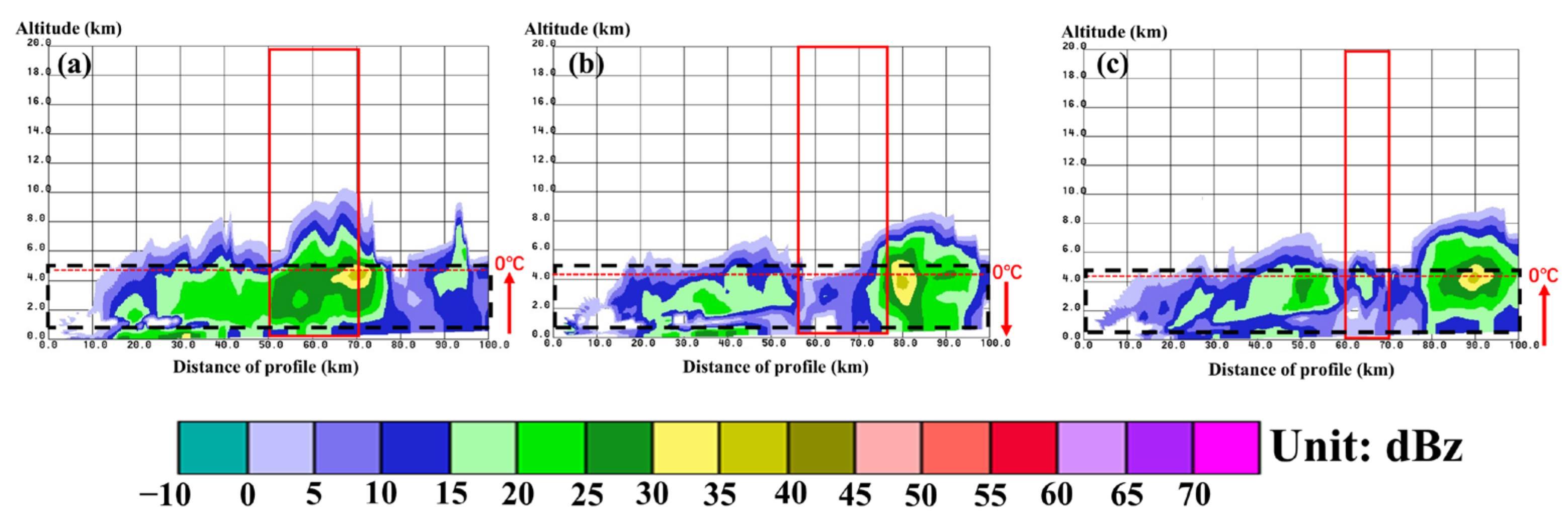

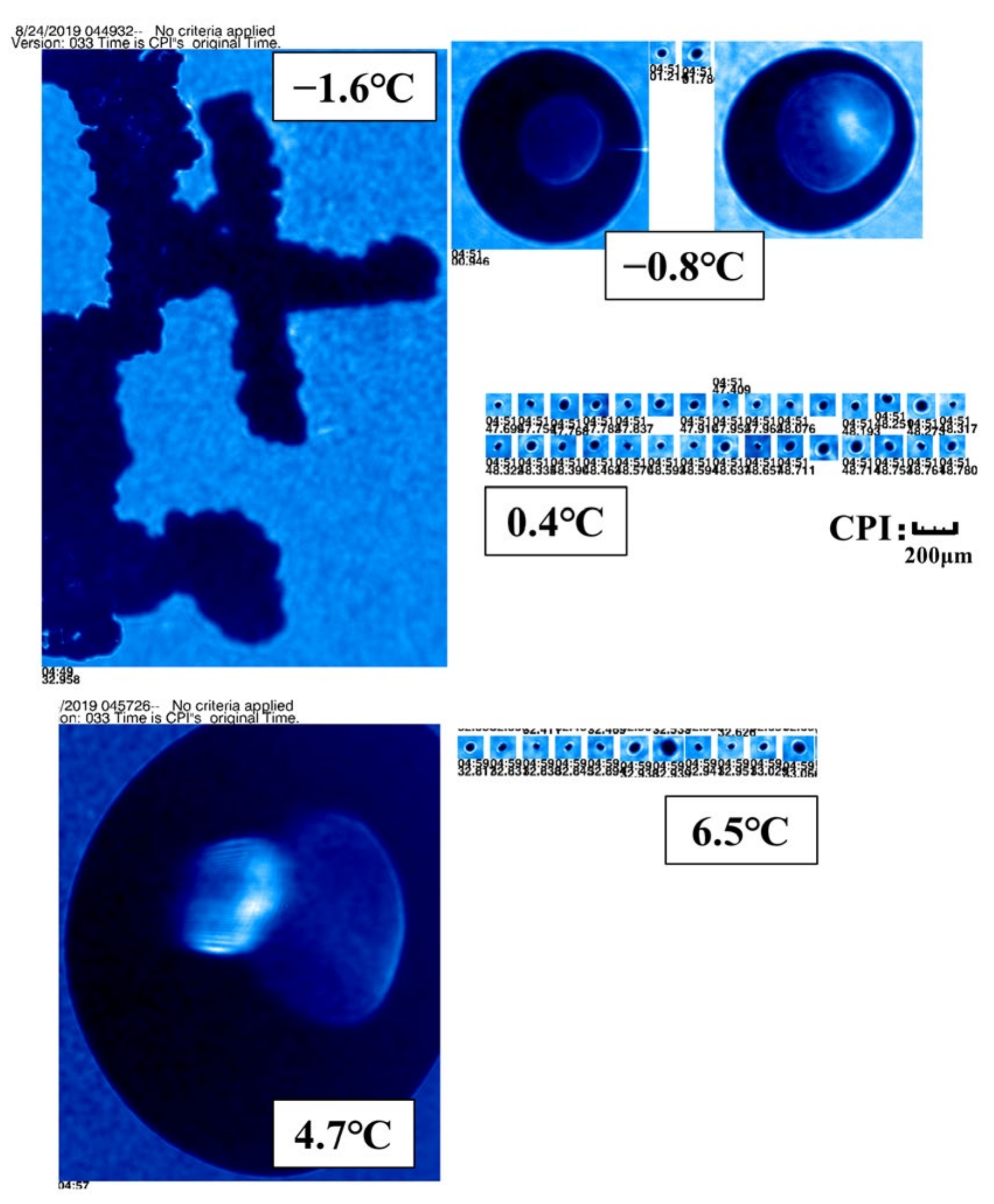
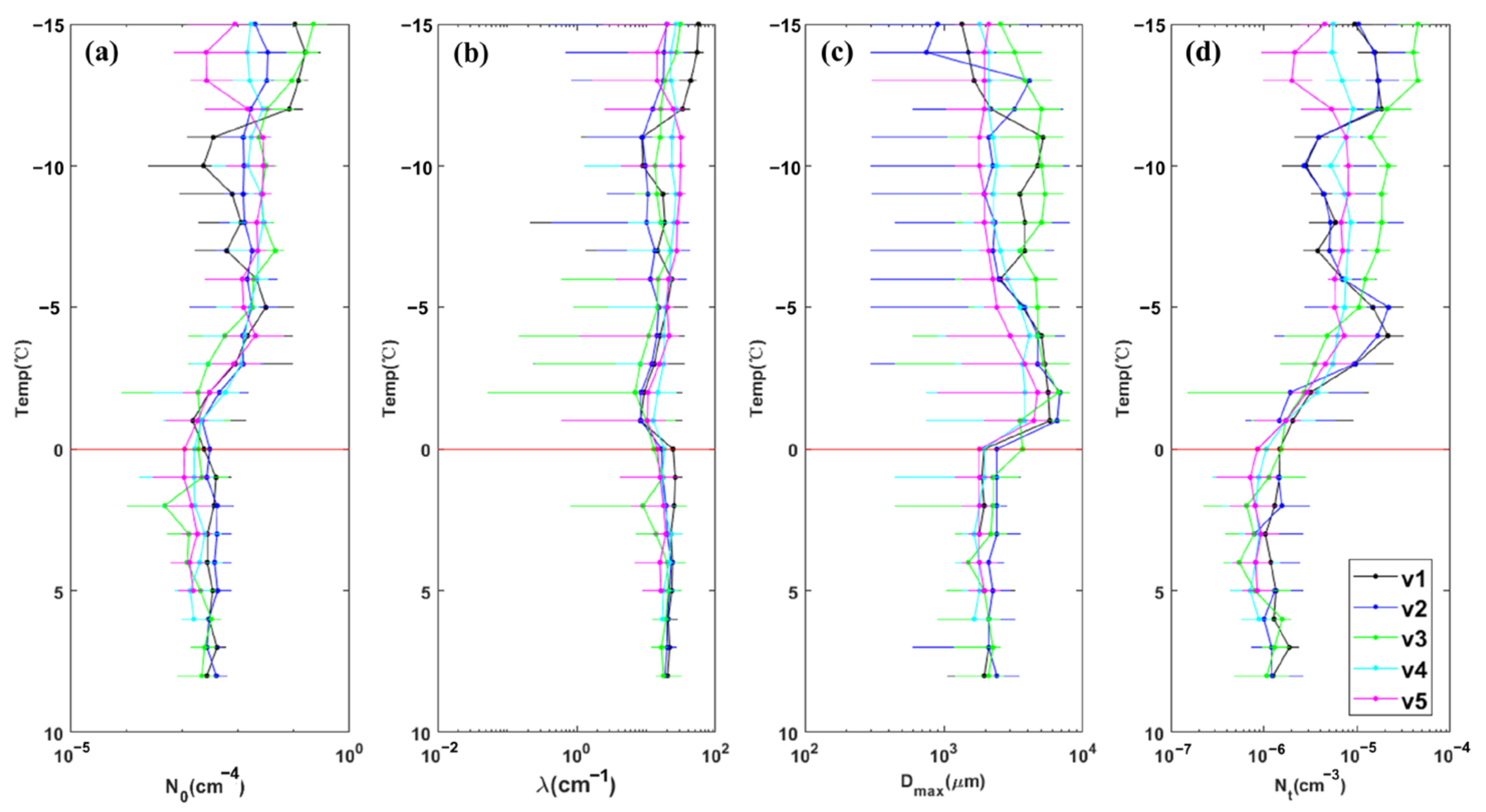
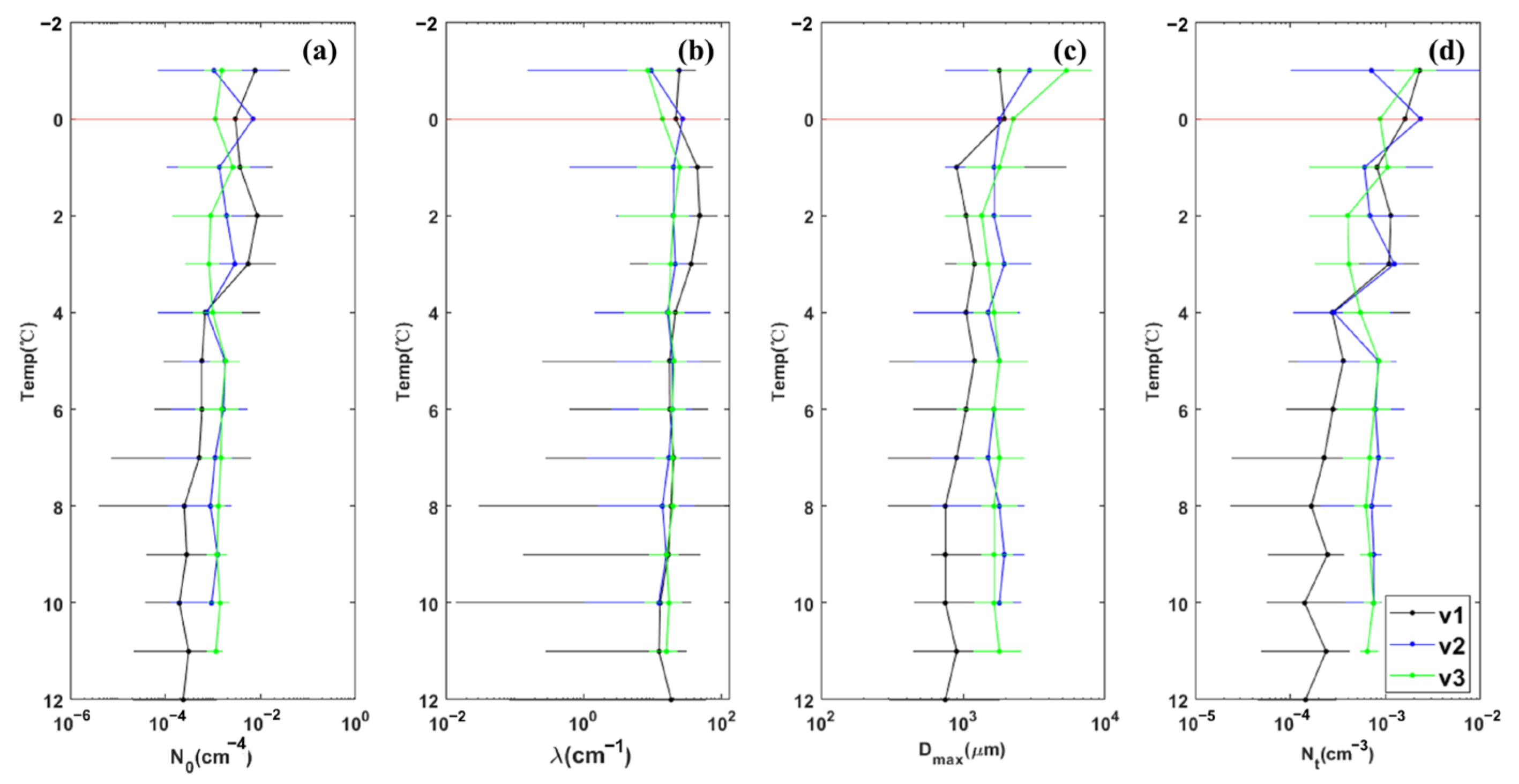
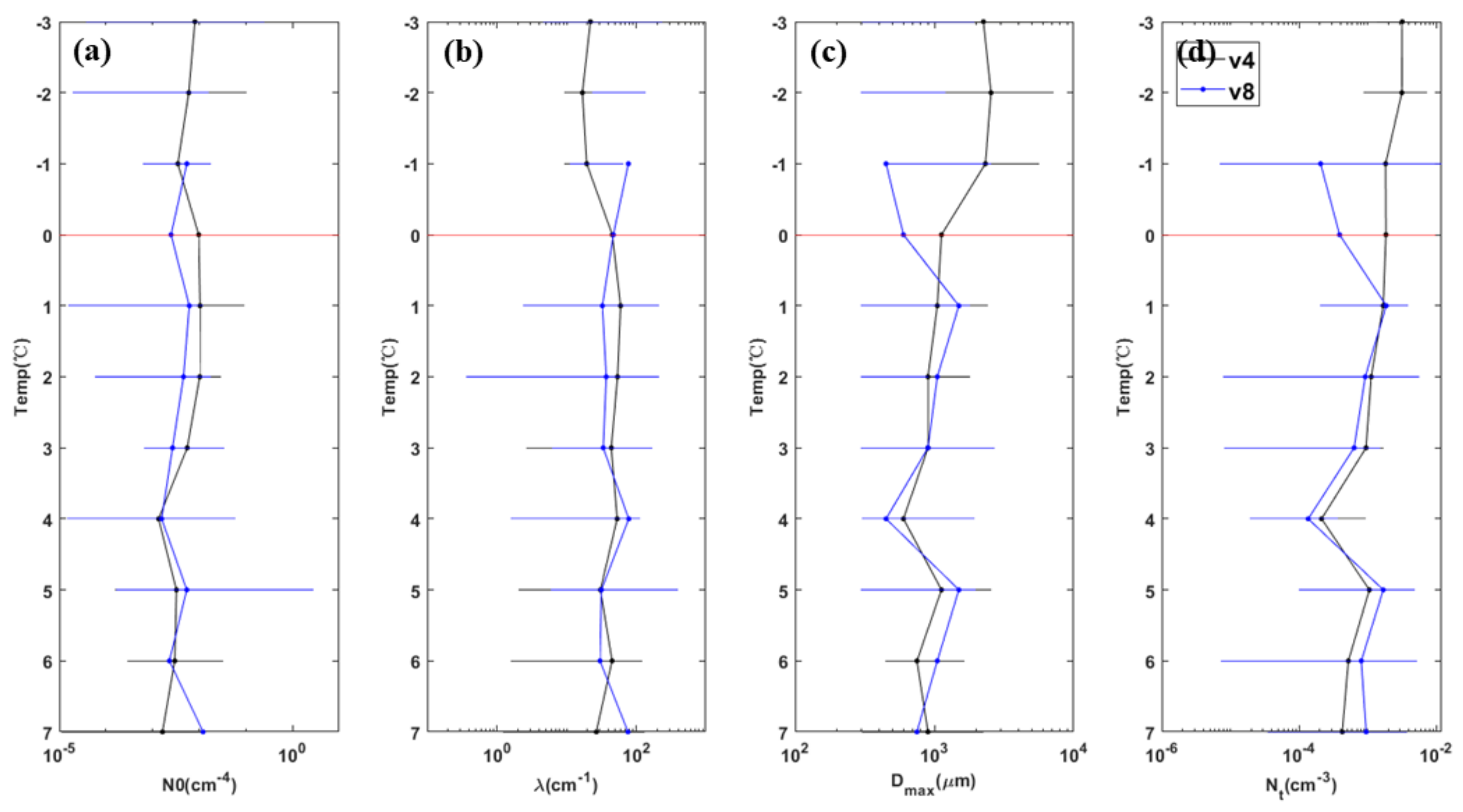



| Flight | Detection Time (Beijing Time) | Range of Height (m) | Range of Temperature (°C) | Rate of Descent (m/s) | Width of Detection (km) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 May 2017 | V1 | 15:37:11–15:53:06 | 7263–1998 | −15.4–8.1 | 5.51 | 10.72 |
| V2 | 16:08:32–16:23:38 | 7263–2121 | −15.7–8.2 | 5.68 | 9.99 | |
| V3 | 16:31:10–16:48:59 | 7267–2107 | −15.6–8.6 | 4.83 | 9.40 | |
| V4 | 17:27:07–17:39:54 | 7247–2009 | −16.1–5.5 | 6.83 | 11.51 | |
| V5 | 17:48:59–18:04:27 | 7256–2011 | −15.9–4.9 | 5.65 | 7.90 | |
| 21 May 2018 | V1 | 13:17:43–13:54:07 | 4971–784 | −1.2–12.4 | 1.92 | 16.18 |
| V2 | 14:04:17–14:30:00 | 4975–810 | −1.8–10.3 | 2.70 | 13.39 | |
| V3 | 14:32:32–14:49:50 | 4958–590 | −1.6–11.3 | 4.21 | 7.35 | |
| 24 August 2019 | V4 | 12:46:39–13:04:59 | 5297–2463 | −3–7.3 | 2.58 | 11.10 |
| V8 | 14:07:30–14:24:38 | 5328–2502 | −2.3–7.3 | 2.75 | 10.47 |
| Instrument Name | Equipment Manufacturer | Measuring Range | Resolution | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passive Cavity Aerosol Spectrometer Probe | DMT | 30 channels, 0.1~3 μm | 0.1 μm | Used for the detection of an aerosol particle spectrum |
| Fast Cloud Droplet Probe | SPEC | 21 channels, 2~50 μm | 3 μm | Cloud particle spectrum |
| Cloud Droplet Probe (CDP) | DMT | 30 channels, 2~50 μm | Cloud particle spectrum | |
| Cloud Imaging Probe (CIP) | DMT | 62 channels, 25~1500 μm | 25 μm | Used to obtain a high-definition crystal grain spectrum and 2-dimensional particle image of ice, snow, cloud |
| Precipitation Imaging Probe (PIP) | DMT | 62 channels, 100~6200 μm | 100 μm | Used to obtain precipitation particle spectrum and image |
| Cloud Imaging Probe | SPEC | 10~2000 μm | 2.3 μm | Used for cloud droplets, snow and ice crystals, raindrop images |
| 2D-S Optical | SPEC | 10~1280 μm | 100 μm | Used for cloud droplets, snow and ice crystals, raindrop images |
| High Volume Precipitation Spectrometer (HVPS) | SPEC | 150~19,200 μm | 150 μm | Used to obtain a clear precipitation particle spectrum and particle 2-dimensional image |
| LWC | DMT | 0~3 g m−3 | Liquid water content | |
| TWC | Nevzorov | 0.005~3 g m−3 | Liquid water content, ice, and snow crystal water content | |
| AIMMS-20 | Aventech | Temperature: −50~50 °C Vertical velocity: 0~50 m s−1 Altitude: 0~13.7 km | Temperature: 0.3 °C Velocity: 0.75 m s−1 Altitude: 18.3 m | Used for measuring high temperature, pressure, humidity, wind, and aircraft motion parameters |
| Detection | Height of 0 °C Layer (m) | CDP (cm−3) (Max/Average) | CIP (cm−3) (Max/Average) | HVPS (cm−3) (Max/Average) | w (m/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Updraft (Max/Average) | Downdraft (Max/Average) | ||||||
| 2017 | V1 | 3764 | 725/55 | 19.17/0.54 | 4.2/1.3 | −5.1/−1.0 | |
| V2 | 3612 | 980/106 | 26.7/0.87 | 7/2.3 | −4.2/−0.6 | ||
| V3 | 3706 | 948/49 | 2.67/0.66 | 6.2/2.3 | −2.2/−0.4 | ||
| V4 | 3346 | 261/19 | 0.39/0.09 | 10/2.7 | −1.9/−0.4 | ||
| V5 | 3451 | 360/17 | 0.79/0.14 | 4.3/0.9 | −8.4/−1.1 | ||
| 2018 | V1 | 4737 | 1419/14 | 17/0.56 | 14.4/2.9 | −4.6/−1.5 | |
| V2 | 4201 | 299/8.99 | 5.92/0.23 | 9.6/2.4 | −2.1/−0.4 | ||
| V3 | 4265 | 114/5.76 | 3.43/0.28 | 9.1/3.1 | −0.6/−0.2 | ||
| 2019 | V4 | 4496 | 1190/217 | 3.44/0.17 | 3.7/1.4 | −3.9/−0.9 | |
| V8 | 4708 | 693/139 | 0.08/9.2 | 3.3/1.4 | −5.7/−1.1 | ||
| Relation | a | b | c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.6 | −0.16129 | −5.50 | 0.60 | ||
| Above the 0 °C Layer | 5.61 | 44.59 | 0.47 | ||
| Below the 0 °C Layer | 12.11 | 107.82 | 0.32 | ||
| 5.02 | −0.80 | 0.77 |
| Detection Temperature (°C) | The Maximum Particle Number Concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hou et al. (2021) [1] | −12~0 | 10−1 | 10−6~10−2 | 10−1~101 |
| Heymsfiled et al. (2015) [22] | −4~4 | 10−1 | 0.01~100 | 10~25 |
| Feng et al. (2021) [11] | −20~0 | 102 | 0~104 | 10~104 |
| Xiong et al. (2023) | −15.9~8.6 | 10−2 | 10−5~100 | 10−2~102 |
| Xiong et al. (2023) | −1.8~12.4 | 10−2 | 10−6~100 | 10−2~102 |
| Xiong et al. (2023) | −2.3~7.3 | 10−2 | 10−5~100 | 10−1~102 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Study on the Vertical Structure and the Evolution of Precipitation Particle Spectrum Parameters of Stratocumulus Clouds over North China Based on Aircraft Observation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082168
Xiong J, Liu X, Wang J. Study on the Vertical Structure and the Evolution of Precipitation Particle Spectrum Parameters of Stratocumulus Clouds over North China Based on Aircraft Observation. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(8):2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082168
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Jingyuan, Xiaoli Liu, and Jing Wang. 2023. "Study on the Vertical Structure and the Evolution of Precipitation Particle Spectrum Parameters of Stratocumulus Clouds over North China Based on Aircraft Observation" Remote Sensing 15, no. 8: 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082168
APA StyleXiong, J., Liu, X., & Wang, J. (2023). Study on the Vertical Structure and the Evolution of Precipitation Particle Spectrum Parameters of Stratocumulus Clouds over North China Based on Aircraft Observation. Remote Sensing, 15(8), 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082168






