Water Quality and Flooding Impact of the Record-Breaking Storm Gloria in the Ebro Delta (Western Mediterranean)
Abstract
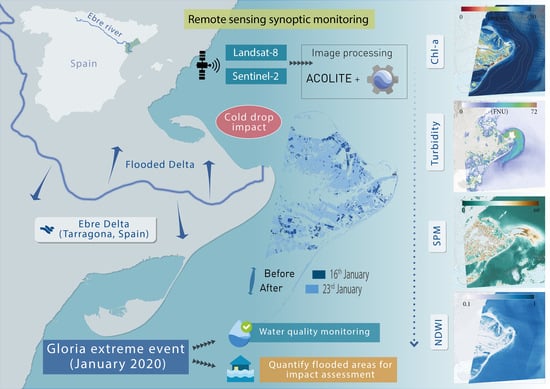
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Satellite Imagery: Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2
2.2. Water Quality Monitoring
2.3. Flooding Mapping
3. Results
3.1. Multi-Sensor Approach: Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 Satellites
3.2. Water Quality Monitoring
3.2.1. Turbidity and Suspended Particulate Matter
3.2.2. Chlorophyll-a
3.3. Flooding Monitoring
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abram, N.; Gattuso, J.-P.; Prakash, A.; Cheng, L.; Chidichimo, M.P.; Crate, S.; Enomoto, H.; Garschagen, M.; Gruber, N.; Harper, S.; et al. Framing and Context of the Report. In IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate; Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D.C., Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Tignor, M., Poloczanska, E., Mintenbeck, K., Alegría, A., Nicolai, M., Okem, A., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 73–129. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, M.L.; Intralawan, A.; Vázquez, G.; Pérez-Maqueo, O.; Sutton, P.; Landgrave, R. The coasts of our world: Ecological, economic and social importance. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 63, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobday, A.J.; Alexander, L.V.; Perkins, S.E.; Smale, D.A.; Straub, S.C.; Oliver, E.C.J.; Benthuysen, J.A.; Burrows, M.T.; Donat, M.G.; Feng, M.; et al. A hierarchical approach to defining marine heatwaves. Prog. Oceanogr. 2016, 141, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.R.; Lilley, M.; Shutler, J.; Lowe, C.; Artioli, Y.; Torres, R.; Berdalet, E.; Tyler, C.R. Assessing risks and mitigating impacts of harmful algal blooms on mariculture and marine fisheries. Rev. Aquac. 2019, raq.12403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frölicher, T.L.; Laufkötter, C. Emerging risks from marine heat waves. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, E.C.J.; Perkins-Kirkpatrick, S.E.; Holbrook, N.J.; Bindoff, N.L. Anthropogenic and Natural Influences on Record 2016 Marine Heat waves. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, S44–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen Gupta, A.; Thomsen, M.; Benthuysen, J.A.; Hobday, A.J.; Oliver, E.; Alexander, L.V.; Smale, D.A. Drivers and impacts of the most extreme marine heatwave events. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdalet, E.; Marrasé, C.; Pelegrí, J.L. Resumen Sobre la Formación y Consecuencias de la Borrasca Gloria (19–24 Enero 2020); Institut de Ciències del Mar, CSIC: Barcelona, Spain, 2020; 38p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelats, E.; Soriano-González, J.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Alcaraz, C. Combined Flooding and Water Quality Monitoring during Short Extreme Events Using Sentinel 2: The Case Study of Gloria Storm in Ebro Delta. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 3, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amores, A.; Marcos, M.; Carrió, D.S.; Gómez-Pujol, L. Coastal impacts of Storm Gloria (January 2020) over the north-western Mediterranean. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 1955–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soreide, N.N.; Woody, C.E.; Holt, S.M. Overview of ocean based buoys and drifters: Present applications and future needs. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE Oceans 2001. An Ocean Odyssey. Conference Proceedings (IEEE Cat. No.01CH37295), Honolulu, HI, USA, 5–8 November 2001; pp. 2470–2472. [Google Scholar]
- Sendra, S.; Parra, L.; Lloret, J.; Jiménez, J.M. Oceanographic Multisensor Buoy Based on Low Cost Sensors for Posidonia Meadows Monitoring in Mediterranean Sea. J. Sens. 2015, 2015, 920168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Osuna, J.F.; Ocampo-Torres, F.J.; Gutiérrez-Loza, L.; Valenzuela, E.; Castro, A.; Alcaraz, R.; Ulloa, L.R. Coastal buoy data acquisition and telemetry system for monitoring oceanographic and meteorological variables in the Gulf of Mexico. Measurement 2021, 183, 109841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union-Copernicus Marine Service. Global Ocean 1/12° Physics Analysis and Forecast Updated Dail; Mercator Ocean International: Toulouse, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Copernicus Marine Service. Global Ocean Biogeochemistry Analysis and Forecast; Mercator Ocean International: Toulouse, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- F-Pedrera Balsells, M.; Grifoll, M.; Fernandez-Tejedor, M.; Espino, M. Short-Term Response of Chlorophyll a Concentration Due to Intense Wind and Freshwater Peak Episodes in Estuaries: The Case of Fangar Bay (Ebro Delta). Water 2021, 13, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Chittimalli, S.K.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; Vellucci, V. Sentinel-2/Landsat-8 product consistency and implications for monitoring aquatic systems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 220, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Fernández, R.; Escalante, O.M.; Mamán, L.; Navarro, G. New capabilities of Sentinel-2A/B satellites combined with in situ data for monitoring small harmful algal blooms in complex coastal waters. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, W.; Tian, Y.Q.; Yu, Q. Monitoring dissolved organic carbon by combining Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 satellites: Case study in Saginaw River estuary. Lake Huron. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Benito, C.V.; Navarro, G.; Caballero, I. Using Copernicus Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3 data to monitor harmful algal blooms in Southern Chile during the COVID-19 lockdown. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faridatul, M.I.; Wu, B.; Zhu, X. Assessing long-term urban surface water changes using multi-year satellite images: A tale of two cities. Dhaka and Hong Kong. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Space Agency (ESA). E. Sentinel-2 User Handbook. ESA Stand. Doc. Date 2015, Volume 1, pp. 1–64. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/documents/247904/685211/Sentinel-2_User_Handbook (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- European Space Agency (ESA). Sentinel-2 MSI Technical Guide 2017. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/web/sentinel/technicalguides/sentinel-2-msi (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.; Anderson, M.; Belward, A.; Bindschadler, R.; Cohen, W.; Wynne, R. Free access to Landsat imagery. Science 2008, 320, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, E.J.; Kvaran, G. Landsat-8 operational land imager design. characterization and performance. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10286–10305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K.G. ACOLITE Processing for Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8: Atmospheric Correction and Aquatic Applications. In Proceedings of the Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric correction of metre-scale optical satellite data for inland and coastal water applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q. Adaptation of the dark spectrum fitting atmospheric correction for aquatic applications of the Landsat and Sentinel-2 archives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.; Neukermans, G. Calibration and validation of a generic multisensor algorithm for mapping of turbidity in coastal waters. In Proceedings of the SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, Berlin, Germany, 9 September 2010; p. 74730H. [Google Scholar]
- Katlane, R.; Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.; Zargouni, F. Optical remote sensing of turbidity and total suspended matter in the Gulf of Gabes. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazirova, K.; Alferyeva, Y.; Lavrova, O.; Shur, Y.; Soloviev, D.; Bocharova, T.; Strochkov, A. Comparison of in situ and remote-sensing methods to determine turbidity and concentration of suspended matter in the estuary zone of the mzymta river. black sea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric correction of Sentinel-3/OLCI data for mapping of suspended particulate matter and chlorophyll-a concentration in Belgian turbid coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Roca, M.; Santos-Echeandía, J.; Bernárdez, P.; Navarro, G. Use of the Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 Satellites for Water Quality Monitoring: An Early Warning Tool in the Mar Menor Coastal Lagoon. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.R. Normalized difference chlorophyll index: A novel model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-González, J.; Angelats, E.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Diogene, J.; Alcaraz, C. First results of phytoplankton spatial dynamics in two NW-Mediterranean bays from chlorophyll-a estimates using Sentinel 2: Potential implications for aquaculture. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahet, F.; Ouillon, S.; Forget, P. A three-component model of ocean color and its application in the Ebro River mouth area. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 72, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahet, F.; Ouillon, S.; Forget, P. Colour classification of coastal waters of the Ebro river plume from spectral reflectances. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1639–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Mangin, A.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; Smith, B.; Alikas, K.; Arai, K.; Warren, M. ACIX-Aqua: A global assessment of atmospheric correction methods for Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 over lakes, rivers, and coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Alikas, K.; Anstee, J.; Barbosa, C.; Binding, C.; Ruiz-Verdù, A. Simultaneous retrieval of selected optical water quality indicators from Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and Sentinel-3. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 270, 112860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Steinmetz, F.; Navarro, G. Evaluation of the first year of operational Sentinel-2A data for retrieval of suspended solids in medium-to-high-turbidity waters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Nim, C.J.; Son, S.; Shi, W. Characterization of turbidity in Florida’s Lake Okeechobee and Caloosahatchee and St. Lucie estuaries using MODIS-Aqua measurements. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5410–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, J.A.; Guillén, J.; Gracia, V.; Palanques, A.; Garcıa, M.A.; Sánchez-Arcilla, A.; Rodríguez, G. Water and sediment fluxes on the Ebro Delta shoreface: On the role of low-frequency currents. Mar. Geol. 1999, 157, 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, P.L.; Amos, C.L. Location Maps of Major River Plumes and Their Relationship to Prodelta Distribution; European Co-Ordination on Mediterranean and Black Sea Prodeltas (EURODELTA), Deliverable 2c WK2, School of Ocean and Earth Science, University of Southampton: Southampton, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Canals, M.; Arnau, P.; Liquete, C.; Colas, S.; Casamor, J.L. Catalogue and Data Set on River Systems from Mediterranean Watersheds of the Iberian Peninsula; Technical Report; Universitat de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2004; p. 220. [Google Scholar]
- Arnau, P.; Liquete, C.; Canals, M. River mouth plume events and their dispersal in the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Oceanogr.-Wash. DC-Oceanogr. Soc. 2004, 17, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, N.; Fiandrino, A.; Fraunie, P.; Ouillon, S.; Forget, P.; Naudin, J.J. Suspended matter dispersion in the Ebro ROFI: An integrated approach. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Ruiz, J.; Navarro, G. Sentinel-2 satellites provide near-real-time evaluation of catastrophic floods in the western Mediterranean. Water 2019, 11, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, M.; Barale, V.; Snaith, H.M. Multisensor monitoring of plume dynamics in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. J. Coast. Conserv. 2003, 9, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, M.; Barale, V. Multi-sensor remote sensing of coastal discharge plumes: A Mediterranean test site. In Remote Sensing of the European Seas; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 475–486. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Nóvoa, D.; deCastro, M.; Des, M.; Costoya, X.; Mendes, R.; Gómez-Gesteira, M. Characterization of Iberian turbid plumes employing synoptic patterns obtained through MODIS imagery. J. Sea Res. 2017, 126, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Nóvoa, D.; Mendes, R.D.; Decastro, M.; Dias, J.M.; Sánchez-Arcilla, A.; Gómez-Gesteira, M. Analysis of the influence of river discharge and wind on the Ebro turbid plume using MODIS-Aqua and MODIS-Terra data. J. Mar. Syst. 2015, 142, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestres, M.; Sierra, J.P.; Sánchez-Arcilla, A.; Del Río, J.G.; Wolf, T.; Rodríguez, A.; Ouillon, S. Modelling of the Ebro River plume. Validation with field observations. Sci. Mar. 2003, 67, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, J.A.; Price, I.; Jeansou, E.; Zielinski, O.; van der Woerd, H.J. Citizens and satellites: Assessment of phytoplankton dynamics in an NW Mediterranean aquaculture zone. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 47, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallin, M.A.; Corbett, C.A. How hurricane attributes determine the extent of environmental effects: Multiple hurricanes and different coastal systems. Estuaries Coasts 2006, 29, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Mukherjee, D.; Chen, S. Assessment of Hurricane Ivan impact on chlorophyll-a in Pensacola Bay by MODIS 250 m remote sensing. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llebot, C.; Solé, J.; Delgado, M.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Camp, J.; Estrada, M. Hydrographical forcing and phytoplankton variability in two semi-enclosed estuarine bays. J. Mar. Syst. 2011, 86, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, I.; Falco, S.; Rodilla, M.; Sierra, J.P.; Río, J.D.; Mosso, C. Salinity, nutrient and chlorophyll a vertical variations in the Ebro River Plume. J. Coast. Res. 2006, III, 1828–1832. [Google Scholar]
- Jordi, A.; Basterretxea, G.; Anglès, S. Influence of ocean circulation on phytoplankton biomass distribution in the Balearic Sea: Study based on sea-viewing wide field-of-view sensor and altimetry satellite data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2009, 114, C11005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artigas, M.L.; Llebot, C.; Ross, O.N.; Neszi, N.Z.; Rodellas, V.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Masqué, P.; Piera, J.; Estrada, M.; Berdalet, E. Understanding the Spatio-Temporal Variability of Phytoplankton Biomass Distribution in a Microtidal Mediterranean Estuary. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2012, 101, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alfonso, M.; Lin-Ye, J.; García-Valdecasas, J.M.; Pérez-Rubio, S.; Luna, M.Y.; Santos-Muñoz, D.; Álvarez-Fanjul, E. Storm Gloria: Sea state evolution based on in situ measurements and modeled data and its impact on extreme values. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 646873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, P.; Moré, G.; Pons, X. Monitoring winter flooding of rice fields on the coastal wetland of Ebre delta with multitemporal remote sensing images. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 2495–2498. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, F.; Tzortziou, M. Capturing dissolved organic carbon dynamics with Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 in tidally influenced wetland–estuarine systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 145910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarouche, K.; Akpınar, A. Increasing trend on storm wave intensity in the Western Mediterranean. Climate 2021, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, C.; Caiola, N. Sea-level rise. marine storms and the resilience of Mediterranean coastal wetlands: Lessons learned from the Ebro Delta. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2021, 73, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Santalla, I.; Díez-Martínez, A.; Navarro, N. Vulnerability Analysis of the Riumar Dune Field in El Garxal Coastal Wetland (Ebro Delta. Spain). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Image | Month | Date | Satellite |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | January | 5 | L8 |
| 2 | January | 6 | S2B |
| 3 | January | 8 | S2A |
| 4 | January | 11 | S2A |
| 5 | January | 16 | S2B |
| 6 | January | 18 | S2A |
| 7 | January | 23 | S2B |
| 8 | January | 26 | S2B |
| 9 | January | 31 | S2A |
| 10 | February | 5 | S2B |
| 11 | February | 6 | L8 |
| 12 | February | 10 | S2A |
| 13 | February | 17 | S2A |
| 14 | February | 22 | S2B |
| 15 | February | 22 | L8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caballero, I.; Roca, M.; Dunbar, M.B.; Navarro, G. Water Quality and Flooding Impact of the Record-Breaking Storm Gloria in the Ebro Delta (Western Mediterranean). Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010041
Caballero I, Roca M, Dunbar MB, Navarro G. Water Quality and Flooding Impact of the Record-Breaking Storm Gloria in the Ebro Delta (Western Mediterranean). Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(1):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010041
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaballero, Isabel, Mar Roca, Martha B. Dunbar, and Gabriel Navarro. 2024. "Water Quality and Flooding Impact of the Record-Breaking Storm Gloria in the Ebro Delta (Western Mediterranean)" Remote Sensing 16, no. 1: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010041
APA StyleCaballero, I., Roca, M., Dunbar, M. B., & Navarro, G. (2024). Water Quality and Flooding Impact of the Record-Breaking Storm Gloria in the Ebro Delta (Western Mediterranean). Remote Sensing, 16(1), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010041