Radar-Based Precipitation Nowcasting Based on Improved U-Net Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Typical Rainfall Data
2.3. Radar Echo Dataset
3. Methods
3.1. Deep-Learning Models
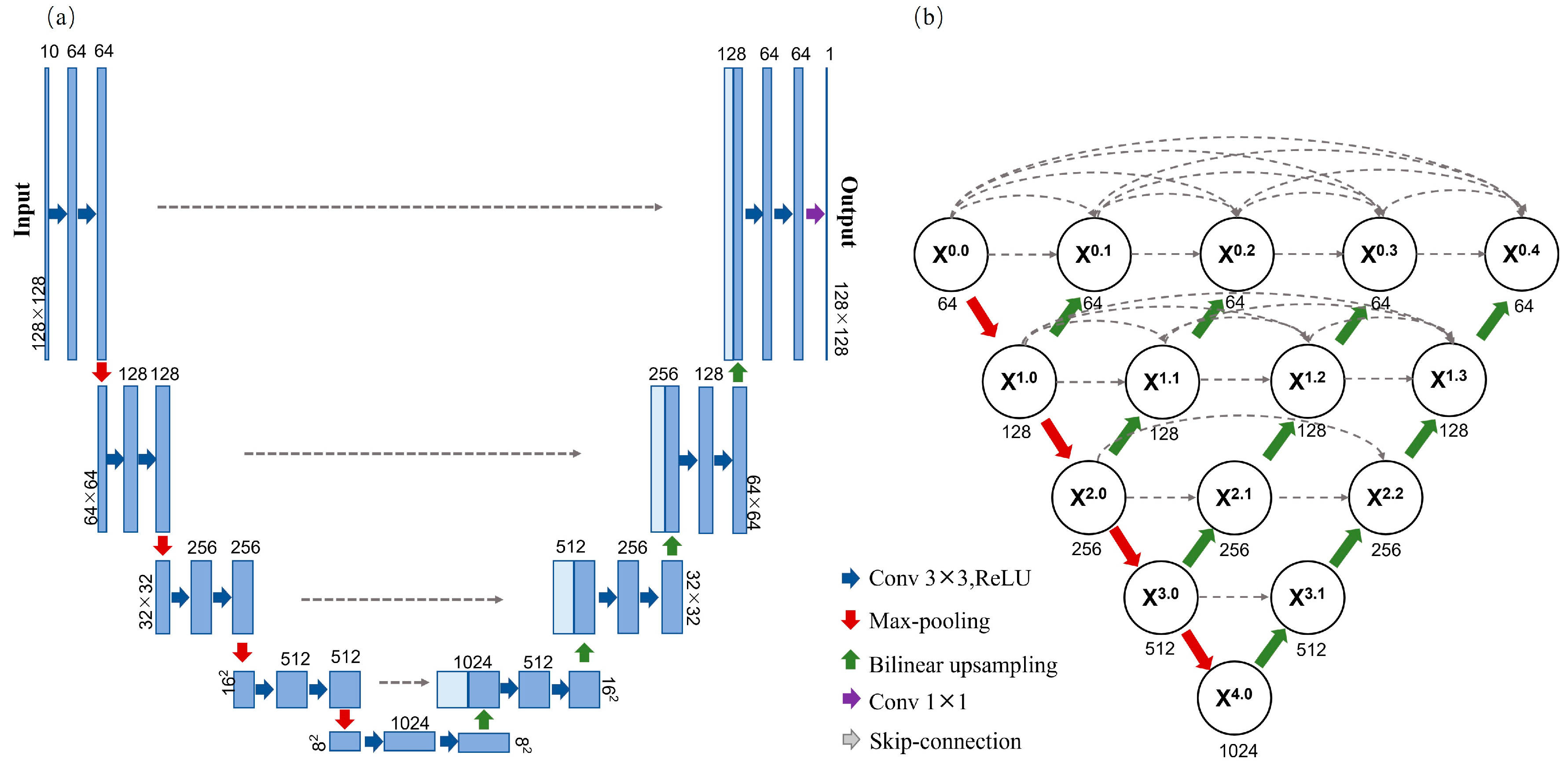
3.1.1. Control Model
3.1.2. DR2A-UNet
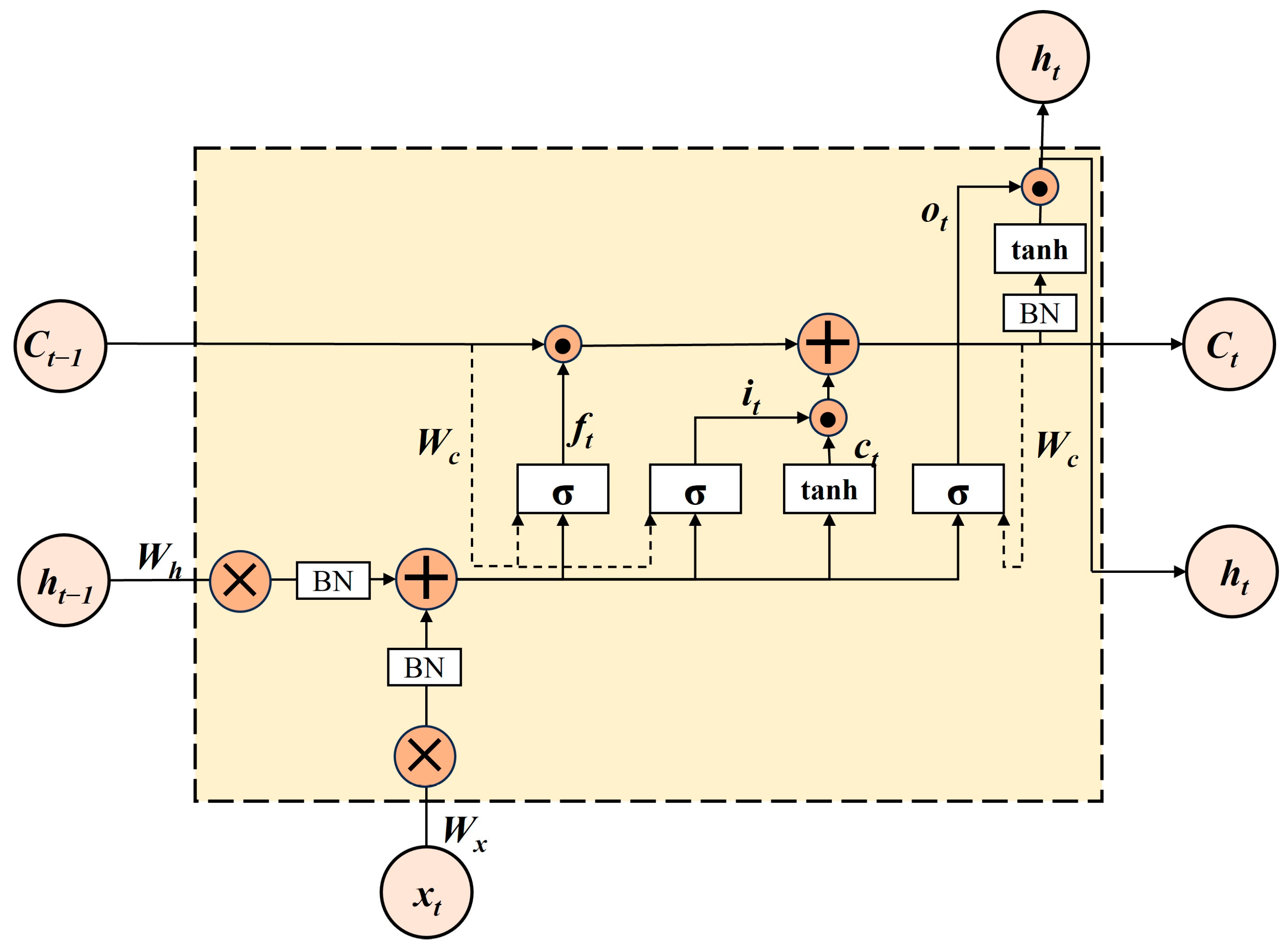
3.1.3. Conv-LSTM
3.2. Loss Function
3.3. Experimental Setup
3.4. Quantitative Rainfall Estimation
3.5. Evaluation Metrics
4. Results
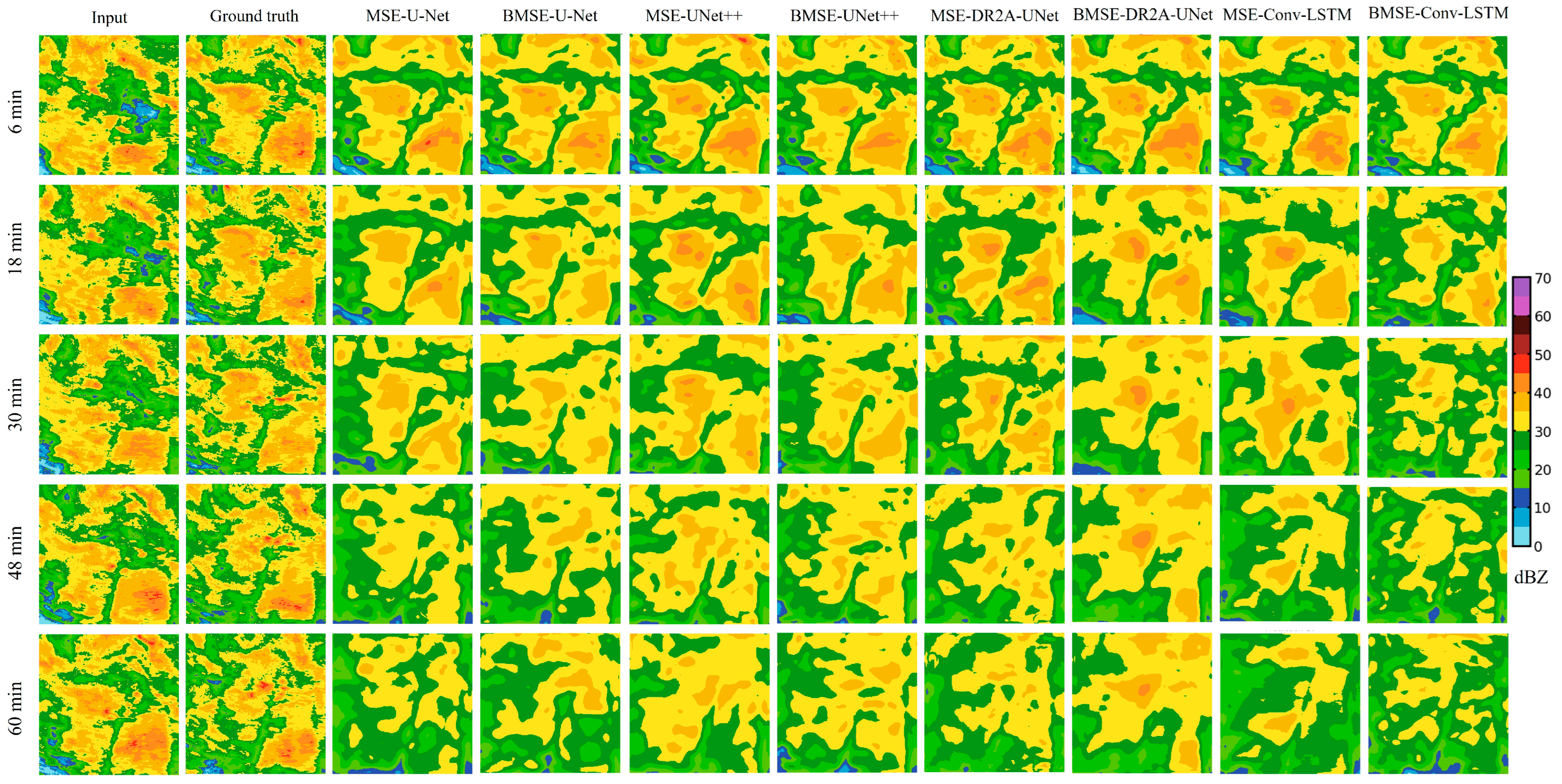
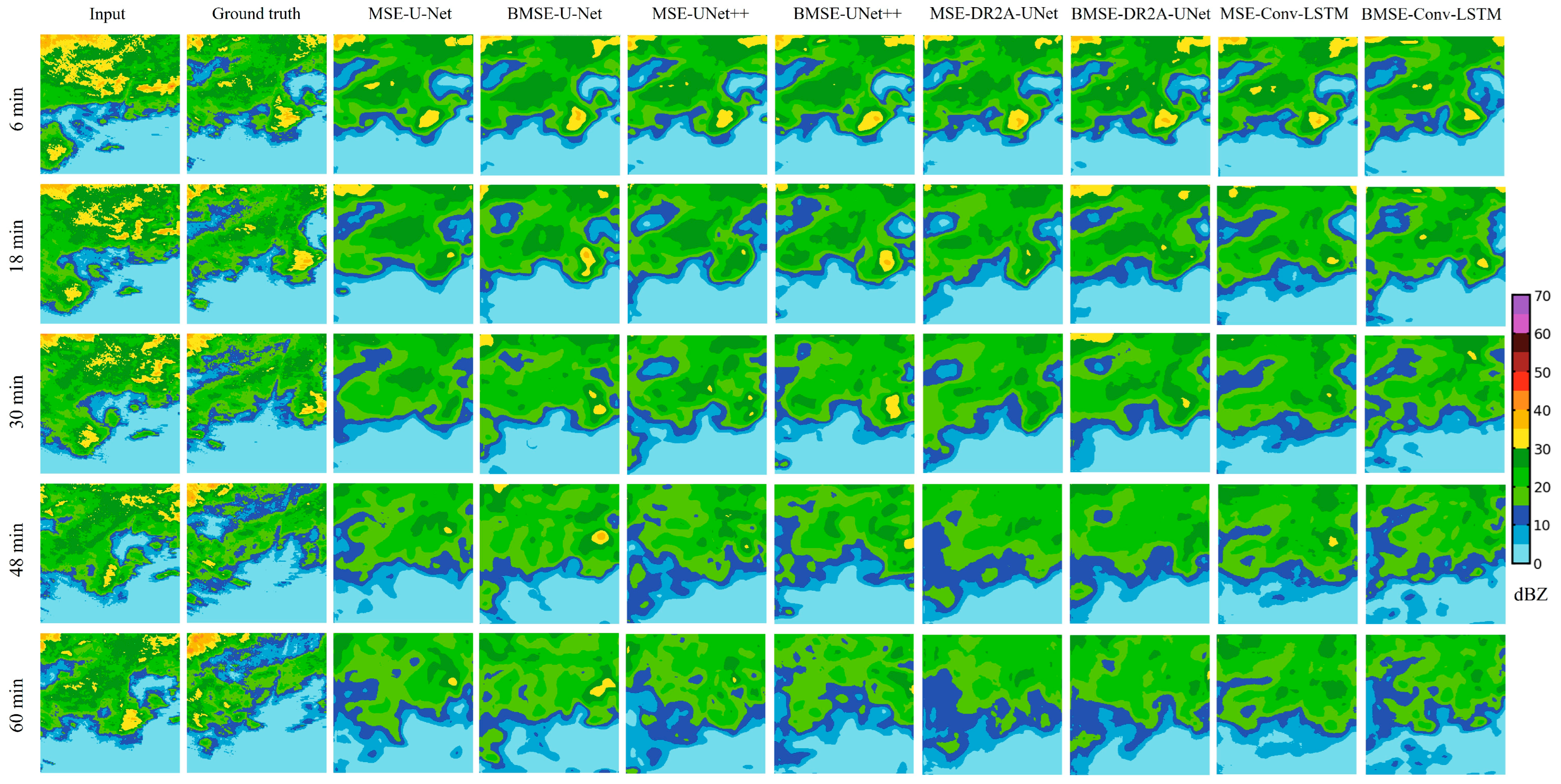
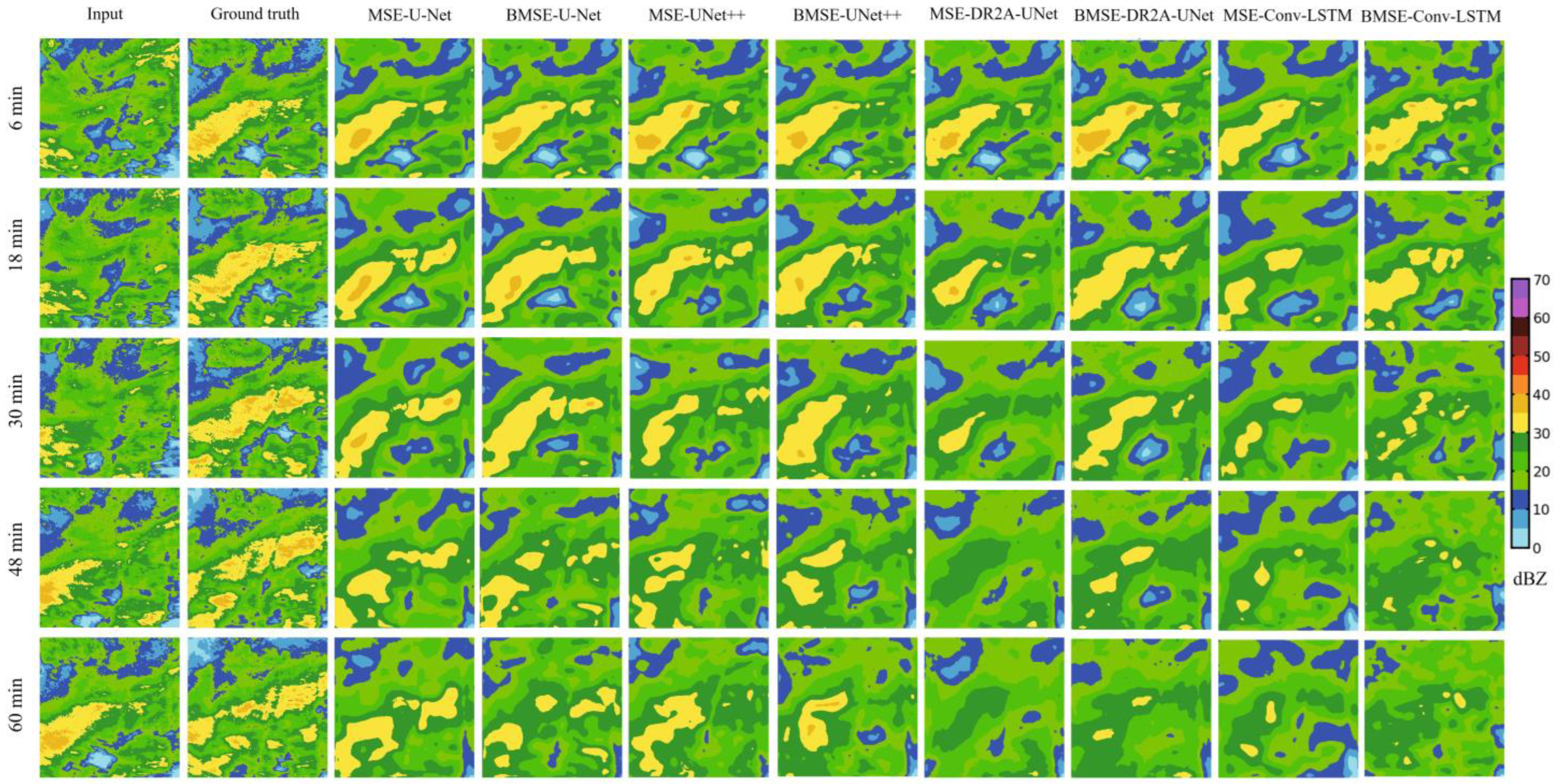
4.1. Echo Extrapolation Results of Different Deep-Learning Methods
4.2. Echo Extrapolation Results of Different Lead Times
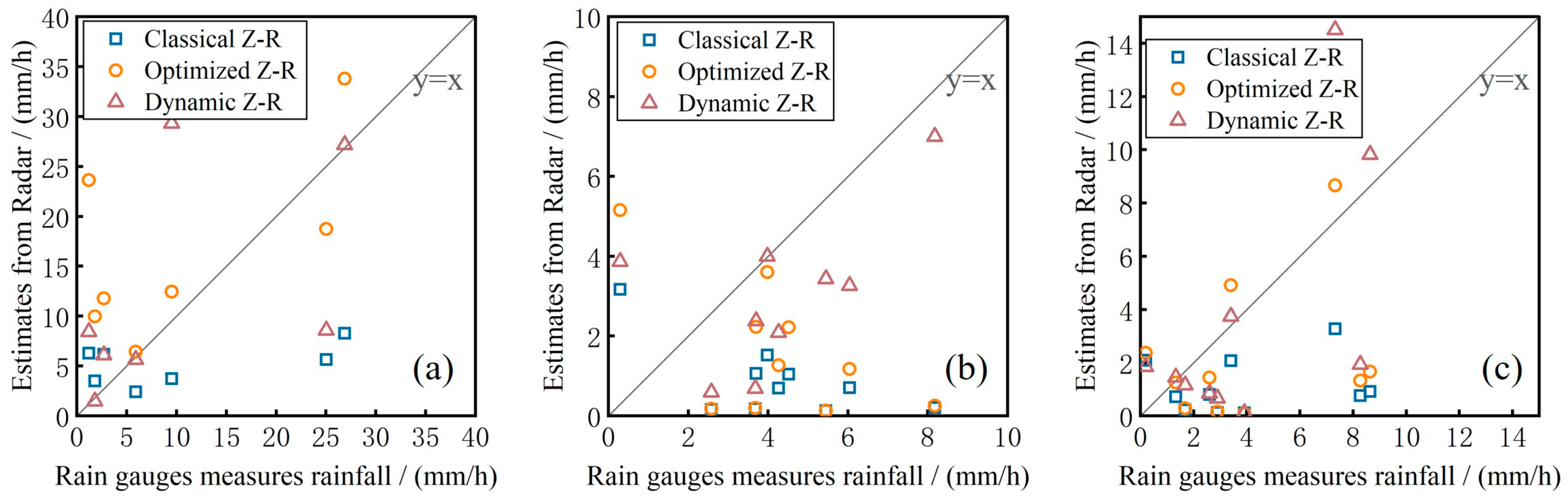
4.3. Accuracy Evaluation of Quantitative Rainfall Estimation
4.4. Evaluation of Rainfall Nowcasting Accuracy
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- For the 1 h-lead-time echo extrapolation, the model with the BMSE loss function had significantly better echo extrapolation than the model with the MSE loss function, which can more accurately predicted the development of the echoes. The echo extrapolation results by DR2A-UNet had some improvement compared with the U-Net and U-Net++ models, which was especially significant in the echo extrapolation of the strong rainfall process. For the echoes of weak rainfall intensities, the difference of the nowcasted results by different models was not significant. With the continuation of the lead time, the prediction accuracy of the models decreased significantly and there was a clear homogenization trend for the strong echoes. DR2A-UNet was better than the reference model in extrapolating the process and intensity of the echo changes. At the 2 h lead time, the evaluation index of the extrapolation accuracy decreases by about 20% compared with the 1 h lead time, and the extrapolation effect of DR2A-UNet is better.
- (2)
- The rainfall estimated using the dynamic Z-R relationship had the highest accuracy and correlation with the actual rainfall. The rainfall estimated using the optimized Z-R relationship had the second highest accuracy, and the classical Z-R relationship had the worst accuracy, so it was more appropriate to use the dynamic Z-R relationship to estimate rainfall. In the 1 h lead time, all deep-learning models were able to nowcast the rainfall process. DR2A-UNet achieved a higher accuracy and correlation for all types of rainfall, which was consistent with the results of the echo extrapolation. There were more outliers in the U-Net and U-Net++ nowcasted rainfall, which was related to the larger FAR in the echo extrapolation. The accuracy of the nowcasted rainfall for the 2 h lead time by each model was worse, and it was difficult to nowcast the actual rainfall process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, P.; Yan, P.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Lyu, J.; He, B.; Duan, W.; Wang, S.; Zha, X. Historical and comparative overview of sponge campus construction and future challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 907, 167477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Long, M.; Chen, K.; Xing, L.; Jin, R.; Michael, J.; Wang, J. Skilful nowcasting of extreme precipitation with NowcastNet. Nature 2023, 619, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, K.; Chao, L.; Chen, G.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, C. Investigating the Feasibility of Using Satellite Rainfall for the Integrated Prediction of Flood and Landslide Hazards over Shaanxi Province in Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, R.O.; Brauer, C.C.; van Heeringen, K.J.; Uijlenhoet, R.; Weerts, A.H. Large-sample evaluation of radar rainfall nowcasting for flood early warning. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR031591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, D.; Ma, L.; Shan, H. Hybrid Weighting Loss for Precipitation Nowcasting from Radar Images. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 3738–3742. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, A.; Li, R.; Pan, B.; Chen, H.; Ni, G.; Chen, M. Enhancing spatial variability representation of radar nowcasting with generative adversarial networks. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, R.O.; De Cruz, L.; Dewettinck, W.; Brauer, C.C.; Uijlenhoet, R.; van Heeringen, K.J.; Weerts, A.H. Scale-dependent blending of ensemble rainfall nowcasts and numerical weather prediction in the open-source pysteps library. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2023, 149, 1335–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, M.R.; Behrangi, A. A comparison of correction factors for the systematic gauge-measurement errors to improve the global land precipitation estimate. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yeung, D.Y.; Wong, W.K.; Woo, W.C. Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS 2015, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 802–810. [Google Scholar]
- Weisman, M.L.; Davis, C.; Wang, W.; Manning, K.W.; Klemp, J.B. Experiences with 0–36-h explicit convective forecasts with the WRF-ARW model. Weather Forecast. 2008, 23, 407–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, M.; Luo, P.; Duan, W.; Hu, M. Quantitative Model Construction for Sustainable Security Patterns in Social–Ecological Links Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Cao, Z.; Luo, P.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; He, B. Urban Flood-Related Remote Sensing: Research Trends, Gaps and Opportunities. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Li, X.; Wen, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, X. A novel LSTM model with interaction dual attention for radar echo extrapolation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zha, X.; Luo, P.; Wang, S.; Cao, Z.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, M.; He, B. A quantitative analysis of research trends in flood hazard assessment. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2023, 37, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Chen, N. A spatiotemporal deep learning model ST-LSTM-SA for hourly rainfall forecasting using radar echo images. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, S.; Tan, J. TSRC: A Deep Learning Model for Precipitation Short-Term Forecasting over China Using Radar Echo Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Barrington, L.; Bromberg, C.; Burge, J.; Gazen, C.; Hickey, J. Machine learning for precipitation nowcasting from radar images. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.12132. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.B.; Pan, X.; Li, H. Towards a More Realistic and Detailed Deep-Learning-Based Radar Echo Extrapolation Method. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Chandrasekar, V. Advancing radar nowcasting through deep transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Niu, D.; Zhang, T.; Chen, P.; Chen, X.; Li, Y. Two-Stage UA-GAN for Precipitation Nowcasting. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Xu, F.; Qian, Z.; Cai, Z. A Forecast-Refinement Neural Network Based on DyConvGRU and U-Net for Radar Echo Extrapolation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 53249–53261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.G.; Mehrkanoon, S. Broad-UNet: Multi-scale feature learning for nowcasting tasks. Neural Netw. 2021, 144, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, T.; He, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Shen, B. Prediction of Radar Echo Space-Time Sequence Based on Improving TrajGRU Deep-Learning Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuper, M.; Ehret, U. Quantitative precipitation estimation with weather radar using a data- and information-based approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 3711–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, L.; Claps, P.; Laio, F. Time-dependent Z-R relationships for estimating rainfall fields from radar measurements. Nat. Hazard. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.B.; Chen, H.N.; Chandrasekar, V. A dynamic approach to quantitative precipitation estimation using multiradar multigauge network. IEEE. Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6376–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Zeng, J.; Ma, L.; Guan, L. Short-term dynamic radar quantitative precipitation estimation based on wavelet transform and support vector machine. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, D.; Riegler, M.A.; Johansen, D.; Halvorsen, P.; Johansen, H.D. Doubleu-net: A deep convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 33rd International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Rochester, MN, USA, 28–30 July 2020; pp. 558–564. [Google Scholar]
- Alom, M.Z.; Yakopcic, C.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Nuclei segmentation with recurrent residual convolutional neural networks based U-Net (R2U-Net). In Proceedings of the NAECON 2018-IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference, Dayton, OH, USA, 23–26 July 2018; pp. 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Liang, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Ge, Y. Convective precipitation nowcasting using U-Net model. IEEE. Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Li, X.; Ye, Y.; Xie, P.; Li, Y. A generative adversarial gated recurrent unit model for precipitation nowcasting. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, D.; Rosenfeld, D.; Wolff, D.B. Climatologically tuned reflectivity-rain rate relations and links to area-time integrals. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1990, 29, 1120–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, W.Y.; Yoo, C. Real-time bias correction of rainfall nowcasts using biward tracking method. J. Hydrol. 2023, 622, 129642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Gao, Z.; Han, W. Application of a Radar Echo Extrapolation-Based Deep Learning Method in Strong Convection Nowcasting. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehu, B.; Haberlandt, U. Relevance of merging radar and rainfall gauge data for rainfall nowcasting in urban hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, E.; ten Veldhuis, M.-C.; van de Giesen, N. Spatial and temporal variability of rainfall and their effects on hydrological response in urban areas—A review. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3859–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foresti, L.; Sideris, I.V.; Nerini, D.; Beusch, L.; Germann, U. Using a 10-year radar archive for nowcasting precipitation growth and decay: A probabilistic machine learning approach. Weather Forecast. 2019, 34, 1547–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, H.A.; Vivoni, E.R.; Gochis, D.J. Limits to flood forecasting in the Colorado Front Range for two summer convection periods using radar nowcasting and a distributed hydrologic model. J. Hydrometeorl. 2013, 14, 1075–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yin, Z.; Qin, G.; Guo, L.; Li, H. Integration of Satellite Precipitation Data and Deep Learning for Improving Flash Flood Simulation in a Poor-Gauged Mountainous Catchment. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouget, V.; Brajard, J.; Charantonis, A.; Filoche, A. Fusion of Rain Radar Images and Wind Forecasts in a Deep Learning Model Applied to Rain Nowcasting. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Chu, Z. An adaptive rainfall estimation algorithm for dual-polarization radar. IEEE. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1004805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

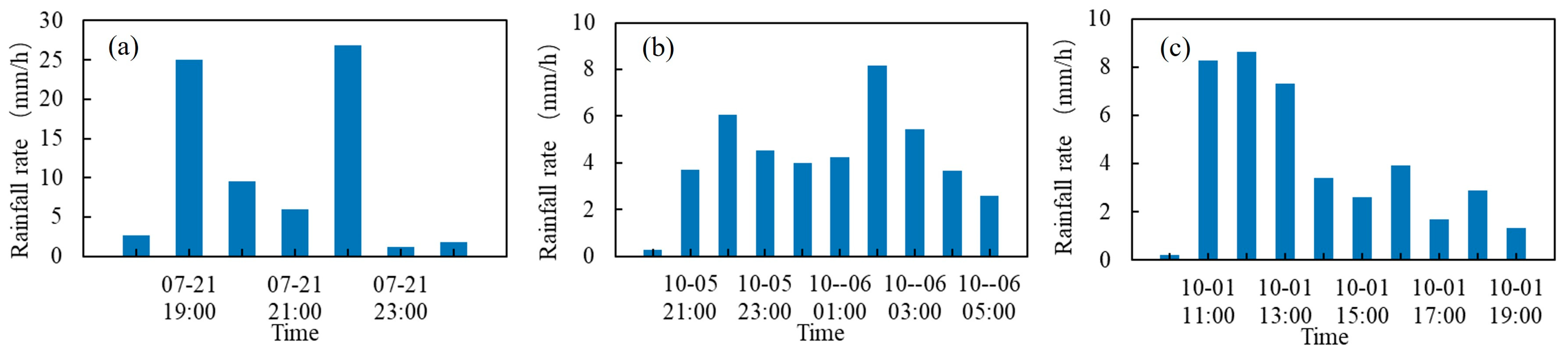


| Event | Start Time | End Time | Total Rainfall/mm | Maximum Rainfall Intensity/(mm/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20210721 | 21 July. T18:00 | 21 July. T24:00 | 73.1 | 26.7 |
| 20211005 | 5 October. T20:00 | 6 October. T05:00 | 42.7 | 8.2 |
| 20221001 | 1 October. T10:00 | 1 October. T19:00 | 40.2 | 8.6 |
| Event | Loss Function | Model | POD | FAR | CSI | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dBZ > 20/> 30 | dBZ > 20/> 30 | dBZ > 20/> 30 | dBZ > 20/> 30 | |||
| 20210721 | MSE | U-Net | 0.62/0.25 | 0.24/0.54 | 0.55/0.19 | 0.62/0.24 |
| U-Net++ | 0.75/0.33 | 0.22/0.58 | 0.62/0.25 | 0.67/0.26 | ||
| DR2A-UNet | 0.76/0.41 | 0.20/0.55 | 0.65/0.28 | 0.71/0.35 | ||
| Conv-LSTM | 0.63/0.18 | 0.30/0.64 | 0.51/0.22 | 0.56/0.28 | ||
| BMSE | U-Net | 0.70/0.31 | 0.18/0.48 | 0.65/0.29 | 0.70/0.33 | |
| U-Net++ | 0.85/0.39 | 0.17/0.48 | 0.69/0.28 | 0.75/0.31 | ||
| DR2A-UNet | 0.86/0.47 | 0.16/0.47 | 0.71/0.31 | 0.77/0.36 | ||
| Conv-LSTM | 0.64/0.21 | 0.25/0.62 | 0.52/0.18 | 0.57/0.24 | ||
| 20211005 | MSE | U-Net | 0.45/0.24 | 0.56/0.76 | 0.19/0.09 | 0.31/0.10 |
| U-Net++ | 0.52/0.30 | 0.51/0.73 | 0.21/0.11 | 0.35/0.14 | ||
| DR2A-UNet | 0.49/0.28 | 0.53/0.79 | 0.25/0.08 | 0.34/0.12 | ||
| Conv-LSTM | 0.41/0.08 | 0.56/0.93 | 0.17/0.02 | 0.21/0.03 | ||
| BMSE | U-Net | 0.50/0.32 | 0.57/0.72 | 0.28/0.10 | 0.29/0.10 | |
| U-Net++ | 0.53/0.36 | 0.52/0.71 | 0.24/0.10 | 0.36/0.13 | ||
| DR2A-UNet | 0.59/0.35 | 0.53/0.73 | 0.32/0.12 | 0.38/0.13 | ||
| Conv-LSTM | 0.52/0.13 | 0.59/0.90 | 0.26/0.02 | 0.30/0.03 | ||
| 20221001 | MSE | U-Net | 0.53/0.20 | 0.34/0.69 | 0.40/0.10 | 0.45/0.13 |
| U-Net++ | 0.59/0.21 | 0.34/0.63 | 0.41/0.14 | 0.47/0.16 | ||
| DR2A-UNet | 0.61/0.25 | 0.33/0.61 | 0.43/0.15 | 0.48/0.20 | ||
| Conv-LSTM | 0.50/0.18 | 0.46/0.77 | 0.39/0.07 | 0.42/0.11 | ||
| BMSE | U-Net | 0.66/0.26 | 0.39/0.71 | 0.42/0.12 | 0.47/0.15 | |
| U-Net++ | 0.73/0.32 | 0.34/0.67 | 0.52/0.14 | 0.56/0.19 | ||
| DR2A-UNet | 0.77/0.36 | 0.36/0.69 | 0.48/0.13 | 0.52/0.17 | ||
| Conv-LSTM | 0.53/0.20 | 0.43/0.79 | 0.36/0.10 | 0.40/0.14 |
| Event | Model | POD | FAR | CSI | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dBZ > 20/> 30 | dBZ > 20/> 30 | dBZ > 20/> 30 | dBZ > 20/> 30 | ||
| 20210721 | U-Net | 0.62/0.28 | 0.26/0.55 | 0.54/0.23 | 0.59/0.28 |
| U-Net++ | 0.73/0.36 | 0.29/0.54 | 0.52/0.22 | 0.57/0.26 | |
| DR2A-UNet | 0.79/0.35 | 0.25/0.52 | 0.59/0.26 | 0.66/0.24 | |
| 20211005 | U-Net | 0.41/0.26 | 0.68/0.88 | 0.22/0.06 | 0.25/0.08 |
| U-Net++ | 0.47/0.28 | 0.66/0.82 | 0.23/0.08 | 0.29/0.11 | |
| DR2A-UNet | 0.46/0.27 | 0.64/0.79 | 0.27/0.10 | 0.31/0.11 | |
| 20221001 | U-Net | 0.50/0.17 | 0.48/0.77 | 0.32/0.08 | 0.35/0.06 |
| U-Net++ | 0.43/0.18 | 0.50/0.82 | 0.26/0.06 | 0.28/0.05 | |
| DR2A-UNet | 0.55/0.17 | 0.46/0.75 | 0.35/0.09 | 0.37/0.11 |
| Event | Z-R Relationship | σ/mm | CC | Bias/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20210721 | Classical | 1.03 | 0.51 | −5.29 |
| Optimized | 1.16 | 0.63 | 6.25 | |
| Dynamic | 0.98 | 0.52 | 1.95 | |
| 20211005 | Classical | 1.01 | −0.66 | −3.38 |
| Optimized | 0.97 | −0.61 | −2.63 | |
| Dynamic | 0.59 | 0.41 | −0.65 | |
| 20221001 | Classical | 1.01 | 0.19 | −2.91 |
| Optimized | 0.90 | 0.33 | −1.81 | |
| Dynamic | 0.86 | 0.65 | −0.42 |
| Event | Model | σ(1 h/2 h)/mm | CC (1 h/2 h) | Bias (1 h/2 h)/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20210721 | U-Net | 1.24/1.06 | 0.36/0.30 | 1.64/−2.93 |
| U-Net++ | 1.18/1.11 | 0.37/0.21 | 1.76/−1.53 | |
| DR2A-UNet | 1.04/1.11 | 0.42/0.32 | 0.80/−2.21 | |
| 20211005 | U-Net | 0.58/0.77 | 0.71/0.41 | −1.98/−2.54 |
| U-Net++ | 0.72/0.78 | 0.49/0.44 | −2.33/−1.42 | |
| DR2A-UNet | 0.59/0.67 | 0.73/0.58 | −2.10/−2.26 | |
| 20221001 | U-Net | 0.88/0.91 | 0.37/0.18 | −1.27/−1.95 |
| U-Net++ | 1.01/0.92 | 0.42/0.32 | −0.70/−1.08 | |
| DR2A-UNet | 0.85/0.86 | 0.41/0.40 | −1.12/−1.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Li, J. Radar-Based Precipitation Nowcasting Based on Improved U-Net Model. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101681
Tan Y, Zhang T, Li L, Li J. Radar-Based Precipitation Nowcasting Based on Improved U-Net Model. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(10):1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101681
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Youwei, Ting Zhang, Leijing Li, and Jianzhu Li. 2024. "Radar-Based Precipitation Nowcasting Based on Improved U-Net Model" Remote Sensing 16, no. 10: 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101681
APA StyleTan, Y., Zhang, T., Li, L., & Li, J. (2024). Radar-Based Precipitation Nowcasting Based on Improved U-Net Model. Remote Sensing, 16(10), 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101681






