Estimating Bermudagrass Aboveground Biomass Using Stereovision and Vegetation Coverage
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To investigate the effectiveness of RGB-depth cameras in measuring the height of the crop above the ground using stereovision and to quantify vegetation coverage from RGB images using pixel segmentation.
- To develop aboveground biomass prediction function with crop height and vegetation coverage as the potential independent variables.
2. Materials and Methods
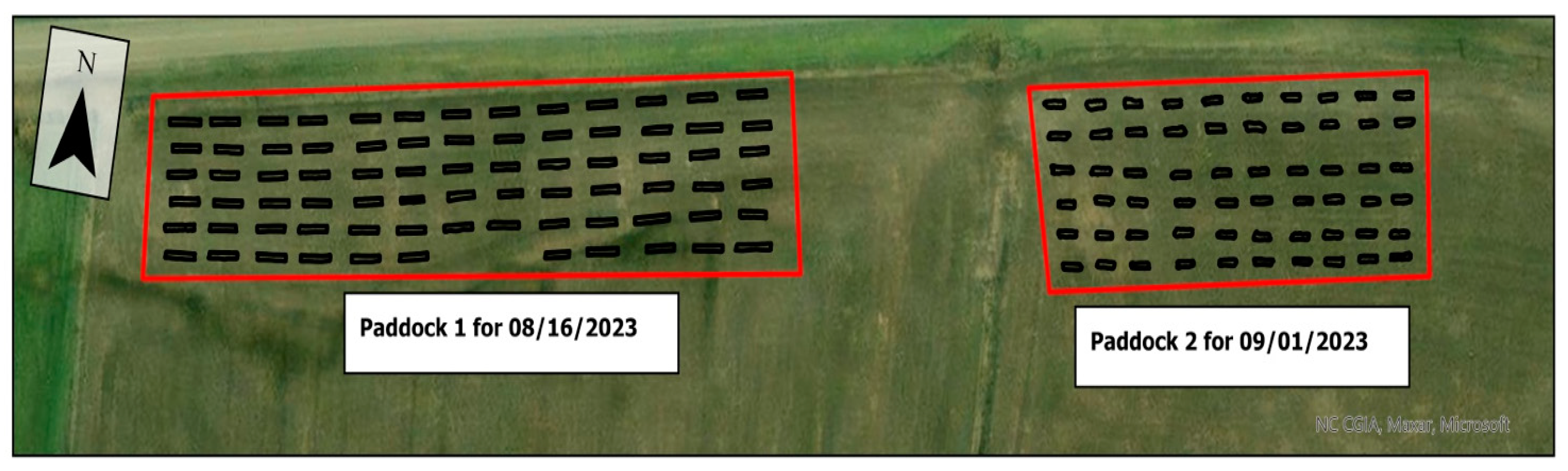
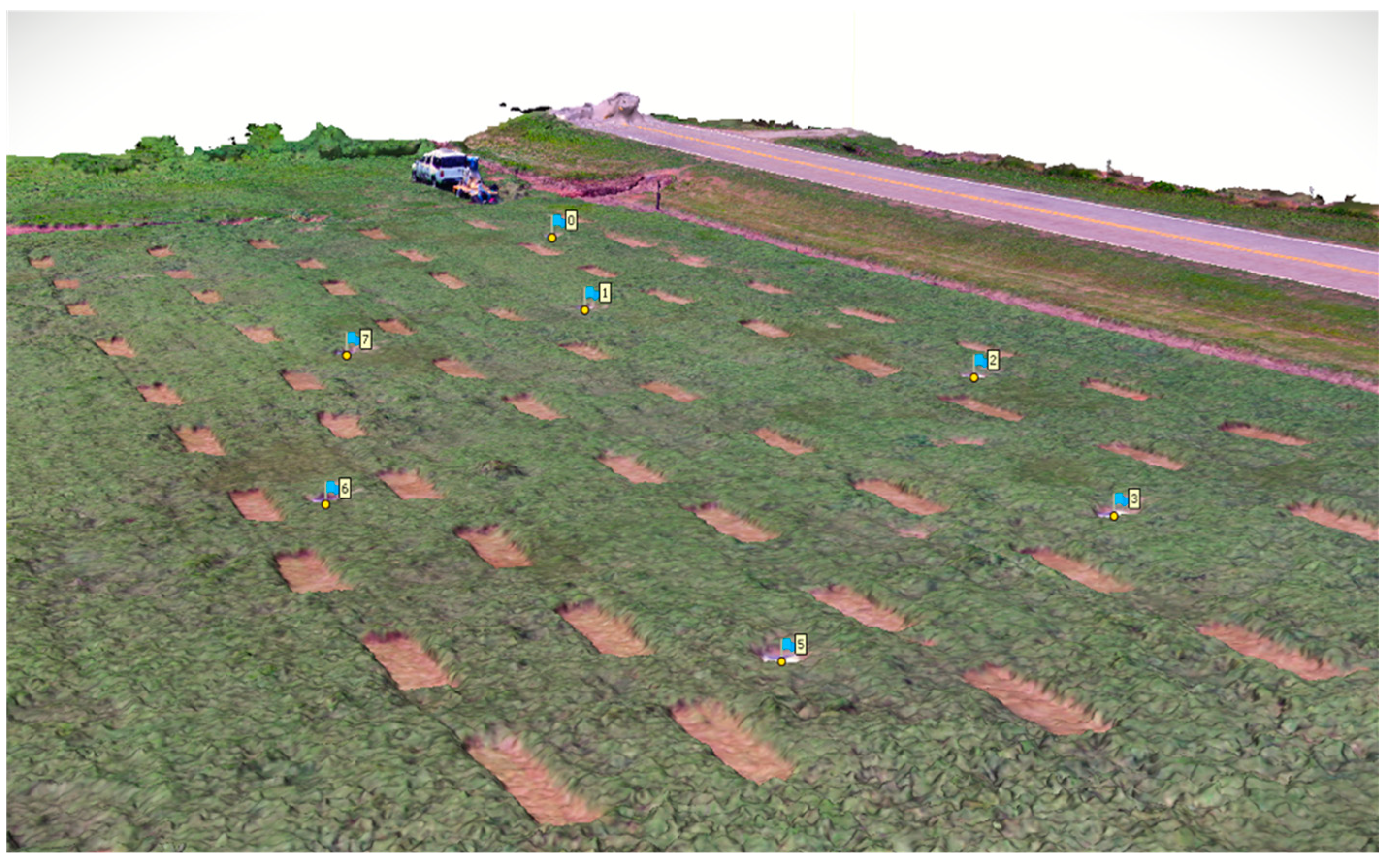
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Design
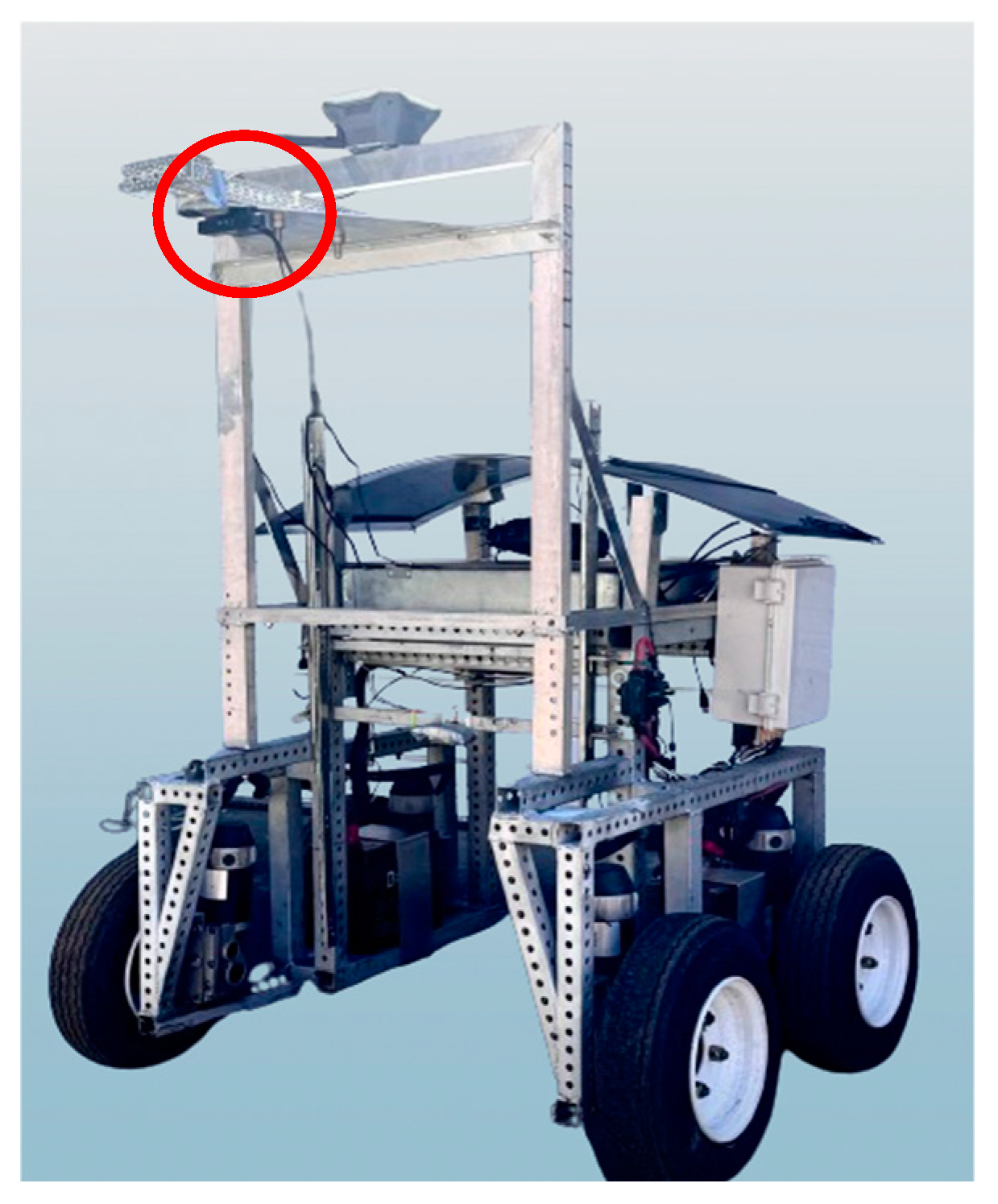
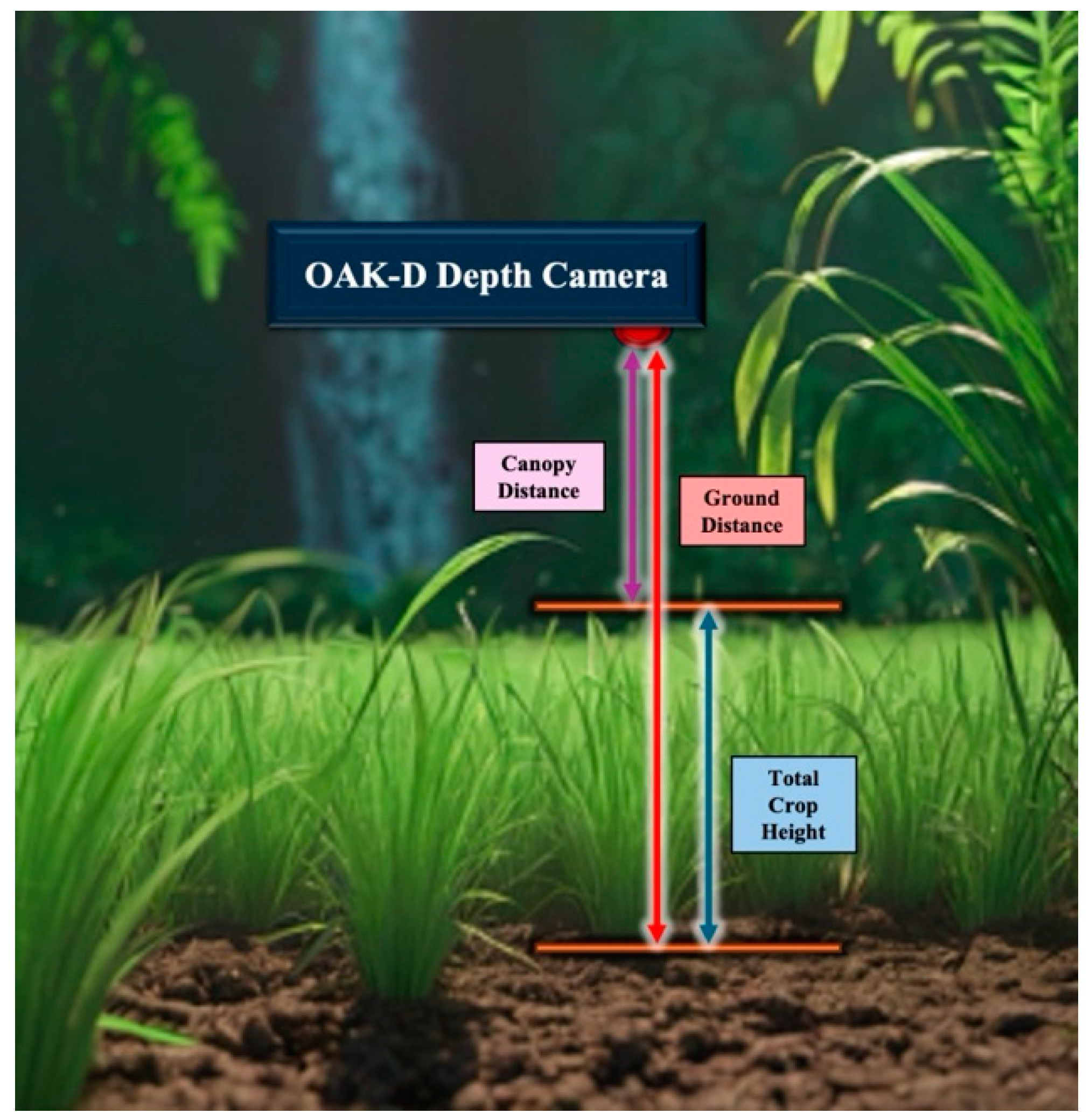
2.2. OAK-D Stereovision Depth Camera and Its Installation
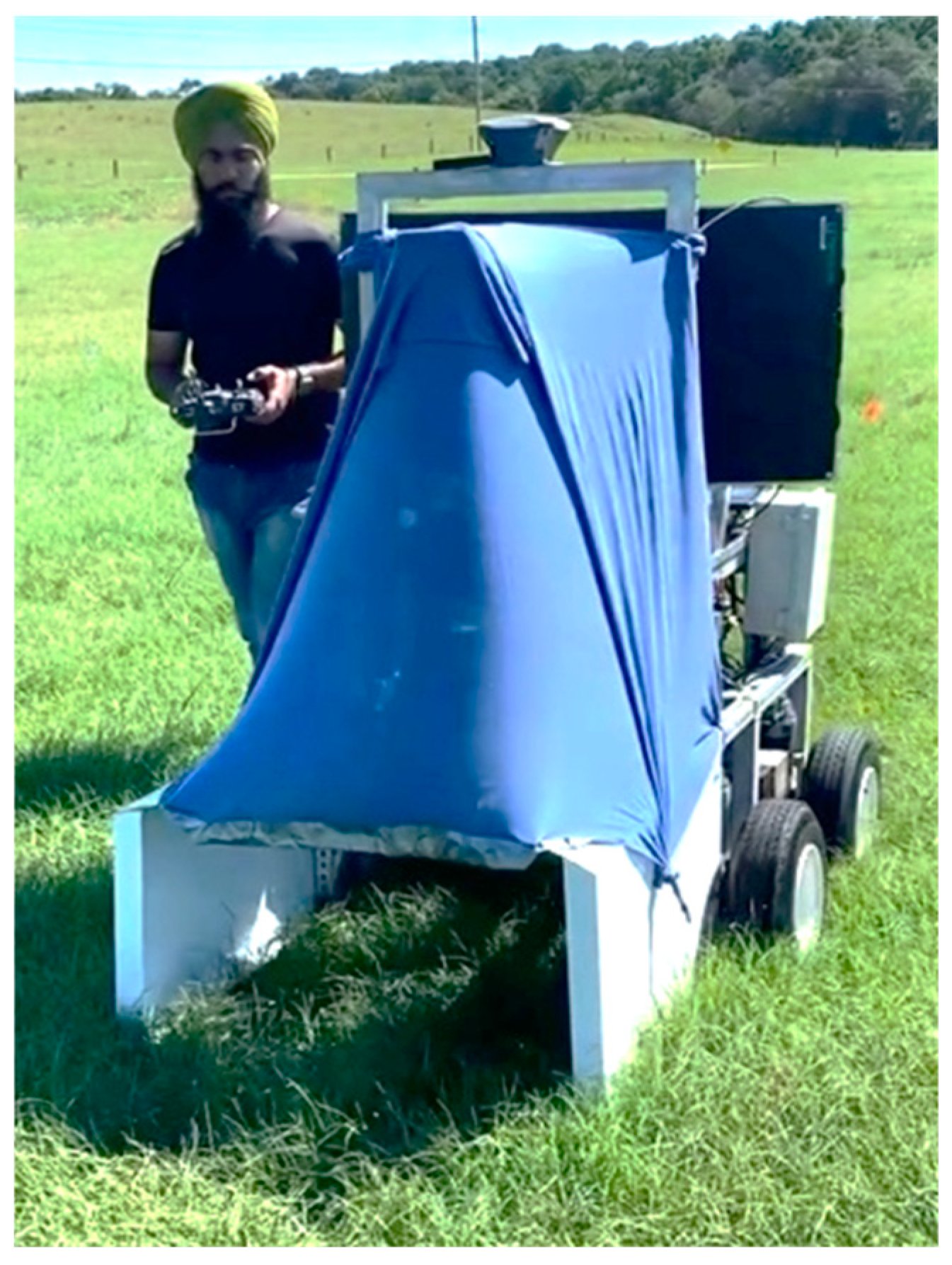
2.3. Data Collection Procedures
2.3.1. Measurement of Crop Height and Vegetation Coverage
2.3.2. Postharvest Field View with UAV
- To identify the region of interest (harvested areas) for post-processing and eliminating the non-relevant data.
- To geolocate the plots in the field based on the coordinates measured with RTK-GPS.
- To measure the exact harvested area of the plots excluding the non-harvested regions of marked plots.
2.4. Challenges in Data Collection and Solutions
2.5. Harvesting and Weighing of Plots for Wet Biomass Yield Calculations
2.6. Plot Subsampling for Dry Matter Calculations
2.7. Post-Processing of Recorded Data and Development of Prediction Function
2.7.1. Generating Orthomosaics from UAV RGB Images
2.7.2. Extraction of Crop Height from Raw Data
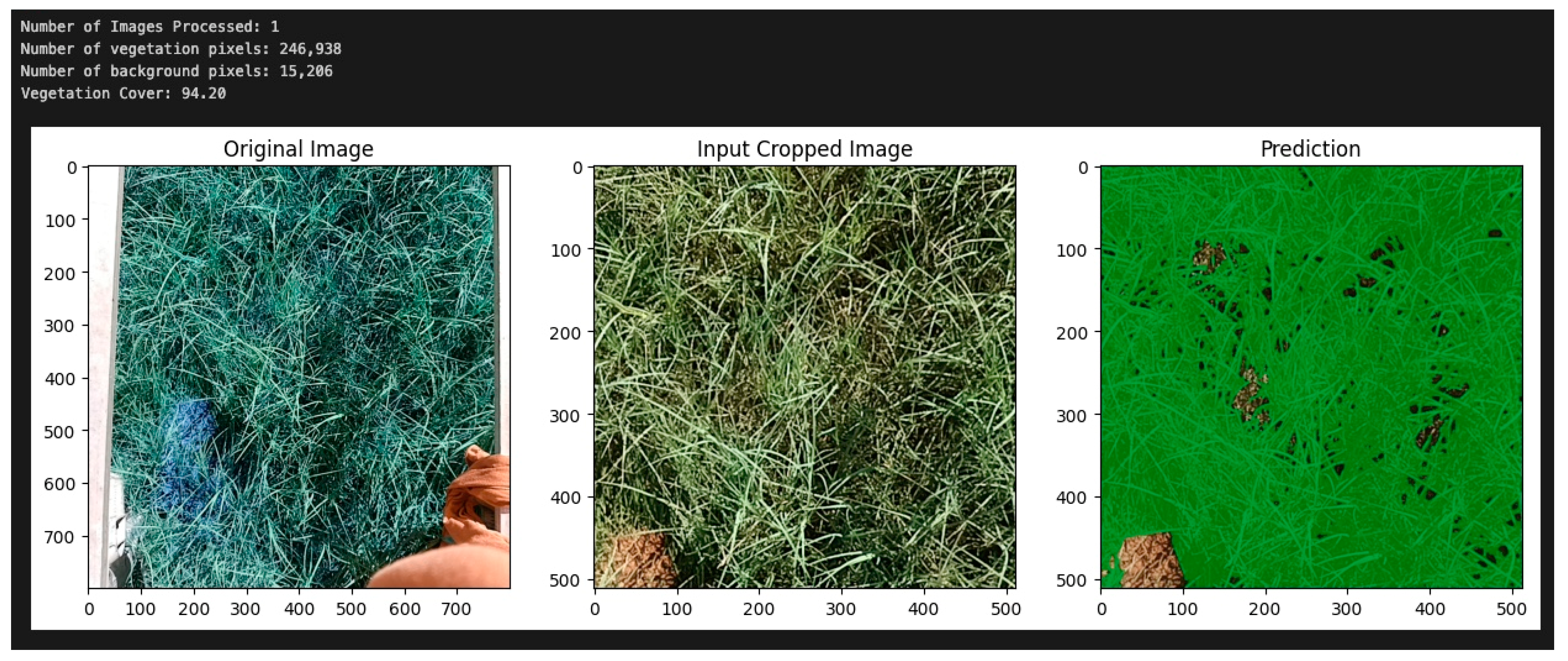
2.7.3. Vegetation Coverage from RGB Images
2.7.4. Development of the Prediction Function
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Correlation Analysis
3.2. Regression Analysis
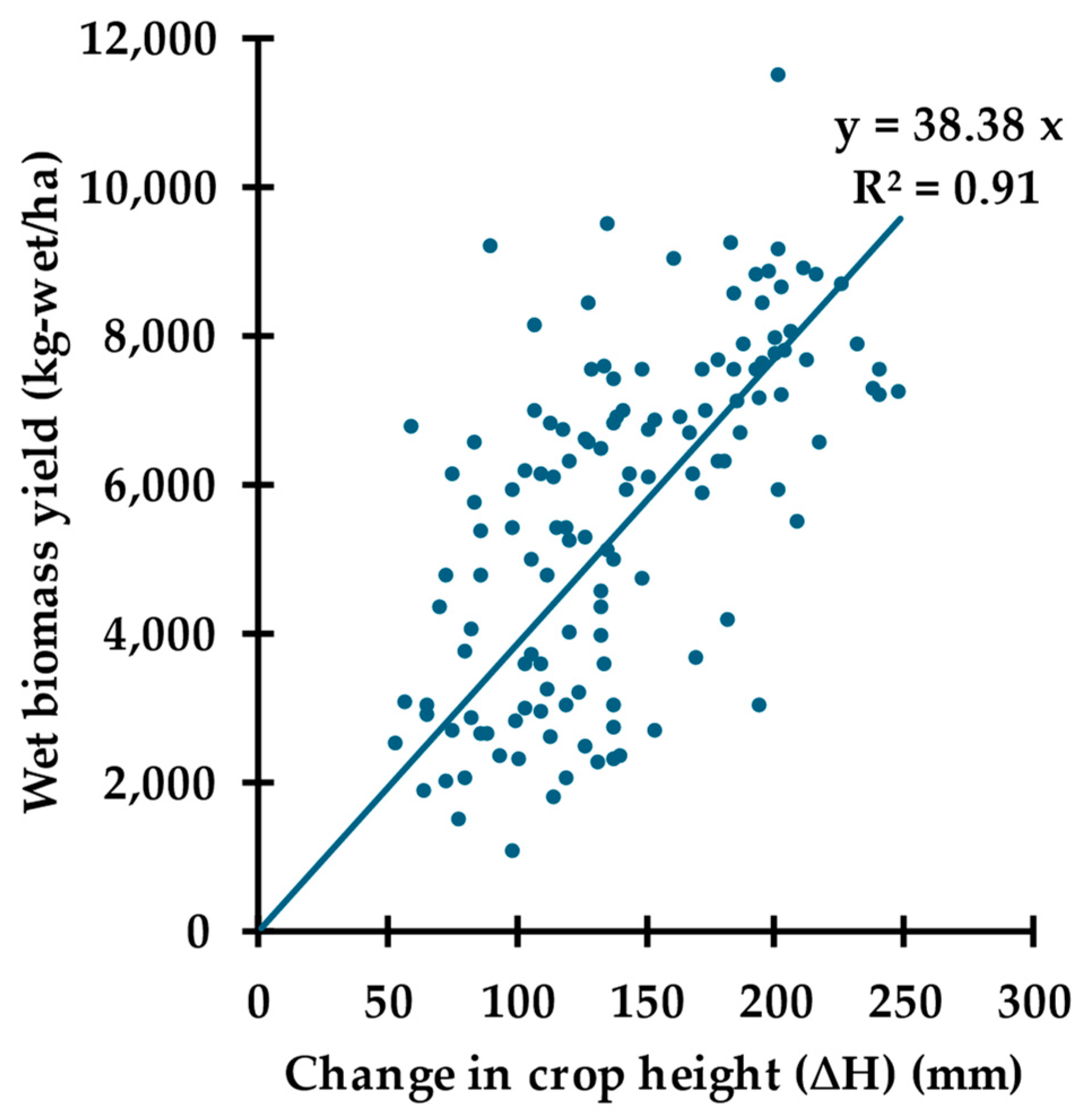
3.2.1. ∆H as the Independent Variable (βw(∆H))
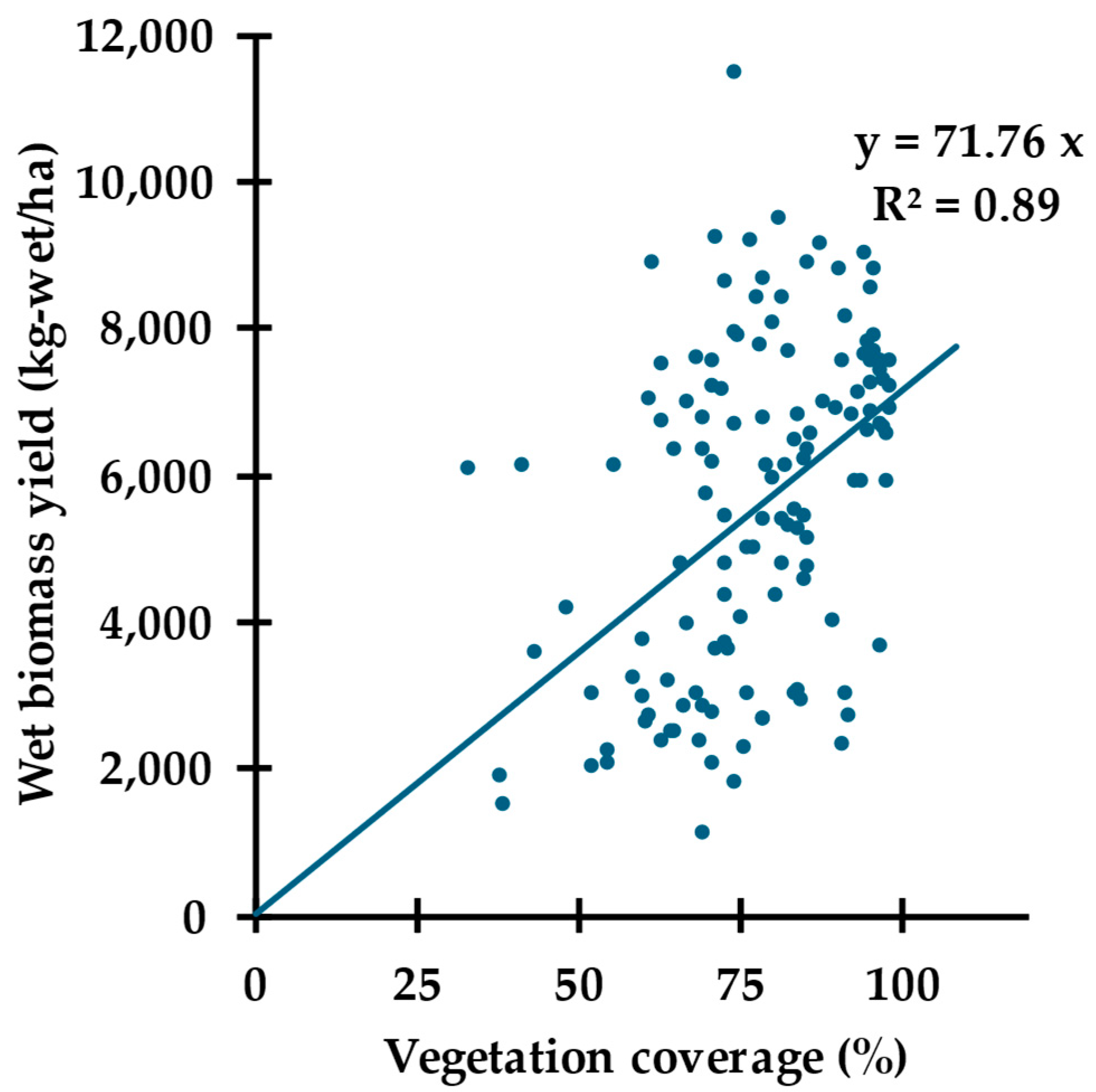
3.2.2. VC as the Independent Variable (βw(VC))
3.2.3. Compare and Contrast between the βw(∆H) and βw(VC)
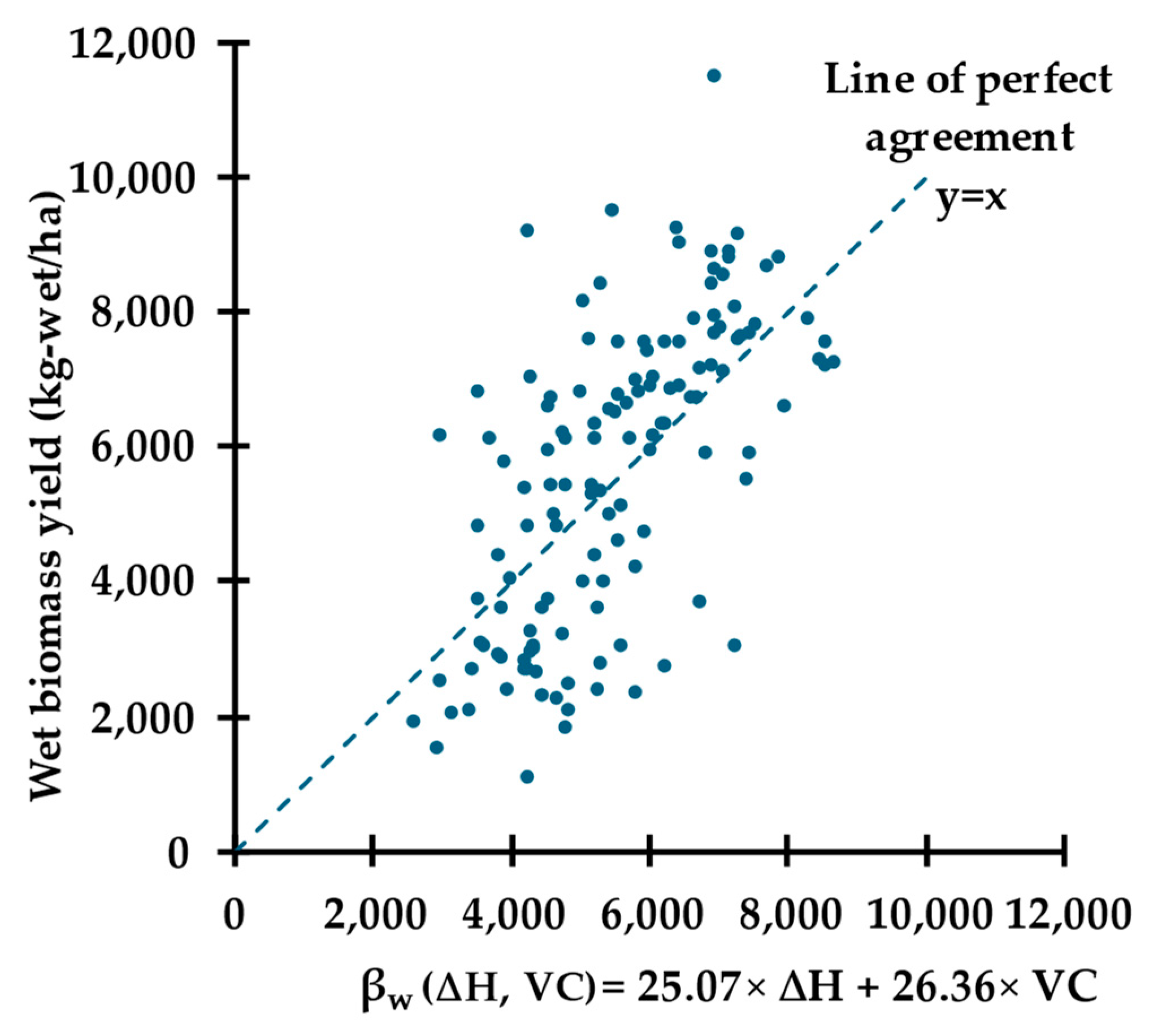
3.2.4. Incorporation of ∆H and VC into a Multiple Linear Regression Function (βw(∆H, VC))
3.2.5. Impact of Combining VC with ∆H on βw Performance (βw(∆H) vs. βw(∆H, VC))
3.3. Dry Matter Fraction
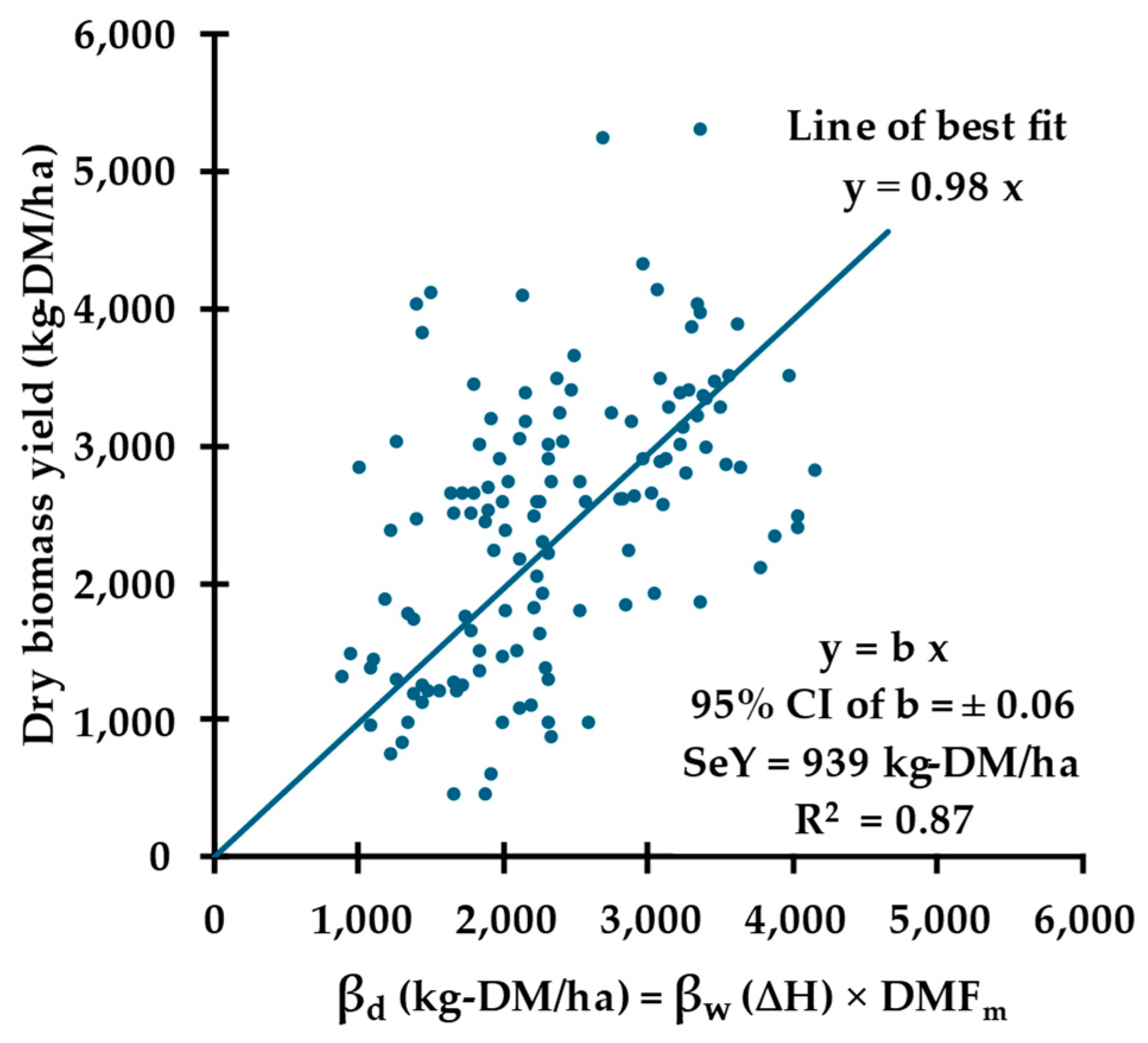
3.4. Prediction of Dry Biomass Yield (βd)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Squires, V.R.; Dengler, J.; Feng, H.; Hua, L. Grasslands of the World: Diversity, Management and Conservation; A Science Publishers Book: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, T.; Mammen, R.; Crawford, R.; Massie, M.; Bishop-Hurley, G.; Kallenbach, R. Agriculture MU Guide- MU Extension, University of Missouri-Columbia. Available online: https://extension.missouri.edu/publications/g4620# (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Drewitz, N.; Goplen, J. Measuring Forage Quality|UMN Extension. Available online: https://extension.umn.edu/forage-harvest-and-storage/measuring-forage-quality (accessed on 2 January 2024).
- Whitbeck, M.; Grace, J.B. Evaluation of non-destructive methods for estimating biomass in marshes of the upper Texas, USA coast. Wetlands 2006, 26, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wulf, H.; Schmid, B.; He, J.S.; Schaepman, M.E. Estimating plant traits of alpine grasslands on the qinghai-tibetan plateau using remote sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2018, 11, 2263–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semela, M.; Ramoelo, A.; Adelabu, S. Testing and Comparing the Applicability of Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 Reflectance Data in Estimating Mountainous Herbaceous Biomass before and after Fire Using Random Forest Modelling. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 4493–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshesha, D.T.; Ahmed, M.M.; Abdi, D.Y.; Haregeweyn, N. Prediction of grass biomass from satellite imagery in Somali regional state, eastern Ethiopia. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.H.M.d.R.; Fernandes Junior, J.d.S.; Adams, J.M.; Lee, M.; Reis, R.A.; Tedeschi, L.O. Using sentinel-2 satellite images and machine learning algorithms to predict tropical pasture forage mass, crude protein, and fiber content. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guerschman, J.; Shendryk, Y.; Henry, D.; Tom Harrison, M. Estimating Pasture Biomass Using Sentinel-2 Imagery and Machine Learning. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.A.; Skidmore, A.; Corsi, F.; van Wieren, S.E.; Sobhan, I. Estimation of green grass/herb biomass from airborne hyperspectral imagery using spectral indices and partial least squares regression. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2007, 9, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, M.H.D.; Becker, R.; Wichern, F.; Kooistra, L. Quantification of Grassland Biomass and Nitrogen Content through UAV Hyperspectral Imagery—Active Sample Selection for Model Transfer. Drones 2022, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Brüninghoff, D.; Hensgen, F.; Wachendorf, M.; Astor, T. Methods for LiDAR-based estimation of extensive grassland biomass. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 156, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.; Badenhorst, P.E.; Shi, F.; Spangenberg, G.C.; Smith, K.F.; Daetwyler, H.D. Design of an Unmanned Ground Vehicle and LiDAR Pipeline for the High-Throughput Phenotyping of Biomass in Perennial Ryegrass. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hütt, C.; Bolten, A.; Hüging, H.; Bareth, G. UAV LiDAR Metrics for Monitoring Crop Height, Biomass and Nitrogen Uptake: A Case Study on a Winter Wheat Field Trial. PFG J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. Geoinformation Sci. 2023, 91, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, M.T.; Lamb, D.W.; Ozdogan, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Thenkabail, P.S. A Combination of Plant NDVI and LiDAR Measurements Improve the Estimation of Pasture Biomass in Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea var. Fletcher). Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.D.C.; Edwards, J.; McDonald, G.; Kuchel, H. Estimating Biomass and Canopy Height with LiDAR for Field Crop Breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 473161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grüner, E.; Astor, T.; Wachendorf, M. Biomass Prediction of Heterogeneous Temperate Grasslands Using an SfM Approach Based on UAV Imaging. Agronomy 2019, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batistoti, J.; Marcato, J.; ítavo, L.; Matsubara, E.; Gomes, E.; Oliveira, B.; Souza, M.; Siqueira, H.; Filho, G.S.; Akiyama, T.; et al. Estimating Pasture Biomass and Canopy Height in Brazilian Savanna Using UAV Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Koc, A.B.; Aguerre, M.J. Aboveground Biomass Estimation of Tall Fescue using Aerial and Ground-based Systems. In Proceedings of the 2023 ASABE Annual International Meeting, Omaha, NE, USA, 9–12 July 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legg, M.; Bradley, S. Ultrasonic Arrays for Remote Sensing of Pasture Biomass. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, A.B.; Erwin, C.; Aguerre, M.J.; Chastain, J.P. Estimating Tall Fescue and Alfalfa Forage Biomass Using an Unmanned Ground Vehicle. In Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 458, pp. 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.; Trotter, M.; Robson, A.; Schneider, D.; Frizell, L.; Saint, A.; Lamb, D.; Blore, C. Estimating pasture biomass with active optical sensors. Adv. Anim. Biosci. 2017, 8, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.C.; Astatkie, T.; Cooper, J.M.; Fredeen, A.H. A Comparison of Methods Used to Determine Biomass on Naturalized Swards. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2005, 191, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, M.; Li, Q.; Ghafoor, A.; Zhu, J.; Li, B.; Ma, Y. Using the plant height and canopy coverage to estimation maize aboveground biomass with UAV digital images. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 151, 126957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.; Kirkby, M.; Geeson, N. Desertification Indicator System for Mediterranean Europe. Manual on: Key Indicators of Desertification and Mapping Environmentally Sensitive Areas to Desertification. European Commission, Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development, EUR 18882, 87 p. Available online: https://esdac.jrc.ec.europa.eu/public_path/shared_folder/projects/DIS4ME/indicator_descriptions/vegetation_cover.htm# (accessed on 2 January 2024).
- Flombaum, P.; Sala, O.E. A non-destructive and rapid method to estimate biomass and aboveground net primary production in arid environments. J. Arid. Environ. 2007, 69, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirrmann, M.; Hamdorf, A.; Garz, A.; Ustyuzhanin, A.; Dammer, K.H. Estimating wheat biomass by combining image clustering with crop height. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 121, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OAK-D—DepthAI Hardware Documentation 1.0.0 Documentation. Available online: https://docs.luxonis.com/projects/hardware/en/latest/pages/BW1098OAK/ (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Luxonis Field of View Calculator. Available online: https://fov.luxonis.com/?horizontalFov=80&verticalFov=55&horizontalResolution=1280&verticalResolution=800 (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Serouart, M.; Madec, S.; David, E.; Velumani, K.; Lozano, R.L.; Weiss, M.; Baret, F. SegVeg: Segmenting RGB Images into Green and Senescent Vegetation by Combining Deep and Shallow Methods. Plant Phenomics 2022, 2022, 9803570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, M.; Cavalli, D.; Cabassi, G.; Bechini, L.; Pricca, N.; Paolo, D.; Marinoni, L.; Vigoni, A.; Degano, L.; Gallina, P.M. Improved estimation of herbaceous crop aboveground biomass using UAV-derived crop height combined with vegetation indices. Precis. Agric. 2023, 24, 587–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, C.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Feng, G.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Q. Estimating the maize biomass by crop height and narrowband vegetation indices derived from UAV-based hyperspectral images. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hütt, C.; Isselstein, J.; Komainda, M.; Schöttker, O.; Sturm, A. UAV LiDAR-based grassland biomass estimation for precision livestock management. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2024, 18, 017502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, R.T. Comparing Bermudagrass and Bahiagrass Cultivars at Different Stages of Harvest for Dry Matter Yield and Nutrient Content. Master’s Thesis, Louisiana State University LSU Scholarly Repository, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, A.B.; MacInnis, B.M.; Aguerre, M.J.; Chastain, J.P.; Turner, A.P. Alfalfa Biomass Estimation Using Crop Surface Modeling and NDVI. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2023, 39, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Technique/System | Platform | Site Scale | Coefficient of Determination (R2) of Biomass Prediction Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral reflectance | Satellite (Landsat-8, Sentinal-2) | Large scale and farm scale | 0.20–0.92 [5,6,7,8,9] |
| Unmanned aerial vehicle (Hyperspectral camera) | Farm scale | 0.42–0.92 [10,11] | |
| LiDAR | Unmanned aerial vehicle and Unmanned ground vehicle | Farm scale and large scale | 0.61–0.74 [12,13,14,15,16] |
| Structure from motion | Unmanned aerial vehicle | Farm scale | 0.59–0.88 [17,18,19] |
| Ultrasound sensor | Unmanned ground vehicle | Farm scale | 0.73–0.80 [20,21] |
| Meter stick, rising plate meter | Manual measurements | Farm scale | 0.11–0.86 [22,23] |
| Camera Specifications | Color Camera * | Stereo Pair ** |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor | IMX378 (PY011 AF) | OV9282 (PY010 FF) |
| DFOV/HFOV/VFOV | 81°/69°/55° | 81°/72°/49° |
| Resolution | 12 MP (4056 × 3040) | 1 MP (1280 × 800) |
| Focus | AF: 8 cm–∞ or FF: 50 cm–∞ | FF: 19.6 cm–∞ |
| Max framerate | 60 FPS | 120 FPS |
| F-number | 1.8 ± 5% | 2.0 ± 5% |
| Lens size | 1/2.3 inch (11 mm) | 1/4 inch (6.4 mm) |
| Effective focal length | 4.81 mm | 2.35 mm |
| Pixel size | 1.55 μm × 1.55 μm | 3 µm × 3 μm |
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Flight altitude (m) | 18.29 |
| Front overlap (%) | 75 |
| Side overlap (%) | 75 |
| Flight speed (m/s) | 1.8 (Auto Set) |
| Perimeter 3D | ON |
| Crosshatch 3D | ON |
| βw(∆H) | βw(VC) | βw (∆H, VC) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average WBY (kg-wet/ha) | 5585 | 5585 | 5585 |
| n | 131 | 131 | 131 |
| R2 (c ≠ 0) | 0.38 | 0.18 | 0.42 * |
| R2 (c = 0) | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.92 * |
| p-value of regression (c = 0) | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| SeY (kg-wet/ha) | 1824 | 2040 | 1726 |
| CV | 33% | 37% | 31% |
| b1 | 38.38 | 0 | 25.07 |
| p-value (b1) | p < 0.001 | NA | p < 0.001 |
| 95% confidence interval (b1) | ±2.11 | NA | ±6.85 |
| b2 | 0 | 72.76 | 26.36 |
| p-value (b2) | NA | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| 95% confidence interval (b2) | NA | ±4.47 | ±12.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, J.; Koc, A.B.; Aguerre, M.J.; Chastain, J.P.; Shaik, S. Estimating Bermudagrass Aboveground Biomass Using Stereovision and Vegetation Coverage. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16142646
Singh J, Koc AB, Aguerre MJ, Chastain JP, Shaik S. Estimating Bermudagrass Aboveground Biomass Using Stereovision and Vegetation Coverage. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(14):2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16142646
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Jasanmol, Ali Bulent Koc, Matias Jose Aguerre, John P. Chastain, and Shareef Shaik. 2024. "Estimating Bermudagrass Aboveground Biomass Using Stereovision and Vegetation Coverage" Remote Sensing 16, no. 14: 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16142646
APA StyleSingh, J., Koc, A. B., Aguerre, M. J., Chastain, J. P., & Shaik, S. (2024). Estimating Bermudagrass Aboveground Biomass Using Stereovision and Vegetation Coverage. Remote Sensing, 16(14), 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16142646






