How Useful Are Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Observations for Inland Water Temperature Monitoring and Warming Trend Assessment in Temperate Lakes in Poland?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
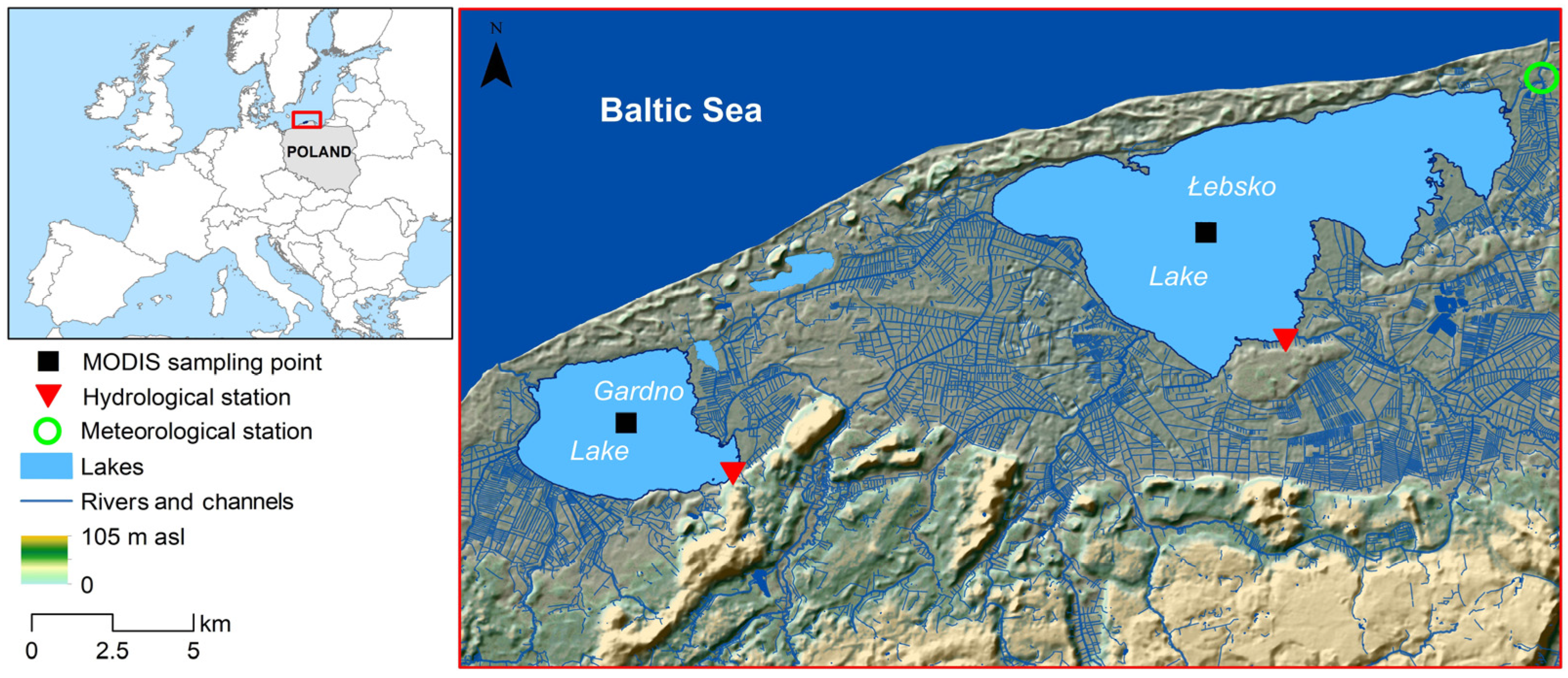
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. LST Datasets
2.2.2. In Situ Datasets
2.3. Methods
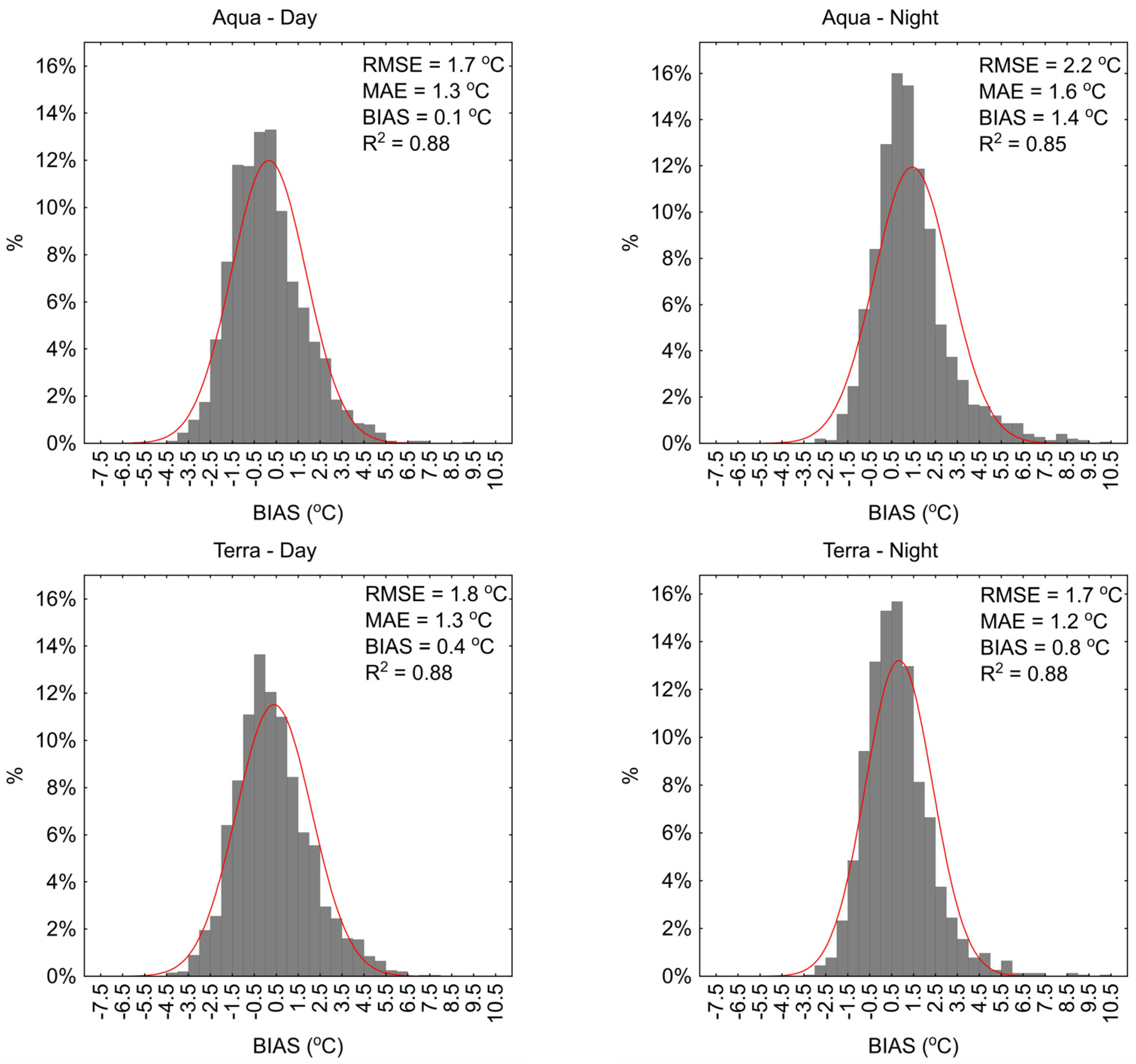
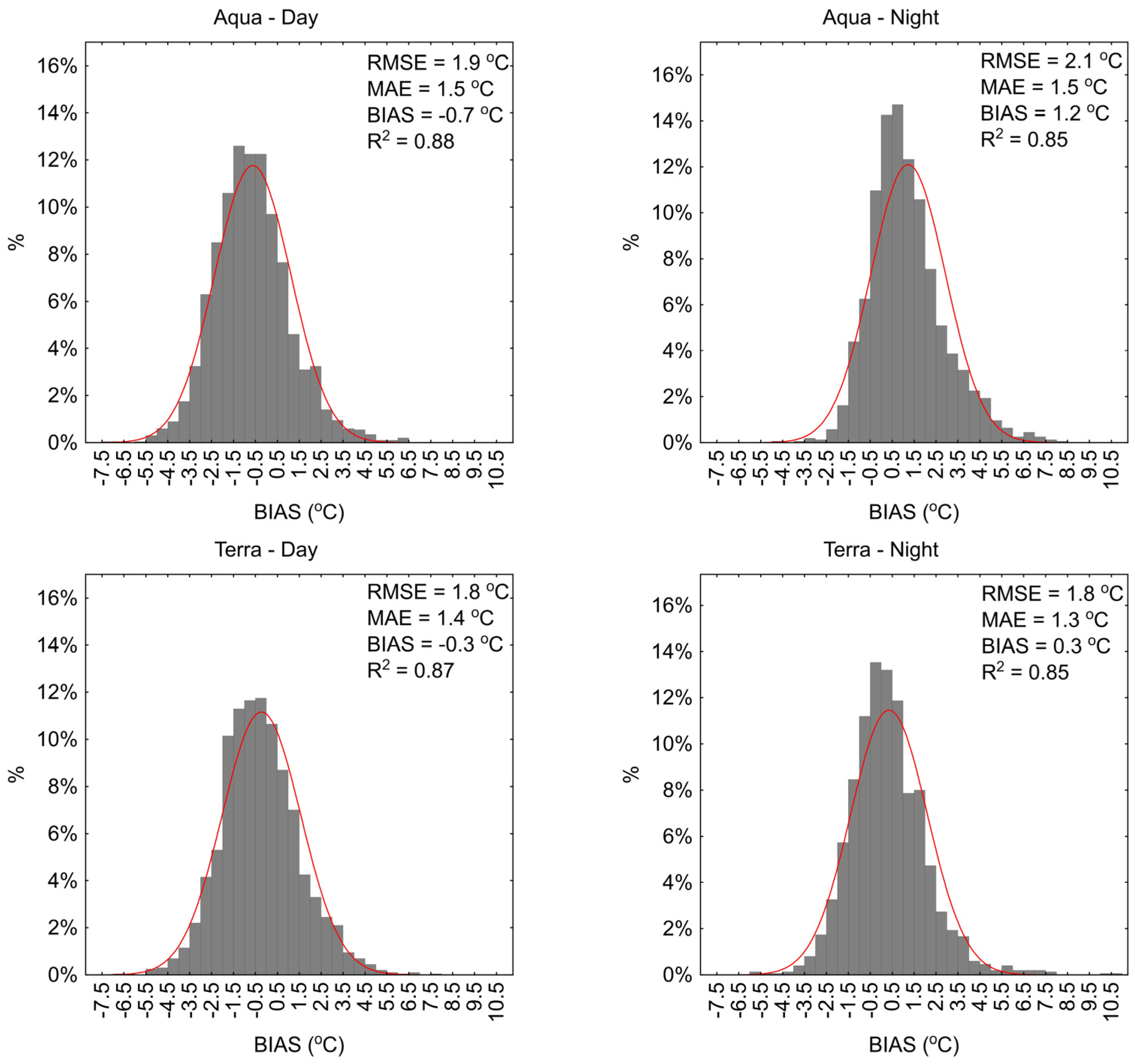
2.3.1. MODIS Products Validation
2.3.2. Assessment of the Suitability of MODIS Data for Estimating Water Temperature Trends in Lakes
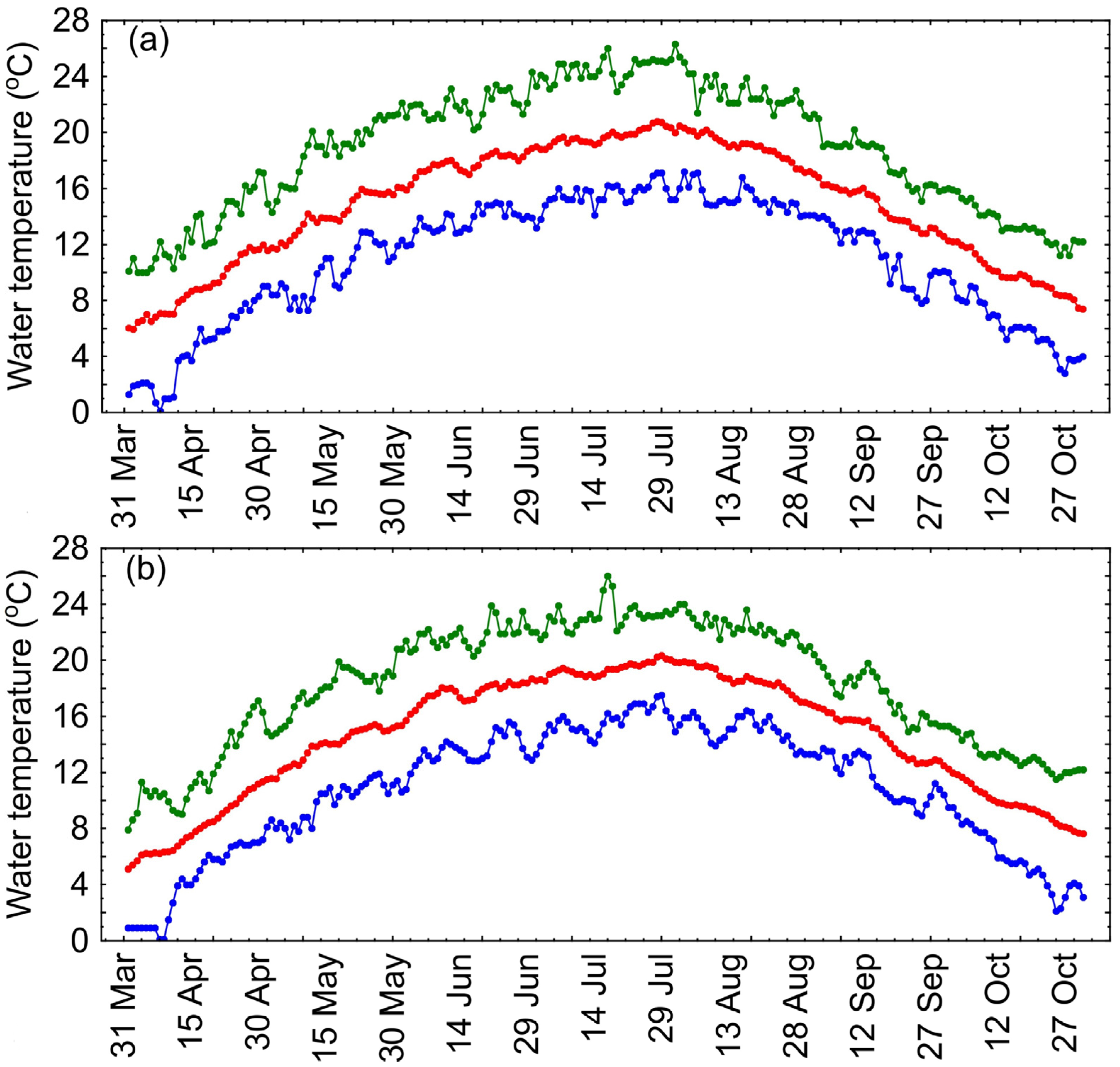
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tariq, A.; Shu, H.; Kuriqi, A.; Siddiqui, S.; Gagnon, A.S.; Lu, L.; Linh, N.T.T.; Pham, Q.B. Characterization of the 2014 Indus River Flood Using Hydraulic Simulations and Satellite Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhao, J.; Ai, B.; Sun, S.; Yang, Z. Machine Learning Based Long-Term Water Quality in the Turbid Pearl River Estuary, China. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2022, 127, e2021JC018017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamirbekkyzy, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, T.; Duulatov, E.; Gafurov, A.; Omorova, E.; Gafurov, A. Hydrological Forecasting under Climate Variability Using Modeling and Earth Observations in the Naryn River Basin, Kyrgyzstan. Water 2022, 14, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, R.E.; Soulard, C.E.; Waller, E.K.; Walker, J.J. Analysis of Surface Water Trends for the Conterminous United States Using MODIS Satellite Data, 2003–2019. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR031399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavula, G.; Brezonik, P.; Thenkabail, P.; Johnson, T.; Bauer, M. Estimating the surface temperature of Lake Malawi using AVHRR and MODIS satellite imagery. Phys. Chem. Earth 2009, 34, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tan, W.; Su, H. Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Variation Process of Dianchi Lake Surface Water Temperature Based on MODIS Remote Sensing Images. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 658, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, M.H.; Cardoso, M.A.; Motta Marques, D.; Bonnet, M.-P.; Fragoso, C.R. High Spring Warming Rates in an Extensive Subtropical Shallow Lakes System Detected Using MODIS Imagery. ACS ES T Water 2024, 4, 1518–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choiński, A. Katalog Jezior Polski; Wydawnictwo Naukowe UAM: Poznąń, Poland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, E.A.; Burningham, H.; Thompson, J.R. Impacts of climate change and hydrological management on a coastal lake and wetland system. Ir. Geogr. 2019, 52, 21–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowski, J.; Antonowicz, J. Właściwości chemiczne osadów dennych jeziora Dołgie Wielkie. Słupskie Pr. Biol. 2005, 2, 123–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kujawa-Pawlaczyk, J.; Pawlaczyk, P. Planowanie ochrony siedlisk nadmorskich w obszarze Natura 2000 na przykładzie obszaru Jezioro Wicko i Modelskie Wydmy PLH320068. Przegląd Przyr. 2019, 30, 27–57. [Google Scholar]
- Senze, M.; Kowalska-Góralska, M.; Pokorny, P.; Kruszyński, W. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Hydromacrophytes from Five Coastal Lakes (North-Western Poland, Baltic Sea). Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2017, 65, 1265–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychert, K.; Myszka, M.; Wielgat-Rychert, M.; Skuza, E. Importance of tintinnids and Mesodinium rubrum in communities of planktonic ciliates in the shallow brackish lakes Gardno and Lebsko (northern Poland). Balt. Coast. Zone 2017, 21, 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Plewa, K.; Perz, A.; Wrzesiński, D.; Sobkowiak, L. Probabilistic Assessment of Correlations of Water Levels in Polish Coastal Lakes with Sea Water Level with the Application of Archimedean Copulas. Water 2019, 11, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozińska, N.; Bąkowska, M. Effects of Heavy Metals in Lake Water and Sediments on Bottom Invertebrates Inhabiting the Brackish Coastal Lake Łebsko on the Southern Baltic Coast. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Różyński, G.; Cerkowniak, G.R. Resilience of Coastal Lake Barriers in Poland in Light of Geological and Bathymetric Data and Hydrodynamic Simulations. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 815405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ptak, M.; Yaseend, Z.M.; Daia, J.; Sivakumar, B. Forecasting surface water temperature in lakes: A comparison of approaches. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptak, M.; Choiński, A.; Piekarczyk, J.; Pryłowski, T. Application of Landsat satellite thermal images in the analysis of the temperature of Polish lakes. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jańczaka, J. (Ed.) Atlas Jezior Polski: Praca Zbiorowa. T.2, Jeziora Zlewni Rzek Przymorza i Dorzecza Dolnej Wisły; Instytut Meteorologii i Gospodarki Wodnej: Warszawa, Poland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; Hook, S.; Hulley, G. MODIS/Terra Land Surface Temperature/Emissivity Daily L3 Global 1km SIN Grid V061 [Data Set]. NASA EOSDIS Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center. 2021. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mod11a1v061/ (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Wan, Z.; Hook, S.; Hulley, G. MODIS/Aqua Land Surface Temperature/Emissivity Daily L3 Global 1km SIN Grid V061 [Data Set]. NASA EOSDIS Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center. 2021. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/myd11a1v061/ (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Available online: https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Wan, Z.; Hook, S.; Hulley, G. MODIS/Terra Land Surface Temperature/Emissivity 8-Day L3 Global 1km SIN Grid V061 [Data Set]. NASA EOSDIS Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center. 2021. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mod11a2v061/ (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Wan, Z.; Hook, S.; Hulley, G. MODIS/Aqua Land Surface Temperature/Emissivity 8-Day L3 Global 1km SIN Grid V061 [Data Set]. NASA EOSDIS Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center. 2021. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/myd11a2v061/ (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Ptak, M. Possibilities of River Water Temperature Reconstruction Using Statistical Models in the Context of Long-Term Thermal Regime Changes Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.O. Statistical Methods for Environmental Pollution Monitorin; Van Nostrand Reinhold Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1987; p. 320. [Google Scholar]
- Cretaux, J.F.; Berge-Nguyen, M. Aral Sea hydrology from satellite remote sensing. In The Aral Sea: The Devastation and Partial Rehabilitation of a Great Lake; Micklin, P., Aladin, N.V., Plotnikov, I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 273–299. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. Characterizing spatial and temporal variations of surface temperature of Lake Tana (Ethiopia) using MODIS data. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 21–26 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Frassl, M.A.; Boehrer, B. Reconstructing Six Decades of Surface Temperatures at a Shallow Lake. Water 2020, 12, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choiński, A.; Ptak, M.; Strzelczak, A. Present-day evolution of coastal lakes based on the example of Jamno and Bukowo (the Southern Baltic coast). Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2014, 43, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhu, G.; Shi, K.; Qin, B. Validating and Mapping Surface Water Temperatures in Lake Taihu: Results from MODIS Land Surface Temperature Products. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1230–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, J.M. Comparison of shipboard and satellite measurements of surface water temperature and chlorophyll a in Lake Ontario. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2009, 12, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, H.K.; Duguay, C.R.; Solberg, R.; Rudjord, Ø. Impact of satellite-based lake surface observations on the initial state of HIRLAM. Part I: Evaluation of remotelysensed lake surface water temperature observations. Tellus Ser. A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2014, 66, 21534. [Google Scholar]
- Moukomla, S.; Blanken, P.D. Remote sensing of the North American Laurentian Great Lakes’ surface temperature. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosman, E.T.; Horel, J.D. MODIS-derived surface temperature of the Great Salt Lake. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazhu; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Hou, J.; Lei, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, A.; Chen, Y.; Ding, B.; Li, X. A strict validation of MODIS lake surface water temperature on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zheng, H.; Wu, Y.; Fan, L.; Wen, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, B. An integrated dataset of daily lake surface water temperature over the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 3411–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesch, D.C.; Jaquet, J.-M.; Hauser, A.; Wunderle, S. Lake surface water temperature retrieval using advanced very high resolution radiometer and Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer data: Validation and feasibility study. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2005, 110, C12014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoniewska, M. Diurnal course of cloud cover in Poland in the following decades of the year (based on years 1990–2000). J. Educ. Health Sport 2016, 6, 730–740. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Zhao, W.; Cai, J.; Yang, Y.; Fu, H. Evaluation of consistency among MODIS land surface temperature products for monitoring surface warming trend over the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Space Sci. 2023, 10, e2022EA002611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptak, M.; Sojka, M.; Choiński, A.; Nowak, B. Effect of environmental conditions and morphometric parameters on surface water temperature in Polish lakes. Water 2018, 10, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ji, F.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Hu, S. Increased Warming Efficiencies of Lake Heatwaves Enhance Dryland Lake Warming over China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
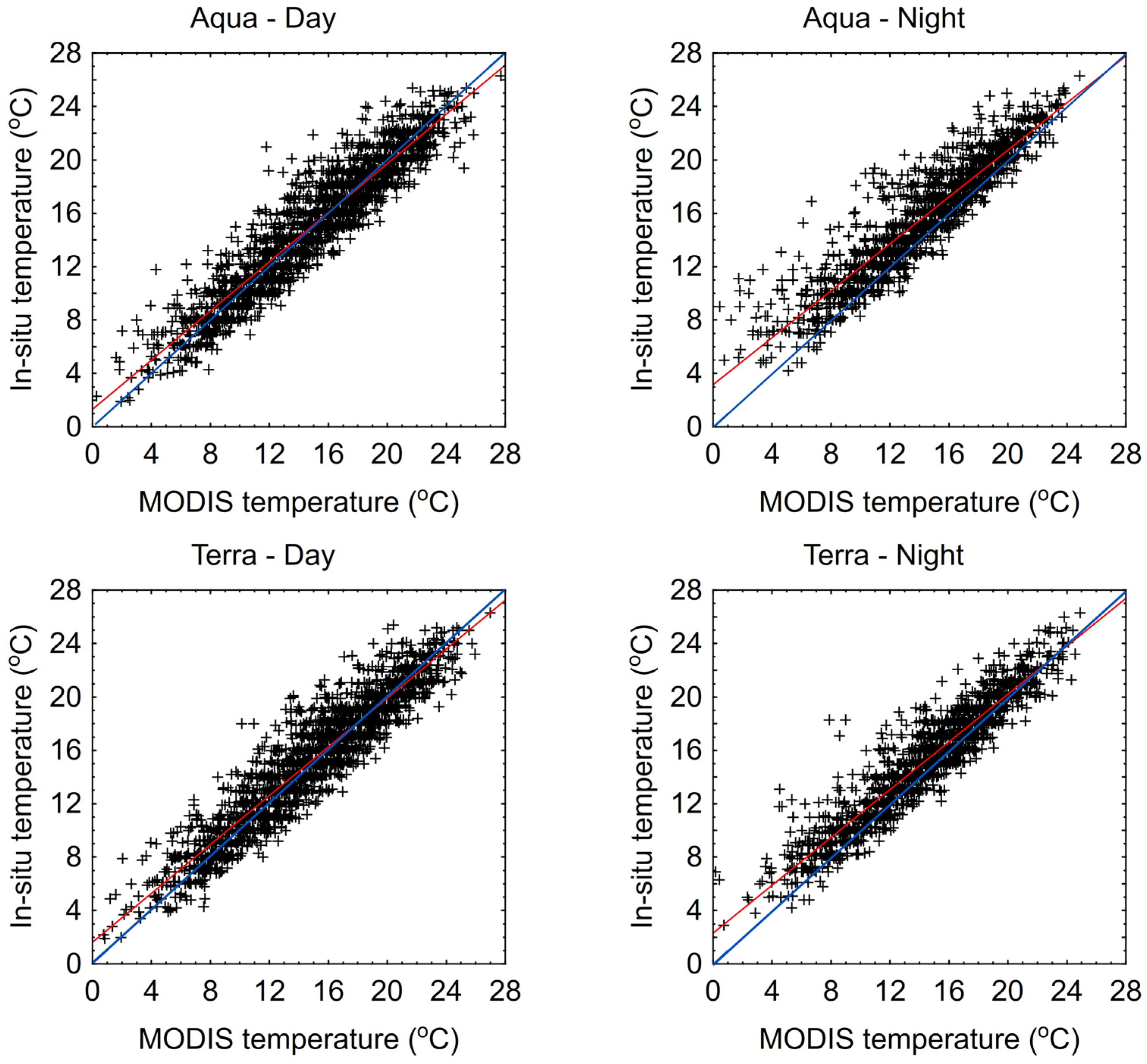
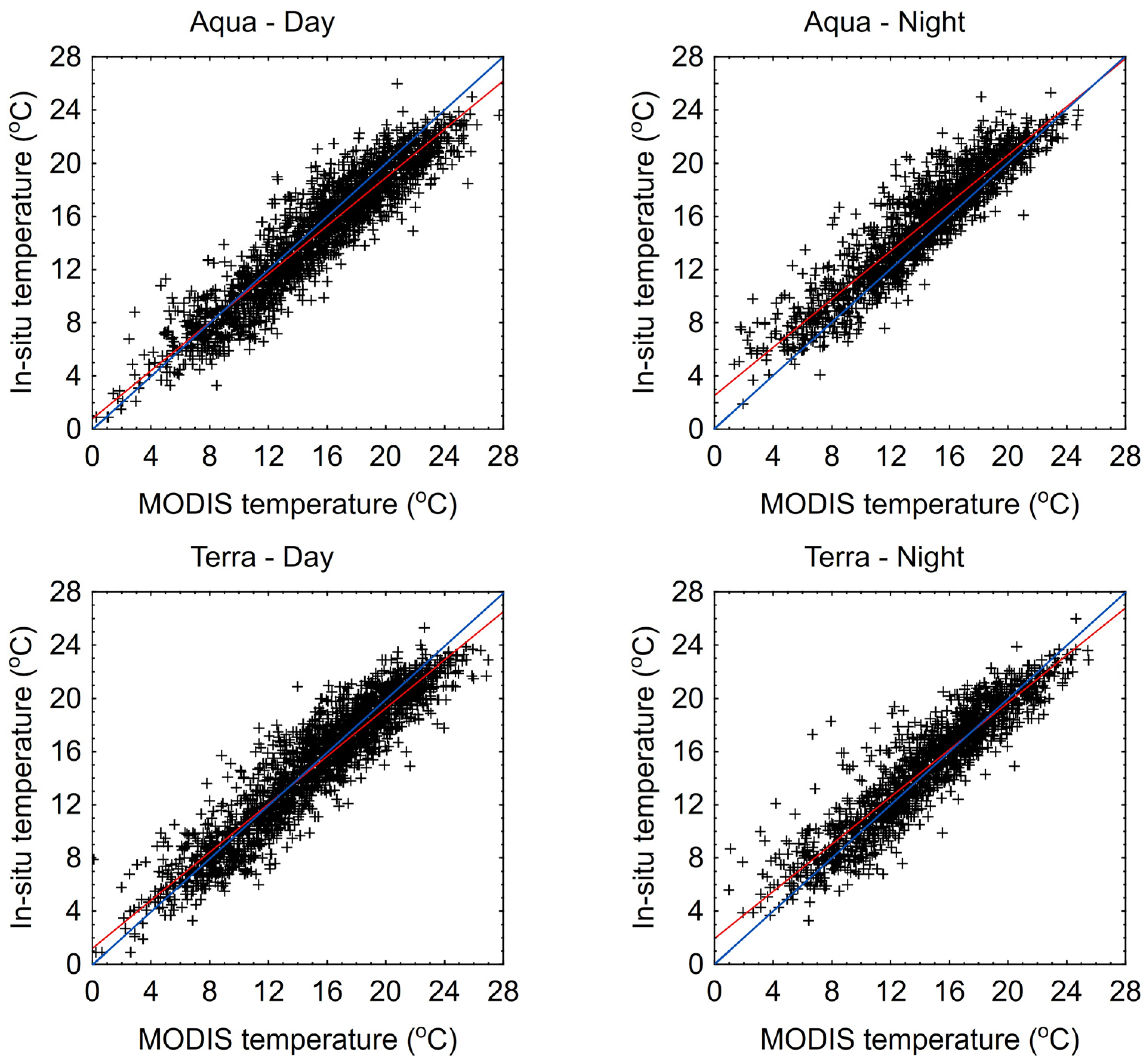
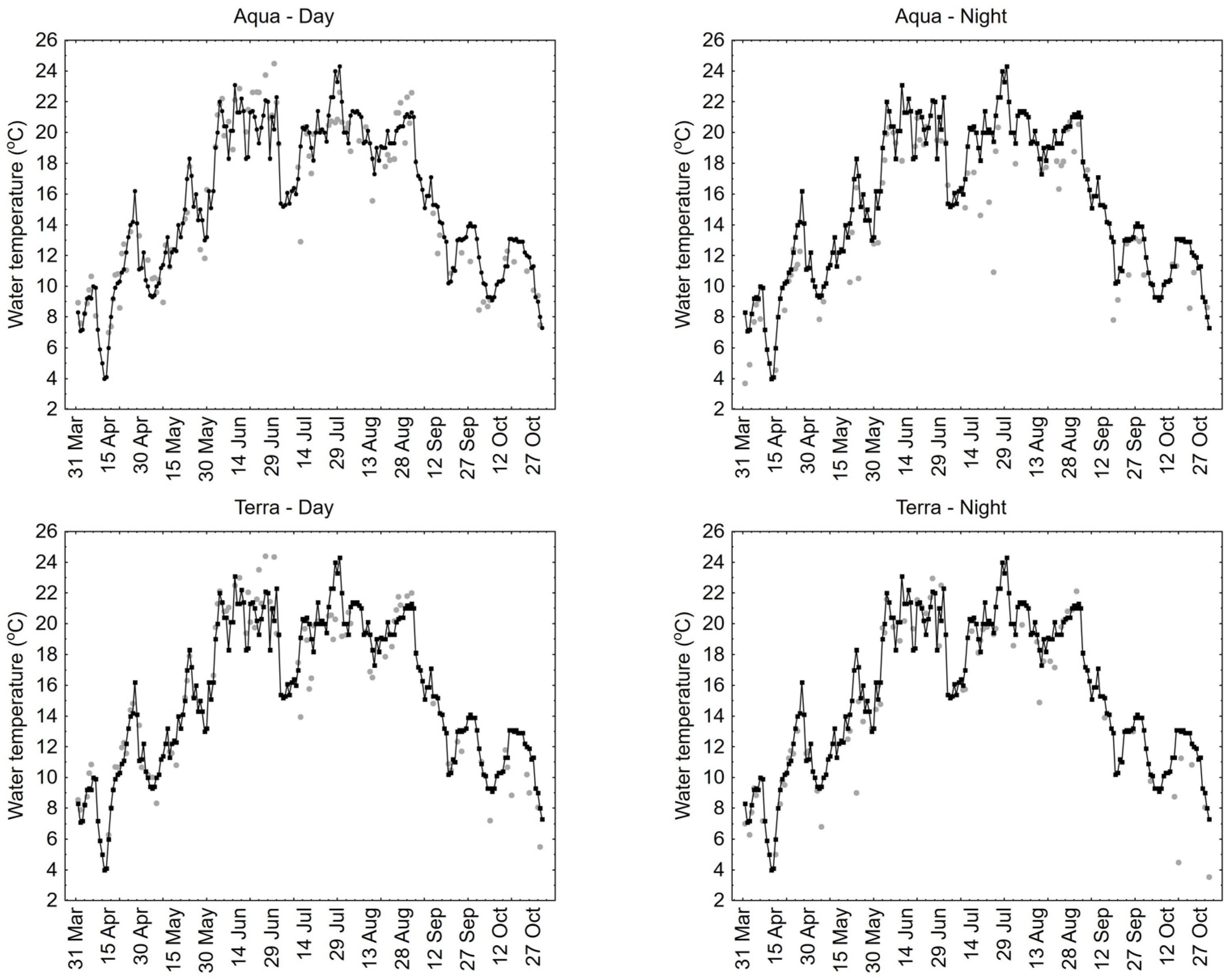
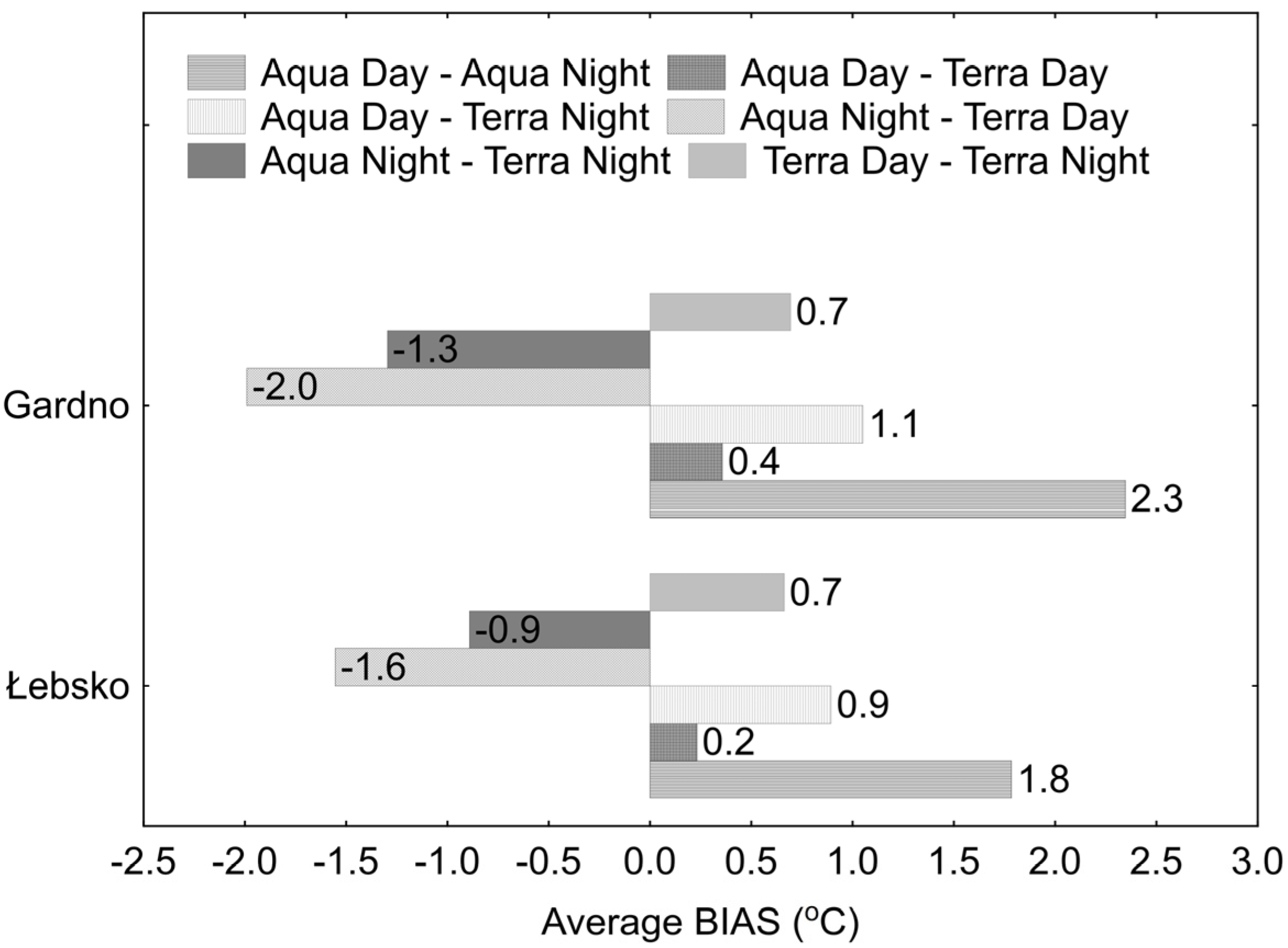
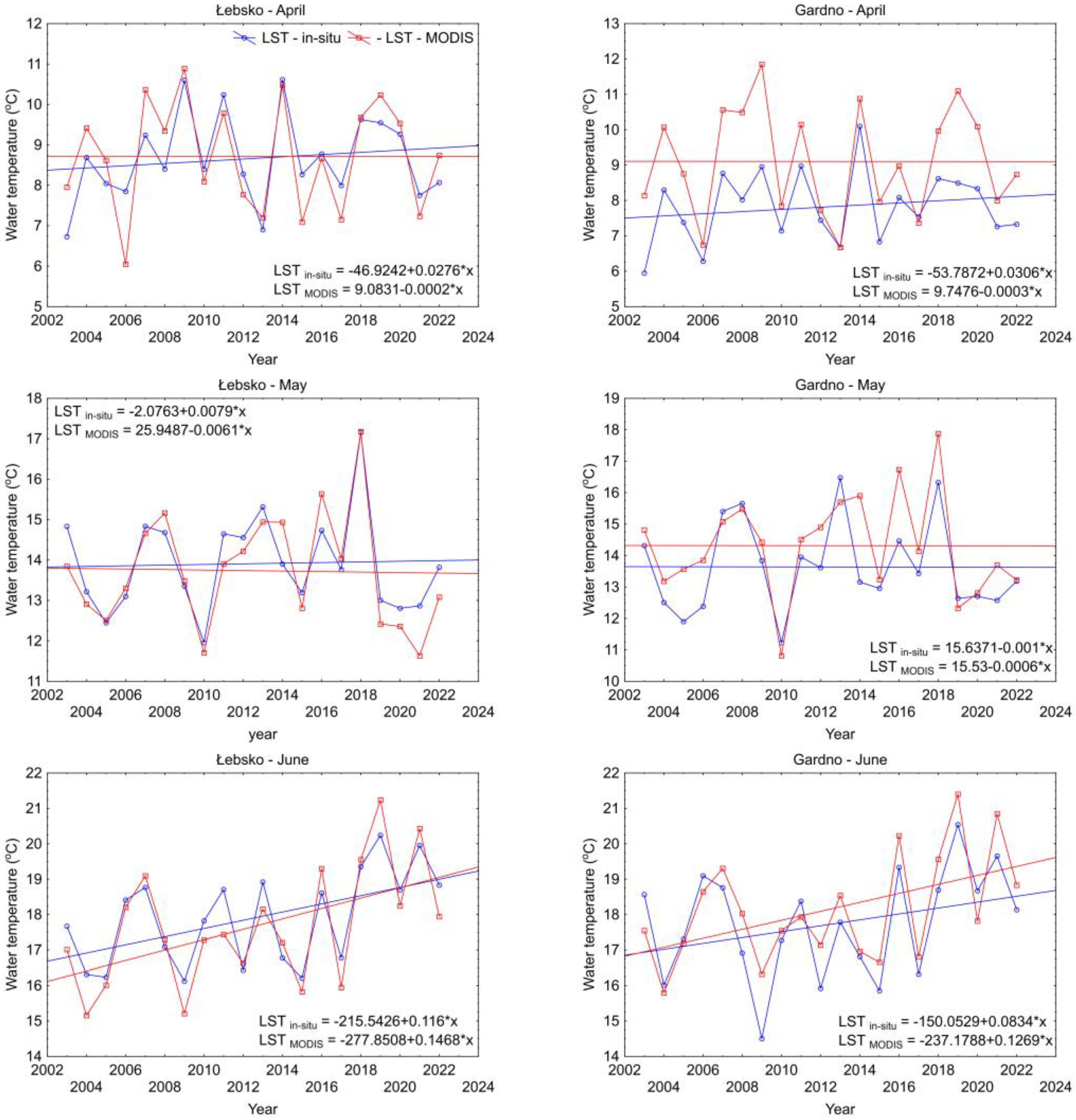
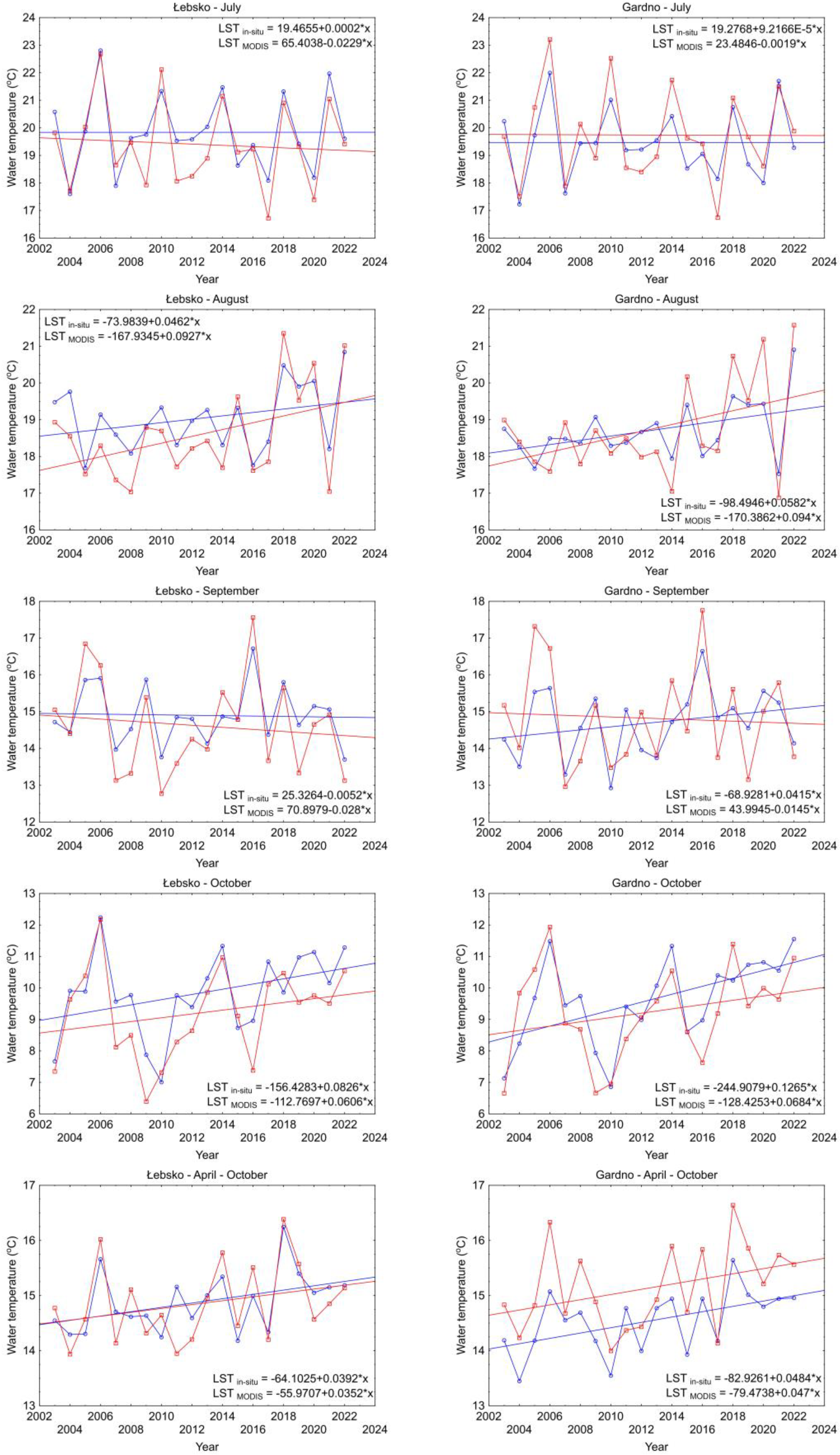
| Month | Łebsko | Gardno | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE (°C) | MAE (°C) | BIAS (°C) | R2 (-) | RMSE (°C) | MAE (°C) | BIAS (°C) | R2 (-) | |
| April | 0.77 | 0.64 | −0.05 | 0.66 | 1.53 | 1.30 | −1.28 | 0.72 |
| May | 0.59 | 0.48 | 0.17 | 0.83 | 1.14 | 0.88 | −0.68 | 0.66 |
| June | 0.67 | 0.59 | 0.24 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.74 | −0.43 | 0.77 |
| July | 0.85 | 0.67 | 0.44 | 0.78 | 0.85 | 0.75 | −0.28 | 0.77 |
| August | 0.72 | 0.63 | 0.44 | 0.83 | 0.69 | 0.56 | −0.03 | 0.79 |
| September | 0.72 | 0.60 | 0.28 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.80 | −0.13 | 0.56 |
| October | 0.95 | 0.81 | 0.63 | 0.75 | 0.92 | 0.81 | 0.38 | 0.68 |
| April–October | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.64 | −0.60 | 0.74 |
| Period | S Statistics | Z-Value | Sen’s Slope (°C Per Decade) | p-Value | S Statistics | Z-Value | Sen’s Slope (°C Per Decade) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Situ—Łebsko | MODIS—Łebsko | |||||||
| April | 3 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.944 | −7 | −0.21 | −0.28 | 0.834 |
| May | 3 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.944 | −5 | −0.14 | −0.07 | 0.889 |
| June | 67 | 2.31 | 1.28 | 0.021 | 59 | 2.03 | 1.62 | 0.042 |
| July | 21 | 0.70 | 0.55 | 0.484 | 3 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.944 |
| August | 37 | 1.26 | 0.61 | 0.208 | 35 | 1.19 | 0.97 | 0.234 |
| September | 15 | 0.49 | 0.33 | 0.624 | −5 | −0.14 | −0.06 | 0.889 |
| October | 41 | 1.40 | 0.80 | 0.162 | 31 | 1.05 | 0.67 | 0.294 |
| April–October | 49 | 1.68 | 0.42 | 0.093 | 49 | 1.68 | 0.44 | 0.093 |
| Period | In Situ—Gardno | MODIS—Gardno | ||||||
| April | 1 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 1.000 | −7 | −0.21 | −0.17 | 0.834 |
| May | 3 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.944 | 3 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.944 |
| June | 39 | 1.33 | 1.16 | 0.184 | 57 | 1.96 | 1.45 | 0.050 |
| July | 17 | 0.56 | 0.39 | 0.576 | 9 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.780 |
| August | 45 | 1.54 | 0.72 | 0.124 | 37 | 1.26 | 1.04 | 0.208 |
| September | 29 | 0.98 | 0.50 | 0.327 | 9 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.780 |
| October | 67 | 2.31 | 1.12 | 0.021 | 29 | 0.98 | 0.75 | 0.327 |
| April–October | 63 | 2.17 | 0.43 | 0.030 | 45 | 1.54 | 0.55 | 0.124 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sojka, M.; Ptak, M.; Szyga-Pluta, K.; Zhu, S. How Useful Are Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Observations for Inland Water Temperature Monitoring and Warming Trend Assessment in Temperate Lakes in Poland? Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2727. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152727
Sojka M, Ptak M, Szyga-Pluta K, Zhu S. How Useful Are Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Observations for Inland Water Temperature Monitoring and Warming Trend Assessment in Temperate Lakes in Poland? Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(15):2727. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152727
Chicago/Turabian StyleSojka, Mariusz, Mariusz Ptak, Katarzyna Szyga-Pluta, and Senlin Zhu. 2024. "How Useful Are Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Observations for Inland Water Temperature Monitoring and Warming Trend Assessment in Temperate Lakes in Poland?" Remote Sensing 16, no. 15: 2727. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152727
APA StyleSojka, M., Ptak, M., Szyga-Pluta, K., & Zhu, S. (2024). How Useful Are Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Observations for Inland Water Temperature Monitoring and Warming Trend Assessment in Temperate Lakes in Poland? Remote Sensing, 16(15), 2727. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152727











