South-to-North Water Diversion Halting Long-Lived Subsidence in Tianjin, North China Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
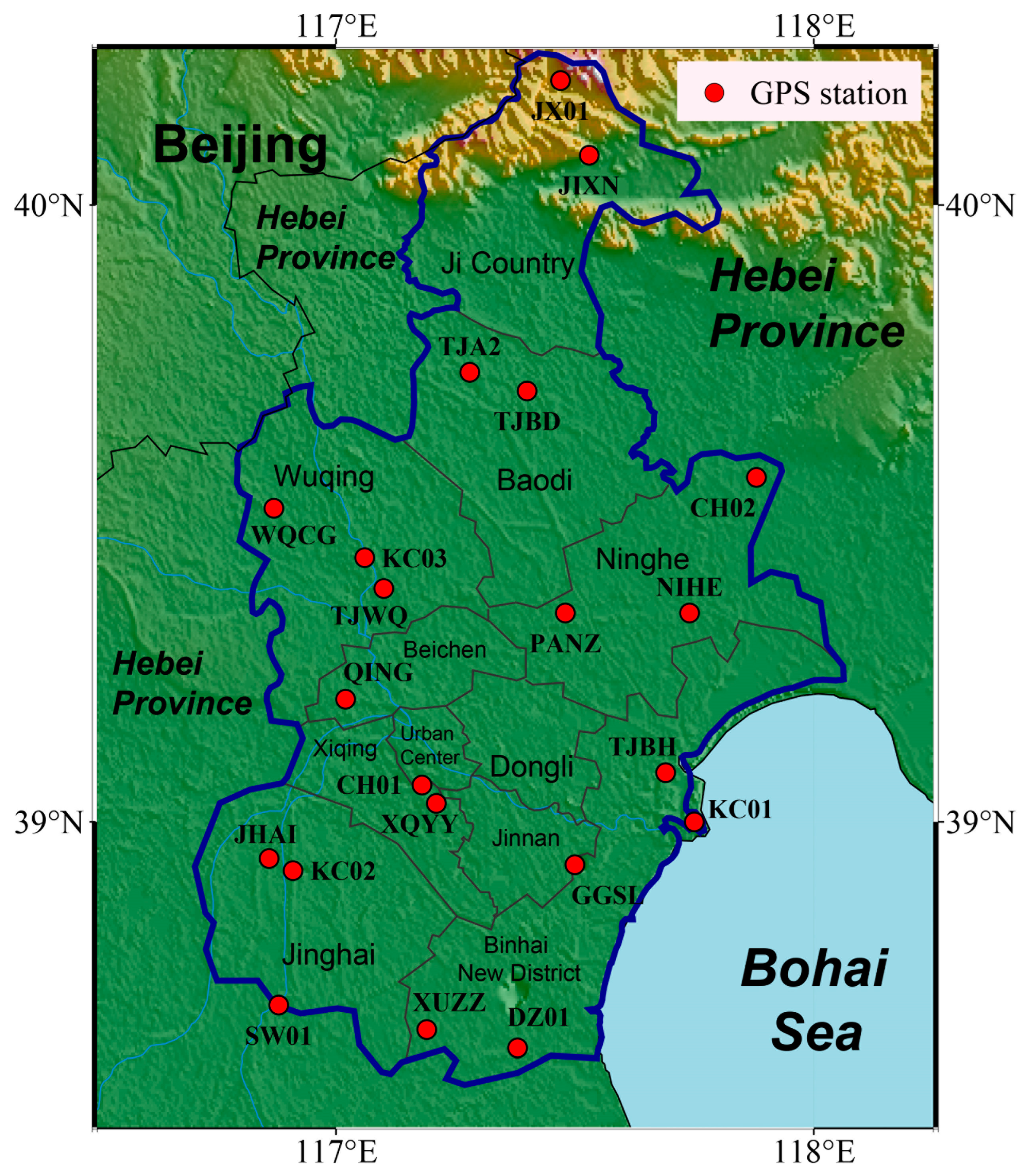
2.1. Geographical Background of Study Area
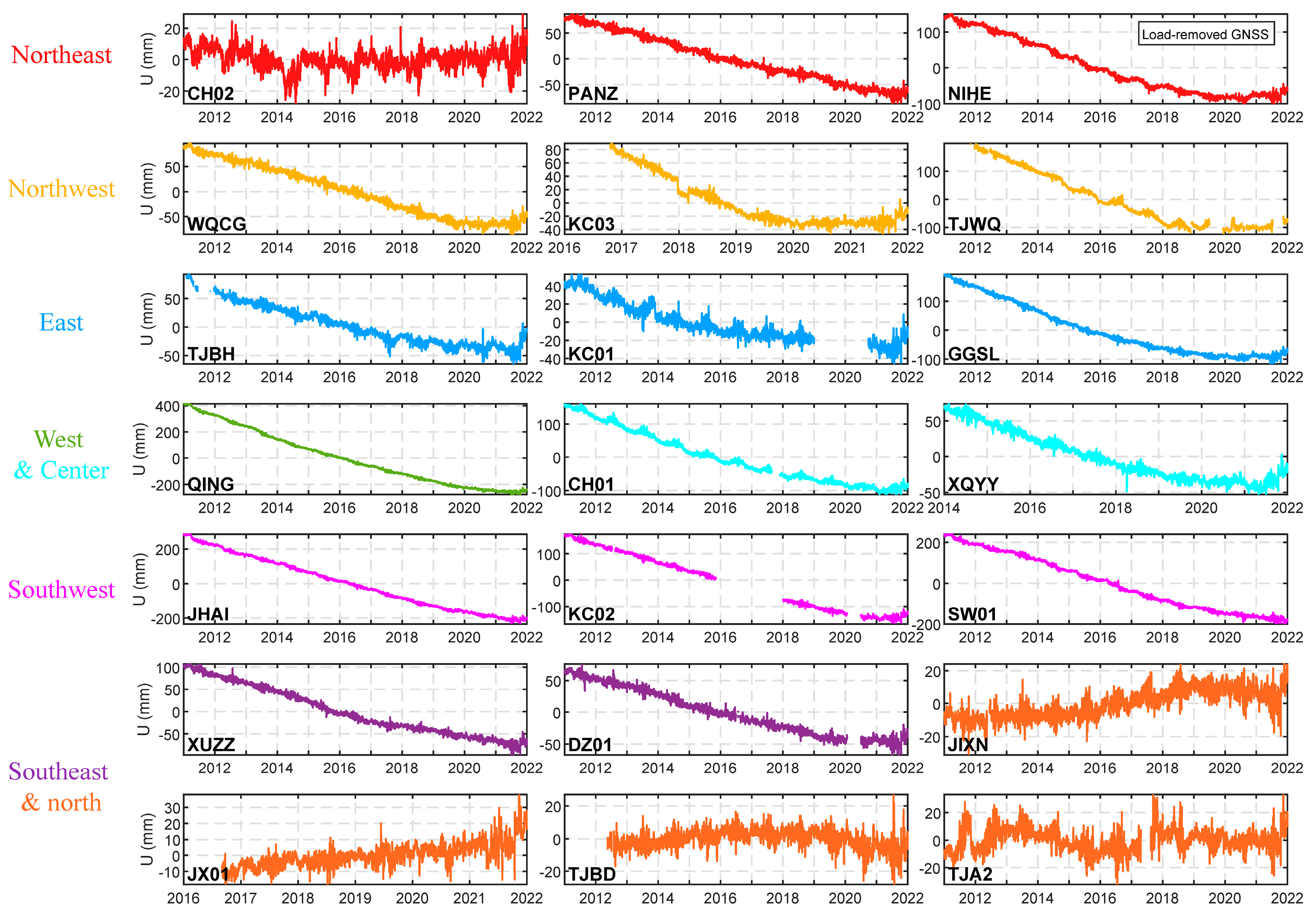
2.2. GNSS Vertical Position Time Series
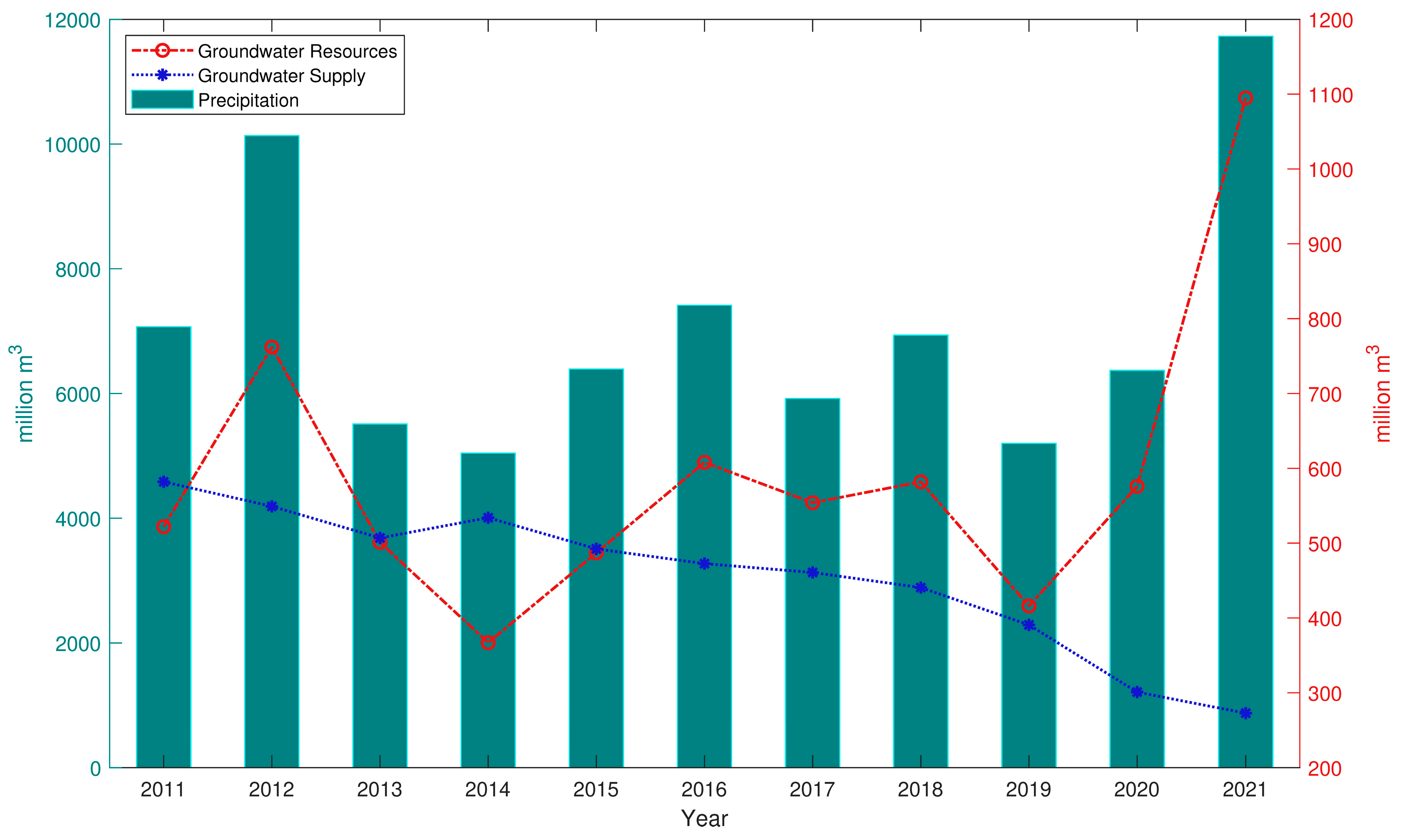
2.3. Tianjin Water Resources Bulletin
3. Methodology
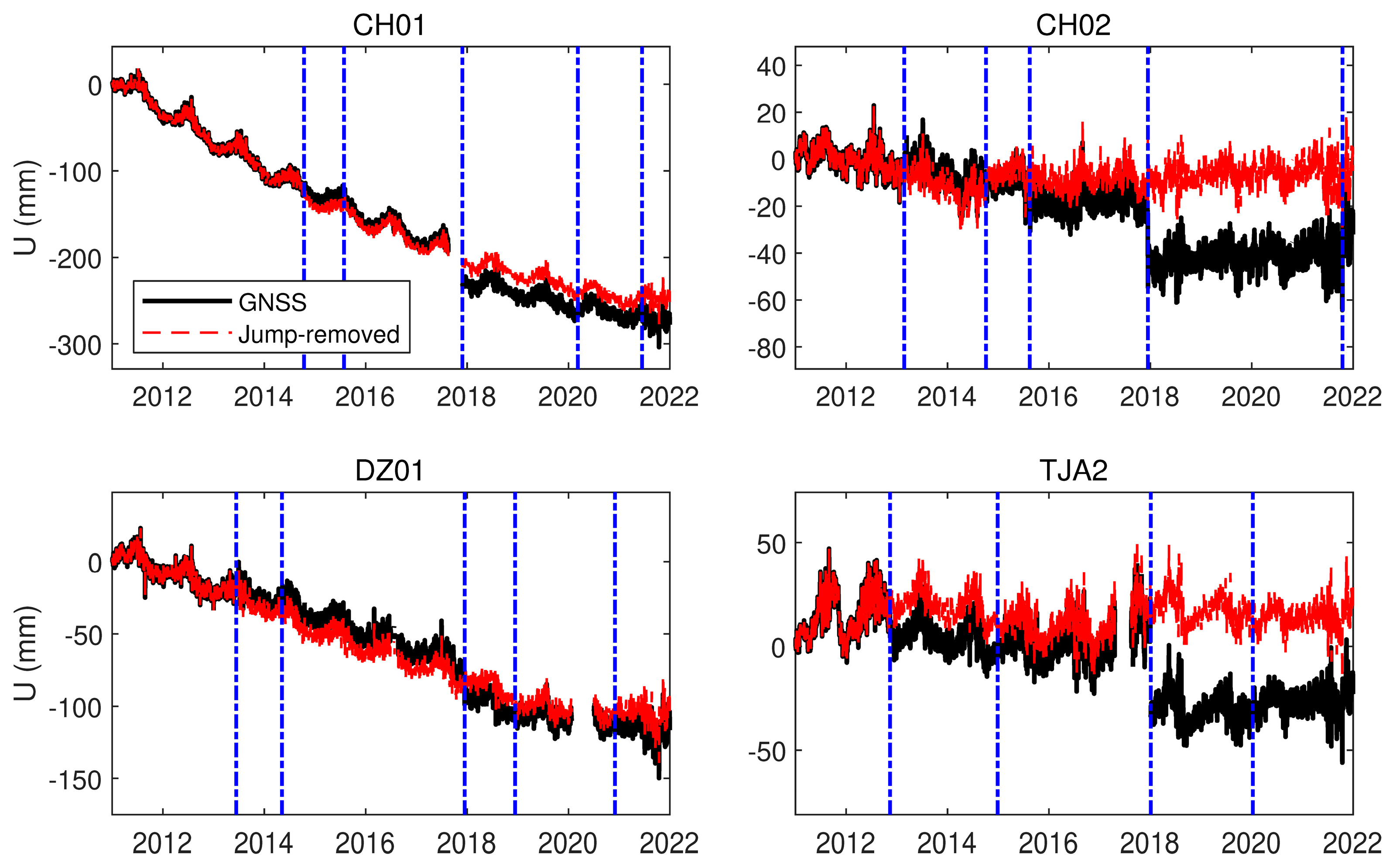
3.1. Correcting Jumps in GNSS Data with Variable Rates
3.2. Implementing the Well-Modeled Corrections
3.3. Modeling GNSS Position Time Series
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Crustal Subsidence from GNSS Time Series
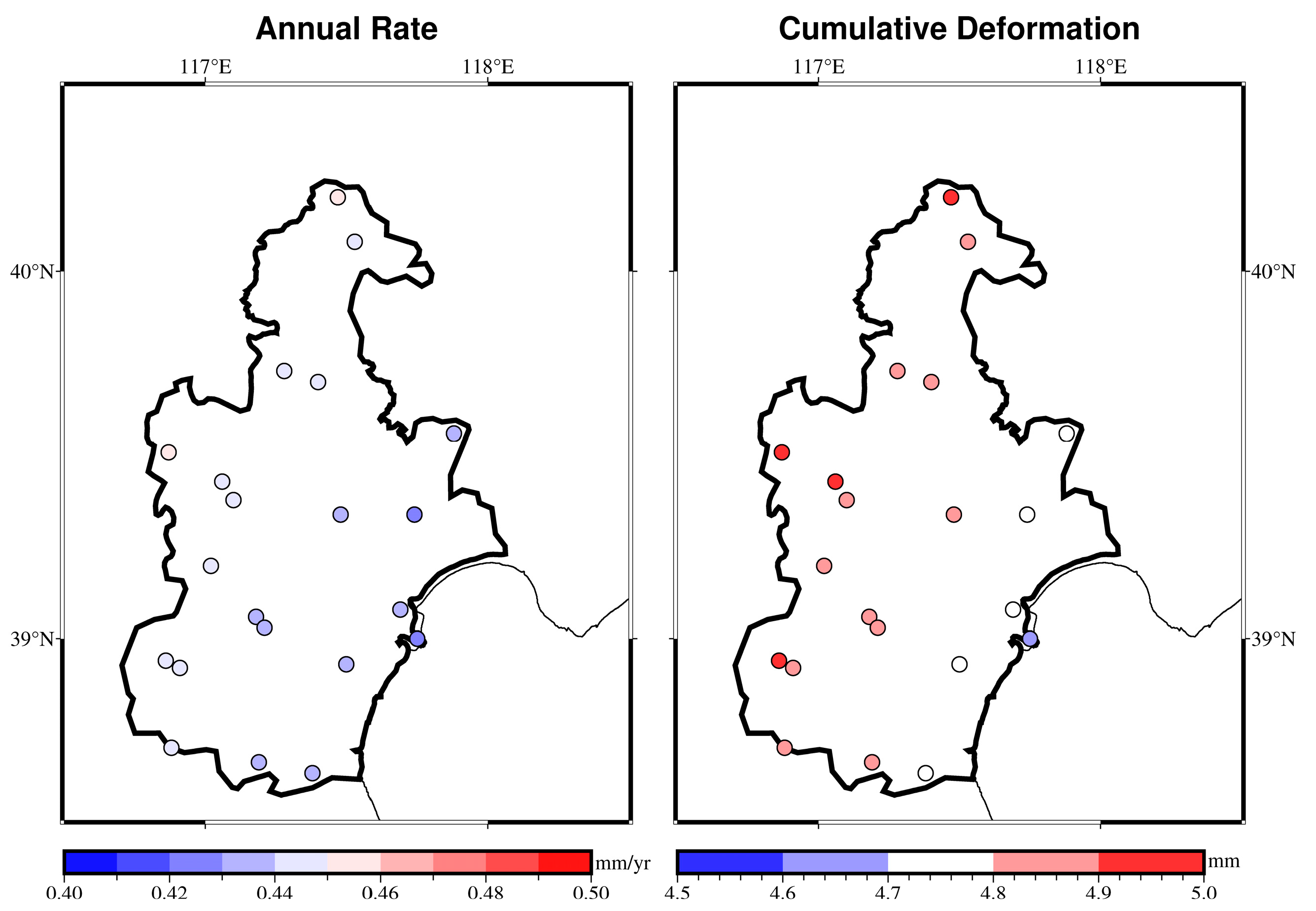
4.2. Spatial Distribution of Cumulative Subsidence
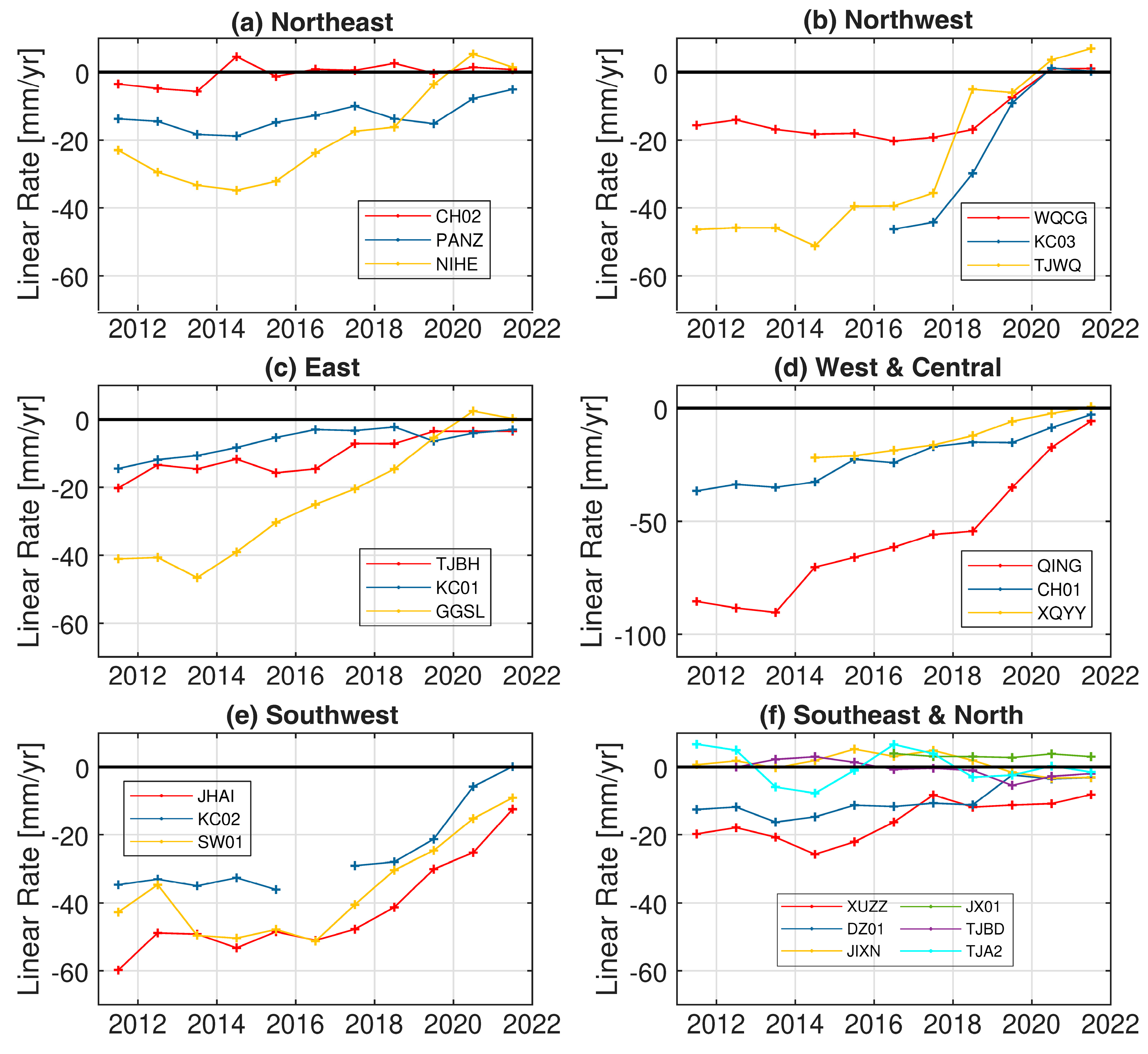
4.3. Deformation Rates during Different Periods
5. Discussion
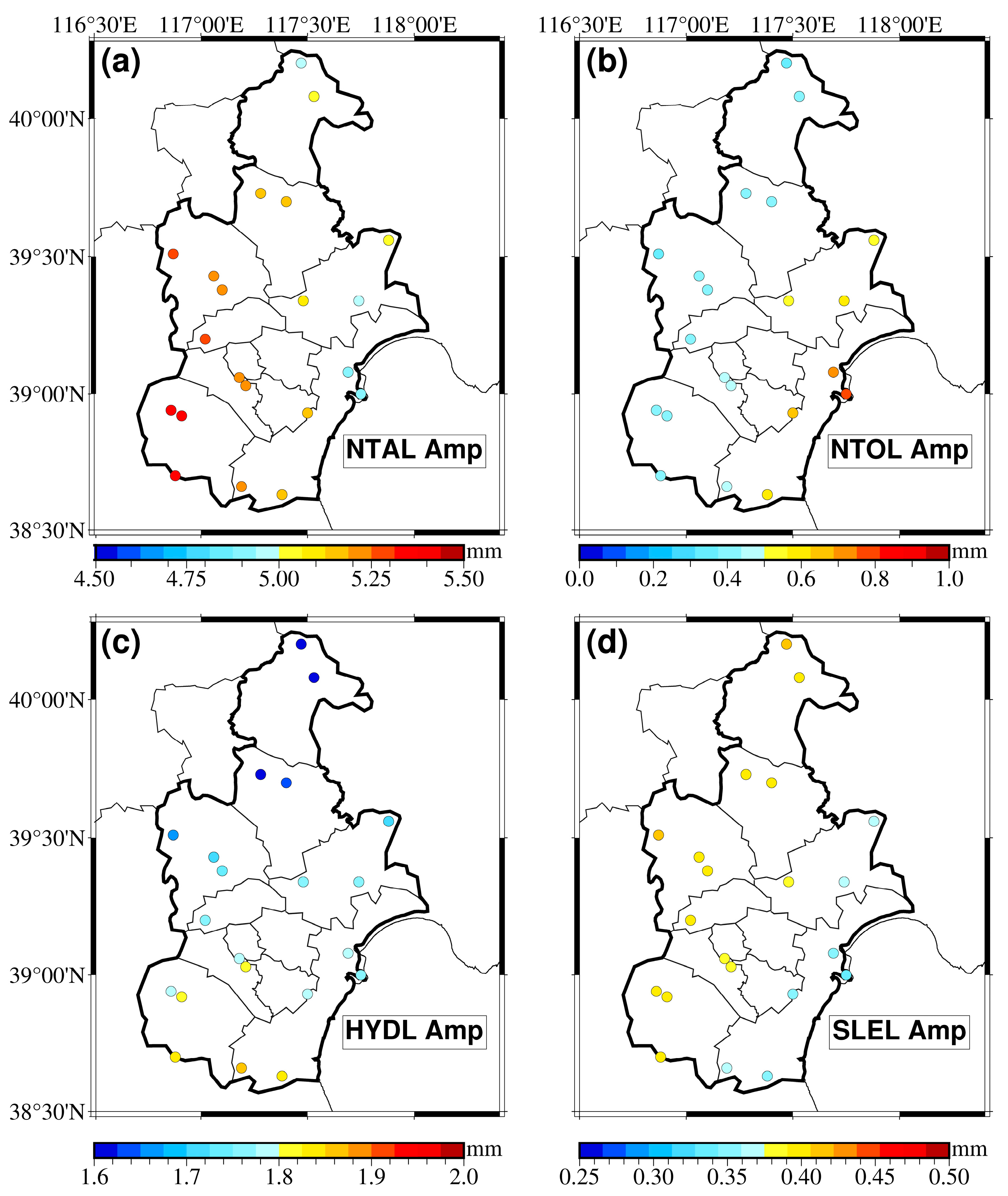
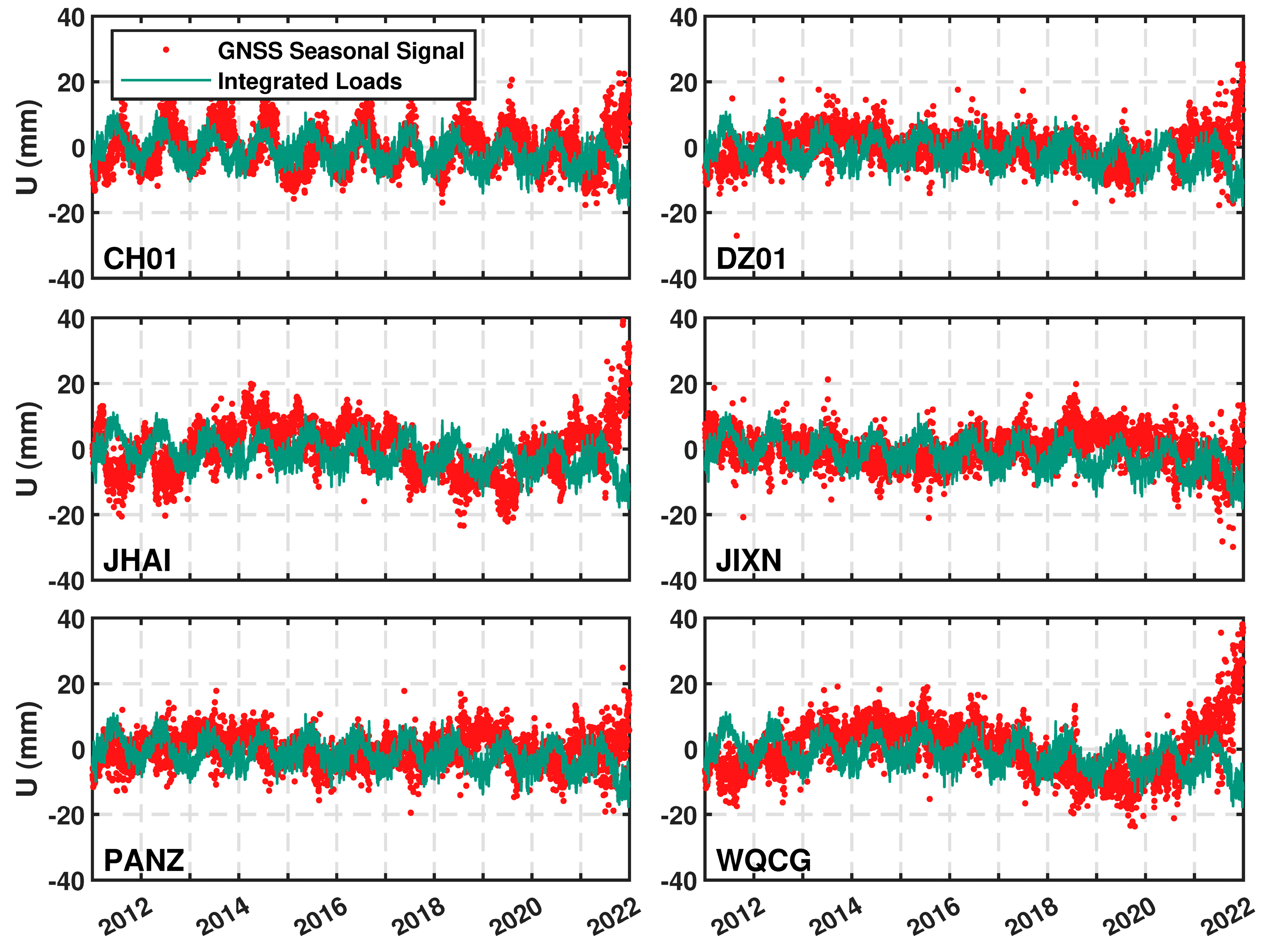
5.1. Impact of Model Predictions on Seasonal Deformation
5.2. Attribution Analysis of Weakened Subsidence in Different Regions
5.3. Relationship between Groundwater Resources and Subsidence
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, W.; Shum, C.; Zhong, M.; Pan, Y. Groundwater Storage Changes in China from Satellite Gravity: An Overview. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; O’Connor, D.; Hou, D.; Jin, Y.; Li, G.; Zheng, C.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Luo, J. Groundwater depletion and contamination: Spatial distribution of groundwater resources sustainability in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, S.M.; Zheng, C. Global change and the groundwater management challenge. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3031–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hou, E. Groundwater dynamic response mechanism and quantity vulnerability assessment under the influence of human activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 22046–22064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Zhong, M.; Lemoine, J.M.; Biancale, R.; Hsu, H.T.; Xia, J. Evaluation of groundwater depletion in North China using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data and ground-based measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Shi, L.; Zeng, J.; Yang, J.; Zha, Y.; Yao, Y.; Cao, G. Estimation of actual irrigation amount and its impact on groundwater depletion: A case study in the Hebei Plain, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Ge, L.; Ng, A.H.-M.; Lian, X.; Zhu, Q.; Horgan, F.G.; Zhang, Q. Analysis of the impact of the South-to-North water diversion project on water balance and land subsidence in Beijing, China between 2007 and 2020. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ling, M.; Chen, F.; Ding, Y.; Lv, C. Practices of groundwater over-exploitation control in Hebei Province. Water Policy 2020, 22, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, G.; Li, W.; Li, T.; Jiao, J.J. Groundwater-derived land subsidence in the North China Plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, G.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Bao, Y. Land Subsidence in Tianjin, China: Before and after the South-to-North Water Diversion. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, C. Long-term groundwater storage changes and land subsidence development in the North China Plain (1971–2015). Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, B.; Yao, Y.; Wu, W.; Meng, G.; Chen, Q. Geodetic and hydrological measurements reveal the recent acceleration of groundwater depletion in North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhong, B.; Li, X.; Zheng, K.; Liang, H.; Cao, J.; Yan, X.; Lyu, H. Analysis of groundwater changes (2003–2020) in the North China Plain using geodetic measurements. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Cao, G.; Zhao, C.; Liu, R.; Wang, H. Quantifying the influence of long-term overexploitation on deep groundwater resources across Cangzhou in the North China Plain using InSAR measurements. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Peng, J.; Ji, L. Deformation at longyao ground fissure and its surroundings, North China Plain, revealed by ALOS PALSAR PS-InSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 67, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zou, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y. Vertical Displacements Driven by Groundwater Storage Changes in the North China Plain Detected by GPS Observations. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lixin, Y.; Fang, Z.; He, X.; Shijie, C.; Wei, W.; Qiang, Y. Land subsidence in Tianjin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 62, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Gong, H.; Du, D.; Wang, H.; Teatini, P. Land Subsidence Evolution and Simulation in the Western Coastal Area of Bohai Bay, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, G.; Bao, Y.; Su, G.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Preventing Subsidence Reoccurrence in Tianjin: New Preconsolidation Head and Safe Pumping Buffer. Ground Water 2024. Early View. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, G.; Wu, Y.; Zhan, W.; Zheng, Z.; Chang, L.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of land subsidence caused by groundwater depletion in the North China plain during the past six decades. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, H. South-to-north Water Transfer Schemes for China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2002, 18, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, J.; Xue, L.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, B.; Hu, L. Characterization of Aquifer System and Groundwater Storage Change Due to South-to-North Water Diversion Project at Huairou Groundwater Reserve Site, Beijing, China, Using Geodetic and Hydrological Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Xue, Y.; Wu, J.; Yan, X.; Yu, J. Progression and mitigation of land subsidence in China. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 24, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Duan, Q.; Yeh, P.J.-F.; Pan, Y.; Gong, H.; Moradkhani, H.; Gong, W.; Lei, X.; Liao, W.; Xu, L.; et al. Sub-regional groundwater storage recovery in North China Plain after the South-to-North water diversion project. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Long, D.; Scanlon, B.R.; Burek, P.; Zhang, C.; Han, Z.; Butler, J.J.; Pan, Y.; Lei, X.; Wada, Y. Human Intervention Will Stabilize Groundwater Storage across the North China Plain. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Xiong, C.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Chen, X.; An, H.; Qin, L. Coupled processes of groundwater dynamics and land subsidence in the context of active human intervention, a case in Tianjin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-M.; Kong, F.-Z.; Zhan, C.-S. Assessment of water resources carrying capacity in Tianjin City of China. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 857–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.; Zheng, G.; Loáiciga, H.A.; Guo, W.; Zhou, H.; Chai, J. Long-term groundwater level changes and land subsidence in Tianjin, China. Acta Geotech. 2020, 16, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-X.; Lyu, H.-M.; Shen, J.S.; Arulrajah, A. Geological and hydrogeological environment in Tianjin with potential geohazards and groundwater control during excavation. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Q.; Yang, S. Noise analysis of continuous GPS coordinate time series for CMONOC. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 49, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, T.; King, R.; Floyd, M.; McClusky, S. GAMIT reference manual: GPS analysis at MIT, release 10.7; department of Earth. Atmos. Planet. Sci. 2018. Available online: http://geoweb.mit.edu/gg/docs/GAMIT_Ref.pdf (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Ghaderpour, E. JUST: MATLAB and python software for change detection and time series analysis. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderpour, E.; Vujadinovic, T. Change Detection within Remotely Sensed Satellite Image Time Series via Spectral Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razeghi, M.; Tregoning, P.; Shirzaei, M.; Ghobadi-Far, K.; McClusky, S.; Renzullo, L. Characterization of Changes in Groundwater Storage in the Lachlan Catchment, Australia, Derived from Observations of Surface Deformation and Groundwater Level Data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2022JB024669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, R.; Dobslaw, H. Numerical simulations of global-scale high-resolution hydrological crustal deformations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 5008–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Dehecq, A. An assessment of the ICE6G_C(VM5a) glacial isostatic adjustment model. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 3939–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard Peltier, W.; Argus, D.F.; Drummond, R. Comment on “An assessment of the ICE-6G_C (VM5a) glacial isostatic adjustment model” by Purcell et al. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-J.; Fu, Y.; Bürgmann, R.; Hsu, S.-Y.; Lin, C.-C.; Tang, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-M. Assessing seasonal and interannual water storage variations in Taiwan using geodetic and hydrological data. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2020, 550, 116532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Yuan, L.; Cheng, S.; Feng, W.; Tang, M.; Yang, X. Insights into hydrological drought characteristics using GNSS-inferred large-scale terrestrial water storage deficits. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2022, 578, 117294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Kaihua, W.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Ma, Y.; Ma, J. Prospect and theory of GNSS coordinate time series analysis. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2018, 43, 2112–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, G.; Yu, X.; Sun, X.; Bao, Y.; Xiao, G.; Gan, W.; Shen, S. Rapid Land Subsidence in Tianjin, China Derived from Continuous GPS Observations (2010–2019). Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2020, 382, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Gong, H.; Gao, M.; Chen, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, C. Recent Ground Subsidence in the North China Plain, China, Revealed by Sentinel-1A Datasets. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Wang, S.; Lee, C.; Li, M. Characteristics and trends of land subsidence in Tanggu, Tianjin, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2002, 61, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Hou, T.; Li, Y. Evolution of Groundwater Dynamic under the Influence of Treatment of Groundwater Overexploitation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebe Plain. J. China Hydrol. 2022, 5, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.-L.; Xu, Y.-S. Numerical evaluation of land subsidence induced by groundwater pumping in Shanghai. Can. Geotech. J. 2011, 48, 1378–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Shen, S.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, X.L. 1D Analysis of Land Subsidence in Shanghai. Lowl. Technol. Int. 2005, 7, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatopoulos, C.; Petridis, P.; Parcharidis, I.; Foumelis, M. A method predicting pumping-induced ground settlement using back-analysis and its application in the Karla region of Greece. Nat. Hazards 2018, 92, 1733–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhu, T.; Tang, W.; Jiang, M.; Jiang, H.; Yang, C.; Zhan, W.; Ming, Z.; Zhang, S. Inferring decelerated land subsidence and groundwater storage dynamics in Tianjin–Langfang using Sentinel-1 InSAR. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 1526–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K. Principles of Soil Mechanics: I—Phenomena of Cohesion of Clays; Engineering News-Record: New York, NY, USA, 1925; Volume 95. [Google Scholar]
- Ziaie, A.; Rahnama, M.B. Prediction of Single Well Land Subsidence Due to Ground Water Drainage. Int. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 2, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Shen, W.-B.; Wu, W.; Zhang, B.; Pan, Y. Recent Surface Deformation in the Tianjin Area Revealed by Sentinel-1A Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, P.; Luis, J.F.; Uieda, L.; Scharroo, R.; Wobbe, F.; Smith, W.H.F.; Tian, D. The Generic Mapping Tools Version 6. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2019, 20, 5556–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Guo, H.; Qiu, K.; Tang, M.; Yang, X.; Liu, J. South-to-North Water Diversion Halting Long-Lived Subsidence in Tianjin, North China Plain. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3213. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173213
Jiang Z, Zhu J, Guo H, Qiu K, Tang M, Yang X, Liu J. South-to-North Water Diversion Halting Long-Lived Subsidence in Tianjin, North China Plain. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(17):3213. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173213
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Zhongshan, Juyan Zhu, Haipeng Guo, Keshan Qiu, Miao Tang, Xinghai Yang, and Jinyu Liu. 2024. "South-to-North Water Diversion Halting Long-Lived Subsidence in Tianjin, North China Plain" Remote Sensing 16, no. 17: 3213. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173213
APA StyleJiang, Z., Zhu, J., Guo, H., Qiu, K., Tang, M., Yang, X., & Liu, J. (2024). South-to-North Water Diversion Halting Long-Lived Subsidence in Tianjin, North China Plain. Remote Sensing, 16(17), 3213. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173213








