Local Weather and Global Climate Data-Driven Long-Term Runoff Forecasting Based on Local–Global–Temporal Attention Mechanisms and Graph Attention Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
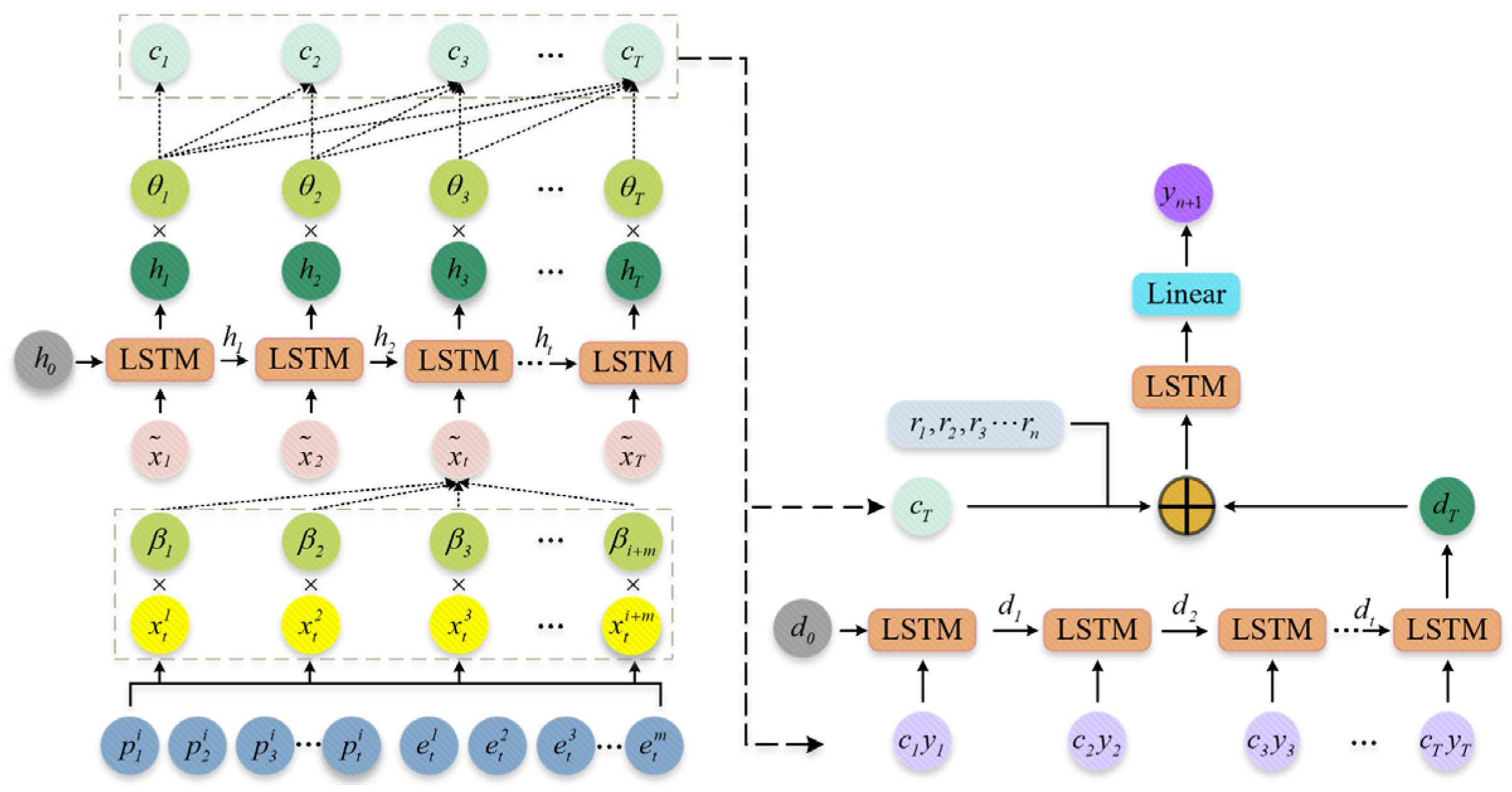
2.1. GAT–LGTA–LSTM Model
2.1.1. Graph Attention Network
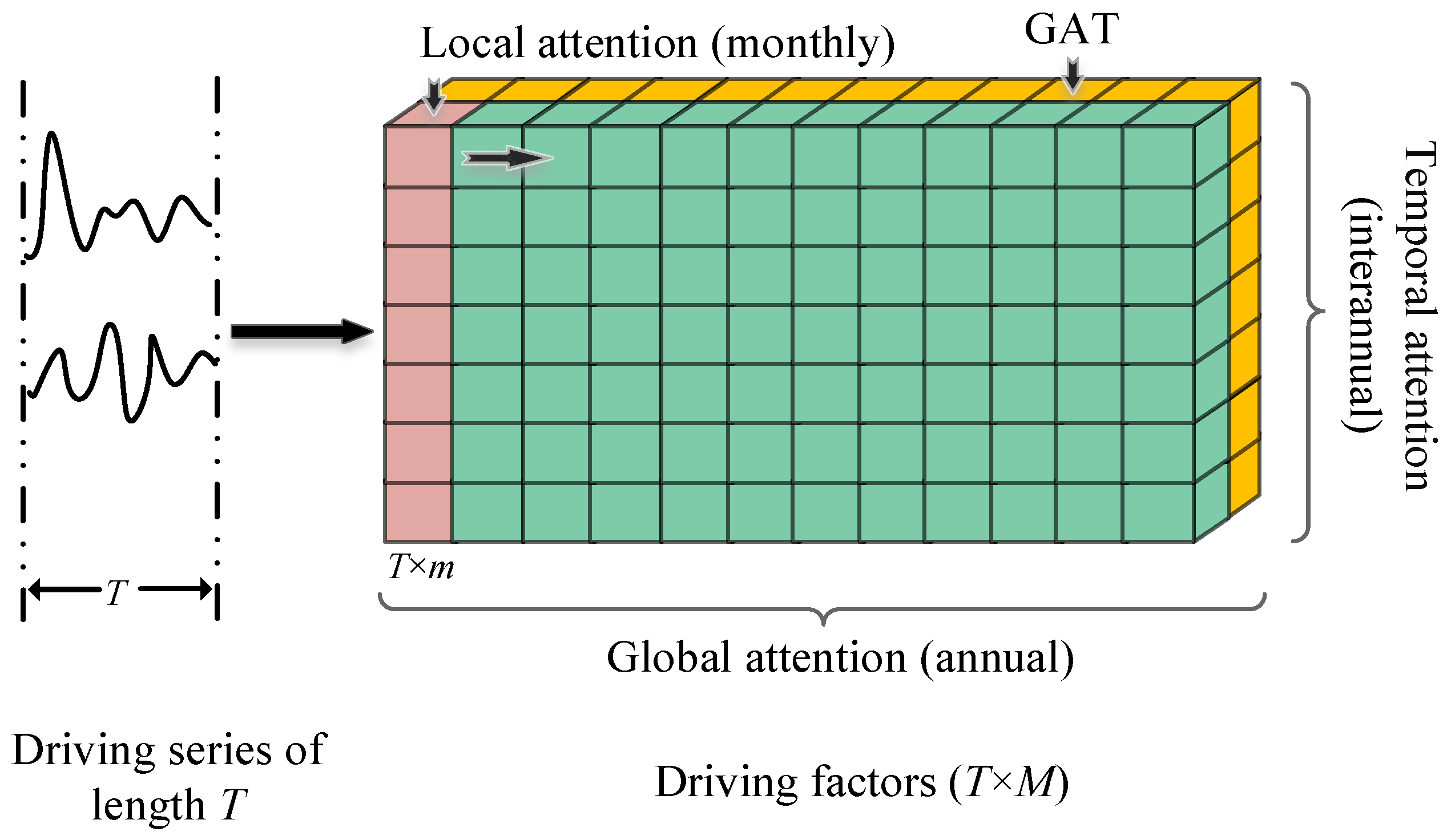
2.1.2. Extracting Crucial Information by LGAT and GAT
2.1.3. The Structure of the GAT–LGTA–LSTM Model
2.1.4. Comparative Models
2.2. Maximal Information Coefficient
2.3. Performance Metrics
3. Study Area and Model Parameters
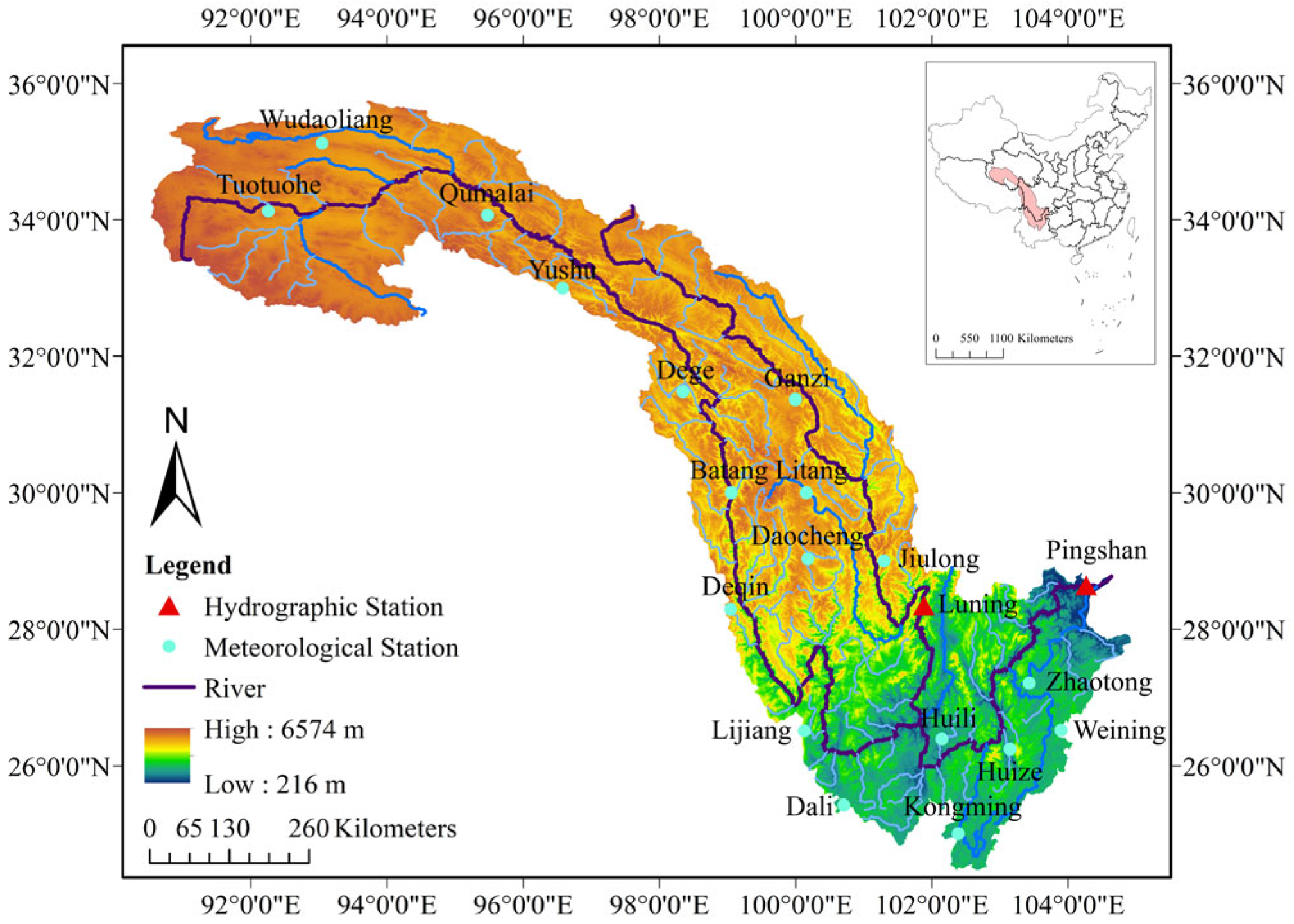
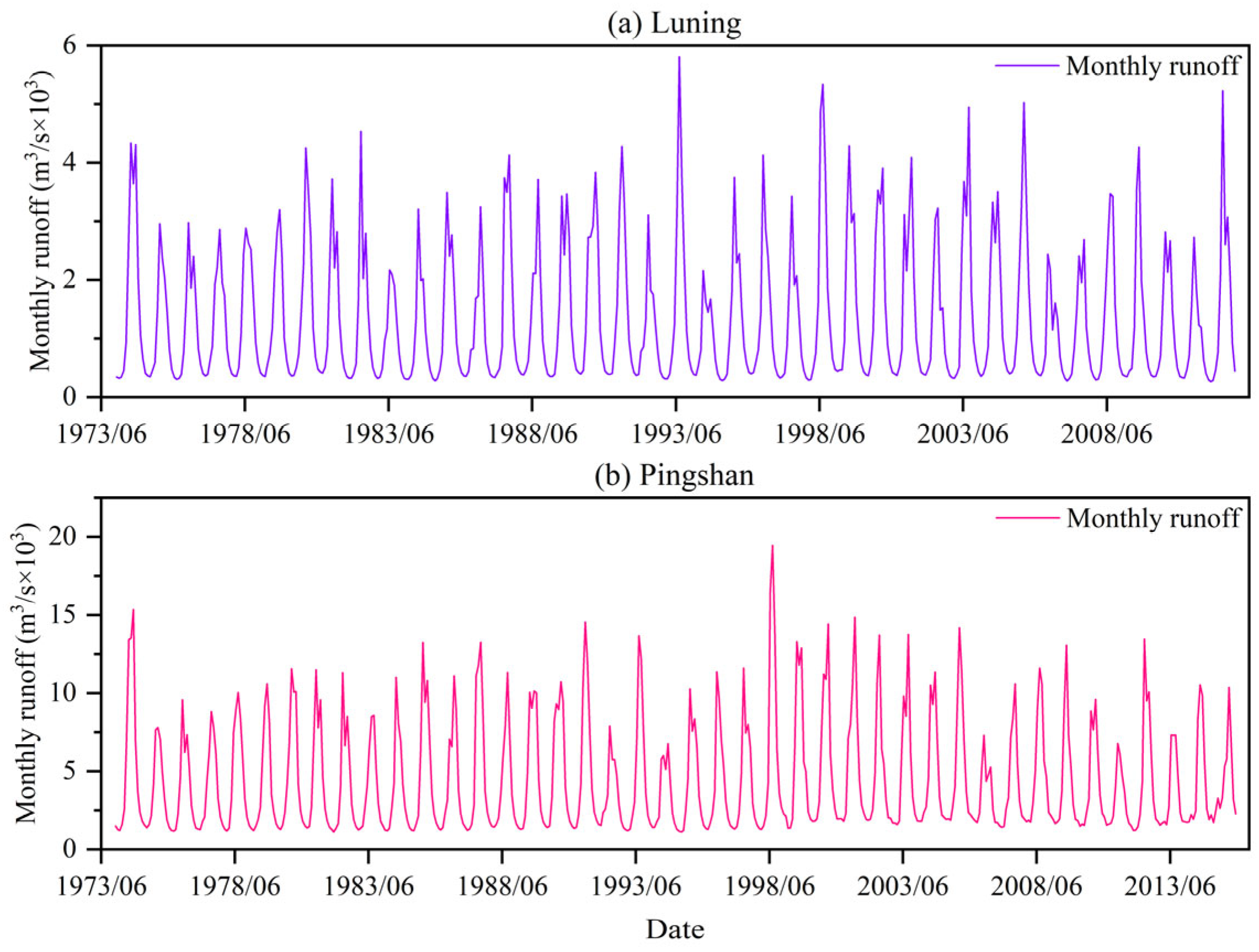
3.1. Data and Study Area
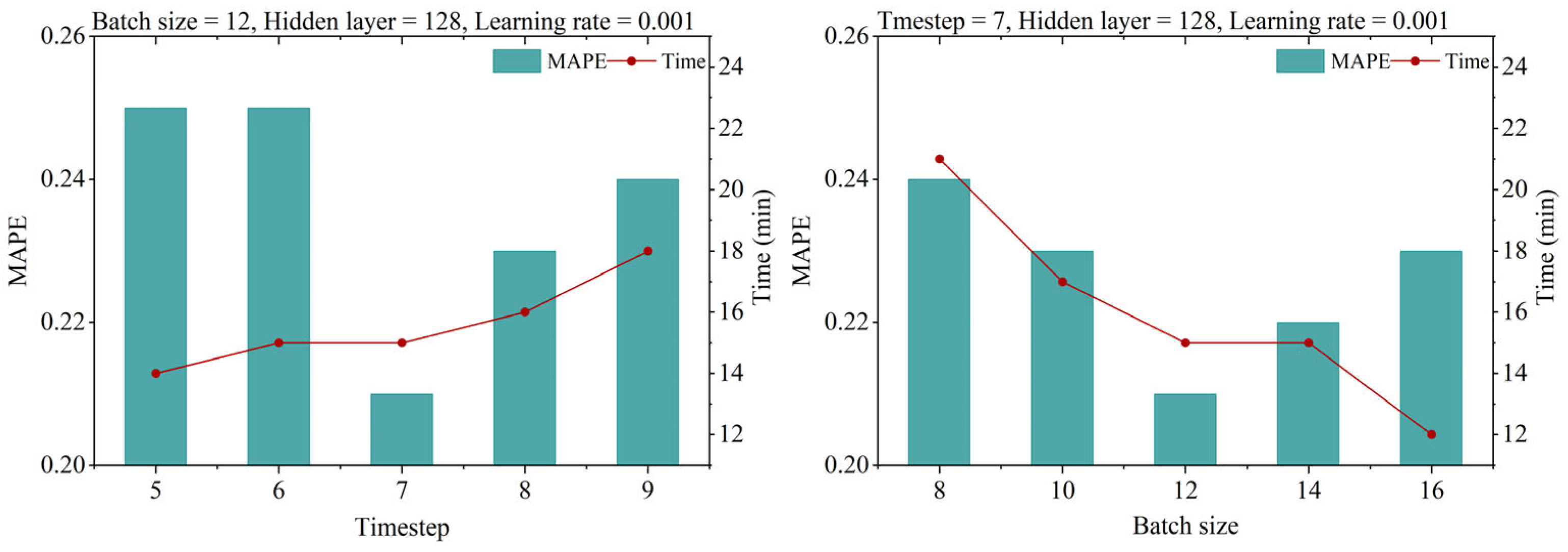
3.2. Hyperparameters of Models and Settings
4. Results
4.1. Model Comparison and Analysis
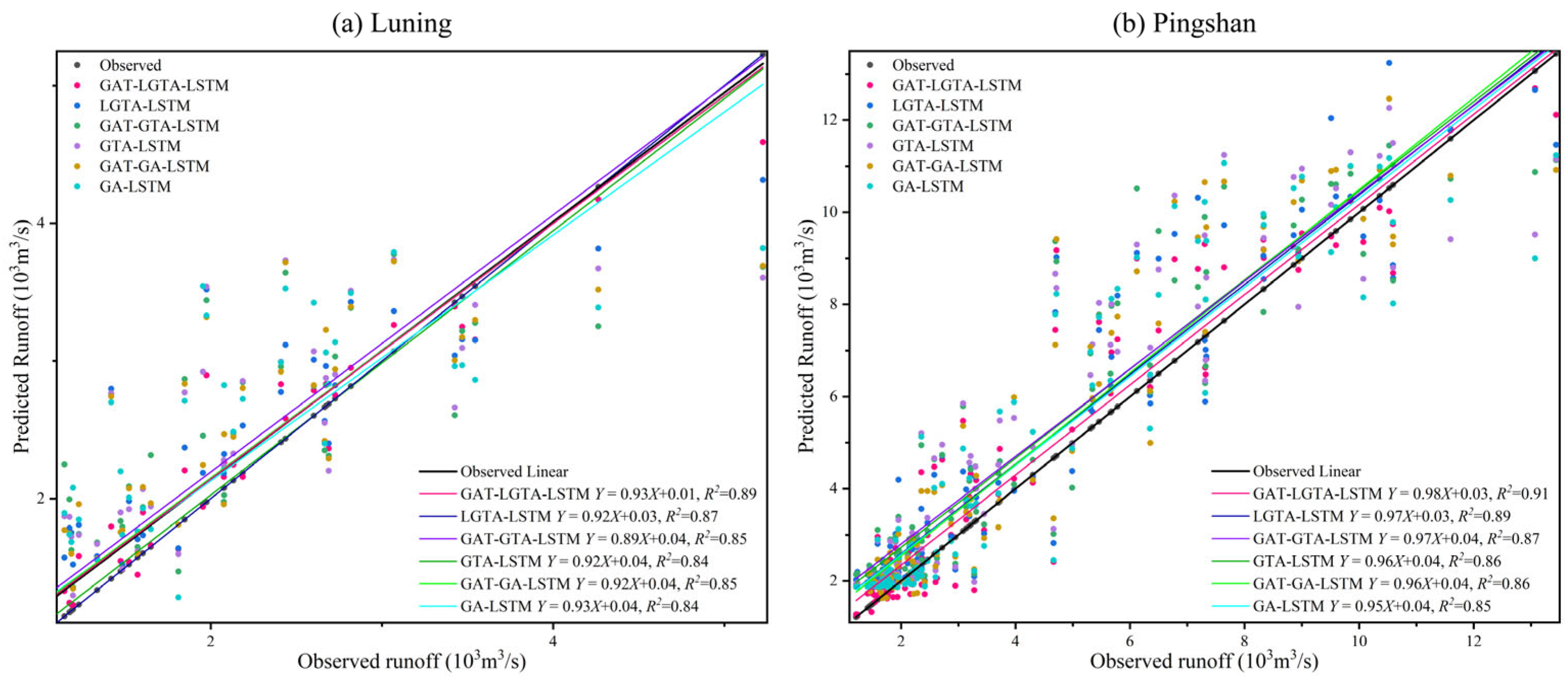
4.2. Evaluation of Prediction Results
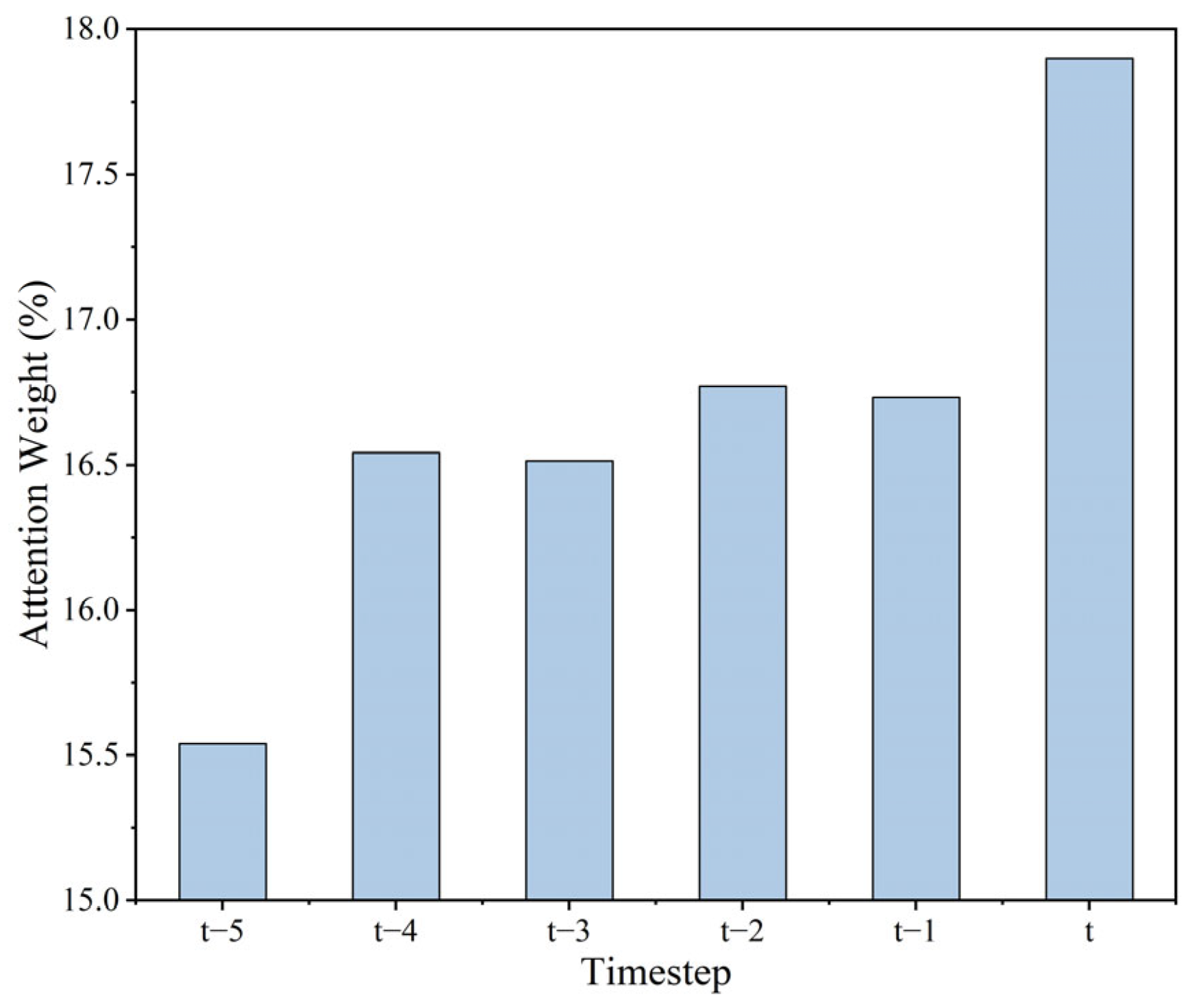
4.3. Visual Attention Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Underlying Mechanisms Used in the Proposed Model for Extracting Global Climate Indices Information
5.2. Underlying Mechanisms Used in the Proposed Model to Extract Precipitation Information
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Hydrographic Station | Prediction Month | Number | Name | Related Index Month |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pingshan | December | 09 | PNA | January |
| 20 | SOI | January | ||
| 09 | PNA | March | ||
| 19 | AMO | June | ||
| 05 | TPR1 | August | ||
| 06 | TPR2 | August | ||
| 19 | AMO | August | ||
| 06 | TPR2 | November | ||
| January | 18 | WPWP | August | |
| 19 | AMO | August | ||
| 18 | WPWP | September | ||
| February | 18 | WPWP | March | |
| 17 | IOWP | June | ||
| 18 | WPWP | June | ||
| 18 | WPWP | July | ||
| 18 | WPWP | August | ||
| 19 | AMO | August | ||
| 18 | WPWP | September | ||
| March | 16 | WHWP | August | |
| 18 | WPWP | August | ||
| 19 | AMO | August | ||
| 18 | WPWP | September | ||
| 18 | WPWP | October | ||
| April | 17 | IOWP | January | |
| 06 | TPR2 | March | ||
| 20 | SOI | March | ||
| 18 | WPWP | August | ||
| 19 | AMO | August | ||
| 07 | AO | October | ||
| 18 | WPWP | October | ||
| May | 05 | TPR1 | April | |
| 06 | TPR2 | April | ||
| 08 | NAO | April | ||
| 19 | AMO | May | ||
| 15 | Niño A | October | ||
| 08 | NAO | October | ||
| 02 | APV | November | ||
| 06 | TPR2 | December | ||
| 21 | QBO | December | ||
| June | 11 | Niño 1 + 2 | January | |
| 12 | Niño 3 | February | ||
| 01 | WPSH | May | ||
| July | 15 | Niño A | January | |
| 11 | Niño 1 + 2 | January | ||
| 19 | AMO | February | ||
| 17 | IOWP | June | ||
| 09 | PNA | August | ||
| August | 19 | AMO | February | |
| 02 | APV | April | ||
| 12 | Niño 3 | April | ||
| 09 | PNA | August | ||
| 03 | NHPV | September | ||
| 04 | EAT | November | ||
| September | 19 | AMO | March | |
| 21 | QBO | April | ||
| 02 | APV | July | ||
| 03 | NHPV | August | ||
| 08 | NAO | August | ||
| October | 16 | WHWP | April | |
| 05 | TPR1 | September | ||
| 06 | TPR2 | September | ||
| 04 | EAT | September | ||
| November | 20 | SOI | January | |
| 13 | Niño 4 | July | ||
| 06 | TPR2 | October | ||
| 04 | EAT | October | ||
| Luning | December | 06 | TPR2 | November |
| 15 | Niño A | June | ||
| 19 | AMO | June | ||
| January | 06 | TPR2 | December | |
| 18 | WPWP | August | ||
| 19 | AMO | August | ||
| February | 06 | TPR2 | January | |
| 18 | WPWP | July | ||
| 07 | AO | December | ||
| March | 16 | WHWP | August | |
| 15 | Niño A | June | ||
| 18 | WPWP | August | ||
| 06 | TPR2 | February | ||
| April | 18 | WPWP | September | |
| 06 | TPR2 | March | ||
| 18 | WPWP | October | ||
| May | 21 | QBO | July | |
| 16 | WHWP | September | ||
| 02 | APV | October | ||
| 10 | AZC | October | ||
| 06 | TPR2 | April | ||
| June | 01 | WPSH | May | |
| 11 | Niño 1 + 2 | January | ||
| 21 | QBO | July | ||
| July | 19 | AMO | February | |
| 12 | Niño 3 | May | ||
| 21 | QBO | June | ||
| 09 | PNA | August | ||
| 15 | Niño A | January | ||
| 11 | Niño 1 + 2 | January | ||
| August | 12 | Niño 3 | April | |
| 09 | PNA | August | ||
| 03 | NHPV | September | ||
| 10 | AZC | November | ||
| September | 07 | AO | February | |
| 03 | NHPV | August | ||
| 02 | APV | August | ||
| October | 10 | AZC | March | |
| 09 | PNA | April | ||
| 13 | Niño 4 | September | ||
| 06 | TPR2 | September | ||
| November | 16 | WHWP | March | |
| 19 | AMO | June | ||
| 06 | TPR2 | October | ||
| 08 | NAO | August |
References
- Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hua, C.; Shu, Z. A Review of Medium-Long Term Runoff Prediction. Water Resour. Prot. 2023, 39, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, B.; Chen, L.; Yang, B.; Li, S.; Leng, Z. Influences of the Runoff Partition Method on the Flexible Hybrid Runoff Generation Model for Flood Prediction. Water 2023, 15, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J. Application of a New Hybrid Deep Learning Model That Considers Temporal and Feature Dependencies in Rainfall–Runoff Simulation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.; Kiem, A.S.; Willgoose, G. A linked surface water-groundwater modelling approach to more realistically simulate rainfall-runoff non-stationarity in semi-arid regions. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Han, D.; Wang, G.; Shen, C. Physics-guided deep learning for rainfall-runoff modeling by considering extreme events and monotonic relationships. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, A.; AghaKouchak, A.; Phillips, T.J. Evaluation of CMIP5 continental precipitation simulations relative to satellite-based gauge-adjusted observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Demir, I. Distributed long-term hourly streamflow predictions using deep learning–A case study for State of Iowa. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2020, 131, 104761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Luo, J.; Li, P.; Zuo, G.; Xie, J. A hybrid model based on variational mode decomposition and gradient boosting regression tree for monthly runoff forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 865–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, G.B.; Gibbs, M.S.; Dandy, G.C.; Maier, H.R. A hybrid approach to monthly streamflow forecasting: Integrating hydrological model outputs into a Bayesian artificial neural network. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chang, J.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Y. Monthly streamflow prediction using modified EMD-based support vector machine. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, M.; Chua, L.H.C.; Quek, C.; Qin, X. A fully-online Neuro-Fuzzy model for flow forecasting in basins with limited data. J. Hydrol. 2017, 545, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Feng, K.; Cheng, P.; Li, R.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L. Adaptive prediction for effluent quality of wastewater treatment plant: Improvement with a dual-stage attention-based LSTM network. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 359, 120887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, C.; Lei, X.; Yuan, Y.; Muhammad Adnan, R. Monthly runoff forecasting based on LSTM–ALO model. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk A 2018, 32, 2199–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widya, L.K.; Rezaie, F.; Lee, W.; Lee, C.-W.; Nurwatik, N.; Lee, S. Flood susceptibility mapping of Cheongju, South Korea based on the integration of environmental factors using various machine learning approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 364, 121291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, I.F.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, L.-C.; Chang, F.-J. Exploring a Long Short-Term Memory based Encoder-Decoder framework for multi-step-ahead flood forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.; Xu, B.; Zhong, P.-A.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H.; Yue, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J. Long-term probabilistic streamflow forecast model with “inputs–structure–parameters” hierarchical optimization framework. J. Hydrol. 2023, 622, 129736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursun, A.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Peng, D.; Zheng, B. Enhancing streamflow simulation in large and human-regulated basins: Long short-term memory with multiscale attributes. J. Hydrol. 2024, 630, 130771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjani, M.; Mahdianpari, M.; Mohammadimanesh, F. CNN-BiLSTM: A Novel Deep Learning Model for Near-Real-Time Daily Wildfire Spread Prediction. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Qin, H.; Liu, G.; Yang, X.; Xu, Z.; Jia, B.; Zhang, Q. A Method for Spatiotemporally Merging Multi-Source Precipitation Based on Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P. Raw Water Supply System Operation and Risk Research with Considering Forecast Uncertainty under Low Water Scenario. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Zhejiang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Jia, B.; Hu, G. Monthly runoff prediction based on teleconnection factors selection using random forest model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2022, 41, 32–45. [Google Scholar]
- Urbanowicz, R.J.; Meeker, M.; La Cava, W.; Olson, R.S.; Moore, J.H. Relief-based feature selection: Introduction and review. J. Biomed. Inform. 2018, 85, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.-H.; Vu, T.M.; Chen, P.-Y. Multiple drought indices and their teleconnections with ENSO in various spatiotemporal scales over the Mekong River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158589. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y. Nonlinear Responses of Extreme Streamflow to Climate Variability in Europe. Ph.D. Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Libera, D.A.; Kheimi, M.; Sankarasubramanian, A.; Wang, D. The roles of climate forcing and its variability on streamflow at daily, monthly, annual, and long-term scales. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunjo, S.T.; Fuwape, I.A. Nonlinear characterization and interaction in teleconnection patterns. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 2723–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Xu, H.; Ma, J. Atmospheric Circulation Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events and Impact of Sea Surface Temperature over the Southern China in the Autumn of 2016. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci 2021, 45, 1023–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Tong, X.; Xie, H. Combined influence of solar activity and ENSO on hydrological processes in Yoshino River basin, Japan. AWS Adv. Water Sci. 2017, 28, 671–680. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Su, H.; Wen, J. Classification of flower image based on attention mechanism and multi-loss attention network. Comput. Commun. 2021, 179, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ge, K.; Zhang, X.; Lin, L. Real-time attention based look-alike model for recommender system. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 2765–2773. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Shao, F.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L. Improved Architecture and Training Strategies of YOLOv7 for Remote Sensing Image Object Detection. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Wu, Y.; Li, X. Attention mechanism for neural machine translation: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 5th Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC), Xi’an China, 15–17 October 2021; pp. 1485–1489. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Kang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, P.; Song, S. A hybrid model integrating Elman neural network with variational mode decomposition and Box–Cox transformation for monthly runoff time series prediction. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 3673–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.; Zohren, S. Time-series forecasting with deep learning: A survey. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2021, 379, 20200209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ruan, Y. Interpretable deep learning model for building energy consumption prediction based on attention mechanism. Energy Build. 2021, 252, 111379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qin, H.; Mao, J.; Cao, X.; Fu, G. High temporal resolution urban flood prediction using attention-based LSTM models. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Guo, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J. Exploration of dual-attention mechanism-based deep learning for multi-step-ahead flood probabilistic forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2023, 622, 129688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jin, A.; Shi, W. A hybrid self-adaptive DWT-WaveNet-LSTM deep learning architecture for karst spring forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2024, 634, 131128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Liu, P.; Xie, K.; Li, H.; Xia, Q.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, J. An attention-based LSTM model for long-term runoff forecasting and factor recognition. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 024004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, D.; Wu, X.; Tang, A. Dsanet: Dual self-attention network for multivariate time series forecasting. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Beijing, China, 3–7 November 2019; pp. 2129–2132. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, T.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Shi, Z.; Zeng, Q. Contextual Sa-Attention Convolutional LSTM for Precipitation Nowcasting: A Spatiotemporal Sequence Forecasting View. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 12479–12491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Feng, J.; Lu, T. Context and temporal aware attention model for flood prediction. In Proceedings of the Advances in Multimedia Information Processing–PCM 2018: 19th Pacific-Rim Conference on Multimedia, Hefei, China, 21–22 September 2018; Proceedings, Part I 19, 2018. pp. 545–555. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, j.; Jia, j.; Hao, Q.; Wang, D. Research on medium and long-term runoff forecast based on Copula entropy-random forest model. Yangtze River 2021, 52, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, Z. Interpretable spatio-temporal attention LSTM model for flood forecasting. Neurocomputing 2020, 403, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Luan, D.; Zhao, S.; Liao, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, J.; Pei, Q. Flood Discharge Prediction Based on Remote-Sensed Spatiotemporal Features Fusion and Graph Attention. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, S.; Li, S.S. Combining remote sensing with physical flow laws to estimate river channel geometry. River Res. Appl. 2018, 34, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M. Satellite Remote Sensing of Mixing Dynamics at a Large River Confluence. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Veličković, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Lio, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph attention networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10903. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Wan, B.; Li, C.; Tian, G.; Hou, Y.; Yuan, K. Dyadic relational graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based human interaction recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 115, 107920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Ha, K.-J.; Bae, D.-H. Projected response of global runoff to El Niño-Southern oscillation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 084037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Jin, F.; Si, Y.; Li, Z. Runoff change controlled by combined effects of multiple environmental factors in a headwater catchment with cold and arid climate in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, Q.; Liang, H.; Yang, Z. Temporal–spatial evolution of lagged response of runoff to rainfall in Karst drainage basin, Central Guizhou of China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 147, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, M.; Yan, P.; Li, G.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, H.; Yin, S. Deep learning attention mechanism in medical image analysis: Basics and beyonds. IJNDI Int. J. Netw. Dyn. Intell. 2023, 2, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, B. Parallel spatio-temporal attention-based TCN for multivariate time series prediction. Neural. Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 13109–13118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Yan, J.; Demir, I. A rainfall-runoff model with LSTM-based sequence-to-sequence learning. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR025326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Ercan, A.; Nagasato, T.; Kiyama, M.; Amagasaki, M. Use of one-dimensional CNN for input data size reduction in LSTM for improved computational efficiency and accuracy in hourly rainfall-runoff modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 359, 120931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.G.; Nikoo, M.R.; Rastad, D.; Nematollahi, B. A comparative study of data-driven models for runoff, sediment, and nitrate forecasting. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 341, 118006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, M.-T.; Pham, H.; Manning, C.D. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.04025. [Google Scholar]
- Reshef, D.N.; Reshef, Y.A.; Finucane, H.K.; Grossman, S.R.; McVean, G.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Lander, E.S.; Mitzenmacher, M.; Sabeti, P.C. Detecting novel associations in large data sets. Science 2011, 334, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, R.J.; Maier, H.R.; Dandy, G.C.; Fernando, T.M.K.G. Non-linear variable selection for artificial neural networks using partial mutual information. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2008, 23, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Han, J.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G. A new seq2seq architecture for hourly runoff prediction using historical rainfall and runoff as input. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.-M.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.-C. An ensemble model for monthly runoff prediction using least squares support vector machine based on variational modal decomposition with dung beetle optimization algorithm and error correction strategy. J. Hydrol. 2024, 629, 130558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, S.; Shao, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. A new method to improve precipitation estimates by blending multiple satellite/reanalysis-based precipitation products and considering observations and terrestrial water budget balance. J. Hydrol. 2024, 635, 131188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ju, Y.; Li, Z. Satellite-based reconstruction and spatiotemporal variability analysis of actual evapotranspiration in the Jinshajiang River basin, China. AWS 2021, 32, 182–191. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Wang, D.; Qin, L.; Deng, A.; Xing, L. The characteristic and cause of runoff variation in Jinsha River basin. South-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 21, 248–257. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Fang, H.; Huang, L.; Ouyang, W. Changing runoff due to temperature and precipitation variations in the dammed Jinsha River. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Gao, L.; Zuo, X.; Zhong, F. Statistical analyses of spatial and temporal variabilities in total, daytime, and nighttime precipitation indices and of extreme dry/wet association with large-scale circulations of Southwest China, 1961–2016. Atmos. Res. 2019, 219, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, E.; Wang, Y.; Bao, Y. Assessing spatiotemporal variation of heat waves during 1961–2016 across mainland China. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 3036–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Luo, X.; Meng, L.; Zhang, S.; Cai, W.; Wang, W. Impacts of climate change-related flood events in the Yangtze River Basin based on multi-source data. Atmos. Res. 2021, 263, 105819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Chen, J.; Corzo, G.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Xiong, L.; Liu, D.; Xia, J. Coupling Deep Learning and physically based hydrological models for monthly streamflow predictions. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR035618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Feng, T.; Shi, J.; Zhang, P. Voice activity detection using a local-global attention model. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 195, 108802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; He, S.; Tabatabaie, M. Extreme-Aware Local-Global Attention for Spatio-Temporal Urban Mobility Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 39th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), Anaheim, CA, USA, 3–7 April 2023; pp. 1059–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Tang, S.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Q. Image caption with global-local attention. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; pp. 2374–3468. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.; Wang, X.-F.; He, J.-H.; Zhang, W.-J.; Wu, J. The approach of the previous anomalous heat content in the western Pacific warm pool affecting the summer rainfall over the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Chin. J. Geophys. 2014, 57, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, K.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, S.; Liu, P.; Wu, M. Detecting multidecadal variation of short-term drought risk by combining frequency analysis and Fourier transformation methods: A case study in the Yangtze River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2024, 631, 130803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Wang, G.-X.; Oluwafemi, A.; Munir, S.; Hu, Z.-Y.; Shakoor, A.; Imran, M.A. Temperature trends and elevation dependent warming during 1965–2014 in headwaters of Yangtze River, Qinghai Tibetan Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 556–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Feng, J.; Sun, C. Impact of preceding summer North Atlantic Oscillation on early autumn precipitation over central China. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2013, 6, 417–422. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Duan, A. Relative contributions of the Tibetan Plateau thermal forcing and the Indian Ocean Sea surface temperature basin mode to the interannual variability of the East Asian summer monsoon. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 2697–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jin, F.F.; Stuecker, M.F.; Wittenberg, A.T.; Timmermann, A.; Ren, H.L.; Kug, J.S.; Cai, W.; Cane, M. Unraveling El Niño’s impact on the East Asian monsoon and Yangtze River summer flooding. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 11375–11382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, M.; Yao, X.; Wang, X. Associated impact mechanism of heavy rain and floods in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze river basin based on ocean-atmosphere anomaly patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Li, H.; Zhao, K.; Yang, Q.; Sun, H. The relationship of variability of summer temperature between Northeast China and the Northern Hemisphere and the impacts of the polar vortex. Sci. Meteorol. Sin. 2009, 29, 633–644. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, B.; Lian, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, S. Impacts of Arctic Oscillation and polar vortex anomalies on winter temperature over Eurasian continent. Progress. Inquisitiones Mutat. Clim. 2012, 8, 434–439. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Rao, J.; Guo, D.; Lu, Q.; Shi, C. Northern winter stratospheric polar vortex regimes and their possible influence on the extratropical troposphere. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 60, 3167–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ding, L. Impacts of intra-seasonal variability of the East Asian trough and the Siberian high on East Asian temperatures in the northern winter. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 47, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P. Influences of ENSO, NAO, IOD and PDO on seasonal precipitation regimes in the Yangtze River basin, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Singh, V.P.; Gu, X.; Kong, D.; Xiao, M. Impacts of ENSO and ENSO Modoki+A regimes on seasonal precipitation variations and possible underlying causes in the Huai River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, P.; Wu, C. Spatiotemporal characteristics of regional extreme precipitation in Yangtze River basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xi, H.; Zhang, J. Response of Runoff to Extreme Climate Change in the Upper Reaches of the Heihe River. J. Park. Dis. 2020, 39, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, H.M.; Fan, Y.T.; Zhang, R.B.; Yu, S.L.; Zhang, T.W.; Shou, W.W.; Liu, W.P. Streamflow variation in the eastern Pamirs and its response to climate change. ACCR 2021, 17, 352. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Luo, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z. Analysing the influences of ENSO and PDO on water discharge from the Yangtze River into the sea. Hydrol. Process 2018, 32, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linderholm, H.W.; Ou, T.; Jeong, J.H.; Folland, C.K.; Gong, D.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D. Interannual teleconnections between the summer North Atlantic Oscillation and the East Asian summer monsoon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D13107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Zou, L.; Shan, L.; She, D. Spatio-temporal variability of dryness/wetness in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Basin and correlation with large-scale climatic factors. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2019, 131, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, D.; Jiang, D.; Hu, A.; Lang, X. Variations in northeast Asian summer precipitation driven by the Atlantic multidecadal oscillation. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 1682–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, J.; Huang, R.; Chen, W. Influence of tropical western Pacific warm pool thermal state on the interdecadal change of the onset of the South China Sea summer monsoon in the late-1990s. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2015, 8, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; James, J.; Liu, Y. Spatial-temporal graph attention networks: A deep learning approach for traffic forecasting. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 166246–166256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Liu, B.; Jia, Y.; Fu, Z. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Precipitation and Runoff Response in Yalong River Basin. Pearl River 2023, 44, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.; Huang, X.; Yang, P.; Gao, Y.; Xi, Y.; Li, J. Characteristics of runoff and its hysteresis effect on rainfall in Yalong River basin. In Proceedings of the 2016 Chinese Hydraulic Engineering Society Annual Conference, Chengdu, China, 19 October 2016; pp. 506–512. [Google Scholar]




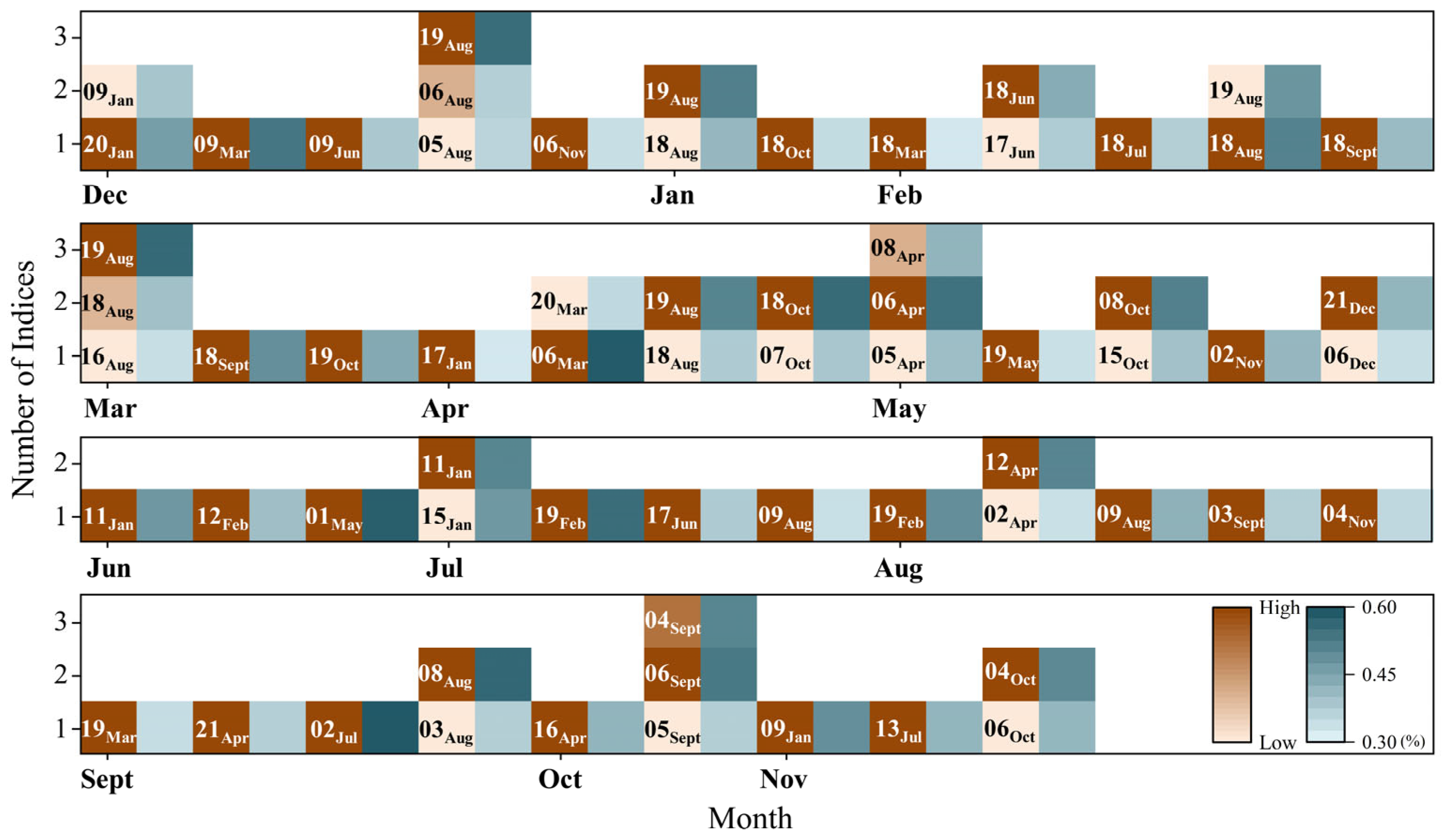


| Categories | Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Climate indices | 01 | WPSH | Western Pacific Subtropical High Ridge Position Index |
| 02 | APV | Asia Polar Vortex Intensity Index | |
| 03 | NHPV | Northern Hemisphere Polar Vortex Central Intensity Index | |
| 04 | EAT | East Asian Trough Intensity Index | |
| 05 | TPR1 | Tibet Plateau Region 1 Index | |
| 06 | TPR2 | Tibet Plateau Region-2 Index | |
| 07 | AO | Arctic Oscillation | |
| 08 | NAO | North Atlantic Oscillation | |
| 09 | PNA | Pacific North American Index | |
| 10 | AZC | Asian Zonal Circulation Index | |
| Sea Surface Temperature (SST) Indices | 11 | Niño 1 + 2 | Extreme Eastern Tropical Pacific SST (0–10S, 90–80W) |
| 12 | Niño 3 | Eastern Tropical Pacific SST (5N–5S, 150–90W) | |
| 13 | Niño 4 | Central Tropical Pacific SST (5N–5S, 160E−150W) | |
| 14 | Niño 3.4 | East Central Tropical Pacific SST (5N–5S, 170–120W) | |
| 15 | Niño A | Western Tropical Pacific SST (25N–35N, 130–150E) | |
| 16 | WHWP | Western Hemisphere Warm Pool Index | |
| 17 | IOWP | Indian Ocean Warm Pool Strength Index | |
| 18 | WPWP | Western Pacific Warm Pool Area Index | |
| 19 | AMO | Atlantic Multi-decadal Oscillation Index | |
| Other Indices | 20 | SOI | Southern Oscillation Index |
| 21 | QBO | Quasi-Biennial Oscillation Index |
| Station | Model | Training | Testing | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSE | KGE | MAPE | MAE (m3/s) | NSE | KGE | MAPE | MAE (m3/s) | ||
| Luning | GAT–LGTA–LSTM | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.22 | 225.83 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.24 | 251.59 |
| LGTA–LSTM | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.23 | 241.64 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.26 | 287.42 | |
| GAT–GTA–LSTM | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.24 | 257.28 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.29 | 303.18 | |
| GTA–LSTM | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.26 | 275.72 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.35 | 344.75 | |
| GAT–GA–LSTM | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.25 | 263.85 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.32 | 312.74 | |
| GA–LSTM | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.26 | 281.11 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.35 | 330.65 | |
| Pingshan | GAT–LGTA–LSTM | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.16 | 642.19 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.18 | 683.29 |
| LGTA–LSTM | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.23 | 720.01 | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.25 | 812.33 | |
| GAT–GTA–LSTM | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.24 | 739.55 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.27 | 869.98 | |
| GTA–LSTM | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.25 | 750.50 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.30 | 995.08 | |
| GAT–GA–LSTM | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.25 | 784.06 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.27 | 893.82 | |
| GA–LSTM | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.25 | 769.46 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.31 | 920.79 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, B.; Chen, L.; Yi, B.; Li, S.; Leng, Z. Local Weather and Global Climate Data-Driven Long-Term Runoff Forecasting Based on Local–Global–Temporal Attention Mechanisms and Graph Attention Networks. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3659. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193659
Yang B, Chen L, Yi B, Li S, Leng Z. Local Weather and Global Climate Data-Driven Long-Term Runoff Forecasting Based on Local–Global–Temporal Attention Mechanisms and Graph Attention Networks. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(19):3659. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193659
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Binlin, Lu Chen, Bin Yi, Siming Li, and Zhiyuan Leng. 2024. "Local Weather and Global Climate Data-Driven Long-Term Runoff Forecasting Based on Local–Global–Temporal Attention Mechanisms and Graph Attention Networks" Remote Sensing 16, no. 19: 3659. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193659
APA StyleYang, B., Chen, L., Yi, B., Li, S., & Leng, Z. (2024). Local Weather and Global Climate Data-Driven Long-Term Runoff Forecasting Based on Local–Global–Temporal Attention Mechanisms and Graph Attention Networks. Remote Sensing, 16(19), 3659. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193659








