Abstract
Research on augmentation and supplement systems for navigation systems has become a significant aspect in comprehensive positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) studies. The BeiDou-3 navigation satellite system (BDS-3) has constructed a dynamic inter-satellite network to gain more observation data than ground monitoring stations. Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites have advantages in their kinematic velocity and information carrying rate and can be used as satellite-based monitoring stations for navigation satellites to make up for the distribution limitation of ground monitoring stations. This study constructs multi-source observation links with satellite-to-ground, inter-satellite and satellite-based observation data, proposes an orbit synchronization method for navigation satellites and LEO satellites and verifies the influence thereof on orbit accuracy with different observation data. The experimental results under conditions of real and simulated observation data showed the following: (1) With the support of satellite-based observation links, the orbit accuracy of the BDS-3 MEO satellites could be improved significantly, with a 78% improvement with the simulation data and a 76% improvement with the real data. When the navigation satellites leave the monitoring area of the ground monitoring stations, the accuracy reduction tendency of the orbit prediction could also be slowed down with the support of the LEO satellites and the accuracy could be maintained within centimeters. (2) Comparing the orbit accuracy with the support of the satellite-to-ground observation links, the orbit accuracy of the MEO satellites could be improved by 65.5%, 73.7% and 79.4% with the support of the 6, 12 and 60 LEO satellites, respectively. When the observation geometry and the covering multiplicity meet the basic requirement of orbit determination, the improvements to the orbit accuracy decrease with the growth of LEO satellite numbers. (3) The accuracy of orbit determination with the support of the LEO satellites or the inter-satellite links was at the centimeter level for both, verifying that inter-satellite links and satellite-based links can be used as each other’s backups for navigation satellites. (4) The accuracy of orbit determination with the multi-source observation links was also at the centimeter level, which was not better than the results with the support of the satellite-to-ground and inter-satellite links or the satellite-to-ground and satellite-based links.
1. Introduction
The BeiDou-3 navigation satellite system (BDS-3) has officially provided positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) services to global users since 31 July 2020. Compared with the BDS-2 [1,2], it has realized the leap from providing a regional service to a global service. The progress from the Beidou-2 regional service to the Beidou-3 global service is inseparable from the engineering implementation of inter-satellite link technology [3]. The BDS-3 possesses a dynamic wireless network with precision measurement and data transmission functions, which can realize the rapid distribution and return of information throughout the whole constellation. The inbound rate of the effective data within inter-satellite planning can reach about 95% [4], and the average age of data for the BDS-3 MEO satellite is 1.07 h [5,6]. Due to the inter-satellite ranging error being better than 10 cm [7], it can effectively support the improvement of orbit determination and the long-time prediction of satellite clock parameters [8]. Therefore, inter-satellite links have become a significant supplement for satellite-to-ground observation links.
As the concept of comprehensive PNT are proposed [9], LEO satellites are also proposed to supplement the satellite-to-ground observation links of the global navigation satellite system (GNSS). Research on the use of LEO satellites as an augmentation system started earlier in the United States. The high-integrity global positioning system (iGPS) was the earliest navigation and timing system, using both LEO satellites and MEO satellites. The MEO satellites of the global positioning system (GPS) provide high-precision timing and positioning services for Iridium satellites in low Earth orbits. The Iridium satellites carry GNSS receivers and support high-precision orbit determination and time synchronization for MEO satellites. Due to the coverage limitation of the Iridium satellites, the positioning accuracy is only 20 to 50 m. In recent years, more and more programs for LEO augmentation constellations have been proposed. The European Union has carried out research on the Kepler system, which consists of the Galileo navigation satellite system and 4–6 LEO satellites, to achieve centimeter-level augmentation positioning accuracy [10,11].
LEO satellites equipped with GPS single-frequency receivers, such as LANDSAT-4 and LANDSAT-5, have not realized high-precision orbit determination. In 1992, the TOPEX/POSEIDON satellite, equipped with a dual-frequency GPS receiver, achieved great success, as its orbit determination accuracy was better than 4 cm [12]. Since then, various research works on LEO orbit determination were carried out for the CHAMP satellite, GRACE satellite, Jason satellite and other LEO satellites [13,14,15,16], verifying that the LEO satellites initially had the conditions to be used as high-dynamic monitoring stations. With the launch of the LEO satellites in China, such as “Feng Yun”, “Luojia” and “CentiSpace Constellation”, research on the orbit augmentation determination of BDS satellites with the support of the satellite-based observation data has been gradually carried out. Zeng T. [17] and Zhao Q. [18] conducted preliminary augmentation tests for BDS-2 satellite orbit determination, with the support of the satellite-based observation data of the Feng Yun-3C (FY3C) satellite. The test results showed that the orbit accuracy of the BDS-2 satellite could be effectively improved. Shen D. [19] determined that the orbit accuracy of BDS-3 satellites could be improved by 92% with the augmentation of the “Hong Yan” satellites. With these studies, the feasibility and value of the engineering applications for LEO satellites as satellite-based monitoring stations has been gradually verified.
This study firstly constructs muti-source observation links with satellite-to-ground, inter-satellite and satellite-based observation data to gain a suitable observation geometry condition and to weaken the correlation of the inter-epoch observation equations in the process of orbit determination. Then, an orbit determination method for the BDS-3 and LEO satellites is proposed based on the analysis of the correction models and strategies. Finally, the accuracy of orbit determination for the BDS-3 satellites and LEO satellites is evaluated, with the support of different observation data.
2. Orbit Determination Method
2.1. Design of the Multi-Source Observation Network
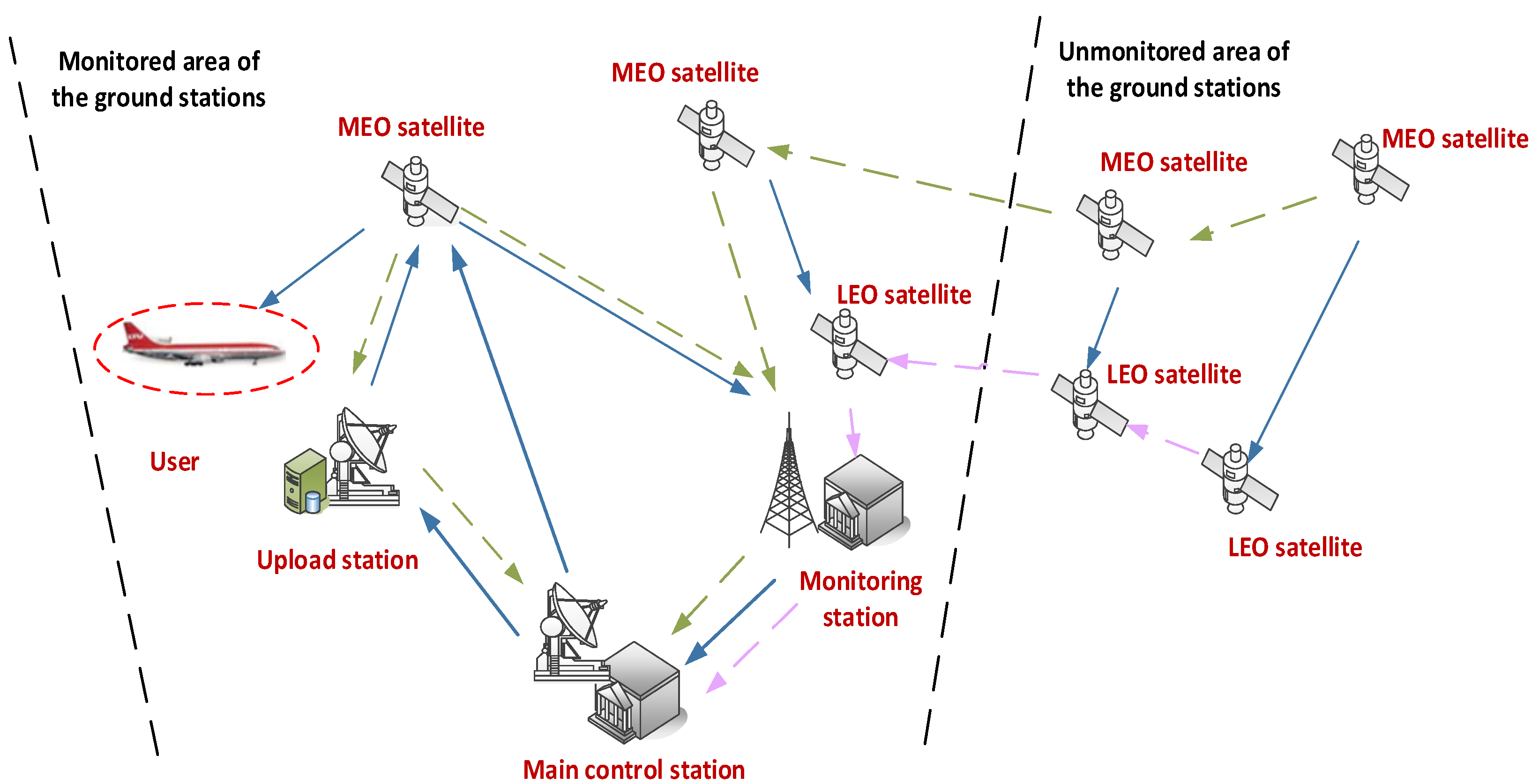
The satellite-to-ground observation network of the BDS-3 mainly only includes monitoring stations located in China, which cannot track the entire arc of the BDS-3 MEO satellites. The tracking rate is no more than 40% with only the support of satellite-to-ground observation links. If a satellite is not in the covering range of the ground monitoring stations, no observation data can be gained by the main control station. With the application of inter-satellite links, inter-satellite ranging data can be gained by the main control station. Nevertheless, the navigation messages broadcast by the satellites cannot be transmitted between the satellites and returned to the main control station. When LEO satellites are added, more observation data and navigation messages can be gained and returned to the main control station.
As shown in Figure 1, multi-source observation links consist of satellite–ground, inter-satellite and satellite-based observation links. Inter-satellite and satellite-based observation links can effectively increase the tracking and monitoring arcs of navigation satellites and make up for the distribution limitations of ground monitoring stations.
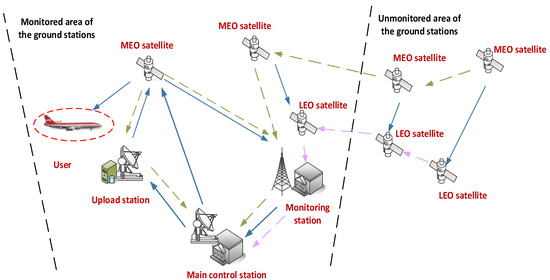
Figure 1.
Multi-source observation network.
The satellite-to-ground observation links refer to observation links between the ground monitoring stations and the satellites. The ground monitoring stations mainly consist of the main control station, upload stations and monitoring stations. The main control station should collect and process returned observation data and generate corresponding navigation messages. The upload stations should receive and inject navigation messages generated by the main control station and return the observed ranging data and navigation messages to the main control station. The monitoring stations should send the observed ranging data and navigation messages back to the main control station.
The inter-satellite observation links refer to observation links between navigation satellites. The inter-satellite pseudo ranging data can be transported to the main control station.
The satellite-based observation links refer to observation links between navigation satellites and LEO satellites. The satellite-based ranging data and received navigation messages can be transported to the main control station.
2.2. Construction of Multi-Source Observation Equations
According to the multi-source observation links mentioned above, three kinds of observation equations can be constructed:
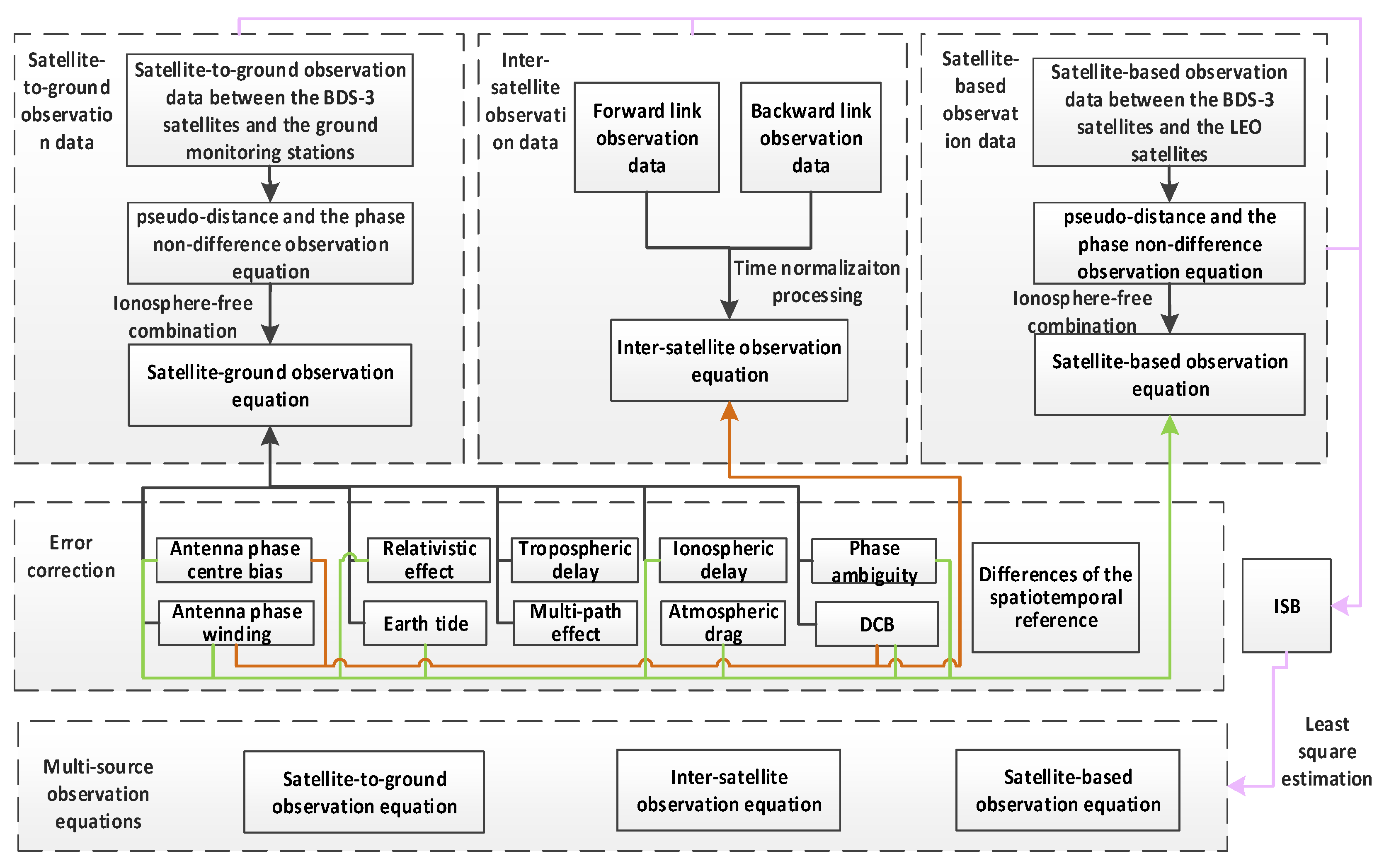
For the satellite-to-ground observation equation, the pseudo-distance and phase undifferenced data should be combined and linearized by the ionosphere-free method. Various system errors should be corrected. These errors mainly include the satellite clock error, differential code bias (DCB), relativistic effect, tropospheric delay, antenna phase center bias, Earth tide and multipath effect error.
For the inter-satellite observation equation, the characteristics of the Ka-phased array time division system should be considered. When the sending time and the receiving time are reduced to the same observation time, bidirectional observation equations can be established, with various errors corrected. These errors mainly include relativity errors, antenna phase center correction and the inter-satellite link device delay.
For the satellite-based observation equation, the method is basically the same as the satellite-to-ground observation equation. Compared with the satellite-to-ground observation model equation, the influence of tropospheric errors can be ignored, as the orbit of LEO satellites is above the troposphere, but antenna phase winding and cycle slip repair should be considered.
For the multi-source observation equations, differences in spatiotemporal reference and DCB should be fully considered, as they could be seen as inter-system bias (ISB). If there is a tight coupling relationship between the BDS-3 satellites and LEO satellites, the parameter adjustment method (PAM) can be applied to calibrate the ISB. The processing chart of the multi-source observation equations is shown in Figure 2 and the correction methods for observation errors are shown in Table 1.
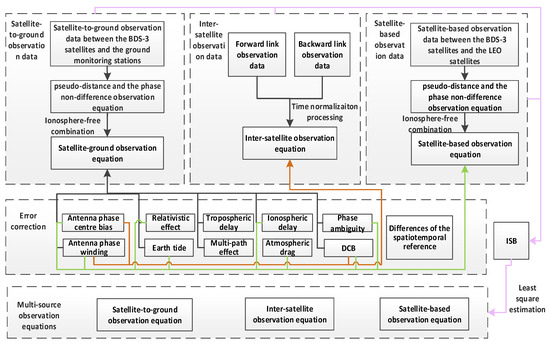
Figure 2.
Processing chart of multi-source observation equations.

Table 1.
Correction methods for observation errors.
In conclusion, the multi-source observation equations can be described as follows:
where , and , respectively, represent the satellite-to-ground, satellite-based and inter-satellite ranging data at reference time ; , and are, respectively, the observation noises of the corresponding observation v; , and are corresponding weight matrixes; is the normalized calculation time; is the orbit state parameters of the navigation satellites; is the state parameters of the ground monitoring stations; is the orbit state parameters of the LEO satellites; is the state parameters related to the observation data, such as the carrier phase ambiguity, clock difference parameters or inter-satellite link device delay; is the partial derivative matrix of the ranging data and the estimated parameters () at the time ; is the partial derivative matrix of the ranging data and the estimated parameters () at the time ; is the partial derivative matrix of the ranging data and the estimated parameters () at the time .
2.3. Model for Orbit Determination
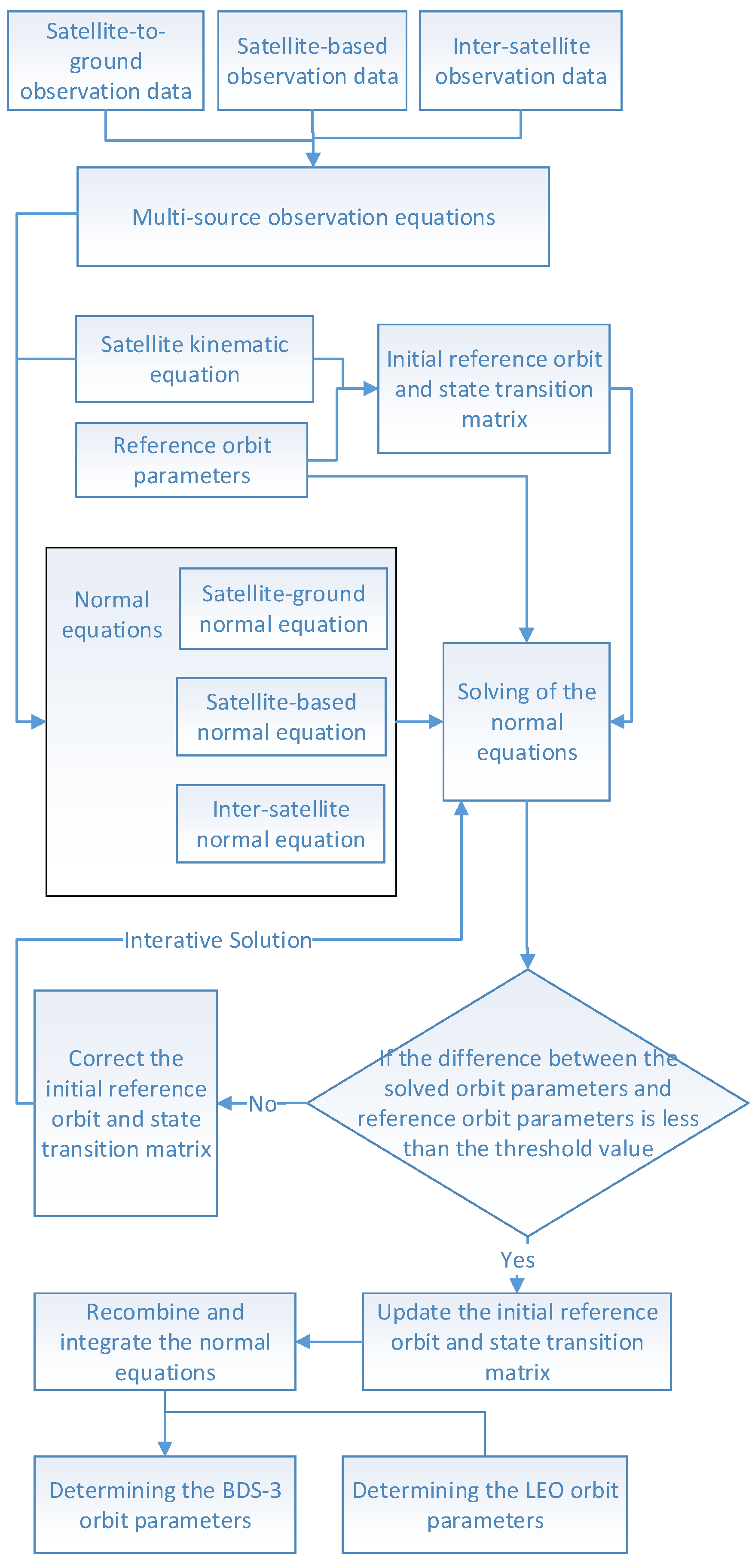
According to Newton’s second law, kinematics equations for navigation satellites and LEO satellites can be established in an inertial coordinate system. By combining kinematics equations with the observation equations, the normal equations for the combined orbit errors can be set up to obtain the orbit parameters. Then, the orbit parameters should be compared with reference orbit parameters to determine whether it is necessary to perform iterative calculations of the normal equations and correct the initial state parameters. The calculating chart is shown in Figure 3.
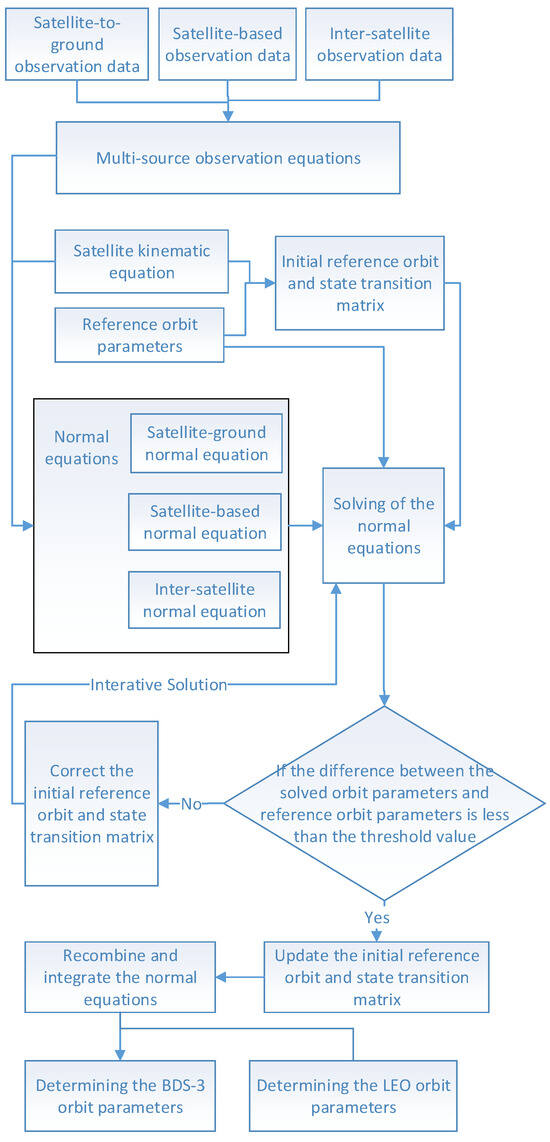
Figure 3.
Calculating chart for the normal equations.
3. Test Analysis
3.1. Choosing of Constellations and Ground Monitoring Stations
3.1.1. Design of Constellation
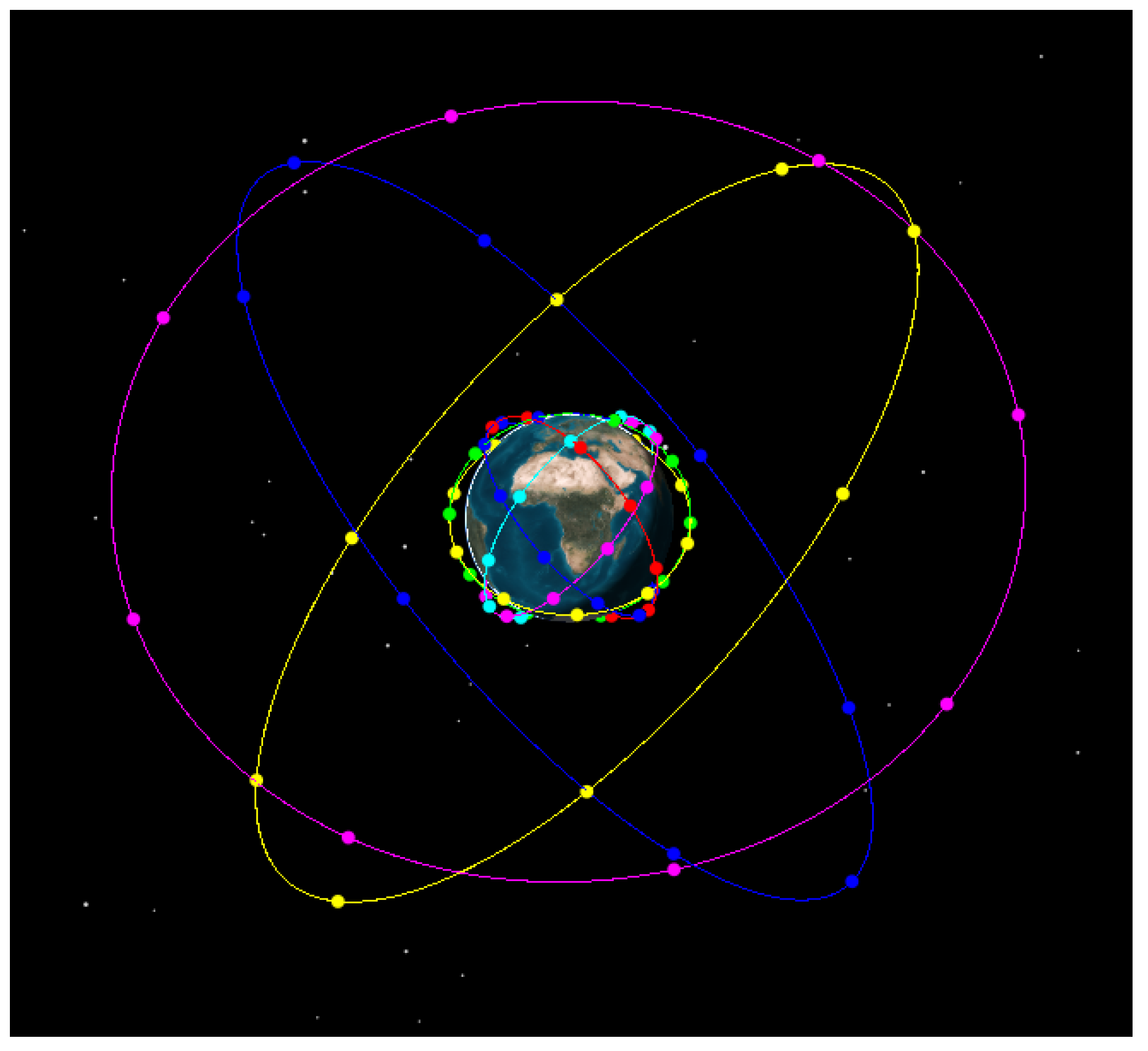
Considering that the main purpose of this paper is to design an LEO constellation that can enhance the existing service and monitoring areas of BDS-3 MEO satellites and have similar regression characteristics to BDS-3 MEO satellite, a Walker 60/6/1 LEO constellation was designed, with typical LEO constellations used as a reference, such as “Yunhai” and “Jason-3”. The orbital altitude of the LEO satellite was 1000 km and inclination is 55°. Then, a hybrid constellation with 24 BDS-3 MEO satellites and 60 LEO satellites was constructed, which is shown in Figure 4.
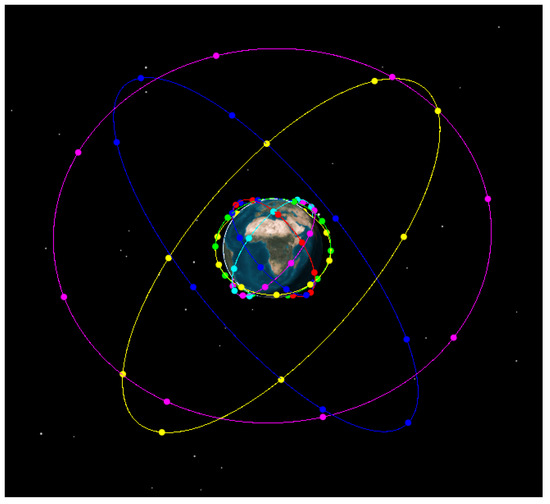
Figure 4.
Designed constellation with BDS-3 MEO satellites and 60 LEO satellites. (The satellites in blue, yellow and pink lines are BDS-3 MEO satellites and the satellites in low orbit lines are LEO satellites).
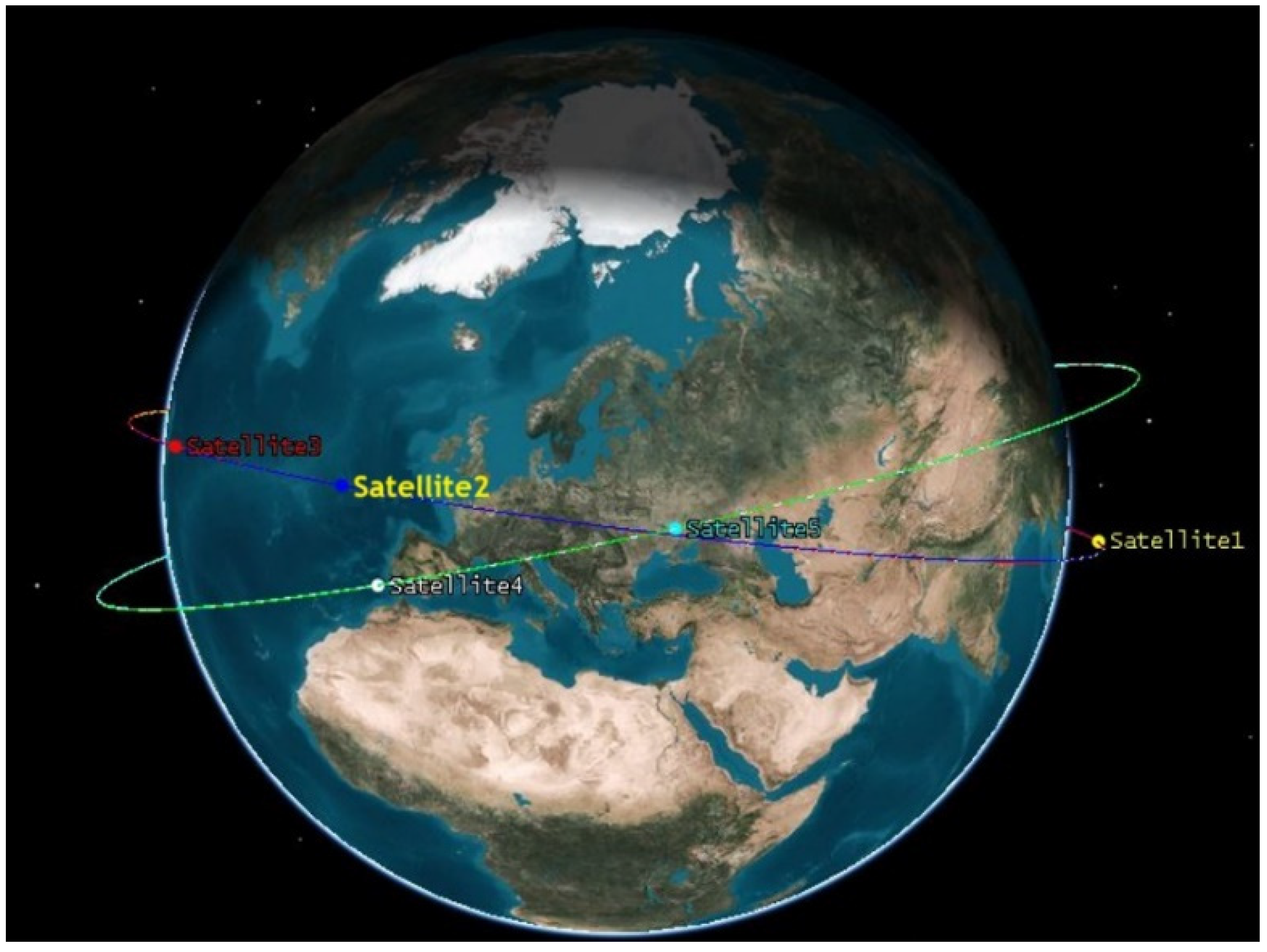
In addition to the construction of the simulation constellation, a hybrid constellation under the conditions of real observation data was also constructed, which consisted of BDS satellites and five LEO satellites. The LEO satellites were equipped with BDS monitoring receivers, whose orbits are shown in Figure 5.
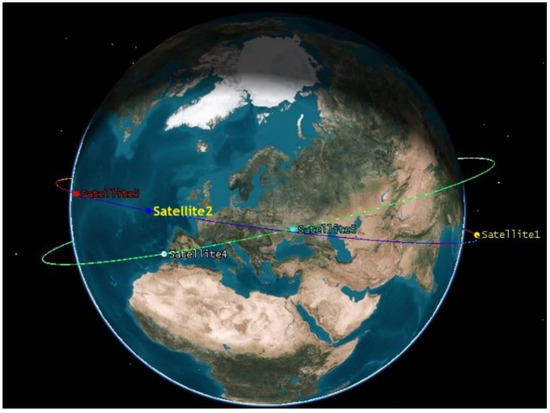
Figure 5.
LEO constellation with 5 LEO satellites.
3.1.2. Selection of Monitoring Stations
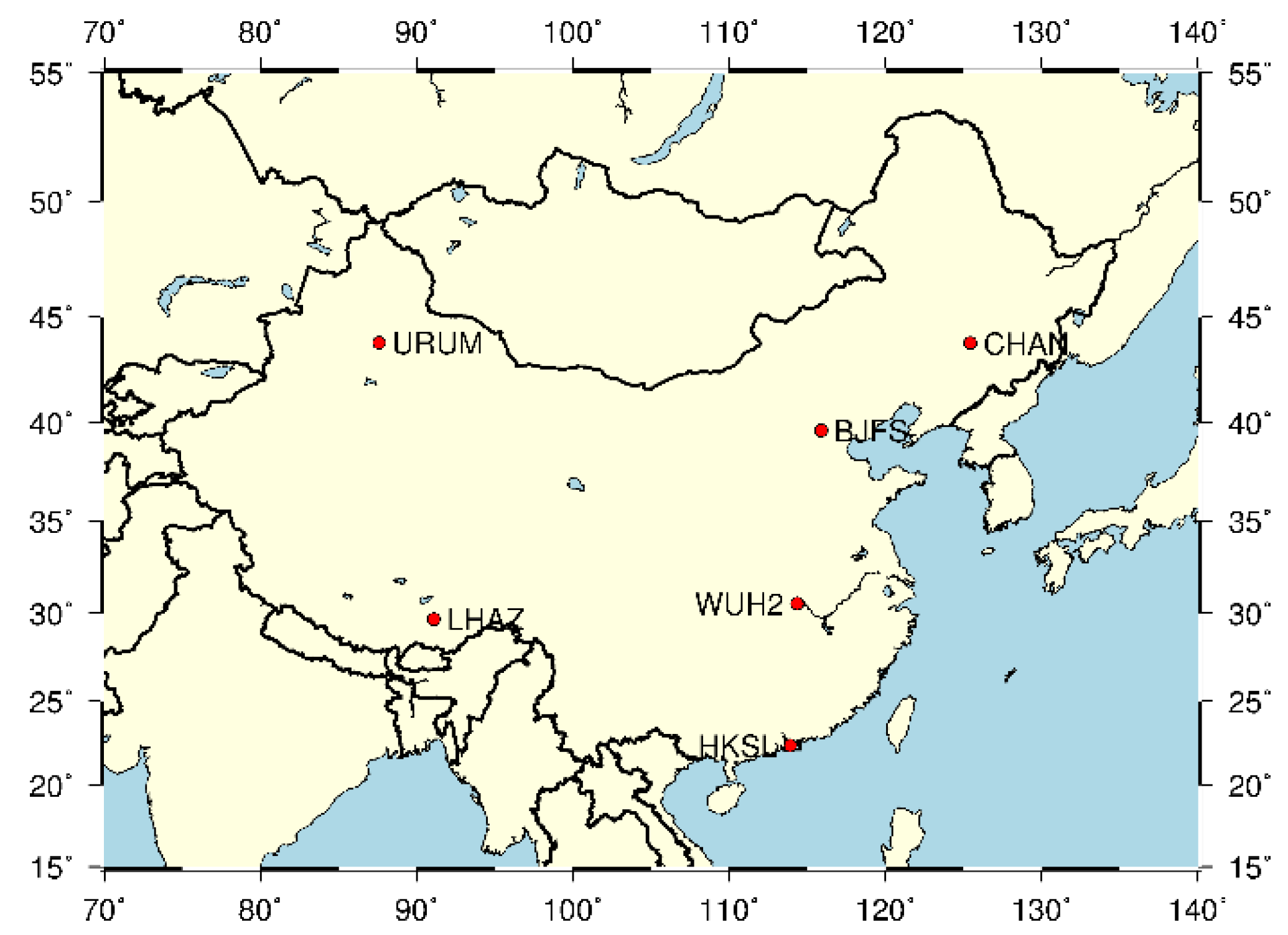
In tests with simulated data, the BJFS, CHAN, HKSL, LHAZ, URUM and WUH2 stations of the international GNSS service (IGS) in China were selected as the ground motoring stations, with consideration of the dispersibility and actual distribution of BDS-3 monitoring stations. The distribution of the chosen stations is shown in Figure 6.
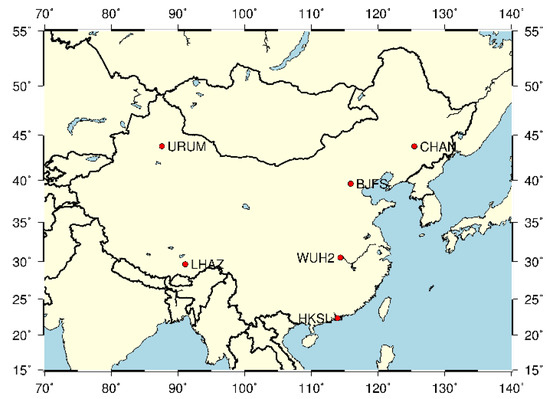
Figure 6.
Distribution of the chosen stations (simulated data).
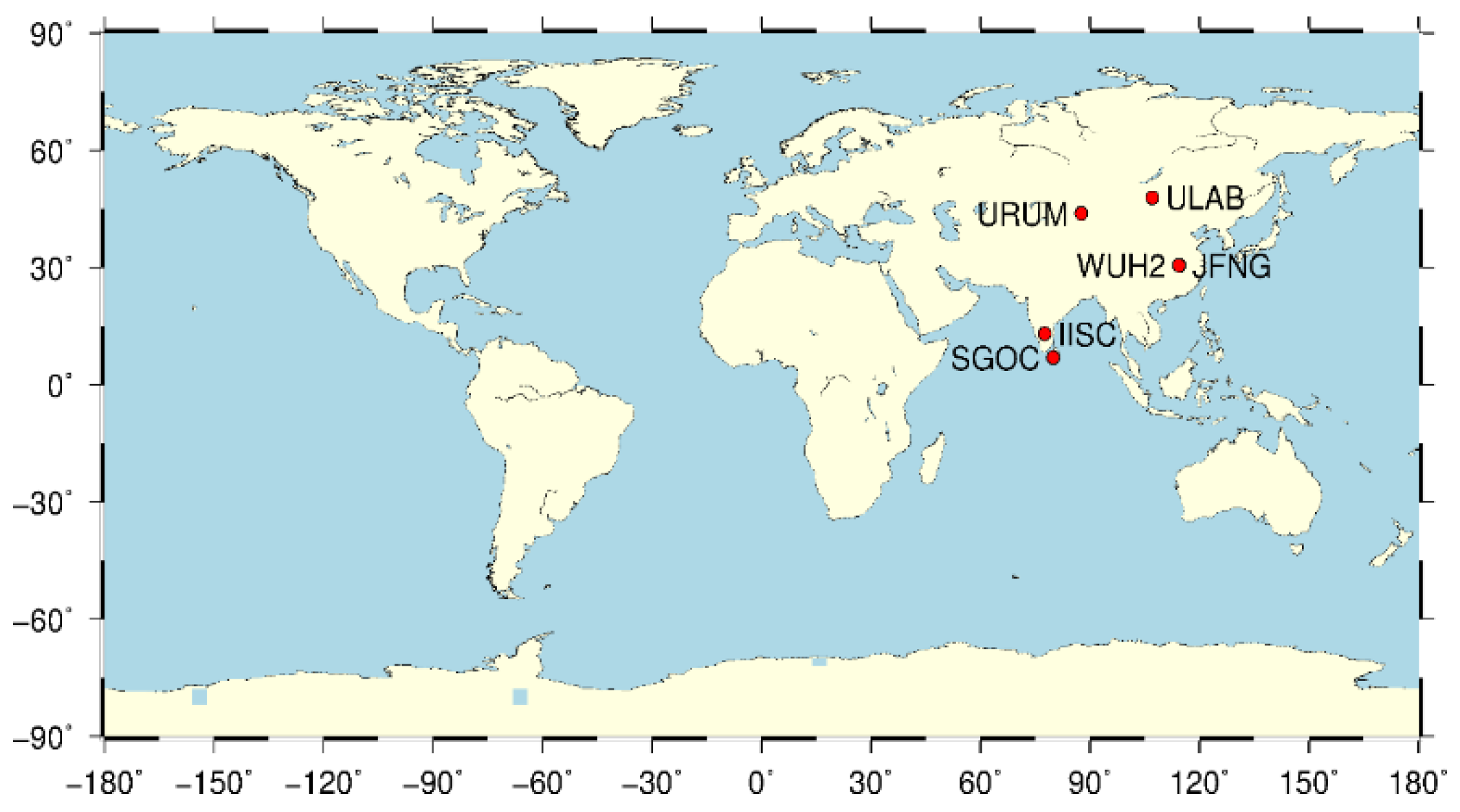
In tests with real data, the URUM, WUH2, JFNG, URUM, IISC and SGOC stations of the IGS around China were selected, according to quality of observed data from 2019. The distribution of the chosen stations is shown in Figure 7.
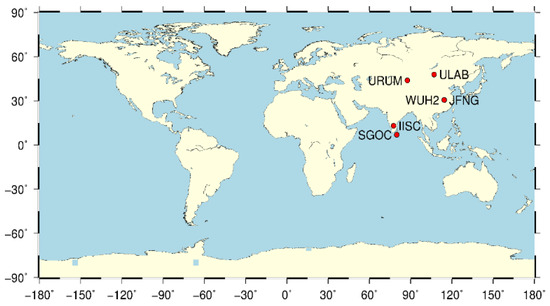
Figure 7.
Distribution of the chosen stations (real data).
3.1.3. Coverage Analysis of Multi-Source Observation Links
For the constellation with 24 BDS-3 MEO satellites and 60 LEO satellites, the coverage capability of the multi-source observation links was evaluated.
The test results showed that:
- (1)
- As shown in Figure 8, the coverage ratio of more than one satellite-to-ground observation link was less than 40%.
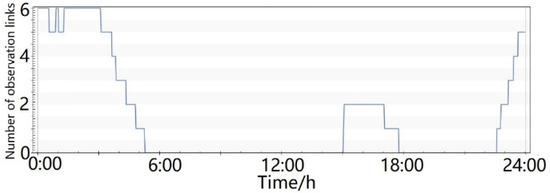 Figure 8. Number of satellite-to-ground observation links.
Figure 8. Number of satellite-to-ground observation links. - (2)
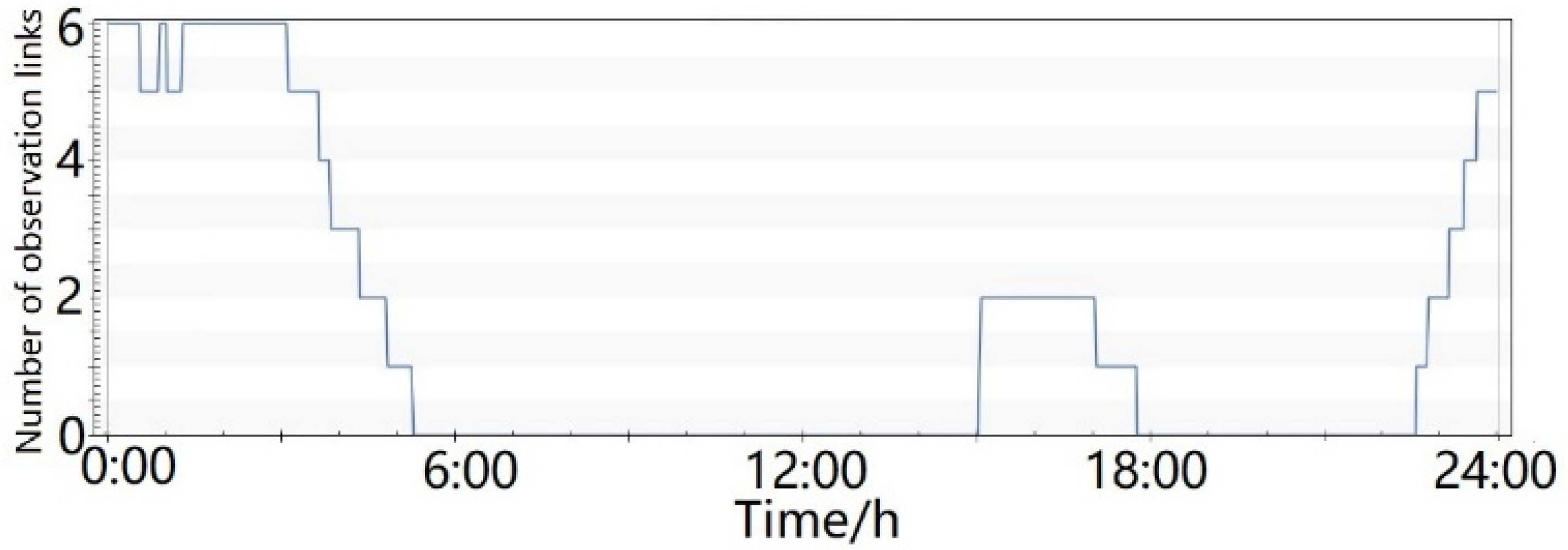
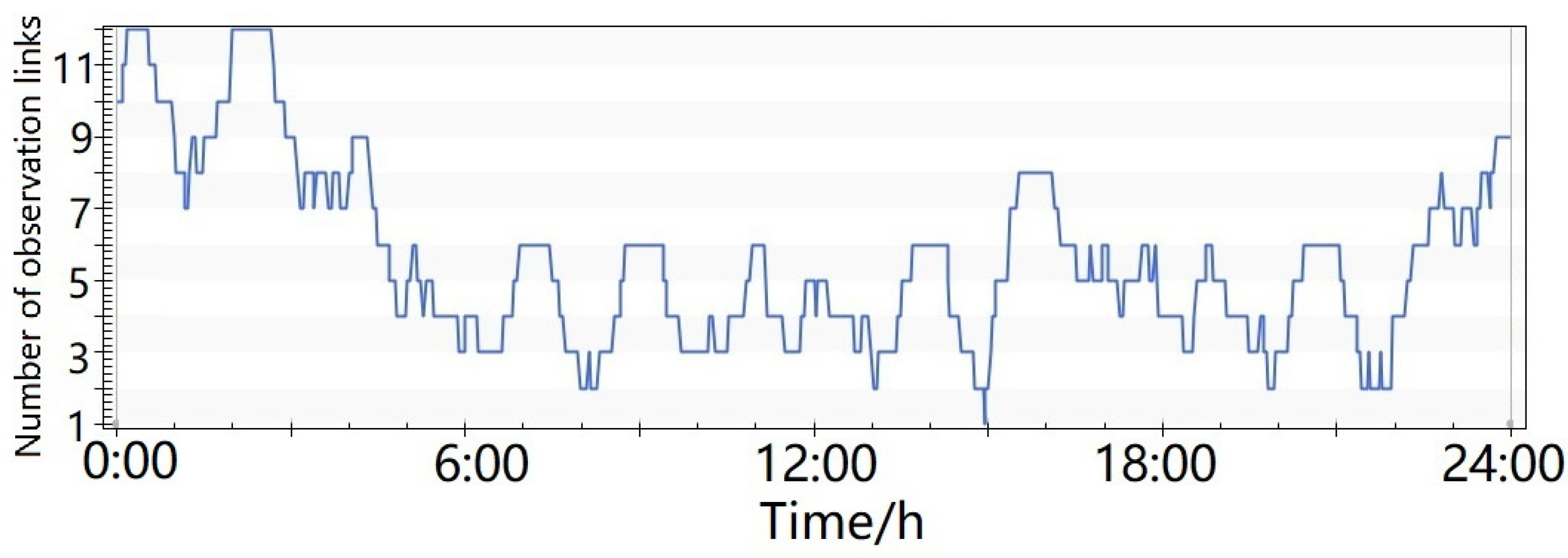
- As shown in Figure 9, one MEO satellite could be constantly tracked by the ground monitoring stations and six LEO satellites. The six LEO satellites were located in six orbital planes, respectively. The maximum coverage number was 12.
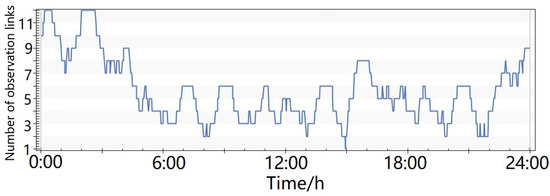 Figure 9. Number of satellite-to-ground and satellite-based observation links, with the support of 6 LEO satellites.
Figure 9. Number of satellite-to-ground and satellite-based observation links, with the support of 6 LEO satellites. - (3)
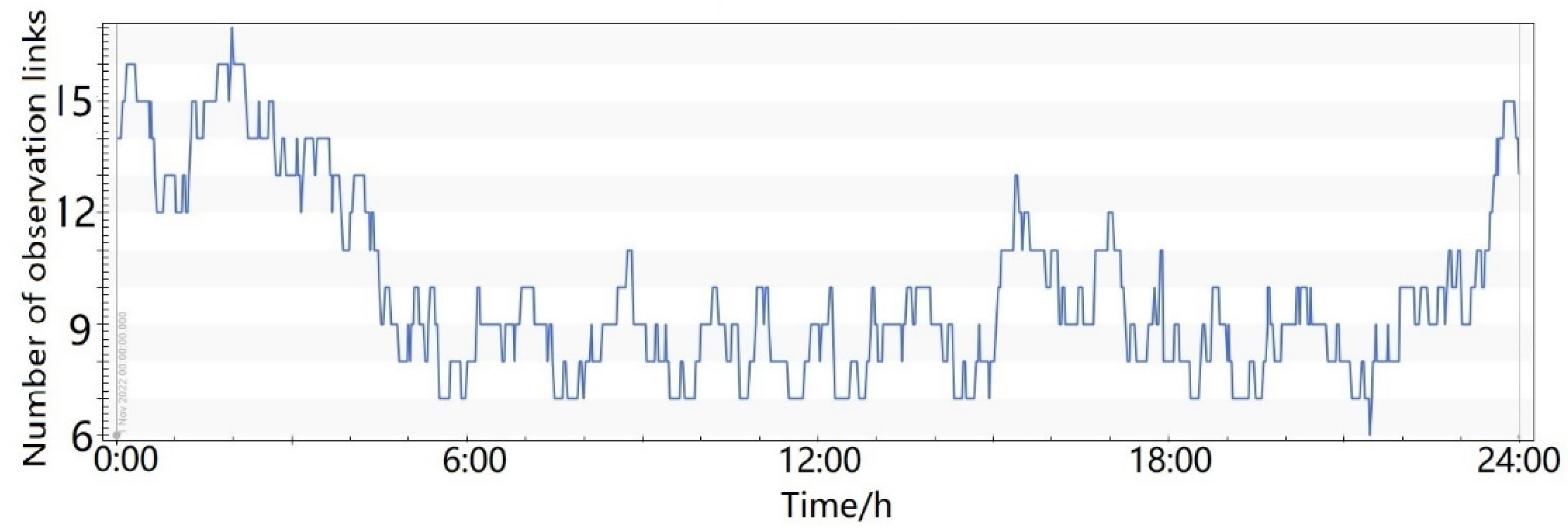
- As shown in Figure 10, the number of observation links could be effectively improved by adding six more LEO satellites. The minimum number of observation links was six, meeting the requirements of precise orbit determination.
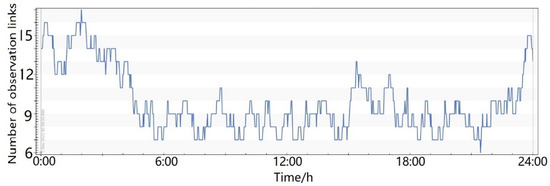 Figure 10. Number of satellite-to-ground and satellite-based observation links, with the support of 12 LEO satellites.
Figure 10. Number of satellite-to-ground and satellite-based observation links, with the support of 12 LEO satellites.
3.2. Test of Orbit Determination for BDS-3 Satellites and LEO Satellites
3.2.1. Strategies for Orbit Determination
Based on the normal equations mentioned above, the strategies for orbit determination could be further refined, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Strategies for orbit determination.
3.2.2. Test Scenarios for Orbit Determination with Simulated Data
By constructing scenarios with different observation data, the orbit determination accuracy could be determined in different scenarios. The designed test scenarios are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Test scenarios of orbit determination with simulated data.
The evaluation results of orbit determination over one day showed that:
- (1)
- As shown in Figure 11, the accuracies of orbit determination in the radial (R), tangential (T), normal (N) and three-dimensional (3D) directions were, respectively, 0.050 m, 0.128 m, 0.133 m and 0.191 m in Scenario 1. Accuracy would gradually increase when the satellite left the ground monitoring area and would become more than 0.4 m. Compared with Scenario 1, the accuracy could be improved as satellite-based observation links were added. Accuracy in the 3D direction was 0.067 m in Scenario 2. When the satellite left the ground monitoring area, the accuracy was still within 0.1 m.
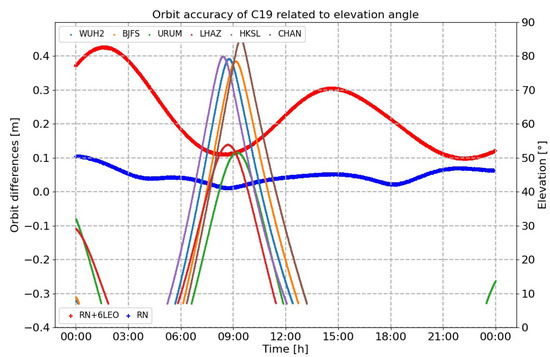 Figure 11. Compared results of orbit determination under conditions of different elevation angles in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2 (the colorful lines are the observation angles related to different monitoring stations; the blue dots and the red dots are, respectively, the results for orbit determination with different observation links in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2).
Figure 11. Compared results of orbit determination under conditions of different elevation angles in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2 (the colorful lines are the observation angles related to different monitoring stations; the blue dots and the red dots are, respectively, the results for orbit determination with different observation links in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2). - (2)
- As shown in Figure 12, the three-dimensional accuracy of orbit determination in Scenario 3 was 0.051 m, which is a 24% improvement compared with the results of Scenario 2.
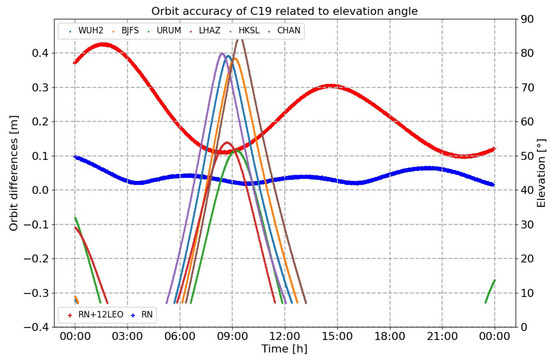 Figure 12. Compared results of orbit determination under conditions of different elevation angles in Scenario 1 and Scenario 3.
Figure 12. Compared results of orbit determination under conditions of different elevation angles in Scenario 1 and Scenario 3. - (3)
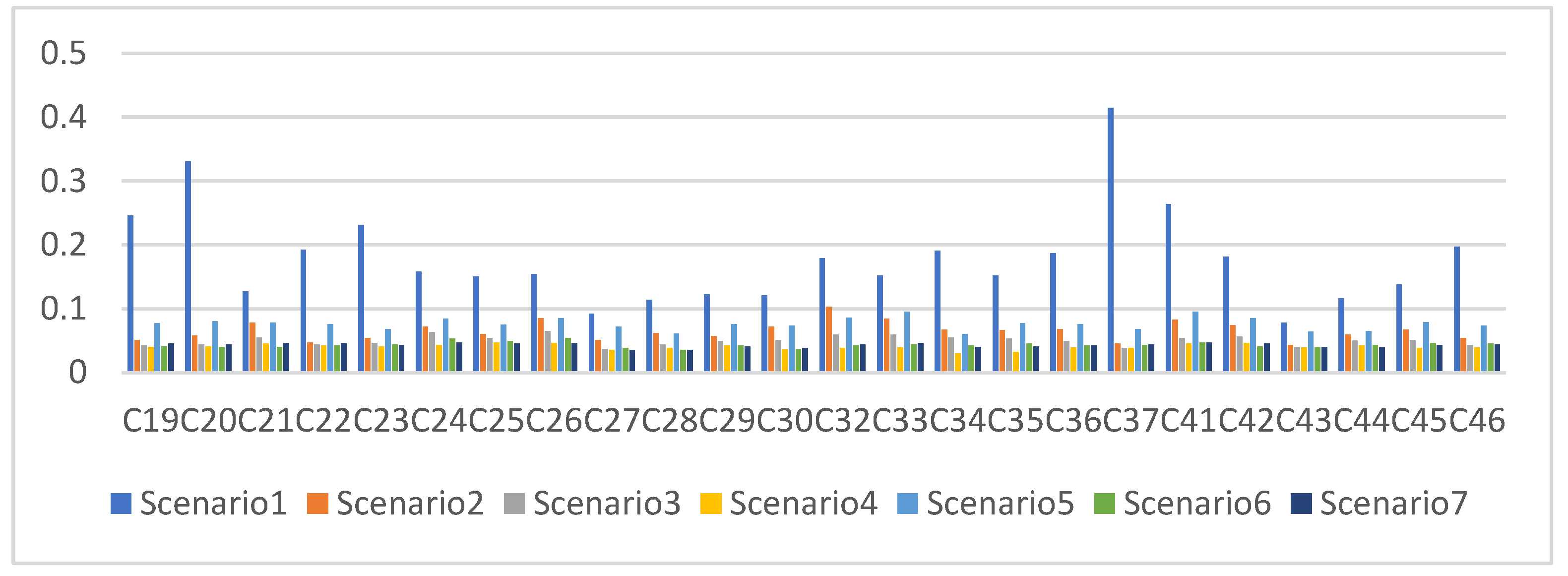
- As shown in Table 4 and Figure 13, the three-dimensional accuracy of the orbit determination in Scenario 1 to Scenario 4 was, respectively, 0.194 m, 0.067 m, 0.051 m and 0.04 m. The addition of LEO satellites could effectively improve the orbit accuracy of MEO satellites.
 Table 4. Accuracy of orbit determination over one day (unit: m).
Table 4. Accuracy of orbit determination over one day (unit: m).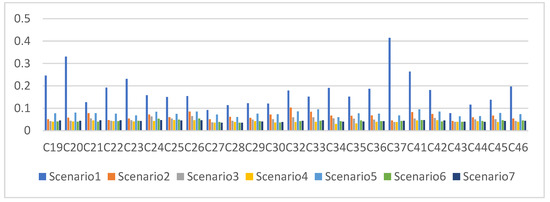 Figure 13. Statistical results of the three-dimensional position errors in Scenarios 1 to 7 (one day).
Figure 13. Statistical results of the three-dimensional position errors in Scenarios 1 to 7 (one day).
The results for Scenario 1, Scenario 2 and Scenario 5 were, respectively, 0.194 m, 0.067 m and 0.077 m, verifying that LEO satellites and inter-satellite links are both important augmentation means of improving the visual arc of MEO satellites, and that their augmentation effects are basically the same.
The results for Scenario 5, Scenario 6 and Scenario 7 were, respectively, 0.077 m, 0.043 m and 0.043 m, meaning that accuracy could be improved with the addition of the satellite-based links. Nevertheless, the results could not be further improved by adding more LEO satellites.
The evaluation results of the orbit determination over 7 days are shown in the Table 5. It can be seen that:

Table 5.
Accuracy of orbit determination in Scenario 1 to 7 (unit: m).
- (1)
- The results in the R direction were, respectively, 0.050 m, 0.020 m, 0.013 m and 0.008 m in Scenario 1 to Scenario 4. Compared with Scenario 1, the improvement rates were, respectively, 60%, 74% and 84%. Similarly, the improvement rates were, respectively, 69%, 75% and 77% in the T direction and 67%, 70% and 78% in the N direction. The improvement in the different directions was basically the same with the support of LEO satellites.
- (2)
- The results in the R direction were, respectively, 0.005 m, 0.006 m and 0.007 m in Scenario 5 to Scenario 7. The decrease rates were, respectively, 20% and 40% compared with Scenario 5. Nevertheless, results in the T direction were, respectively, 0.033 m, 0.031 m and 0.030 m, meaning that there were slight increases in the T direction. The improvement rates were, respectively, 6% and 9%. The results in the N direction showed slight decreases with the addition of six LEO satellites and could be slightly improved when more LEO satellites are added. This might be accompanied by more errors in the R direction when more satellite-based observation links are added.
- (3)
- The results in the 3D direction were, respectively, 0.191 m, 0.063 m, 0.041 m and 0.059 m in Scenario 1, Scenario 2, Scenario 4 and Scenario 5. Compared with Scenario 1, the improvement rates were, respectively, 67%, 78% and 69%, meaning that the augmentation performance of the LEO constellation might be better than the inter-satellite links when the LEO constellation consists of a certain number of LEO satellites.
- (4)
- The results in the 3D direction were, respectively, 0.059 m, 0.059 m and 0.057 m in Scenario 5 to Scenario 7, meaning that the augmentation performance of the multi-source observation links was not better than the results obtained with the support of the satellite-to-ground and inter-satellite links. For the observation equations, the weights of the satellite-to-ground, inter-satellite and satellite-based observation links were set the same. Satellite-to-ground and satellite-based links both contain pseudo ranging and phase observation data, while inter-satellite links only contain pseudo ranging data, with more systematic errors. This might be the reason for the decrease in accuracy observed with the addition of more observation links.
3.2.3. Test Scenarios of Orbit Determination with Real Data
Based on real observation data from16 BDS-3 MEO satellites and five LEO satellites from 20 January 2019, the accuracy of orbit determination was evaluated, using the post-orbit precision products released by the MGEX analysis center of Wuhan University as a reference. The designed test scenarios are listed in Table 6.

Table 6.
Test scenarios of orbit determination with real data.
It could be seen that:
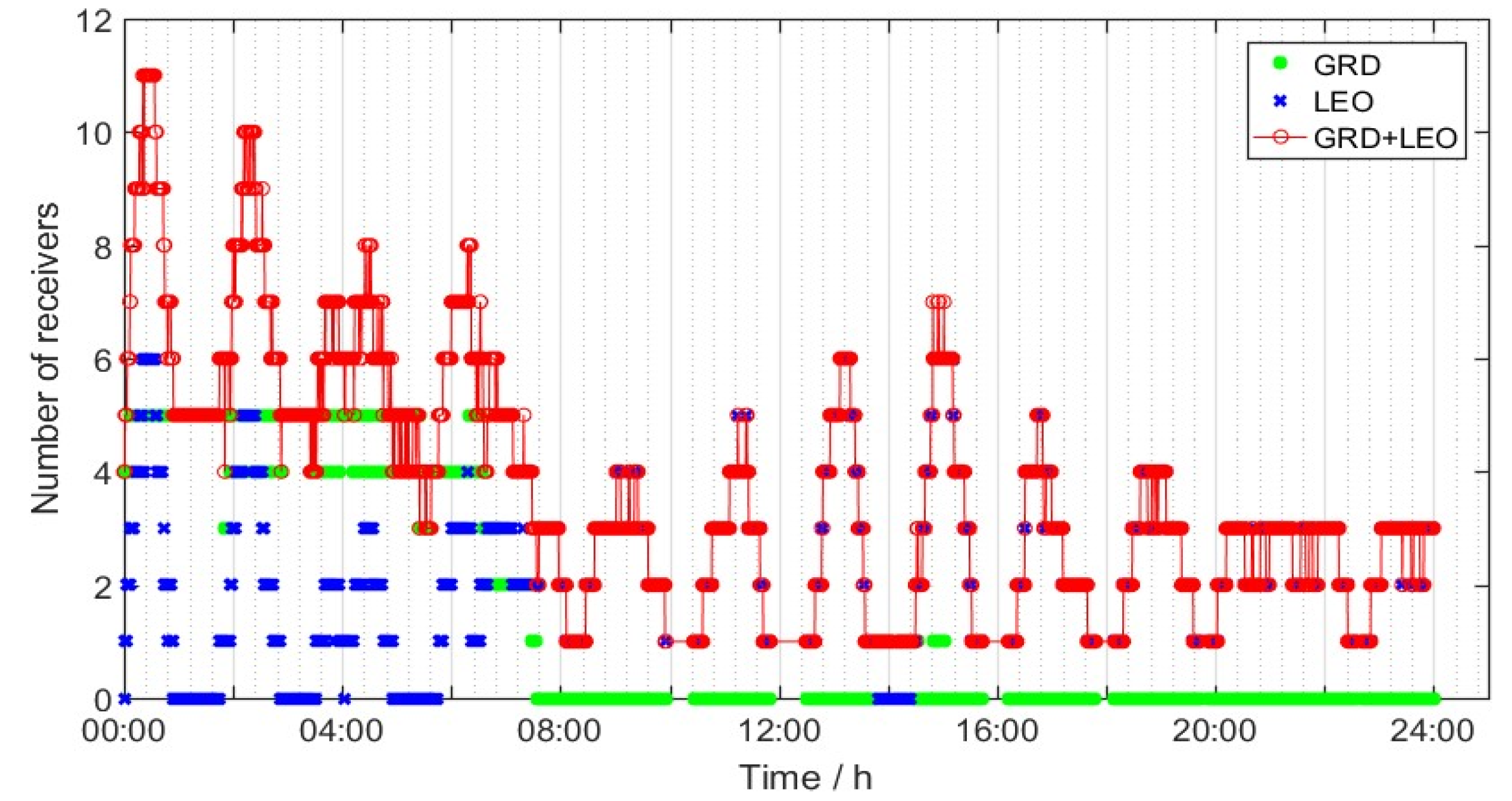
- (1)
- As shown in Figure 14, the tracking arc of the receivers located in the six ground monitoring stations to a single MEO satellite was rather short. As satellite-based receivers equipped on the LEO satellites were added, the full-arc tracking could be realized. The average number of effective observation links could reach three.
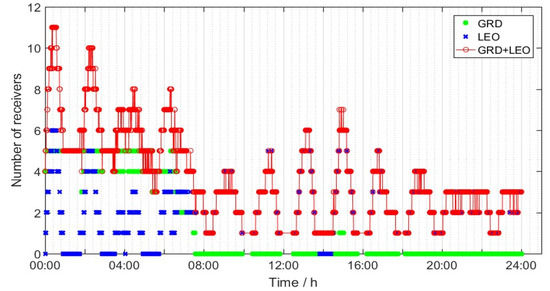 Figure 14. Number of satellite-to-ground and satellite-based receivers.
Figure 14. Number of satellite-to-ground and satellite-based receivers. - (2)
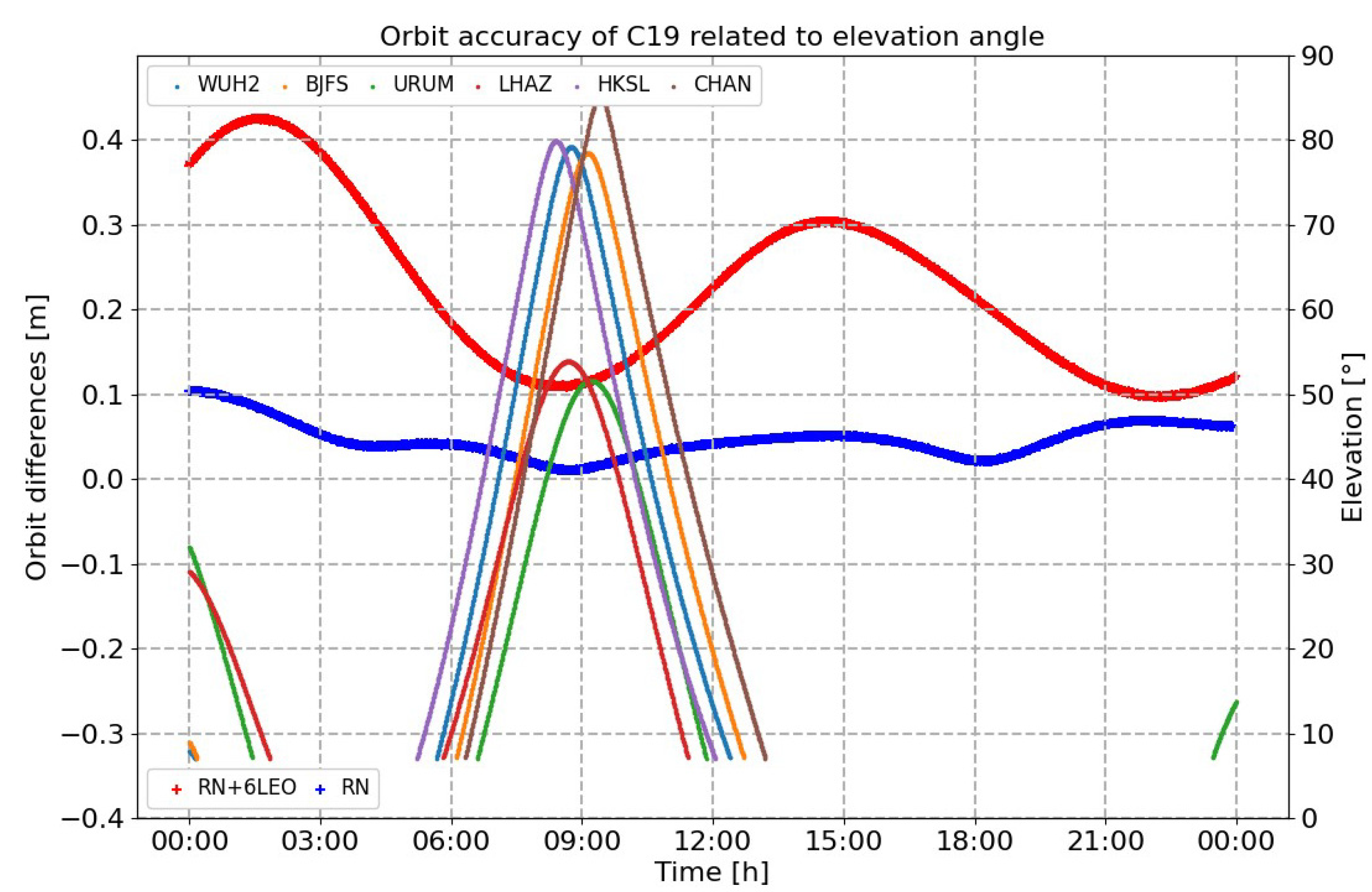
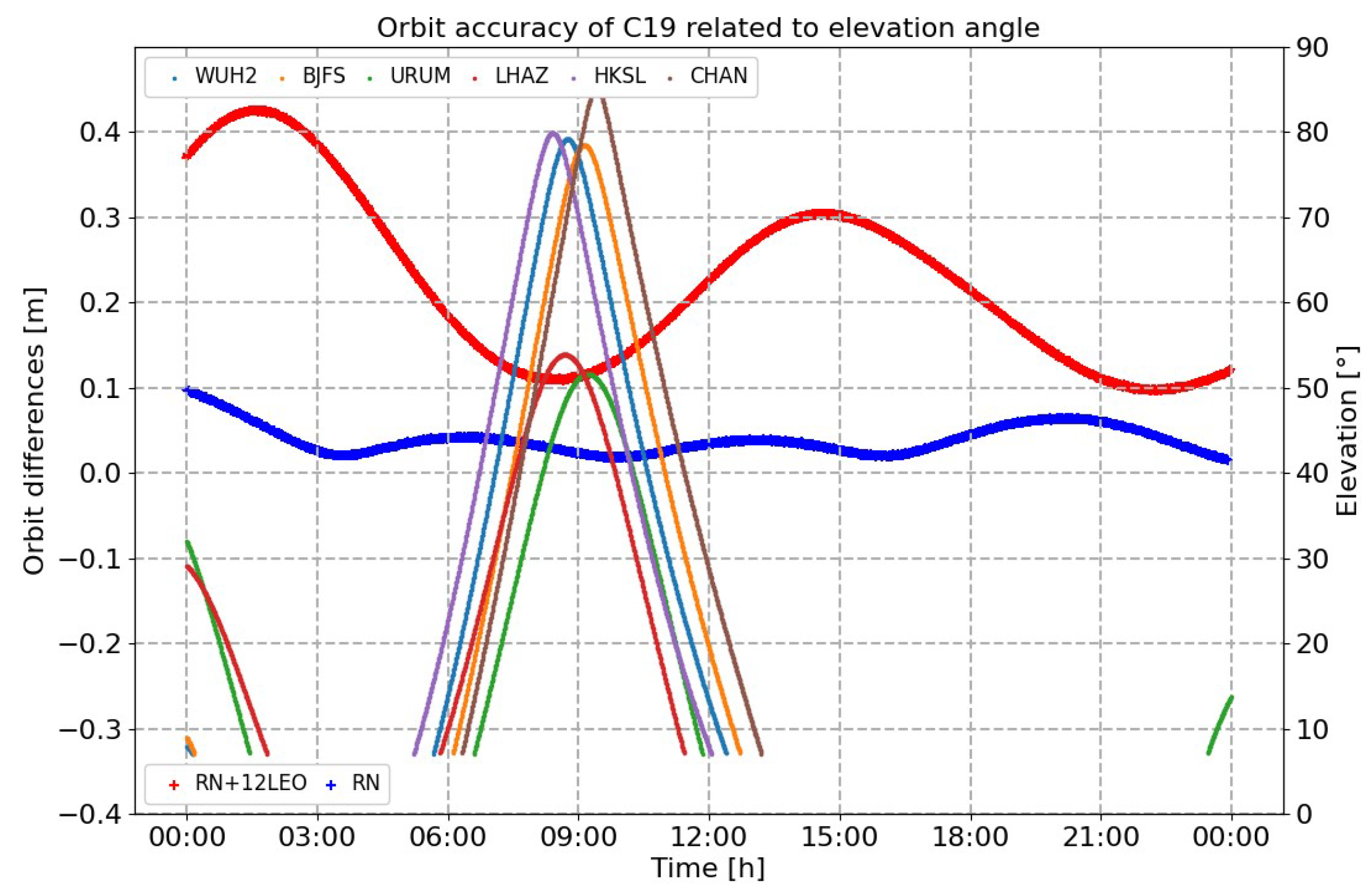
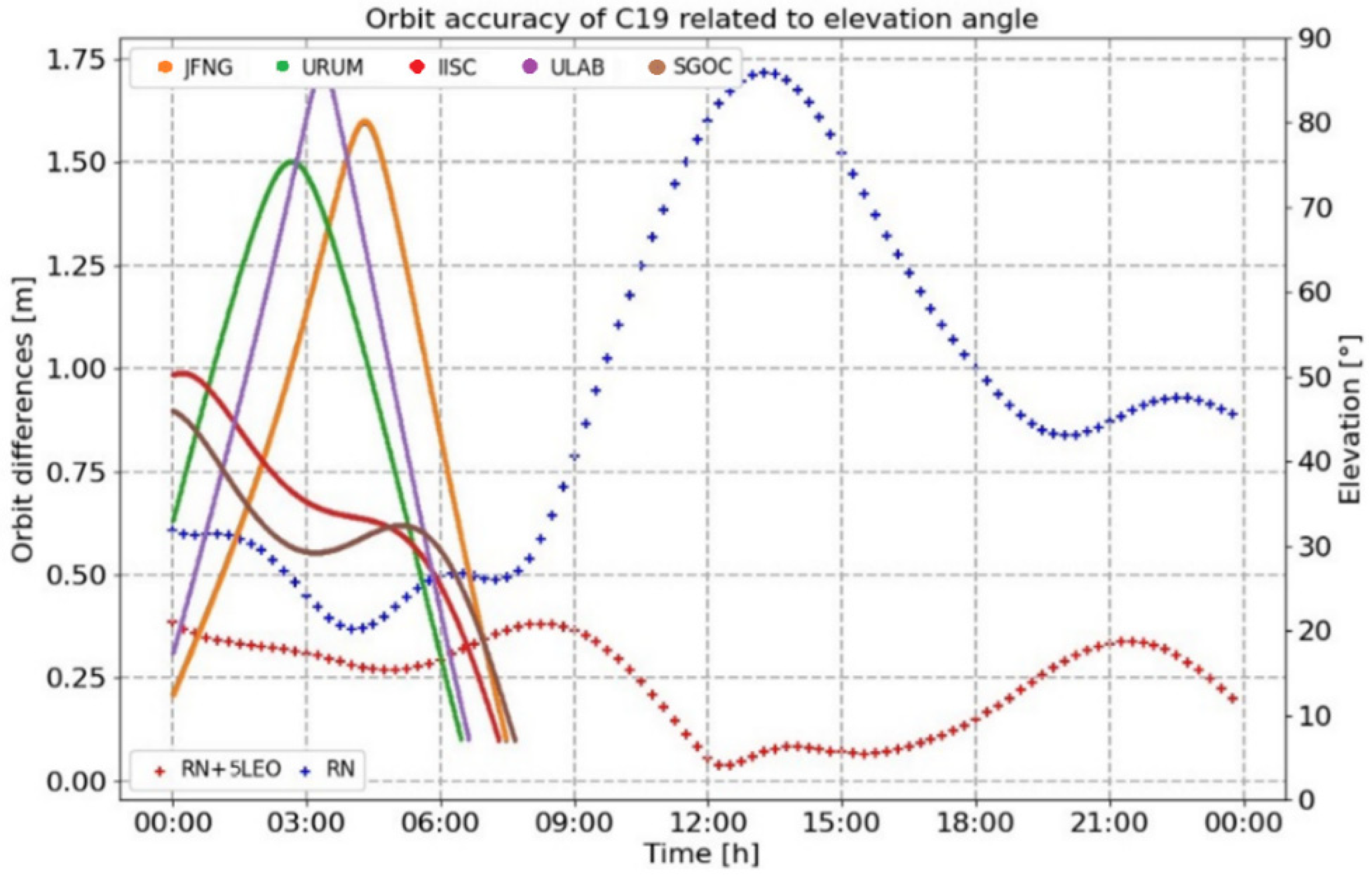
- As shown in Figure 15, the accuracy of orbit determination for the C19 satellite was, respectively, 0.217 m, 0.929 m, 0.355 m and 1.018 m in the R, T, N and 3D directions, with the support of the satellite-to-ground observation links. Compared with Scenario 1, this result could be, respectively, improved by 84%, 88%, 60% and 82%. Similarly, the accuracy would gradually increase when the satellite left the ground monitoring area, which could be more than 1.7 m.
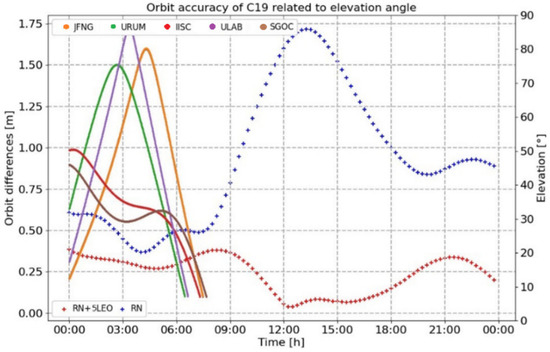 Figure 15. Compared results of orbit determination under conditions of different elevation angles in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2 (real data).
Figure 15. Compared results of orbit determination under conditions of different elevation angles in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2 (real data). - (3)
- As shown in Table 7, the accuracy of orbit determination was, respectively, 0.287 m, 1.131 m, 0.607 m and 1.334 in the R, T, N and 3D directions, with the support of the satellite–ground observation links. Compared with Scenario 1, these results could be, respectively, improved by 72%, 78%, 71% and 76%. The evaluation results of the whole constellation are basically consistent with the results from one satellite.
 Table 7. Accuracy of orbit determination with real data (unit: m).
Table 7. Accuracy of orbit determination with real data (unit: m).
4. Conclusions
With the construction of multi-source observation links, an orbit determination method is proposed to simultaneously determine the orbit of navigation satellites and LEO satellites. Through the designed tests with different observation links, some conclusions could be gained from this study, as follows:
- (1)
- With the support of 6, 12 and 60 LEO satellites, the accuracy of orbit determination for BDS-3 MEO satellites under conditions of simulation tests could be, respectively, improved by 65.5%, 73.7% and 79.4%. Nevertheless, the scope for further improvements in accuracy is limited when the observation geometry meets the requirements of basic orbit determination.
- (2)
- With the addition of five LEO satellites, the accuracy of orbit determination based on real data could be, respectively, improved by 72%, 78%, 71% and 76% in the R, T, N and 3D directions. The augmentation effects of satellite-based observation data are basically the same in different directions.
- (3)
- The accuracy of orbit determination could be augmented significantly with the addition of LEO satellites. When the navigation satellite leaves the monitoring area of the ground monitoring stations, the reduction in the orbit accuracy can also be slowed down with the support of the satellite-based observation links.
- (4)
- With the support of either inter-satellite or LEO satellites, the accuracy of orbit determination was at the centimeter level. Inter-satellite links and satellite-based links could be used as each other’s backups for navigation satellites.
- (5)
- The augmentation results of the multi-source observation links were not better than the results obtained with the support of the satellite-to-ground and inter-satellite links or the satellite-to-ground and satellite-based links. This might be caused by some unconsidered systematic errors. For the observation equations, the weights of the satellite-to-ground, inter-satellite and satellite-based observation links were set to be the same, something which should be further improved.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, data curation and writing—original draft preparation, J.X.; software and validation, K.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 12103077).
Data Availability Statement
The Beijing Satellite Navigation Center provided all the test data used in this work. All data will be made available for scientific research purposes by request to the Beijing Satellite Navigation Centre.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhou, S.; Hu, X.; Wu, B.; Li, L.; Qu, W.; Guo, R.; He, F.; Cao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Shi, X.; et al. Orbit determination and time synchronization for a GEO/IGSO satellite navigation constellation with regional tracking network. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2011, 54, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A.; Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Teunissen, P.; Nakamura, S. Initial assessment of the COMPASS/Beidou-2 regional navigation satellite system. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, X. Satellite-ground two-way measuring method and performance evaluation of BDS-3 inter-satellite link system. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 157530–157540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.; Guo, R.; Tang, C.; Liu, S.; Xin, J.; Guo, J.; Tian, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Precise orbit determination for BDS-3 GEO satellites enhanced by intersatellite links. GPS Solut. 2022, 27, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, R.; Tang, C.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, L.; Xu, J. Inter-satellite link enhanced orbit determination for BeiDou-3. J. Navig. 2020, 73, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.; Tang, C.; Guo, R.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, J.; Pan, J.; Su, M. BeiDou-3 broadcast clock estimation by integration of observations of regional tracking stations and inter-satellite links. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Hu, X.G.; Tang, C.P.; Guo, R.; Zhu, L.; Li, R.; Pan, J.; Zhou, S. Orbit determination and time synchronization for new-generation Beidou satellites: Preliminary results. Sci. Sin-Phys. Mech. Astron. 2016, 46, 119502. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Hu, X.; Tang, C.; Zhou, S.; Li, R.; Zhu, L.; Tang, G.; Hu, G.; Chang, Z.; Wu, S.; et al. System error calibration for time division multiple access inter-satellite payload of new-generation Beidou satellites. China Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 2671–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Y. Concepts of comprehensive PNT and related key technologies. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2016, 45, 505–510. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, C. Kepler-satellite navigation without clocks and ground infrastructure. In Proceedings of the 31st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2018), Miami, FL, USA, 24–28 September 2018; pp. 849–856. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, C. Kepler-a proposal for next generation satellite navigation systems. In Proceedings of the Munich Satellite Navigation Summit, Munich, Germany, 5–7 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Melbourne, W.G.; Tapley, B.D.; Yunck, T.P.; Davis, E.S. The GPS flight experiment on TOPEX/POSEIDON. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 2171–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, B.; Bar-Sever, Y.; Bertiger, W.; Desai, S.; Willis, P. One-centimeter orbit determination for Jason-1: New GPS-based strategies. Mar. Geod. 2004, 27, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, H.; Jäggi, A.; Meyer, U.; Visser, P.; van den IJssel, J.; van Helleputte, T.; Heinze, M.; Hugentobler, U. GPS-derived orbits for the GOCE satellite. J. Geod. 2010, 85, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Tapley, B.; Bettadpur, S.; Rim, H.; Nagel, P. Precise orbit determination for CHAMP using accelerometer data. Adv. Astronaut. Sci. 2012, 112, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Xu, J. On the singularity problem in orbital mechanics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 429, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zeng, T.; Sui, L.; Jia, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Q. Results and analysis of BDS precise orbit determination with the enhancement of Fengyun-3C. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 824–833. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Yang, G.; Liao, M.; Ma, H.; Liu, J. Enhanced orbit determination for Bei Dou satellites with Feng Yun-3C onboard GNSS data. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Meng, Y.; Bian, L.; Lei, W.; Wang, Y.; Yan, T.; Xie, J. A global navigation augmentation system based on LEO communication constellation. J. Terahertz Sci. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2019, 17, 209–2014. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).