Abstract
Synthetic aperture radar tomography (TomoSAR) has gained significant attention for three-dimensional (3D) imaging in urban environments. A notable limitation of traditional TomoSAR approaches is their primary focus on persistent scatterers (PSs), disregarding targets with temporal decorrelated characteristics. Temporal variations in coherence, especially in urban areas due to the dense population of buildings and artificial structures, can lead to a reduction in detectable PSs and suboptimal 3D reconstruction performance. The concept of partially coherent scatterers (PCSs) has been proven effective by capturing the partial temporal coherence of targets across the entire time baseline. In this study, an novel approach based on an iterative sub-network generation method is introduced to leverage PCSs for enhanced 3D reconstruction in dynamic environments. We propose a coherence constraint iterative variance analysis approach to determine the optimal temporal baseline range that accurately reflects the interferometric coherence of PCSs. Utilizing the selected PCSs, a 3D imaging technique that incorporates the iterative generation of sub-networks into the SAR tomography process is developed. By employing the PS reference network as a foundation, we accurately invert PCSs through the iterative generation of local star-shaped networks, ensuring a comprehensive coverage of PCSs in study areas. The effectiveness of this method for the height estimation of PCSs is validated using the TerraSAR-X dataset. Compared with traditional PS-based TomoSAR, the proposed approach demonstrates that PCS-based elevation results complement those from PSs, significantly improving 3D reconstruction in evolving urban settings.
1. Introduction
SAR tomography (TomoSAR) is a powerful method for three-dimensional (3D) imaging [1,2]. The height resolution is acquired by multi-angle coherent measurements of the same area [3]. In spaceborne multi-pass SAR tomographic processing, the atmospheric phase screen (APS) is a significant factor affecting the accuracy of tomographic imaging [4,5]. The reference network (RN) method was originally proposed in persistent scatterer interferometry (PSI) research to tackle the APS problem and was then employed in TomoSAR research [6,7]. The PSs exhibit high coherence throughout the entire temporal baseline and can be selected using the amplitude dispersion index or coherence coefficient [8]. In urban areas, buildings and artificial structures typically exhibit a high density of persistent scatterers (PSs), resulting in favorable elevation inversion outcomes when employing PS-based TomoSAR methods. However, rapid urbanization has given rise to the emergence, migration, and disappearance of buildings and other targets, which can significantly alter the scattering characteristics of these targets over temporal baselines. These changing areas often exhibit a sparse distribution of PSs, which hinder the effectiveness of SAR tomography, including APS correction based on PSs and 3D reconstruction over the entire scene. This issue is particularly pronounced in the process of acquiring SAR tomographic datasets through multi-pass spaceborne SAR systems. Partially coherent scatterers (PCSs), characterized by high interferometric coherence over a partial temporal baseline, are introduced to capture temporary coherence in long time-series SAR datasets. PCSs exhibit features similar to those of PSs, particularly regarding amplitude stability and interferometric phase stability within their coherent intervals. Considering the potential of PCS for the dynamic monitoring of changing areas, this paper proposes a novel approach for the tomographic application of PCSs, demonstrating their capability to describe dynamic variations.
In recent years, significant attention has been devoted to the detection and application of PCS points. Accurate detection of substantial changes in the time series of individual pixels is essential for selecting PCSs. The Bayesian stepwise detectors [9], which consider Gaussian approximations of amplitude series, have been employed for detecting mutations. In [10], the genetic algorithms have also been utilized to estimate the start and end times of PCSs through interferometric phase series analysis, aiding in the detection of surface subsidence. An InSAR analysis approach was used for identifying and extracting the temporarily coherent points [11,12]. The PCS is identified based on the spatial characteristics of the range and azimuth offsets of coherent radar scatterers. The detected PCSs are introduced to efficient ground deformation mapping, even from a relatively smaller set of interferograms. In [13], a novel Quasi-PS (QPS) technique is presented to relax the stringent conditions of PS methods in multi-master interferometric SAR (MT-INSAR) processing. This approach enhances point density and performance in natural environments compared with traditional PS-based methods. Additionally, statistical methods are also applied to PSC detection as the distribution of an amplitude series is linked to the coherence properties of ground targets [14]. An analysis of variance (ANOVA) detector has been proposed in [15] to identify temporal changes of PCSs. Assuming a Gaussian distribution for amplitude time series, this method analyzes variance and employs differences within and outside coherent intervals to develop an F-test detector. Alternatively, a method based on Rayleigh distribution assumptions distinguishes significant changes by analyzing both the amplitude and interferometric phase [16]. A unified Rayleigh test and F-test are sequentially applied to select potential PCSs and automatically determine step times. The interferometric phase of these PCSs is then used to provide precise insights into temporal variations in target scattering characteristics. A classification method has been proposed to evaluate changes based on the distribution of PCSs [17], distinguishing between significant changes due to building alterations, seasonal variations, and minor surface deformations.
However, applying existing methods to PCSs in dynamic regions poses several challenges. Although current methods are effective at identifying PCS points, they primarily focus on superficial features of detected PCSs, such as change locations and distribution densities. The elevation information inherent in PCS points, which is crucial for monitoring vertical dynamic changes in evolving regions, is often neglected. This oversight impedes a comprehensive analysis of vertical changes using multi-temporal SAR datasets. As an effective 3D reconstruction method, the potential of applying SAR tomography to the processing of PCSs has yet to be explored. To fully leverage PCSs for tomographic applications, two critical challenges must be addressed. First, a standardized criterion is required to determine the precise temporal intervals during which PCS points are suitable for SAR tomography. This is crucial due to the unique distribution characteristics of PCSs along temporal baselines, which differ significantly from traditional PS points. Second, the irregular distribution of PCS points poses difficulties in achieving comprehensive spatial coverage and capturing precise elevation information. These challenges must be overcome to enable the effectiveness of PCS-based TomoSAR applications.
To tackle these challenges, we propose a novel 3D reconstruction method for PCS points through iterative sub-network generation. Initially, a coherence-constrained optimized ANOVA detection method specifically tailored for PCS selection is proposed. This approach integrates coherence interval verification to improve the reliability of the ANOVA results for the TomoSAR application. Drawing inspiration from the two-tier network approach in SAR tomography, our method employs a high-quality PS reference network as the main framework and iteratively constructs local star networks for a comprehensive coverage of the identified PCSs. Subsequently, the unified network of PCSs and PSs is used to accurately invert the height map of PCS points. Experiments have been conducted on the TerraSAR-X multi-pass dataset, which observes an urban area with variations over time. By incorporating PCS points into the SAR tomography imaging process, we achieve a notable improvement for monitoring dynamic changes in urban environments.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows. Section 2 introduces the SAR tomography based on the reference network technique and concept of PCSs. Section 3 presents the proposed PCS selection method, along with the novel two-tier network for the tomograpchic inversion of PCSs. The experimental results and analysis are outlined in Section 4. Section 5 presents the discussion and Section 6 is the conclusion.
2. Basic Theory for SAR Tomography and PCS
2.1. Signal Model of Three-Dimensional SAR Tomography
For a multi-pass space-borne TomoSAR system, the consideration involves a stack of N co-registered single-look complex (SLC) images, and the n-th component of complex-valued measurement signal at a given azimuth-range pixel can be represented as [18]:
For simplicity, the notation is omitted. Here, denotes the reflectivity vector requiring reconstruction along slant elevation s, and the spatial frequency is denoted by with a perpendicular baseline ; represents the APS and contains the noise error [19]. Model (1) can also be approximated as:
where and are modeled as a zero-mean complex circular Gaussian random vector.
2.2. Reference Network Method
A crucial step prior to tomographic reconstruction involves the removal of the APS, as outlined in Equation (1). Considering the spatial low-pass and temporal high-pass characteristics of [20,21], the APS correction is accomplished through the reference network (RN) method, which establishes a network connecting PSs and performs APS removal via the phase differencing of adjacent items [6]. The overall process of the RN method consists of PS selection, network construction, relative elevation inversion, and network adjustment.
Firstly, PS selection is conducted using the amplitude diversity index (ADI) threshold method. The ADI is defined as [8]:
Pixels with ADI values below a certain threshold are considered PS candidates.
Next, assuming the presence of two adjacent with a distance of less than a set threshold , ensuring :
The value of is generally less than 1 km [22]. By subtracting the signal phase of from that of , APS removal is achieved through phase differencing. Then, a differenced signal and the expression is given by:
Equation (5) models the differential signal as a single scatterer at a relative elevation , where and represent the elevations of and . Therefore, we employ tomographic processing to estimate the , which involves tomographic inversion and scatterer detection [23,24,25]. This method differs from PSI processing in that it utilizes both amplitude and phase information to improve estimation accuracy [26].
The RN can be established using various network models, such as Delaunay and ant colony networks, to connect PSs with arcs that exhibit high relative estimation accuracy. In this study, the ant colony network is employed, and the residue-to-signal ratio (RSR) [26] of is used to assess the quality of connectivity for the corresponding edges, as defined by Equation (6):
Ultimately, the absolute elevation of all PSs in the RN can be determined through network integration relative to a reference SPS using the weighted least squares (WLS) estimator [6].
Here, represents a weight diagonal matrix, with RSR serving as weighting coefficients, denotes the relative elevations of P PS arcs, and represents the absolute elevation of Q PSs in the RN. The relationship between and is given by
where is the transformation matrix, which only consists of 0, 1, and −1, indicating the transformational relations from arcs to points.
2.3. Partially Coherent Scatterer (PCS)
2.3.1. Concept of PCS
The concept of PCS was introduced to account for temporal variations in the scattering behavior of specific scatterers [9]. PCS is characterized by pixels displaying PS characteristics only during certain continuous time intervals within the overall time series. The presence of PCS can be influenced by various factors, with dynamic variations in human activity and building conditions playing a significant role in urban environments.
2.3.2. Coherent Intervals and Step Change Positions
For PCSs, two critical data characteristics are introduced: coherent intervals and step change positions [9,10,13]. Step change positions refer to specific points in the time series where noticeable changes in scattering characteristics occur. Additionally, coherent intervals are continuous time segments where the PCS exhibits high coherence and stable scattering properties. Conversely, the remaining time baselines display incoherent characteristics.
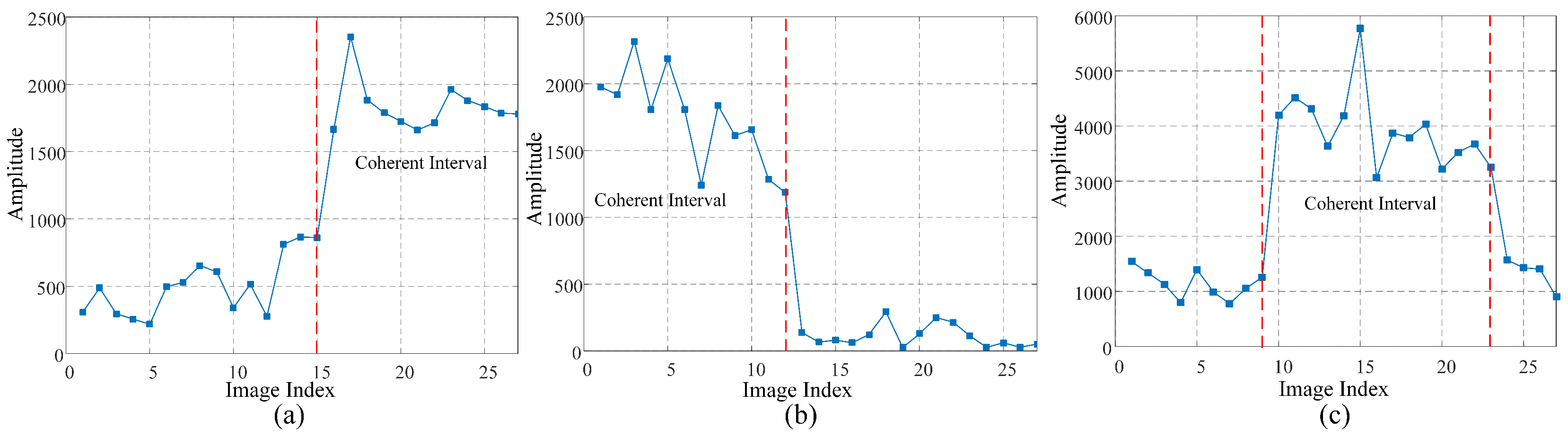
Based on the typical positions of coherent intervals within the observation period and considering their physical significance, PCS can be classified into three distinct types, as illustrated in Figure 1.
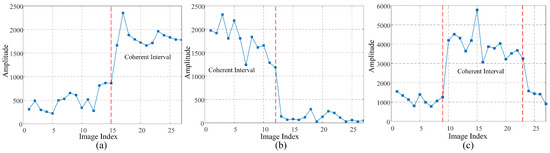
Figure 1.
Three types of PCSs based on the division of coherence intervals. (a) Appearing-type PCS (APCS). (b) Disappearing-type PCS (DPCS). (c) Visiting-type PCS (VPCS). The red dashed lines represent the image index when coherence of PCS changes.
- Appearing-type PCS (APCS). As shown in Figure 1a, the coherence interval of APCS starts from the step change position to the end of the time series. APCS initially presents as incoherent and turns coherent after the step change position. In urban areas, APCS may represent the new construction of buildings or the emergence of artificial targets.
- Disappearing-type PCS (DPCS). As shown in Figure 1b, the coherence interval of DPCS starts from the first acquisition time to the step change position. DPCS initially presents as coherent and turns incoherent after the step change position. The existence of DPCS may indicate the demolition of buildings, relocation of artificial targets, or the obstruction phenomenon due to the emergence of APCS.
- Visiting-type PCS (VPCS). As illustrated in Figure 1c, the coherence interval of VPCS is situated between two consecutive step change positions. VPCS differs from the above two types of PCSs, which have only one step change position, in terms of the least number of step change positions. In practical scenarios, VPCS is more likely to be observed in long time series, where the complete occurrence and disappearance of the target can be monitored.
The characterization of amplitude distributions is essential for distinguishing and modeling PCSs in SAR image sequence [15]. The presence of at least one coherent interval and one step change position is a key indicator of PCSs. Analyzing amplitude time series allows researchers to develop hypothesis tests for detecting PCSs within SAR datasets. The application of PCSs is crucial for accurate deformation monitoring and land surface change detection, particularly in urban environments.
3. Detection and 3D Reconstruction of PCS
3.1. PCS Detection for TomoSAR Based on Coherence Constraint Iterative Variance Analysis
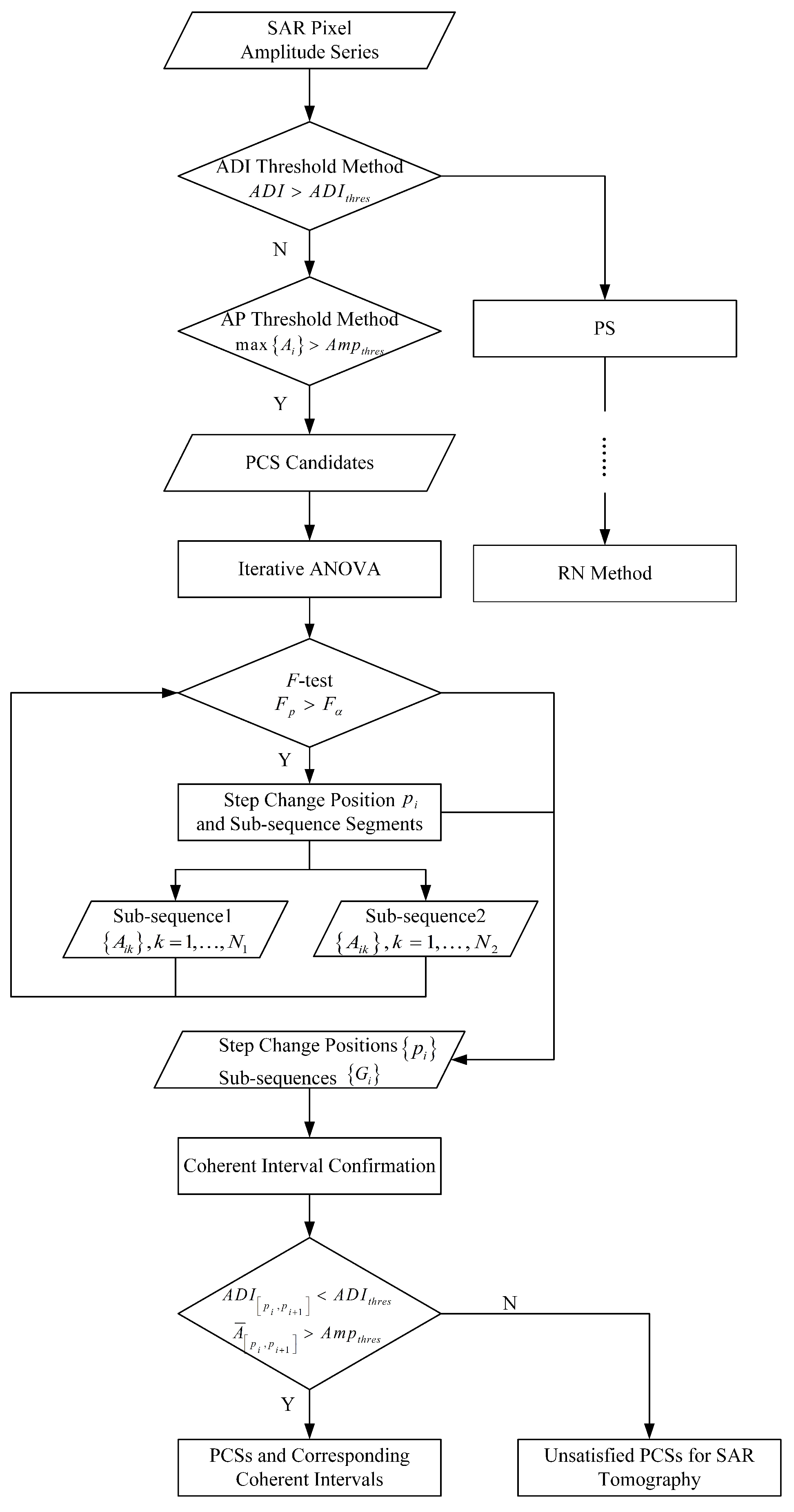
This section presents a method for selecting PCSs from multi-temporal SAR dataset based on a coherence constraint iterative analysis of variance. The methodology comprises three main components.
- Selecting PCS candidates to identify the existence of PCS at each pixel.
- Iteratively searching for step change positions of PCS candidates using ANOVA, considering the possibility of multiple positions.
- Confirming the identified step change positions and coherent intervals. As the time series are segmented into multiple sub-intervals, only coherent intervals suitable for SAR tomography processing are derived by imposing the coherence constraint.
Assume that the SAR dataset contains N co-registered SLC images; the amplitude time series at a specific pixel can be denoted by . The specific explanations of each step are provided below.
3.1.1. PCS Candidates Selection
Firstly, PS candidates are identified from using an ADI threshold. The selected PSs are utilized for subsequent TomoSAR processing based on the RN method. For the remaining non-PS pixels, the amplitude peak threshold (APT) method is employed to select PCS candidates. When the peak value of exceeds the specified threshold, it is considered as a potential pixel containing PCS.
Here, is typically chosen as the mean of all pixel amplitude values [6].
3.1.2. Iterative Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
The ANOVA method dissects the overall variance of pixel amplitude series into between-group variance and within-group variance to assess the significance of distinctions among sub-sequences. Assuming the step change position lies between , the original sequence is partitioned into two parts . A hypothesis test is conducted to ascertain if the two sub-sequences follow the same distribution and if the position represents a step change.
Because the ADI characterizes the interferometric coherence of pixels, the hypothesis test statistic should be related to both the variance and mean of the pixel amplitude time series. The detection statistic for the ANOVA method is defined as:
Here, represents the mean of the entire pixel amplitude sequence, denotes the within-group means, and represents the within-group variance of the divided sub-sequences. The variance between sequences reflects the differences in means among different sub-sequences, while the within-sequence variance indicates the degree of variation among individuals within the same sub-sequence. follows an F distribution with degrees of freedom .
Equation (11) allows for the design of a test threshold based on significance level and degrees of freedom . Then, the hypothesis test is defined as:
where indicates that the two sub-sequences do not belong to the same distribution, the pixel is considered a PCS, and the position is a potential step change position. The significance level typically ranges between 0.01 and 0.1, with a higher corresponding to lower . For all positions satisfying Equation (13), the final step change point position is determined as:
Given that there may be multiple coherent intervals in the amplitude series, corresponding to more than one potential step change position, an iterative search for these step change positions is conducted as follows:
- Step 1: Search for a single step change position. Employ ANOVA to identify the initial step change position, denoted as .
- Step 2: Iterative search for additional step change positions.Following Step 1, divide the amplitude series into two intervals based on :. Perform Step 1 within these newly defined sub-intervals. Note that will vary due to changes in the length of the sub-sequences, which affects the degrees of freedom. Consequently, must be updated at each iteration.
- Step 3: Finalize the division of the amplitude series.Repeat Steps 1 and 2 iteratively to search for additional step change positions. Continue this process until no further step change positions can be identified from subsequent divisions. Assuming all step change positions are , the amplitude series are divided into M segments:
3.1.3. Coherent Interval Confirmation
Establish constraints for the corresponding sub-sequences within the segments , , acquired in Equation (14), *to assess their suitability for TomoSAR processing.
- Coherence constraint. The amplitude series within coherence intervals should exhibit both a higher average amplitude and a lower ADI simultaneously. This can be formally expressed as:
- Observation quantity constraint. To ensure the feasibility and accuracy of the tomographic inversion, the suitable coherence intervals must contain a sufficient number of observations. Assuming that the minimum required number of observations for SAR tomography is D, the coherence interval for PCSs must meet the following condition [27,28]:
The flowchart of the proposed PCS detection methodology is presented in Figure 2. Additionally, the algorithm for the coherence constraint ANOVA is detailed in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 Coherence constraint ANOVA |
|
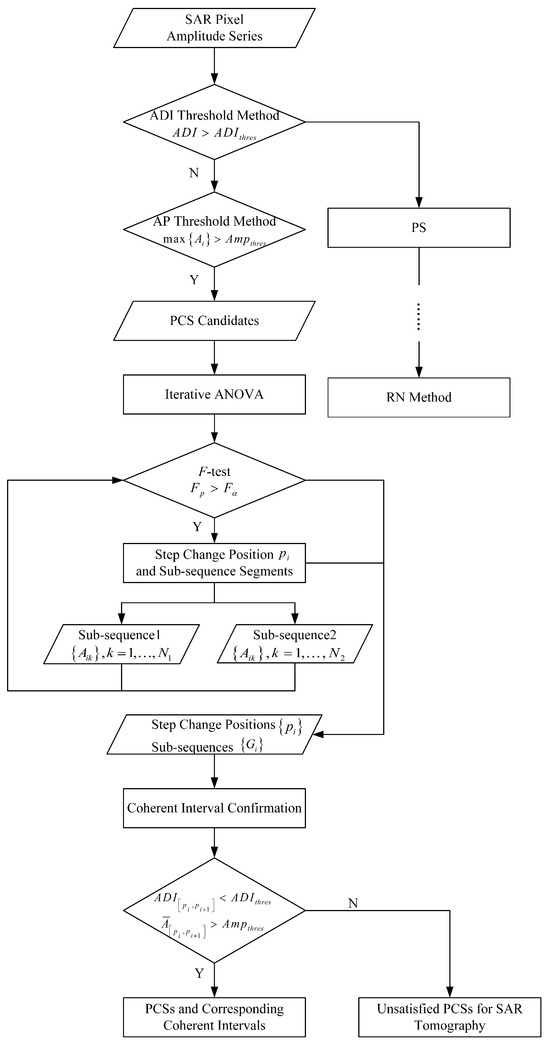
Figure 2.
Flowchart of PCS detection based on iterative ANOVA and coherent interval confirmation.
3.2. Three-Dimensional Imaging of PCS by Iterative Sub-Network Generation Method
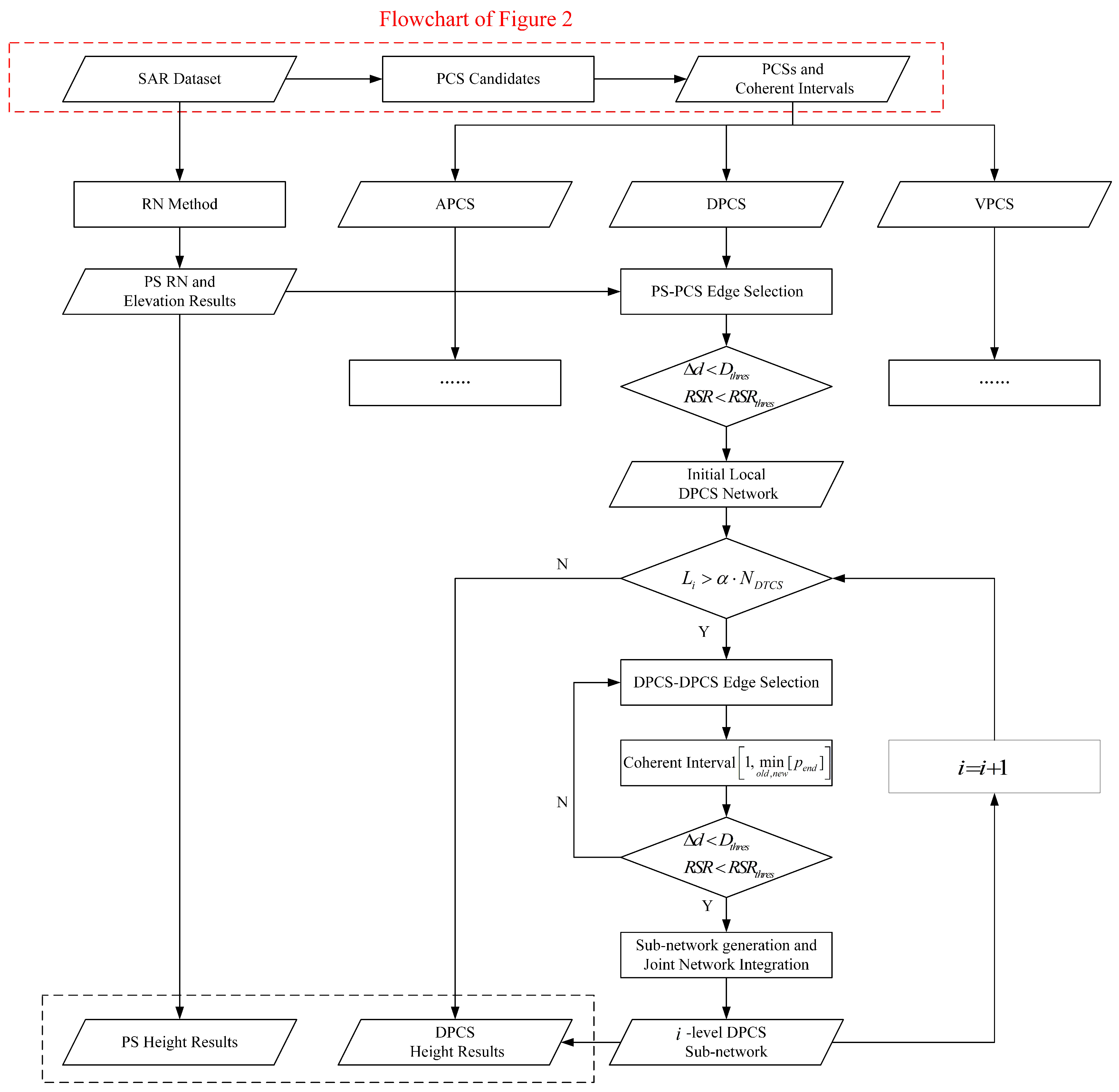
This section introduces a technique for the 3D imaging of detected PCSs through iterative sub-network generation. The proposed inversion process aims to improve the comprehensiveness and effectiveness of SAR tomography, particularly in dynamic environments. This inversion process is designed to enhance the comprehensiveness and effectiveness of SAR tomography in dynamic environments. In this novel method, the PS reference network and elevation outcomes are initially obtained from Section 2.2, serving as the reference data for the height inversion of PCSs. A local sub-network, connecting PCSs with resolved PSs, is then constructed to enable the APS correction and relative elevation inversion for the PCSs.
However, the distribution of PCSs in buildings and artificial structures exhibits regional clustering characteristics. Additionally, the geographic area of PCSs often differs from that of PSs, leading to an insufficient number of reference PSs used to establish reliable connections between PCSs and PSs.
To address this issue, the proposed method dynamically expands the local sub-network to connect PCSs. By using the existing network of connected PCSs as the basis for generating subsequent layers, we ultimately achieve a comprehensive coverage of the PCSs and height inversion. Specifically, reliable connections between PSs and PCSs are established to create the initial sub-network. Subsequently, PCSs within the first-level sub-network serve as new references to identify reliable connections with unlinked PCSs, thereby forming the second-level sub-network. This iterative process continues until the size of the newly generated sub-network is below a specified constraint. For each sub-network, the elevations of newly connected PCSs are determined layer by layer through network integration and then incorporated into the final elevation results for all PCSs.
Given the characteristics of PCSs, the observed data series used for tomographic imaging should be within coherent intervals. Additionally, height inversion processing should be performed separately for different types of PCSs as outlined in Section 2.3.
3.2.1. Initial Sub-Network Generation
Initially, each PCS is connected with the closest PS to form a PS–PCS edge, constituting the first-level sub-network surrounding the reference network. Phase differencing between the endpoints are conducted for each edge to correct the APS error. The differential signal retains solely the observed sequences within the coherent interval of the PCS points, then undergoes tomographic imaging and relative elevation estimation. Ultimately, only high-quality PS–PCS edges meeting the imaging quality criteria are preserved, leading to the initial distribution of the star-shaped network, where the terminal points of each edge represent newly connected PCSs.
Assuming that the PS reference network contains a total number of Q PSs and P PS edges. The specific form of the relative elevation vector , the absolute elevation vector S, and the transformation matrix G can be represented as
where . Assuming that a total number of PCSs are detected in the initial local network, corresponding to high-quality PS–PCS edges. Then, the distance and imaging quality constraints for each edge are defined by:
where represents the spatial distance between the two endpoints and denotes the residual energy ratio according to Equation (4) and (6). At this stage, the reference network and the first-level local network can be jointly represented as:
where , , | represents the vector concatenation operation. The newly added PCS elevation values and the corresponding relative elevations of the edges are, respectively, expressed as:
According to the correspondence of PS–PCS edges, can be decomposed as follows:
where and represent the transformation matrix between , , and , respectively. Consequently, Equation (20) can be transformed as:
Let ; then, Equation (22) can be expressed in a similar form to Equation (20):
This enables the solution for through the WLS estimator for network integration:
is a weighted diagonal matrix where the diagonal elements correspond to the quality of the tomographic imaging of the differential signals corresponding to the newly generated PS–PCS edges.
3.2.2. Iterative Sub-Network Generation
The initial local network is used to connect PCSs with the PS reference network. However, due to the spatial distribution characteristics of PCSs, there are a number of unconnected PCSs unsatisfying the constraints in Equation (18). Therefore, it is necessary to expand the initial sub-network through an iterative sub-network method.
The newly generated sub-network is used to connect the remaining unconnected PCSs with the connected PCSs in the previously generated sub-network. The sub-network iteration process is based on the connected PCSs, seeking high-quality PCS–PCS edges between them with unconnected PCS points. Then, a new layer of sub-network and elevation inversion is obtained. During the generation of the initial network, the time interval of the PS–PCS edge differential signal remains consistent with PCS as the coherent interval of PCS is contained in that of PS (entire time baseline). However, during the iterative generation of the sub-network, it is necessary to select a common coherent interval based on the positional relationship of the connected PCSs. The common coherent interval of two endpoints, whose coherent intervals are and , can be calculated:
Specifically, is for the newly generated APCS–APCS edge and is for DPCS–DPCS edge. Additionally, for the newly generated PCS–PCS edges, it is also necessary to satisfy constraints in Equation (19).
Assuming the number of iterations is i with the relative elevation vector and transformation matrix in each iteration update. By utilizing the WLS estimator based on Equations (21)–(24), the elevation values of the newly connected PCS points in the i-th level sub-network can be calculated as follows:
The above sub-network iteration is repeated until a sufficient number of PCSs cannot be connected. The termination criterion for the iteration process is defined as:
where represents the number of newly connected PCS, is the total number of PCSs, and is a scaling factor indicating the proportion of newly connected PCSs to the total PCSs. signifies that a certain number of high-quality PS–PCS edges can still be established at this stage, allowing for the construction of the next-level sub-network based on the newly connected PCSs. Conversely, Equation (27) indicates that the newly established sub-network only covers a small portion of the PCSs, leading to the conclusion of the iteration process.
Ultimately, the elevation results connecting all PCSs in the entire local network through sub-network iteration are obtained.
This approach helps prevent the excessive localization of the generated sub-network, ensuring a wider coverage of PCSs. The flowchart of the proposed height inversion of PCSs by the iterative network generation method is given in Figure 3.
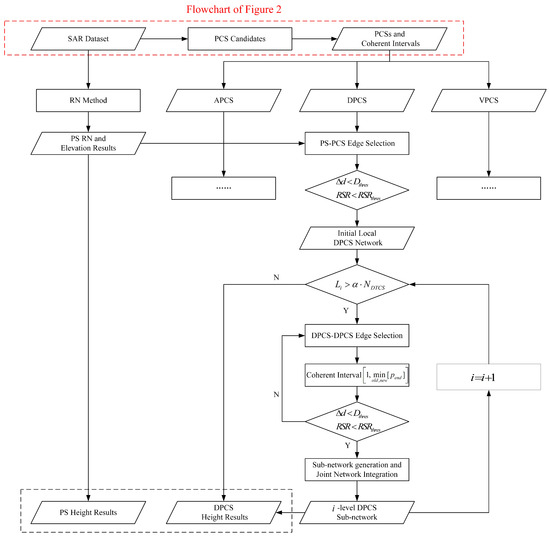
Figure 3.
Flowchart of the proposed height inversion of the PCSs iterative network generation method. The red dashed box represents the flowchart of the PCS detection method in Section 3.1.
The flowchart input consists of an SAR dataset with N images, generating height results for PSs and PCSs. It primarily details the processing steps for DPCSs, as those for APCSs and VPCSs are similar only with distinct criteria for common coherence intervals calculation. The processing procedures in Figure 3 for different types of PCSs are independent, enhancing the length of common overlap coherent intervals. These characteristics improve sub-network edge connections and tomographic imaging reliability.
4. Results
4.1. Introduction to the SAR Dataset
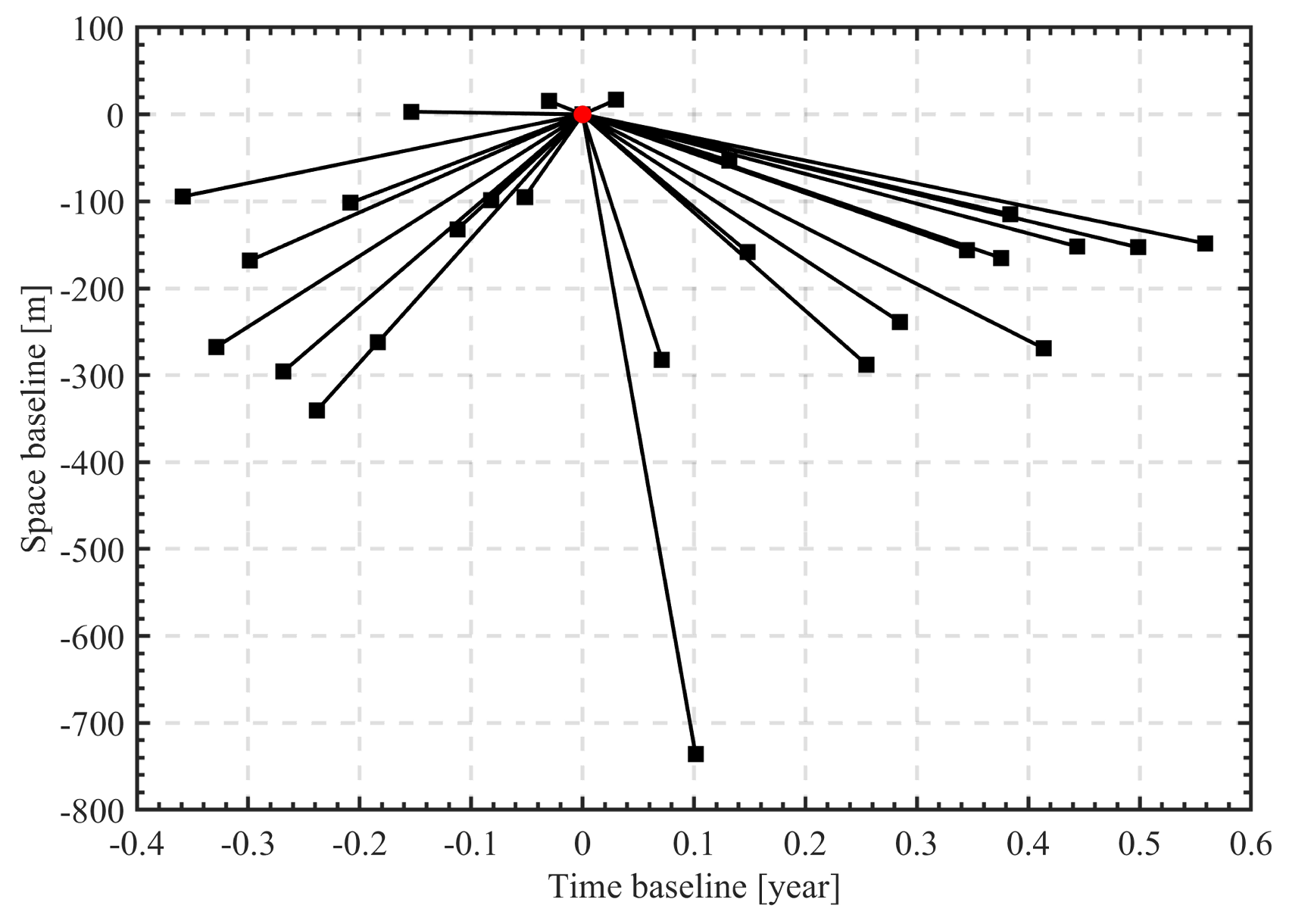
In our experiments, we utilized 27 high-resolution TerraSAR-X images in staring spotlight mode, acquired between 5 January 2016 and 30 November 2016. The images feature a range spacing resolution of 0.6 m, azimuth spacing resolution of 0.24 m, and HH polarization mode. The study site was situated in the Bao’an District of Shenzhen, China. Figure 4 illustrates the distribution of the temporal baseline and spatial perpendicular baseline, with the image being captured on 10 July 2016 being designated as the master image. As the temporal baseline spanned approximately 0.9 years, the deformation factor was not accounted in this study, while only 3D TomoSAR results were obtained.
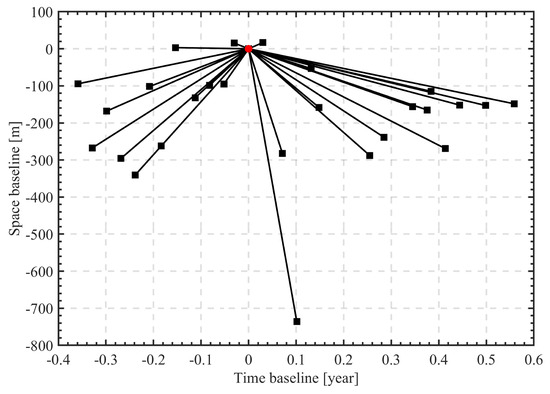
Figure 4.
Spatial–Temporal baseline distribution of the SAR images. The highlighted red circle represents the master image.
The average amplitude map of the study area is depicted in Figure 5a. It discerns the presence of tall buildings, large warehouses, and artificial platforms, which serve as typical point-like scatterers crucial for SAR tomography in an urban environment. Figure 5b displays the distribution of PSs, with a total of 17,136 PSs being identified in the region using [29]. Notably, Figure 5b highlights variations in the distribution of PSs among buildings within the same area, with only certain structures displaying significant PS point densities. Several building structures with high amplitude are ignored from being classified as PSs. In order to elucidate the causative factors behind this phenomenon, Figure 5c,d showcases Google optical images captured in January 2016 and December 2016, corresponding to the approximate first and last acquisition temporal baseline.
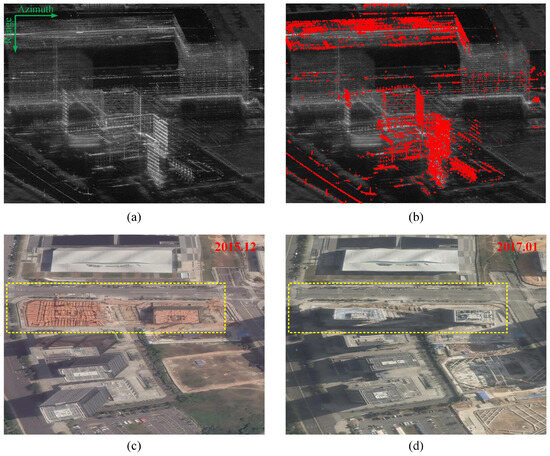

Figure 5.
SAR and optical image of the study area. (a) SAR average amplitude map. (b) PS distribution map. (c) Google optical image acquired in December 2015. (d) Google optical image acquired in January 2017.
The comparison of the two optical images reveals the consistent presence of the Bao’an District Library and three central office buildings throughout the observation period. In contrast, the construction of the Haina Baichuan Towers (the highlighted twin-tower structure) from January to December 2016 transformed the vacant land into highrise structures. This change helps to explain the spatial distribution of PSs in Figure 5b as PS primarily corresponds to stable strong scatterers across the entire time baseline. Figure 5 highlights the limitations of PSs in capturing scatterers within the transitional region. The sparse distribution ultimately hampers the overall efficacy of SAR tomography. Nowadays, the accelerated pace of urbanization further accentuates the significance and essentiality of investigating and analyzing PCS in regions where high coherence is sustained within partial time baselines.
4.2. PCS Detection Results
The iterative ANOVA method was performed to detect PCSs on the dataset, yielding a set of PCSs and step change positions of each PCS. Then, the coherent constraint is applied on the data sub-sequences to determine the PCS set suitable for SAR tomography processing. The parameters set in the experiment are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Parameters of PCS detection.
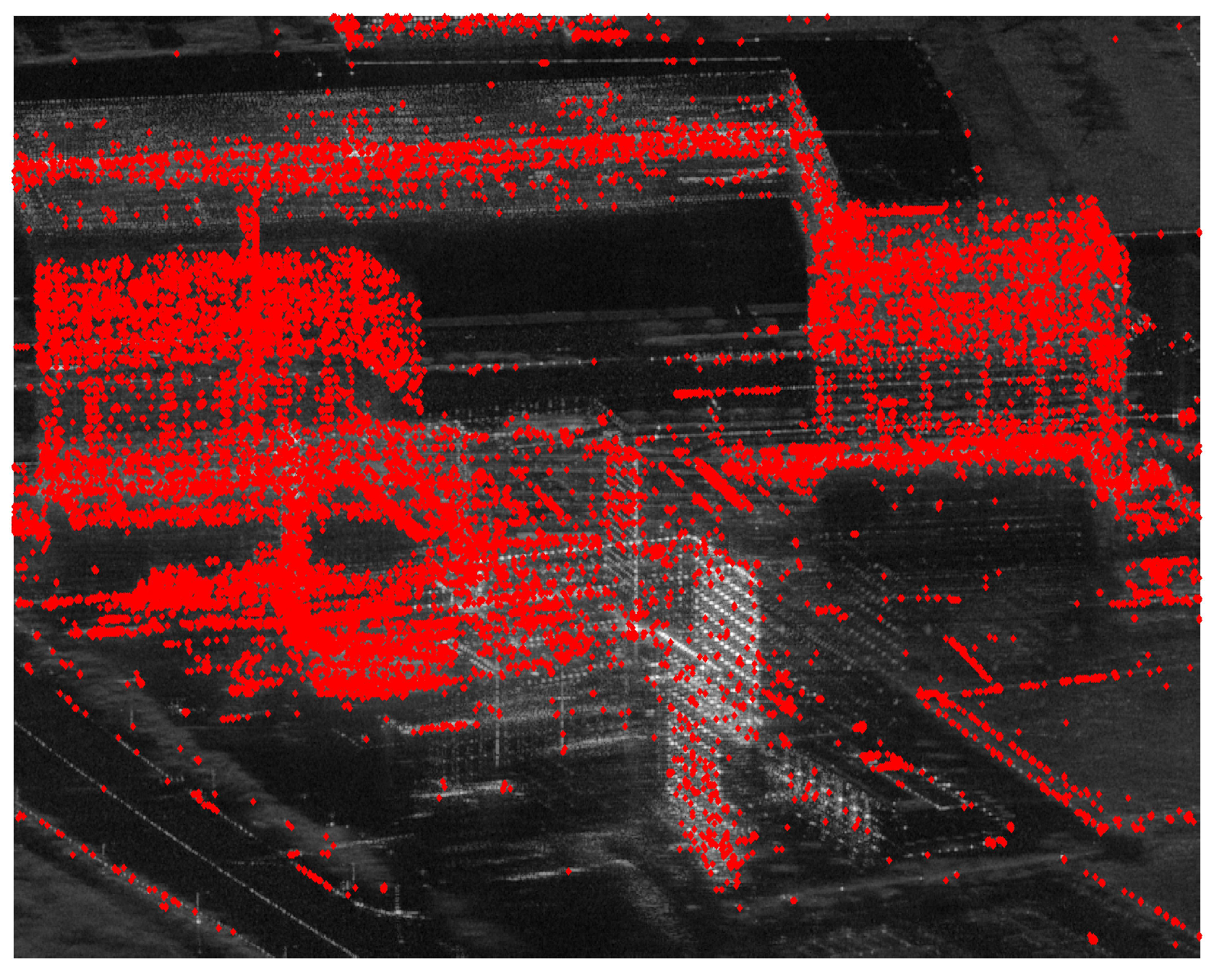
Figure 6 illustrates the distribution of PCSs using the proposed method, with a total of 21,172 detected PCSs primarily concentrated in areas exhibiting strong scattering from buildings, artificial targets, and roads. Analyzing the distribution of PCSs reveals significant insights. On the one hand, comparing with the distribution of PSs in Figure 5b, PCSs effectively cover regions of buildings where PSs fail to account for them. This phenomenon suggests that these strong point-like scatterers in the SAR average amplitude image exhibit partial coherence within the temporal baseline. A detailed structural information of buildings are more pronounced by the PCS presentation.
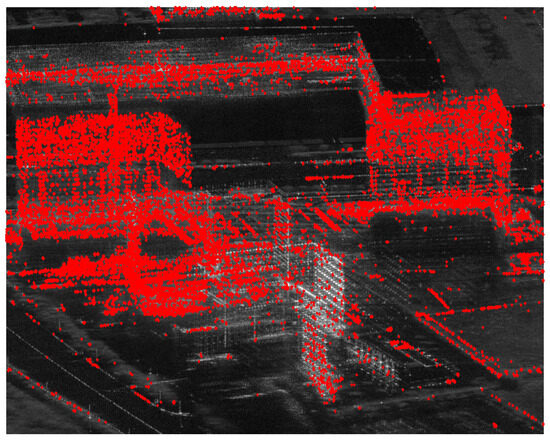
Figure 6.
PCS distribution map.
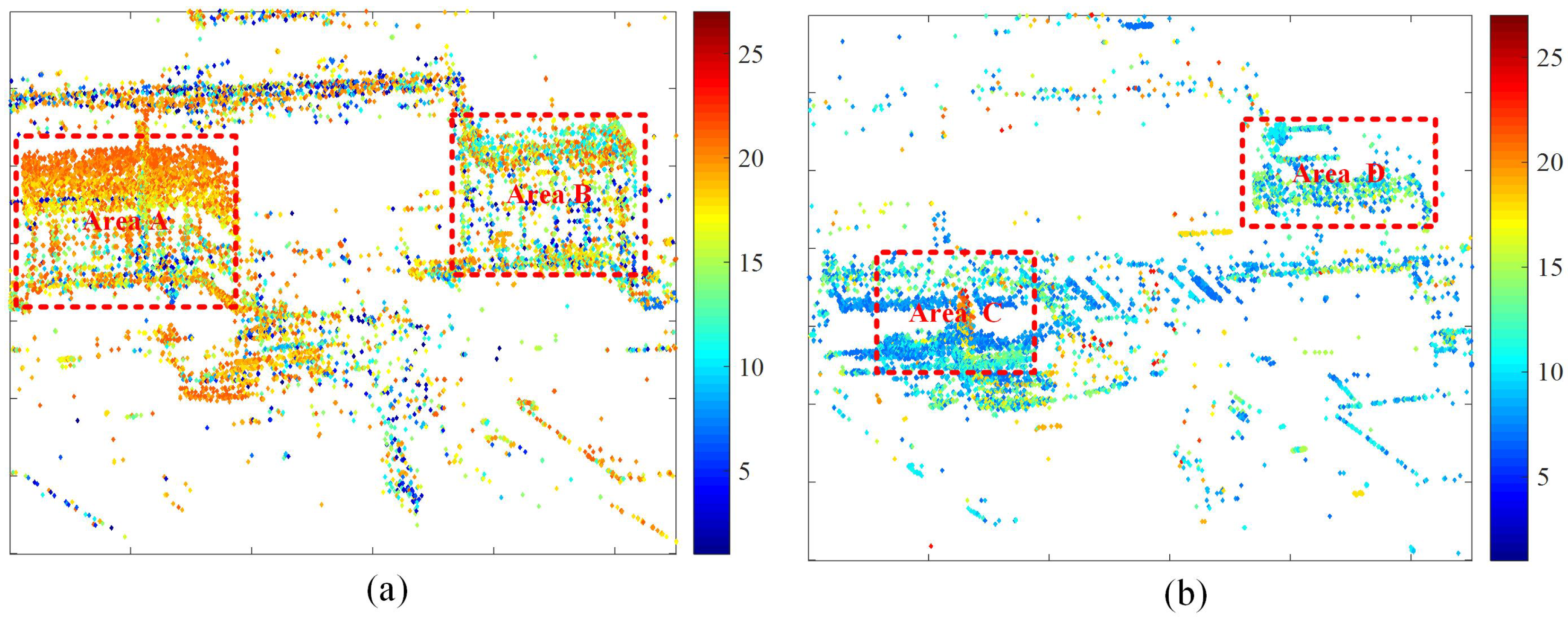
Given the relative short temporal baseline coverage of the study SAR dataset, the likelihood of VPCS occurrence is low. As a result, subsequent SAR tomography processing will focus on other two specific types of PCS: APCS and DPCS. Figure 7 presents the distribution of APCS and DPCS in the study area, with a common color bar indicating the step change points.
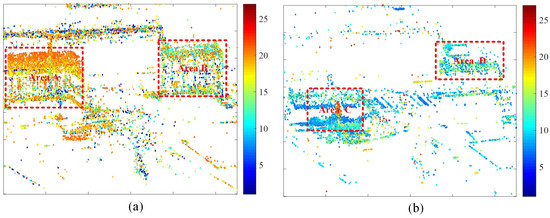
Figure 7.
Distribution of different types of PCSs. (a) APCS. (b) DPCS. The color bar represents the step change positions.
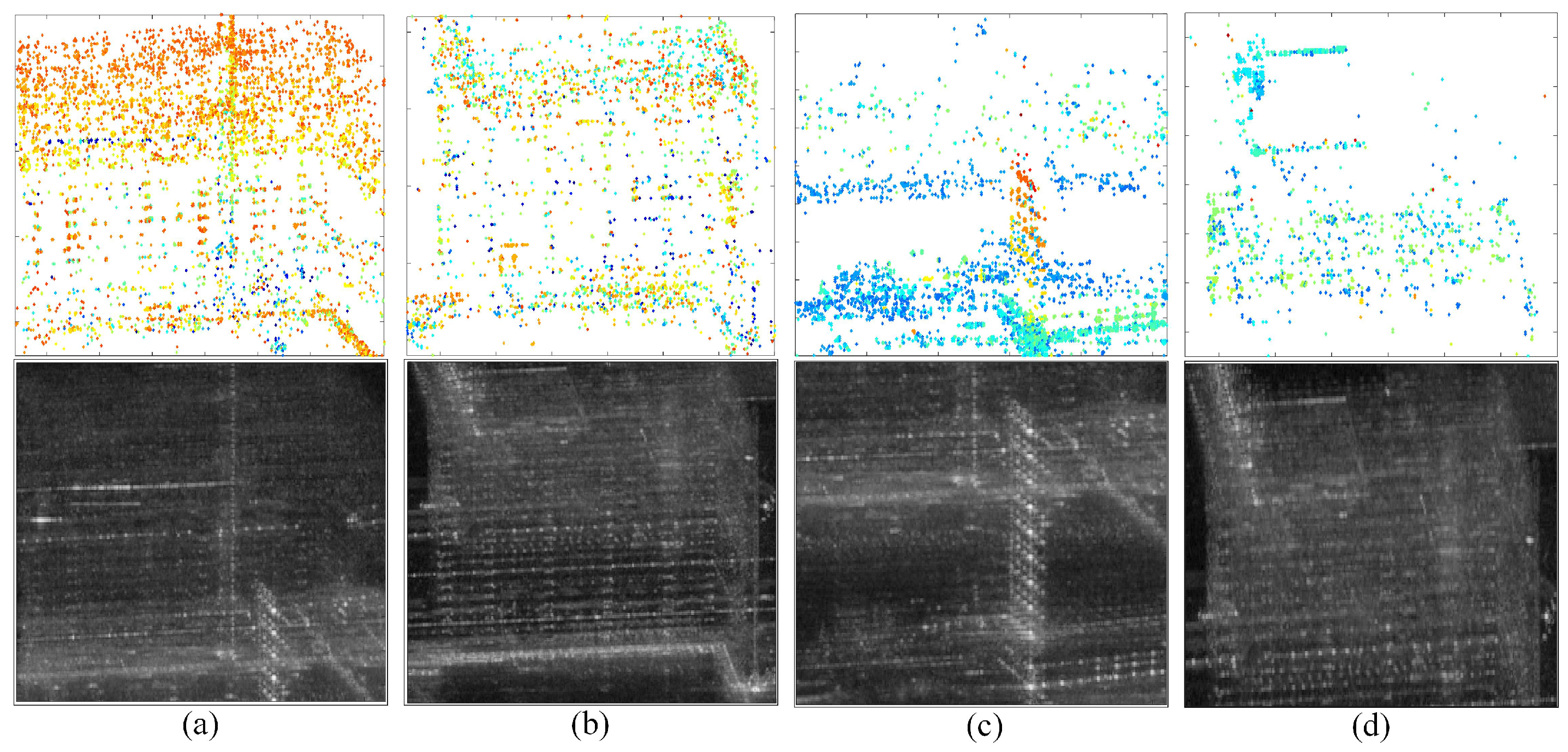
In Figure 7a, a total of 13,183 APCSs are detected. Notably, Area A and Area B are highlighted with dense PCSs, which indicate scatterers associated with dynamic activities. The detailed information refers to Figure 8a,b. Examination of Figure 8a reveals that the step change positions on building targets in Area A closely match the construction activities in the real world, where APCSs on the roofs appear later than on the base of buildings. In Figure 7b, a total of 8492 DPCSs are detected. Representative DPCSs can be found in Area C and D; some of them are obscured by neighboring buildings or are covered by the newly appeared scatterers within the same areas. Further elaboration is available in Figure 8c,d. In Figure 8c, significant DPCSs are situated at the base and exterior walls of buildings. We examine the azimuth locations of Figure 8a,c. Due to the proximity of A and C in the SAR azimuth direction, height changes of the target in the near end of range direction Area A can cause occlusion effects on the far end of range direction Area C. As the height of buildings in Area A increases, the occluded area expands gradually, with taller targets being occluded later. This explains the proportional relationship between the color bar of step change positions and target height. Notably, DPCSs in Figure 8d mainly cluster around buildings with square shapes. Comparing this with the distribution of Figure 8b, the DPCS in Area D is covered by the newly appeared scatterers within the same areas of Area B.
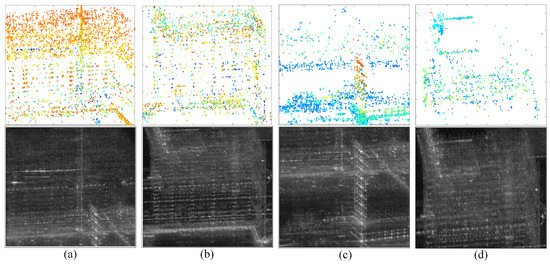
Furthermore, the cumulative count of APCS and DPCS reaches 21,675, surpassing the total PCSs of 21,172 in Figure 6. This indicates instances where pixels are flagged as both APCS and DPCS points.
4.3. Height Estimation of PCSs
The elevation inversion method based on the proposed iterative sub-network generation is applied to the above-detected PCSs. Subsequently, the vertical height of each scatterer is calculated using the transformation , with being the incidence angle [30]. The vertical height point cloud of the obtained PCSs are analyzed to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
4.3.1. Height Estimation of PS
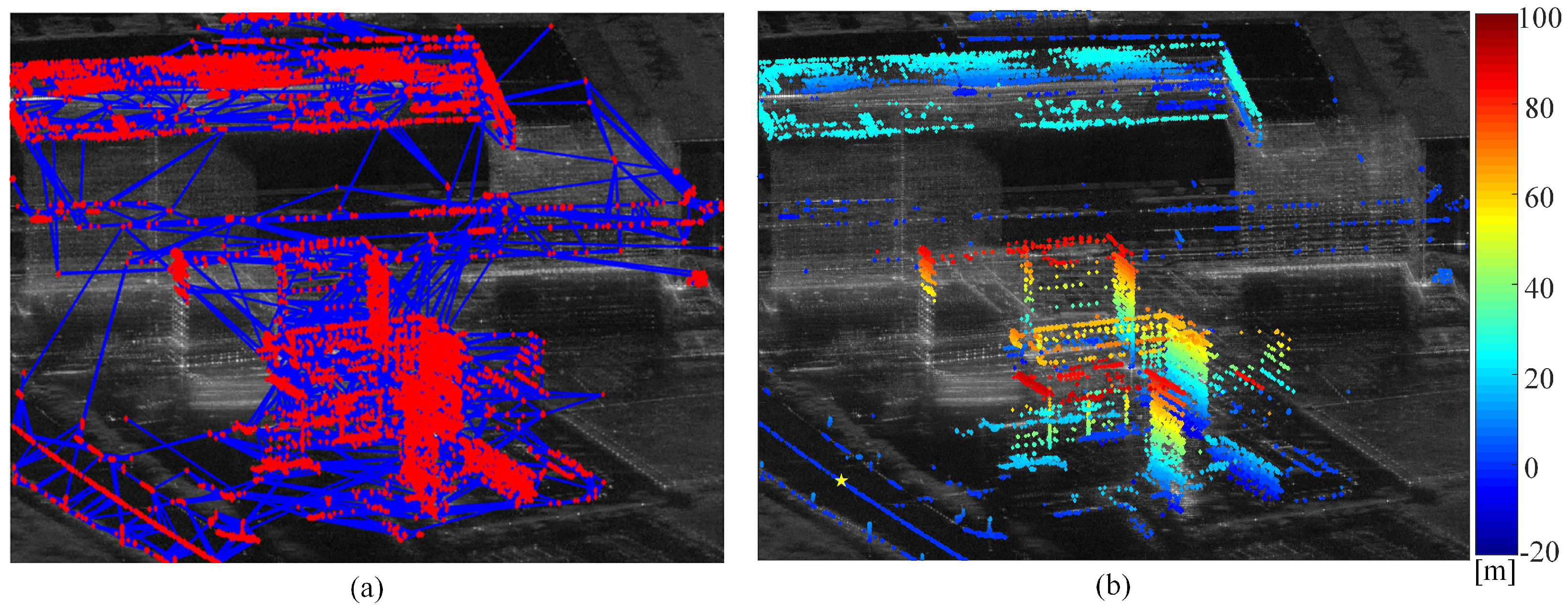
To serve as a reference for the elevation inversion of PCSs, the PS reference network, depicted in Figure 9a, was generated, comprising a total of 16,512 connected PSs. The height point cloud map of PSs was obtained by network integration, as illustrated in Figure 9b. One PS, located on the road, was selected as a reference point with its height set to zero.
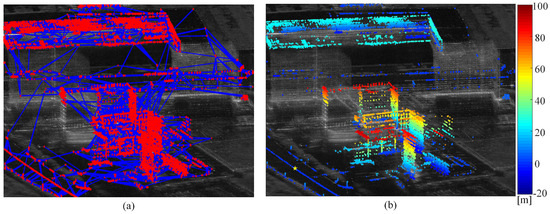
Figure 9.
Distribution of PS RN and height map of PSs. (a) Distribution of the PS RN. (b) Height map of PSs. The selected reference point with zero height is located on the left side of the road, indicated by a yellow pentagon star.
4.3.2. PCS Sub-Network
The proposed iterative sub-network generation method was applied to the APCSs and DPCSs, using the PS RN depicted in Figure 9 as references. The parameters employed in the sub-network generation process are detailed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Parameters of PCS sub-network generation.
Specifically, the iteration process ends until the number of PCSs in the sub-network generated iteratively is less than 0.01 times of the total number of each type of PCS, disregarding subsequent sub-networks with few edges being generated thereafter.
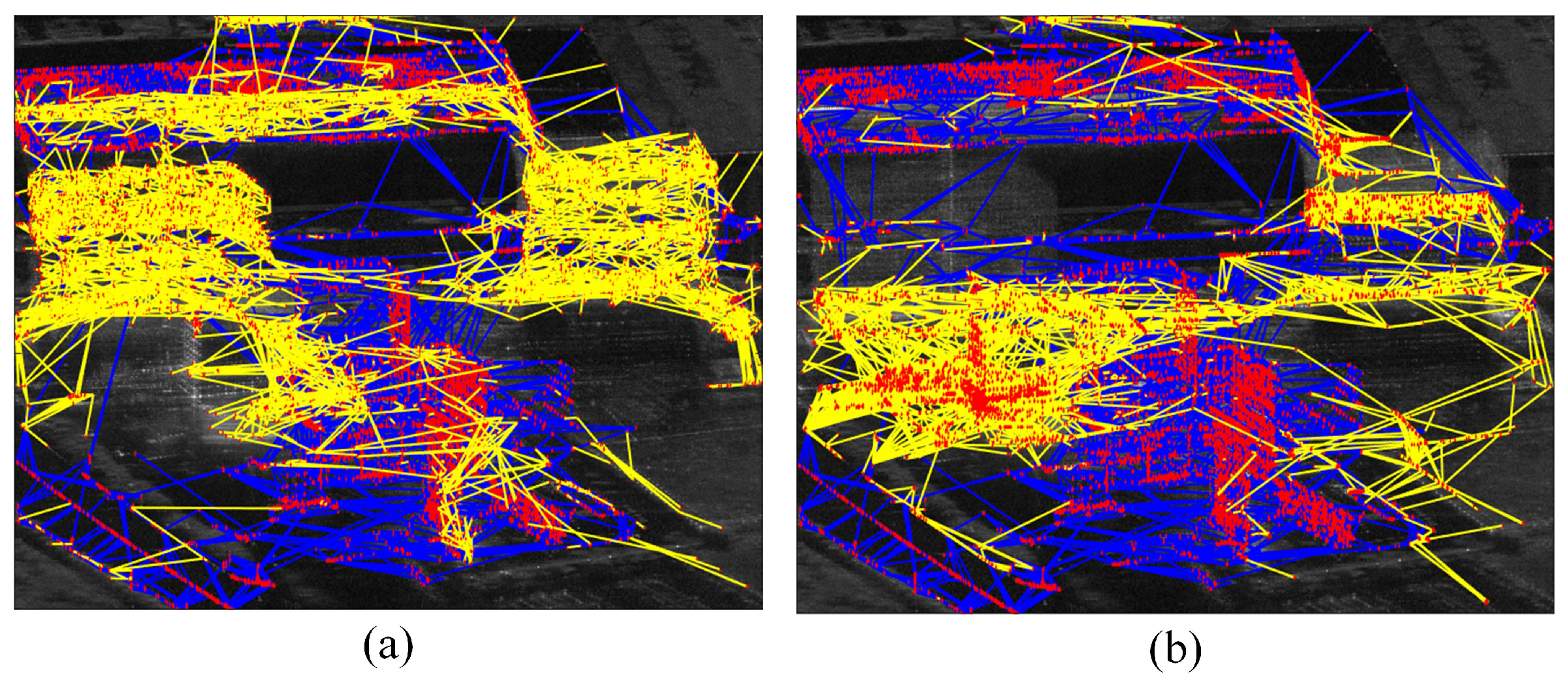
The results of the final generated PCS sub-network with the distribution of PS RN are depicted in Figure 10. In Figure 10a, the DPCS sub-network is connected to a total of 8845 DPCSs, with a network coverage rate of 67.09% for the detected APCS in Figure 7a. In Figure 10b, the APCS sub-network is connected to a total of 5042 DPCSs, with a network coverage rate of 59.37% for the detected DPCS in Figure 7b. The coverage rates of two types of PCSs are both over half of the detected PCSs, being connected to the iteratively generated sub-network.
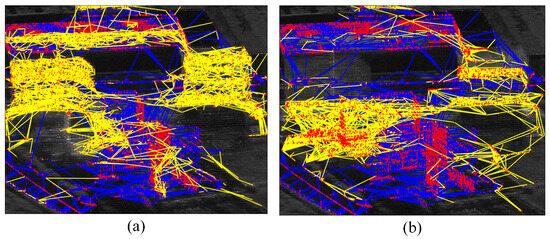
Figure 10.
Distribution of the PCS sub-network. (a) APCS sub-network. (b) DPCS sub-network. The yellow edges represent newly generated connections to the PCSs. The blue color indicates the PS RN while yellow color represents the subnetwork.
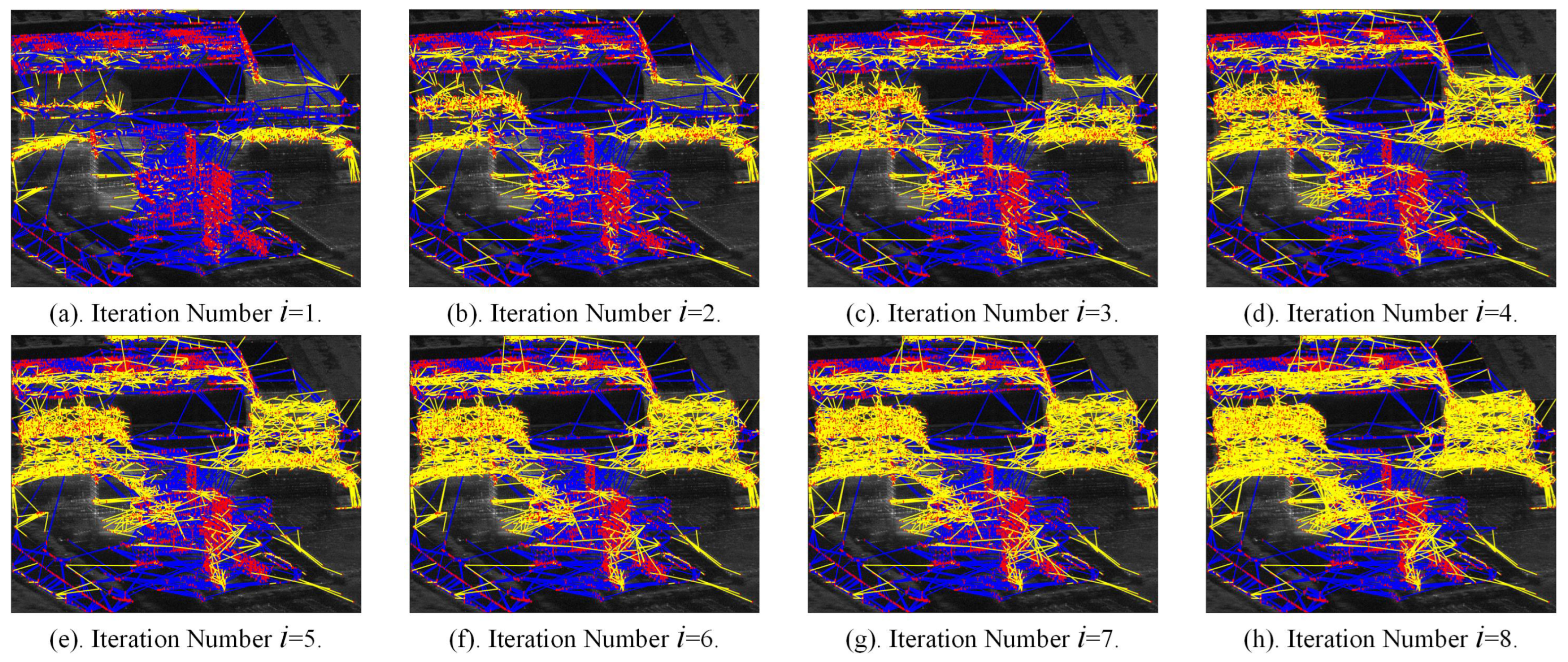
To better demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, Figure 11 illustrates the iterative generation process of the APCS sub-network shown in Figure 10a. Figure 11a displays the first-level sub-network connected to the PS RN, where there are newly added PS–APCS edges. Due to the clustered distribution of PS and APCS points across different regions, PS–APCS edges are formed only between some boundary points in some overlapping areas, resulting in a limited number of high-quality connections. Figure 11b–h show high-quality APCS–APCS edges identified in each iteration. As iterations progress, the sub-networks increasingly cover most buildings around APCS points. Table 3 records the size of each iteratively generated sub-network and the proportion of connected APCSs relative to the total number. The results reveal that as iterations increase, the number of APCSs in the new sub-network decreases. After five iterations, the network coverage of newly generated sub-networks drops below 5%, limiting the distribution of newly connected APCSs. Beyond eight iterations, the overall network coverage gain from finding new APCS points is around 1%. The set of scaling factor can reduce time complexity in large-scale scene processing. This novel network generation method improves the APCS coverage by 3.11 times compared with the strategy of traditional two-tier network using only PSs as references, effectively enabling elevation inversion for more APCSs.
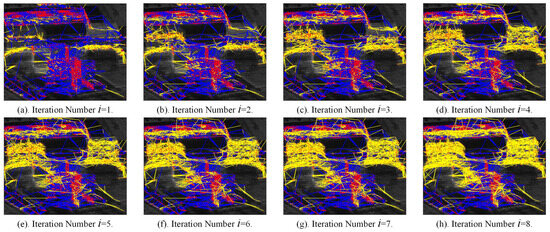
Figure 11.
The iterative generation process of the APCS sub-network, where (a–h) represents iteration number 1–8. Red points are PSs and APCSs, blue edges denote edges in the PS RN, and yellow edges indicate those in the newly generated sub-network.

Table 3.
Size of each sub-network iterative generation of the APCS.
4.3.3. PCS Height Point Cloud Map
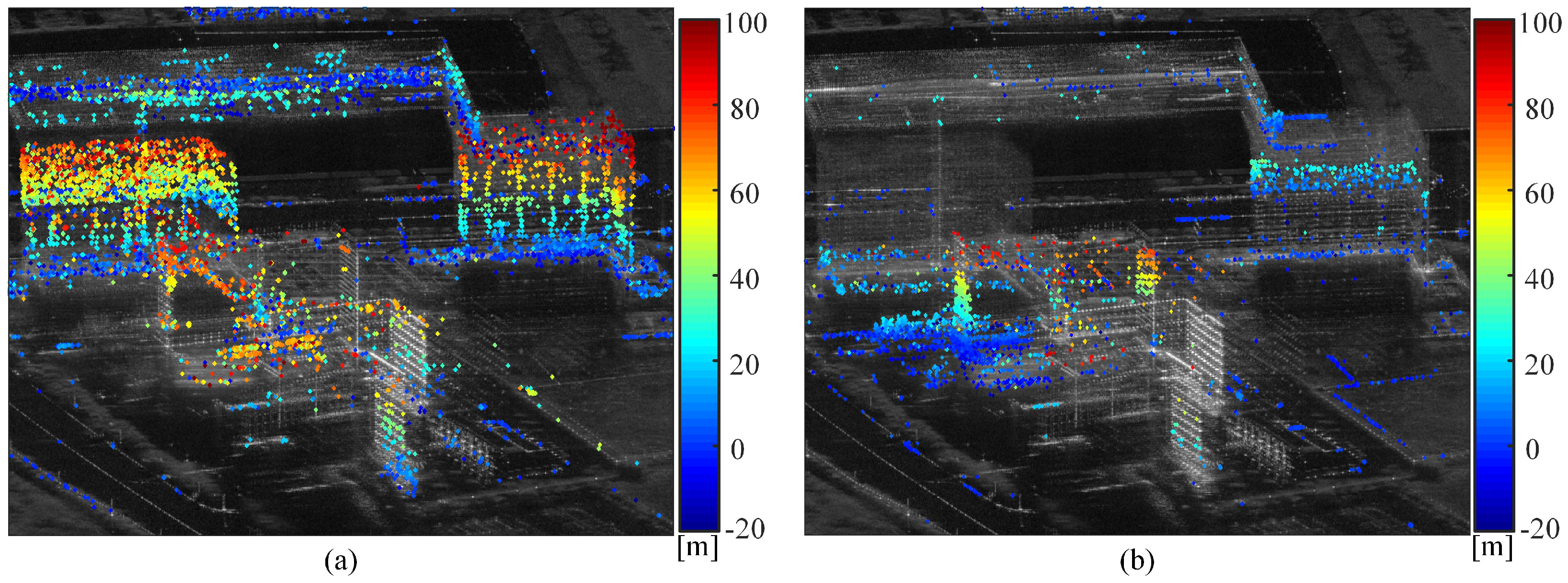
The heights for both APCS and DPCS are estimated by the proposed method in Section 3.2. Figure 12 illustrates the height point cloud map of APCS and DPCS. For ease of comparison, the positions of the reference point with zero height was kept consistent with the height map of PS in Figure 9b.
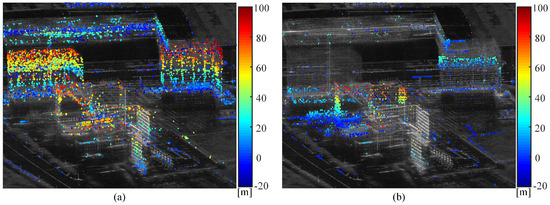
Figure 12.
Height point cloud map of different types of PCS. (a) APCS. (b) DPCS.
Figure 11a ,b represents the estimated height point cloud map of APCSs and DPCSs, respectively. It can be observed that the proposed PCS height inversion method effectively retrieves height information for most buildings within the distribution of PCSs. Figure 12a demonstrates a successful inversion of height information for newly constructed buildings within the temporal baseline, as exemplified by two twin-tower structures shown in the optical image of Figure 5. The observed vertical upward trend in point cloud heights confirms the accuracy of the inversion results for APCS points, aligning with real-world observations. Figure 12b primarily displays the height map of disappeared, occluded, and covered targets within the temporal baseline. This includes the successful inversion of heights for occluded exterior walls in Area C and covered rectangular buildings in Area D. Compared with the step change position map in Figure 7, the height maps of APCS and DPCS points offer a more intuitive means to analyze the building information in the changing area.
In addition, integrating the height of PCSs with PSs yields a more detailed representation of building heights in the study area.
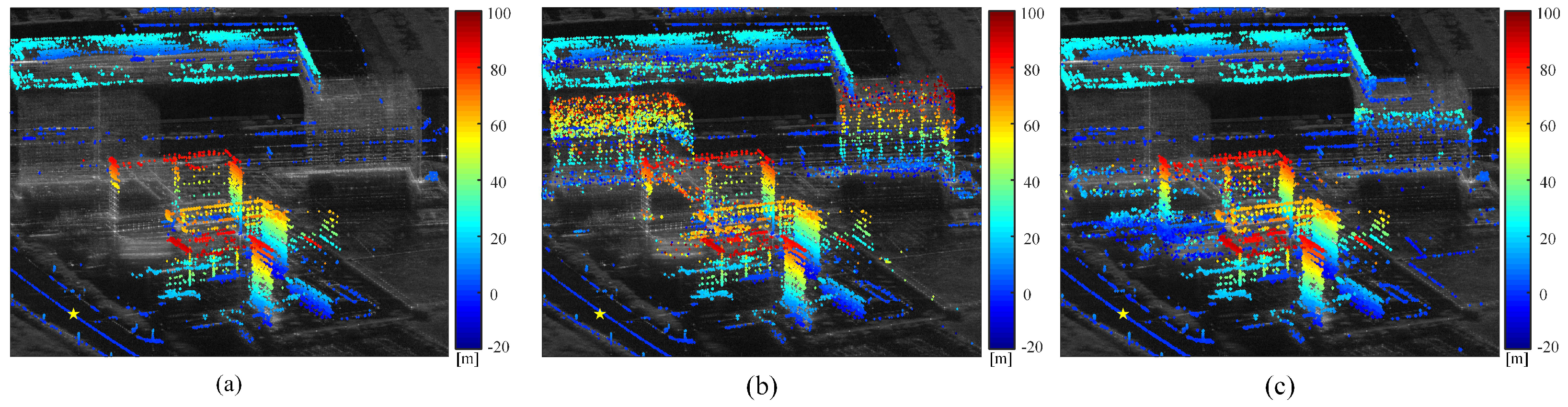
Figure 13 compares the height point cloud of PSa obtained by traditional SAR tomography methods with the joint height point cloud with PCSs using the proposed method. Figure 13b includes 16,512 PSs and 8845 APCSs, while Figure 13c includes 16,512 PSs and 5042 DPCSs. The height distribution of PCSs in adjacent regions is consistent with PSs, with no significant change in the overall height range. Compared with Figure 13a, which displays only PSs, the unified height point cloud map aligns more closely with the distribution of strong scatterers in the SAR average amplitude image. As APCSs are designed to describe targets that maintain interferometric stability until the final time baseline, their height results provide a supplement of existing building and man-made structure heights. Additionally, the use of DPCSs facilitates the extraction of historical height information, aiding in the reconstruction of obscured areas.
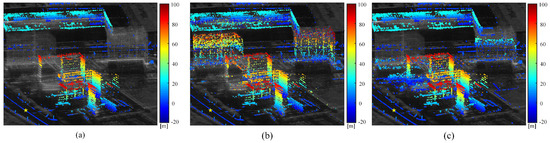
Figure 13.
(a) Height point cloud map of PS. (b) Unified height point cloud map of PS and APCS. (c) Unified height point cloud map of PS and DPCS. The selected reference point with zero height is the same as in Figure 10b.
In summary, the proposed method effectively addresses challenges for the height inversion of PCSs, enabling the retrieval of height information for nearly all targets of interest in the study area. Especially, it facilitates height estimation for changing areas using SAR tomography.
5. Discussion
The proposed method effectively addresses the challenges associated with the height inversion of PCSs. As shown in Figure 12 and Figure 13, the novel method enables the accurate retrieval of height information for nearly all targets of interest within the study area. The major advantages of this approach is its ability to facilitate height estimation in changing areas using SAR tomography. Moreover, the height estimates obtained from PCSs complement the elevation information derived from PSs, leading to substantial improvements in the overall 3D reconstruction performance. By expanding the range of usable scatterers, particularly in dynamic urban settings, the proposed method offers significant advantages over conventional approaches that predominantly rely on PSs.
Furthermore, the PCS-based TomoSAR method proposed in this paper is primarily designed for an urban environment dominated by point-like scatterers. However, despite its effectiveness in urban environments, the PCS-based TomoSAR method has limitations when applied to distributed scatterers (DSs) and volumetric scatterers, such as those found in natural landscapes. The current workflow, which is optimized for PSs and PCSs, is not equipped to handle temporal changes in these more complex scattering environments. As such, modifying the existing processing framework to accommodate data with varying resolutions and diverse scattering characteristics is a key focus for future research. These modifications will be essential for extending the applicability of the proposed method beyond urban environments, ensuring its effectiveness in a wider range of landscapes.
In summary, while the current approach demonstrates significant improvements in urban 3D reconstruction, addressing the limitations associated with distributed and volumetric scatterers remains an important direction for future work. Enhancing the method to handle these challenges will further expand its utility in both urban and natural environments.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we present a novel method that utilizes PCSs to enhance 3D reconstruction in dynamic urban environments through SAR tomography. This method incorporates an iterative sub-network generation technique to optimize the use of PCSs, addressing the limitations associated with traditional PS-based approaches. A coherence-constrained iterative variance analysis method is employed to determine the suitable time–baseline ranges for PCS application in TomoSAR. Additionally, we propose a sub-network generation approach that connects PCSs based on a reference network of PSs. This optimized network construction method effectively accounts for the distribution of PCSs, providing comprehensive coverage and ensuring their effective contribution to 3D reconstruction.
Compared with conventional methods that predominantly rely on PSs, the proposed approach significantly expands the range of usable scatterers, particularly in time-variant urban environments. Validation with the TerraSAR-X dataset demonstrates that the height estimates of PCSs offer complementary elevation information to that obtained from PSs, resulting in substantial improvements in 3D reconstruction performance in evolving urban settings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W. and Z.D.; formal analysis, X.W.; funding acquisition, Z.D. and A.Y.; methodology, X.W. and Y.W.; resources, X.W. and X.C.; supervision, Z.D. and X.C.; validation, X.W. and Y.W.; writing, X.W. and Z.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported partly by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62101568 and 62371460), partly by the Postdoctoral Innovative Talents Support Program (BX20230473), and partly by the Scientific Research Program of the National University of Defense Technology (ZK21-06).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the German Aerospace Center (DLR) for providing the high-resolution TerraSAR-X datasets. We are also grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Reigber, A.; Moreira, A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2142–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, G.; Lombardini, F.; Serafino, F. Three-dimensional multipass SAR focusing: Experiments with long-term spaceborne data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, D.; Fornaro, G.; Pauciullo, A.; Zhu, X.; Bamler, R. Tomographic Imaging and Monitoring of Buildings with Very High Resolution SAR Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IIEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2005, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.F.; Lin, H. Robust detection of single and double persistent scatterers in urban built environments. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 54, 2124–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Q.; Hu, J.; Du, Z.G.; Hou, J.X.; Zheng, W.J.; Liu, J.H. A Network Optimized Ridge Estimator for Robust PSI Parameter Estimation and Its Application on Deformation Monitoring of Urban Area. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 5436–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Colesanti, C.; Perissin, D.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Evaluating the effect of the observation time on the distribution of SAR permanent scatterers. In Proceedings of the FRINGE 2003 Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 10–14 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Perissin, D.; Ferretti, A. Urban-Target Recognition by Means of Repeated Spaceborne SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 12, 4043–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, X.L.; Lu, Z. Ground settlement monitoring based on temporarily coherent points between two SAR acquisitions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 1, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Ding, X.L.; Jung, H.S.; Feng, G.C.; Lee, C.W. Mapping ground surface deformation using temporarily coherent point SAR interferometry: Application to Los Angeles Basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, T. Repeat-pass SAR interferometry with partially coherent targets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 1, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, M.; Motagh, M. Improved persistent scatterer analysis using amplitude dispersion index optimization of dual polarimetry data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 1, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozan, D.; Daniele, P. Detection of Multitransition Abrupt Changes in Multitemporal SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 3239–3247. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.M.; Wu, J.C.; Chang, L.; Hanssen, R.F. Incorporating Temporary Coherent Scatterers in Multi-Temporal InSAR Using Adaptive Temporal Subsets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 10, 7658–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.M.; Wu, J.C. Detecting spatio-temporal urban surface changes using identified temporary coherent scatterers. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2021, 6, 1304–1317. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. Demonstration of Super-Resolution for Tomographic SAR Imaging in Urban Environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3150–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, G.; Serafino, F.; Soldovieri, F. Three-dimensional focusing with multipass SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 3, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, Y. Trans-ionospheric Synthetic Aperture Radar Observation: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2024; Early Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doin, M.P.; Lasserre, C.; Peltzer, G. Corrections of stratified tropospheric delays in SAR interferometry: Validation with global atmospheric models. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 1, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, J.M.; Hanssen, R.; Kampes, B.M.; Fusco, A.; Adam, N. Physical analysis of atmospheric delay signal observed in stacked. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 21 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, O.; Hajnsek, I.; Wegmuller, U. Spaceborne SAR Tomography in Urban Areas. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. Tomographic SAR Inversion by L1-norm Regularization—The Compressive Sensing Approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3839–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Dong, Z.; Yu, A.X.; Wu, M.Q.; Li, D.X.; Zhang, Y.S. New approaches for robust and efficient detection of persistent scatterers in SAR tomography. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, G.; Serafino, F. Imaging of Single and Double Scatterers in Urban Areas via SAR Tomography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3497–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.L.; Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. Nonlocal Compressive Sensing-Based SAR Tomography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 5, 3015–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, A.; Peng, X. An improved bridge reference network for 3-D SAR tomography based on regional growing strategy. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2398072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.J.; Xu, G.; Yu, H.W.; Wang, H.; Pei, H.; Hong, W. Array 3-D SAR Tomography Using Robust Gridless Compressed Sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5205013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri, S.; Rodriguez, G.F.; Zhu, X.X. Geocoding Error Correction for InSAR Point Clouds. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).