Inversion of Near-Surface Aerosol Equivalent Complex Refractive Index Based on Aethalometer, Micro-Pulse Lidar and Portable Optical Particle Profiler
Abstract
:1. Introduction
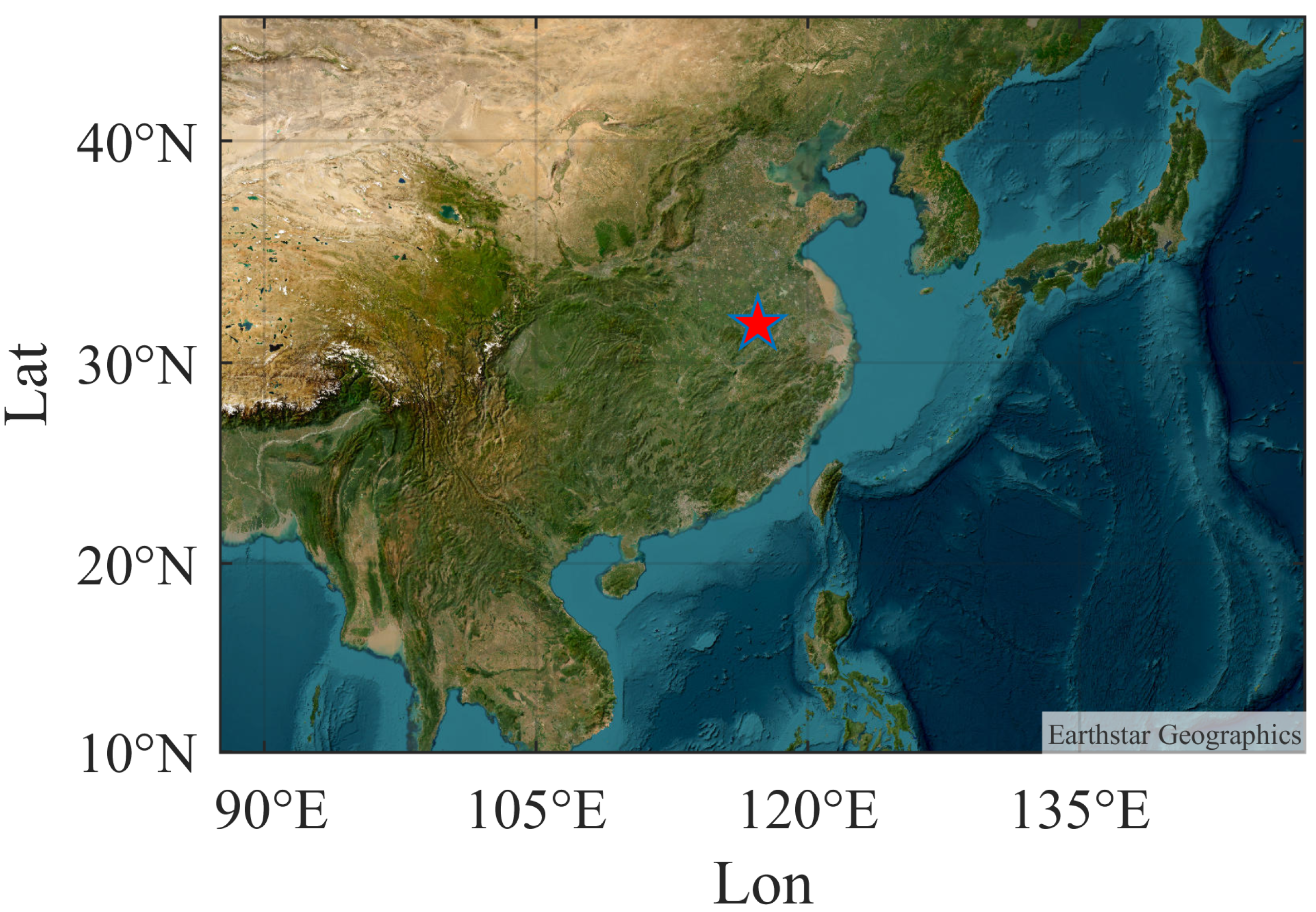
2. Experimental Site and Instrument Introduction
2.1. Portable Optical Particle Profiler
2.2. Micro-Pulse Lidar
2.3. Aethalometer
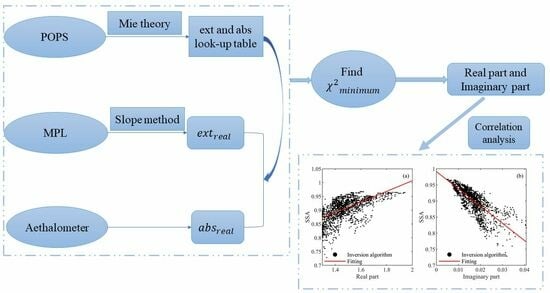
3. Inversion Algorithm and Analysis of Experimental Results
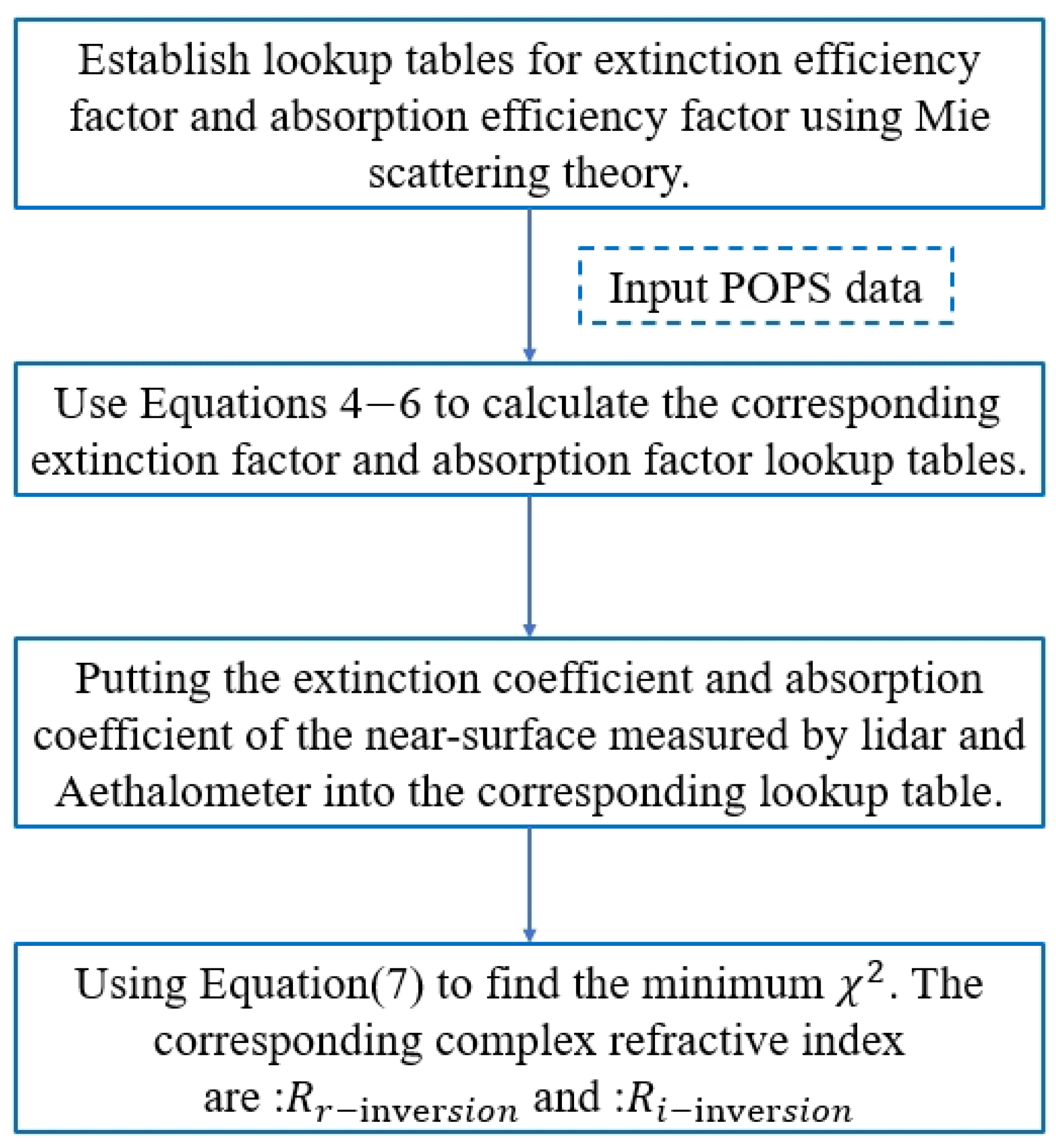
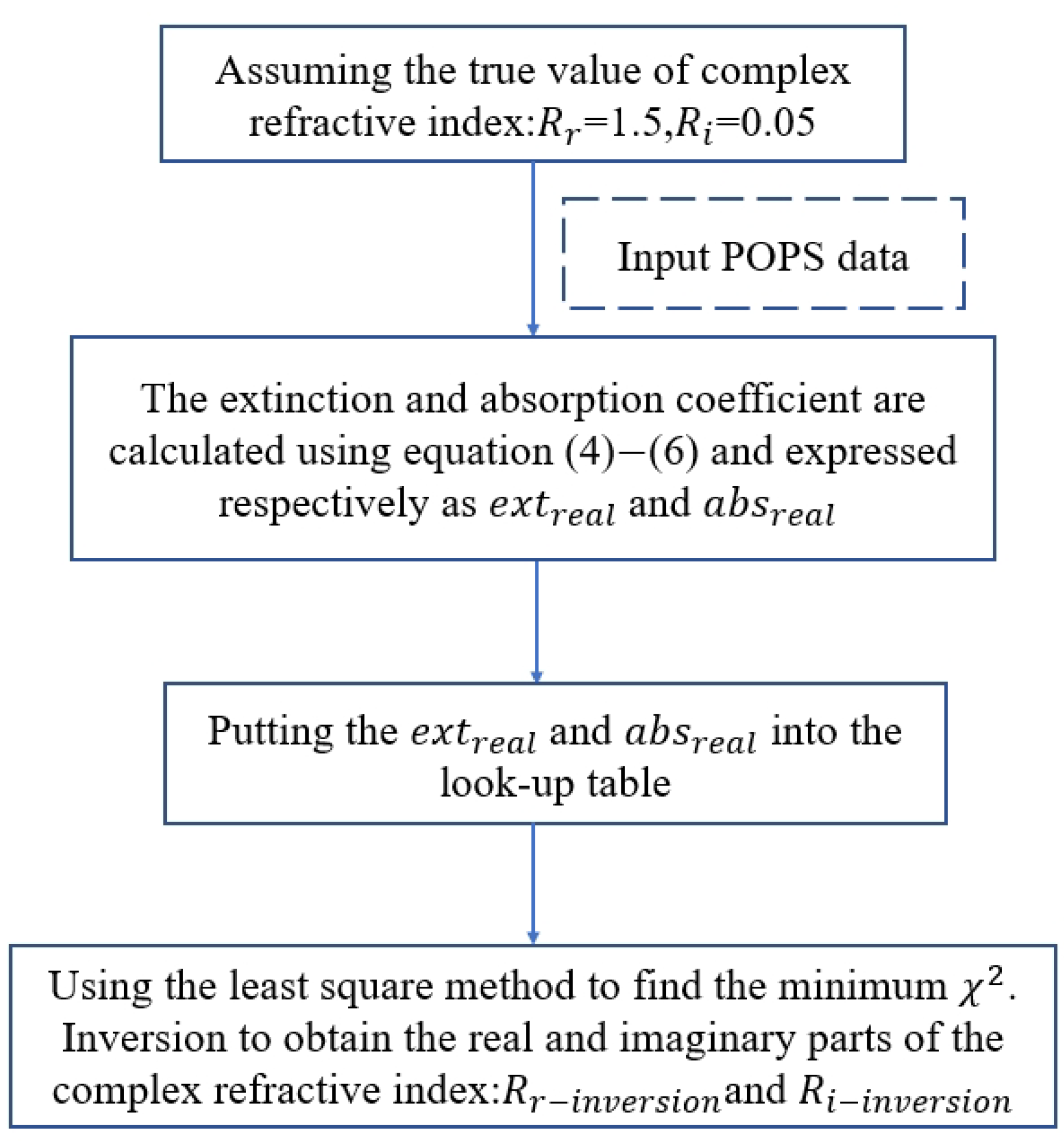
3.1. Introduction to Algorithms
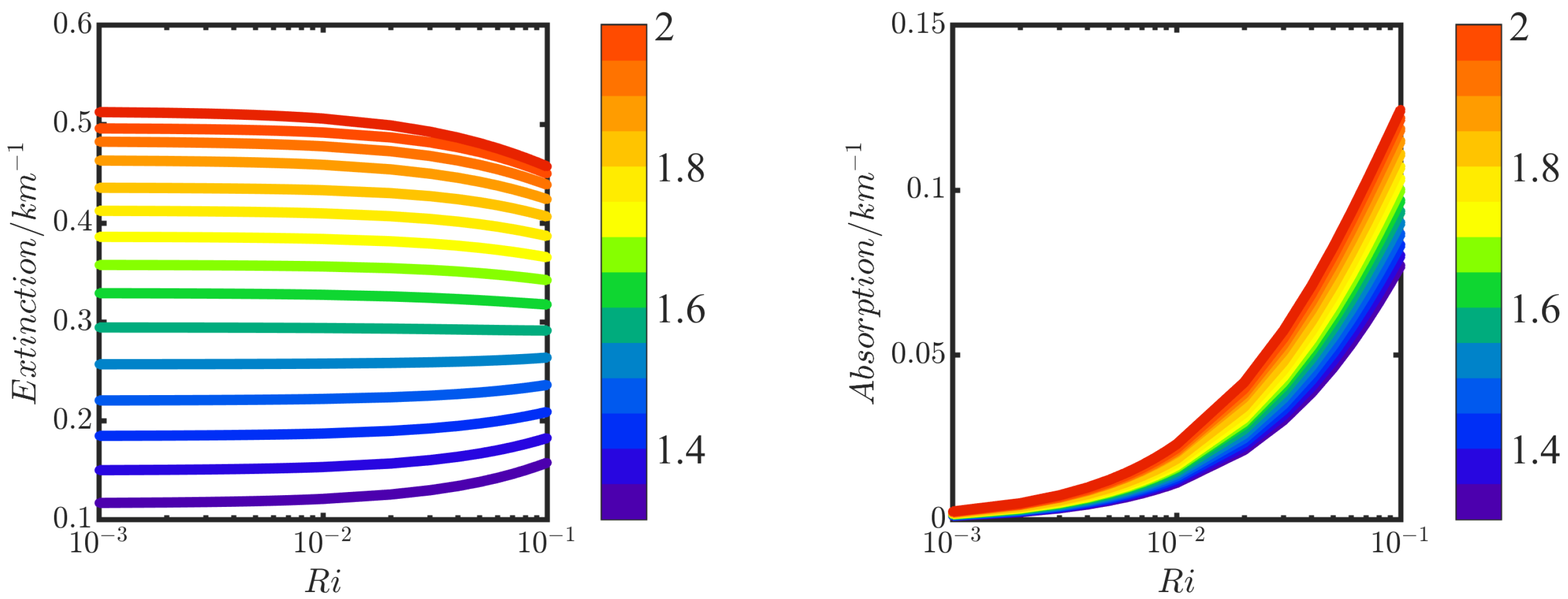
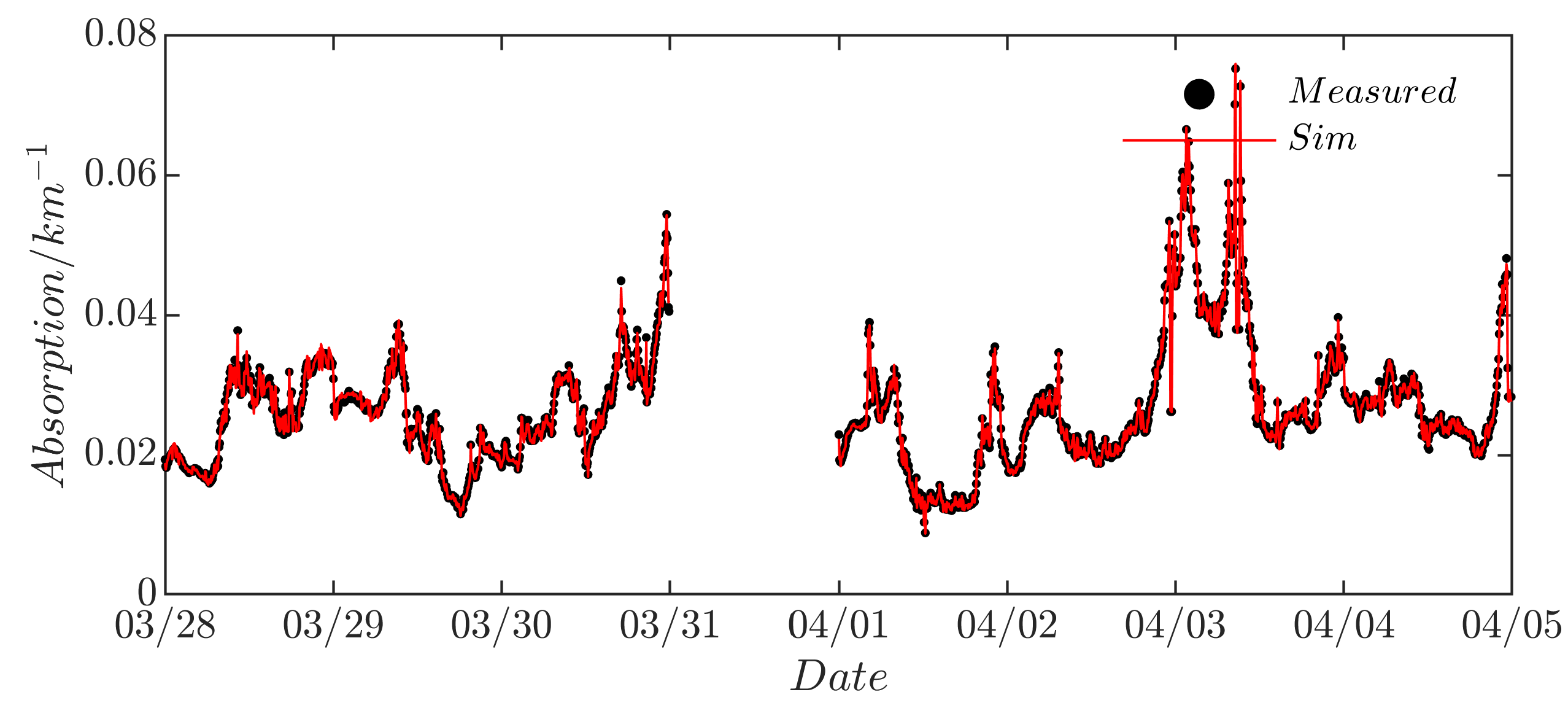
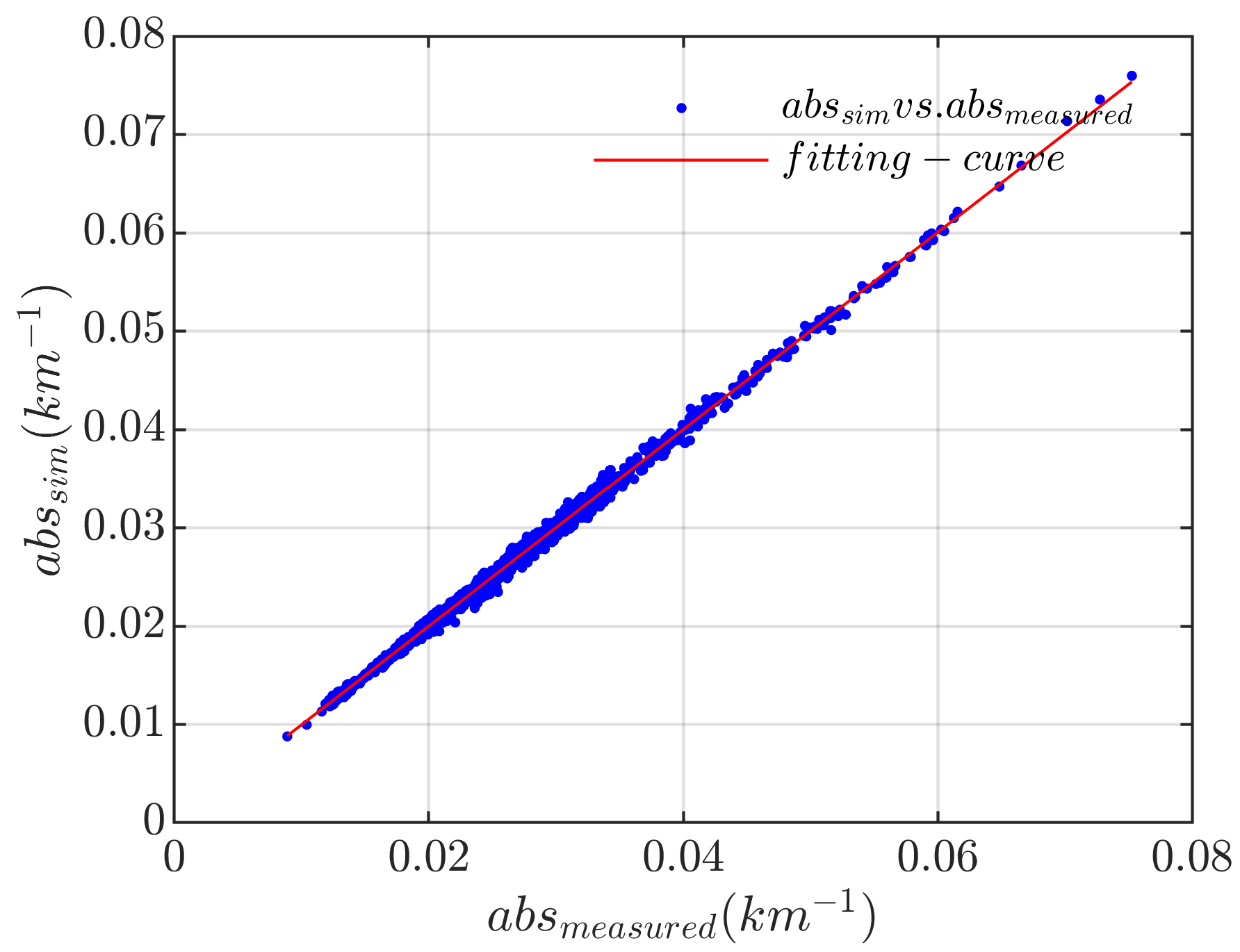
3.2. Simulation Analysis
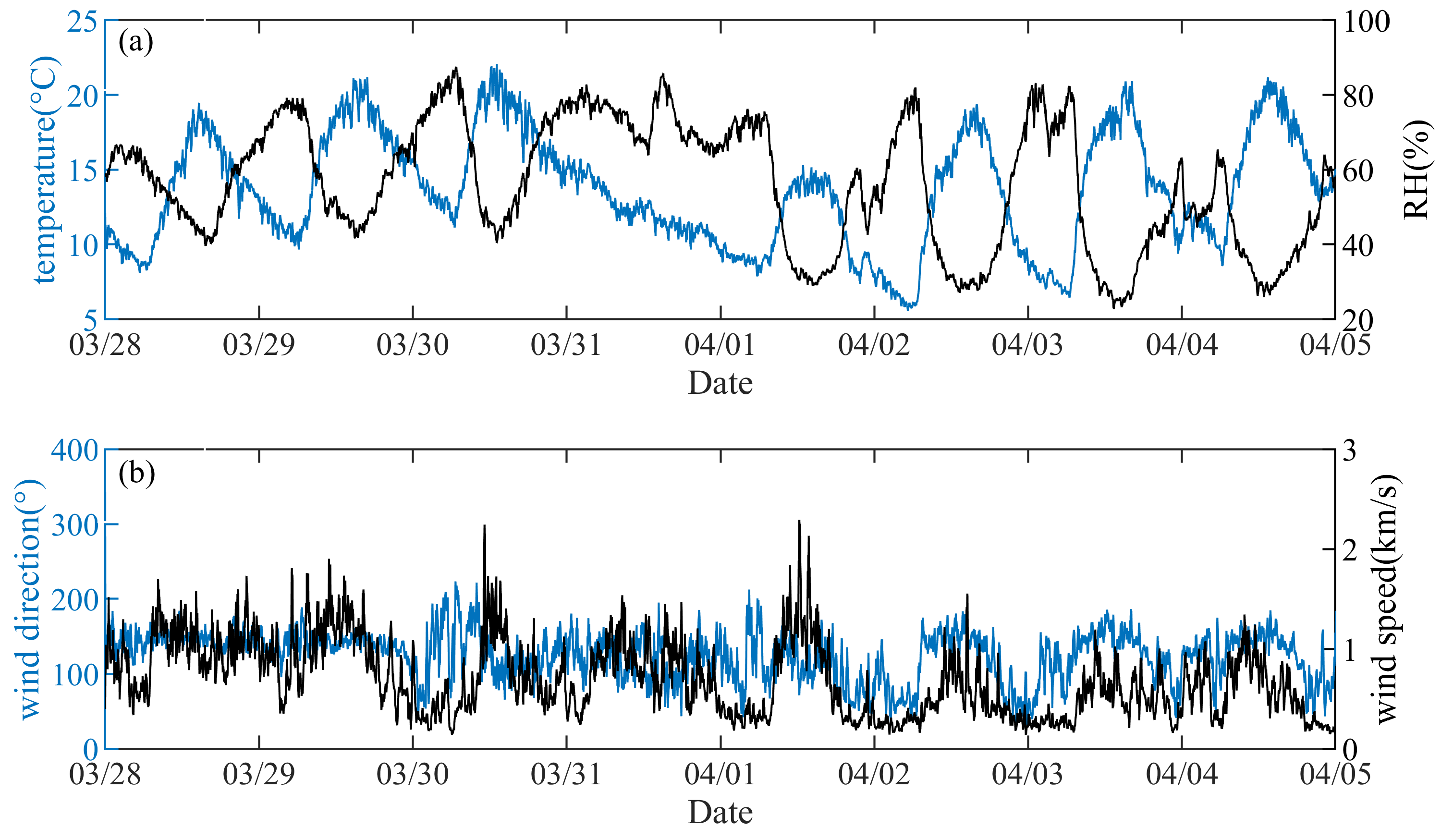
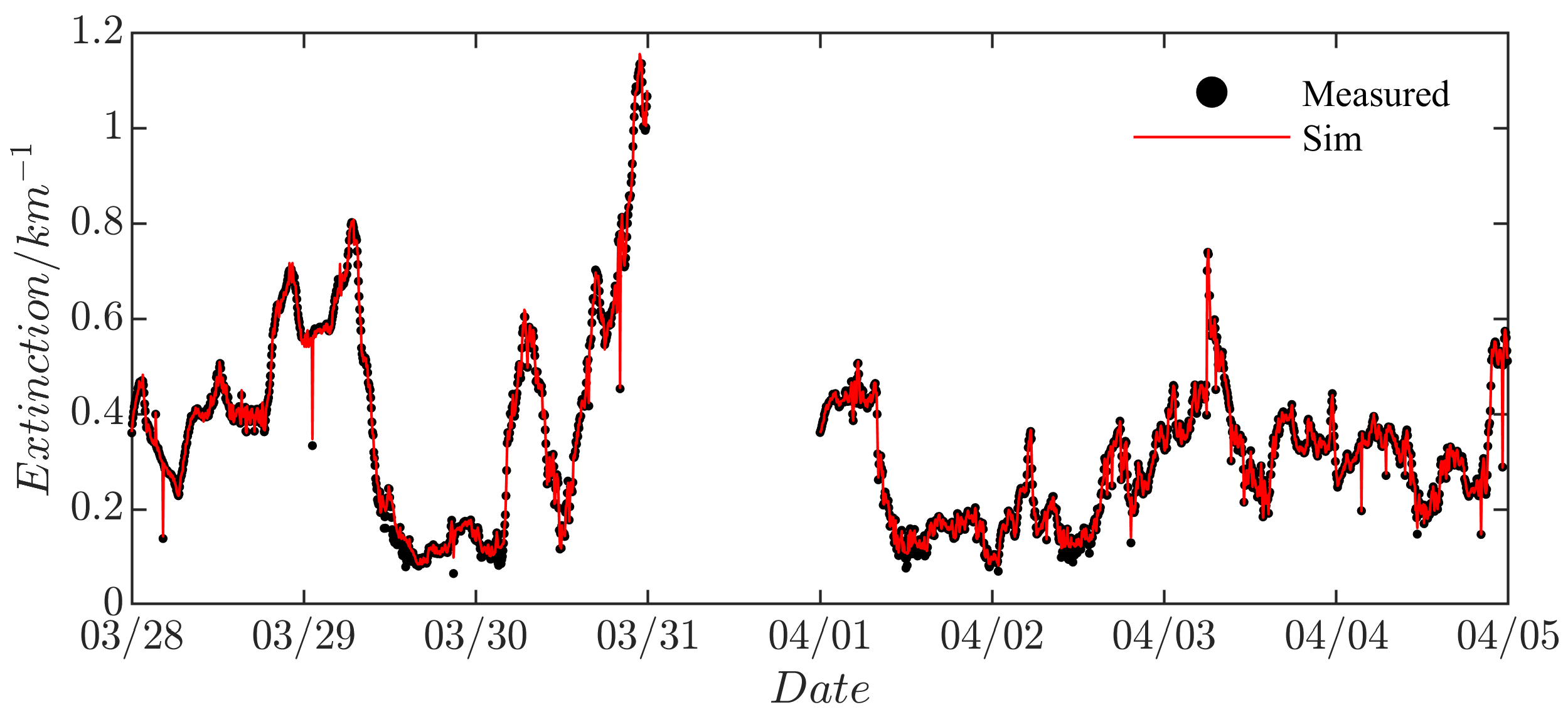
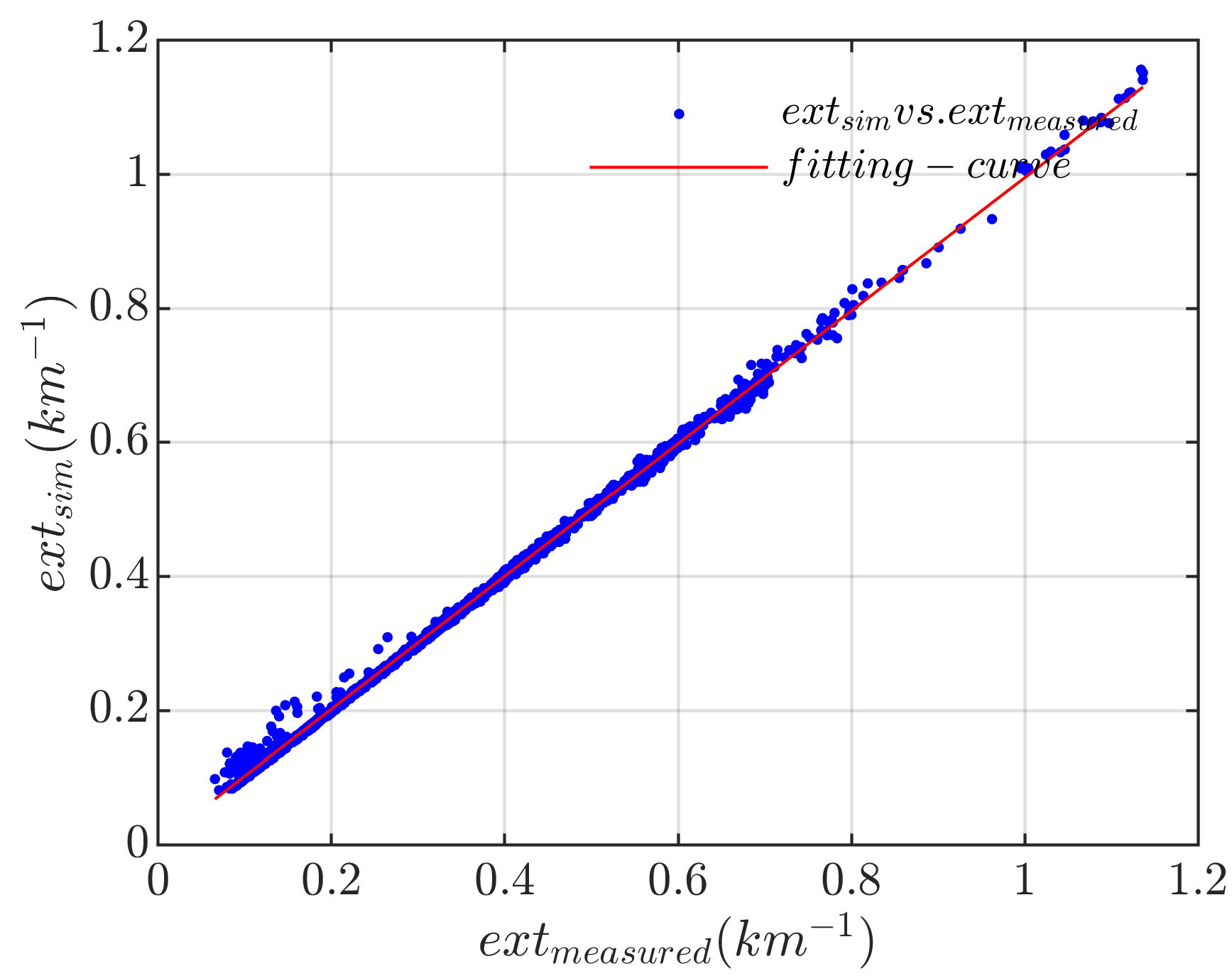
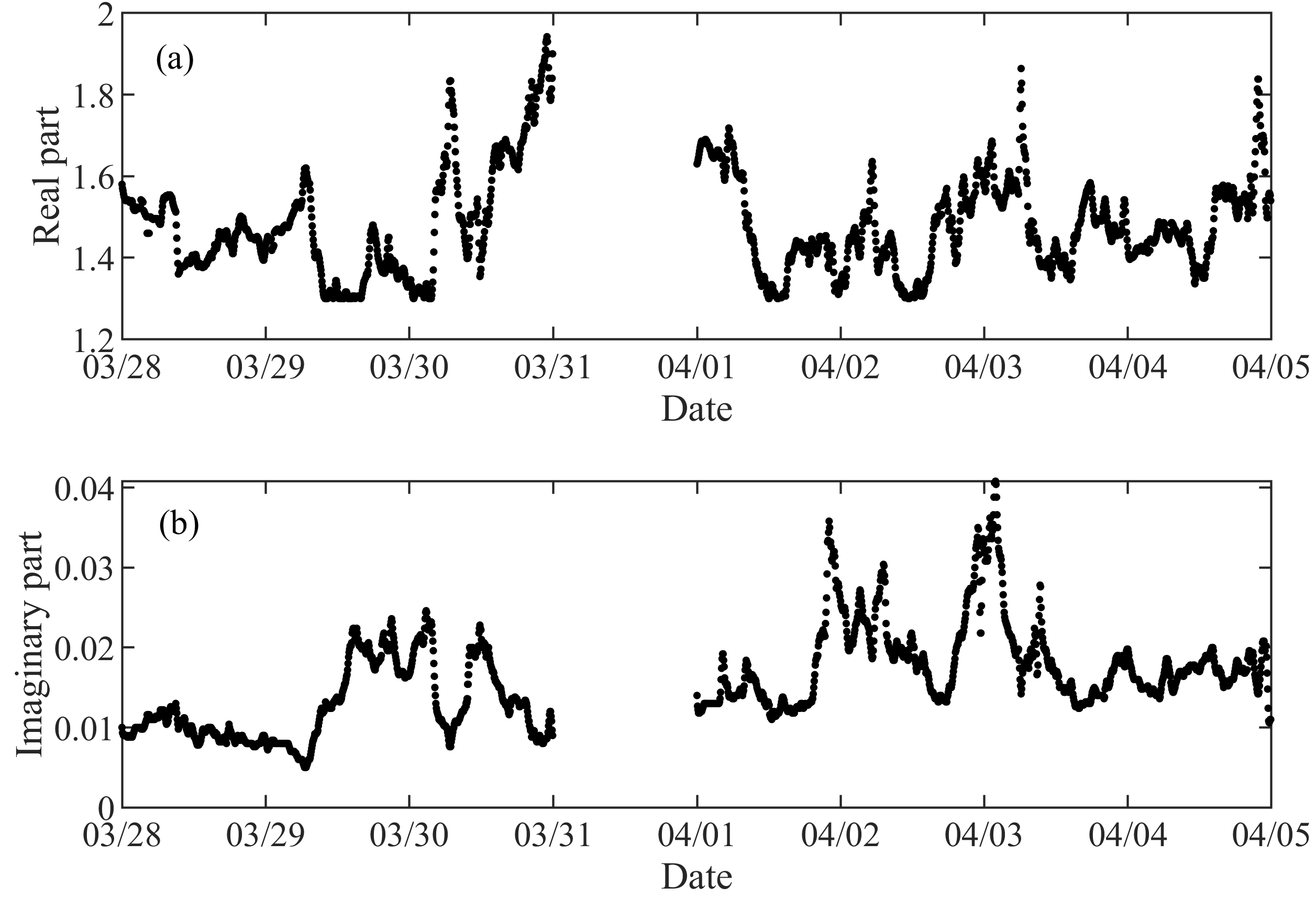
3.3. Analysis of Inversion Results from Experimental Observations
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The reliability of the optimization algorithm for aerosol equivalent complex refractive index inversion was simulated. The results show that, compared with the single-point method, the multi-point constraint method is less sensitive to instrumental errors, can better eliminate the interference of some errors from the instrumental observation data, and the inversion results have better reliability than those of the single-point method.
- (2)
- According to the retrieval results, the mean value of the equivalent refractive index of the aerosols observed during the test period is 1.48 − i0.017.
- (3)
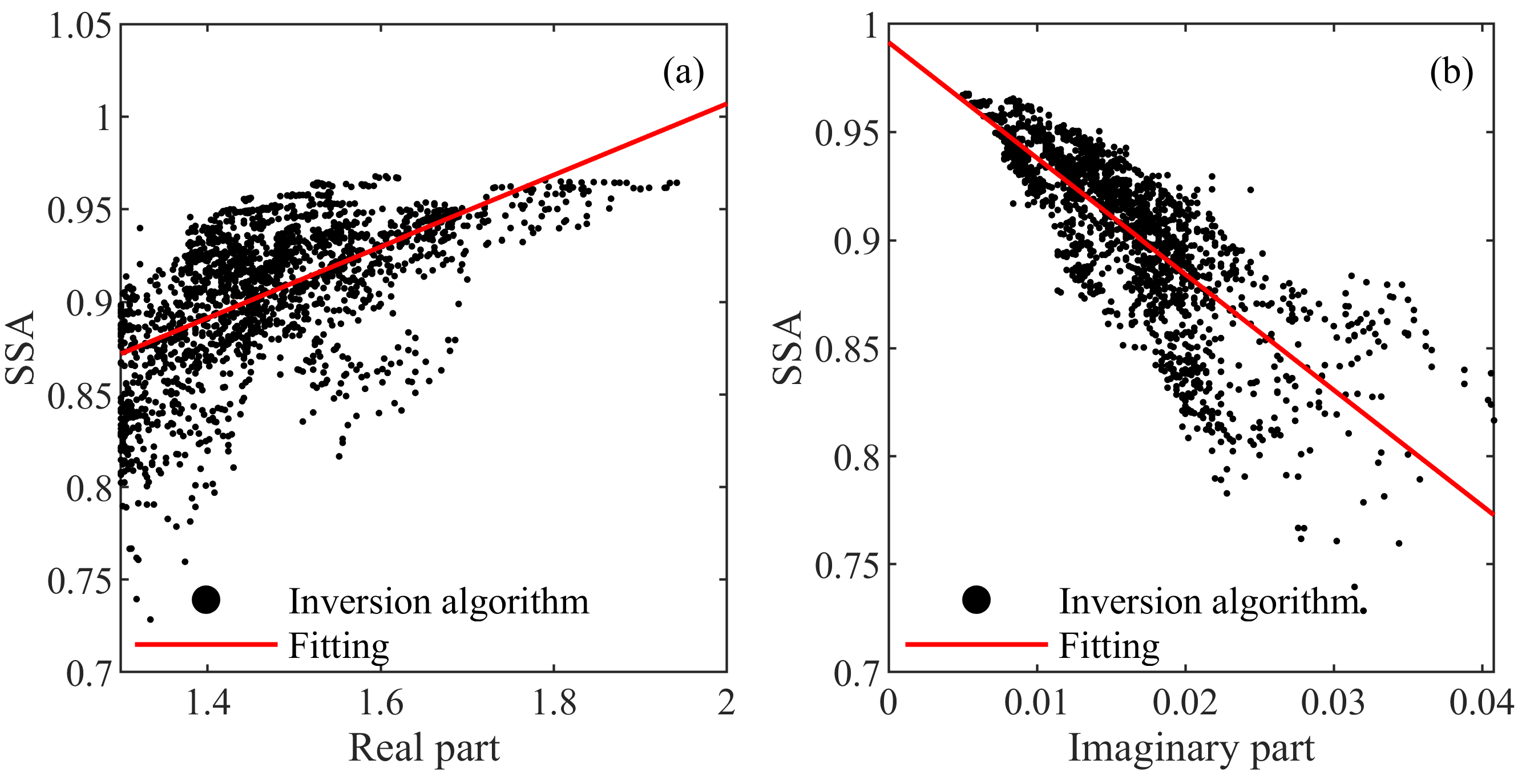
- The correlation between the real and imaginary parts of the aerosol refractive index and SSA was analyzed. The results show a positive correlation () between the real part and the SSA and a negative correlation () between the imaginary part and the SSA.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lenoble, J. Atmospheric Radiative Transfer; Studies in Geophysical Optics and Remote Sensing; Deepak Publishing: Morar Gwalior, India, 1993; Available online: https://books.google.sk/books?id=WDBRAAAAMAAJ (accessed on 24 December 2023).
- Liousse, C.; Devaux, C.; Dulac, F.; Cachier, H. Aging of savanna biomass burning aerosols: Consequences on their optical properties. J. Atmos. Chem. 1995, 22, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegen, I.; Fung, I. Contribution to the atmospheric mineral aerosol load from land surface modification. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 18707–18726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization; Regional Office for Europe. Health Aspects of Air Pollution: Results from the WHO Project “Systematic Review of Health Aspects of Air Pollution in Europe”; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. 2007: Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Reisinger, A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; 104p. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Cui, S.; Luo, T.; Chen, S.; Yang, K.; Ma, X.; Sun, G.; Li, X. Characteristics of Aerosol Extinction Hygroscopic Growth in the Typical Coastal City of Qingdao, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluvshtein, N.; Flores, J.M.; Riziq, A.A.; Rudich, Y. An Approach for Faster Retrieval of Aerosols’ Complex Refractive Index Using Cavity Ring-Down Spectroscopy. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Mao, M.; Chen, H.B. Characterization of optically effective complex refractive index of black carbon composite aerosols. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2020, 198, 105180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, J.C.; Chazette, P. Vertical profiles of urban aerosol complex refractive index in the frame of ESQUIF airborne measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Lu, C.; Yuan, L.; Shi, S. The Optical Properties of Aerosols at the Summit of Mount Tai in May and June and the Retrieval of the Complex Refractive Index. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenkova, P.N.; Chernov, D.G.; Panchenko, M.V. Complex refractive index in the model of the vertical profile of aerosol optical characteristics in the troposphere of Western Siberia. Proc. SPIE 2022, 12341, 1234138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Mao, M. Optically effective complex refractive index of coated black carbon aerosols: From numerical aspects. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 7507–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, P.; Boucher, O.; Graham, B.; Beck, J.; Mayol-Bracero, O.L.; Roberts, G.C.; Maenhaut, W.; Artaxo, P.; Andreae, M.O. Refractive index of aerosol particles over the Amazon tropical forest during LBA-EUSTACH 1999. J. Aerosol Sci. 2003, 34, 883–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandler, K.; Schütz, L.; Deutscher, C.; Ebert, M.; Hofmann, H.; Jäckel, S.; Jaenicke, R.; Knippertz, P.; Lieke, K.; Massling, A.; et al. Size distribution, mass concentration, chemical and mineralogical composition and derived optical parameters of the boundary layer aerosol at Tinfou, Morocco, during SAMUM 2006. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2009, 61, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazette, P.; Liousse, C. A case study of optical and chemical ground apportionment for urban aerosols in Thessaloniki. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stier, P.; Feichter, J.; Kinne, S.; Kloster, S.; Vignati, E.; Wilson, J.; Ganzeveld, L.; Tegen, I.; Werner, M.; Balkanski, Y.; et al. The aerosol-climate model ECHAM5-HAM. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1125–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Sinyuk, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Holben, B.N.; Mishchenko, M.; Yang, P.; Eck, T.F.; Volten, H.; Munoz, O.; Veihelmann, B.; et al. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2006, 111, D11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, M.; Cheng, Y.F.; Birmili, W.; Massling, A.; Wehner, B.; Müller, T.; Leinert, S.; Kalivitis, N.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Wiedensohler, A. Hygroscopic properties of atmospheric aerosol particles over the Eastern Mediterranean: Implications for regional direct radiative forcing under clean and polluted conditions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4251–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schkolnik, G.; Chand, D.; Hoffer, A.; Andreae, M.O.; Erlick, C.; Swietlicki, E.; Rudich, Y. Constraining the density and complex refractive index of elemental and organic carbon in biomass burning aerosol using optical and chemical measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riziq, A.A.; Erlick, C.; Dinar, E.; Rudich, Y. Optical properties of absorbing and non-absorbing aerosols retrieved by cavity ring down (CRD) spectroscopy. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.; Li, X.B.; Qin, W.B.; Liu, Z.Y.; Lu, X.Y.; Dai, C.M.; Miao, X.K.; Weng, N.Q. Research on the characteristics of aerosol size distribution and complex refractive index in typical areas of China. Infrared Laser Eng. 2018, 47, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Mao, M.; Yin, Y. A Numerical Study of Dependencies of Aerosol Scattering and Absorption on Its Refractive Index. Chin. J. Light Scatt. 2017, 29, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, D.; Weinzierl, B.; Petzold, A.; Kandler, K.; Ansmann, A.; Mueller, T.; Tesche, M.; Freudenthaler, V.; Esselborn, M.; Heese, B.; et al. Mineral dust observed with AERONET Sun photometer, Raman lidar, and in situ instruments during SAMUM 2006: Shape-independent particle properties. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2010, 115, D11207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.S.; Telg, H.; McLaughlin, R.J.; Ciciora, S.J.; Watts, L.A.; Richardson, M.S.; Schwarz, J.P.; Perring, A.E.; Thornberry, T.D.; Rollins, A.W.; et al. A light-weight, high-sensitivity particle spectrometer for PM2.5 aerosol measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.S.; Xu, Q.S.; Xu, C.D.; Yu, D.S.; Chen, X.W. Calculation of Whole Atmospheric Aerosol Optical Depth Based on Micro-Pulse Lidar. Acta Opt. Sin. 2017, 37, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.L.; Jiang, L.H.; Feng, S. Mie scattering lidar echo signal processing methods. Infrared Laser Eng. 2012, 41, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kunz, G.J.; de Leeuw, G. Inversion of lidar signals with the slope method. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klett, J.D. Lidar inversion with variable backscatter/extinction ratios. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.L.; Jiang, L.H.; Feng, S. Return signals processing method of Mie scattering lidar. Infrared Laser Eng. 2012, 41, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Drinovec, L.; Mocnik, G.; Zotter, P.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Ruckstuhl, C.; Coz, E.; Rupakheti, M.; Sciare, J.; Mueller, T.; Wiedensohler, A.; et al. The “dual-spot” Aethalometer: An improved measurement of aerosol black carbon with real-time loading compensation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, R.M.; Sofowote, U.; Su, Y.; Debosz, J.; Noble, M.; Jeong, C.H.; Wang, J.M.; Hilker, N.; Evans, G.J.; Doerksen, G.; et al. Ambient measurements and source apportionment of fossil fuel and biomass burning black carbon in Ontario. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 161, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolik, I.N.; Toon, O.B. Incorporation of mineralogical composition into models of the radiative properties of mineral aerosol from UV to IR wavelengths. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 9423–9444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claquin, T.; Schulz, M.; Balkanski, Y.J. Modeling the mineralogy of atmospheric dust sources. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 22243–22256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Gelencsér, A. Black carbon or brown carbon? The nature of light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3131–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samset, B.H.; Stjern, C.W.; Andrews, E.; Kahn, R.A.; Myhre, G.; Schulz, M.; Schuster, G.L. Aerosol Absorption: Progress Towards Global and Regional Constraints. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2018, 4, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Wei, W.S.; Wu, X.P.; Cao, X.; Tang, X.L. An Approach to Decouple Aerosol Absorption Coefficients Using Aethalometer Observational Data. Desert Oasis Meteorol. 2011, 5, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchstetter, T.W.; Novakov, T.; Hobbs, P.V. Evidence that the spectral dependence of light absorption by aerosols is affected by organic carbon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, 21208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, R.W.; Russell, P.B.; Hignett, P. Wavelength Dependence of the Absorption of Black Carbon Particles: Predictions and Results from the TARFOX Experiment and Implications for the Aerosol Single Scattering Albedo. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, G.X. Studies on Extinction efficiency factor properties of aerosol particle and the fit of size distribution. Chin. J. Quantum Electron. 2004, 21, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.W.; Liu, D.; Xie, C.B.; Wang, Z.Z.; Wang, B.X.; Zhong, Z.Q.; Ma, H.; Wang, Y.J. Multi-Wavelength Fitting Simulation and Inversion of Atmospheric Aerosol Spectrum Distribution. Acta Opt. Sin. 2017, 37, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, L.A.; Levin, E.J.T.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Obrist, D.; Moosmüller, H.; Lewis, K.A.; Arnott, W.P.; McMeeking, G.R.; Sullivan, A.P.; Wold, C.E.; et al. Optical closure experiments for biomass smoke aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 9017–9026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, D.; Ansmann, A.; Wagner, F.; Franke, K.; Althausen, D. European pollution outbreaks during ACE 2: Microphysical particle properties and single-scattering albedo inferred from multiwavelength lidar observations. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2002, 107, AAC 3-1–AAC 3-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virkkula, A.; Koponen, I.K.; Teinila, K.; Hillamo, R.; Kerminen, V.M.; Kulmala, M. Effective real refractive index of dry aerosols in the Antarctic boundary layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Bin | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | 115 | 125 | 135 | 150 | 165 | 185 | 210 | 250 | 350 | 475 | 575 | 855 | 1220 | 1530 | 1990 | 2585 |
| Upper | 125 | 135 | 150 | 165 | 185 | 210 | 250 | 350 | 475 | 575 | 855 | 1120 | 1530 | 1990 | 2585 | 3370 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Luo, T.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, N.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Chen, J.; Zhu, L. Inversion of Near-Surface Aerosol Equivalent Complex Refractive Index Based on Aethalometer, Micro-Pulse Lidar and Portable Optical Particle Profiler. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020279
Ma X, Luo T, Li X, Liu C, Liu N, Liu Q, Zhang K, Chen J, Zhu L. Inversion of Near-Surface Aerosol Equivalent Complex Refractive Index Based on Aethalometer, Micro-Pulse Lidar and Portable Optical Particle Profiler. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(2):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020279
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xuebin, Tao Luo, Xuebin Li, Changyu Liu, Nana Liu, Qiang Liu, Kun Zhang, Jie Chen, and Liming Zhu. 2024. "Inversion of Near-Surface Aerosol Equivalent Complex Refractive Index Based on Aethalometer, Micro-Pulse Lidar and Portable Optical Particle Profiler" Remote Sensing 16, no. 2: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020279
APA StyleMa, X., Luo, T., Li, X., Liu, C., Liu, N., Liu, Q., Zhang, K., Chen, J., & Zhu, L. (2024). Inversion of Near-Surface Aerosol Equivalent Complex Refractive Index Based on Aethalometer, Micro-Pulse Lidar and Portable Optical Particle Profiler. Remote Sensing, 16(2), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020279