Mapping and Analyzing the Spatiotemporal Patterns and Drivers of Multiple Ecosystem Services: A Case Study in the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
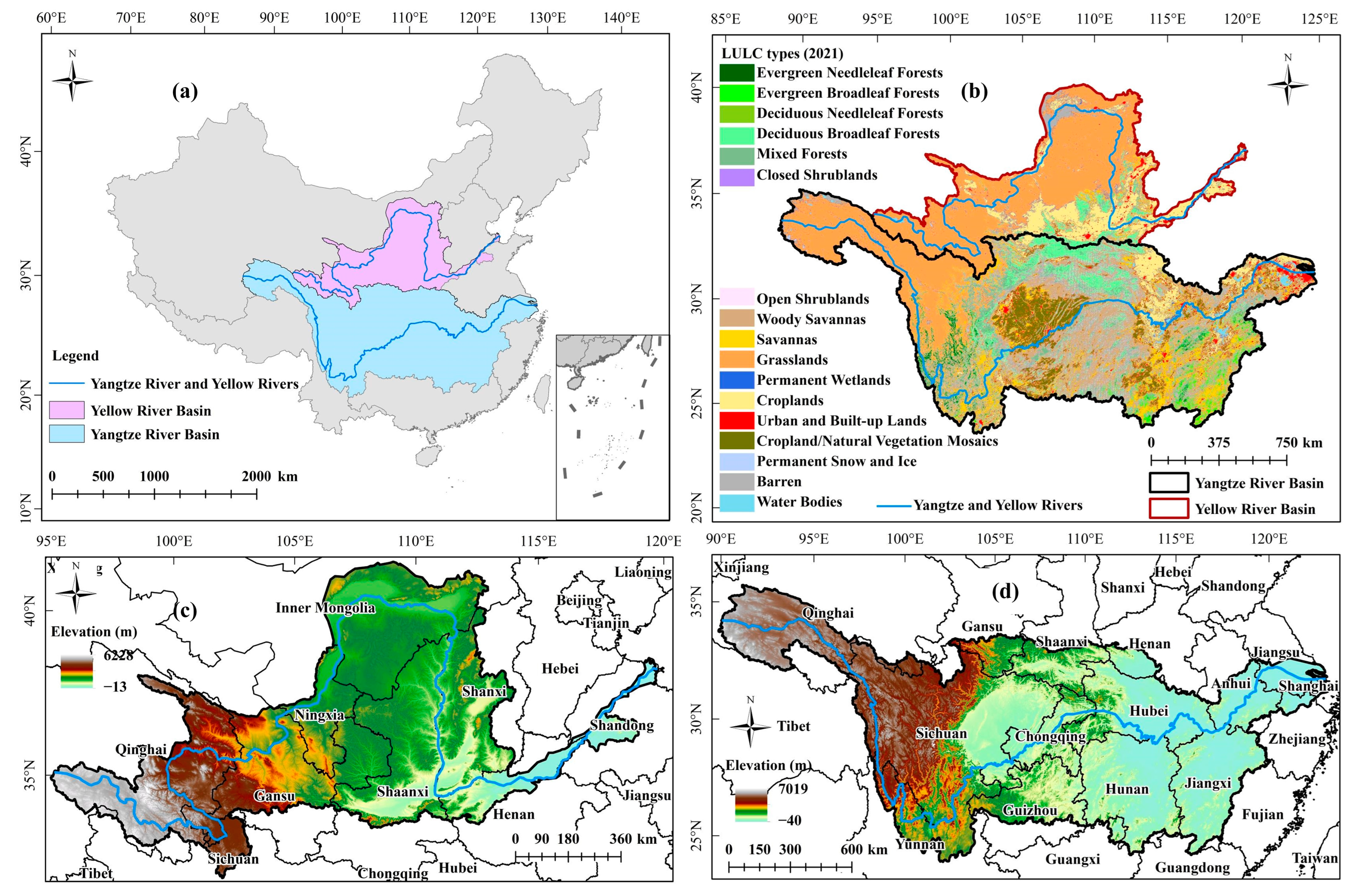
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Processing
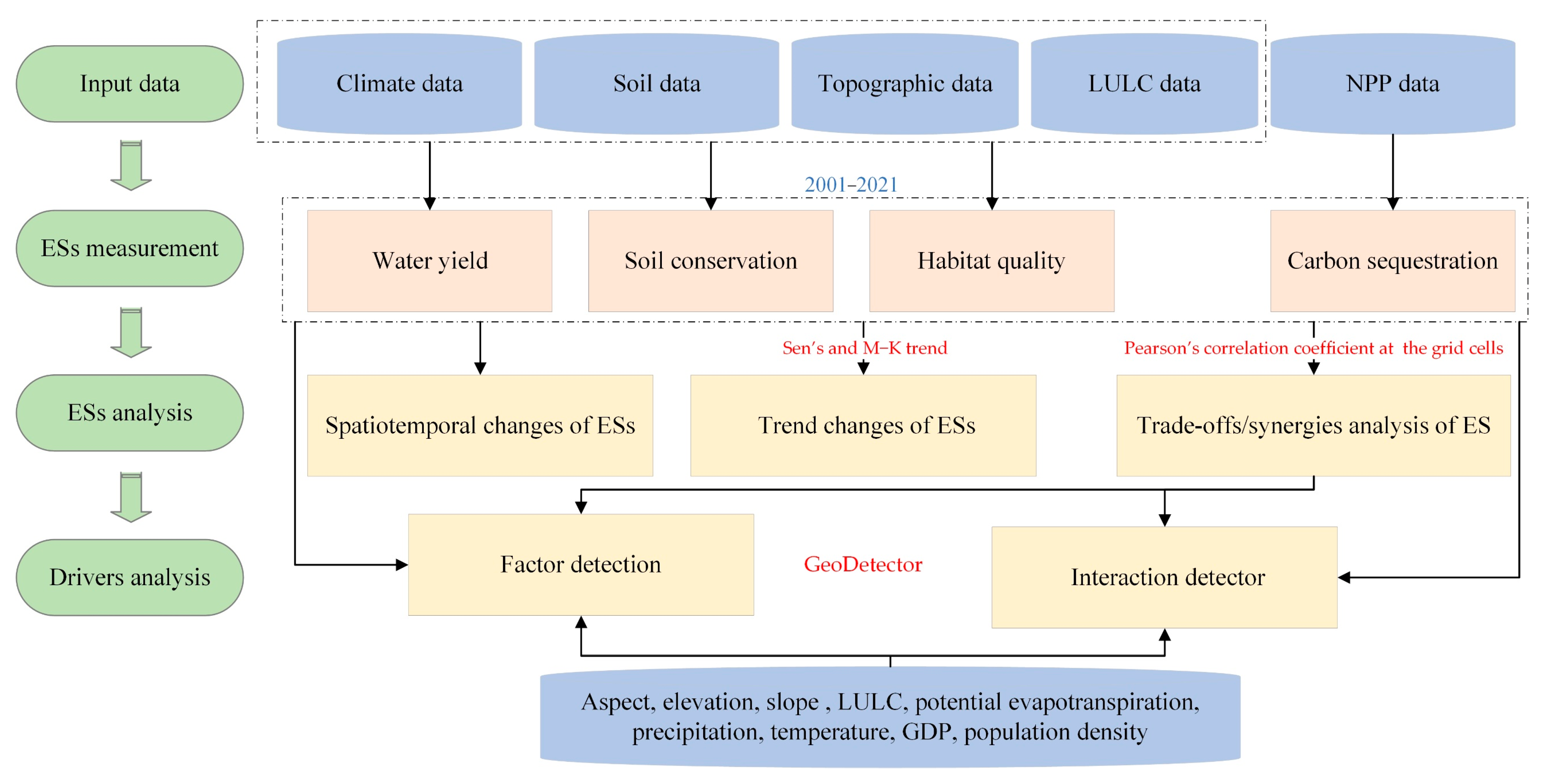
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. ES Assessment Methods
2.3.2. Trend Analysis
2.3.3. Trade-Offs/Synergies Analysis
2.3.4. GeoDetector Analysis
3. Results
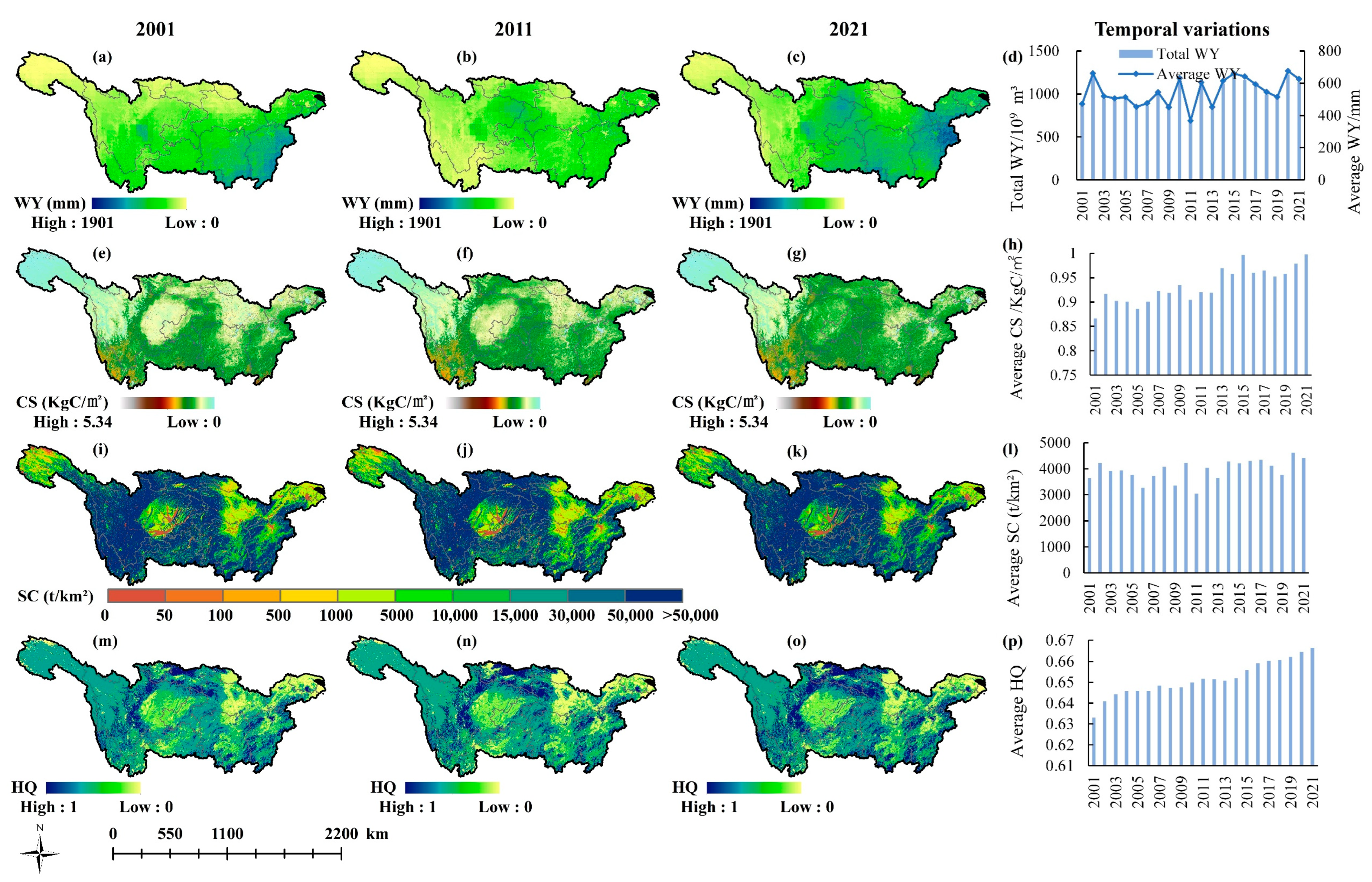
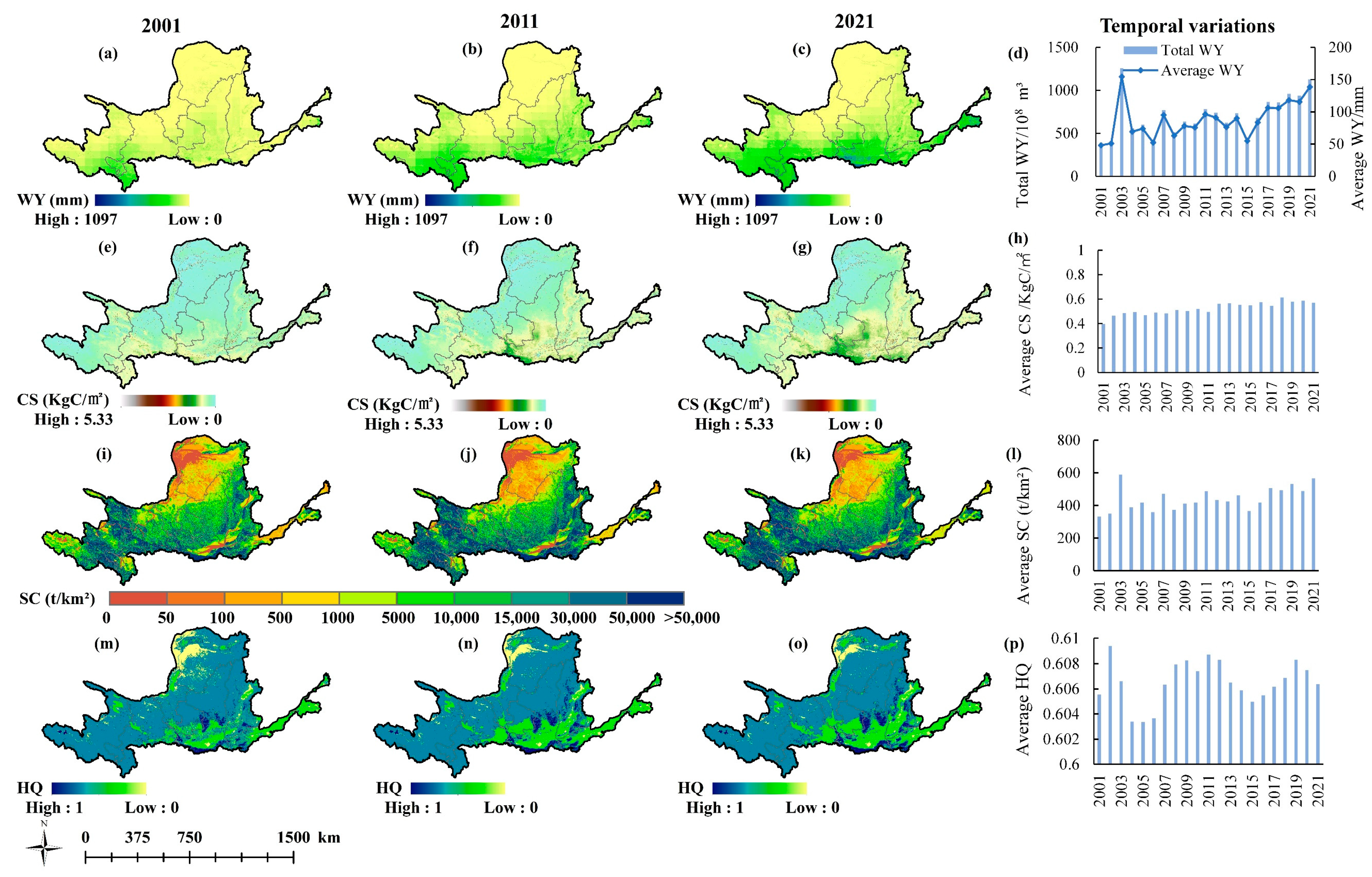
3.1. Spatiotemporal and Trend Changes of ESs
3.1.1. Spatiotemporal Changes of ESs
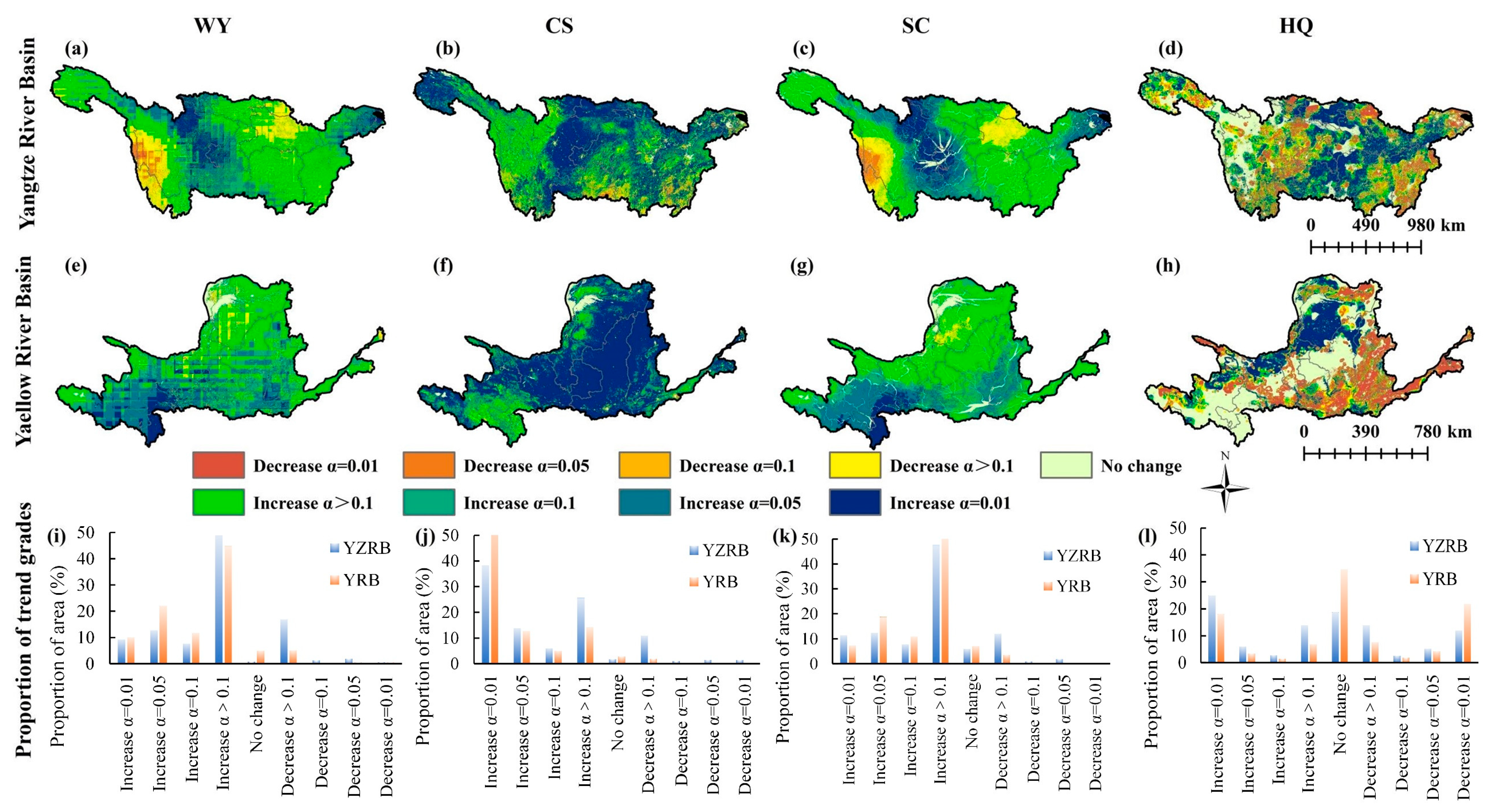
3.1.2. Trend Changes of ESs
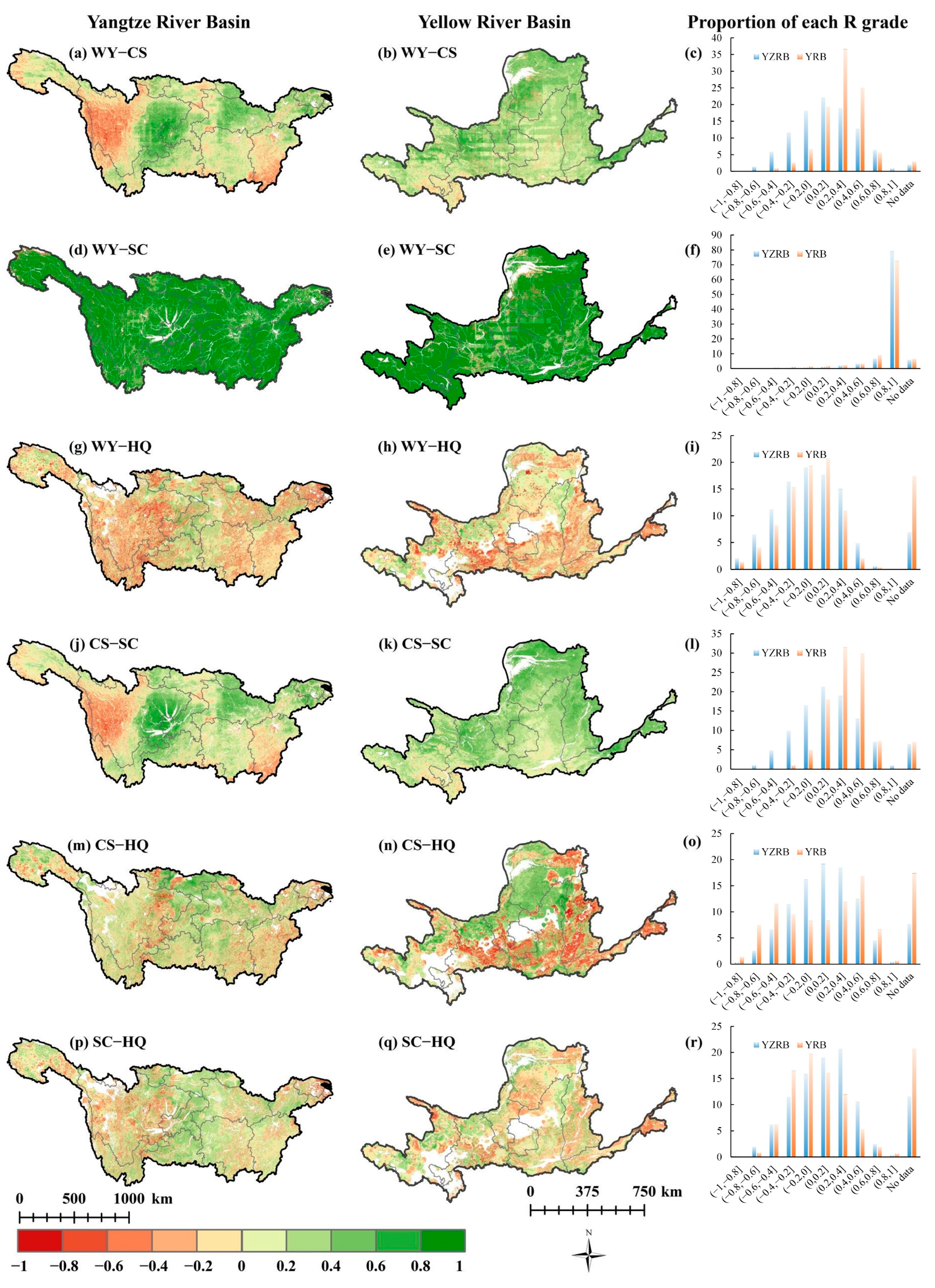
3.2. Trade-Offs/Synergies Analysis of ES
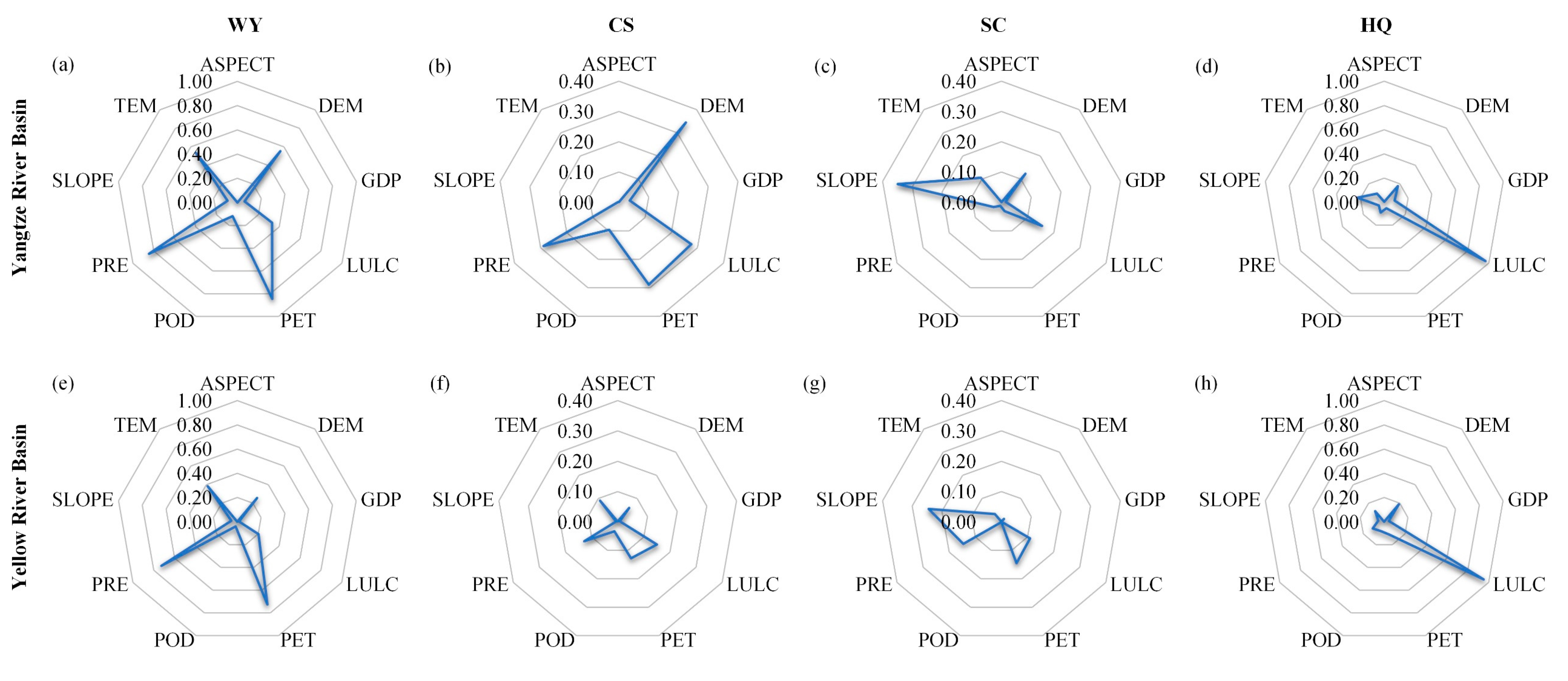
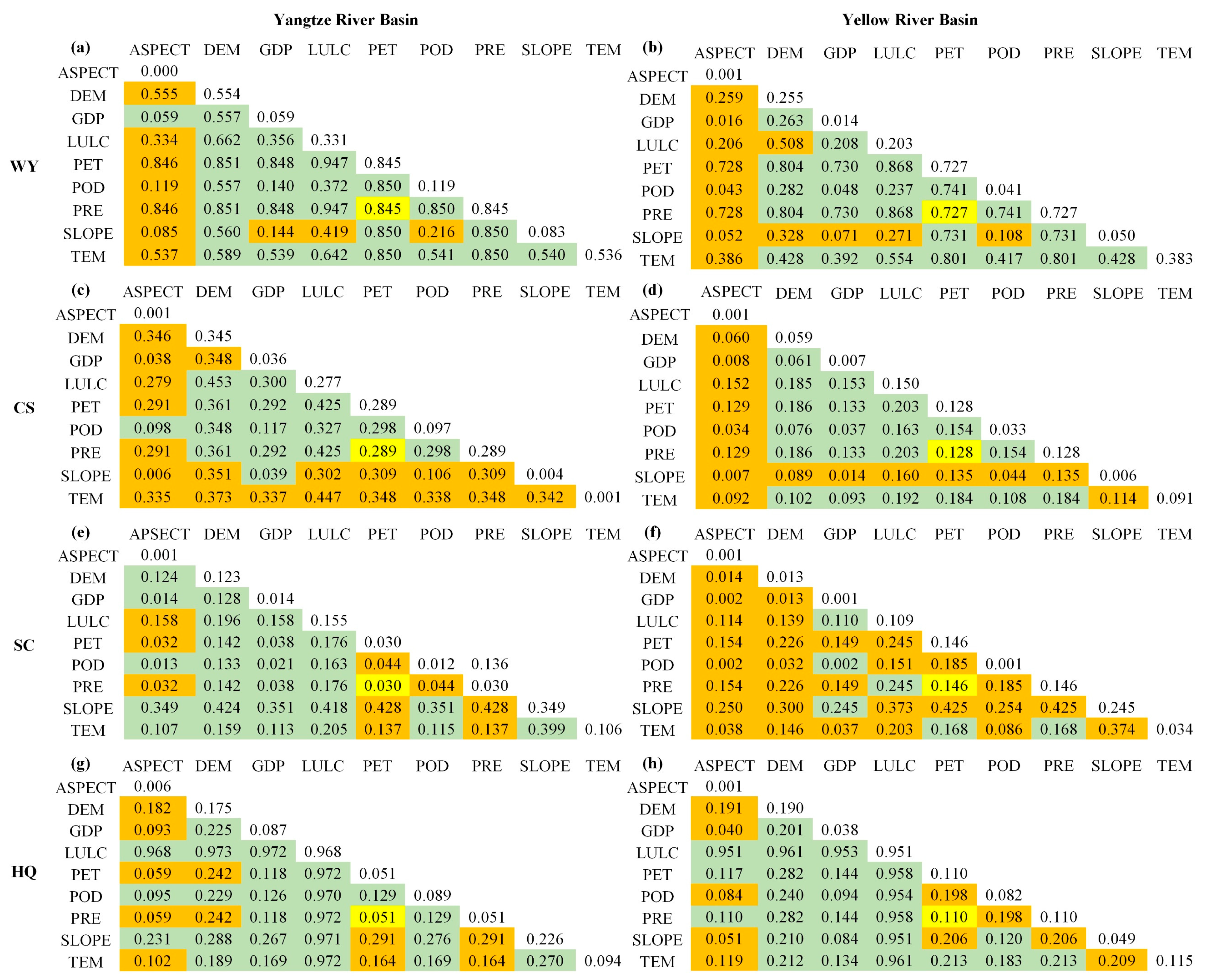
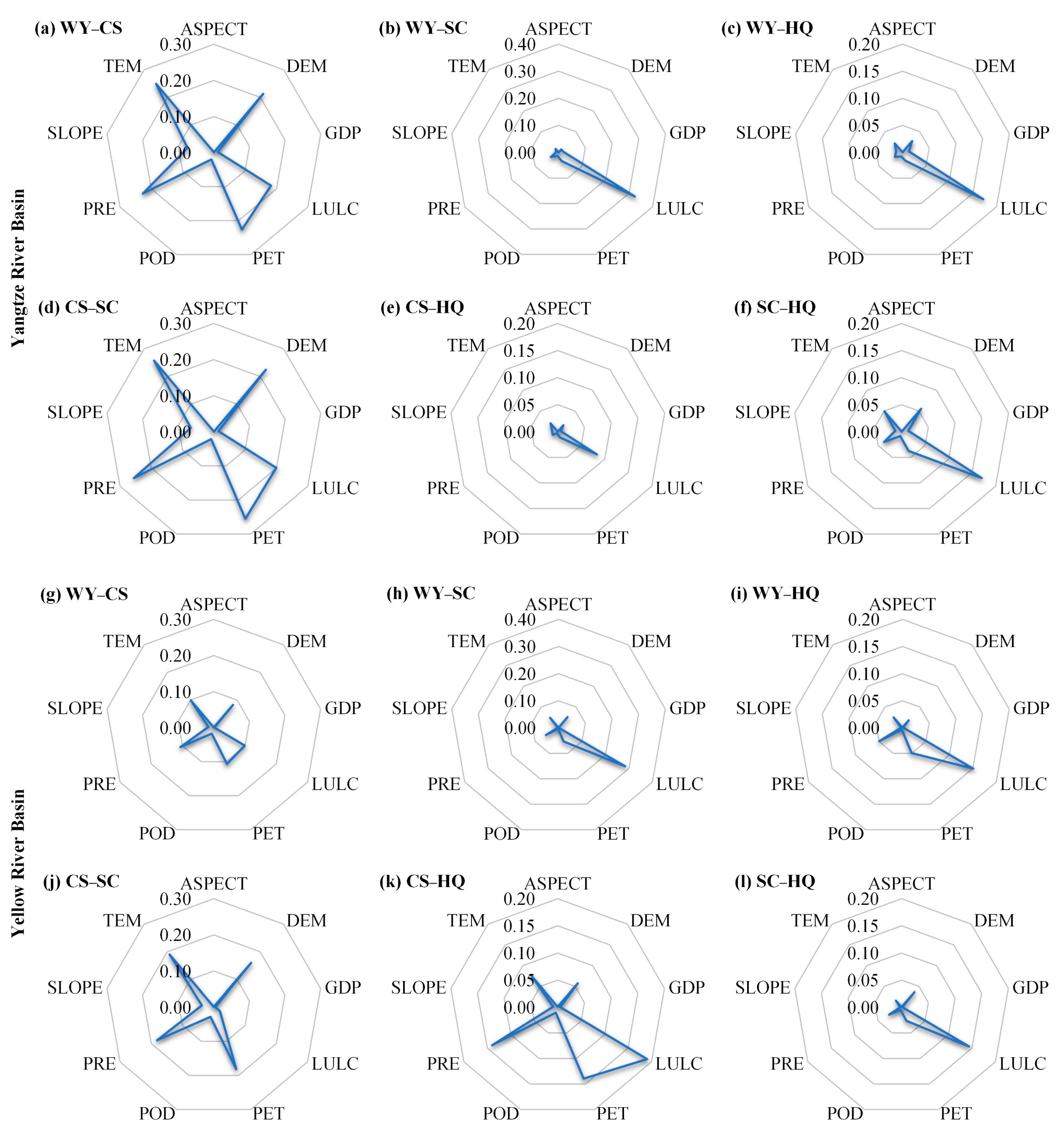
3.3. Driving Factors Analysis in Different ESs
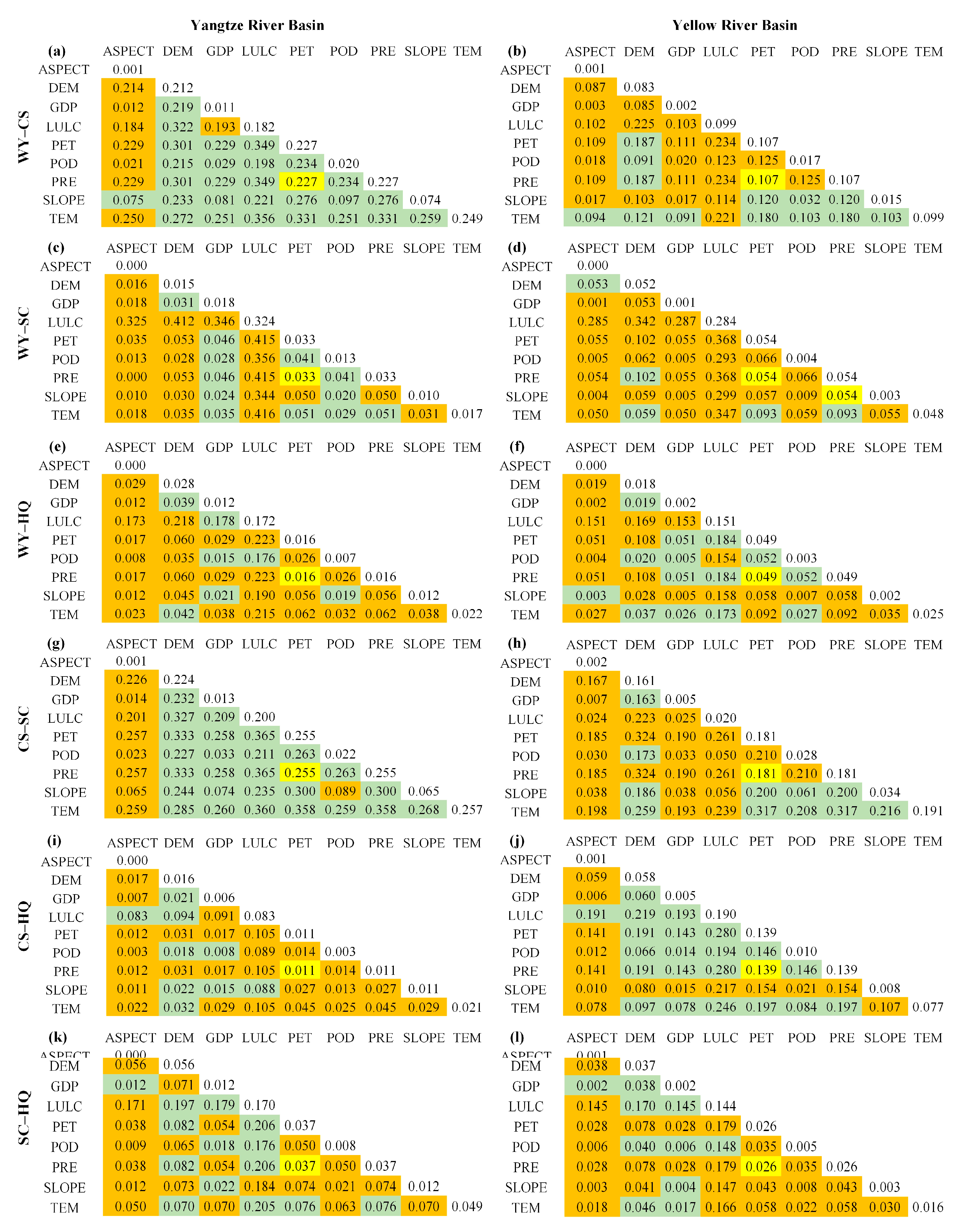
3.4. Driving Factors Analysis of Trade-Offs/Synergies in Different ESs
4. Discussion
4.1. Explanation of Influencing Factors on Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of ESs
4.2. Explanation of Trade-Offs/Synergies among ESs
4.3. Spatiotemporal Scale Effects
4.4. Limitations and Suggestions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| ASPECT | aspect |
| CS | carbon sequestration |
| DEM | elevation |
| ES | ecosystem service |
| GDP | gross domestic product |
| GWR | geographically weighted regression |
| HQ | habitat quality |
| HWSD | Harmonized World Soil Database |
| InVEST | Integrated Valuation of ESs and Tradeoffs |
| LISA | Local Indicators of Spatial Association |
| LULC | land use and land cover |
| M–K | Mann–Kendall |
| NPP | net primary productivity |
| PET | potential evapotranspiration |
| POD | population density |
| PRE | precipitation |
| R | Pearson’s correlation coefficient |
| SC | soil conservation |
| SLOPE | slope |
| SWAT | Soil & Water Assessment Tool |
| TEM | temperature |
| WY | water yield |
| YRB | Yellow River Basin |
| YZRB | Yangtze River Basin |
References
- Scherer-Lorenzen, M.; Gessner, M.O.; Beisner, B.E.; Messier, C.; Paquette, A.; Petermann, J.S.; Soininen, J.; Nock, C.A. Pathways for Cross-Boundary Effects of Biodiversity on Ecosystem Functioning. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2022, 37, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oteros-Rozas, E.; Martín-López, B.; Fagerholm, N.; Bieling, C.; Plieninger, T. Using Social Media Photos to Explore the Relation between Cultural Ecosystem Services and Landscape Features across Five European Sites. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piczak, M.L.; Perry, D.; Cooke, S.J.; Harrison, I.; Benitez, S.; Koning, A.; Peng, L.; Limbu, P.; Smokorowski, K.E.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.; et al. Protecting and Restoring Habitats to Benefit Freshwater Biodiversity. Environ. Rev. 2023, 00, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R. Valuing Natural Capital and Ecosystem Services toward the Goals of Efficiency, Fairness, and Sustainability. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 43, 101096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.; Brander, L.; van der Ploeg, S.; Costanza, R.; Bernard, F.; Braat, L.; Christie, M.; Crossman, N.; Ghermandi, A.; Hein, L.; et al. Global Estimates of the Value of Ecosystems and Their Services in Monetary Units. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, W.V.; Mooney, H.A.; Cropper, A.; Capistrano, D.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chopra, K.; Dasgupta, P.; Dietz, T.; Duraiappah, A.K.; Hassan, R.; et al. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (Program), Ed.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-1-59726-040-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Jiang, Y. Ecosystem-Based Adaptation to Address Urbanization and Climate Change Challenges: The Case of China’s Sponge City Initiative. Clim. Policy 2023, 23, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Xu, D.; Bai, T. Understanding Spatial-Temporal Interactions of Ecosystem Services and Their Drivers in a Multi-Scale Perspective of Miluo Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, L.; White, L.; Miles, A.; Roberts, P. Analysing the Impacts of Air Quality Policies on Ecosystem Services; a Case Study for Telemark, Norway. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon, P.; Steinhoff-Knopp, B.; Burkhard, B. Linking Ecosystem Condition and Ecosystem Services: A Methodological Approach Applied to European Agroecosystems. Ecosyst. Serv. 2022, 53, 101387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Su, X.; Lu, H.; Li, T.; Jin, T.; Zhang, M.; Liu, G. Impacts of Human Activity Intensity on Ecosystem Services for Conservation in the Lhasa River Basin. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2023, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Sun, J.; Cao, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Identifying the Impacts of Natural and Human Factors on Ecosystem Service in the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Liu, B.; Wu, D.; Fu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, P. Spatial Relationships between Ecosystem Services and Socioecological Drivers across a Large-Scale Region: A Case Study in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, A.N.; Jackson, B.M.; Benavidez, R.; Tomscha, S.A. Review of Ecosystem Service Assessments: Pathways for Policy Integration in Southeast Asia. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 49, 101266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, J. The Role of Prices in Conserving Critical Natural Capital. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Van Damme, S.; Uyttenhove, P. A Review of Empirical Studies of Cultural Ecosystem Services in Urban Green Infrastructure. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, M.; Fazey, I.; Cooper, R.; Hyde, T.; Kenter, J.O. An Evaluation of Monetary and Non-Monetary Techniques for Assessing the Importance of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services to People in Countries with Developing Economies. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 83, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, D.; Rekola, M.; Li, N.; Toppinen, A. Monetary Valuation of Forest Ecosystem Services in China: A Literature Review and Identification of Future Research Needs. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 121, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.E.; Garmestani, A.S. An Energy Systems View of Sustainability: Emergy Evaluation of the San Luis Basin, Colorado. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, 72–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wei, H.; Fan, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, B.; Lu, N.; Ren, J.; Dong, X. Energy Modeling Simulation of Changes in Ecosystem Services before and after the Implementation of a Grain-for-Green Program on the Loess Plateau—A Case Study of the Zhifanggou Valley in Ansai County, Shaanxi Province, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, F.; Bagstad, K.; Johnson, G.; Voigt, B. Scientific Instruments for Climate Change Adaptation: Estimating and Optimizing the Efficiency of Ecosystem Service Provision. Econ. Agrar. Recur. Nat. 2011, 11, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, B.; Pagella, T.; Sinclair, F.; Orellana, B.; Henshaw, A.; Reynolds, B.; Mcintyre, N.; Wheater, H.; Eycott, A. Polyscape: A GIS Mapping Framework Providing Efficient and Spatially Explicit Landscape-Scale Valuation of Multiple Ecosystem Services. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 112, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorstius, A.C.; Spray, C.J. A Comparison of Ecosystem Services Mapping Tools for Their Potential to Support Planning and Decision-Making on a Local Scale. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 15, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrouse, B.C.; Clement, J.M.; Semmens, D.J. A GIS Application for Assessing, Mapping, and Quantifying the Social Values of Ecosystem Services. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peh, K.S.-H.; Balmford, A.; Bradbury, R.B.; Brown, C.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Hughes, F.M.R.; Stattersfield, A.; Thomas, D.H.L.; Walpole, M.; Bayliss, J.; et al. TESSA: A Toolkit for Rapid Assessment of Ecosystem Services at Sites of Biodiversity Conservation Importance. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 5, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaks, I. InVEST. Available online: https://naturalcapitalproject.stanford.edu/software/invest (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Sharps, K.; Masante, D.; Thomas, A.; Jackson, B.; Redhead, J.; May, L.; Prosser, H.; Cosby, B.; Emmett, B.; Jones, L. Comparing Strengths and Weaknesses of Three Ecosystem Services Modelling Tools in a Diverse UK River Catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, P.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Sim, S.; Mueller, C. A New Approach to Modeling the Sediment Retention Service (InVEST 3.0): Case Study of the Cape Fear Catchment, North Carolina, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, J.M.; Hasan, S.; Brooks, A.; Curwen, G.; Dyke, J.; Ange, C.S.; Smart, J.C.R. Challenges in Modelling the Sediment Retention Ecosystem Service to Inform an Ecosystem Account—Examples from the Mitchell Catchment in Northern Australia. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 314, 115102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.; Sun, X.; Guo, H.; Shan, R. Comparison of the SWAT and InVEST Models to Determine Hydrological Ecosystem Service Spatial Patterns, Priorities and Trade-Offs in a Complex Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennedy-Frank, P.J.; Muenich, R.L.; Chaubey, I.; Ziv, G. Comparing Two Tools for Ecosystem Service Assessments Regarding Water Resources Decisions. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 177, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decsi, B.; Ács, T.; Jolánkai, Z.; Kardos, M.K.; Koncsos, L.; Vári, Á.; Kozma, Z. From Simple to Complex—Comparing Four Modelling Tools for Quantifying Hydrologic Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Dai, X.; Zhou, J.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Lu, H.; Ye, Y.; et al. Evaluating Trade-Off and Synergies of Ecosystem Services Values of a Representative Resources-Based Urban Ecosystem: A Coupled Modeling Framework Applied to Panzhihua City, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, J.; Jiang, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, L. Identifying Priority Conservation Areas Based on Ecosystem Services Change Driven by Natural Forest Protection Project in Qinghai Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Using InVEST to Evaluate Water Yield Services in Shangri-La, Northwestern Yunnan, China. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Hou, Y.; Li, D.; Hua, T.; Marchi, M.; Paola Forero Urrego, J.; Huang, B.; Zhao, W.; Cherubini, F. Changes in Multiple Ecosystem Services and Their Influencing Factors in Nordic Countries. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zuo, L.; Gao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Du, F.; Zhang, Y. Exploring the Driving Factors of Trade-Offs and Synergies among Ecological Functional Zones Based on Ecosystem Service Bundles. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Robinson, G.M.; Song, B. Experimental Research on Trade-Offs in Ecosystem Services: The Agro-Ecosystem Functional Spectrum. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Liang, Y.; Peng, S.; Huang, J.; Liu, L. Challenges in Trade-off Governance of Ecosystem Services: Evidence from the Loess Plateau in China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Spatio-Temporal Quantification of the Trade-Offs and Synergies among Ecosystem Services Based on Grid-Cells: A Case Study of Guanzhong Basin, NW China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Li, R.; Huang, K. Driving Factors of the Variation of Ecosystem Service and the Trade-off and Synergistic Relationships in Typical Karst Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, J.; Fu, G.; Liu, B.; Pan, L.; Hao, H.; Guan, X. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Ecosystem Services and Trade-Offs/Synergies in Wujiang River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Z.; Yao, W.; Tu, Y. Exploring the Spatial Heterogeneity of Ecosystem Services and Influencing Factors on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dai, E.; Ge, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yu, C. Spatial Heterogeneity of Ecosystem Services and Their Trade-Offs in the Hengduan Mountain Region, Southwest China. Catena 2021, 207, 105632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, H. Trade-off/Synergistic Changes in Ecosystem Services and Geographical Detection of Its Driving Factors in Typical Karst Areas in Southern China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Gu, Y.; Zou, C.; Xu, D.; Wang, L.; Ye, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, X. Temporal Variation and Spatial Scale Dependency of the Trade-Offs and Synergies among Multiple Ecosystem Services in the Taihu Lake Basin of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Alatalo, J.M.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, B. Scale Effects on the Relationships between Land Characteristics and Ecosystem Services- a Case Study in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Change and Tradeoff/Synergy Analysis of Watershed Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jiang, C.; Gao, Y.; Du, J. Natural Driving Mechanism and Trade-off and Synergy Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Multiple Typical Ecosystem Services in Northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 134075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Hu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Liu, L.; Su, S.; Wang, W.; Wu, J. Multifunctional Trade-off/Synergy Relationship of Cultivated Land in Guangdong: A Long Time Series Analysis from 2010 to 2030. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPBES 2019 Global Assessment on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Available online: https://earthlobbyist.com/ipbes-2019-global-assessment-on-biodiversity-and-ecosystems/ (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Yu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y.; Nong, L.; Deng, H. Assessing the Response of Vegetation Change to Drought during 2009–2018 in Yunnan Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47066–47082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Zhen, L.; Miah, M.G.; Ahamed, T.; Samie, A. Impact of Land Use Change on Ecosystem Services: A Review. Environ. Dev. 2020, 34, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Fang, S.; Zhuo, W. Revealing the Driving Mechanisms of Land Surface Temperature Spatial Heterogeneity and Its Sensitive Regions in China Based on GeoDetector. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Wang, J.; Du, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, K. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Ecosystem Services and Its Potential Drivers in Coalfields of Shanxi Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, J.; Hou, W. Quantitative Attribution Analysis of Soil Erosion in Different Geomorphological Types in Karst Areas: Based on the Geodetector Method. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, C. Knowledge Diffusion of Geodetector: A Perspective of the Literature Review and Geotree. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhong, X.; Deng, S.; Xu, H. Assessment of the Impact of LUCC on NPP and Its Influencing Factors in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Catena 2021, 206, 105542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Fu, B.; Ma, R.; Yang, Y.; Lü, Y.; Wu, X. Identifying Ecological Security Patterns Based on the Supply, Demand and Sensitivity of Ecosystem Service: A Case Study in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Zheng, H.; Rao, E.; Xiao, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Li, C. Evaluating Indirect and Direct Effects of Eco-Restoration Policy on Soil Conservation Service in Yangtze River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ma, G.; Yang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, F.; Wang, J.; Yu, F. Assessment of Ecosystem Service Value and Its Differences in the Yellow River Basin and Yangtze River Basin. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budyko, M.I. Climate and Life; International Geophysics Series; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; ISBN 978-0-12-139450-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Long, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, D.; Wu, H.; Li, S. Identifying the Drivers of Water Yield Ecosystem Service: A Case Study in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liang, D.; Xia, J.; Song, J.; Cheng, D.; Wu, J.; Cao, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, Q. Evaluation of Water Conservation Function of Danjiang River Basin in Qinling Mountains, China Based on InVEST Model. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, G.; Pan, J.; Feng, X. Distribution of Available Soil Water Capacity in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2005, 15, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Zhao, W.; Cherubini, F.; Hu, X.; Pereira, P. Sensitivity and Future Exposure of Ecosystem Services to Climate Change on the Tibetan Plateau of China. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 3451–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fu, J. Rainfall Erosivity Estimation under Different Rainfall Amount. Resour. Sci. 2003, 1, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.R.; Arnold, J.G. A System of Erosion—Sediment Yield Models. Soil Technol. 1997, 11, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Ding, S.; Shi, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G. Study of Applying USLE and Geographical Information System IDRISI to Predict Soil Erosion in Small Watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 2, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and Its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-F.; Zhang, T.-L.; Fu, B.-J. A Measure of Spatial Stratified Heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizizi, Y.; Kasimu, A.; Liang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, B. Evaluation of Ecological Space and Ecological Quality Changes in Urban Agglomeration on the Northern Slope of the Tianshan Mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Dong, C.; Kang, X.; Qian, X.; Gu, L. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land Cover Changes and Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment in the Yellow River Basin, 2015–2020. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 332, 117149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Jian, H.; Liu, M.; Lei, S.; Yao, S.; Yan, F. Impacts of Drought and Heat Events on Vegetative Growth in a Typical Humid Zone of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River, China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Ochuodho, T.O.; Yang, J. Impact of Land Use and Climate Change on Water-Related Ecosystem Services in Kentucky, USA. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Nie, S.; Deng, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, X. Evaluation of Water Yield and Its Driving Factors in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, W. Factors affecting carbon sequestration in forests. For. Ecol. 2021, 40–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, D. Quantifying the Temporal and Spatial Patterns of Ecosystem Services and Exploring the Spatial Differentiation of Driving Factors: A Case Study of Sichuan Basin, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 927818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z.; Bai, Y.; Li, R.; Lan, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Chang, S.; Xie, Y. The Global Carbon Sink Potential of Terrestrial Vegetation Can Be Increased Substantially by Optimal Land Management. Commun Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafy, A.-A.; Saha, M.; Fattah, M.A.; Rahman, M.T.; Duti, B.M.; Rahaman, Z.A.; Bakshi, A.; Kalaivani, S.; Nafiz Rahaman, S.; Sattar, G.S. Integrating Forest Cover Change and Carbon Storage Dynamics: Leveraging Google Earth Engine and InVEST Model to Inform Conservation in Hilly Regions. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 152, 110374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Dai, E.; Wu, C. Spatial and Temporal Evolution Characteristics and Driving Factors of Soil Conservation Services on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Catena 2023, 221, 106766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, R.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, M.; Deng, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Identifying Conservation Priority Zones and Their Driving Factors Regarding Regional Ecosystem Services. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Hu, D.; Xiao, Y. Assessing Changes in Soil Conservation Ecosystem Services and Causal Factors in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, S172–S180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filoso, S.; Bezerra, M.O.; Weiss, K.C.B.; Palmer, M.A. Impacts of Forest Restoration on Water Yield: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, X. Regional Ecosystem Services Relationships and Their Potential Driving Factors in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 863–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, T.; Feng, P.; Li, J. Evaluation and Tradeoff-Synergy Analysis of Ecosystem Services in Luanhe River Basin. Ecohydrology 2022, 15, e2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Fu, B.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Tang, Q. Precipitation Gradient Determines the Tradeoff between Soil Moisture and Soil Organic Carbon, Total Nitrogen, and Species Richness in the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallimer, M.; Davies, Z.G.; Diaz-Porras, D.F.; Irvine, K.N.; Maltby, L.; Warren, P.H.; Armsworth, P.R.; Gaston, K.J. Historical Influences on the Current Provision of Multiple Ecosystem Services. Glob. Environ. Change 2015, 31, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, D.; Damm, A.; Hein, L.; Petchey, O.L.; Schaepman, M.E. Spatio-Temporal Trends and Trade-Offs in Ecosystem Services: An Earth Observation Based Assessment for Switzerland between 2004 and 2014. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G. Scale Effect on Spatial Patterns of Ecosystem Services and Associations among Them in Semi-Arid Area: A Case Study in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-J.; Gong, J.-W.; Ma, S.; Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, J. Ecosystem Service Supply–Demand and Socioecological Drivers at Different Spatial Scales in Zhejiang Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 109058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Han, L.; Lv, L.; Shao, H.; Qi, J. Spatiotemporal Variation and Factors Influencing Water Yield Services in the Hengduan Mountains, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M. Contributions of Natural Climate Changes and Human Activities to the Trend of Extreme Precipitation. Atmos. Res. 2018, 205, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, J.; Feng, A.; Jiao, K.; Wu, S.; Zuo, L.; Li, Y.; Yan, R. Concurrent Climate Extremes and Impacts on Ecosystems in Southwest China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dataset | Spatial Resolution | Period | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual precipitation | 0.5° | 2001–2021 | Climate Research Unit Time Series version 4.06, CRU TS4.06 (https://crudata.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/hrg/, accessed on 12 October 2022) |
| Annual evapotranspiration | |||
| Average annual temperature | |||
| Soil data | 1 km | 2013 | HWSD v1.2 (https://data.isric.org, accessed on 13 March 2023) |
| LULC | 500 m | 2001–2021 | MCD12Q1 (https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/search, accessed on 20 March 2023) |
| DTM | 90 m | - | SRTMDEM (https://www.gscloud.cn/, accessed on 29 March 2023) |
| NPP | 500 m | 2001–2021 | MODIS MOD17A3HGF Version 6.1 (https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/search, accessed on 24 March 2023) |
| GDP | 1 km | 2019 | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 29 July 2023) |
| POD | 1 km | 2020 | WorldPop Hub (https://hub.worldpop.org/, accessed on 22 July 2023) |
| Watersheds | - | - | Nine major watersheds in China (https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 7 October 2022) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Bruzzone, L.; Deng, H. Mapping and Analyzing the Spatiotemporal Patterns and Drivers of Multiple Ecosystem Services: A Case Study in the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020411
Yu Y, Xiao Z, Bruzzone L, Deng H. Mapping and Analyzing the Spatiotemporal Patterns and Drivers of Multiple Ecosystem Services: A Case Study in the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(2):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020411
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yuanhe, Zhouxuan Xiao, Lorenzo Bruzzone, and Huan Deng. 2024. "Mapping and Analyzing the Spatiotemporal Patterns and Drivers of Multiple Ecosystem Services: A Case Study in the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins" Remote Sensing 16, no. 2: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020411
APA StyleYu, Y., Xiao, Z., Bruzzone, L., & Deng, H. (2024). Mapping and Analyzing the Spatiotemporal Patterns and Drivers of Multiple Ecosystem Services: A Case Study in the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins. Remote Sensing, 16(2), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020411







