Inter-Calibration of Passive Microwave Satellite Brightness Temperature Observations between FY-3D/MWRI and GCOM-W1/AMSR2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. FY-3D/MWRI Data
2.1.2. GCOM-W1/AMSR2 Data
2.1.3. Auxiliary Data
2.2. Methods
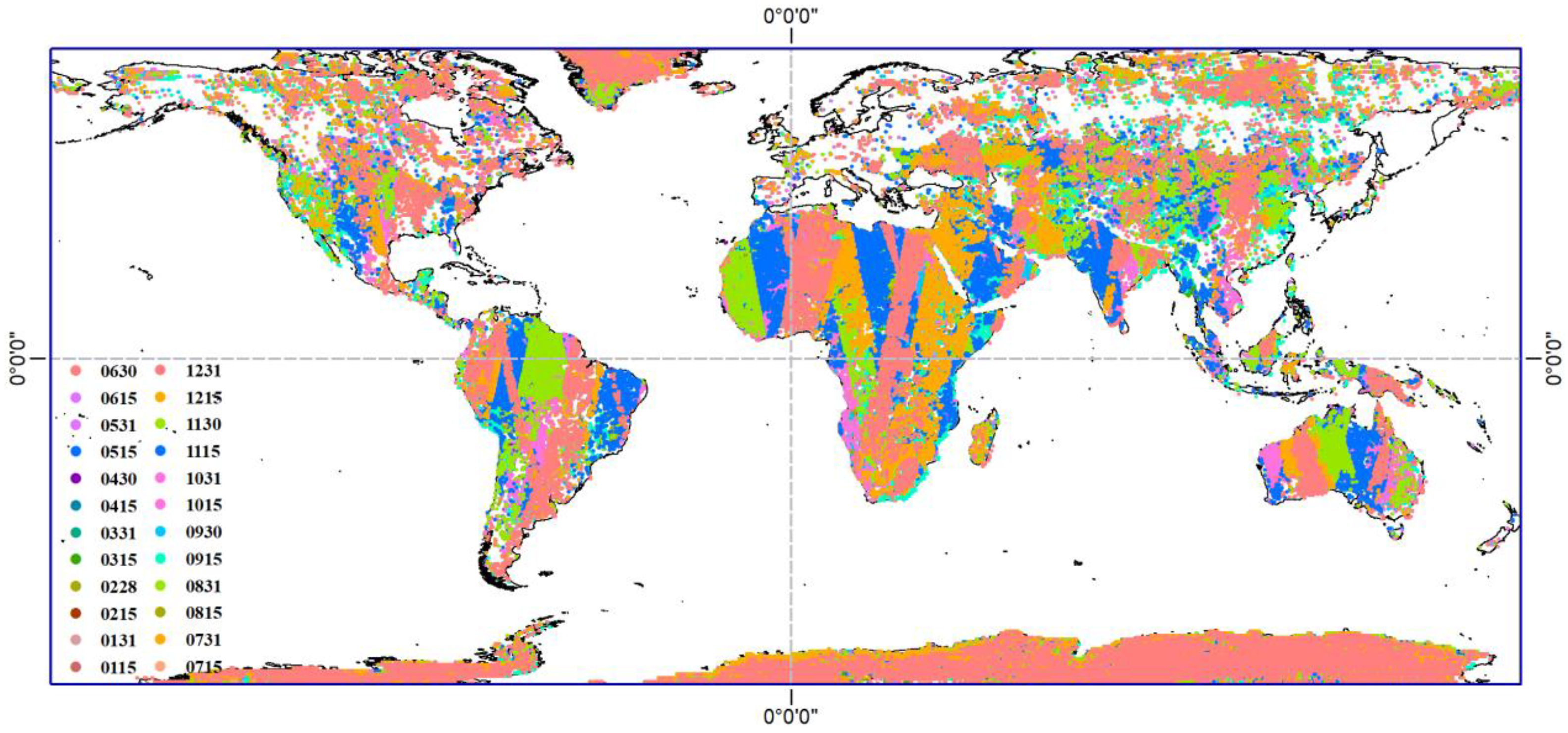
2.2.1. Collocation
- Because the two sensors are observed at different times and clouds vary significantly, we use the FY-4A’s cloud detection product to remove pixels that may be clouds to ensure the accuracy of the obtained two-sensor agreement.
- The data from ocean-covered pixels are removed in this study because sea surface roughness and foam significantly impact the TB observations of different sensors.
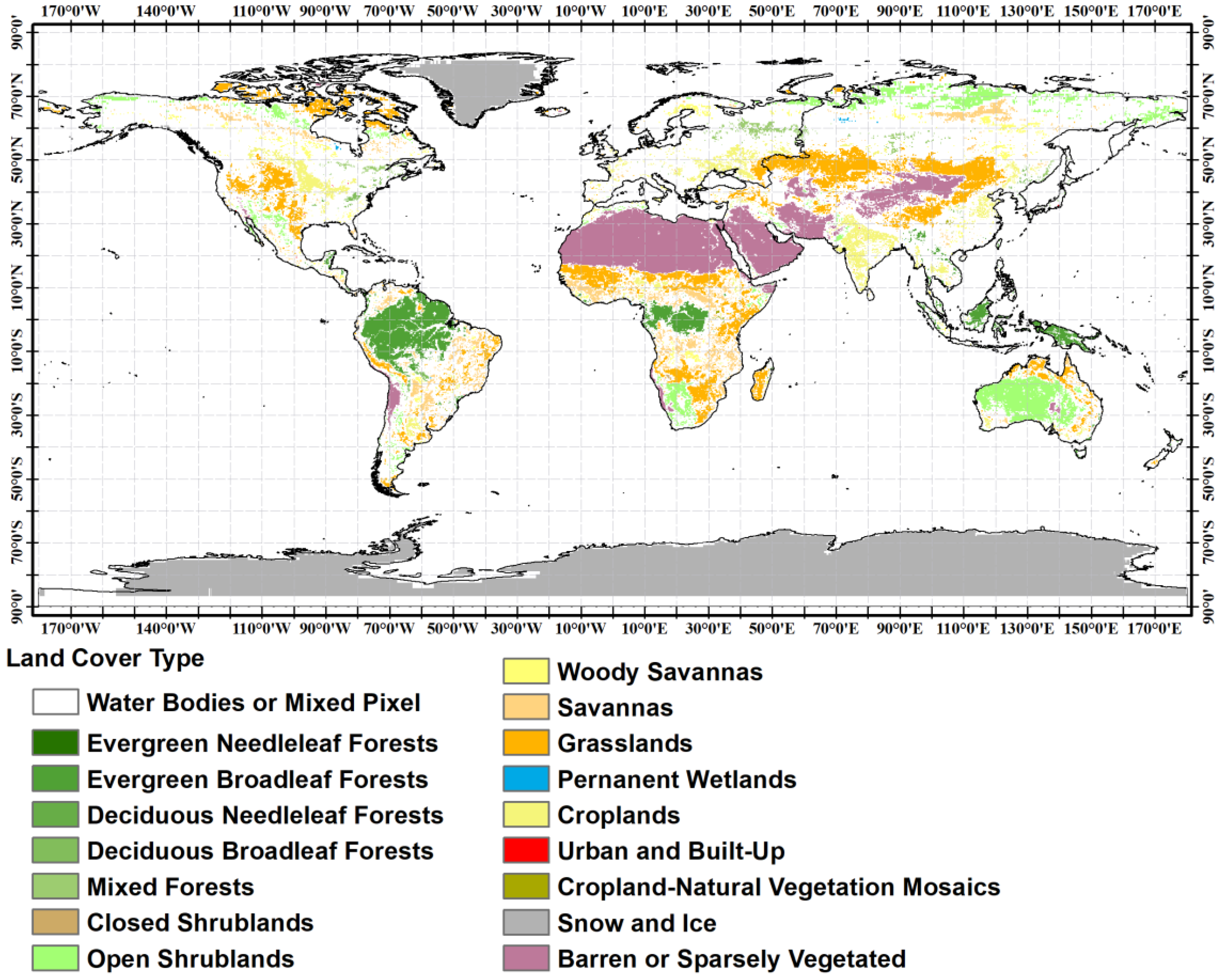
- Due to the low spatial resolution of passive microwave remote sensing, it is easy to produce mixed pixels. The TB observation of mixed pixels has a more significant impact on the difference analysis of the two sensors. In this study, the land cover data at a 500 m spatial resolution are resampled onto a 25 km EASE grid, and the homogeneous and mixed pixels after resampling are distinguished. Then, based on the spatial-temporal matching of the sensors, the resampled land cover data are used to filter the homogeneous subsurface to reduce the interference of mixed image elements.
2.2.2. Error Metrics
3. Results and Analysis
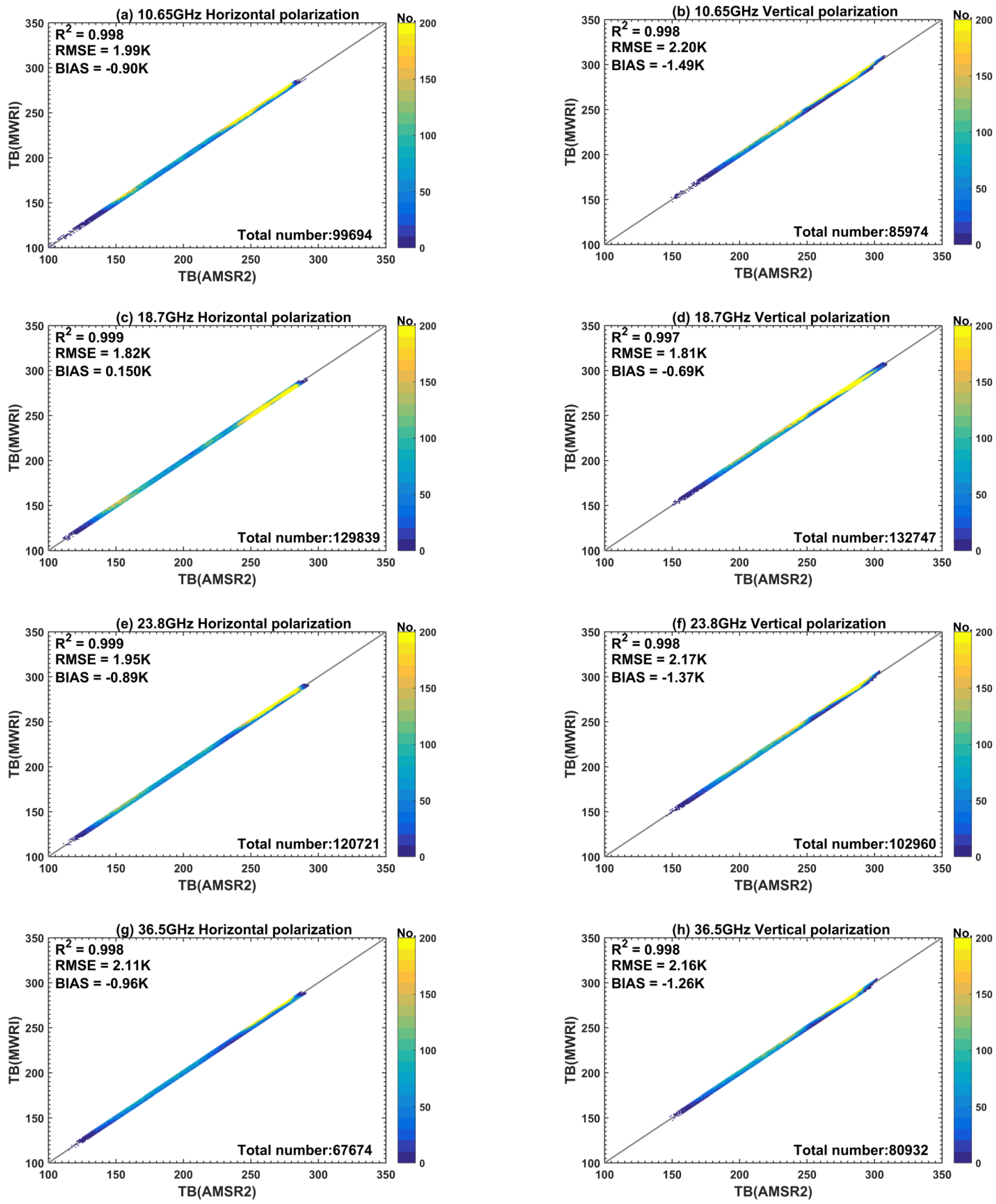
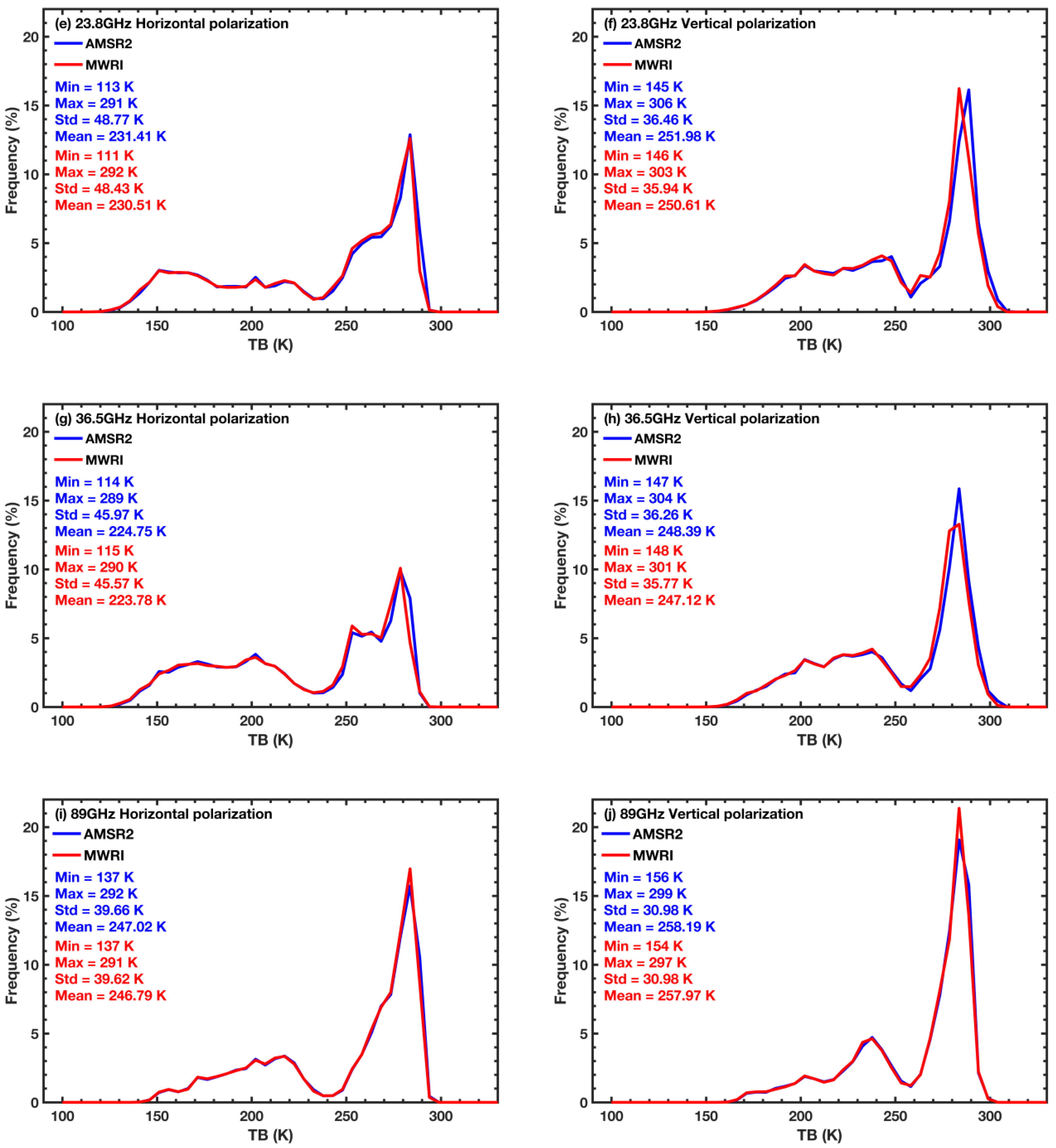
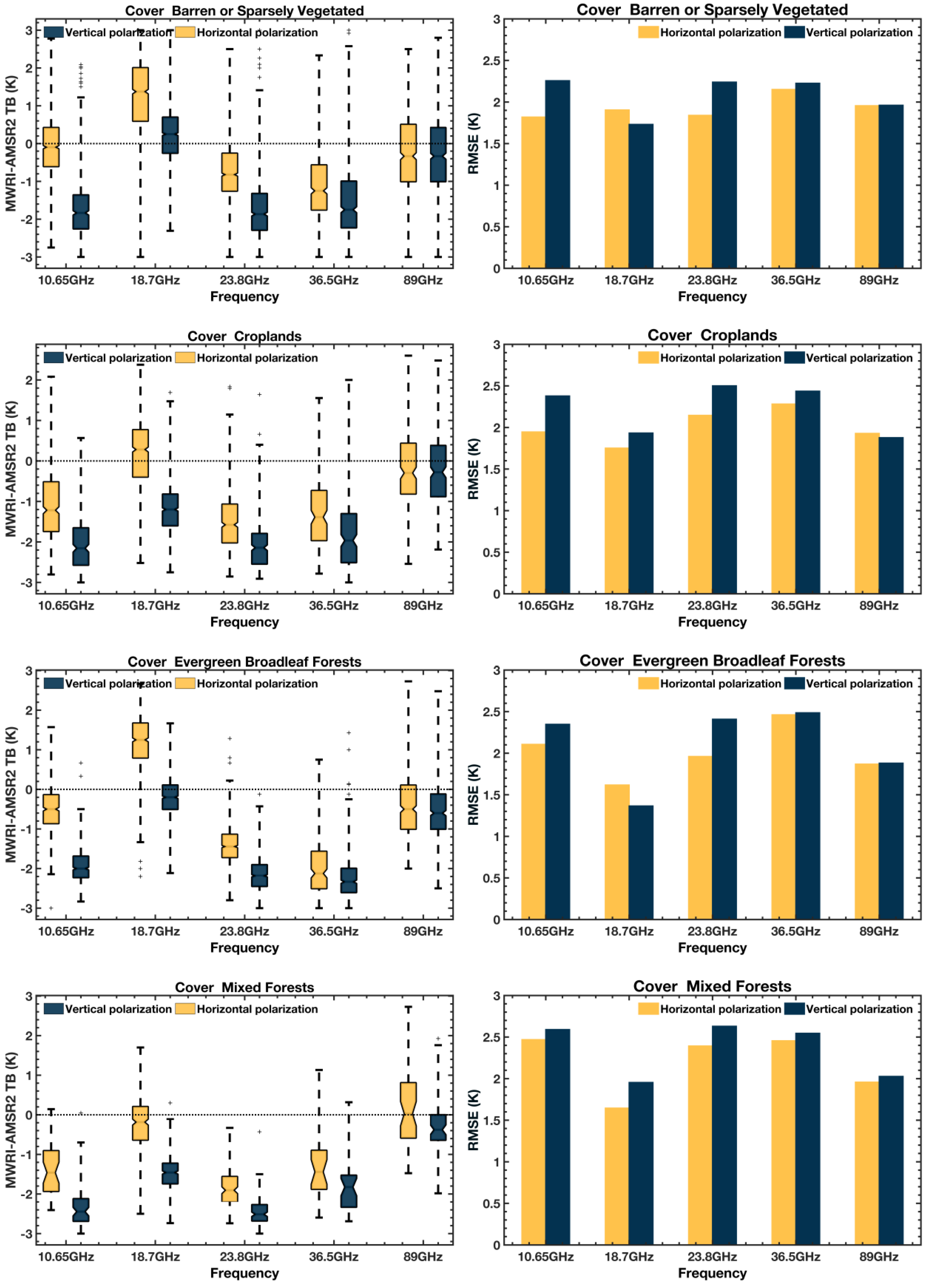
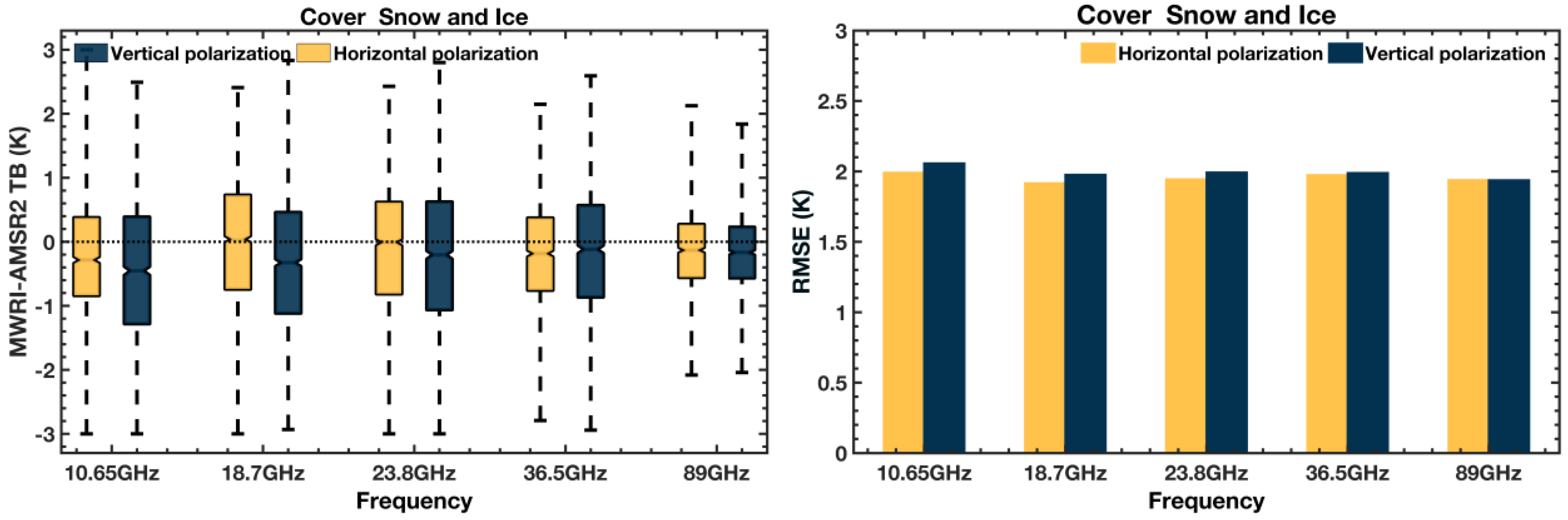
3.1. Overall Assessment
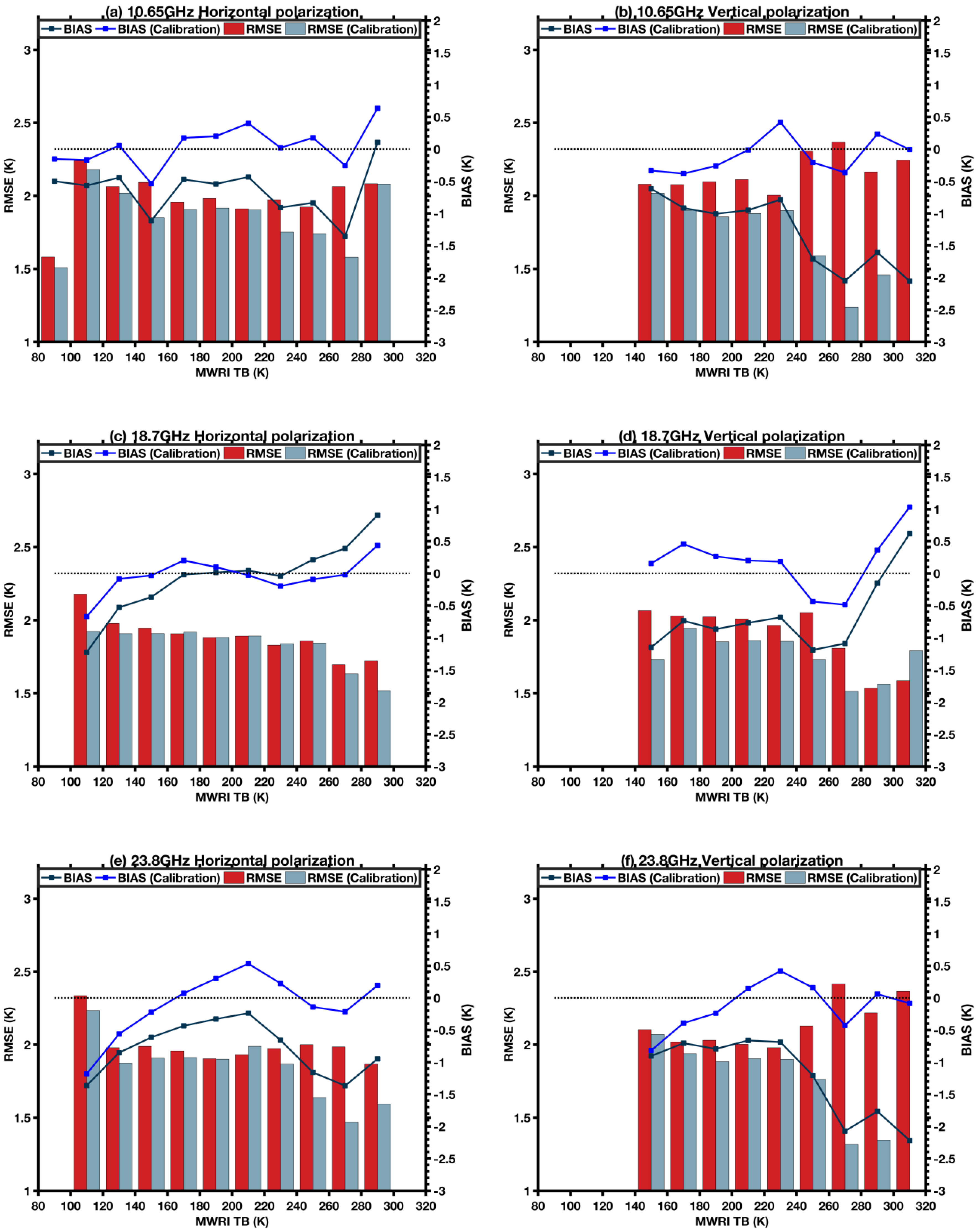
3.2. Inter-Calibration Models and Their Evaluation
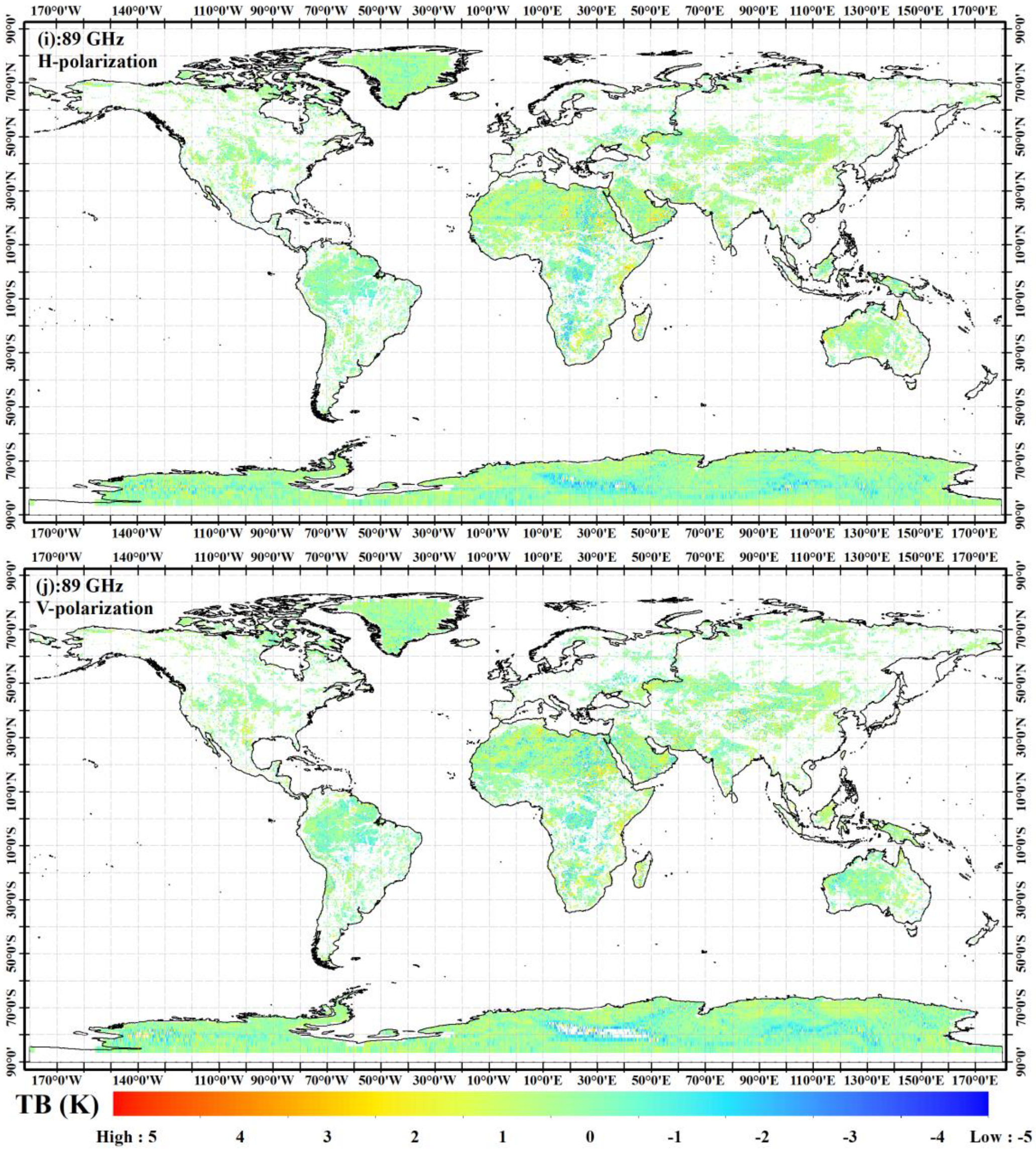
4. Validation and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, N.N.; Colliander, A.; Chan, S.K.; Njoku, E.G.; Li, L. Intercomparisons of Brightness Temperature Observations over Land from AMSR-E and WindSat. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Che, T. Cross-platform calibration of SMMR, SSM/I and AMSR-E passive microwave brightness temperature. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Digital Earth, Beijing, China, 9–12 September 2009; Volume 7841, pp. 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunov, M.E.; Kutuza, B.G. Cosmos-243 as the Starting Point for the Development of Microwave Radiometry Methods of the Earth’s Atmosphere and Surface. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2018, 54, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiso, J.C.; Sullivan, C.W. Satellite microwave and in situ observations of the Weddell Sea ice cover and its marginal ice zone. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1986, 91, 9663–9681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiso, J.C.; Cavalieri, D.J.; Parkinson, C.L.; Gloersen, P. Passive microwave algorithms for sea ice concentration: A comparison of two techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 60, 357–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodison, B.E.; Walker, A.E. Use of snow cover derived from satellite passive microwave data as an indicator of climate change. Ann. Glaciol. 1993, 17, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J. Soil moisture estimation using special satellite microwave/imager satellite data over a grassland region. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.; Schluessel, P. Rainfall, total water, ice water, and water vapor over sea from polarized microwave simulations and Special Sensor Microwave/Imager data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1993, 98, 20737–20759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favrichon, S.; Prigent, C.; Jiménez, C. Inter-calibrating SMMR brightness temperatures over continental surfaces. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 5481–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, E.G.; Stacey, J.M.; Barath, F.T. The Seasat scanning multichannel microwave radiometer (SMMR): Instrument description and performance. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1980, 5, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, T. The Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for the Earth Observing System (AMSR-E), NASDA’s contribution to the EOS for global energy and water cycle studies. Geosci. Remote Sens. IEEE Trans. 2003, 41, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaoka, K.; Kachi, M.; Fujii, H.; Murakami, H.; Hori, M.; Ono, A.; Igarashi, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Oki, T.; Honda, Y.; et al. Global Change Observation Mission (GCOM) for Monitoring Carbon, Water Cycles, and Climate Change. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Pan, M.; Miralles, D.G.; Reichle, R.H.; Wood, E.F. Evaluation of 18 satellite- and model-based soil moisture products using in situ measurements from 826 sensors. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, J. Instrument performance and cross calibration of FY-3C MWRI. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2016—2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, L.; Luojus, K.; Lemmetyinen, J.; Takala, M. Assessing the Performances of FY-3D/MWRI and DMSP SSMIS in GlobSnow-2 Assimilation System for SWE Estimation. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020—2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 2938–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Bell, W.; Bauer, P.; Bormann, N.; Peubey, C. An evaluation of FY-3A satellite data for numerical weather prediction. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 1298–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Kimball, J.S.; Shi, J.; Jones, L.A.; Wu, S.; Sun, R.; Yang, H. Inter-Calibration of Satellite Passive Microwave Land Observations from AMSR-E and AMSR2 Using Overlapping FY3B-MWRI Sensor Measurements. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 8594–8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Martinuzzi, J.M.; Berger, M. Soil moisture retrieval from space: The Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 39, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zeng, J.; Chen, N.; Zhang, X.; Cosh, M.H.; Wang, W. Satellite surface soil moisture from SMAP, SMOS, AMSR2 and ESA CCI: A comprehensive assessment using global ground-based observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Tanguy, M.; Robinson, E.L.; Pinnington, E.; Evans, J.; Ellis, R.; Cooper, E.; Hannaford, J.; Blyth, E.; Dadson, S. Estimation and evaluation of high-resolution soil moisture from merged model and Earth observation data in the Great Britain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroodsma, R.A.; McKague, D.S.; Ruf, C.S. Inter-Calibration of Microwave Radiometers Using the Vicarious Cold Calibration Double Difference Method. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaoka, K.; Kachi, M.; Kasahara, M.; Ito, N.; Nakagawa, K.; Oki, T. Instrument performance and calibration of AMSR-E and AMSR2. In Proceedings of the 8th Symposium on Networking the World with Remote Sensing of ISPRS-Technical-Commission, Kyoto, Japan, 9–12 August 2010; Volume 38, pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chander, G.; Hewison, T.J.; Fox, N.; Wu, X.; Xiong, X.; Blackwell, W.J. Overview of Intercalibration of Satellite Instruments. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1056–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Han, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, C. Impact of FY-3D MWRI Radiance Assimilation in GRAPES 4DVar on Forecasts of Typhoon Shanshan. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 836–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ni, K.; Liu, J.; Li, L. Retrieval of Arctic Sea Ice Motion from FY-3D/MWRI Brightness Temperature Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachi, M.; Naoki, K.; Hori, M.; Imaoka, K. AMSR2 validation results. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Taniguchi, Y.; Imaoka, K. GCOM-W1 AMSR2 Level 1R Product: Dataset of Brightness Temperature Modified Using the Antenna Pattern Matching Technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, A.; Imaoka, K. Intercalibration of Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-2 (AMSR2) Brightness Temperature. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4568–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Liao, K.; Lai, X. Evaluation of nine major satellite soil moisture products in a typical subtropical monsoon region with complex land surface characteristics. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 10, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhao, T.; Lü, H.; Shi, J.; Cosh, M.H.; Ji, D.; Jiang, L.; Cui, Q.; Lu, H.; Yang, K.; et al. Assessment of 24 soil moisture datasets using a new in situ network in the Shandian River Basin of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingson, S.W.; Johnson, J.T. A polarimetric survey of radio frequency interference in C- and X-bands in the continental United States using WindSat radiometery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Instrument Configurations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satellite platform | FY-3D | GCOM-W1 | ||||
| Orbit | Sun-synchronous orbit | Sun-synchronous orbit | ||||
| Sensor | MWRI | AMSR2 | ||||
| Data release date | 1 January 2019 | 25 January 2013 | ||||
| Incidence angle | 53 degrees | 55 degrees | ||||
| Altitude | 836 km | 700 km | ||||
| Equator crossing Time (local time zone) | 2:00 p.m. ascending 2:00 a.m. descending | 1:30 p.m. ascending 1:30 a.m. descending | ||||
| Regression cycle | 5.5 days | 2 days | ||||
| Polarization | Vertical and horizontal | Vertical and horizontal | ||||
| Scan | Conical scan | Conical scan | ||||
| Dynamic range | 3–340 K | 2.7–340 K | ||||
| Swath width | 1400 km | 1450 km | ||||
| Channel Set | ||||||
| Center frequency | MWRI/FY-3D | AMSR2/GCOM-W1 | ||||
| Band width | Polarization | Ground resolution | Band width | Polarization | Ground resolution | |
| GHz | MHz | V.H | km | MHz | V.H | km |
| 6.925/7.3 | 350 | V.H | 35 × 62 | |||
| 10.65 | 180 | V.H | 51 × 85 | 100 | V.H | 24 × 42 |
| 18.7 | 200 | V.H | 30 × 50 | 200 | V.H | 14 × 22 |
| 23.8 | 400 | V.H | 27 × 45 | 400 | V.H | 15 × 26 |
| 36.5 | 900 | V.H | 18 × 30 | 1000 | V.H | 7 × 12 |
| 89 | 2 × 2300 (double sideband) | V.H | 9 × 15 | 3000 | V.H | 3 × 5 |
| Abbreviation | Units | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land cover | m | 500 | yearly | NASA |
| Longitude | deg | Site | Static - | CMDC |
| Latitude | deg | Site | Static - | CMDC |
| Time | h | Site | 1 h | CMDC |
| Cloud detection | m | 4000 | 15 min | FY-4A |
| FY-3D/MWRI (K) | GCOM-W/AMSR2 (K) | (MWRI—AMSR2) (K) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Std | Mean | Min | Max | Std | Mean | ∆Min | ∆Max | ∆Std | ∆Mean | |
| 10.65 H | 99 | 290 | 42.42 | 225.10 | 98 | 287 | 42.64 | 226.00 | 1 | 3 | −0.22 | −0.90 |
| 10.65 V | 149 | 307 | 31.56 | 254.15 | 147 | 309 | 31.98 | 255.65 | 2 | −2 | −0.42 | −1.49 |
| 18.7 H | 111 | 291 | 47.72 | 226.39 | 111 | 291 | 47.44 | 226.24 | 0 | 0 | 0.27 | 0.15 |
| 18.7 V | 150 | 308 | 32.29 | 256.31 | 150 | 308 | 32.13 | 257.00 | 0 | 0 | 0.16 | −0.70 |
| 23.8 H | 111 | 292 | 48.43 | 230.51 | 113 | 291 | 48.77 | 231.41 | −2 | 1 | −0.33 | −0.89 |
| 23.8 V | 146 | 303 | 35.94 | 250.61 | 145 | 306 | 36.46 | 251.98 | 1 | −3 | −0.52 | −1.37 |
| 36.5 H | 115 | 290 | 45.57 | 223.78 | 114 | 289 | 45.97 | 224.75 | 1 | 1 | −0.40 | −0.97 |
| 36.5 V | 148 | 301 | 35.77 | 247.12 | 147 | 304 | 36.26 | 248.39 | 1 | −3 | −0.48 | −1.27 |
| 89 H | 137 | 291 | 39.62 | 246.79 | 137 | 292 | 39.66 | 247.02 | 0 | −1 | −0.05 | −0.24 |
| 89 V | 154 | 297 | 30.98 | 257.97 | 156 | 299 | 30.98 | 258.19 | −2 | −2 | 0.00 | −0.22 |
| Channel | Slope | Intercept (K) | Channel | Slope | Intercept (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.65 H | 1.004 | −0.089 | 10.65 V | 1.012 | −1.572 |
| 18.7 H | 0.994 | 1.297 | 18.7 V | 0.994 | 2.287 |
| 23.8 H | 1.006 | −0.549 | 23.8 V | 1.014 | −2.038 |
| 36.5 H | 1.008 | −0.788 | 36.5 V | 1.012 | −1.806 |
| 89 H | 1.000 | 0.241 | 89 V | 0.998 | 0.700 |
| Channel | Equation | R2 | RMSE (K) | Bias (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.65 H | MWRI = 1.004 × AMSR2 − 0.089 | 0.998 | 1.771 | 0.000 |
| 10.65 V | MWRI = 1.012 × AMSR2 − 1.572 | 0.998 | 1.576 | 0.000 |
| 18.7 H | MWRI = 0.994 × AMSR2 + 1.297 | 0.999 | 1.795 | 0.000 |
| 18.7 V | MWRI = 0.994 × AMSR2 + 2.287 | 0.997 | 1.666 | 0.000 |
| 23.8 H | MWRI = 1.006 × AMSR2 − 0.549 | 0.999 | 1.717 | 0.000 |
| 23.8 V | MWRI = 1.014 × AMSR2 − 2.038 | 0.998 | 1.609 | 0.000 |
| 36.5 H | MWRI = 1.008 × AMSR2 − 0.788 | 0.998 | 1.845 | 0.000 |
| 36.5 V | MWRI = 1.012 × AMSR2 − 1.806 | 0.998 | 1.702 | 0.000 |
| 89 H | MWRI = 1.000 × AMSR2 + 0.241 | 0.998 | 1.926 | 0.000 |
| 89 V | MWRI = 0.998 × AMSR2 + 0.700 | 0.996 | 1.919 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Sun, R.; Wu, S.; Shao, J.; Chen, J. Inter-Calibration of Passive Microwave Satellite Brightness Temperature Observations between FY-3D/MWRI and GCOM-W1/AMSR2. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020424
Xu Z, Sun R, Wu S, Shao J, Chen J. Inter-Calibration of Passive Microwave Satellite Brightness Temperature Observations between FY-3D/MWRI and GCOM-W1/AMSR2. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(2):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020424
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zuomin, Ruijing Sun, Shuang Wu, Jiali Shao, and Jie Chen. 2024. "Inter-Calibration of Passive Microwave Satellite Brightness Temperature Observations between FY-3D/MWRI and GCOM-W1/AMSR2" Remote Sensing 16, no. 2: 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020424
APA StyleXu, Z., Sun, R., Wu, S., Shao, J., & Chen, J. (2024). Inter-Calibration of Passive Microwave Satellite Brightness Temperature Observations between FY-3D/MWRI and GCOM-W1/AMSR2. Remote Sensing, 16(2), 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020424






