Background-Aware Cross-Attention Multiscale Fusion for Multispectral Object Detection
Abstract
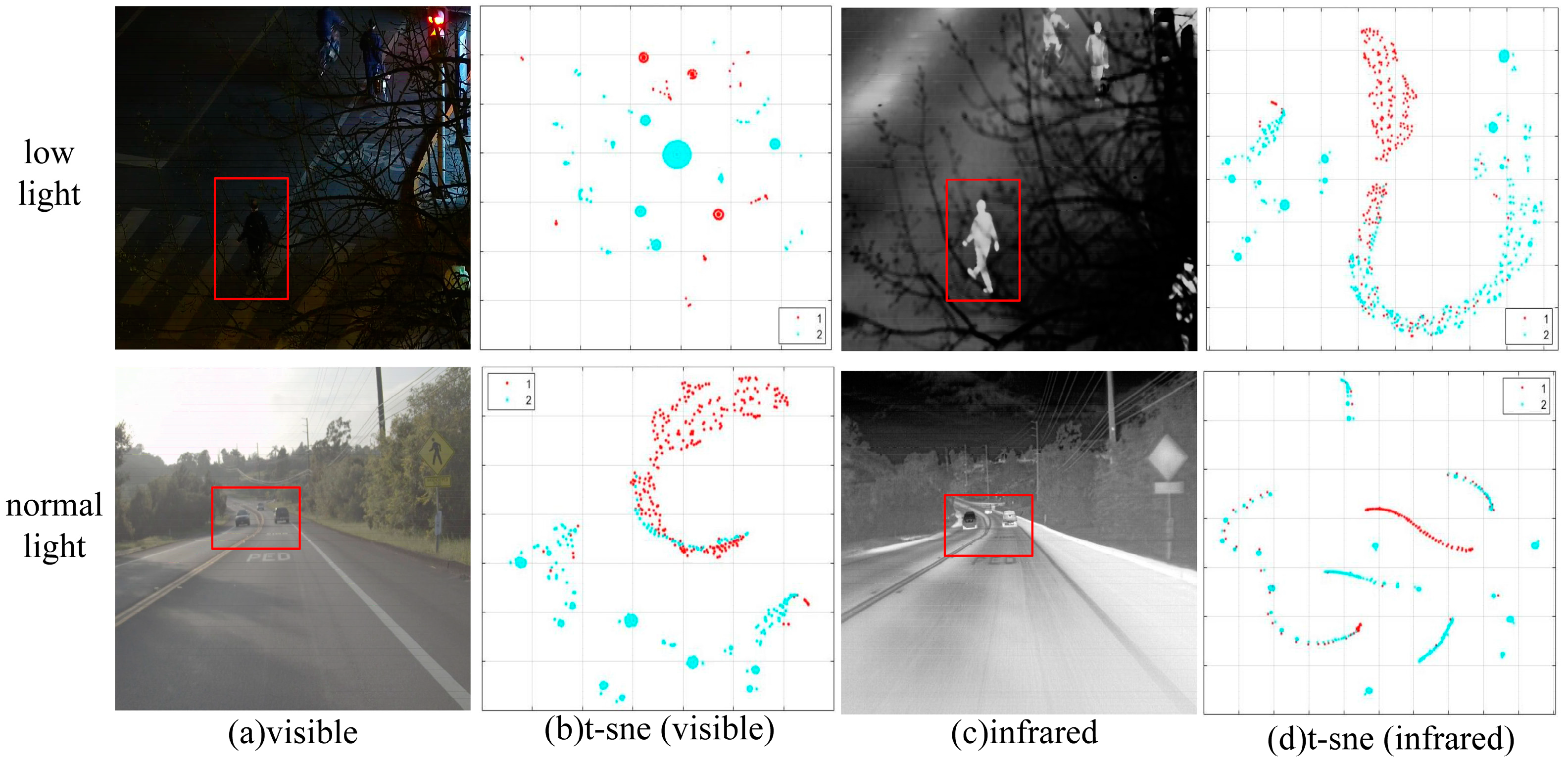
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- A two-stream network BA-CAMF Net is proposed for multispectral object detection. The network achieves reliable detection through the guidance of a priori knowledge and the interaction within modalities;
- (2)
- A BA module is designed to guide the fusion of visible and infrared modality, in which we utilize light conditions and contrast to obtain adaptive fusion weights for two branches;
- (3)
- We put forward a CAMF module consisting of DA and CA modules to enhance inter-modality complement features and intra-modality intrinsic features and to achieve adaptive fusion;
- (4)
- Extensive comparative experiments on three typical multispectral detection datasets (LLVIP, FLIR, and VEDAI) have been carried out, and the results show that the proposed BA-CAMF Net achieves higher detection accuracy than the current State-of-the-Art multispectral detectors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Single-Modality Object Detection
2.2. CNN-Based Multispectral Object Detection
2.3. Illustration-Guided Multispectral Object Detection
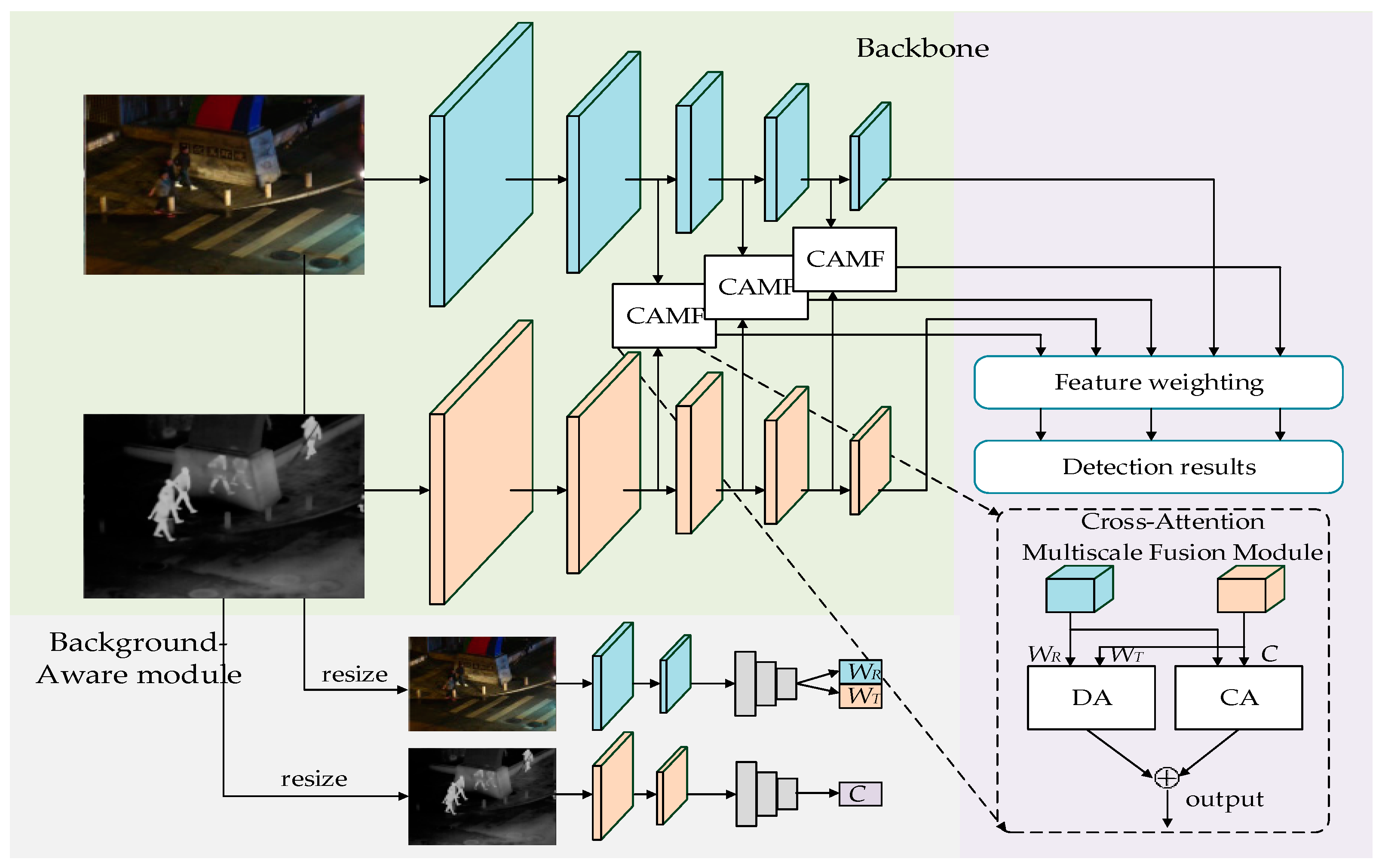
3. Methodology
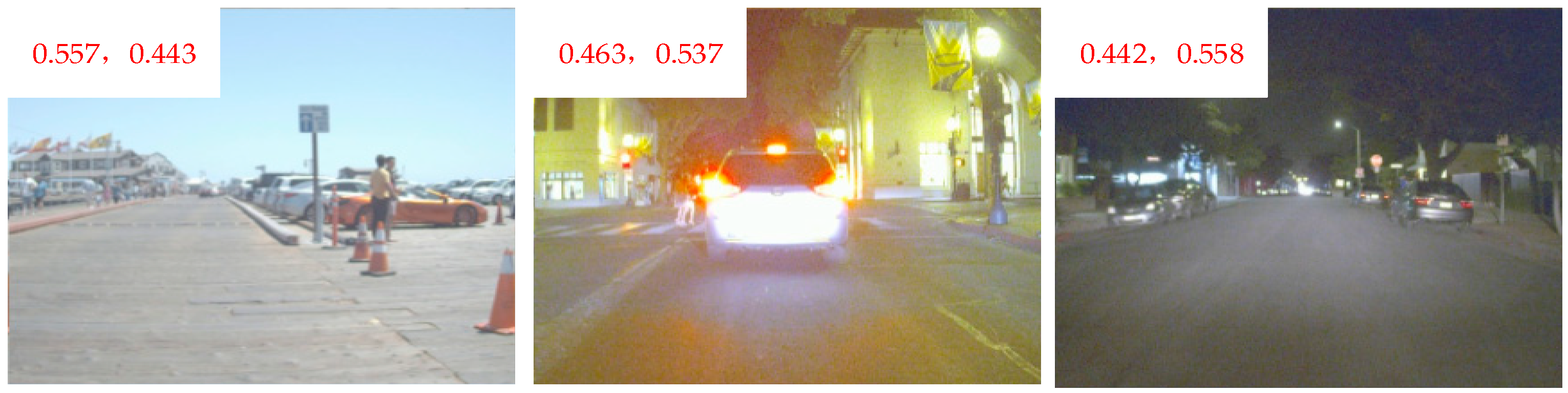
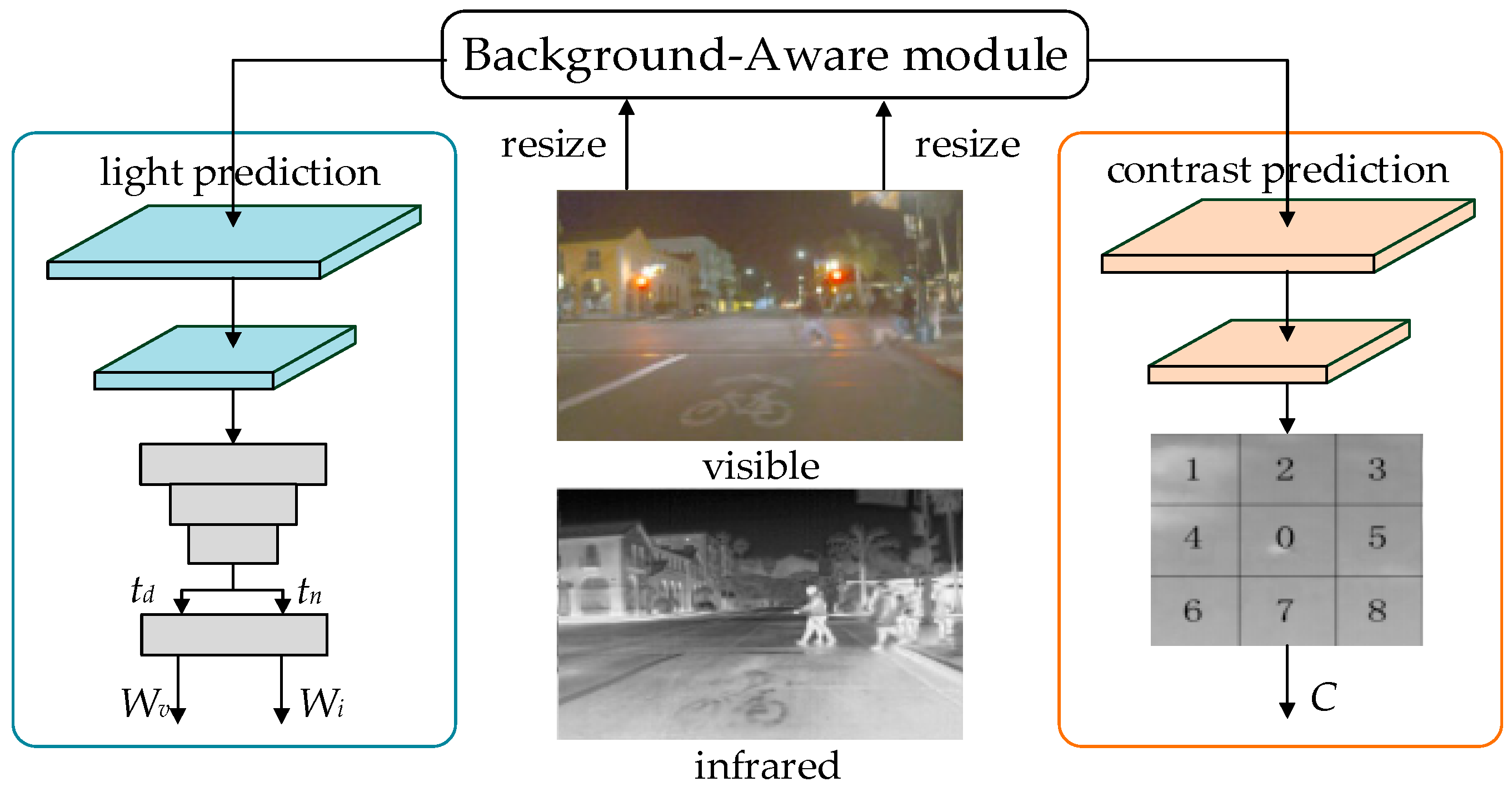
3.1. BA Module
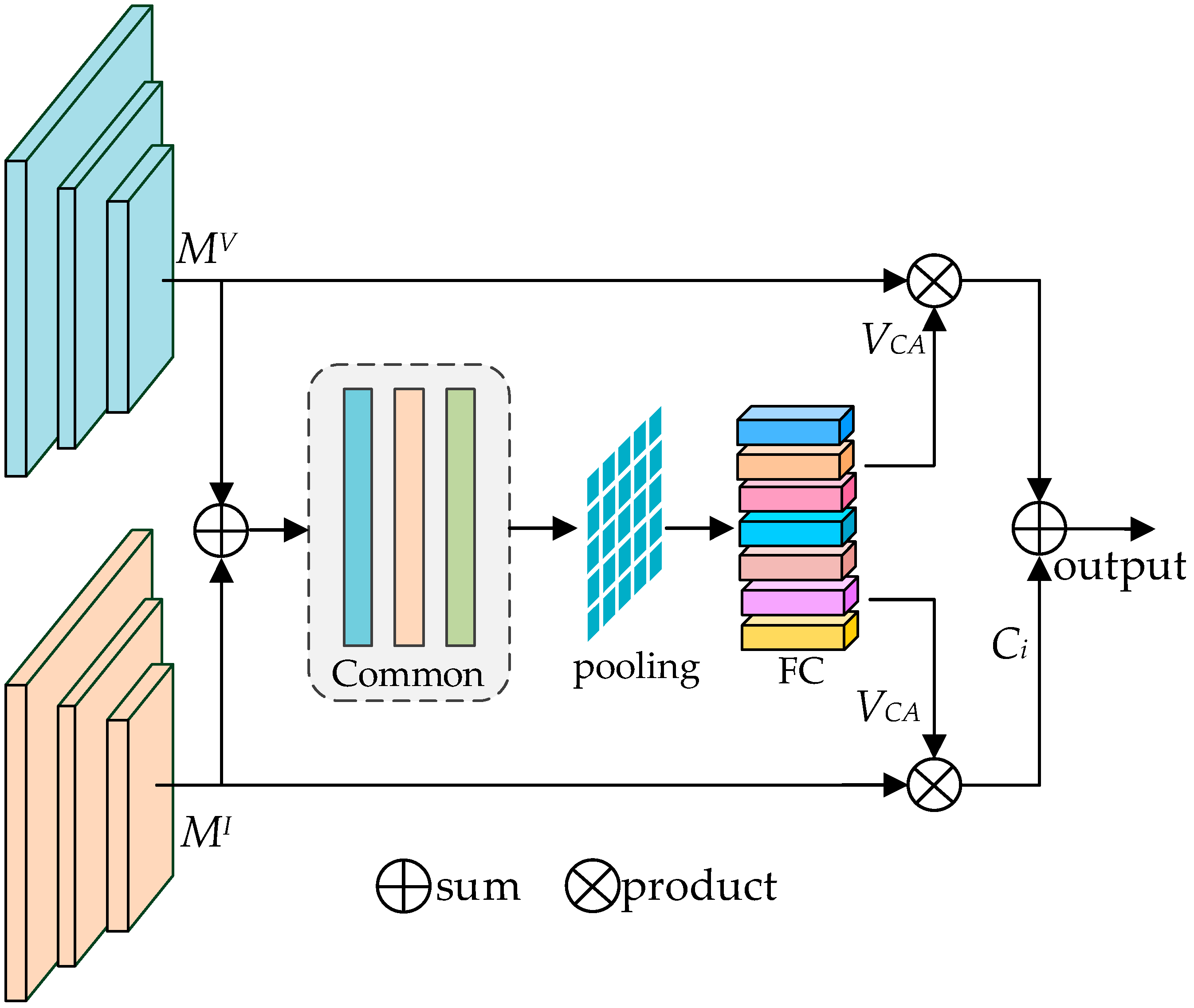
3.2. CAMF Module
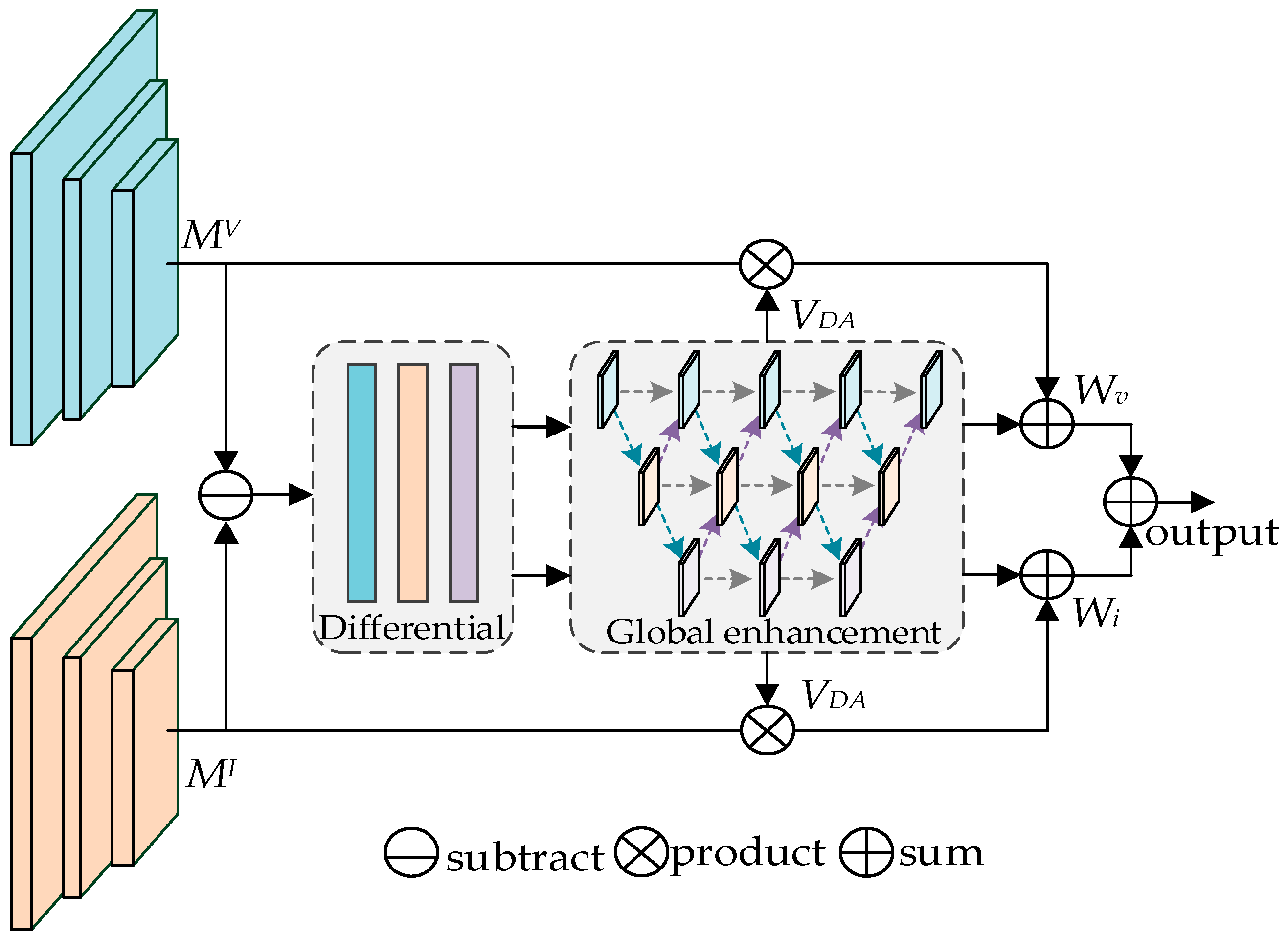
3.2.1. Inter-Modality DA Module
3.2.2. Inter-Modality CA Module
3.2.3. Multiscale Cross-Fusion Strategies
3.3. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Experimental Setup
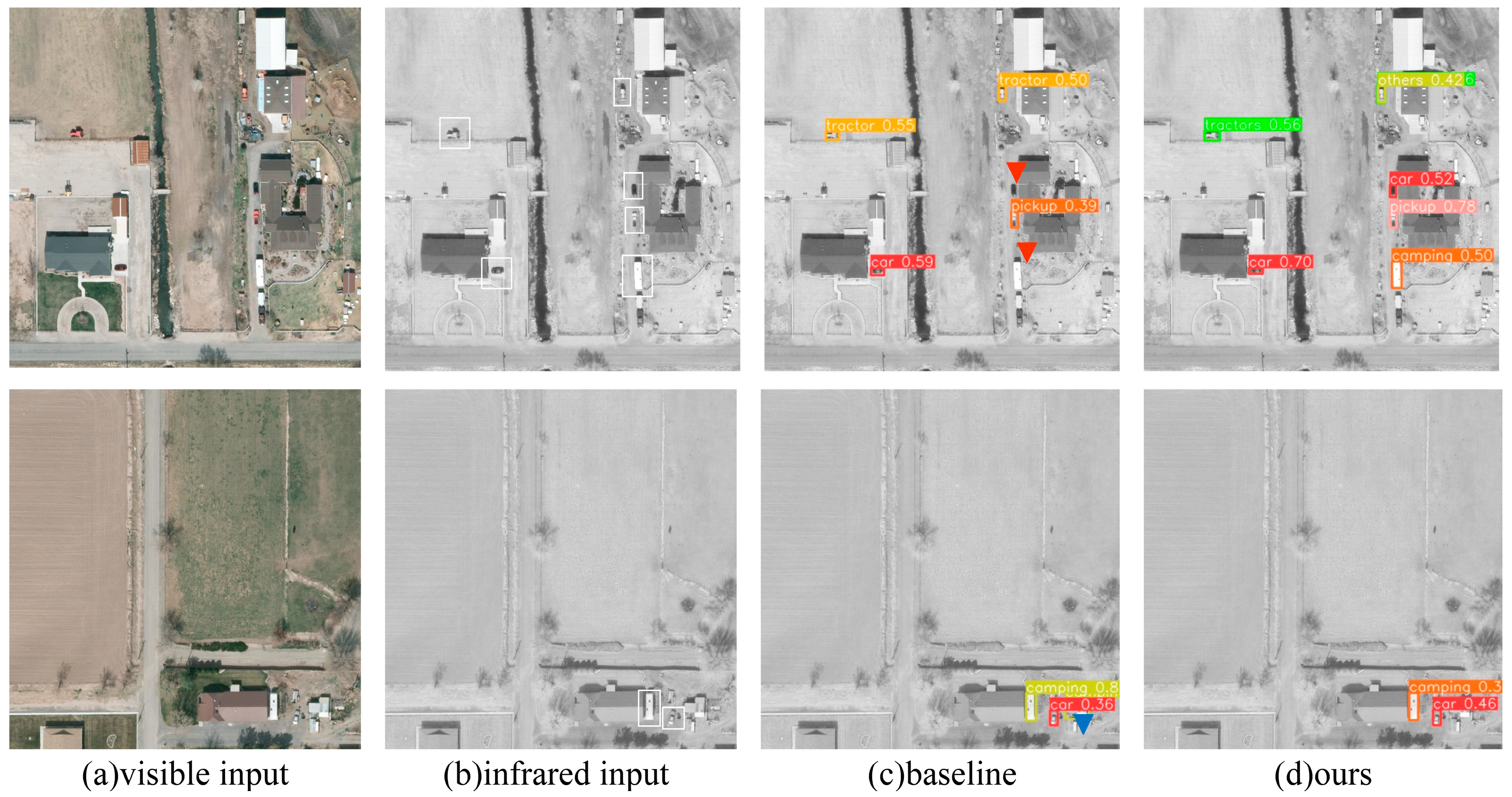
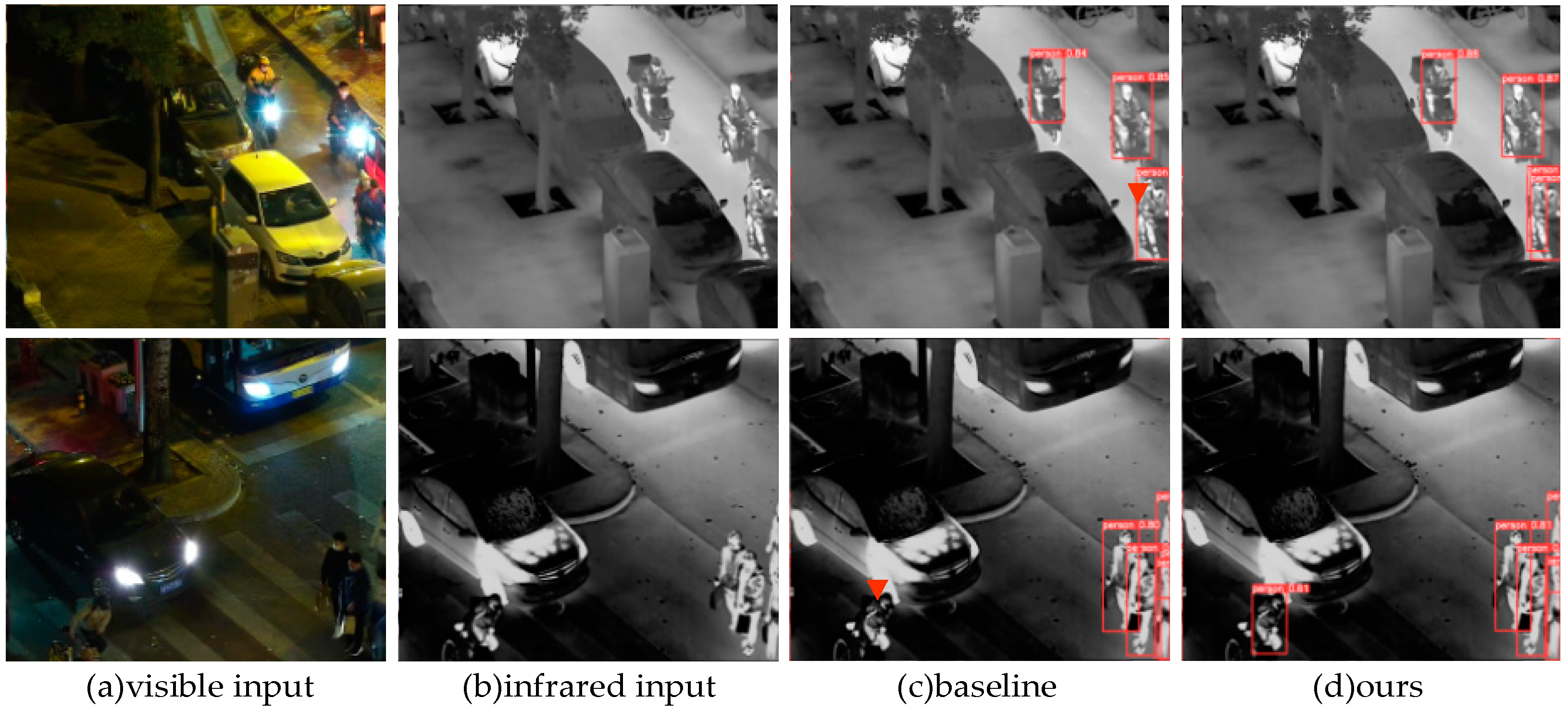
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
4.3.1. On the VEDAI Dataset
4.3.2. On the FLIR Dataset
4.3.3. On the LLVIP Dataset
4.3.4. Inference Time
4.4. Ablation Studies
4.4.1. Necessity of Multiscale Cross-Fusion
4.4.2. Necessity of the Proposed Module
5. Discussion
5.1. Limitations
5.2. Ideas for Future Researches
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, K.; Wan, G.; Cheng, G.; Meng, L.; Han, J. Object detection in optical remote sensing images: A survey and a new benchmark. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 159, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, B.Y.; Lam, W.H.; Ho, H.W.; Shi, X.; Yang, X.; Ma, W.; Wong, S.C.; Chow, A.H. Vehicle re-identification for lane-level travel time estimations on congested urban road networks using video images. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 8, 12877–12893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Haase-Schütz, C.; Rosenbaum, L.; Hertlein, H.; Glaeser, C.; Timm, F.; Wiesbeck, W.; Dietmayer, K. Deep multi-modal object detection and semantic segmentation for autonomous driving: Datasets, methods, and challenges. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 3, 1341–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Bian, J.W.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, M.M. SAMNet: Stereoscopically attentive multi-scale network for lightweight salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3804–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cong, R.; Hou, J.; Zhang, S.; Qian, Y.; Kwong, S. Nested network with two-stream pyramid for salient object detection in optical remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9156–9166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Bai, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, P. YOLO-Lite: An Efficient Lightweight Network for SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Wang, Z. Cross-Modality Attentive Feature Fusion for Object Detection in Multispectral Remote Sensing Imagery. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Peng, L.; Yang, C.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection based on non-convex optimization with Lp-norm constraint. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Ge, J.; Hu, L.; Guo, K.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, W.; Liang, J. RTV-SIFT: Harnessing Structure Information for Robust Optical and SAR Image Registration. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Bao, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, L.; Yan, Y. A potential visionbased measurements technology: Information flow fusion detection method using RGB-thermal infrared images. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 5004813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, F.; Da, H.; Zhao, W. Cross-modality fusion transformer for multispectral object detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00273. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S. Multispectral deep neural networks for pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), York, UK, 19–22 September 2016; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, J.; Fischer, V.; Herman, M.; Behnke, S. Multispectral pedestrian detection using deep fusion convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 24th European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning (ESANN 2016), Bruges, Belgium, 27–29 April 2016; Volume 587, pp. 509–514. [Google Scholar]
- Konig, D.; Adam, M.; Jarvers, C.; Layher, G.; Neumann, H.; Teutsch, M. Fully convolutional region proposal networks for multispectral person detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Song, D.; Tong, R.; Tang, M. Illumination-aware faster R-CNN for robust multispectral pedestrian detection. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 85, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y. Fusion of multispectral data through illumination-aware deep neural networks for pedestrian detection. Inf. Fusion 2019, 50, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Qiao, H.; Huang, K.; Hussain, A. Cross-modality interactive attention network for multispectral pedestrian detection. Inf. Fusion 2019, 50, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, W. Illumination-guided RGBT object detection with inter- and intra-modality fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2508013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sermanet, P.; Eigen, D.; Zhang, X.; Mathieu, M.; Fergus, R.; LeCun, Y. OverFeat: Integrated Recognition, Localization and Detection using Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6229. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 1804, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.; Liao, H. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F. YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO Series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H. YOLOv6: A single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.02696. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Lei, Z. Weakly Aligned Cross-Modal Learning for Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Chen, L.; Cao, X. Improving Multispectral PedestrianDetection by Addressing Modality Imbalance Problems. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Online, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Fromont, E.; Lefevre, S.; Avignon, B. Guided attentive feature fusion for multispectral pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wei, C.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. GLADNet: Low-light enhancement network with global awareness. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 751–755. [Google Scholar]
- Razakarivony, S.; Jurie, F. Vehicle detection in aerial imagery: A small target detection benchmark. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2016, 34, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FREE Teledyne FLIR Thermal Dataset for Algorithm Training. Available online: https://www.flir.com/oem/adas/adas-dataset-form/ (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Jia, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, M.; Tang, W. Llvip: A visible-infrared paired dataset for low-light vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW 2021), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3489–3497. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.; Wang, S.; Duan, P.; Xiao, C.; Dian, R.; Li, S. LRAF-Net: Long-Range Attention Fusion Network for Visible–Infrared Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 13232–13245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; Yi, C.; Yue, L.; Xin, Z. ICAFusion: Iterative Cross-Attention Guided Feature Fusion for Multispectral Object Detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.07504v1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, Z. TFDet: Target-aware Fusion for RGB-T Pedestrian Detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.06361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Model | Modality | Backbone | mAP50 | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| unimodality networks | ||||
| Faster R-CNN | visible | ResNet50 | 64.5% | 38.9% |
| Faster R-CNN | infrared | ResNet50 | 71.2% | 41.6% |
| YOLOv9 | visible | CSPNet+ELAN | 73.4% | 42.5% |
| YOLOv9 | infrared | CSPNet+ELAN | 75.6% | 44.6% |
| multimodality networks | ||||
| CFT | two-stream | CFB | 85.3% | 56.0% |
| LRAF-Net | two-stream | Darknet53 | 85.9% | 59.1% |
| YOLO-Fusion | two-stream | Darknet53 | 78.6% | 49.1% |
| ICAFusion | two-stream | Darknet53 | 76.6% | 44.9% |
| Baseline | two-stream | Darknet53+CSP | 83.9% | 54.2% |
| Ours | two-stream | Darknet53+CSP | 87.2% | 59.8% |
| Model | Modality | Backbone | mAP50 | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| unimodality networks | ||||
| Faster R-CNN | visible | ResNet50 | 64.9% | 28.9% |
| Faster R-CNN | infrared | ResNet50 | 74.4% | 37.6% |
| YOLOv9 | visible | CSPNet+ELAN | 69.5% | 33.4% |
| YOLOv9 | infrared | CSPNet+ELAN | 73.9% | 38.9% |
| multimodality networks | ||||
| CFT | two-stream | CFB | 78.7% | 40.2% |
| LRAF-Net | two-stream | Darknet53 | 80.5% | 42.8% |
| GAFF | two-stream | ResNet18 | 72.9% | 37.5% |
| ICAFusion | two-stream | Darknet53 | 79.2% | 41.4% |
| Baseline | two-stream | Darknet53+CSP | 80.3% | 42.2% |
| Ours | two-stream | Darknet53+CSP | 82.5% | 43.9% |
| Model | Modality | Backbone | mAP50 | mAP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unimodality networks | |||||
| Faster R-CNN | visible | ResNet50 | 91.4% | 49.2% | |
| Faster R-CNN | infrared | ResNet50 | 96.1% | 61.1% | |
| YOLOv9 | visible | CSPNet+ELAN | 90.8% | 50.0% | |
| YOLOv9 | infrared | CSPNet+ELAN | 94.6% | 61.9% | |
| multimodality networks | |||||
| CFT | two-stream | CFB | 97.5% | 63.6% | |
| LRAF-Net | two-stream | Darknet53 | 97.9% | 66.3% | |
| TFDet | two-stream | ResNet18 | 96.0% | 59.4% | |
| ICAFusion | two-stream | Darknet53 | 97.8% | 64.1% | |
| Baseline | two-stream | Darknet53+CSP | 95.9% | 63.5% | |
| Ours | two-stream | Darknet53+CSP | 97.9% | 69.2% | |
| Model | Modality | Backbone | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| unimodality networks | |||
| Faster R-CNN | visible | ResNet50 | 21.7 |
| YOLOv5 | visible | Darknet53 | 42.8 |
| YOLOv9 | visible | CSPNet+ELAN | 25.6 |
| multimodality networks | |||
| TFDet | two-stream | ResNet18 | 7.7 |
| CFT | two-stream | CFB | 21.0 |
| ICAFusion | two-stream | Darknet53 | 38.5 |
| Ours | two-stream | Darknet53+CSP | 21.2 |
| Method | Backbone | mAP50 | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visible | Darknet53+CSP | 68.9% | 33.8% |
| Infrared | Darknet53+CSP | 74.2% | 38.5% |
| Early Fusion | Darknet53+CSP | 75.2% | 38.3% |
| Cross Fusion (ours) | Darknet53+CSP | 82.5% | 43.9% |
| Series Fusion | Darknet53+CSP | 79.5% | 41.6% |
| Late Fusion | Darknet53+CSP | 78.3% | 39.3% |
| Method | Backbone | mAP50 | mAP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BA | CAMF | |||||
| Light | Contrast | DA | CA | |||
| Darknet53+CSP | 76.5% | 38.8% | ||||
| √ | Darknet53+CSP | 78.6% | 39.6% | |||
| √ | Darknet53+CSP | 77.3% | 39.1% | |||
| √ | √ | Darknet53+CSP | 79.8% | 40.2% | ||
| √ | Darknet53+CSP | 80.1% | 39.8% | |||
| √ | Darknet53+CSP | 79.5% | 39.4% | |||
| √ | √ | Darknet53+CSP | 81.2% | 41.4% | ||
| √ | √ | √ | √ | Darknet53+CSP | 82.5% | 43.9% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, R.; Guo, X.; Sun, X.; Zhou, P.; Sun, B.; Su, S. Background-Aware Cross-Attention Multiscale Fusion for Multispectral Object Detection. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214034
Guo R, Guo X, Sun X, Zhou P, Sun B, Su S. Background-Aware Cross-Attention Multiscale Fusion for Multispectral Object Detection. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(21):4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214034
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Runze, Xiaojun Guo, Xiaoyong Sun, Peida Zhou, Bei Sun, and Shaojing Su. 2024. "Background-Aware Cross-Attention Multiscale Fusion for Multispectral Object Detection" Remote Sensing 16, no. 21: 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214034
APA StyleGuo, R., Guo, X., Sun, X., Zhou, P., Sun, B., & Su, S. (2024). Background-Aware Cross-Attention Multiscale Fusion for Multispectral Object Detection. Remote Sensing, 16(21), 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214034






