Testing the Limits of Atmospheric Correction over Turbid Norwegian Fjords
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
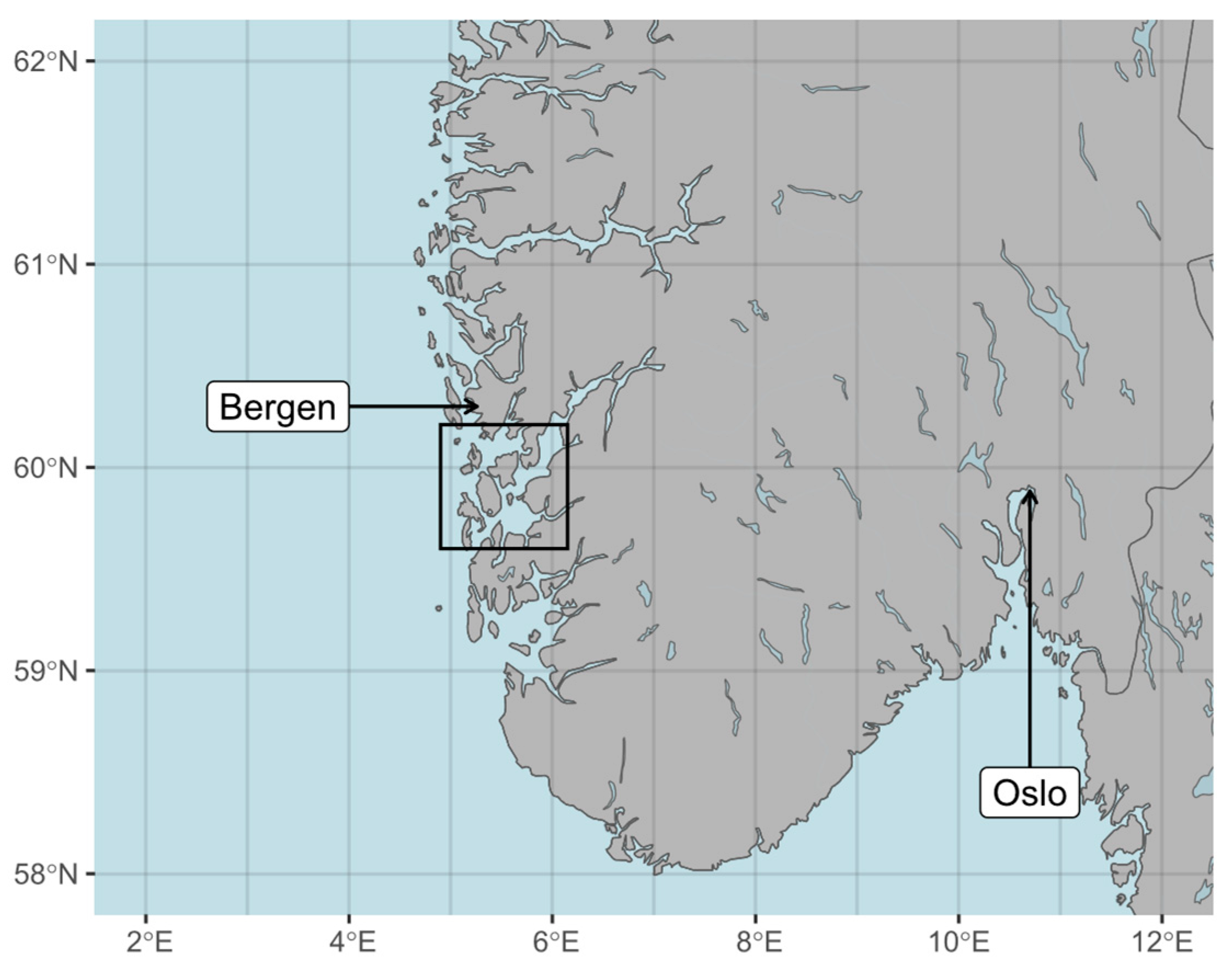
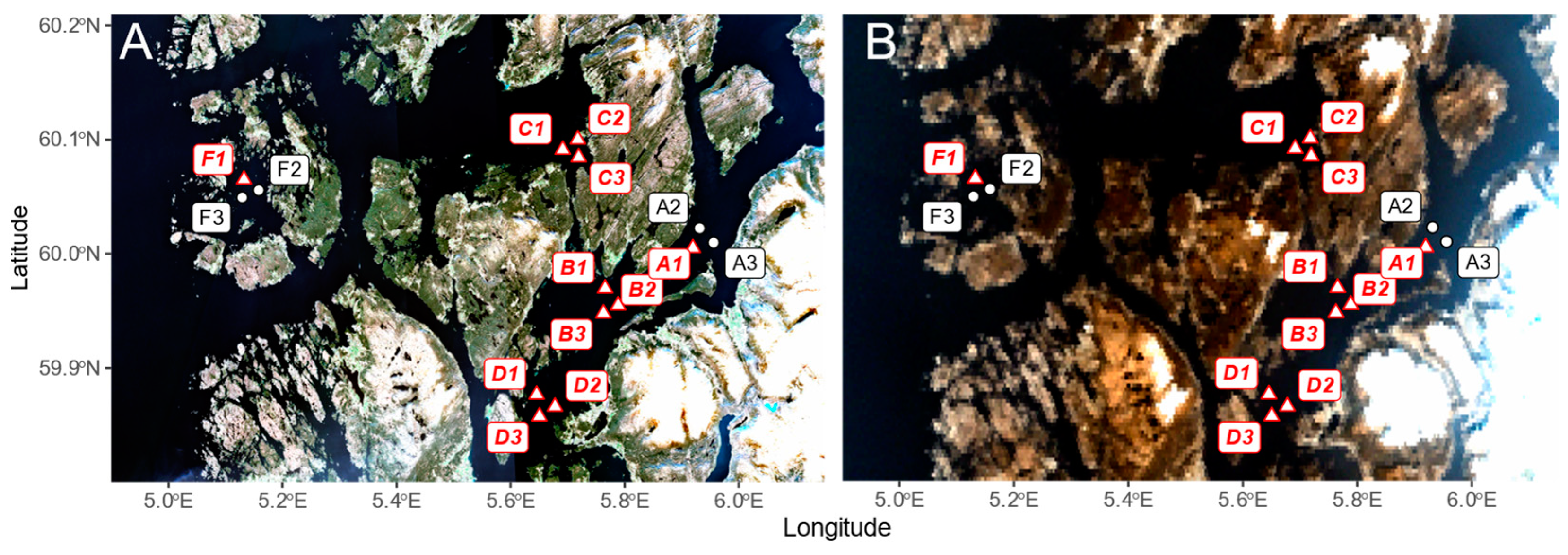
2.1. Study Area
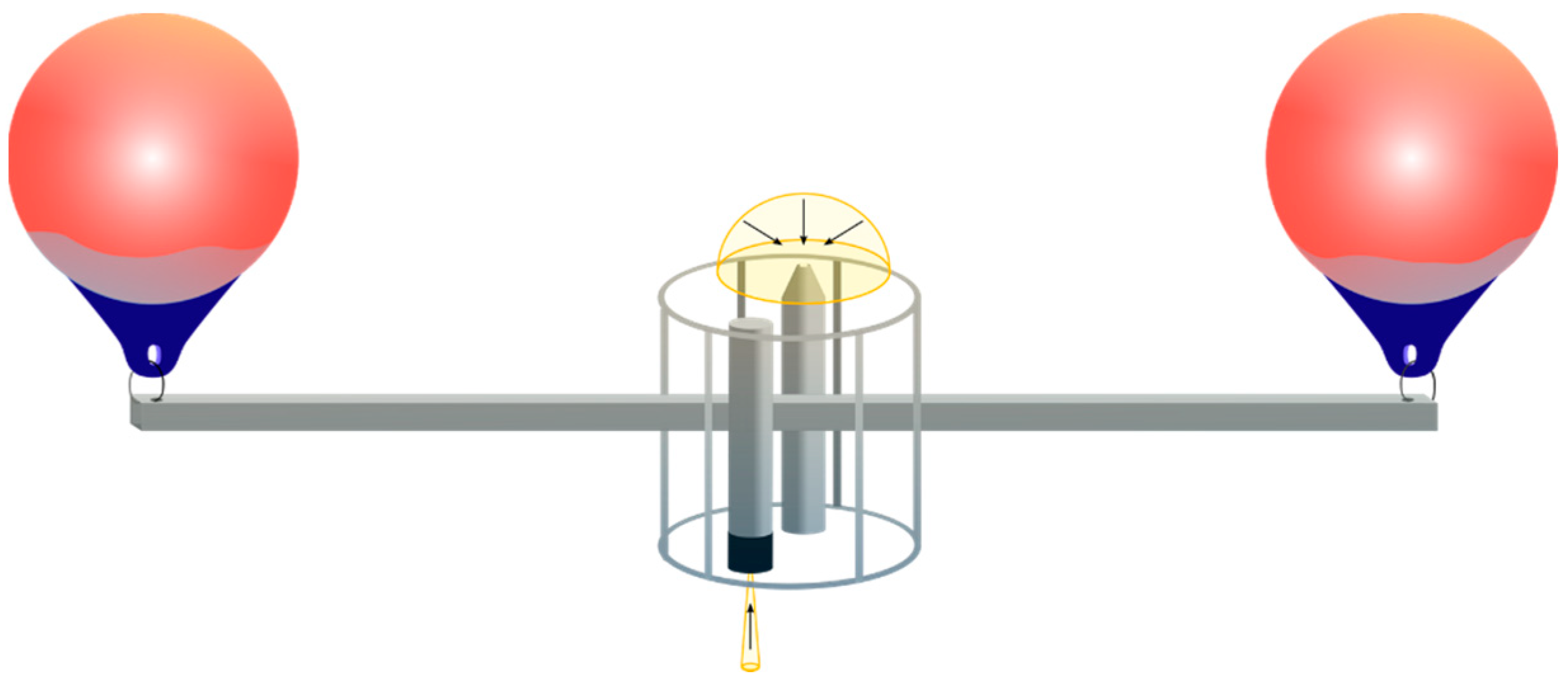
2.2. In Situ Data Collection
2.3. Satellite Data
2.4. Flags
2.5. Atmospheric Correction
2.6. Chlorophyll-a Retrieval Algorithms
2.7. Analysis
3. Results
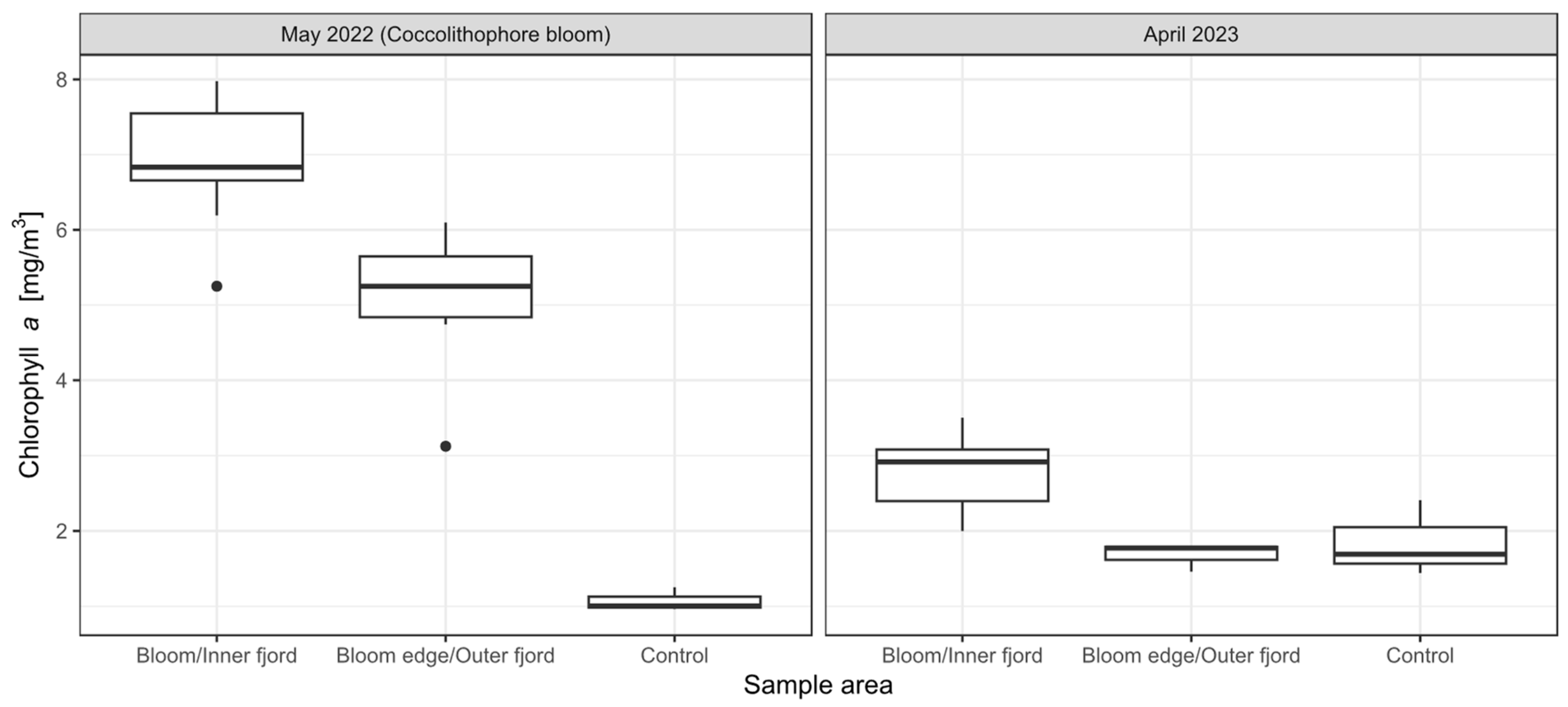
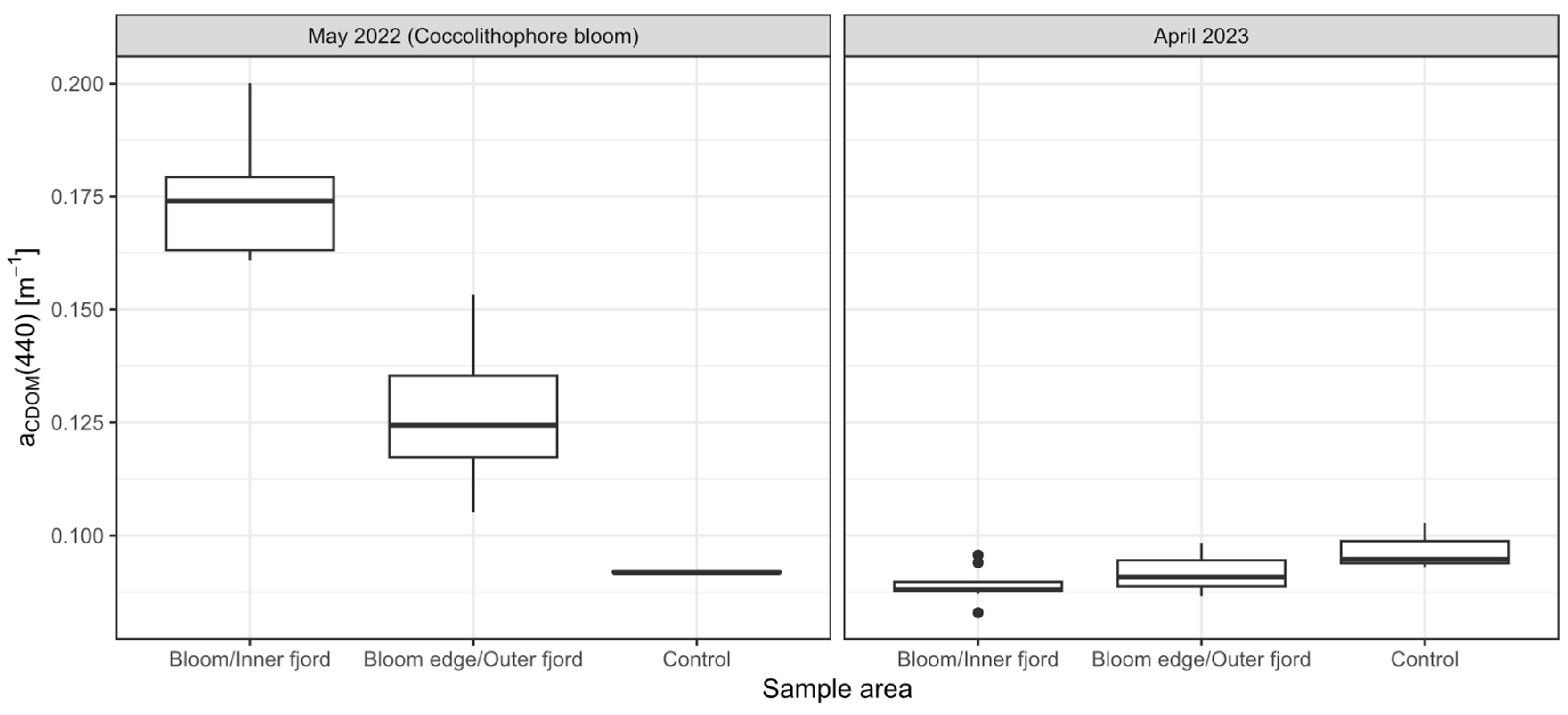
3.1. In Situ Chlorophyll-a, aCDOM(440) and Cell Counts
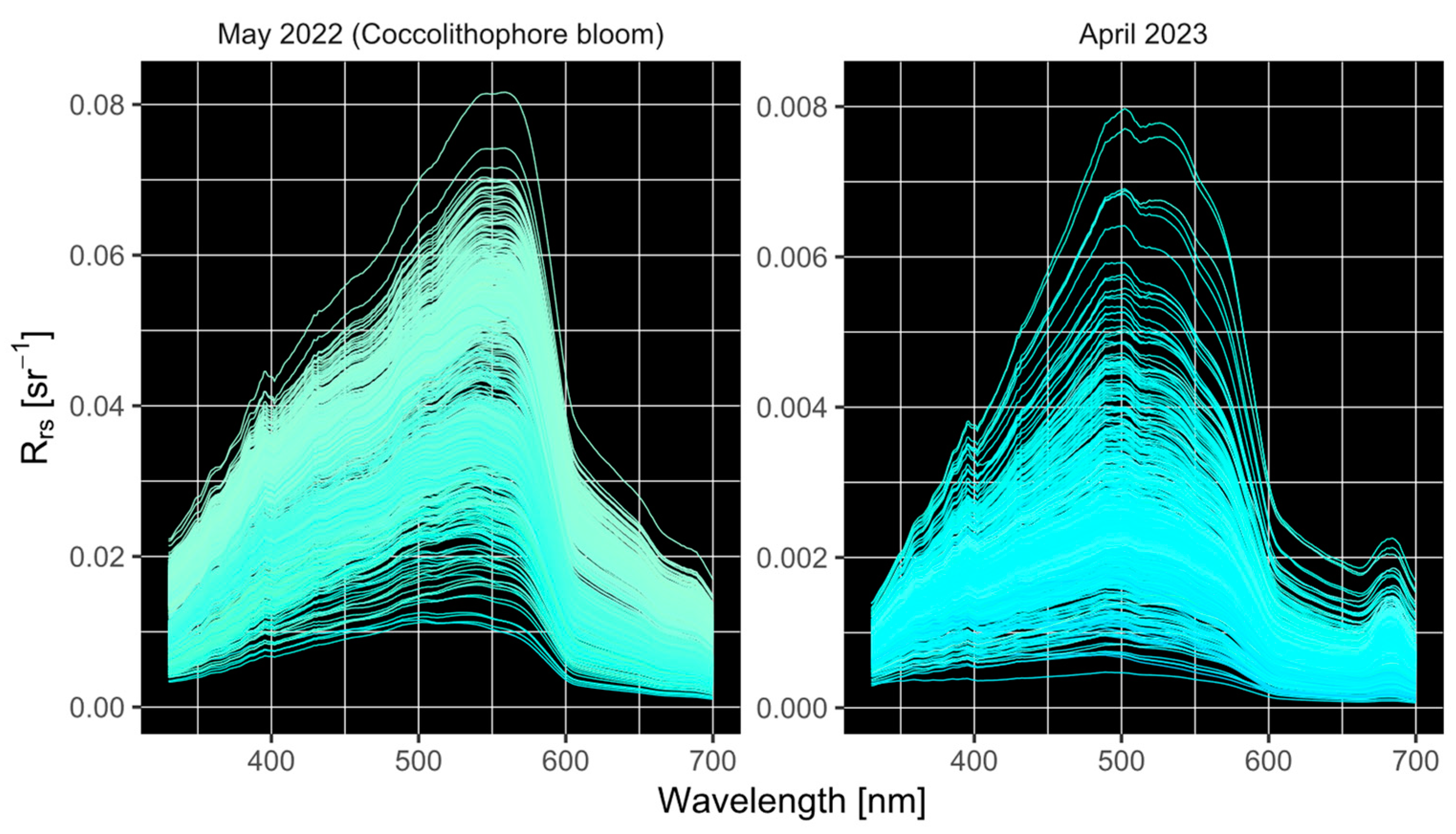
3.2. In Situ Reflectances
3.3. Remote Sensing
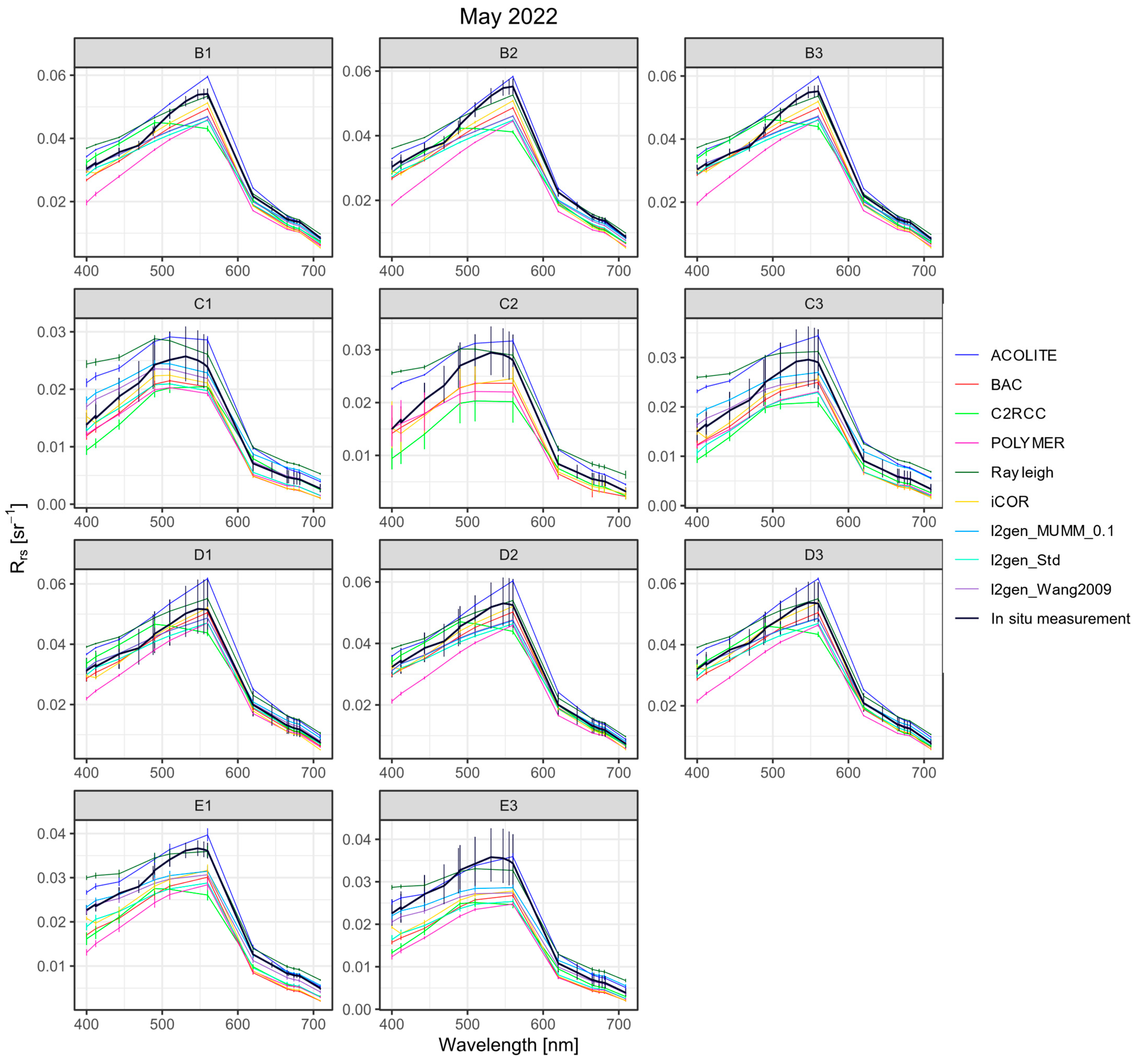
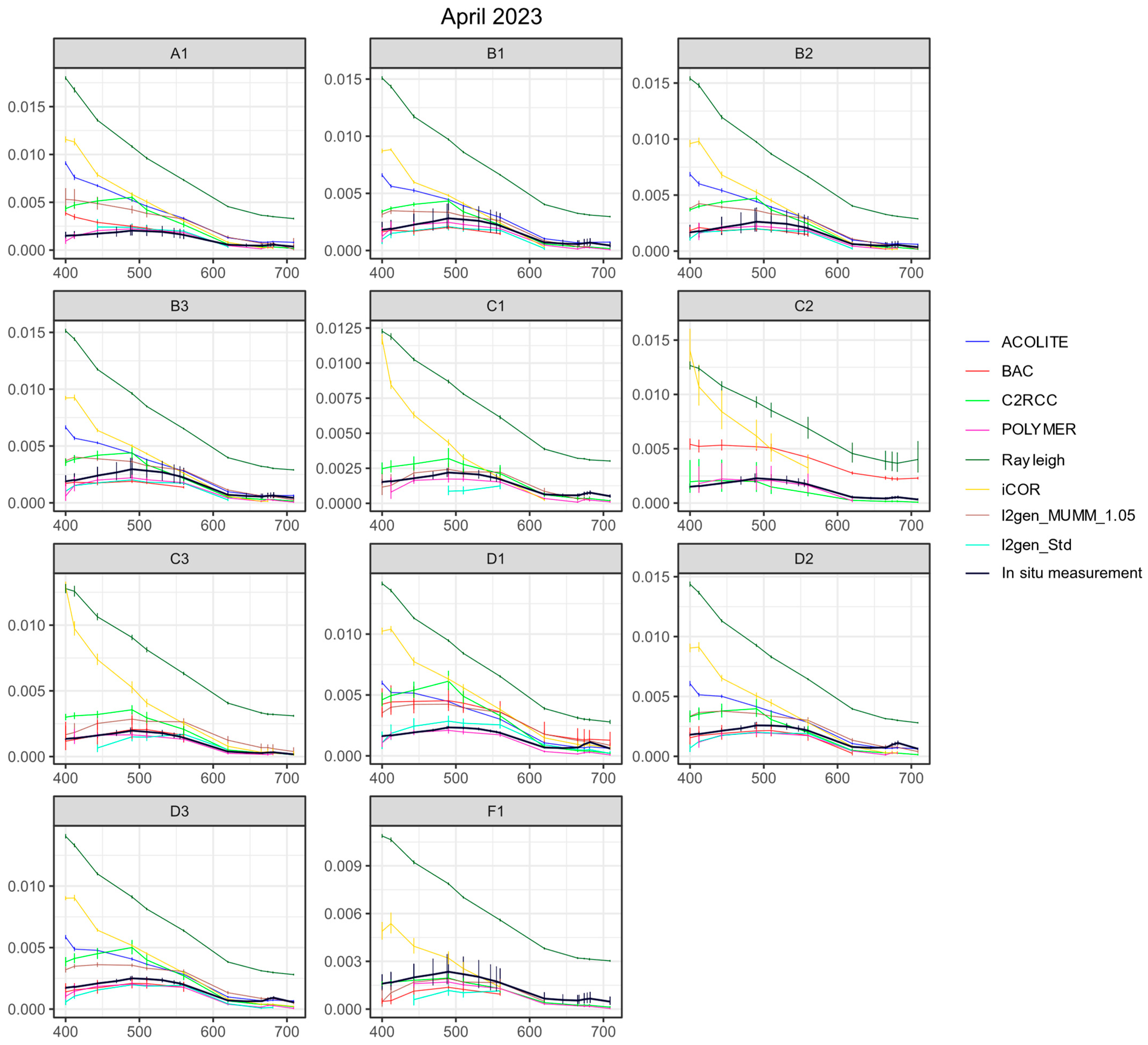
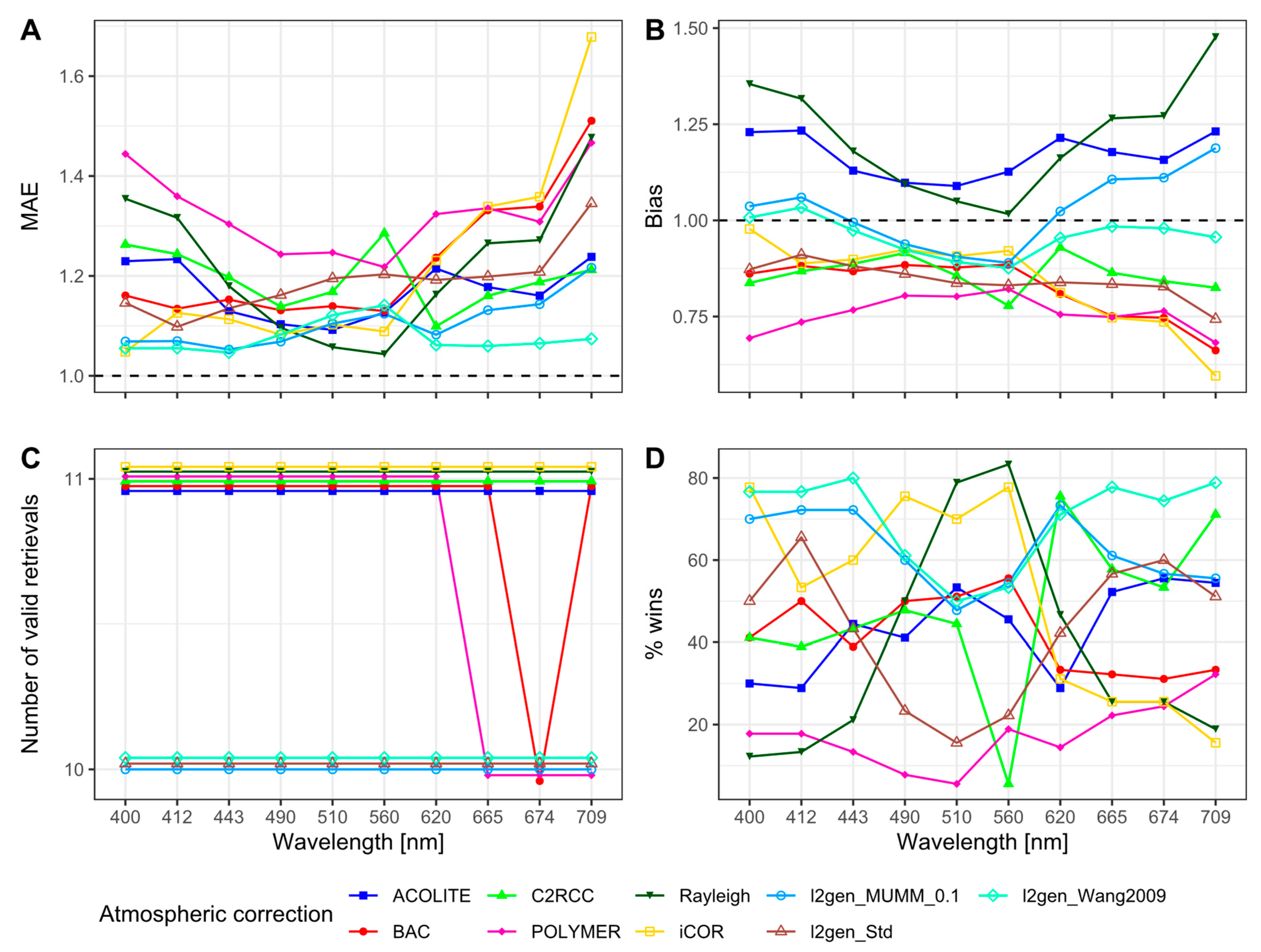
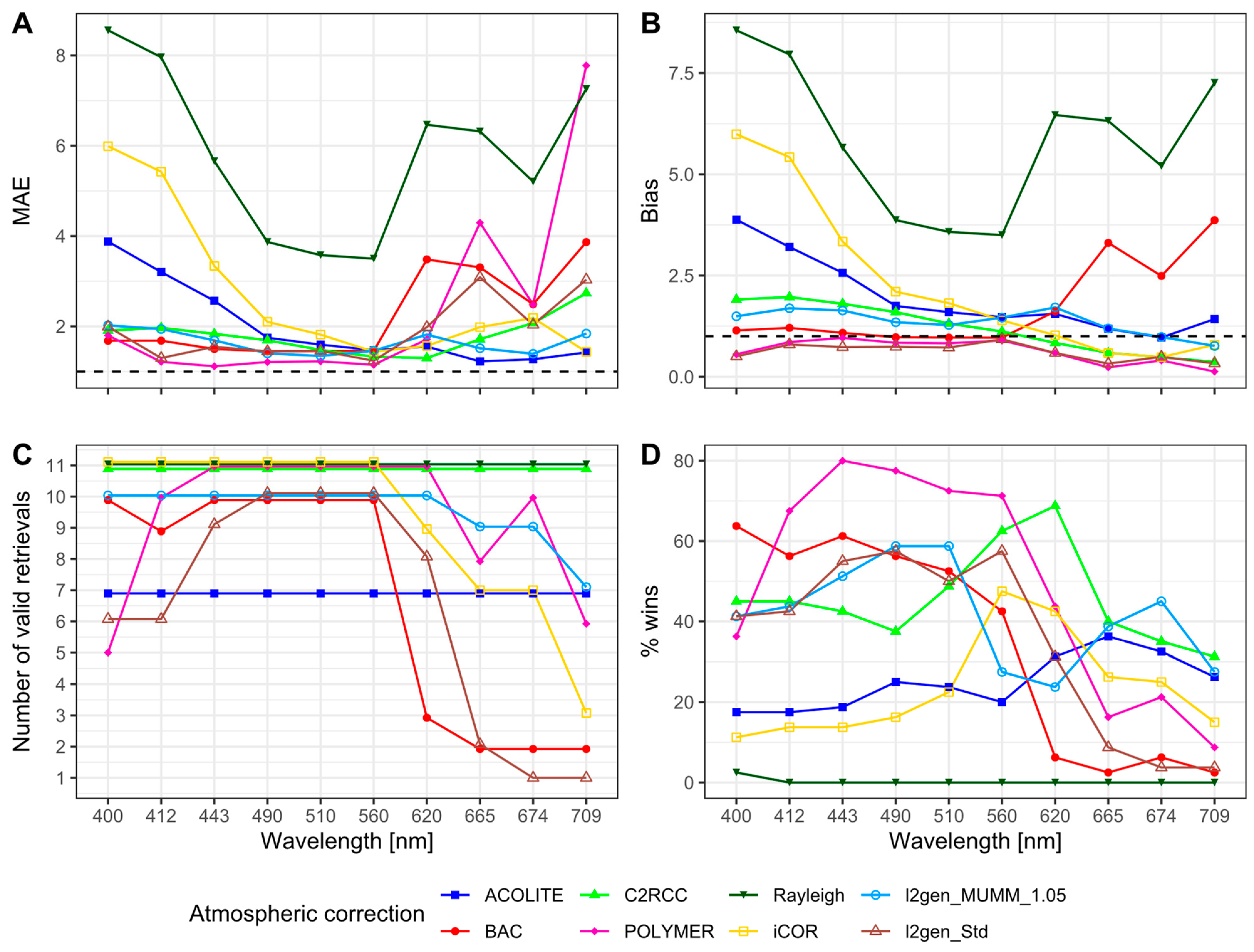
3.3.1. Remote Sensing Reflectances
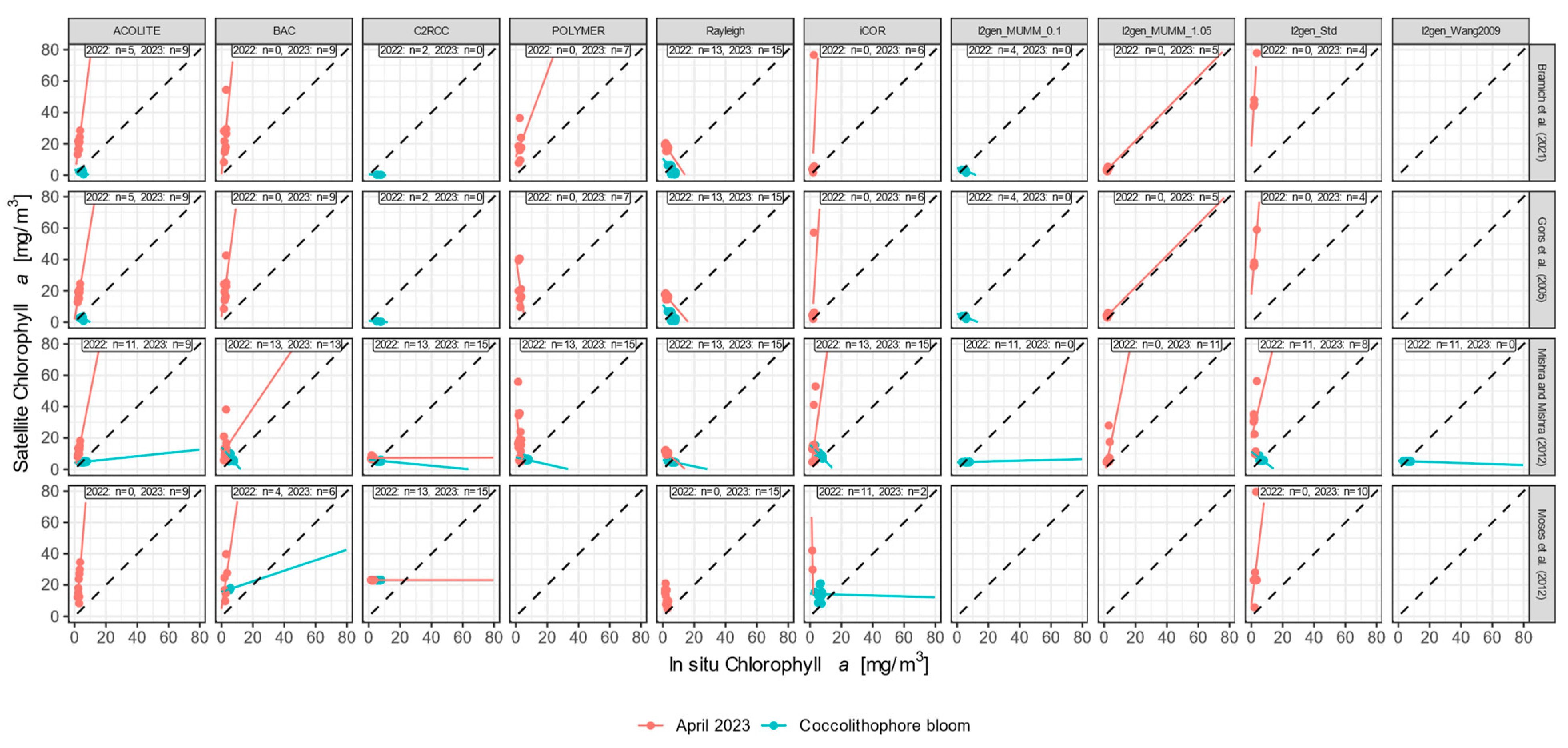
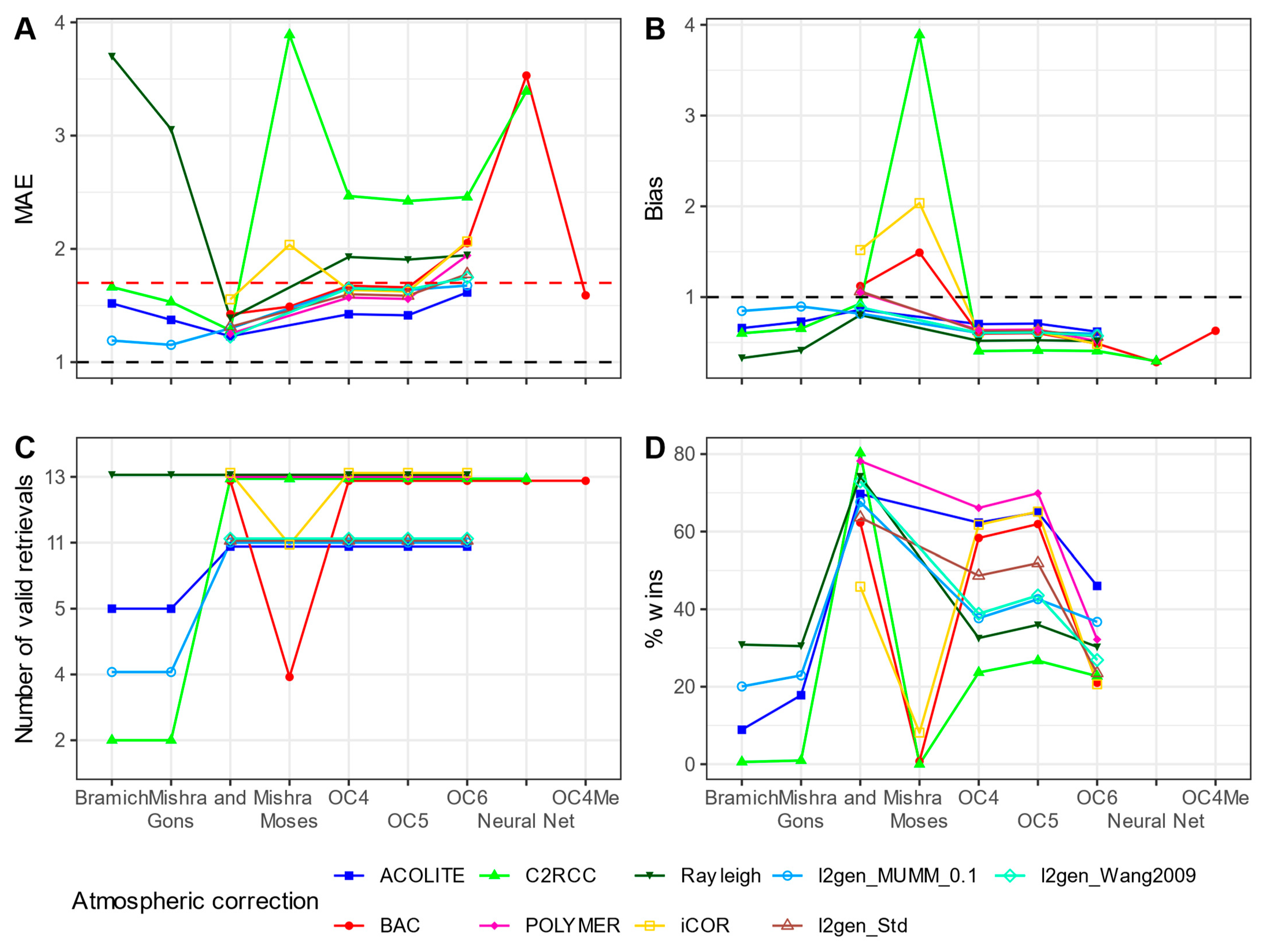
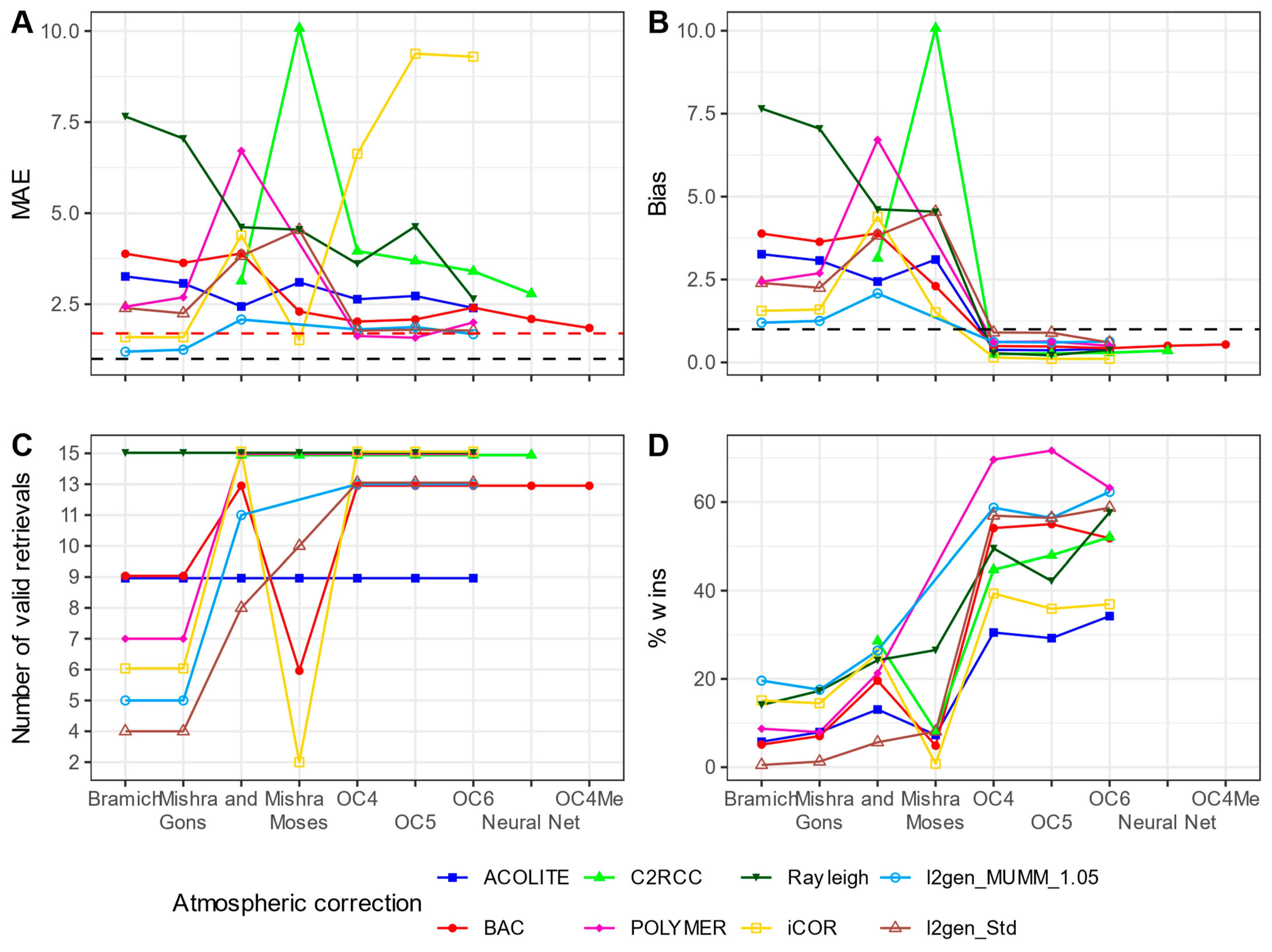
3.3.2. Chlorophyll-a
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hovis, W.A.; Clark, D.K.; Anderson, F.; Austin, R.W.; Wilson, W.H.; Baker, E.T.; Ball, D.; Gordon, H.R.; Mueller, J.L.; El-Sayed, S.Z.; et al. Nimbus-7 Coastal Zone Color Scanner: System Description and Initial Imagery. Science 1980, 210, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhl-Mortensen, P.; Buhl-Mortensen, L. Diverse and Vulnerable Deep-Water Biotopes in the Hardangerfjord. Mar. Biol. Res. 2014, 10, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzetti, S.; Stenersen, J.H.V. A Critical View of the Environmental Condition of the Sognefjord. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 2167–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlson, B.; Andersen, P.; Arneborg, L.; Cembella, A.; Eikrem, W.; John, U.; West, J.J.; Klemm, K.; Kobos, J.; Lehtinen, S.; et al. Harmful Algal Blooms and Their Effects in Coastal Seas of Northern Europe. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.M.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Mountrakis, G.; Quackenbush, L.J. A Meta-Analysis on Harmful Algal Bloom (Hab) Detection and Monitoring: A Remote Sensing Perspective. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOCCG. Observation of Harmful Algal Blooms with Ocean Colour Radiometry; Bernard, S., Lain, L.R., Kudela, R., Pitcher, G., Eds.; Reports of the International Ocean Colour Coordinating Group; IOCCG: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2021; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- IOCCG. Atmospheric Correction for Remotely-Sensed Ocean-Colour Products; Wang, M., Ed.; Reports of the International Ocean Colour Coordinating Group; IOCCG: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2010; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, H.R. Evolution of Ocean Color Atmospheric Correction: 1970–2005. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, P.J.; McKinna, L.I.W.; Boss, E.; Ackleson, S.G.; Craig, S.E.; Gregg, W.W.; Lee, Z.; Maritorena, S.; Roesler, C.S.; Rousseaux, C.S.; et al. An Overview of Approaches and Challenges for Retrieving Marine Inherent Optical Properties from Ocean Color Remote Sensing. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 160, 186–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D.; Stramski, D.; Paul Bissett, W.; Boss, E. Optical Modeling of Ocean Waters: Is the Case 1–Case 2 Classification Still Useful? Oceanography 2004, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Retrieval of Water-Leaving Radiance and Aerosol Optical Thickness over the Oceans with SeaWiFS: A Preliminary Algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, D. OLCI Level 2 Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: Atmospheric Corrections over Case 1 Waters (CWAC). Ref S3-L2-SD-03-C07-LOV-ATBD Version 22. 2010. Available online: https://sentiwiki.copernicus.eu/__attachments/1672112/S3-L2-SD-03-C07-LOV-ATBD%20-%20OLCI%20L2%20ATBD%20Atmospheric%20Corrections%20case%201%20waters%202010%20-%2002.pdf?inst-v=d105f701-8f35-4a57-9bd3-983ac5f50bca (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Mazeran, C.; Hieronymi, M.; Steinmetz, F. Ocean Colour Bright Pixel Correction–Algorithm Theoretical Basis. EUM/18/BPC/ATBD. 2021. Available online: https://www-cdn.eumetsat.int/files/2021-10/S3-OLCI_OC-BPC_ATBD.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric Correction of Metre-Scale Optical Satellite Data for Inland and Coastal Water Applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmann, C.; Doerffer, R.; Peters, M.; Stelzer, K.; Embacher, S.; Ruescas, A. Evolution of the C2RCC Neural Network for Sentinel 2 and 3 for the Retrieval of Ocean Colour Products in Normal and Extreme Optically Complex Waters; European Space Agency: Paris, France, 2016; Volume SP-740. [Google Scholar]
- De Keukelaere, L.; Sterckx, S.; Adriaensen, S.; Knaeps, E.; Reusen, I.; Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Hunter, P.; Neil, C.; Van der Zande, D.; et al. Atmospheric Correction of Landsat-8/OLI and Sentinel-2/MSI Data Using iCOR Algorithm: Validation for Coastal and Inland Waters. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W.; Franz, B.A.; Werdell, P.J. Estimation of Near-Infrared Water-Leaving Reflectance for Satellite Ocean Color Data Processing. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 7521–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Shi, W. Evaluation of MODIS SWIR and NIR-SWIR Atmospheric Correction Algorithms Using SeaBASS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, K.G.; Ovidio, F.; Rijkeboer, M. Atmospheric Correction of SeaWiFS Imagery for Turbid Coastal and Inland Waters. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, F.; Ramon, D. Sentinel-2 MSI and Sentinel-3 OLCI Consistent Ocean Colour Products Using POLYMER. In Remote Sensing of the Open and Coastal Ocean and Inland Waters; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, F.; Deschamps, P.-Y.; Ramon, D. Atmospheric Correction in Presence of Sun Glint: Application to MERIS. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 9783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-J.; Ruddick, K. Model of Remote-Sensing Reflectance Including Bidirectional Effects for Case 1 and Case 2 Waters. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 1236–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric Correction of Sentinel-3/OLCI Data for Mapping of Suspended Particulate Matter and Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Belgian Turbid Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourg, L. MERIS Level 2 Detailed Processing Model. In Document no. PO-TN-MEL-GS-0006; ACRI-ST, 2011; Available online: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/documents/20142/37627/MERIS-Level-2-Detailed-Processing-Model.pdf/075b5eb1-7b3b-52f5-28a4-9fbb5d8e0fb7?t=1703157756360 (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Brewin, R.J.W.; Sathyendranath, S.; Müller, D.; Brockmann, C.; Deschamps, P.-Y.; Devred, E.; Doerffer, R.; Fomferra, N.; Franz, B.; Grant, M.; et al. The Ocean Colour Climate Change Initiative: III. A Round-Robin Comparison on in-Water Bio-Optical Algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balch, W.M.; Gordon, H.R.; Bowler, B.C.; Drapeau, D.T.; Booth, E.S. Calcium Carbonate Measurements in the Surface Global Ocean Based on Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Data. J. Geophys. Res. C Oceans 2005, 110, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansper, A.; Alikas, K. Retrieval of Chlorophyll a from Sentinel-2 MSI Data for the European Union Water Framework Directive Reporting Purposes. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Mangin, A.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; Smith, B.; Alikas, K.; Arai, K.; Barbosa, C.; Bélanger, S.; Binding, C.; Bresciani, M.; et al. ACIX-Aqua: A Global Assessment of Atmospheric Correction Methods for Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 over Lakes, Rivers, and Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ma, R.; Xue, K.; Loiselle, S.A. The Assessment of Landsat-8 OLI Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for Inland Waters. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windle, A.E.; Evers-King, H.; Loveday, B.R.; Ondrusek, M.; Silsbe, G.M. Evaluating Atmospheric Correction Algorithms Applied to OLCI Sentinel-3 Data of Chesapeake Bay Waters. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, F.P.; Pedocchi, F. Evaluation of ACOLITE Atmospheric Correction Methods for Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 in the Río de La Plata Turbid Coastal Waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 215–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendif, E.M.; Nevado, B.; Wong, E.L.Y.; Hagino, K.; Probert, I.; Young, J.R.; Rickaby, R.E.M.; Filatov, D.A. Repeated Species Radiations in the Recent Evolution of the Key Marine Phytoplankton Lineage Gephyrocapsa. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, T.; Merico, A. Emiliania Huxleyi: Bloom Observations and the Conditions That Induce Them. In Coccolithophores: From Molecular Processes to Global Impact; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Berge, G. Discoloration of the Sea Due to Coccolithus Huxleyi “Bloom”. Sarsia 1962, 6, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramich, J.; Bolch, C.J.S.; Fischer, A. Improved Red-Edge Chlorophyll-a Detection for Sentinel 2. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gons, H.J.; Rijkeboer, M.; Ruddick, K.G. Effect of a Waveband Shift on Chlorophyll Retrieval from MERIS Imagery of Inland and Coastal Waters. J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.R. Normalized Difference Chlorophyll Index: A Novel Model for Remote Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Productive Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Saprygin, V.; Gerasyuk, V.; Povazhnyy, V.; Berdnikov, S.; Gitelson, A.A. OLCI-Based NIR-Red Models for Estimating Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Productive Coastal Waters—A Preliminary Evaluation. Environ. Res. Commun. 2019, 1, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Werdell, P.J. Chlorophyll Algorithms for Ocean Color Sensors–OC4, OC5 & OC6. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamre, B.; Stamnes, S.; Stamnes, K.; Stamnes, J. AccuRT: A Versatile Tool for Radiative Transfer Simulations in the Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean System. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1810, 120002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burggraaff, O. Biases from Incorrect Reflectance Convolution. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 13801–13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassan, S.; Ferrari, G.M. A Sensitivity Analysis of the ‘Transmittance–Reflectance’Method for Measuring Light Absorption by Aquatic Particles. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heukelem, L.; Thomas, C.S. Computer-Assisted High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Method Development with Applications to the Isolation and Analysis of Phytoplankton Pigments. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 910, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm-Hansen, O.; Riemann, B. Chlorophyll a Determination: Improvements in Methodology. Oikos 1978, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seegers, B.N.; Stumpf, R.P.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Loftin, K.A.; Werdell, P.J. Performance Metrics for the Assessment of Satellite Data Products: An Ocean Color Case Study. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 7404–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUMETSAT. Recommendations for Sentinel-3 OLCI Ocean Colour Product Validations in Comparison with in Situ Measurements – Matchup Protocols. 2022. Available online: https://user.eumetsat.int/s3/eup-strapi-media/Recommendations_for_Sentinel_3_OLCI_Ocean_Colour_product_validations_in_comparison_with_in_situ_measurements_Matchup_Protocols_V8_B_e6c62ce677.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Ahmad, Z.; Franz, B.A.; McClain, C.R.; Kwiatkowska, E.J.; Werdell, J.; Shettle, E.P.; Holben, B.N. New Aerosol Models for the Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Thickness and Normalized Water-Leaving Radiances from the SeaWiFS and MODIS Sensors over Coastal Regions and Open Oceans. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 5545–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. The NIR-SWIR Combined Atmospheric Correction Approach for MODIS Ocean Color Data Processing. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15722–15733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerffer, R. OLCI L2 ATBD Ocean Colour Turbid Water. Ref S3-L2-SD-03-C11-GKSS-ATBD Version 20. 2010. Available online: https://step.esa.int/docs/extra/OLCI_L2_ATBD_Ocean_Colour_Turbid_Water.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Sterckx, S.; Knaeps, S.; Kratzer, S.; Ruddick, K. SIMilarity Environment Correction (SIMEC) Applied to MERIS Data over Inland and Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, A.; Anderson, G.P.; Acharya, P.K.; Bernstein, L.S.; Muratov, L.; Lee, J.; Fox, M.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Chetwynd, J.H., Jr.; Hoke, M.L. MODTRAN5: 2006 Update. In Algorithms and Technologies for Multispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery XII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006; Volume 6233, pp. 508–515. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, A.; Antoine, D.; Gentili, B. Bidirectional Reflectance of Oceanic Waters: Accounting for Raman Emission and Varying Particle Scattering Phase Function. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 6289–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUMETSAT. Sentinel-3 OLCI L2 Report for Baseline Collection OL_L2M_003. 2021. Available online: https://user.eumetsat.int/s3/eup-strapi-media/Sentinel_3_OLCI_L2_report_for_baseline_collection_OL_L2_M_003_2_B_c8bbc6d986.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Franz, B.A.; Bailey, S.W.; Werdell, P.J.; McClain, C.R. Sensor-Independent Approach to the Vicarious Calibration of Satellite Ocean Color Radiometry. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 5068–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gons, H.J.; Rijkeboer, M.; Ruddick, K.G. A Chlorophyll-Retrieval Algorithm for Satellite Imagery (Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer) of Inland and Coastal Waters. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gons, H.J.; Auer, M.T.; Effler, S.W. MERIS Satellite Chlorophyll Mapping of Oligotrophic and Eutrophic Waters in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4098–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricaud, A.; Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Absorption by Dissolved Organic Matter of the Sea (Yellow Substance) in the UV and Visible Domains. Limnol Ocean. 1981, 26, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Saprygin, V.; Povazhnyi, V. Operational MERIS-Based NIR-Red Algorithms for Estimating Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in Coastal Waters–The Azov Sea Case Study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinkwater, M.; Rebhan, H. Sentinel-3: Mission Requirements Document. Ref EOP-SMO1151MD-Md 2007. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/documents/20142/1564943/Sentinel-3-Mission-Requirements-Document-MRD.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Moore, T.S.; Dowell, M.D.; Franz, B.A. Detection of Coccolithophore Blooms in Ocean Color Satellite Imagery: A Generalized Approach for Use with Multiple Sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.W.; Yoder, J.A. Coccolithophorid Blooms in the Global Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1994, 99, 7467–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.A.E.; Garcia, V.M.T.; Dogliotti, A.I.; Ferreira, A.; Romero, S.I.; Mannino, A.; Souza, M.S.; Mata, M.M. Environmental Conditions and Bio-optical Signature of a Coccolithophorid Bloom in the Patagonian Shelf. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, H.; Ohde, T.; Gerth, M.; Lavik, G.; Leipe, T. Identification of Coccolithophore Blooms in the SE Atlantic Ocean off Namibia by Satellites and In-Situ Methods. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renosh, P.R.; Doxaran, D.; Keukelaere, L.D.; Gossn, J.I. Evaluation of Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for Sentinel-2-MSI and Sentinel-3-OLCI in Highly Turbid Estuarine Waters. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.A.; Simis, S.G.H.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Poser, K.; Bresciani, M.; Alikas, K.; Spyrakos, E.; Giardino, C.; Ansper, A. Assessment of Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for the Sentinel-2A MultiSpectral Imager over Coastal and Inland Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Algorithm | References | Method | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACOLITE | [14,23] | Dark spectrum fitting with sun-glint correction | Needs dark pixels; assumes atmospheric homogeneity if used on subset/tiles |
| BAC | [12,13] | Bright pixel correction | Assumes zero water-leaving reflectance in NIR, flags very bright water pixels, limitations of training dataset for neural net products |
| C2RCC | [15] | Neural network | Limitations of training dataset |
| iCOR | [16] | Dark spectrum fitting with adjacency correction | Needs dark land pixels; assumes atmospheric homogeneity |
| L2gen_Std | [17,47] | Relative humidity-based model selection and iterative NIR | Fails in environments outside scope of empirical optical models |
| L2gen_MUMM | [19] | Aerosol model choice based on user-determined calibration parameters | Requires input of calibration parameters; assumes spatial heterogeneity of 765:865 nm ratio for aerosol and water-leaving reflectance over scene or subscene |
| L2gen_Wang2009 | [18,48] | NIR-SWIR switching | OLCI has no SWIR band; low signal-to-noise ratio of 1020 nm band |
| POLYMER | [20,21] | Spectral matching with sun-glint correction | Neglects CDOM absorption variability, based on the Park and Ruddick (2005) water reflectance model [22] |
| Rayleigh correction | [24] | Molecular scattering estimated from air pressure and sensor geometry | No aerosol correction |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tessin, E.; Hamre, B.; Kristoffersen, A.S. Testing the Limits of Atmospheric Correction over Turbid Norwegian Fjords. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4082. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214082
Tessin E, Hamre B, Kristoffersen AS. Testing the Limits of Atmospheric Correction over Turbid Norwegian Fjords. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(21):4082. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214082
Chicago/Turabian StyleTessin, Elinor, Børge Hamre, and Arne Skodvin Kristoffersen. 2024. "Testing the Limits of Atmospheric Correction over Turbid Norwegian Fjords" Remote Sensing 16, no. 21: 4082. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214082
APA StyleTessin, E., Hamre, B., & Kristoffersen, A. S. (2024). Testing the Limits of Atmospheric Correction over Turbid Norwegian Fjords. Remote Sensing, 16(21), 4082. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214082






