The Geological Investigation of the Lunar Reiner Gamma Magnetic Anomaly Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Geochemical Composition Data
2.2. Topographic and Geomorphological Analysis Method
2.3. Mapping the 1:10,000 Geological Map
- (1)
- Scale determination: the decision to use a 1:10,000 scale for the Reiner Gamma region was carefully considered to balance the need for detailed geological information with the practical limitations of data resolution and map readability. And the primary consideration was the resolution of the image data utilized. This decision was carefully weighed to harmonize the demand for detailed geological information with the practical constraints of data resolution and map readability. The resolution of the image data is crucial due to its impact on the identification and depiction of key geological structures, such as the ejecta blankets’ boundaries of impact craters, magnetic anomaly boundaries, impact crater chains, and lunar rilles. High-resolution data provide intuitive and granular insights into surface features, forming an essential foundation for geological research and analysis. Therefore, the selected scale of 1:10,000 ensures that the map captures the necessary details without compromising readability, thereby maximizing the scientific value and accuracy of the geological information conveyed.
- (2)
- Determination of map content representation: this included not only all the geological structures in the 1:2.5 Million Lunar Geological Map but also the magnetic anomaly bands in this region.
- (3)
- Development of standards and specifications for legends and symbols: the majority of the legends and symbols were inherited from the 1:2.5 Million Lunar Geological Map with the modifications made to represent lunar ridges and rilles as areal structures. Additionally, graphical legends for magnetic anomaly bands have been included.
- (4)
- Establishment of base map databases: through the ArcGIS 10.8, we have created a gdb (geodatabase) file and subsequently established multiple feature classes based on the attribute tables and classifications of geological units from the 1:2.5 Million Lunar Geological Map. Each feature class corresponds to a specific geological unit, thereby organizing the data into distinct groups of feature types.
- (5)
- Geological mapping: the identification and expression of lunar structures, igneous rocks, impact ejecta, and the age of various factors.
- (6)
- Map compilation: establish a mapping template based on the ArcGIS, graphically edit the map units, and label with annotations.
- (7)
- Quality control: topology checking and manual checking.
- (8)
- Map finalization and output.
2.4. Stratigraphic Analysis of the Reiner Gamma Region
3. Results
3.1. Geochemical Compositions in the Reiner Gamma Region
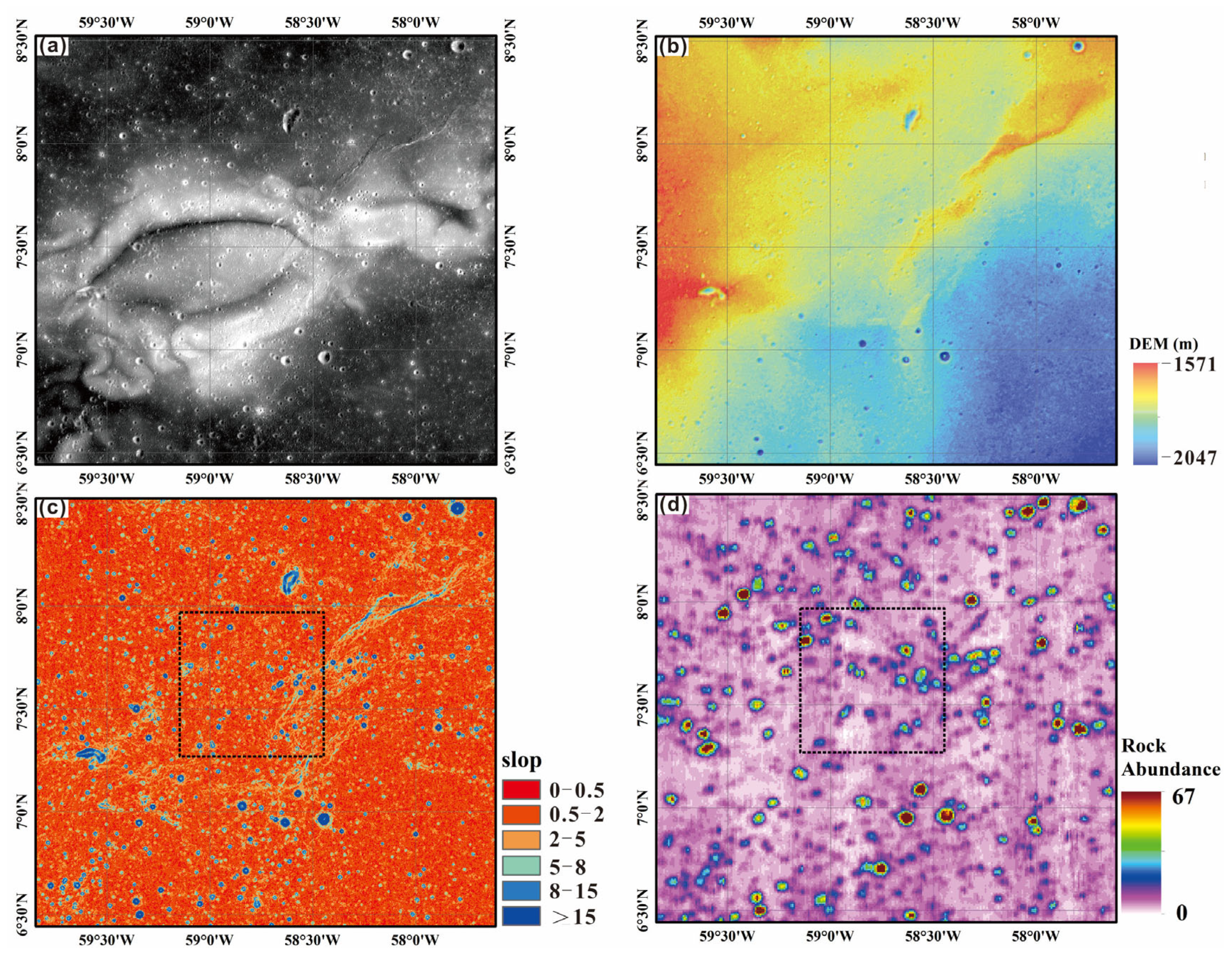
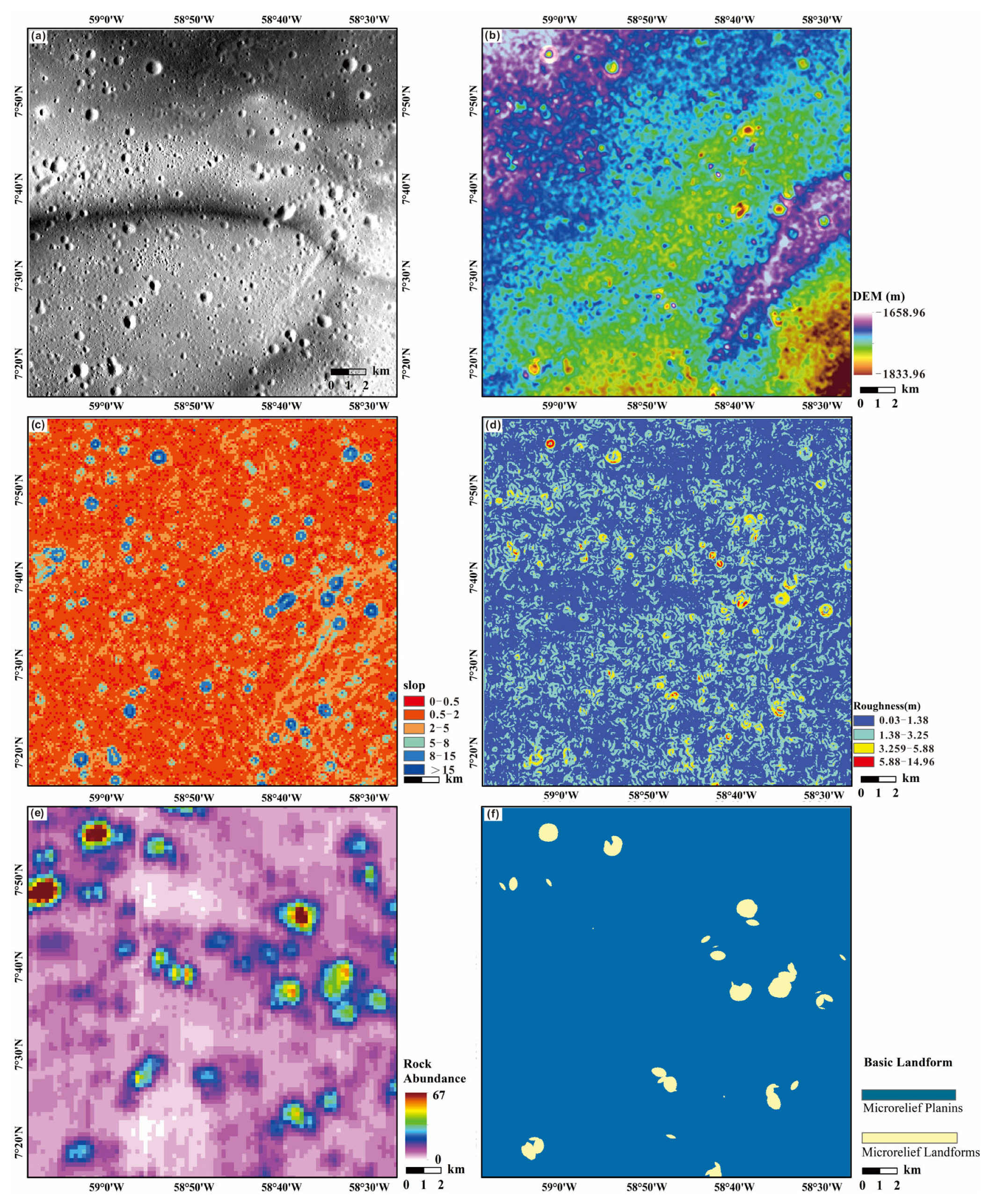
3.2. Topographic and Geomorphological Parameters of the Target in Reiner Gamma Region
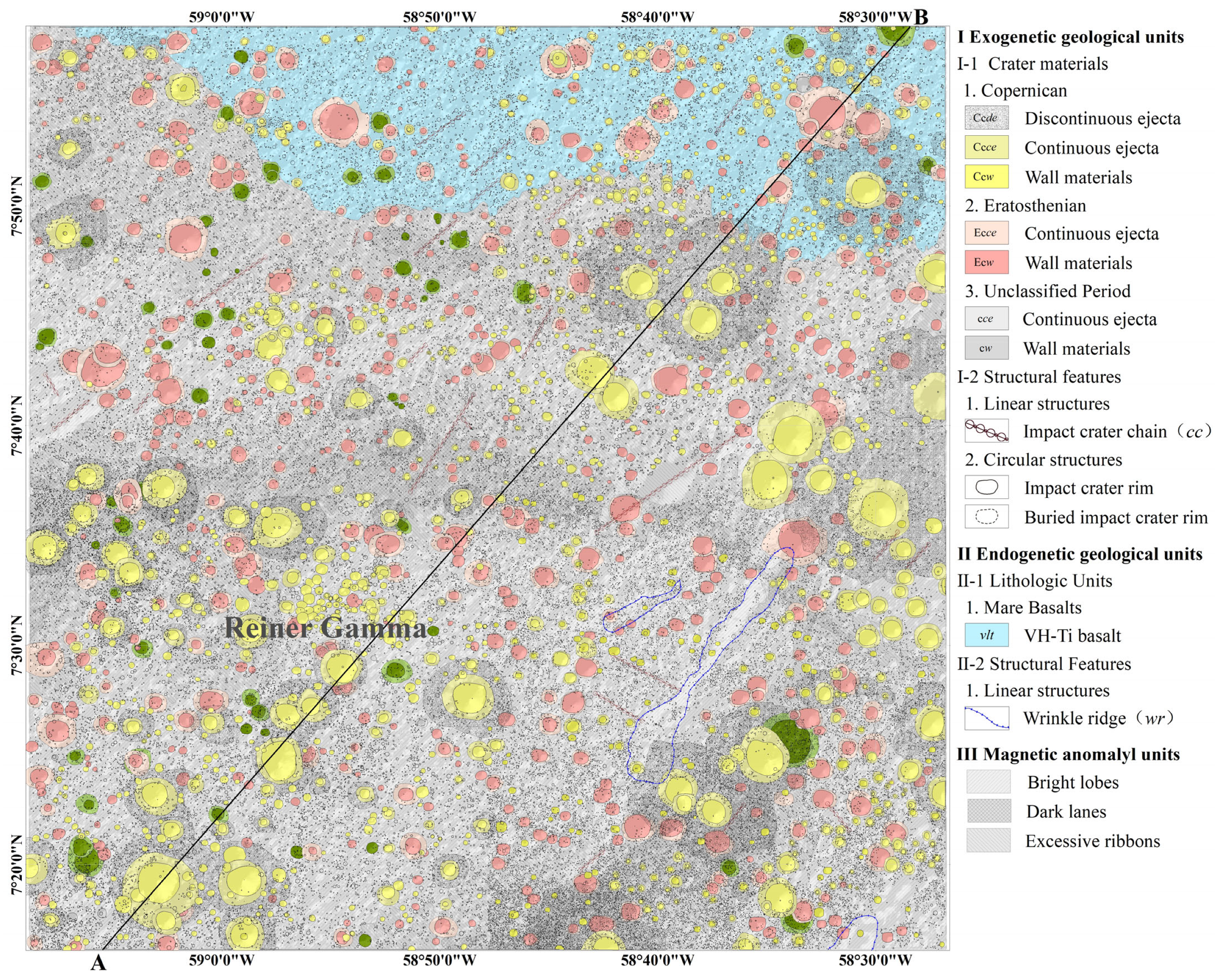
3.3. The 1:10,000 Geological Map of the Target in Reiner Gamma Region
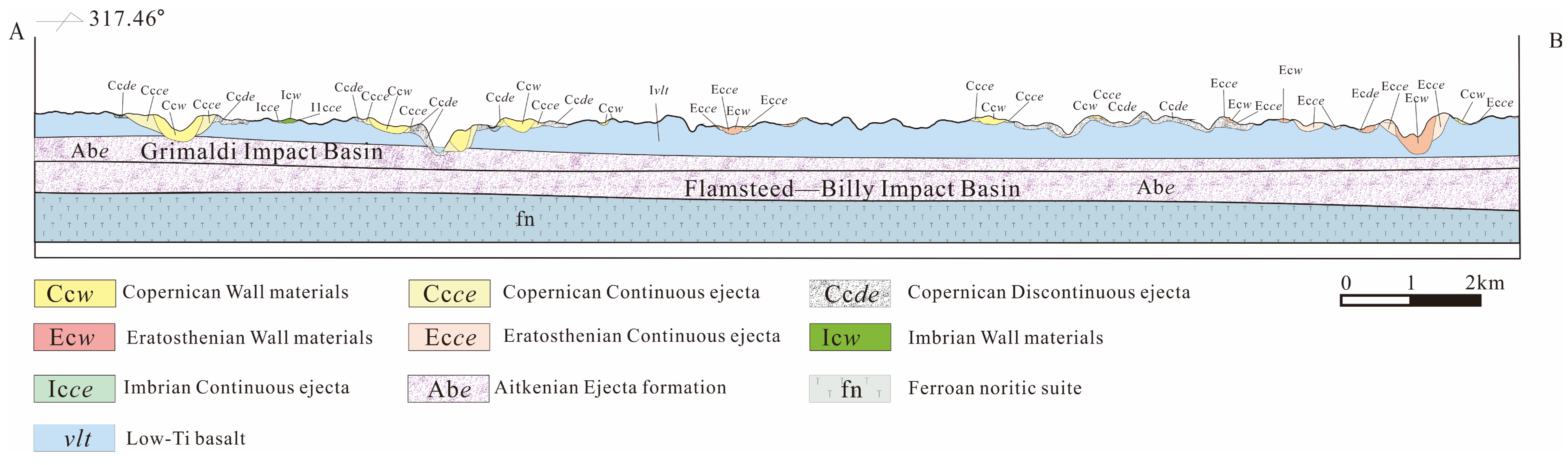
3.4. The Stratigraphic Sequence Within the Target of the Reiner Gamma Region
4. Discussion
4.1. Geochemical Features of the Reiner Gamma Region
4.2. Topographic and Geomorphological Features of the Target in the Reiner Gamma Region
4.3. Geological Evolution of the Reiner Gamma Region
4.3.1. Magma–Oceanian and Aitkenian Periods
4.3.2. Nectarian and Imbrian Periods (3.88~3.16 Ga)
4.3.3. Eratosthenian and Copernican Periods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, A.J.; Tikoo, S.M. An episodic high-intensity lunar core dynamo. Nat. Astron. 2022, 6, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Tikoo, S.M.; Krawczynski, M.J. Possibility of Lunar Crustal Magmatism Producing Strong Crustal Magnetism. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2024, 129, e2023JE008179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mighani, S.; Wang, H.P.; Shuster, D.L.; Borlina, C.S.; Nichols, C.I.O.; Weiss, B.P. The end of the lunar dynamo. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax0883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinberg, A.L.; Soderlund, K.M.; Elkins-Tanton, L.T. A basal magma ocean dynamo to explain the early lunar magnetic field. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 492, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seritan, M.R.K.; Garrick-Bethell, I. Volcanic thermal demagnetization of the Reiner Gamma magnetic anomaly. Icarus 2023, 403, 115601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.P.; Tikoo, S.M. The lunar dynamo. Science 2014, 346, 1246753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, K.; Yin, Y.; Zhai, S.M. Thermal and Dynamo Evolution of the Lunar Core Based on the Transport Properties of Fe-S-P Alloys. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL108131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.J.; Tikoo, S.M.; Andrews-Hanna, J.C. The Case Against an Early Lunar Dynamo Powered by Core Convection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrick-Bethell, I.; Poppe, A.R.; Fatemi, S. The Lunar Paleo-Magnetosphere: Implications for the Accumulation of Polar Volatile Deposits. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 5778–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.; Draper, D.; Boardsen, S.; Done, C.F. When the Moon had a magnetosphere. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc0865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarduno, J.A.; Cottrell, R.D.; Lawrence, K.; Bono, R.K.; Huang, W.T.; Johnson, C.L.; Blackman, E.G.; Smirnov, A.V.; Nakajima, M.; Neal, C.R.; et al. Absence of a long-lived lunar paleo magnetosphere. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poppe, A.R.; Garrick-Bethell, I.; Fatemi, S. Fractionation of Solar Wind Minor Ion Precipitation by the Lunar Paleomagnetophere. Planet. Sci. J. 2021, 2, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.M.; Kim, K.H.; Garrick-Bethell, I.; Jin, H. Magnetic Anomalies Within the Crisium Basin: Magnetization Directions, Source Depths, and Ages. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2019, 124, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, L.L.; Torres, C.B.; Oliveira, J.S.; Wieczorek, M.A.; Stewart, S.T. A New Large-Scale Map of the Lunar Crustal Magnetic Field and Its Interpretation. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2021, 126, e2020JE006667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-K.; Maxwell, R.; Jin, H.; Baek, S.-M.; Ghassemi, O.; Kelley, M.; Lee, H.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, S.; Garrick-Bethell, I. A small lunar swirl and its implications for the formation of the Reiner Gamma magnetic anomaly. Icarus 2019, 319, 869–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, R.E.; Garrick-Bethell, I. Evidence for an Ancient Near-Equatorial Lunar Dipole From Higher Precision Inversions of Crustal Magnetization. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2020, 125, e2020JE006567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.S.; Wieczorek, M.A. Testing the axial dipole hypothesis for the Moon by modeling the direction of crustal magnetization. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2017, 122, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravat, D.; Purucker, M.E.; Olsen, N. Lunar Magnetic Field Models From Lunar Prospector and SELENE/Kaguya Along-Track Magnetic Field Gradients. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2020, 125, e2019JE006187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, H.; Tsunakawa, H.; Takahashi, F.; Shimizu, H.; Matsushima, M.; Team, K.M.L. Near surface magnetic field mapping over the swirls in the SPA region using Kaguya LMAG data. In Proceedings of the European Planetary Science Congress, Rome, Italy, 19–24 September 2010; p. GP42A–03. [Google Scholar]
- Tsunakawa, H.; Takahashi, F.; Shimizu, H.; Shibuya, H.; Matsushima, M. Surface vector mapping of magnetic anomalies over the Moon using Kaguya and Lunar Prospector observations. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2015, 120, 1160–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakita, S.; Johnson, B.C.; Garrick-Bethell, I.; Kelley, M.R.; Maxwell, R.E.; Davison, T.M. Impactor material records the ancient lunar magnetic field in antipodal anomalies. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, D.A.; Schultz, P.H. Electromagnetic properties of impact-generated plasma, vapor and debris. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1999, 23, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, L.L. Central magnetic anomalies of Nectarian-aged lunar impact basins: Probable evidence for an early core dynamo. Icarus 2011, 211, 1109–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, L.L.; Artemieva, N.A. Antipodal effects of lunar basin-forming impacts: Initial 3D simulations and comparisons with observations. Icarus 2008, 193, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikoo, S.M.; Gattacceca, J.; Swanson-Hysell, N.L.; Weiss, B.P.; Suavet, C.; Cournède, C. Preservation and detectability of shock-induced magnetization. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2015, 120, 1461–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.A.; Weiss, B.P.; Stewart, S.T. An Impactor Origin for Lunar Magnetic Anomalies. Science 2012, 335, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrick-Bethell, I.; Weiss, B.P.; Shuster, D.L.; Tikoo, S.M.; Tremblay, M.M. Further evidence for early lunar magnetism from troctolite 76535. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2017, 122, 76–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemingway, D.J.; Tikoo, S.M. Lunar Swirl Morphology Constrains the Geometry, Magnetization, and Origins of Lunar Magnetic Anomalies. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2018, 123, 2223–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.R.; Garrick-Bethell, I. Gravity constraints on the age and formation of the Moon’s Reiner Gamma magnetic anomaly. Icarus 2020, 338, 113465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purucker, M.E.; Head, J.W.; Wilson, L. Magnetic signature of the lunar South Pole-Aitken basin: Character, origin, and age. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2012, 117, 2011je003922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck Syal, M.; Schultz, P.H. Cometary impact effects at the Moon: Implications for lunar swirl formation. Icarus 2015, 257, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.A.; Weiss, B.P.; Breuer, D.; Cébron, D.; Fuller, M.; Garrick-Bethell, I.; Gattacceca, J.; Halekas, J.S.; Hemingway, D.J.; Hood, L.L.; et al. Lunar Magnetism. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2023, 89, 207–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wieczorek, M. Magnetic signatures of lunar impact craters. Icarus 2024, 415, 116049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewett, D.T.; Coman, E.I.; Hawke, B.R.; Gillis-Davis, J.J.; Purucker, M.E.; Hughes, C.G. Lunar swirls: Examining crustal magnetic anomalies and space weathering trends. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, 2010je003656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemingway, D.; Garrick-Bethell, I. Magnetic field direction and lunar swirl morphology: Insights from Airy and Reiner Gamma. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2012, 117, e2012je004165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, P.H.; Srnka, L.J. Cometary collisions on the Moon and Mercury. Nature 1980, 284, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, L.L.; Schubert, G. Lunar Magnetic-Anomalies and Surface Optical-Properties. Science 1980, 208, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, L.L.; Williams, C.R. The lunar swirls: Distribution and possible origins. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988; pp. 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Garrick-Bethell, I.; Lin, R.P.; Sanchez, H.; Jaroux, B.A.; Bester, M.; Brown, P.; Cosgrove, D.; Dougherty, M.K.; Halekas, J.S.; Hemingway, D. Lunar magnetic field measurements with a cubesat. In Proceedings of SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix, A.R.; Greathouse, T.K.; Retherford, K.D.; Mandt, K.E.; Gladstone, G.R.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Hurley, D.M.; Feldman, P.D.; Pryor, W.R.; Stern, S.A.; et al. Lunar swirls: Far-UV characteristics. Icarus 2016, 273, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüsch, O.; Hess, M.; Wöhler, C.; Bickel, V.T.; Marshal, R.M.; Patzek, M.; Huybrighs, H.L.F. Discovery of a Dust Sorting Pro-cess on Boulders Near the Reiner Gamma Swirl on the Moon. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2024, 129, e2023JE007910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, C.M.; Noble, S.K. Space weathering on airless bodies. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2016, 121, 1865–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamford, R.A.; Kellett, B.; Bradford, W.J.; Norberg, C.; Thornton, A.; Gibson, K.J.; Crawford, I.A.; Silva, L.; Gargaté, L.; Bingham, R. Minimagnetospheres above the Lunar Surface and the Formation of Lunar Swirls. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 081101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deca, J.; Divin, A.; Lue, C.; Ahmadi, T.; Horányi, M. Reiner Gamma albedo features reproduced by modeling solar wind standoff. Commun. Phys. 2018, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, L.; Coleman, P., Jr.; Wilhelms, D. The Moon: Sources of the crustal magnetic anomalies. Science 1979, 204, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurata, M.; Tsunakawa, H.; Saito, Y.; Shibuya, H.; Matsushima, M.; Shimizu, H. Mini-magnetosphere over the Reiner Gamma magnetic anomaly region on the Moon. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, e2005gl024097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewett, D.T.; Halekas, J.; Ho, G.C.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Anderson, B.J.; Vines, S.K.; Regoli, L.; Jahn, J.M.; Kollmann, P.; Dene-vi, B.W. Lunar Vertex: PRISM Exploration of Reiner Gamma. In Proceedings of 53rd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference; Lunar and Planetary Institute: Houston, TX, USA, 2022; p. 1131. [Google Scholar]
- Denevi, B.W.; Robinson, M.S.; Boyd, A.K.; Sato, H.; Hapke, B.W.; Hawke, B.R. Characterization of space weathering from Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera ultraviolet observations of the Moon. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2014, 119, 976–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, G.Y.; Besse, S.; Nettles, J.; Combe, J.P.; Clark, R.N.; Pieters, C.M.; Staid, M.; Malaret, E.; Boardman, J.; Green, R.O. Newer views of the Moon: Comparing spectra from Clementine and the Moon Mineralogy Mapper. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2011, 116, e2010JE003728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.S.; Vervelidou, F.; Wieczorek, M.A.; Michelena, M.D. Constraints on the Spatial Distribution of Lunar Crustal Magnetic Sources From Orbital Magnetic Field Data. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2024, 129, e2023JE008125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, L.; Zakharian, A.; Halekas, J.; Mitchell, D.; Lin, R.; Acuña, M.; Binder, A. Initial mapping and interpretation of lunar crustal magnetic anomalies using Lunar Prospector magnetometer data. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2001, 106, 27825–27839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, J.B.; Purucker, M.E.; Sabaka, T.J. Age spot or youthful marking: Origin of Reiner Gamma. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L02205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bando, Y.; Kumamoto, A.; Nakamura, N. Constraint on subsurface structures beneath Reiner Gamma on the Moon using the Kaguya Lunar Radar Sounder. Icarus 2015, 254, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Q.; Liu, J.; Kang, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, R.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, S. A New Robust Lunar Landing Selection Method Using the Bayesian Optimization of Extreme Gradient Boosting Model (BO-XGBoost). Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemelin, M.; Lucey, P.G.; Miljkovic, K.; Gaddis, L.R.; Hare, T.; Ohtake, M. The compositions of the lunar crust and upper mantle: Spectral analysis of the inner rings of lunar impact basins. Planet. Space Sci. 2019, 165, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemelin, M.; Lucey, P.G.; Song, E.; Taylor, G.J. Lunar central peak mineralogy and iron content using the Kaguya Multi-band Imager: Reassessment of the compositional structure of the lunar crust. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2015, 120, 869–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.A.; Pieters, C.; Patchen, A.; Taylor, D.H.S.; Morris, R.V.; Keller, L.P.; Mckay, D.S. Mineralogical and chemical characterization of lunar highland soils: Insights into the space weathering of soils on airless bodies. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2010, 115, e2009je003427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; Xiao, X.; Qiu, D.; Yan, J.; Xiao, L.; Huang, J. New maps of major oxides and Mg # of the lunar surface from additional geochemical data of Chang’E-5 samples and KAGUYA multiband imager data. Icarus 2023, 397, 115505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanaugh, J.F.; Smith, J.C.; Sun, X.L.; Bartels, A.E.; Ramos-Izquierdo, L.; Krebs, D.J.; McGarry, J.F.; Trunzo, R.; Novo-Gradac, A.M.; Britt, J.L.; et al. The Mercury Laser Altimeter instrument for the MESSENGER mission. Space Sci. Rev. 2007, 131, 451–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.E.; Zuber, M.T.; Frey, H.V.; Garvin, J.B.; Head, J.W.; Muhleman, D.O.; Pettengill, G.H.; Phillips, R.J.; Solomon, S.C.; Zwally, H.J.; et al. Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter: Experiment summary after the first year of global mapping of Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2001, 106, 23689–23722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.E.; Zuber, M.T.; Neumann, G.A.; Lemoine, F.G.; Mazarico, E.; Torrence, M.H.; McGarry, J.F.; Rowlands, D.D.; Head, J.W.; Duxbury, T.H.; et al. Initial observations from the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, e2010gl043751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarico, E.; Rowlands, D.D.; Neumann, G.A.; Smith, D.E.; Torrence, M.H.; Lemoine, F.G.; Zuber, M.T. Orbit determination of the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, M.K.; Mazarico, E.; Neumann, G.A.; Zuber, M.T.; Haruyama, J.; Smith, D.E. A new lunar digital elevation model from the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter and SELENE Terrain Camera. Icarus 2016, 273, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cheng, W.; Yan, G. Distribution characteristics and classification schemes of lunar surface elevation. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, H. Technological advancements and promotion roles of Chang’e-3 lunar probe mission. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2013, 56, 2702–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J. Classification of Lunar Landforms Coupled with Morphology and Genesis and Intelligent Identification of Impact Landforms; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kreslavsky, M.A.; Head, J.W.; Neumann, G.A.; Rosenburg, M.A.; Aharonson, O.; Smith, D.E.; Zuber, M.T. Lunar topographic roughness maps from Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA) data: Scale dependence and correlation with geologic features and units. Icarus 2013, 226, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.Y.; Cheng, W.M.; Liu, Q.Y.; Jiao, Y.M.; Liu, J.Z. Morphological differentiation characteristics and classification criteria of lunar surface relief amplitude. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 2365–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandfield, J.L.; Hayne, P.; Williams, J.P.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Paige, D.A. Lunar surface roughness derived from LRO Diviner Radiometer observations. Icarus 2015, 248, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ling, Z.C.; Liu, J.Z.; Chen, S.B.; Ding, X.Z.; Chen, J.P.; Cheng, W.M.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.Z.; et al. Digital and global lithologic mapping of the Moon at a 1:2,500,000 scale. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 2050–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Liu, J.; Head, J.W.; Zhang, F.; Ling, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Ding, X.; Ji, J.; Ouyang, Z. A lunar time scale from the perspective of the Moon’s dynamic evolution. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 67, 234–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.Z.; Guo, D.J.; Liu, J.Z.; Chen, S.B.; Ling, Z.C.; Ding, X.Z.; Han, K.Y.; Chen, J.P.; Cheng, W.M.; Zhu, K.; et al. The 1:2,500,000-scale geologic map of the global Moon. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 1544–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Yue, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhu, K. Characterization and interpretation of the global lunar impact basins based on remote sensing. Icarus 2022, 378, 114952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.Q.; Zhu, K.; Chen, S.B.; Liu, J.Z.; Ling, Z.C.; Ding, X.Z.; Han, K.Y.; Chen, J.P.; Cheng, W.M.; Lei, D.H.; et al. The 1:2,500,000-scale global tectonic map of the Moon. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 1962–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housen, K.R. Crater Ejecta Scaling Laws. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 2485–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiesinger, H.; Head, J.W.; Wolf, U.; Jaumann, R.; Neukum, G. Ages and stratigraphy of mare basalts in Oceanus Procellarum, Mare Nubium, Mare Cognitum, and Mare Insularum. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2003, 108, e2002je001985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiesinger, H.; Head, J.W.; Wolf, U.; Jaumann, R.; Neukum, G. Ages and stratigraphy of lunar mare basalts: A synthesis. In Recent Advances and Current Research Issues in Lunar Stratigraphy (Geological Society of America Special Paper); Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2011; pp. 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, L.A.; Pieters, C.M.; Keller, L.P.; Morris, R.V.; McKay, D.S. Lunar Mare Soils: Space weathering and the major effects of surface-correlated nanophase Fe. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2001, 106, 27985–27999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deca, J.; Hemingway, D.J.; Divin, A.; Lue, C.; Poppe, A.R.; Garrick-Bethell, I.; Lembège, B.; Horányi, M. Simulating the Reiner Gamma Swirl: The Long-Term Effect of Solar Wind Standoff. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2020, 125, e2019JE006219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deca, J.; Poppe, A.R.; Divin, A.; Lembège, B. The Plasma Environment Surrounding the Reiner Gamma Magnetic Anomaly. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2021JA029180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Ling, Z.; Bo, L.; Wu, Z. Photometric behaviors and classification of Reiner Gamma swirl materials. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2016, 32, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Poppe, A.R.; Fatemi, S.; Garrick-Bethell, I.; Hemingway, D.; Holmström, M. Solar wind interaction with the Reiner Gamma crustal magnetic anomaly: Connecting source magnetization to surface weathering. Icarus 2016, 266, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.T.; Barker, M.K.; Mazarico, E.; Sun, X.; Neumann, G.A.; Smith, D.E.; Head, J.W.; Zuber, M.T. Near-infrared Pho-tometry of the Moon’s Surface with Passive Radiometry from the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA). Planet. Sci. J. 2024, 5, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carporzen, L.; Weiss, B.P.; Elkins-Tanton, L.T.; Shuster, D.L.; Ebel, D.; Gattacceca, J. Magnetic evidence for a partially differentiated carbonaceous chondrite parent body. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6386–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cournede, C.; Gattacceca, J.; Gounelle, M.; Rochette, P.; Weiss, B.P.; Zanda, B. An early solar system magnetic field recorded in CM chondrites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 410, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.R.; Lima, E.A.; Weiss, B.P. No nebular magnetization in the Allende CV carbonaceous chondrite. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 404, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.P.; Berdahl, J.S.; Elkins-Tanton, L.; Stanley, S.; Lima, E.A.; Carporzen, L. Magnetism on the Angrite Parent Body and the Early Differentiation of Planetesimals. Science 2008, 322, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Stevens, J.G.; Li, Y.S.; Li, Z.L. Mossbauer Study of the Jilin and Xinyang Meteorites. Hyperfine Interact 1994, 91, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, L.E.; Cassata, W.S.; Wimpenny, J.; Gaffney, A.M.; Shearer, C.K. The formation and evolution of the Moon’s crust inferred from the Sm-Nd isotopic systematics of highlands rocks. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2020, 290, 312–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, B.; Grove, T.L.; Namur, O.; Holtz, F. Crystallization of the lunar magma ocean and the primordial mantle-crust differentiation of the Moon. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 234, 50–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.E.; Morrissey, L.J.; Nemchin, A.A.; Gardiner, N.J.; Snape, J.F. The phases of the Moon: Modelling crystallisation of the lunar magma ocean through equilibrium thermodynamics. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2021, 556, 116721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, J.F.; Draper, D.S. Fractional crystallization of the lunar magma ocean: Updating the dominant paradigm. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2018, 53, 1432–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, G.A.; Taylor, L.A.; Neal, C.R. A Chemical-Model for Generating the Sources of Mare Basalts—Combined Equilibrium and Fractional Crystallization of the Lunar Magmasphere. Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 3809–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.A.; Neumann, G.A.; Nimmo, F.; Kiefer, W.S.; Taylor, G.J.; Melosh, H.J.; Phillips, R.J.; Solomon, S.C.; Andrews-Hanna, J.C.; Asmar, S.W.; et al. The Crust of the Moon as Seen by GRAIL. Science 2013, 339, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, L.E.; Shearer, C.K.; Asmerom, Y.; Papike, J.J. Prolonged KREEP magmatism on the Moon indicated by the youngest dated lunar igneous rock. Nature 2004, 432, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elardo, S.M.; Laneuville, M.; McCubbin, F.M.; Shearer, C.K. Early crust building enhanced on the Moon’s nearside by mantle melting-point depression. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Tronche, E.J.; Steenstra, E.S.; van Westrenen, W. Experimental constraints on the solidification of a nominally dry lunar magma ocean. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 471, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, C.K.; Elardo, S.M.; Petro, N.E.; Borg, L.E.; McCubbin, F.M. Origin of the lunar highlands Mg-suite: An integrated petrology, geochemistry, chronology, and remote sensing perspective. Am. Mineral. 2015, 100, 294–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitten, J.; Head, J.W.; Staid, M.; Pieters, C.M.; Mustard, J.; Clark, R.; Nettles, J.; Klima, R.L.; Taylor, L. Lunar mare deposits associated with the Orientale impact basin: New insights into mineralogy, history, mode of emplacement, and relation to Ori-entale Basin evolution from Moon Mineralogy Mapper (M3) data from Chandrayaan-1. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, e2010je003736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitten, J.L.; Head, J.W. Lunar cryptomaria: Physical characteristics, distribution, and implications for ancient volcanism. Icarus 2015, 247, 150–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, E.K.; Weiss, B.P.; Cassata, W.S.; Shuster, D.L.; Tikoo, S.M.; Gattacceca, J.; Grove, T.L.; Fuller, M.D. A Long-Lived Lunar Core Dynamo. Science 2012, 335, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suavet, C.; Weiss, B.P.; Cassata, W.S.; Shuster, D.L.; Gattacceca, J.; Chan, L.; Garrick-Bethell, I.; Head, J.W.; Grove, T.L.; Fuller, M.D. Persistence and origin of the lunar core dynamo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8453–8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikoo, S.M.; Weiss, B.P.; Buz, J.; Lima, E.A.; Shea, E.K.; Melo, G.; Grove, T.L. Magnetic fidelity of lunar samples and implications for an ancient core dynamo. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 337, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiesinger, M.H.; Gebhart, J.; van der Bogert, C.; Pasckert, J.; Weinauer, J.; Lawrence, S.; Stopar, J.; Robinson, M. Stratigraphy of low shields and mare basalts of the Marius Hills region. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Woodland, TX, USA, 21–25 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, S.J.; Stopar, J.D.; Hawke, B.R.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Cahill, J.T.; Bandfield, J.L.; Jolliff, B.L.; Denevi, B.W.; Robinson, M.S.; Glotch, T.D. LRO observations of morphology and surface roughness of volcanic cones and lobate lava flows in the Marius Hills. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2013, 118, 615–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikoo, S.M.; Weiss, B.P.; Cassata, W.S.; Shuster, D.L.; Gattacceca, J.; Lima, E.A.; Suavet, C.; Nimmo, F.; Fuller, M.D. Decline of the lunar core dynamo. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 404, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Deng, J.; Zhang, S.; Lei, D.; Zeng, X.; Huang, W. The Geological Investigation of the Lunar Reiner Gamma Magnetic Anomaly Region. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4153. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224153
Hu J, Liu J, Liu J, Deng J, Zhang S, Lei D, Zeng X, Huang W. The Geological Investigation of the Lunar Reiner Gamma Magnetic Anomaly Region. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(22):4153. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224153
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Junhao, Jingwen Liu, Jianzhong Liu, Jiayin Deng, Sheng Zhang, Danhong Lei, Xuejin Zeng, and Weidong Huang. 2024. "The Geological Investigation of the Lunar Reiner Gamma Magnetic Anomaly Region" Remote Sensing 16, no. 22: 4153. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224153
APA StyleHu, J., Liu, J., Liu, J., Deng, J., Zhang, S., Lei, D., Zeng, X., & Huang, W. (2024). The Geological Investigation of the Lunar Reiner Gamma Magnetic Anomaly Region. Remote Sensing, 16(22), 4153. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224153






