Characterization of CYGNSS Ocean Surface Wind Speed Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CYGNSS Wind Speed Data Products
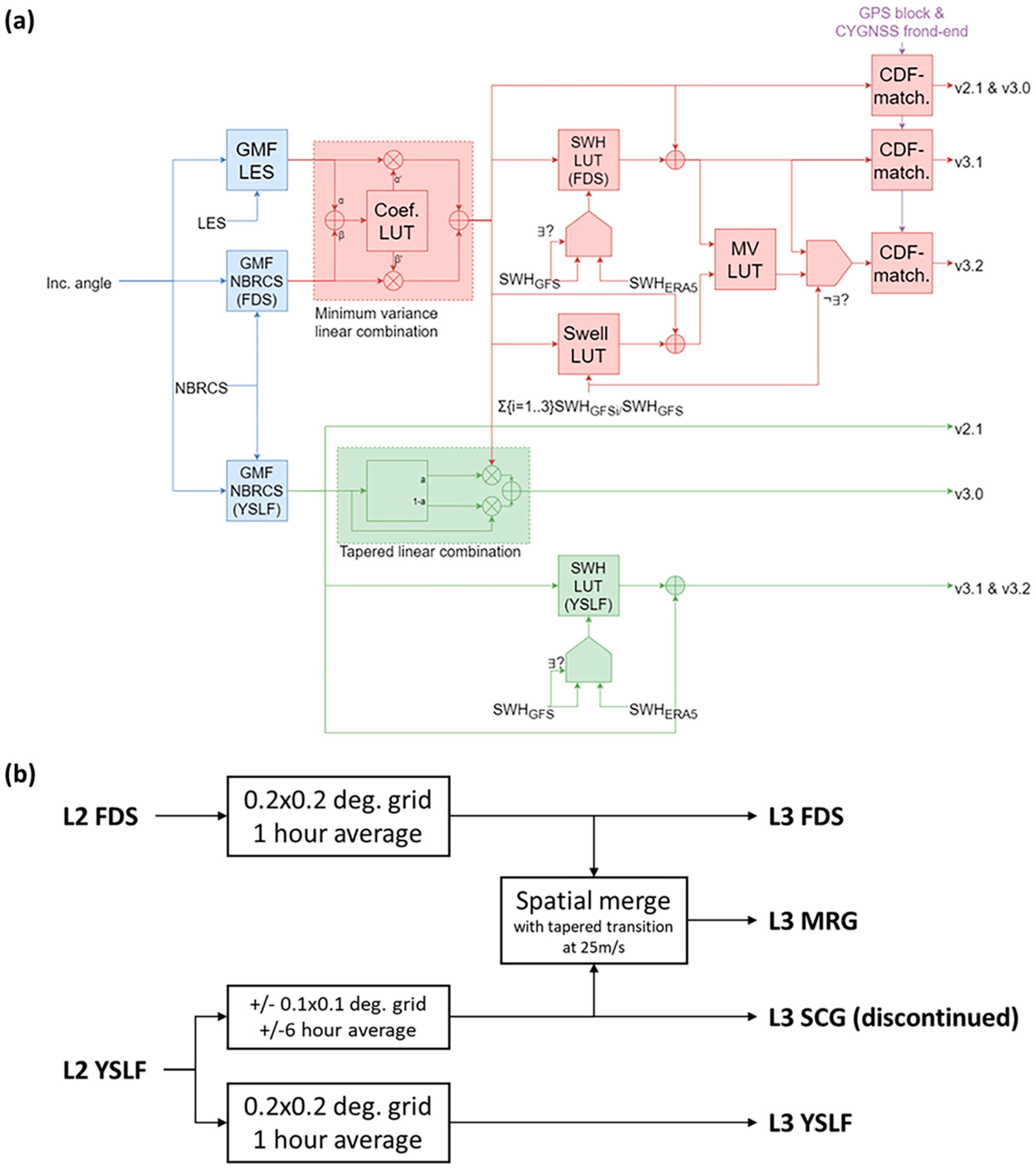
2.1.1. Project v3.2 L2 Fully Developed Seas and L3 Merged Storm Wind Speed
2.1.2. NOAA v1.2 CYGNSS Wind Speed Product
2.2. Reference Wind Speed Products
2.2.1. Buoys
2.2.2. Global Reanalysis Wind Speed Model
2.2.3. Other Satellite Observations of Winds
2.2.4. Storm Winds
3. Results
3.1. Intercomparisons with Reference Wind Speeds
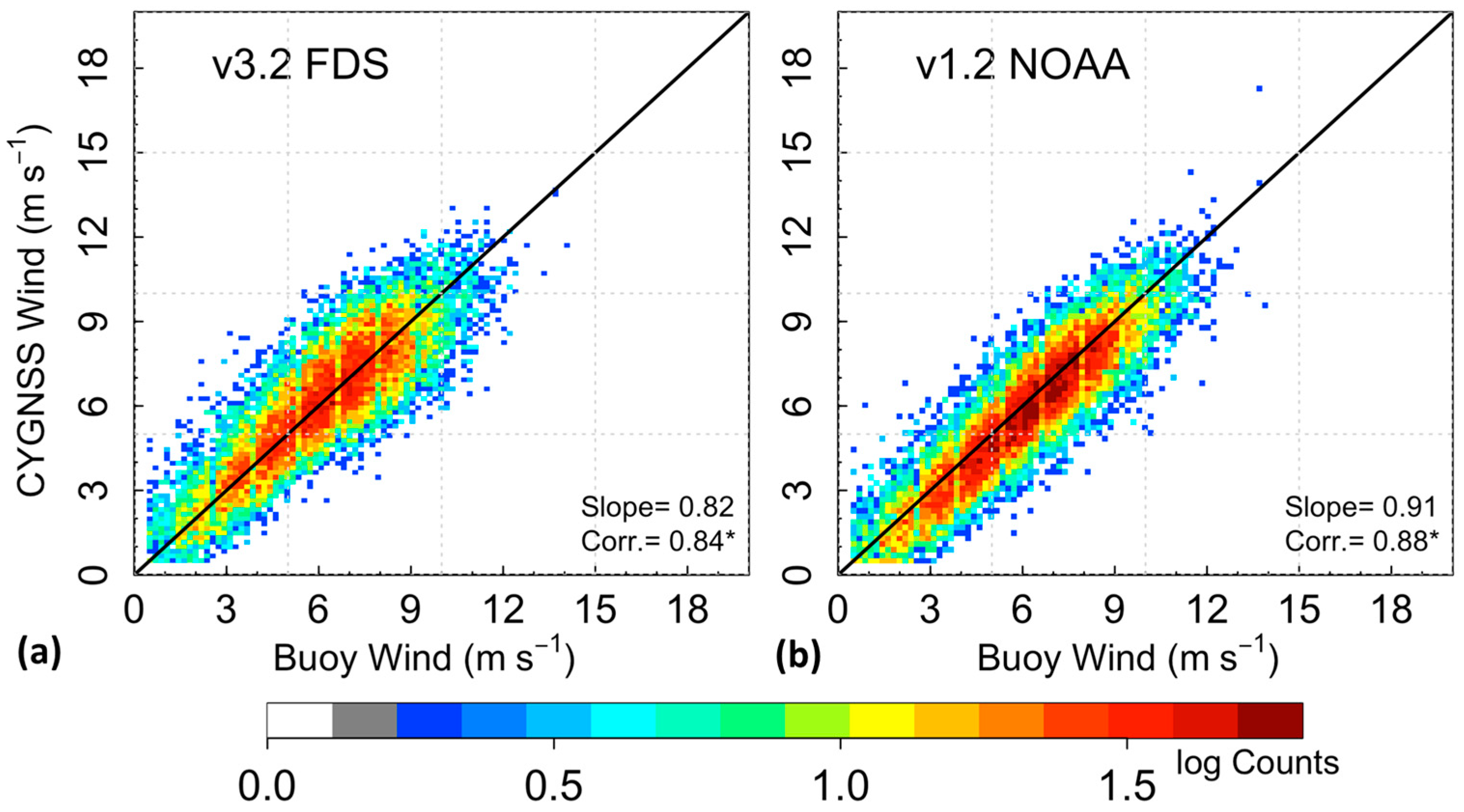
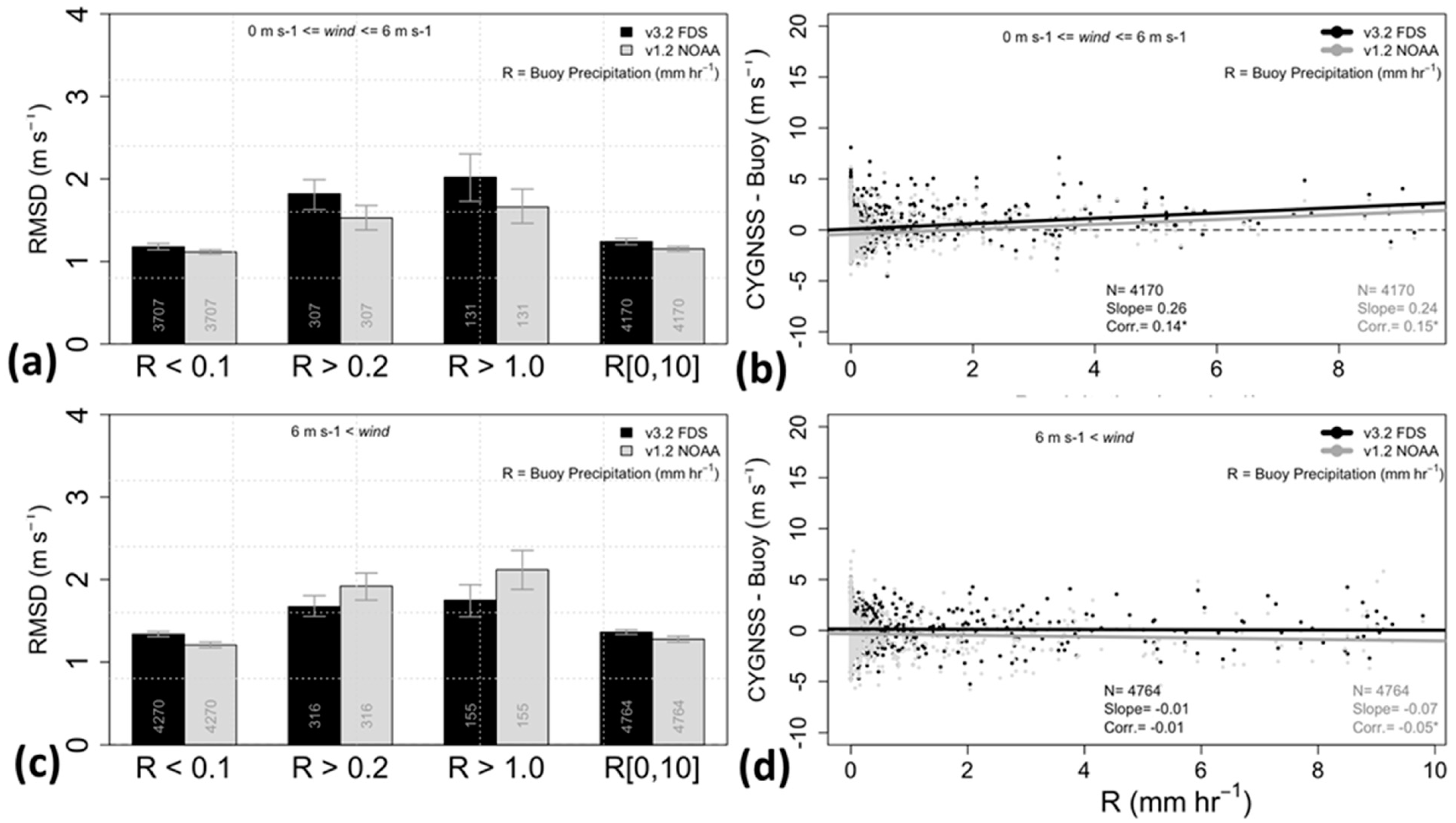
3.1.1. Buoy Intercomparison
RMSD and Bias Assessment Using Buoys
Precipitation Dependence
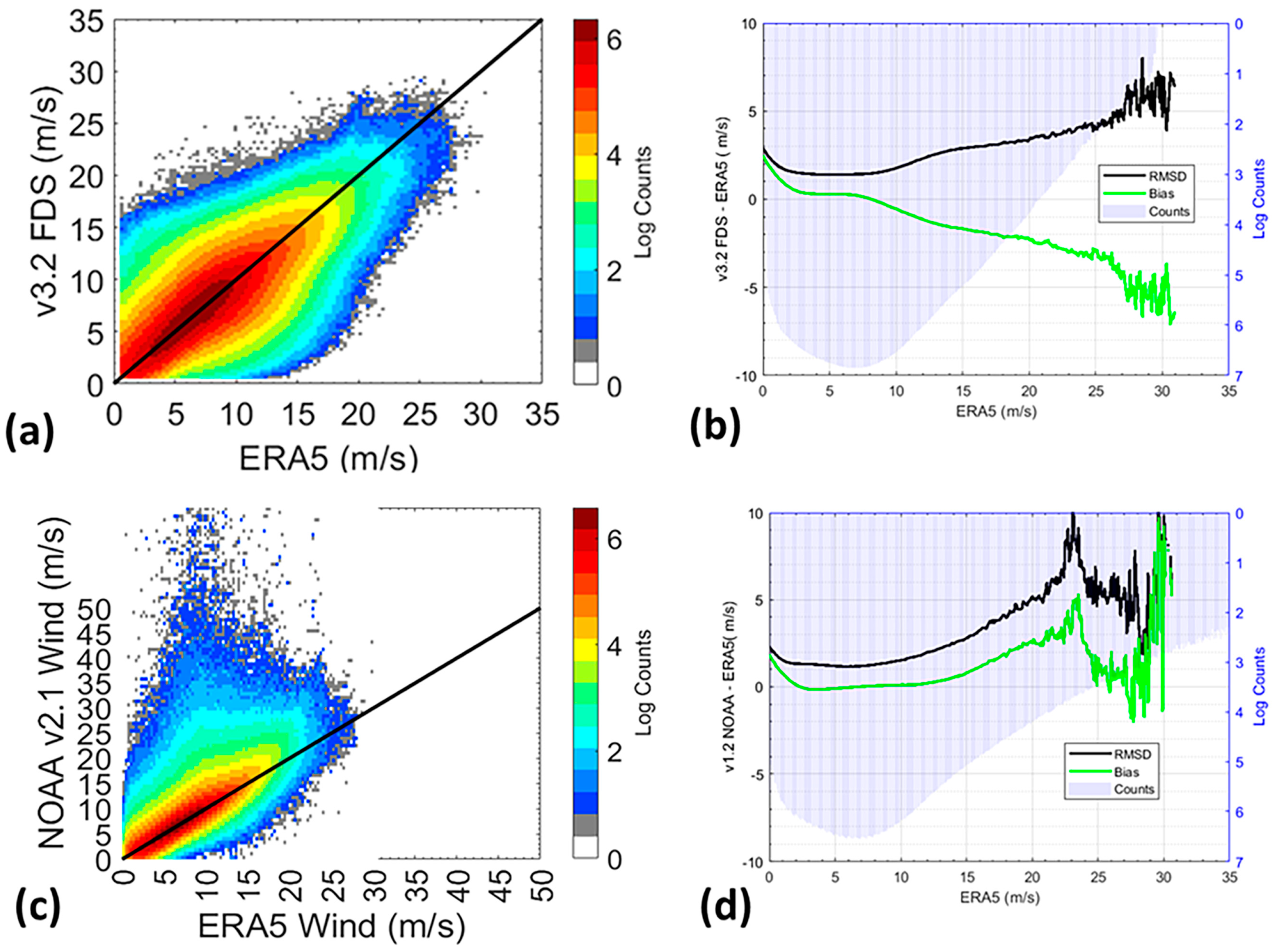
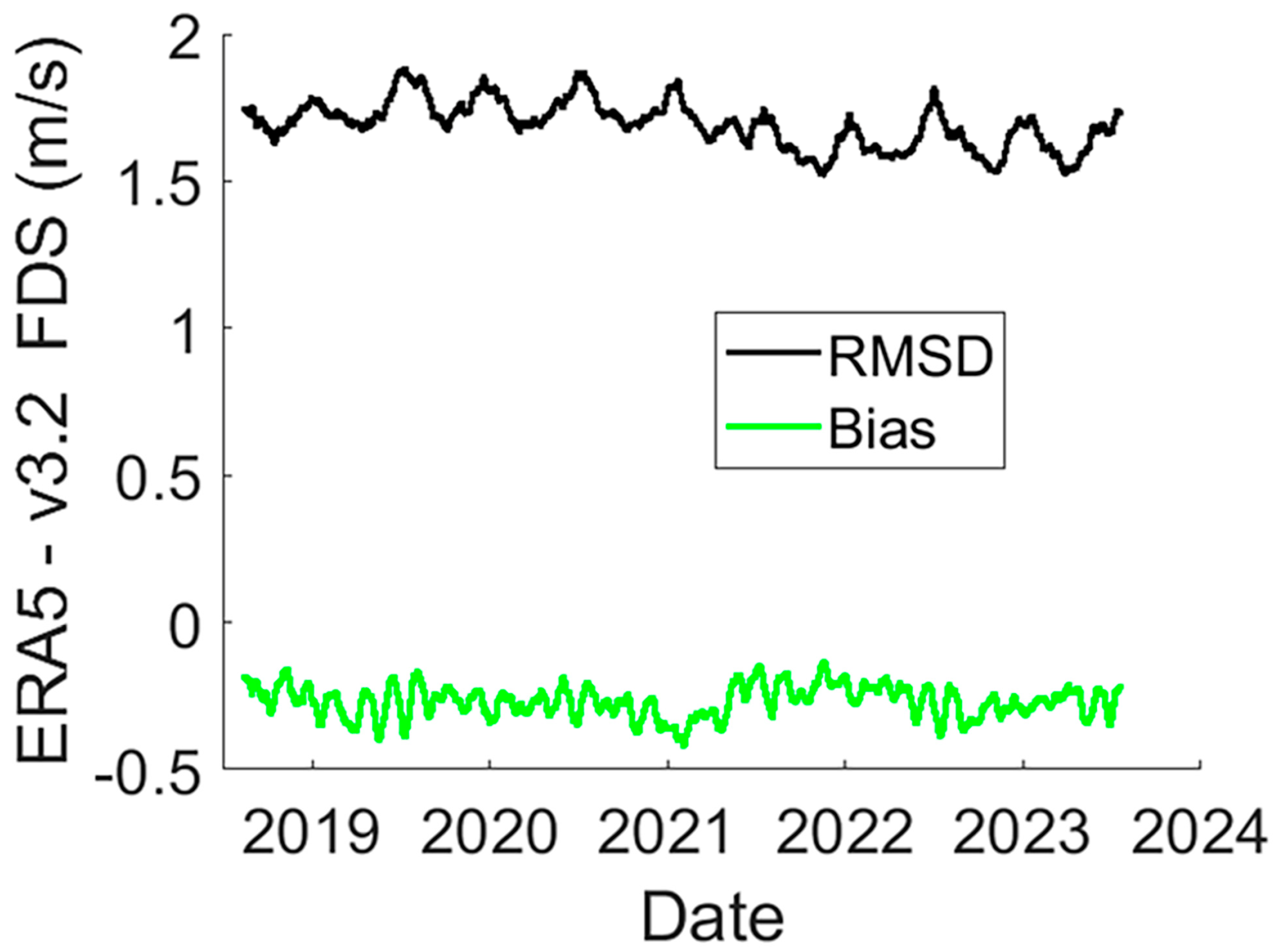
3.1.2. ERA5 Reanalysis Wind Intercomparison
RMSD and Bias Assessment Using ERA5
Dependence of Performance on GPS and CYGNSS Spacecraft
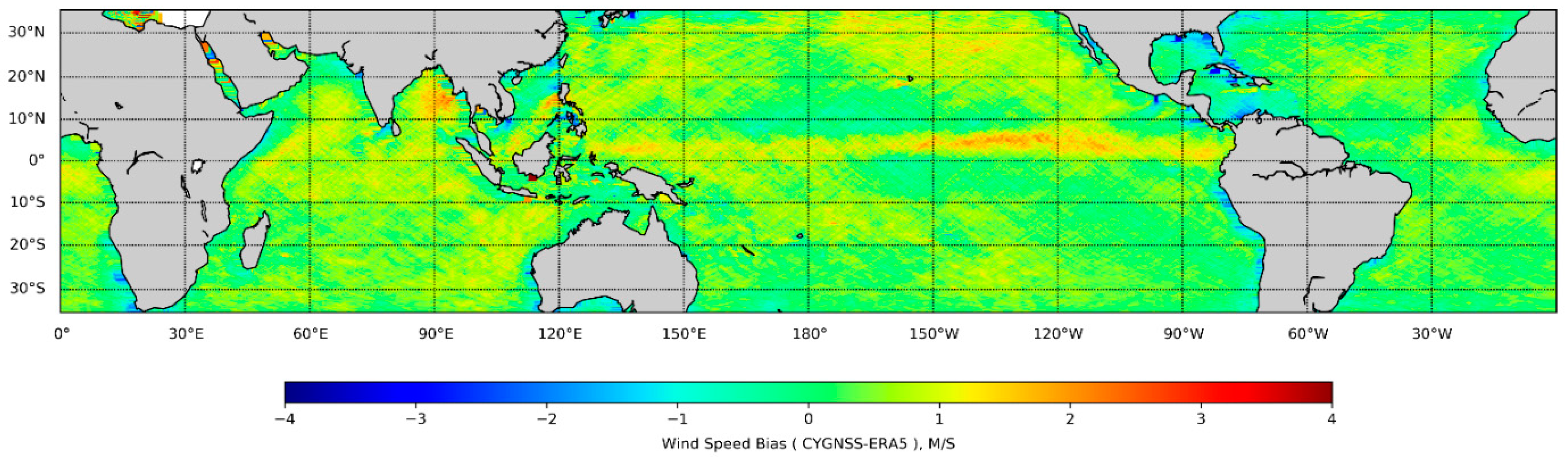
Geographical Bias Distribution
3.2. Triple Colocation Validation
3.2.1. CYGNSS Global Wind Speed Data Products
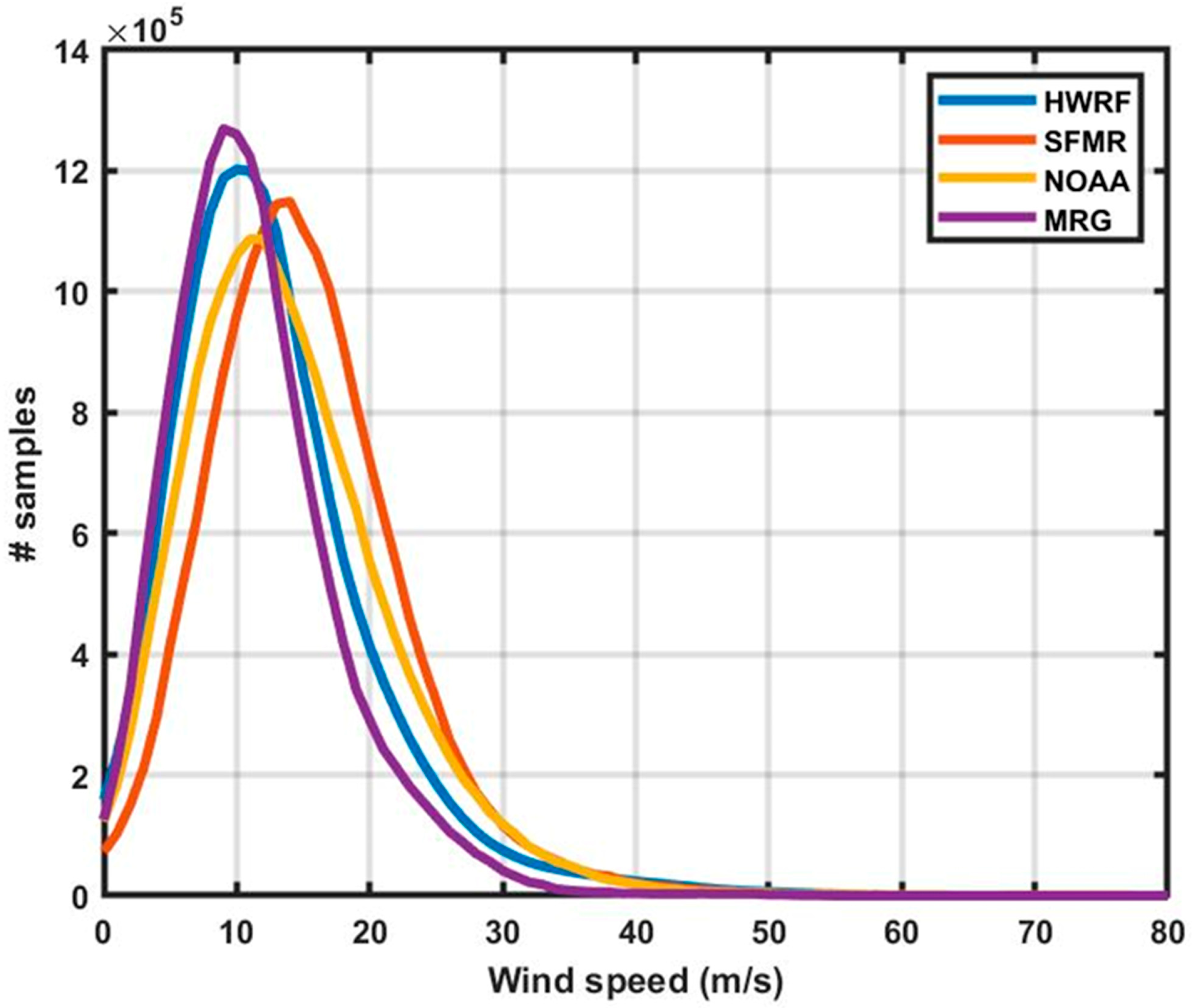
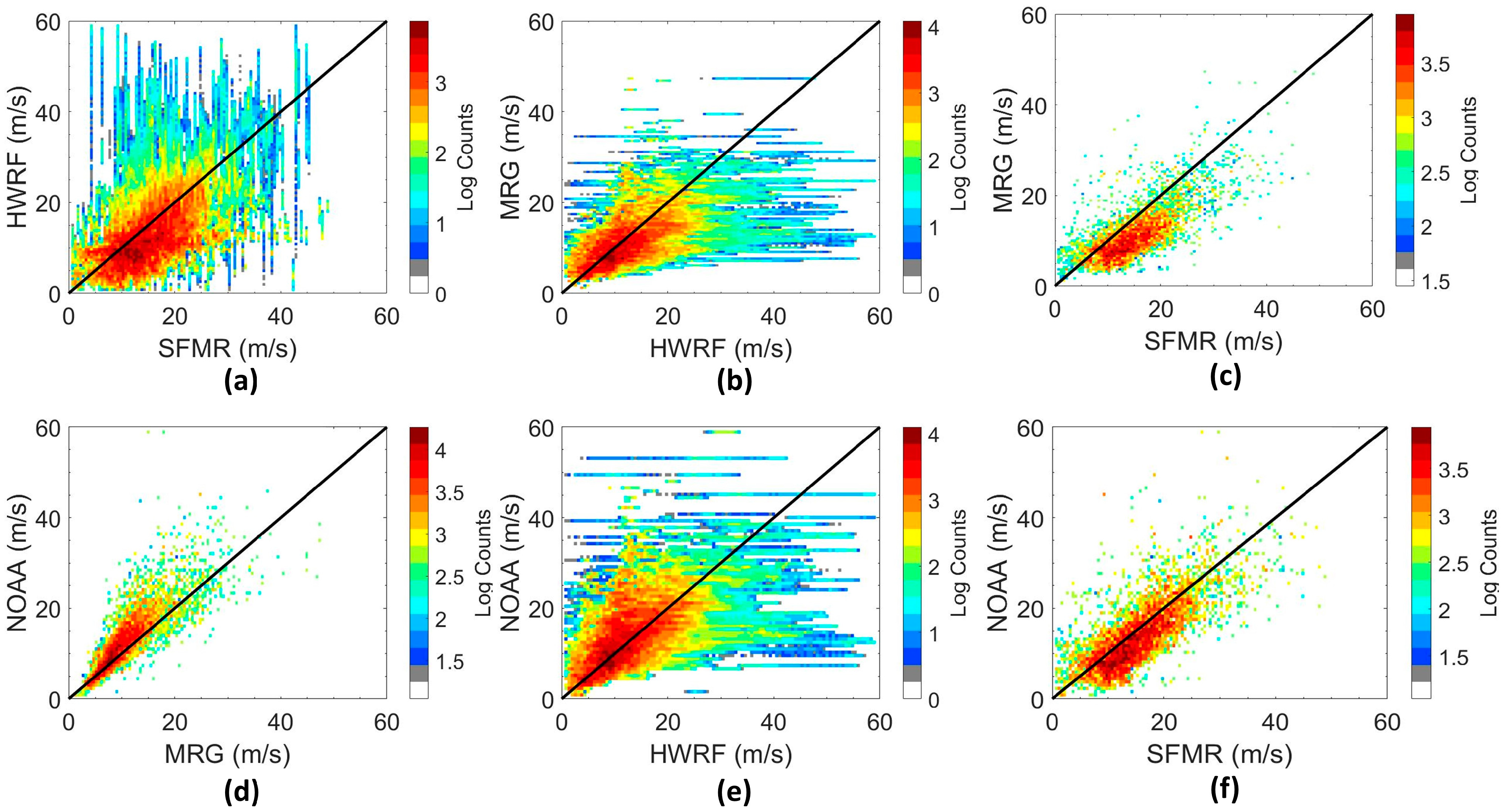
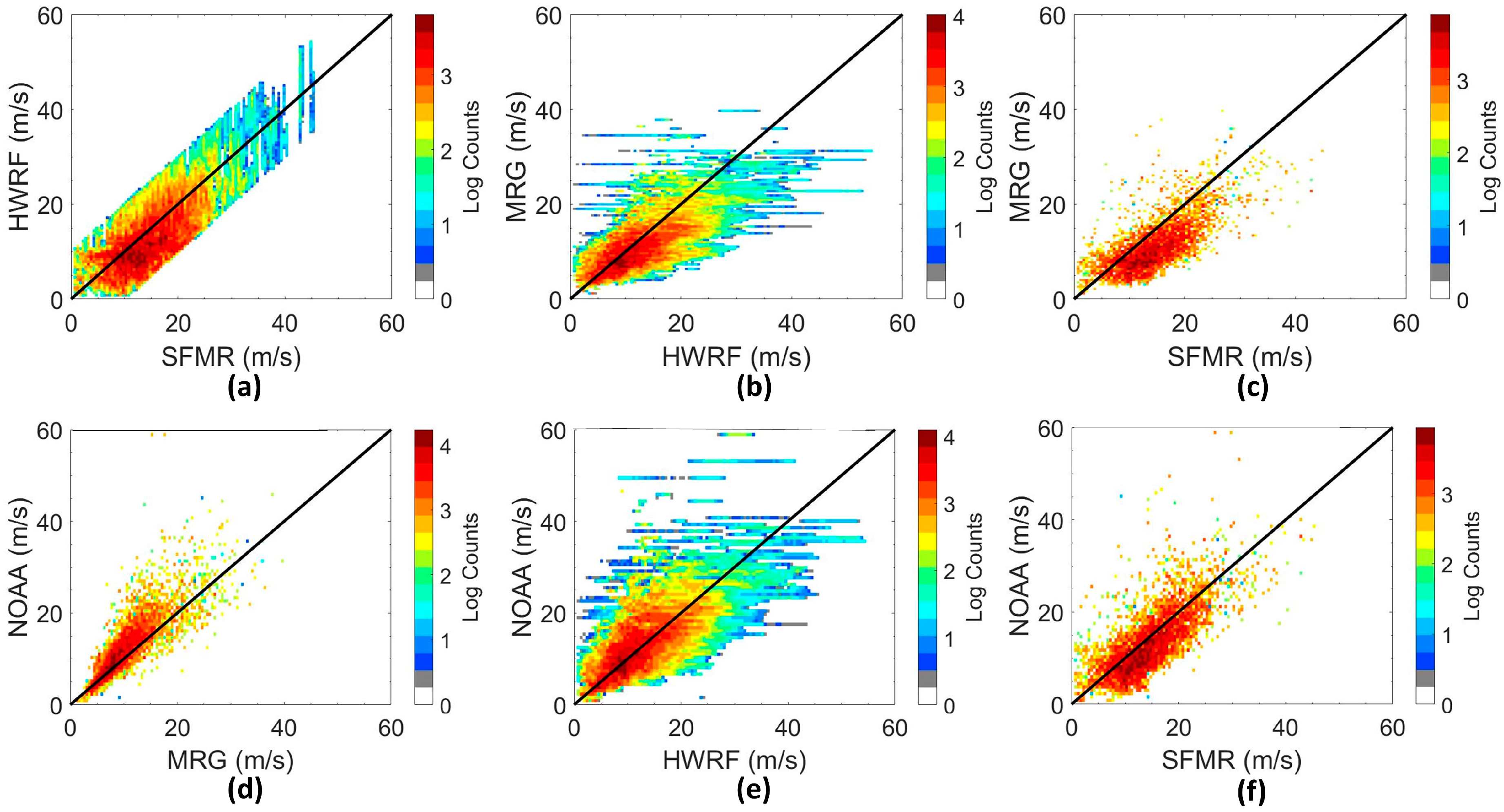
3.2.2. CYGNSS Storm-Specific Data Products
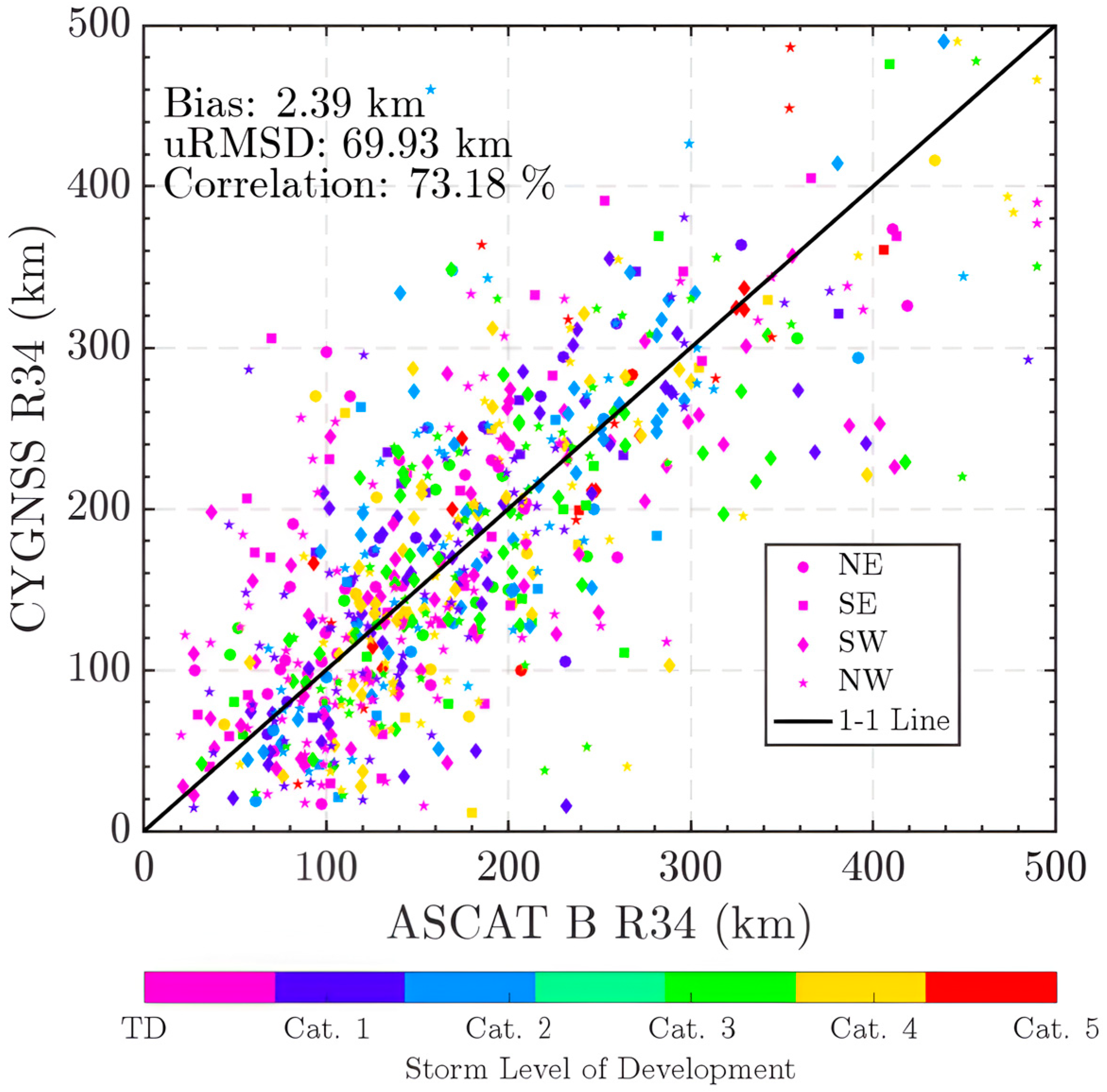
34-Knot Significant Wind Radius, R34, in Storms
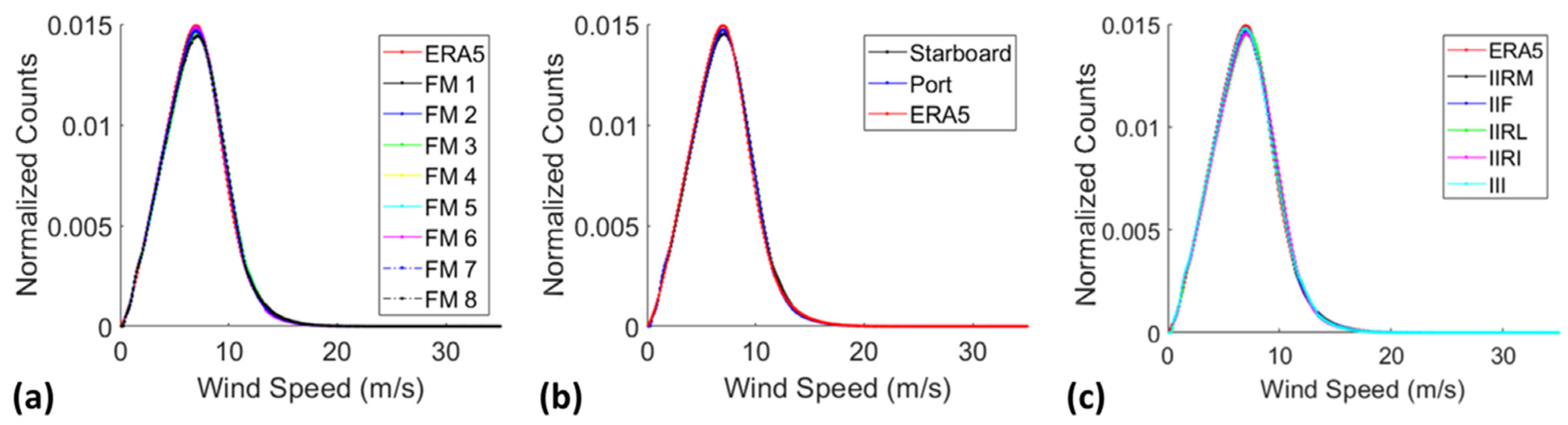
3.3. Sampling Properties
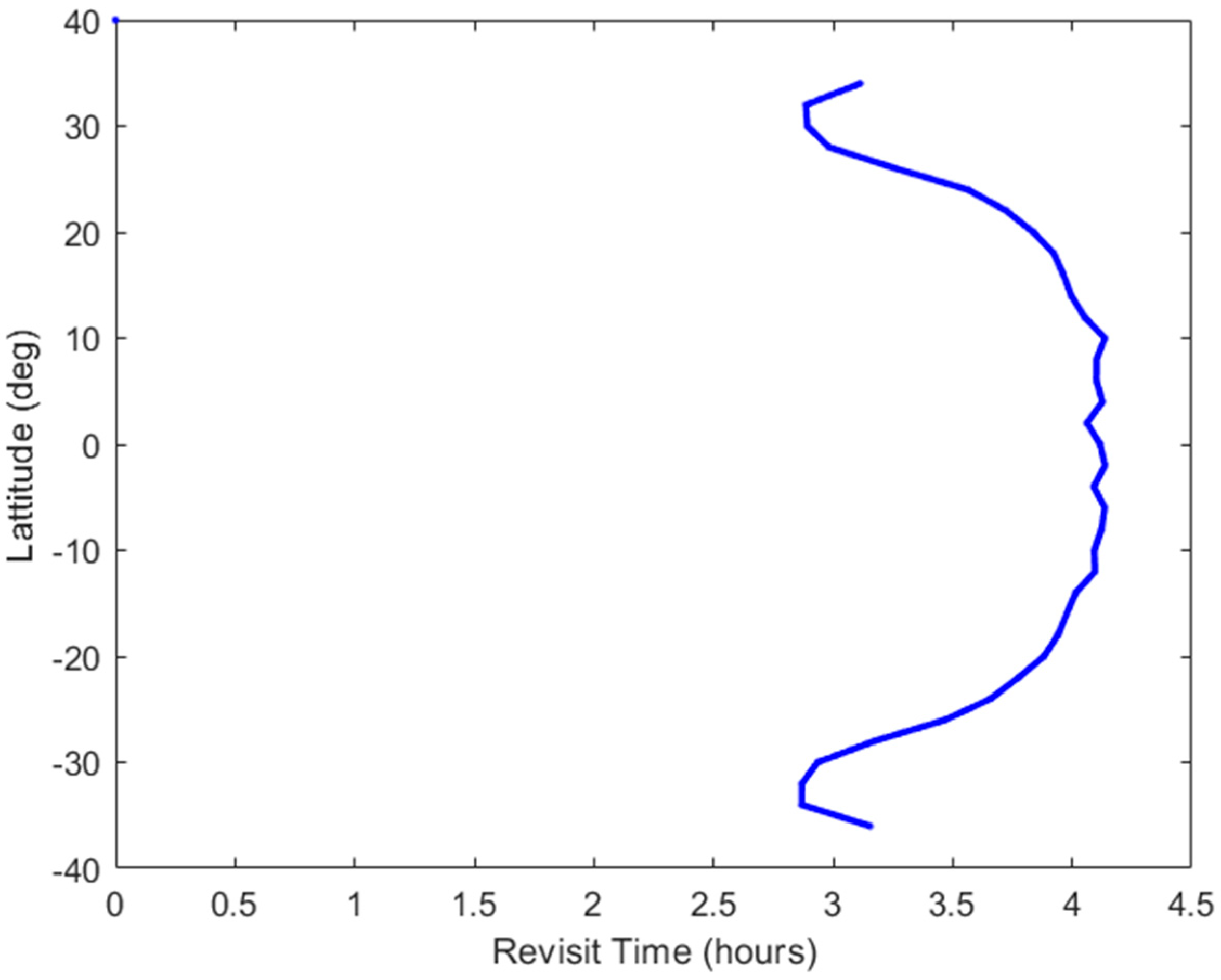
3.3.1. Temporal Sampling of Global Winds
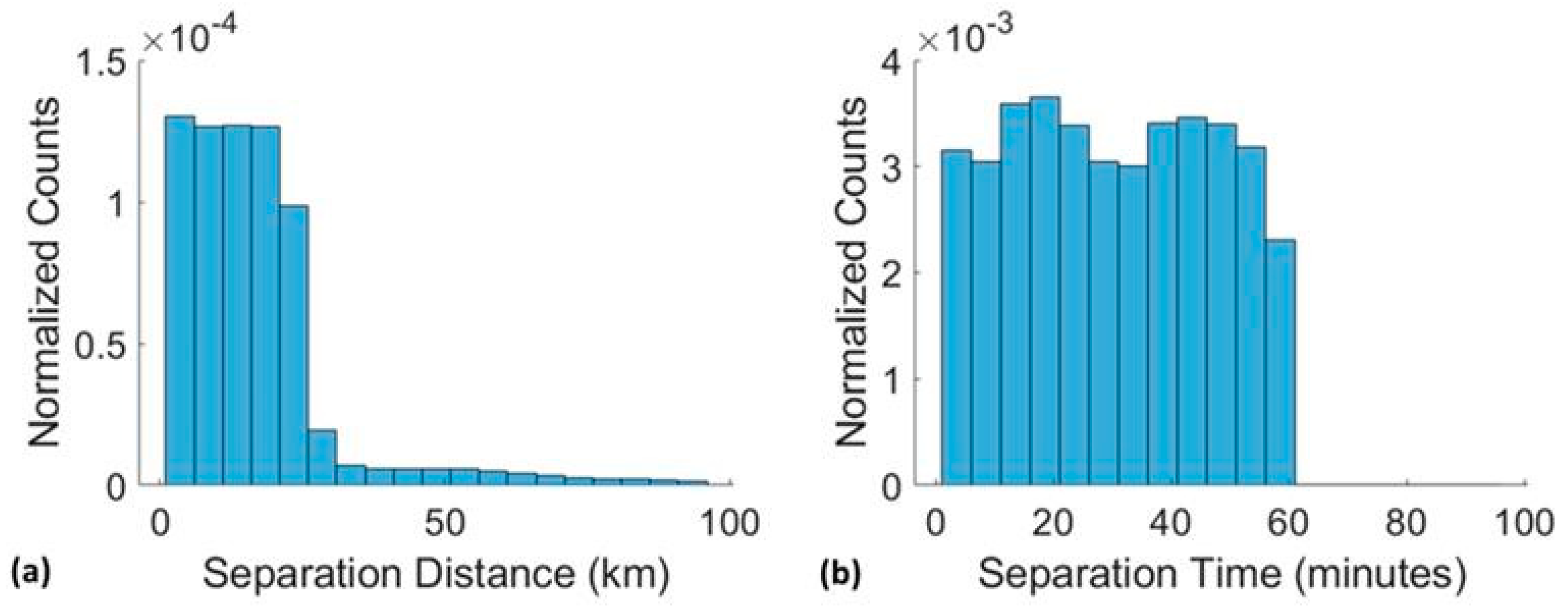
3.3.2. Sampling of Tropical Cyclone Winds
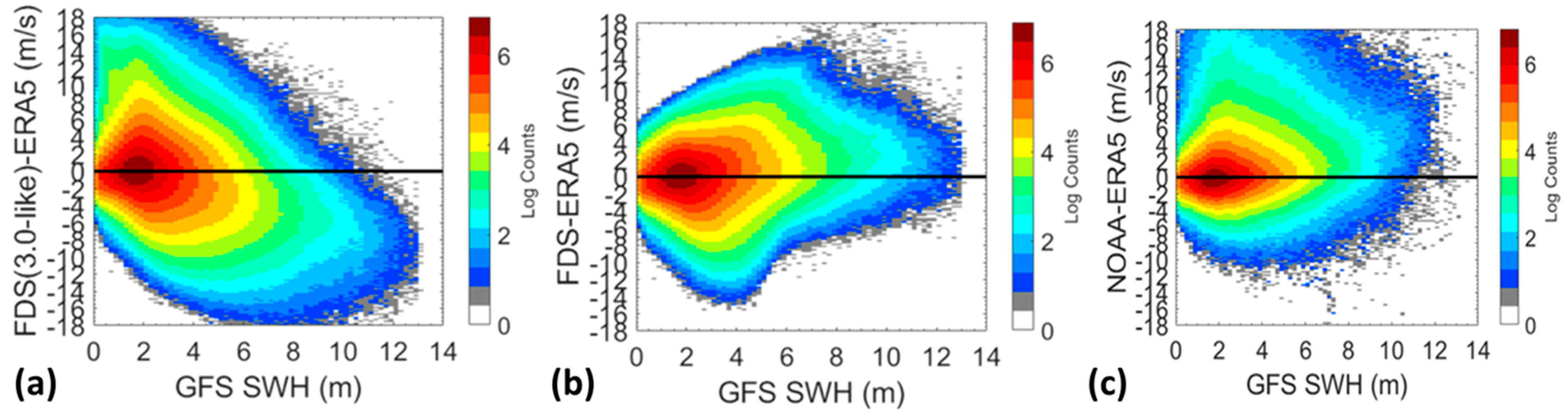
3.4. Sensitivity to Significant Wave Height
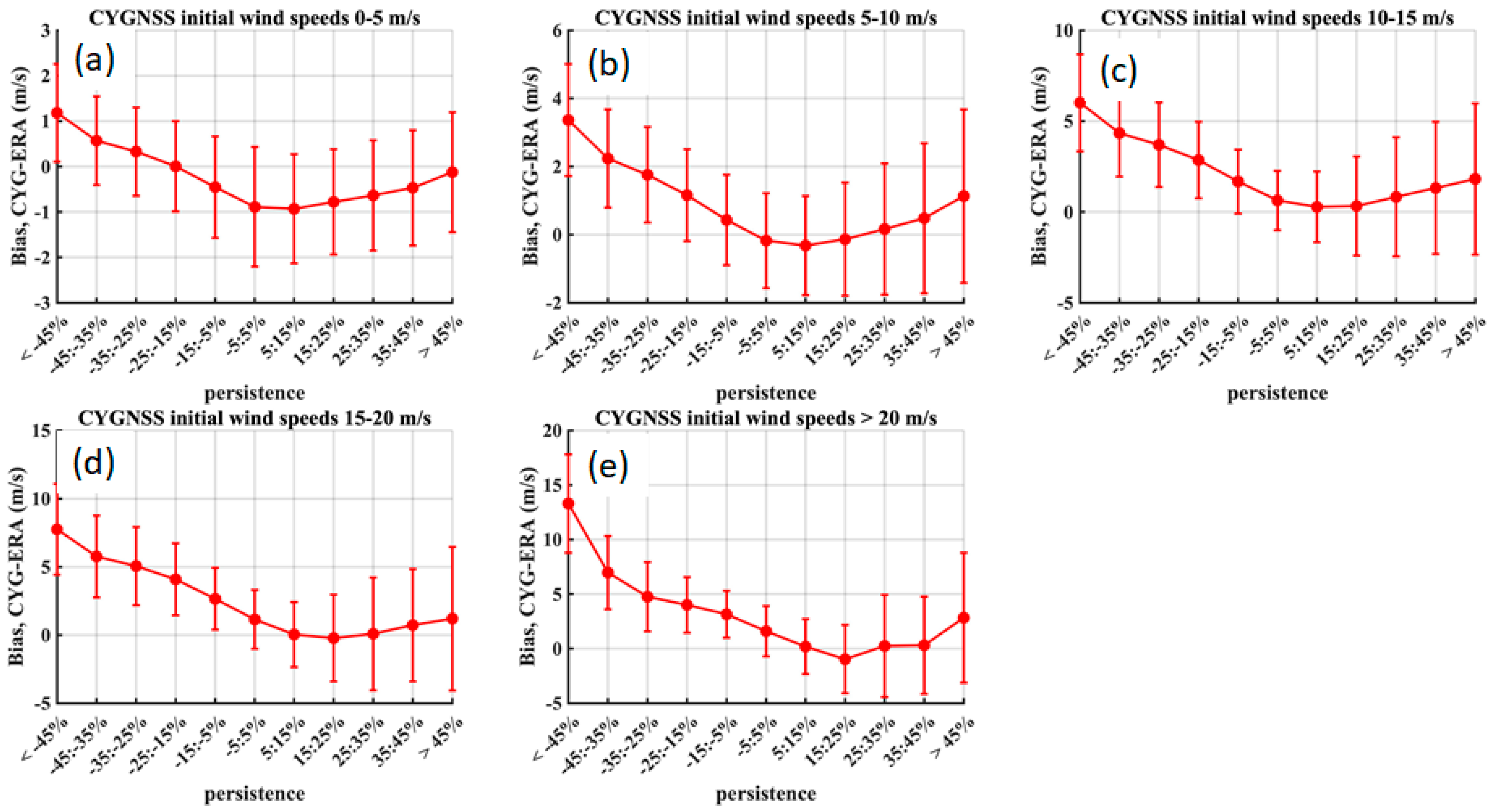
3.5. Sensitivity to Wind Speed Persistence
4. Discussion of Sensitivity to Persistence
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruf, C.S.; Atlas, R.; Chang, P.S.; Clarizia, M.P.; Garrison, J.L.; Gleason, S.; Katzberg, S.J.; Jelenak, Z.; Johnson, J.T.; Majumdar, S.J.; et al. New Ocean Winds Satellite Mission to Probe Hurricanes and Tropical Convection. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, C.; Gleason, S.; McKague, D.S. Assessment of CYGNSS Wind Speed Retrieval Uncertainty. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, C.; Asharaf, S.; Balasubramaniam, R.; Gleason, S.; Lang, T.; McKague, D.; Twigg, D.; Waliser, D. In-Orbit Performance of the Constellation of CYGNSS Hurricane Satellites. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 2009–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asharaf, S.; Waliser, D.; Posselt, D.; Ruf, C.; Zhang, C.; Putra, A. CYGNSS Ocean Surface Wind Validation in the Tropics. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2021, 38, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.C.; Small, E.E. Description of the UCAR/CU Soil Moisture Product. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, C.S.; Chew, C.; Lang, T.; Morris, M.G.; Nave, K.; Ridley, A.; Balasubramaniam, R. A New Paradigm in Earth Environmental Monitoring with the CYGNSS Small Satellite Constellation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreno Luengo, H.; Ruf, C.S. Retrieving Freeze/Thaw Surface State from CYGNSS Measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4302313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, S.; Ruf, C.S.; O’Brien, A.; McKague, D.S. The CYGNSS Level 1 Calibration Algorithm and Error Analysis Based on On-Orbit Measurements. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarizia, M.P.; Ruf, C.S. Wind Speed Retrieval Algorithm for the Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) Mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4419–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, C.S.; Balasubramaniam, R. Development of the CYGNSS Geophysical Model Function for Wind Speed. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freilich, M.; Challenor, P. A New Approach for determining Fully Empirical Altimeter Wind Speed Model Functions. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 25051–25062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarizia, M.P.; Ruf, C.S.; Jales, P.; Gommenginger, C. Spaceborne GNSS-R Minimum Variance Wind Speed Estimator. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6829–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnock, A.M.; Ruf, C.S.; Russel, A.; Al-Khaldi, M.M.; Balasubramaniam, R. CYGNSS Level 3 Merged Wind Speed Data Product for Storm Force and Surrounding Environmental Winds. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 6189–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CYGNSS. CYGNSS Level 2 Science Data Record Version 3.2; PO.DAAC: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2024. Available online: https://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/dataset/CYGNSS_L2_V3.2 (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- CYGNSS. CYGNSS Level 3 MRG Science Data Record Version 3.2.1; PO.DAAC: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2024. Available online: https://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/dataset/CYGNSS_L3_MRG_V3.2.1 (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- Said, F.; Jelenak, Z.; Park, J.; Chang, P.S. The NOAA Track-Wise Wind Retrieval Algorithm and Product Assessment for CyGNSS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4202524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourles, B.; Lumpkin, R.; McPhaden, M.J. The PIRATA Program: History, Accomplishments, and Future Directions. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 1111–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhaden, M.J.; Meyers, G.; Ando, K.; Masumoto, Y.; Murty, V.S.N.; Ravichandran, M.; Syamsudin, F.; Vialard, J.; Yu, L.; Yu, W. RAMA: The Research Moored Array for African-Asian-Australian Monsoon Analysis and Prediction. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhaden, M.J.; Busalacchi, A.J.; Cheney, R.; Donguy, J.-R.; Gage, K.S.; Halpern, D.; Ji, M.; Julian, P.; Meyers, G.; Mitchum, G.T. The Tropical Ocean-Global Atmosphere (TOGA) observing system: A decade of progress. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 14169–14240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asharaf, S.; Posselt, D.J.; Said, F.; Ruf, C.S. Updates on CYGNSS Ocean Surface Wind Validation in the Tropics. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2022, 40, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschmieder, H. Methods and results of definite rain measurements. Mon. Weather Rev. 1934, 62, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, Y.L.; A’hearn, P.; Freitag, H.P.; McPhaden, M.J. Atlas self-siphoning rain gauge error estimates. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2001, 18, 1989–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edson, J.B.; Jampana, V.; Weller, R.A.; Bigorre, S.P.; Plueddemann, A.J.; Fairall, C.W.; Miller, S.D.; Mahrt, L.; Vickers, D.; Hersbach, H. On the Exchange of Momentum Over the Open Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 1589–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, C.W.; Bradley, E.F.; Hare, J.E.; Grachev, A.A.; Edson, J.B. Bulk Parameterization of Air–Sea Fluxes: Updates and Verification for the COARE Algorithm. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 571–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.T. The effects of the variations in sea surface temperature and atmospheric stability in the estimation of average wind speed by SEASAT-SASS. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1984, 14, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, J.; Etcheto, J. Seasat scatterometer versus scanning multichannel microwave radiometer wind speeds: A comparison on a global scale. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 22275–22288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardulli, L. Investigation of calibration changes in the ocean surface wind measurements from the TAO/TRITON buoy array. In Proceedings of the International Ocean Vector Winds Science Team Meeting (IOVWST), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 29–31 May 2024; Available online: https://mdc.coaps.fsu.edu/scatterometry/meeting/past.php#2024 (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- Gualtieri, G. Analysing the uncertainties of reanalysis data used for wind resource assessment: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia, J.P.; Koivisto, M.J.; Olsen, B.T.; Hahmann, A.N.; Sørensen, P.E. Validation of European-scale simulated wind speed and wind generation time series. Appl. Energy 2022, 305, 117794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffelen, A.; Verspeek, J.A.; Vogelzang, J.; Verhoef, A. The CMOD7 Geophysical Model Function for ASCAT and ERS Wind Retrievals. IEEE J. Sel. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, D.W.; Newell, D.; Wentz, F.J.; Krimchansky, S.; Skofronick-Jackson, G.M. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Microwave Imager (GMI): Instrument overview and early on-orbit performance. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3452–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, B.W.; Uhlhorn, E.W. Improved stepped frequency microwave radiometer tropical cyclone surface winds in heavy precipitation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 2392–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Ricciardulli, L.; Wentz, F. Remote Sensing Systems SMAP Daily Sea Surface Winds Speeds on 0.25 Deg Grid, Version 01.0. [NRT or FINAL]; Remote Sensing Systems: Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 2018; Available online: www.remss.com/missions/smap/ (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Liu, Q.; Marchok, T.; Sheinin, D.; Tallapragada, V.; Tong, M.; Tuleya, R.; Yablonsky, R.; Zhang, X. Hurricane Weather Research and Forecasting (HWRF) Model, Scientific Documentation—HWRF v3.4a; Developmental Testbed Center, NOAA/AOML Hurricane Research Division: Miami, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Landsea, C.W.; Franklin, J.L. Atlantic Hurricane Database Uncertainty and Presentation of a New Database Format. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 3576–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavorotny, V.U.; Voronovich, A.G. Scattering of GPS signals from the ocean with wind remote sensing application. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, R.; Ruf, C.S. Characterization of Rain Impact on L-Band GNSS-R Ocean Surface Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, S. Level 1B DDM Calibration Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document, Rev 6. In CYGNSS Project Document 148-0137; University of Michigan Publishing: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2023. Available online: https://archive.podaac.earthdata.nasa.gov/podaac-ops-cumulus-docs/cygnss/open/L1/docs/148-0137_L1B_DDM_Calibration_ATBD_R6.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- Gleason, S.; Johnson, J.; Ruf, C.; Bussy-Virat, C. Characterizing Background Signals and Noise in Spaceborne GNSS Reflection Ocean Observations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffelen, A. Toward the true near-surface wind speed: Error modeling and calibration using triple collocation. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 7755–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, D.; Clarizia, M.P.; Ruf, C.S. Improved CYGNSS Wind Speed Retrieval Using Significant Wave Height Correction. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.D.; Ruf, C.S.; Gleason, S.T. Response time of mean square slope to wind forcing: An empirical investigation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 2809–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, R.; Ruf, C.S. Development and Application of a GNSS-R Error Model for Hurricane Winds. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. 2023, 17, 2336–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| RMSE (m/s) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDS | NOAA | ERA5 | ASCAT | GMI | ||
| Triplet of Matchups | FDS, ERA5, ASCAT | 1.39 | - | 0.71 | 0.42 | - |
| FDS, ERA5, GMI | 1.32 | - | 0.85 | - | 0.41 | |
| FDS, ASCAT, GMI | 1.34 | - | - | 0.57 | 0.31 | |
| NOAA, ERA5, ASCAT | - | 1.00 | 0.66 | 0.49 | - | |
| NOAA, ERA5, GMI | - | 0.93 | 0.74 | - | 0.59 | |
| NOAA, ASCAT, GMI | - | 1.02 | - | 0.46 | 0.45 | |
| ERA5, ASCAT, GMI | - | - | 0.76 | 0.31 | 0.57 | |
| Average RMSE over all triplets | 1.35 | 0.98 | 0.74 | 0.45 | 0.47 | |
| Reference Wind Speed Product | Triplet of Matchups | Wind Speed Range (m/s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 | 10–20 | 20–30 | 30–75 | ||
| RMSE (m/s) | |||||
| SFMR | MRG, HWRF, SFMR | 2.31 | 2.20 | 2.30 | 2.93 |
| NOAA, HWRF, SFMR | 2.32 | 1.97 | 2.19 | 4.26 | |
| HWRF | MRG, HWRF, SFMR | 3.77 | 5.13 | 6.24 | 10.17 |
| NOAA, HWRF, SFMR | 3.35 | 5.37 | 6.55 | 10.33 | |
| Triplet of Matchups | RMSE (km) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BT | ASCAT-B | CYGNSS | SMAP | |
| BT, ASCAT-B, CYGNSS | 46.85 | 36.82 | 58.33 | - |
| BT, CYGNSS, SMAP | 45.57 | - | 49.47 | 53.64 |
| BT, ASCAT-B, SMAP | 40.05 | 43.32 | - | 43.48 |
| ASCAT-B, CYGNSS, SMAP | - | 34.73 | 55.23 | 48.80 |
| Average RMSE over all triplets | 44.2 | 38.3 | 54.3 | 48.6 |
| Number of reports per day | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| % of dataset | 12.1 | 11.1 | 33.7 | 42.6 | 0.52 |
| TD | TS | TY/HU | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wind fields with no R34 values reported | 97% | 81% | 33% |
| Wind fields with at least one R34 value reported that report only 1 quadrant | 74% | 33% | 12% |
| Wind fields with at least one R34 value reported that report 2 quadrants | 12% | 27% | 17% |
| Wind fields with at least one R34 value reported that report 3 quadrants | 9% | 15% | 16% |
| Wind fields with at least one R34 value reported that report all 4 quadrants | 6% | 24% | 54% |
| Wind Speed Range (m/s) | 5–10 m/s | >20 m/s | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % of Samples | 62% | 0.02% | ||||
| Persistence Range | p < −25% | p > −25, p < 25% | p > 25% | p < −25% | p > −25, p < 25% | p > 25% |
| % Samples @Wind Speed 1 (FDS/ERA5 matchup) | 3.27% | 94.88% | 1.85% | 2.93% | 95.38% | 1.69% |
| FDS—ERA5 Bias (m/s) | 2.32 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 9.48 | 2.05 | 1.34 |
| % Samples @Wind Speed 1 (NOAA/ERA5 matchup) | 2.66% | 95.81% | 1.54% | 4.15% | 93.83% | 2.02% |
| NOAA—ERA5 Bias (m/s) | 1.92 | −0.03 | 0.13 | 15.33 | 10.83 | 11.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruf, C.; Al-Khaldi, M.; Asharaf, S.; Balasubramaniam, R.; McKague, D.; Pascual, D.; Russel, A.; Twigg, D.; Warnock, A. Characterization of CYGNSS Ocean Surface Wind Speed Products. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4341. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224341
Ruf C, Al-Khaldi M, Asharaf S, Balasubramaniam R, McKague D, Pascual D, Russel A, Twigg D, Warnock A. Characterization of CYGNSS Ocean Surface Wind Speed Products. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(22):4341. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224341
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuf, Christopher, Mohammad Al-Khaldi, Shakeel Asharaf, Rajeswari Balasubramaniam, Darren McKague, Daniel Pascual, Anthony Russel, Dorina Twigg, and April Warnock. 2024. "Characterization of CYGNSS Ocean Surface Wind Speed Products" Remote Sensing 16, no. 22: 4341. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224341
APA StyleRuf, C., Al-Khaldi, M., Asharaf, S., Balasubramaniam, R., McKague, D., Pascual, D., Russel, A., Twigg, D., & Warnock, A. (2024). Characterization of CYGNSS Ocean Surface Wind Speed Products. Remote Sensing, 16(22), 4341. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224341






