Trajectory PHD and CPHD Filters for the Pulse Doppler Radar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- We derive the recursive equations for PD-TPHD and PD-TCPHD filters. Due to the dimensionality expansion of measurement information, the update process of the TPHD and TCPHD filters is modified. Hence, we establish a new measurement model and rederive the updated formulas for TPHD and TCPHD. The KLD minimization is also required for PD-TPHD and PD-TCPHD filters so that they can propagate the best Poisson multi-trajectory density and IID multi-trajectory density forward, respectively, during the recursive filtering.
- (2)
- Gaussian sequential mixture implementations of PD-TPHD and PD-TCPHD are performed. In the implementations, we model the posterior PHD of trajectories in a Gaussian sequential mixture form. Since the Doppler measurements are incorporated into the TPHD and TCPHD filters as augmented information, the dimension expansion of measurements occurs, so the computational complexity increases inevitably. To address the issue as much as possible, the implementations of the update are divided into two parts. Firstly, we adopt the position measurements to deal with the Gaussian mixture components of the predicted PHD and cardinality. Later on, the Doppler measurements are utilized to update the components. Gaussian sequential mixture filtering is able to obtain a lower computational burden compared to joint filtering while maintaining performance. We hold the fact that the current target states generally have an impact on the trajectory state estimates for recent time steps so that the joint density is propagated in the recent period while the independent density is propagated before this period.
2. Background
2.1. The Relevant Definitions
2.2. Bayesian Filtering Recursion of Trajectory RFS
2.3. TPHD and TCPHD Filters
2.3.1. TPHD Filters
- Each target evolves independently to generate measurements with survival probability and transition probability , and the new targets are born independently.
- The clutter RFS, which belongs to Poisson with density , is independent of the measurements of targets.
- The predicted multi-trajectory RFS governed by the predicted multi-trajectory density represents a Poisson RFS.
2.3.2. TCPHD Filters
- Each target evolves independently to generate measurements with survival probability and transition probability , and the new targets are born independently.
- The clutter RFS, which belongs to the IID cluster with density , is independent of the measurements of targets.
- The predicted multi-trajectory RFS governed by the predicted multi-trajectory density represents an IID cluster RFS.
3. PD-TPHD and PD-TCPHD Filters
3.1. The Model of Measurements
3.2. Updated Step of the PD-TPHD Filter
3.3. Updated Step of the PD-TCPHD Filter
4. Gaussian Sequential Implementations
4.1. Gaussian Sequential Implementation of the PD-TPHD
4.2. Gaussian Sequential Implementation of the PD-TCPHD
| Algorithm 1. The Steps of Pruning and Absorption. |
| Input: The Gaussian components after update steps , . Output: . − and repeat −. - . -, . . . . until . - components with the largest weight are kept. |
4.3. The L-Scan Approximations
4.4. Estimation
5. Simulation Experiments
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Popp, R.L.; Kirubarajan, T.; Pattipati, K.R. Multitarget Multisensor Tracking: Applications and Advances III; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ainsleigh, P.L.; Luginbuhl, T.E.; Willett, P.K. A sequential target existence statistic for joint probabilistic data association. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 57, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Gong, M.G.; Yan, J.K. Cauchy-Schwarz divergence-based set joint probabilistic data association filter for tracking multiple objects in cluttered environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 62, 5100915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, S.S. Multiple hypothesis tracking for multiple target tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2004, 19, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Chen, J.H.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, W.; Xiong, Z.; Yu, J.Y. Iterative multiple hypothesis tracking with tracklet-level association. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 29, 3660–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.Z.; Liu, L.; Bai, X.R.; Zhou, F. A new scatterer trajectory association method for ISAR image sequence utilizing multiple hypothesis tracking algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5103213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, R. Statistical Multisource Multitarget Information Fusion; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mahler, R. Multitarget Bayes filtering via first-order multitarget moments. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 1152–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.-N.; Ma, W.-K. The Gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 4091–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.-N.; Singh, S.; Doucet, A. Sequential Monte Carlo methods for multi-target filtering with random finite sets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2005, 41, 1224–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, R. PHD filters of higher order in target number. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, 43, 1523–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.-N.; Cantoni, A. Analytic implementations of the cardinalized probability hypothesis density filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 3553–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.-A. CPHD filter birth modeling using the probabilistic admissible region. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 54, 1456–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.-T.; Vo, B.-N.; Cantoni, A. The cardinality balanced multi-target multi-Bernoulli filter and its implementations. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.L. An efficient, variational approximation of the best fitting multi-Bernoulli filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.-T.; Vo, B.-N. Labeled random finite sets and multi-object conjugate priors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 3460–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.-N.; Vo, B.-T.; Phung, D. Labeled random finite sets and the Bayes multi-target tracking filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 6554–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Vo, B.-T.; Vo, B.-N.; Dietmayer, K. The labeled multi-Bernoulli filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process 2014, 62, 3245–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, F.; Vo, B.-N.; Vo, B.-T.; Fantacci, C.; Beard, M. Generalized labeled multi-Bernoulli approximation of multi-object densities. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 5487–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, F.C. On implementing 2D rectangular assignment algorithms. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 1679–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.-N.; Vo, B.-T.; Hung, G.H. An efficient implementation of the generalized labeled multi-Bernoulli filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 1975–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.-N.; Vo, B.-T. A multi-scan labeled random finite set model for multi-object state estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 4948–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petetin, Y.; Desbouvries, F. Bayesian multi-object filtering for pairwise Markov chains. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 4481–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieczynski, W.; Desbouvries, F. Kalman Filtering using Pairwise Gaussian Models. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Hong Kong, China, 6 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, C. Cardinalized probability hypothesis density filter based on pairwise Markov chains. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2019, 41, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-H.; Han, C.-Z.; Lian, F.; Zeng, L.-H. Cardinality balanced multi-target multi-Bernoulli filter for pairwise Markov model. Acta Autom. Sin. 2017, 43, 2100–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, R. The pairwise-Markov Bernoulli filter. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 168229–168245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, R. Bernoulli filters for multiple correlated sensors. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 2310–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, L.; Li, H.; Xia, Y. The multiple pairwise Markov chain model-based labeled multi-Bernoulli filter. J. Franklin Inst 2024, 361, 106939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Granstrom, K.; Gao, L.; Battistelli, G.; Kim, S.; Wymeersch, H. 5G mmWave cooperative positioning and mapping using multi-model PHD filter and map fusion. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 3782–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.K.; Fronda, N.; Sukhatme, G.S. Resilience in multirobot multitarget tracking with unknown number of targets through reconfiguration. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2021, 8, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Battistelli, G.; LChisci, L. Random-finite-set-based distributed multirobot SLAM. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2020, 36, 1758–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.C.; Li, G.; He, Y. Distributed GGIW-CPHD-based extended target tracking over a sensor network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Battistelli, G.; Chisci, L. Multiobject fusion with minimum information loss. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Battistelli, G.; Chisci, L.; Wei, P. Distributed joint sensor registration and multitarget tracking via sensor network. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 56, 1301–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.R.; Li, T.C.; Ge, S.J.; Gu, H. Robust CPHD fusion for distributed multitarget tracking using asynchronous sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 22, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, Á.F.; Svensson, L. Trajectory PHD and CPHD filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 5702–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, Á.F. Derivation of the PHD and CPHD filters based on direct Kullback-Leibler divergence minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 5812–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, Á.F.; Svensson, L. Trajectory probability hypothesis density filter. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Information Fusion, Cambridge, UK, 10–13 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- García-Fernández, Á.F.; Svensson, L.; Williams, J.L.; Xia, Y.; Granström, K. Trajectory Poisson Multi-Bernoulli Filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 4933–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, Á.F.; Svensson, L. Tracking Multiple Spawning Targets Using Poisson Multi-Bernoulli Mixtures on Sets of Tree Trajectories. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 1987–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, Á.F.; Ralph, J.; Horridge, P.; Maskell, S. Gaussian trajectory PMBM filter with nonlinear measurements based on posterior linearization. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Information Fusion, Linköping, Sweden, 4 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Musicki, D.; Ellem, R. Efficient and enhanced multi-target tracking with Doppler measurements. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2009, 45, 1400–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Bar-Shalom, Y. Track segment association for GMTI tracks of evasive move-stop-move maneuvering targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 1899–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, R.; Willett, P. Predetection fusion with Doppler measurements and amplitude information. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2012, 37, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.H.; Jiang, J.; Liu, W.J.; Qin, X.; Zhang, W. A sequential converted measurement Kalman filter in the ECEF coordinate system for airborne Doppler radar. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouellette, J.D.; Bounds, W.T.; Dowgiallo, D.J.; Toporkov, J.V.; Hwang, P.A. On the sensitivity of passive multistatic radar amplitude and Doppler measurements to significant wave height. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 19, 3503105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLinden, M.L.W.; Loftus, A.M.; Li, L.; Heymsfield, G.M. Application of nonuniform beam filling Doppler velocity error correction on airborne radar measurements. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 19, 3509905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Bae, S.H.; Shin, V. Joint initialization and tracking of multiple moving objects using doppler information. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 3447–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurav, S.; Yimin, D.Z.; Moeness, G.A.; Braham, H. Group sparsity based multi-target tracking in passive multi-static radar systems using doppler-only measurements. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 3619–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesco, P. Multi-sensor δ—GLMB filter for multi-target tracking using Doppler only measurements. In Proceedings of the European Intelligence and Security informatics Conference, Manchester, UK, 7–9 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.H.; Jiang, J.; Liu, W.J.; Feng, X.; Gao, L.; Qin, X. Augmented state GM-PHD filter with registration errors for multi-target tracking by Doppler radars. Signal Process. 2016, 120, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.Y.; Jiang, L.B.; Yang, Q.W.; Zhao, Y.J.; Wang, Z. Adaptive PHD filter with RCS and Doppler feature for space targets tracking via space-based radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 3750–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Zhao, T.Z.; Wu, W.H.; Lu, M.L.; Xiong, L. The multi-target tracking algorithm based on the MM-GLMB filter with Doppler information. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Robotics, Control and Automation Engineering, Wuhan, China, 4–6 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- García-Fernández, Á.F.; Rahmathullah, A.S.; Svensson, L. A metric on the space of finite sets of trajectories for evaluation of multi-target tracking algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 3917–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

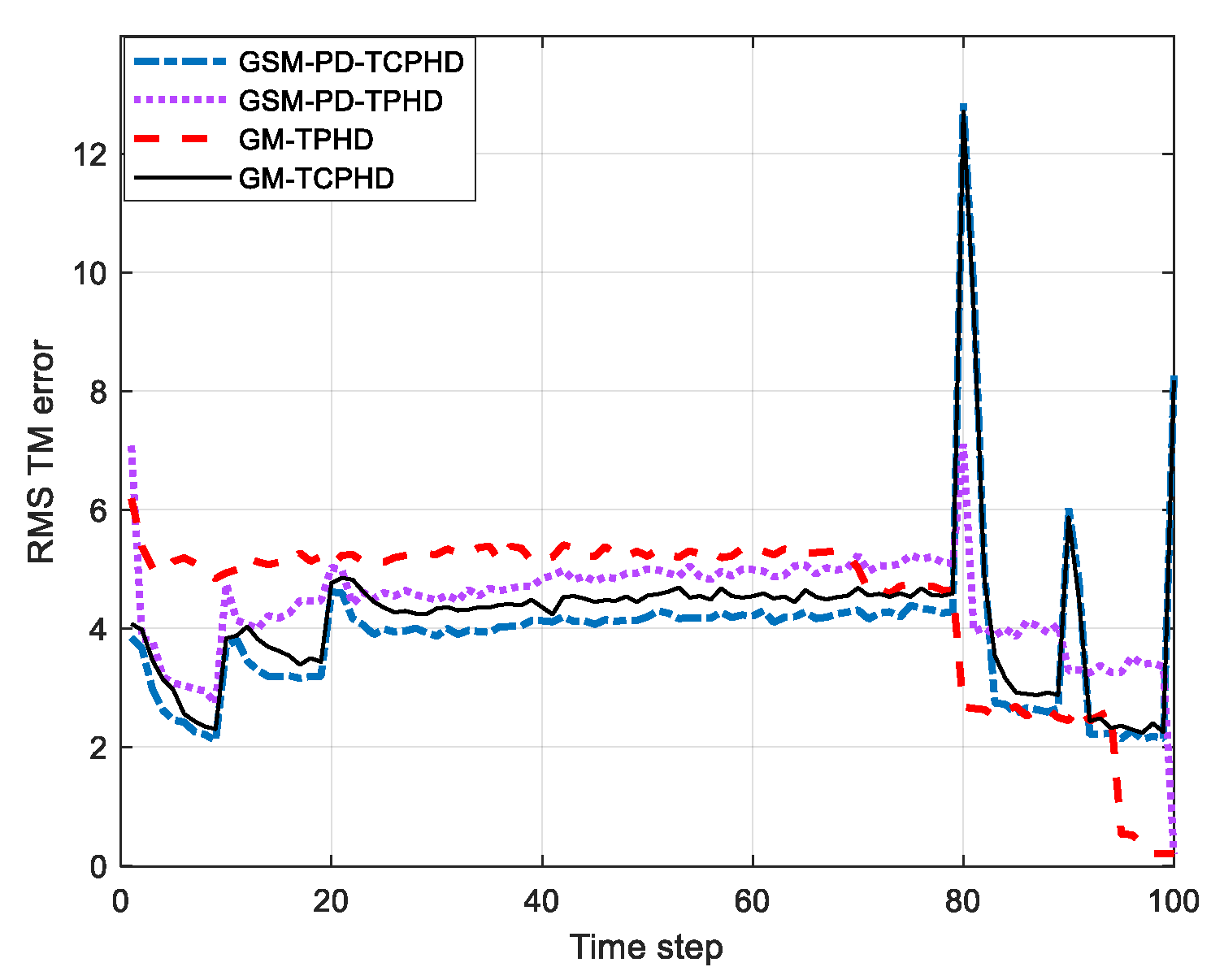


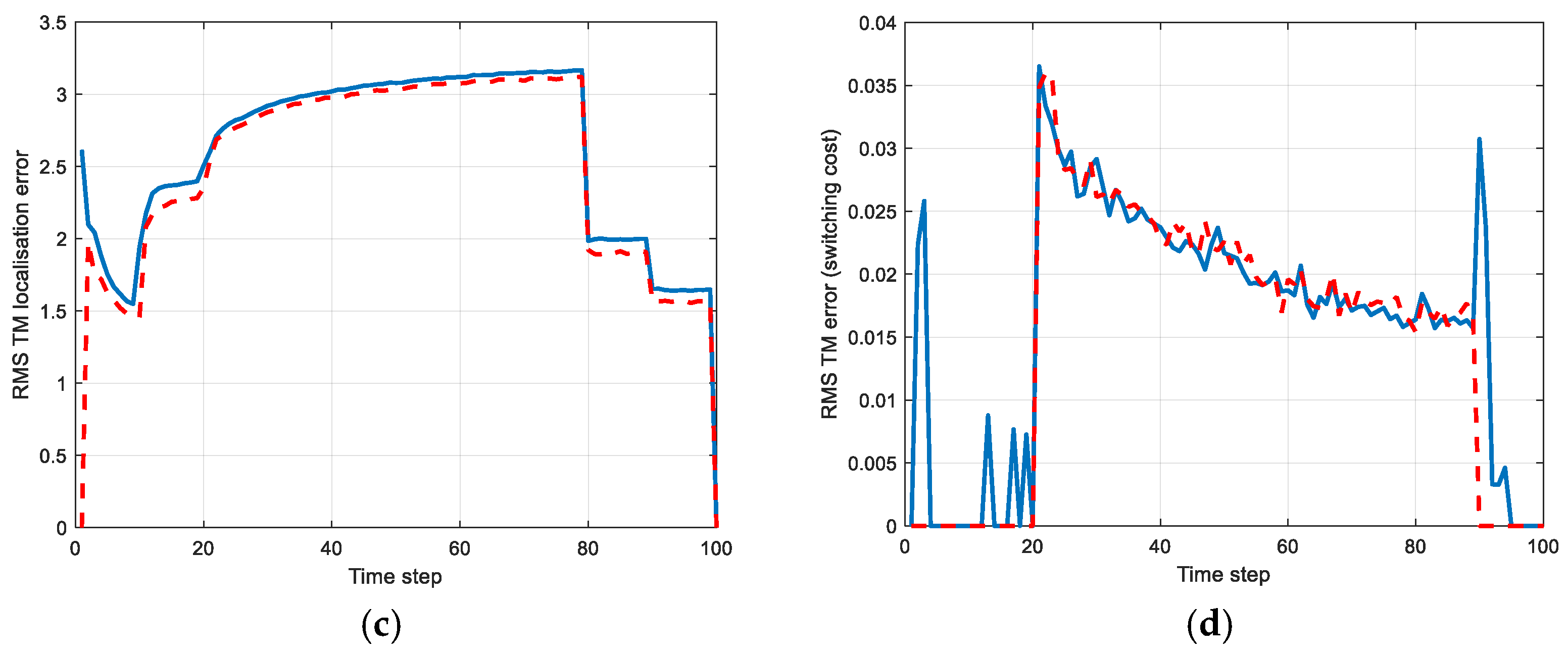
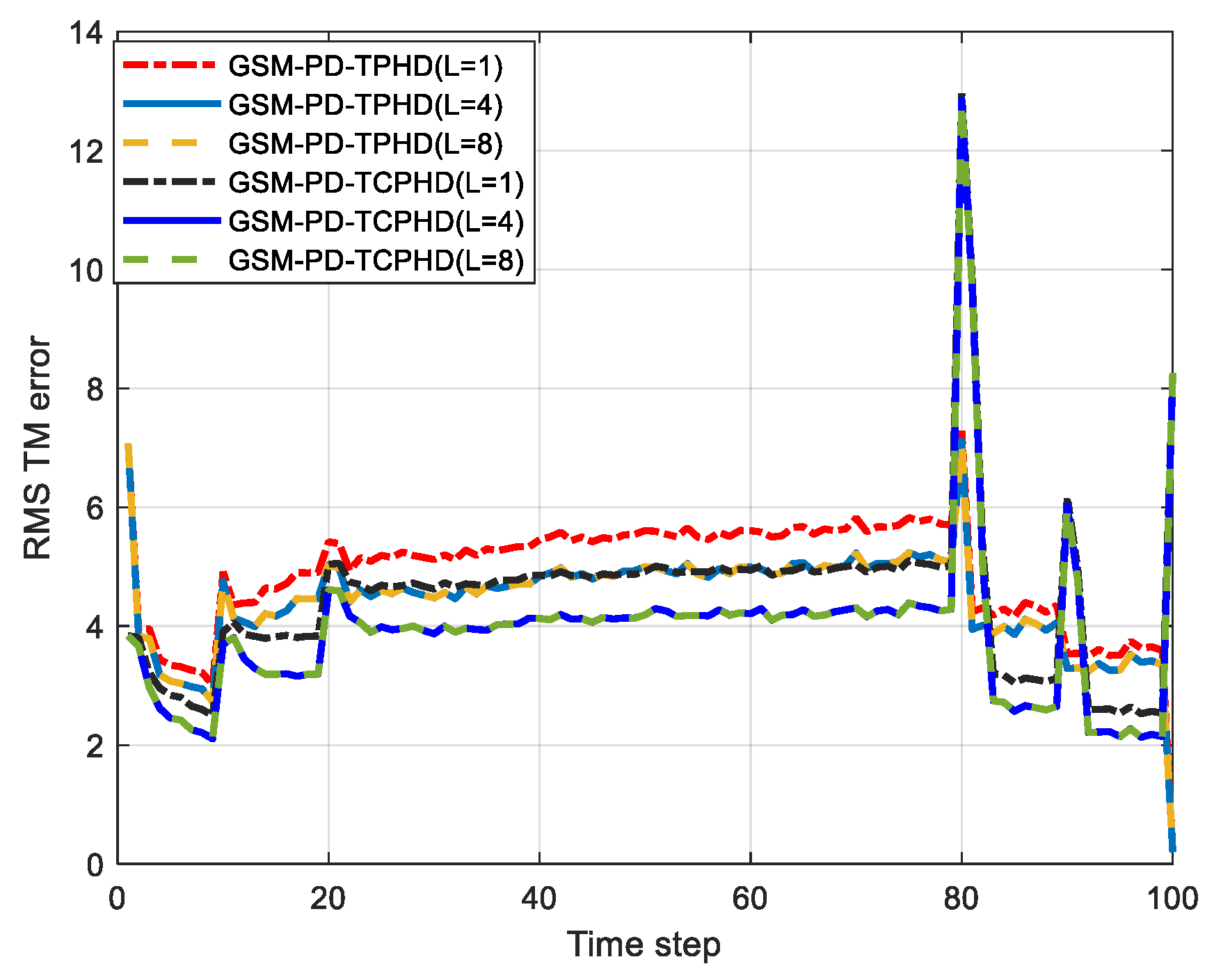
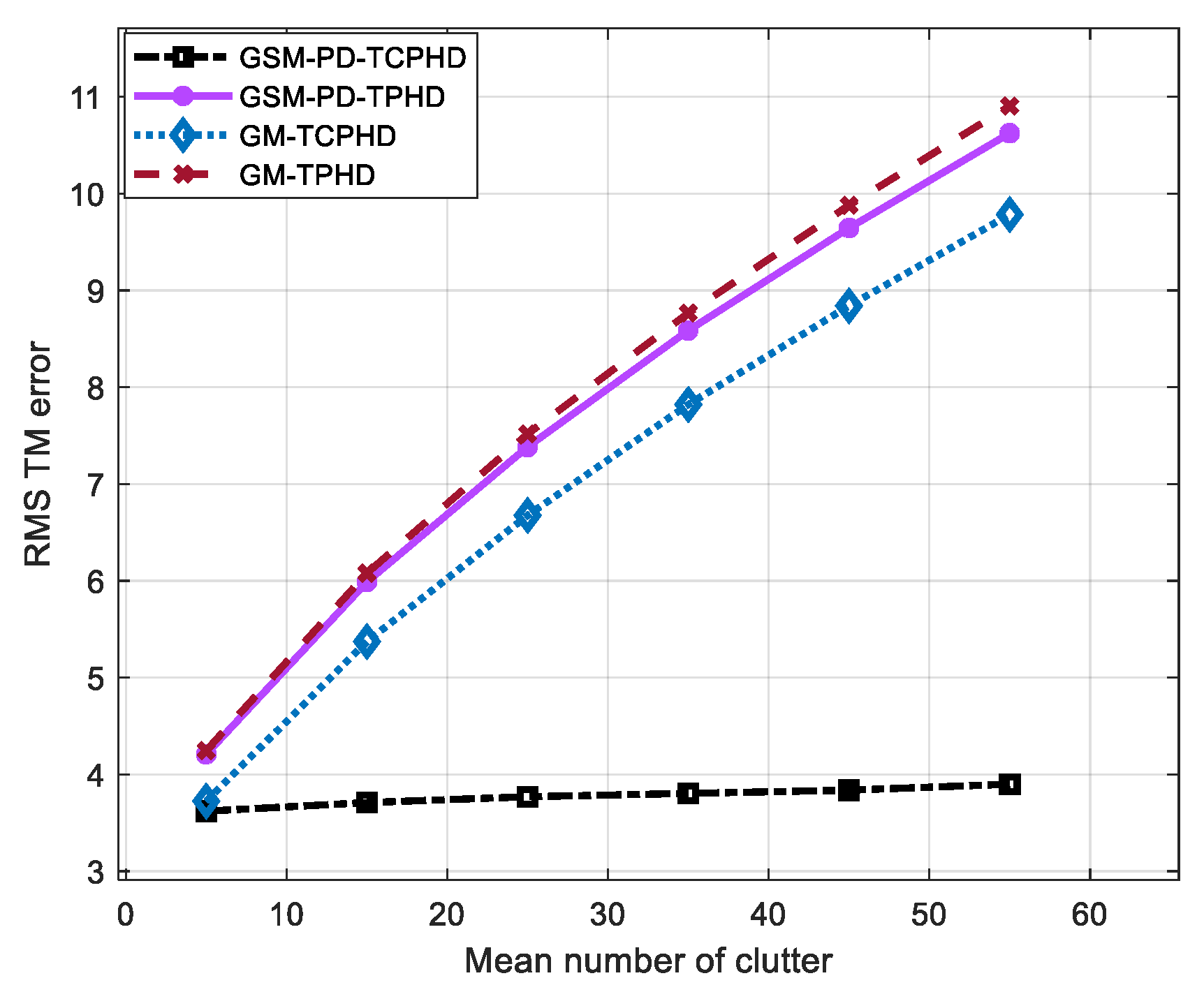
| Birth Time/s | Death Time/s | Initial States | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target 1 | 1 | 80 | |
| Target 2 | 10 | 80 | |
| Target 3 | 10 | 80 | |
| Target 4 | 10 | 80 | |
| Target 5 | 20 | 100 | |
| Target 6 | 20 | 100 | |
| Target 7 | 20 | 90 |
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 15 | 30 | |
| PD-TPHD | 1.85 | 1.93 | 2.09 | 2.52 | 3.66 | 8.05 |
| PD-TCPHD | 2.21 | 2.31 | 2.52 | 3.11 | 4.33 | 9.55 |
| TPHD | 1.47 | 1.53 | 1.68 | 1.81 | 2.51 | 5.26 |
| TCPHD | 1.78 | 1.83 | 1.97 | 2.26 | 2.83 | 5.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, B. Trajectory PHD and CPHD Filters for the Pulse Doppler Radar. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244671
Zhang M, Zhao Y, Niu B. Trajectory PHD and CPHD Filters for the Pulse Doppler Radar. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(24):4671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244671
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Mei, Yongbo Zhao, and Ben Niu. 2024. "Trajectory PHD and CPHD Filters for the Pulse Doppler Radar" Remote Sensing 16, no. 24: 4671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244671
APA StyleZhang, M., Zhao, Y., & Niu, B. (2024). Trajectory PHD and CPHD Filters for the Pulse Doppler Radar. Remote Sensing, 16(24), 4671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244671






