Toward a More Robust Estimation of Forest Biomass Carbon Stock and Carbon Sink in Mountainous Region: A Case Study in Tibet, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data Collection
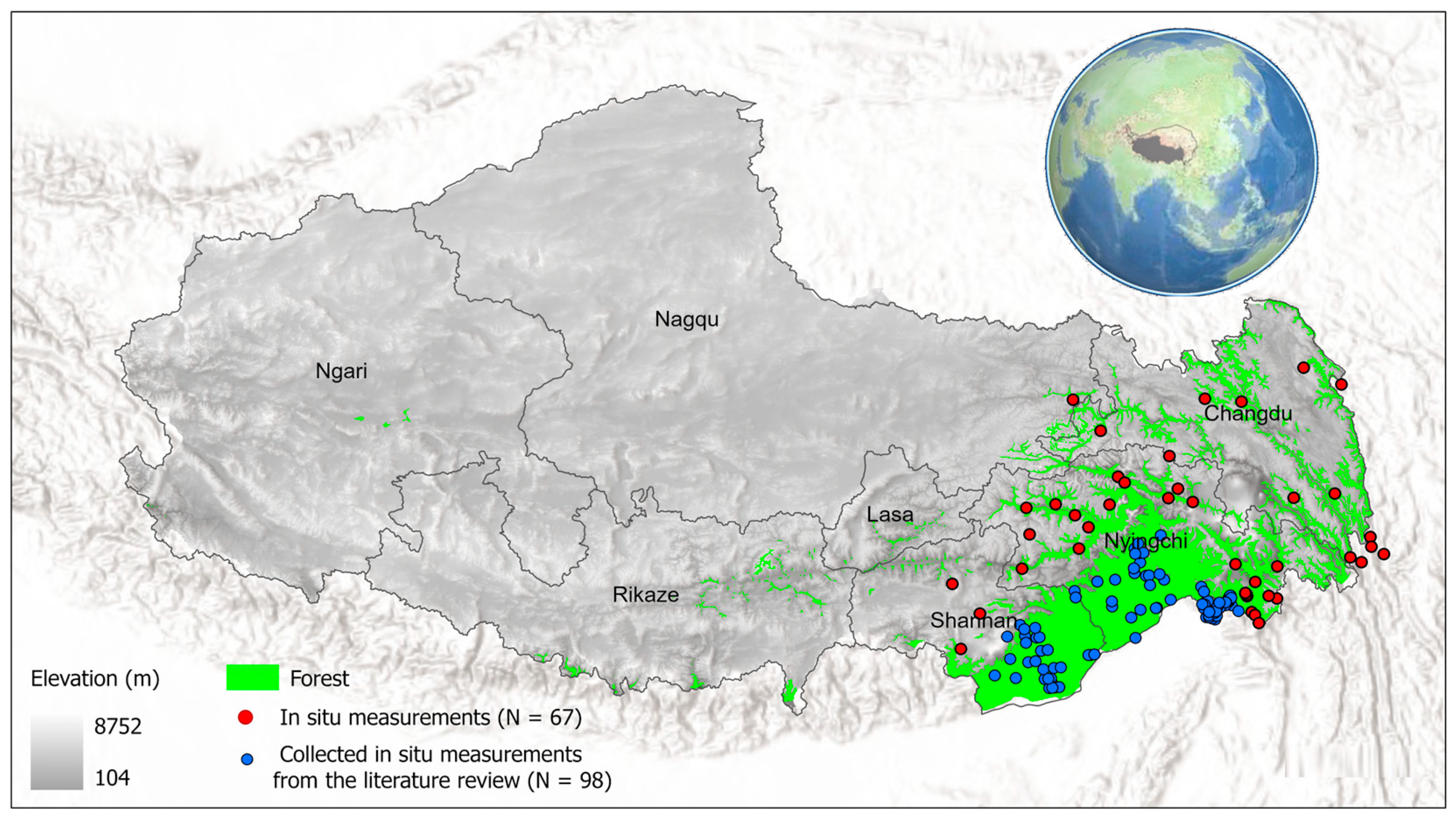
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Forest Inventory Data
2.3. Microwave Remote Sensing Images
2.4. Optical Remote Sensing Image
3. Method
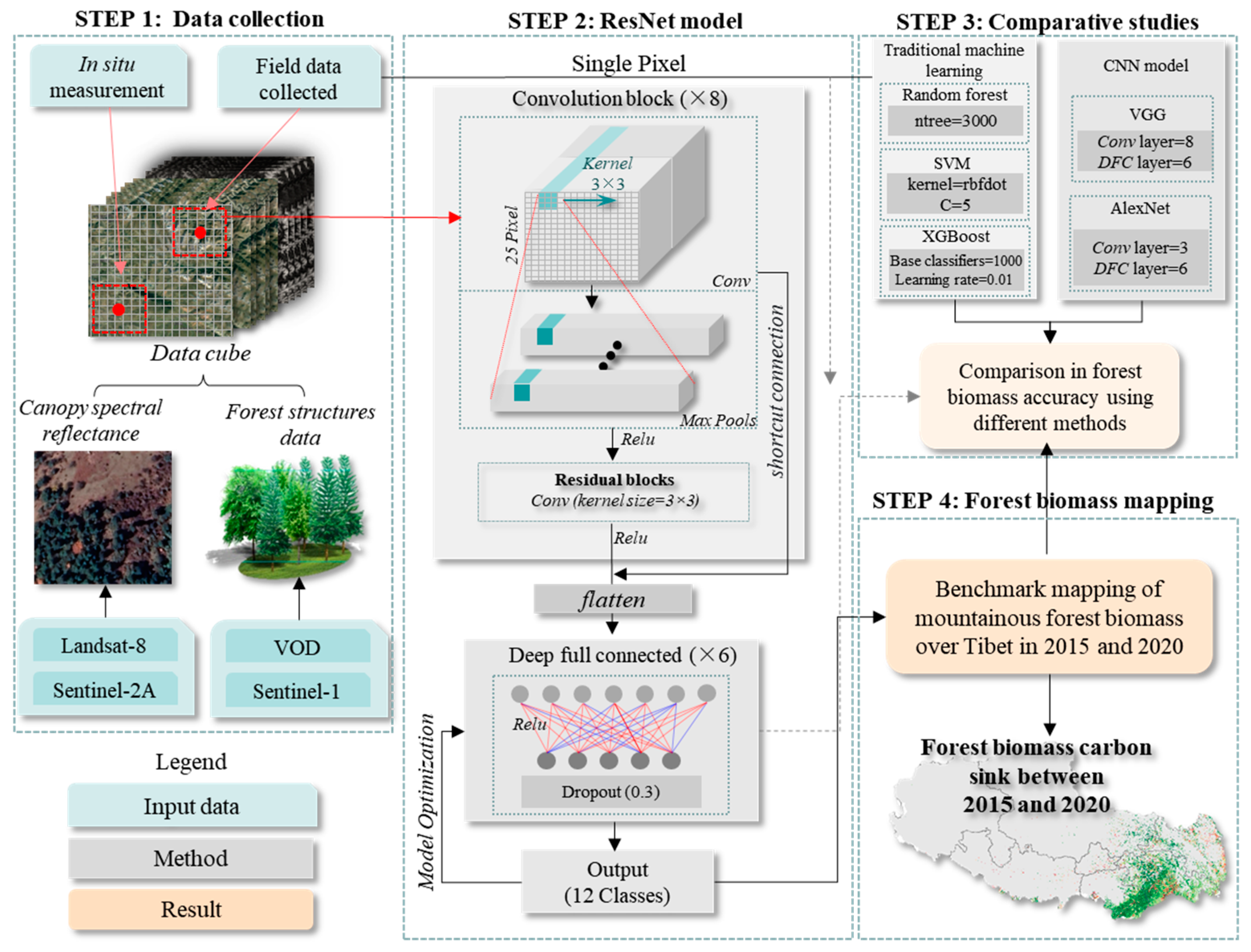
3.1. ResNet CNN Model
3.2. Other Machine Learning
3.3. Validation and Accuracy Assessment
4. Result and Discussion
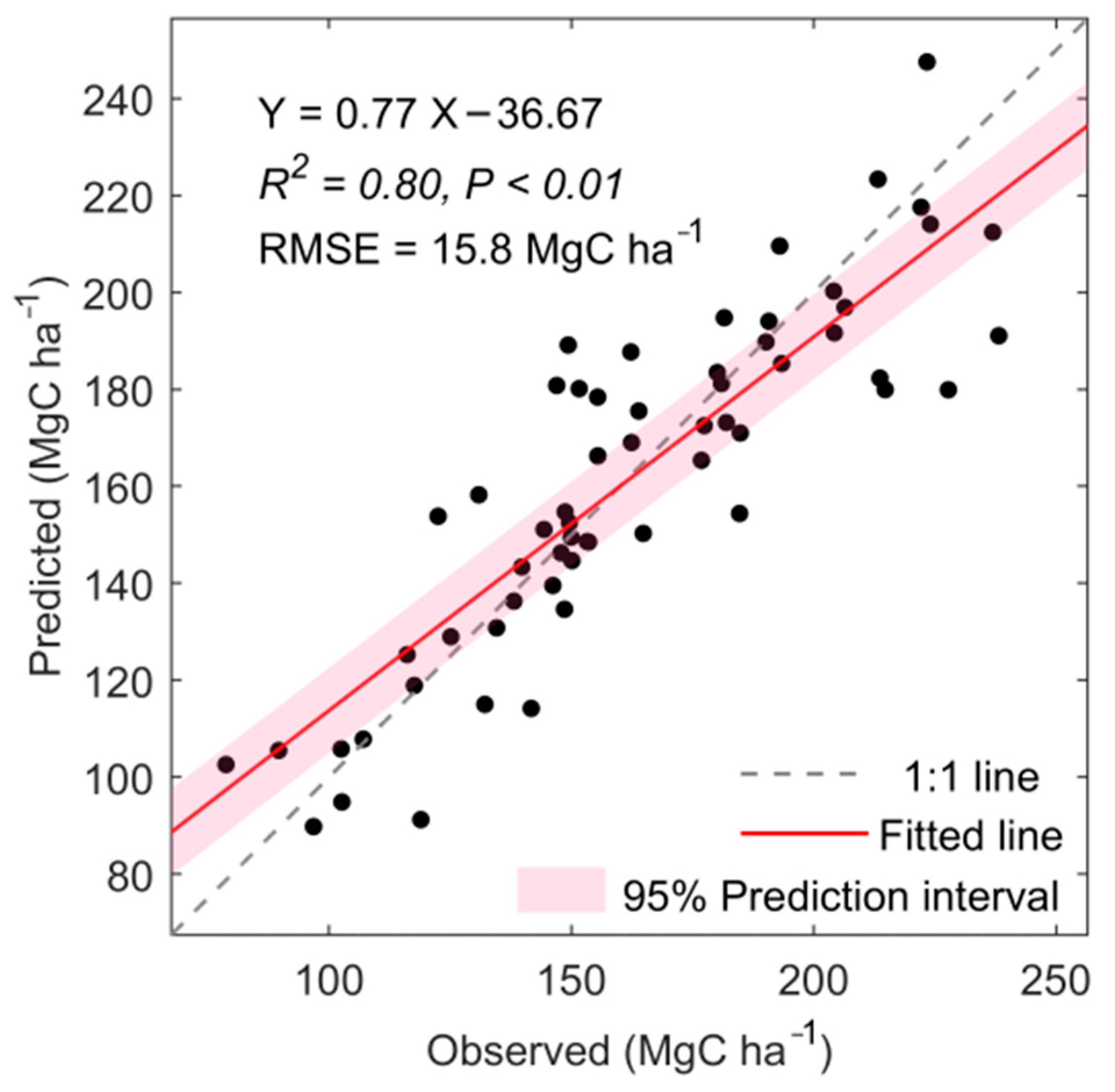
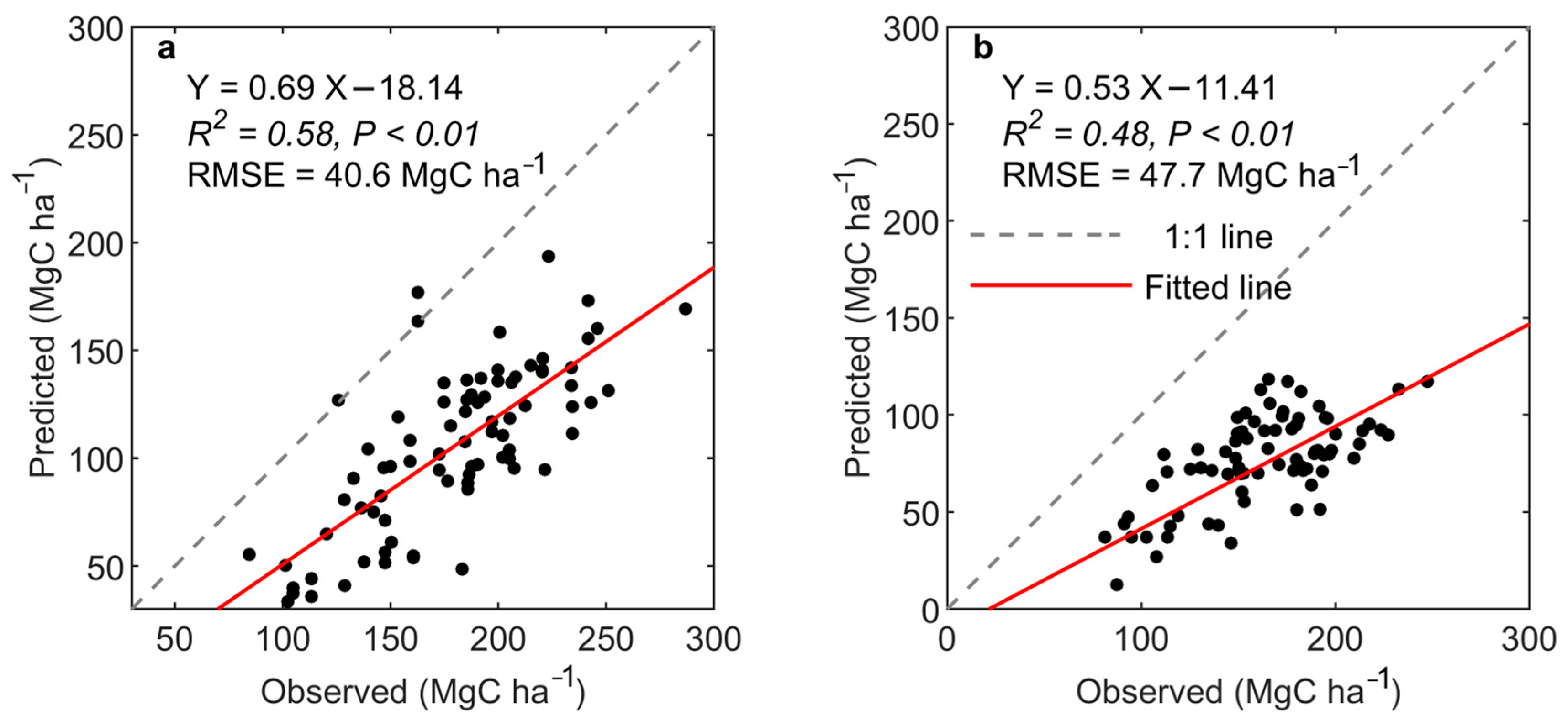
4.1. Validation of Mountain Forest Biomass Mapping
4.2. Comparative Studies
4.2.1. Comparison in Different Field Sampling Strategies
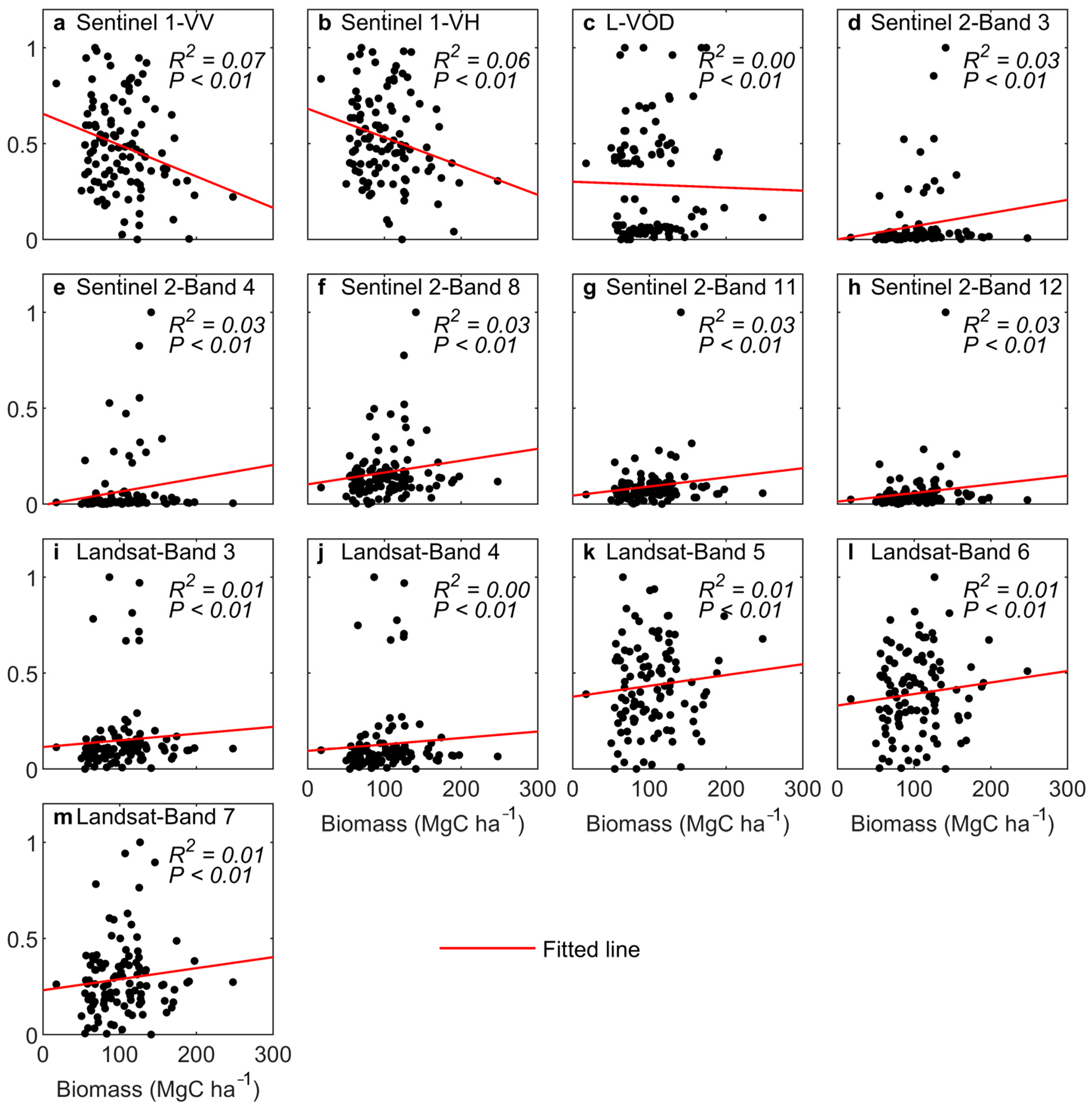
4.2.2. Comparison of Different Sources of Remote Sensing Data
4.2.3. Comparison with Pixel-Based Method
4.2.4. Comparison with Other Advanced Deep Learning Methods
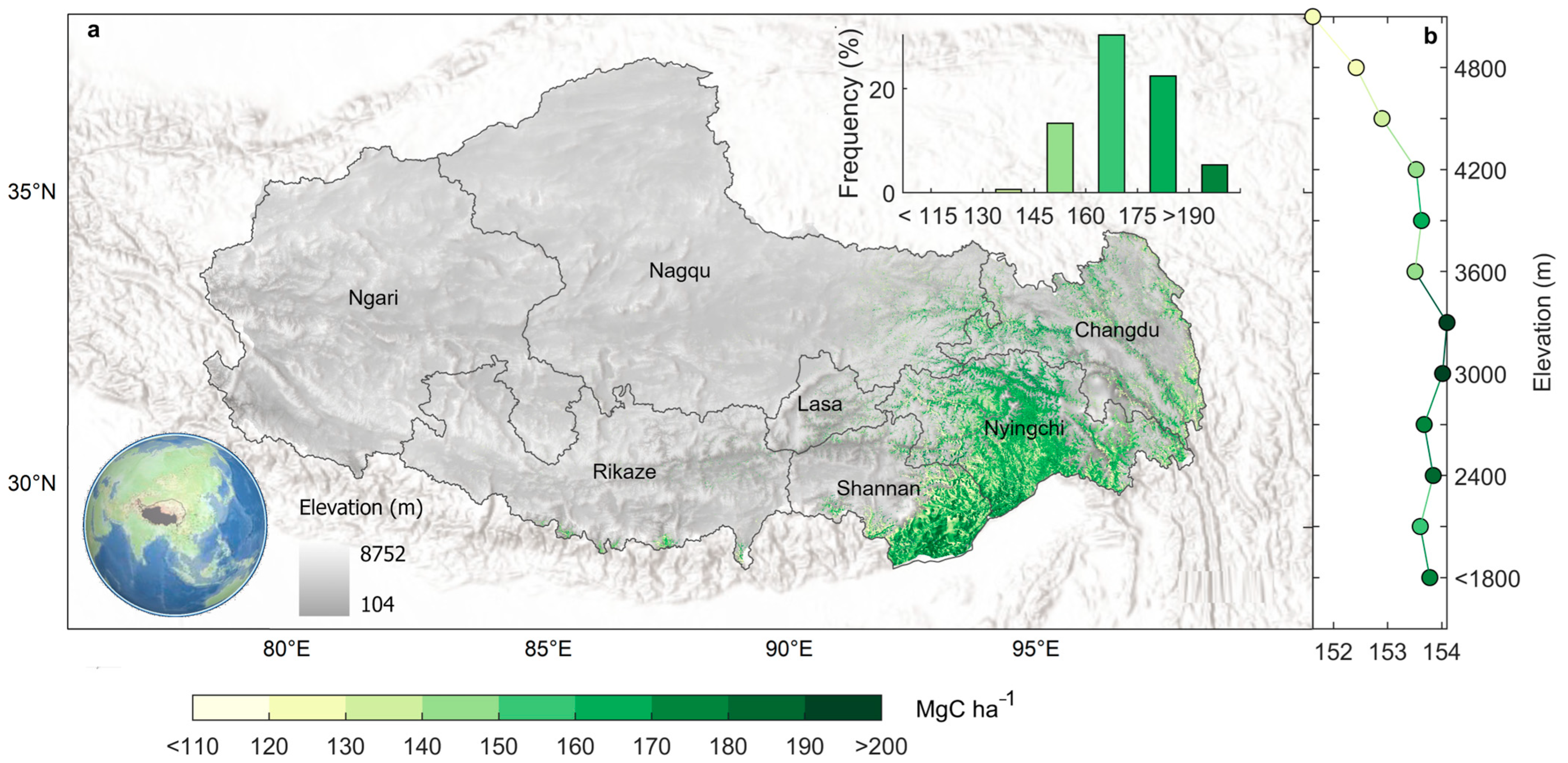
4.3. Benchmark Mapping of Mountainous Forest Biomass over Tibet
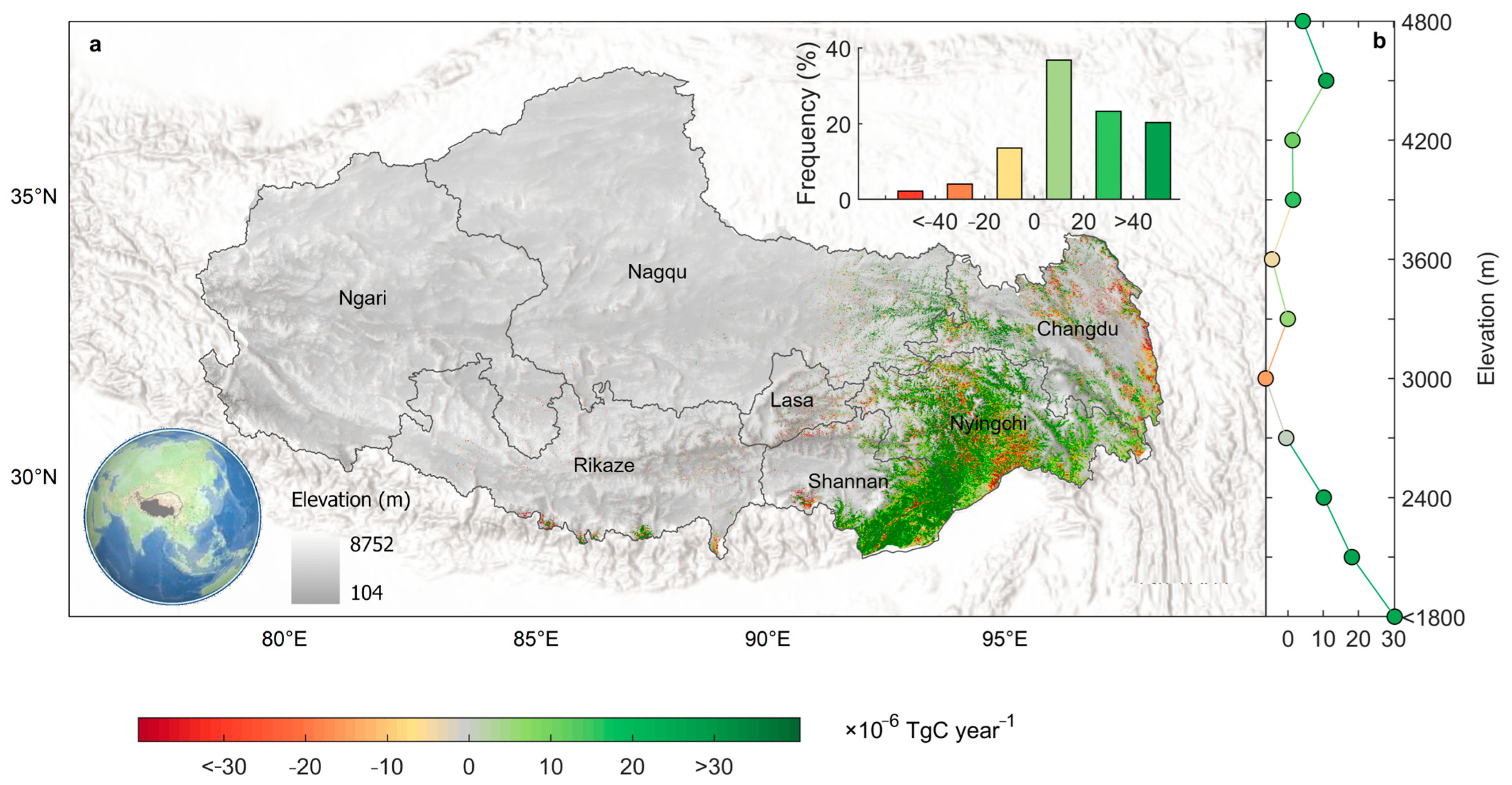
4.4. Forest Biomass Carbon Sink over Tibet
4.5. Limitation and Perspective
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Price, M.F.; Gratzer, G.; Duguma, L.A.; Kohler, T.; Maselli, D.; Romeo, R. Mountain Forests in a Changing World: Realizing Values, Adressing Challenges; FAO/SDC: Rome, Italy, 2011; pp. 1–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Sun, W.; Chang, J.; Zhu, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fang, J.; et al. Terrestrial carbon sinks in China and around the world and their contribution to carbon neutrality. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 861–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, S.; Yue, C.; Ding, J.; Guo, Z. Perspectives on the role of terrestrial ecosystems in the ‘carbon neutrality’strategy. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Birdsey, R.A.; Fang, J.; Houghton, R.; Kauppi, P.E.; Kurz, W.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Shvidenko, A.; Lewis, S.L.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. A Large and Persistent Carbon Sink in the World’s Forests. Science 2011, 333, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonan, G.B. Forests and climate change: Forcings, feedbacks, and the climate benefits of forests. Science 2008, 320, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diogo, I.J.S.; dos Santos, K.; da Costa, I.R.; dos Santos, F.A.M. Effects of topography and climate on Neotropical mountain forests structure in the semiarid region. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2021, 24, e12527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, S.; Chen, J.C.; Chen, C.T.; Jump, A.S. Strong topographic sheltering effects lead to spatially complex treeline advance and increased forest density in a subtropical mountain region. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 3756–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; De Jeu, R.A.M.; Canadell, J.G.; Mccabe, M.F.; Evans, J.P.; Wang, G. Recent reversal in loss of global terrestrial biomass. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, M.; Boyd, D.S.; Foody, G.M.; Vetrivel, A. Estimating tropical forest biomass with a combination of SAR image texture and Landsat TM data: An assessment of predictions between regions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 70, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepaschenko, D.; Shvidenko, A.; Usoltsev, V.; Lakyda, P.; Luo, Y.; Vasylyshyn, R.; Lakyda, I.; Myklush, Y.; See, L.; McCallum, I.; et al. A dataset of forest biomass structure for Eurasia. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, C.; Donoghue, M.; Fabbro, T.; Häuse, C.; Nogués-Bravo, D.; Arroyo, M.T.K.; Soberon, J.; Speers, L.; Spehn, E.M.; Sun, H.; et al. Creative use of mountain biodiversity databases: The Kazbegi research agenda of GMBA-DIVERSITAS. Mt. Res. Dev. 2007, 27, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wang, A.; Liang, S.; Zhou, W. Eco-environmental vulnerability evaluation in mountainous region using remote sensing and GIS—A case study in the upper reaches of Minjiang River, China. Ecol. Model. 2006, 192, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, A. An adjusted two-leaf light use efficiency model for improving GPP simulations over mountainous areas. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Li, A.; Lei, G.; Zhang, Z.; Nan, X. Global high-resolution mountain green cover index mapping based on Landsat images and Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 162, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, A. Development of a topographic-corrected temperature and greenness model (TG) for improving GPP estimation over mountainous areas. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 295, 108193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkuor, G.; Zoungrana, J.B.B.; Dimobe, K.; Ouattara, B.; Vadrevu, K.P.; Tondoh, J.E. Above-ground biomass mapping in West African dryland forest using Sentinel-1 and 2 datasets-A case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, S.; Srinet, R.; Padalia, H. Mapping forest height and aboveground biomass by integrating ICESat-2, Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data using Random Forest algorithm in northwest Himalayan foothills of India. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiche, J.; Mullissa, A.; Slagter, B.; Gou, Y.; Tsendbazar, N.-E.; Odongo-Braun, C.; Vollrath, A.; Weisse, M.J.; Stolle, F.; Pickens, A.; et al. Forest disturbance alerts for the Congo Basin using Sentinel-1. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 024005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Lu, D.; Wang, G.; Wu, C.; Huang, Y.; Yu, S. Examining Spectral Reflectance Saturation in Landsat Imagery and Corresponding Solutions to Improve Forest Aboveground Biomass Estimation. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serrano, P.M.; Cárdenas Domínguez, J.L.; Corral-Rivas, J.J.; Jiménez, E.; López-Sánchez, C.A.; Vega-Nieva, D.J. Modeling of aboveground biomass with Landsat 8 OLI and machine learning in temperate forests. Forests 2019, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Li, C.; Liu, Z. Forest aboveground biomass estimation using Landsat 8 and Sentinel-1A data with machine learning algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Jeganathan, C.; Sharma, L.K.; Nathawat, M.S. A review of radar remote sensing for biomass estimation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 1779–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.; Wagner, J.; Hochschild, V. Above-ground biomass estimates based on active and passive microwave sensor imagery in low-biomass savanna ecosystems. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 046027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Saatchi, S.S.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Pongratz, J.; Bloom, A.A.; Bowman, K.; Worden, J.; Liu, J.; Yin, Y.; et al. Changes in global terrestrial live biomass over the 21st century. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleason, C.J.; Im, J. Forest biomass estimation from airborne LiDAR data using machine learning approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 125, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchard, E.T.A.; Saatchi, S.S.; Woodhouse, I.H.; Nangendo, G.; Ribeiro, N.S.; Williams, M.; Ryan, C.M.; Lewis, S.L.; Feldpausch, T.R.; Meir, P. Using satellite radar backscatter to predict above-ground woody biomass: A consistent relationship across four different African landscapes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostan, F.; Riegger, S.; Pitz, W.; Torre, A.; Torres, R. The C-SAR instrument for the GMES sentinel-1 mission. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 215–218. [Google Scholar]
- Sonobe, R. Combining ASNARO-2 XSAR HH and Sentinel-1 C-SAR VH/VV polarization data for improved crop mapping. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.M.; Behera, M.D. Aboveground biomass estimation using multi-sensor data synergy and machine learning algorithms in a dense tropical forest. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 96, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, E.; Paloscia, S.; Pettinato, S.; Fontanelli, G.; Mura, M.; Zolli, C.; Maselli, F.; Chiesi, M.; Bottai, L.; Chirici, G. The potential of multifrequency SAR images for estimating forest biomass in Mediterranean areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 200, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, A.; Lohberger, S.; Staengel, M.; Siegert, F. SAR-Based Estimation of Above-Ground Biomass and Its Changes in Tropical Forests of Kalimantan Using L- and C-Band. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Brandt, M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Verger, A.; Tagesson, T.; Diouf, A.A.; Rasmussen, K.; Mbow, C.; Wang, Y.; Fensholt, R. Remote sensing of vegetation dynamics in drylands: Evaluating vegetation optical depth (VOD) using AVHRR NDVI and in-situ green biomass data over West African Sahel. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fan, L.; Frappart, F.; Ciais, P.; Sun, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Moisy, C.; Wigneron, J.-P. An alternative AMSR2 vegetation optical depth for monitoring vegetation at large scales. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 263, 112556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, N.J.; Mialon, A.; Mermoz, S.; Bouvet, A.; Richaume, P.; Al Bitar, A.; Al-Yaari, A.; Brandt, M.; Kaminski, T.; Le Toan, T.; et al. An evaluation of SMOS L-band vegetation optical depth (L-VOD) data sets: High sensitivity of L-VOD to above-ground biomass in Africa. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 4627–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Ciais, P.; Chave, J.; Brandt, M.; Fensholt, R.; Saatchi, S.S.; Bastos, A.; Al-Yaari, A.; Hufkens, K.; et al. Satellite-observed pantropical carbon dynamics. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigneron, J.P.; Fan, L.; Ciais, P.; Bastos, A.; Brandt, M.; Chave, J.; Saatchi, S.; Baccini, A.; Fensholt, R. Tropical forests did not recover from the strong 2015–2016 El Niño event. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Y.; Tian, F.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Tagesson, T.; Du, J.; Brandt, M.; Liu, Y.; Zou, L.; Kimball, J.S.; Fensholt, R. Reliability of using vegetation optical depth for estimating decadal and interannual carbon dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 285, 113390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konings, A.G.; Saatchi, S.S.; Frankenberg, C.; Keller, M.; Leshyk, V.; Anderegg, W.R.L.; Humphrey, V.; Matheny, A.M.; Trugman, A.; Sack, L.; et al. Detecting forest response to droughts with global observations of vegetation water content. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 6005–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtzman, N.M.; Anderegg, L.D.L.; Kraatz, S.; Mavrovic, A.; Sonnentag, O.; Pappas, C.; Cosh, M.H.; Langlois, A.; Lakhankar, T.; Tesser, D.; et al. L-band vegetation optical depth as an indicator of plant water potential in a temperate deciduous forest stand. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Wei, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, L.; Luo, X.; Shi, Y.; Pei, X.; Lei, N.; Song, C.; Li, J.; et al. Machine learning-based estimates of aboveground biomass of subalpine forests using Landsat 8 OLI and Sentinel-2B images in the Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve, Eastern Tibet Plateau. J. For. Res. 2022, 33, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, P.; Xiong, Q.; Lu, H.; Lai, C.; Axmacher, J.C. Mountain forest biomass dynamics and its drivers in southwestern China between 1979 and 2017. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xin, C.; Xiang, H. Large Earthquake Magnitude Prediction In Taiwan Based On Deep Learning Neural Network. Neural Netw. World 2018, 28, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Fan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lin, X.; Chang, J. Forest type and height are important in shaping the altitudinal change of radial growth response to climate change. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Hu, L.; Zhou, H. Deep learning based multi-temporal crop classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattenborn, T.; Leitloff, J.; Schiefer, F.; Hinz, S. Review on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in vegetation remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ran, F.; Chang, R.; Yang, Y.; Luo, J.; Fan, J. Variations in the live biomass and carbon pools of Abies georgei along an elevation gradient on the Tibetan Plateau, China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 329, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, G.; Huang, M.; Chang, R.; Ran, F. Forest biomass carbon stocks and variation in Tibet’s carbon-dense forests from 2001 to 2050. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H. The Tropical Forests of Southern China and Conservation of Biodiversity. Bot. Rev. 2017, 83, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ciais, P.; Guenet, B.; Peng, S.; Chang, J.; Chaplot, V.; Khudyaev, S.; Peregon, A.; Piao, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Temporal response of soil organic carbon after grassland-related land-use change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 4731–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Barham, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; Ghemawat, S.; Irving, G.; Isard, M.; et al. TensorFlow: A system for large-scale machine learning. In Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 16), Savannah, GA, USA, 2–4 November 2016; Volume 16, pp. 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Del Moral, P.; Doucet, A.; Jasra, A. On adaptive resampling strategies for sequential Monte Carlo methods. Bernoulli 2012, 18, 252–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartold, M.; Kluczek, M. A Machine Learning Approach for Mapping Chlorophyll Fluorescence at Inland Wetlands. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Lv, G.; Ren, S.; Ding, J.; Chen, B.; Qu, J.; Wang, Y.; Piao, S. The current and future of terrestrial carbon balance over the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 66, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spawn, S.A.; Sullivan, C.C.; Lark, T.J.; Gibbs, H.K. Harmonized global maps of above and belowground biomass carbon density in the year 2010. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruehr, S.; Keenan, T.F.; Williams, C.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, X.; Bastos, A.; Canadell, J.G.; Prentice, I.C.; Sitch, S.; Terrer, C. Evidence and attribution of the enhanced land carbon sink. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 518–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Lian, X.; Huang, K.; He, M.; Zhao, C.; Liu, D. Socioeconomic and Environmental Changes in Global Drylands. In Dryland Social-Ecological Systems in Changing Environments; Springer: Singapore, 2014; pp. 161–201. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Feng, C.; Liu, F.; Li, J. Biodiversity conservation in China: A review of recent studies and practices. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2020, 2, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, J.; Shen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, A.; Wang, S.; Liang, E.; Piao, S. Enhanced habitat loss of the Himalayan endemic flora driven by warming-forced upslope tree expansion. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 6, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Multi-Source Remote Sensing Dataset | Band | Description | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel 1 | VV | Vertical transmit–Vertical receive | 10 m |
| VH | Vertical transmit–Horizontal receive | ||
| VOD SMOS-ICV2-RE06 | L-VOD | VOD | 0.25° |
| Sentinel-2A | Band 3 | Green | 10 m |
| Band 4 | Red | ||
| Band 8 | Near-infrared | ||
| Band 11 | Shortwave infrared | ||
| Band 12 | Shortwave infrared | ||
| Landsat 8 OLI | Band 3 | Green | 30 m |
| Band 4 | Red | ||
| Band 5 | Near-infrared | ||
| Band 6 | Shortwave infrared | ||
| Band 7 | Shortwave infrared |
| R2 | RMSE (MgC ha−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| Elevation gradient sampling (Total, N = 67) | 0.63 | 22.4 |
| Traditional random sampling (N = 98) | 0.53 | 24.6 |
| Elevation gradient sampling (interval = 200 m, N = 32) | 0.59 | 23.9 |
| Elevation gradient sampling (interval = 300 m, N = 19) | 0.56 | 24.7 |
| Elevation gradient sampling (interval = 500 m, N = 12) | 0.51 | 24.8 |
| Features | R2 | RMSE (MgC ha−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-2A + Landsat OLI | 0.65 | 23.3 |
| Sentinel-1 | 0.57 | 28.7 |
| Sentinel-2A + Landsat OLI + Sentinel-1 | 0.78 | 18.1 |
| Sentinel-2A + Landsat OLI + Sentinel-1 + VOD | 0.80 | 15.8 |
| Algorithm | R2 | RMSE (MgC ha−1) |
|---|---|---|
| ResNet | 0.80 | 15.8 |
| DNN | 0.68 | 24.1 |
| XGBoost | 0.66 | 23.3 |
| RF | 0.59 | 29.3 |
| SVM | 0.56 | 30.4 |
| Algorithm | R2 | RMSE (MgC ha−1) |
|---|---|---|
| ResNet | 0.80 | 15.8 |
| VGG | 0.74 | 18.2 |
| AlexNet | 0.70 | 21.1 |
| Biomass (MgC ha−1) | Carbon Stocks (PgC) | Carbon Sink (TgC year−1) | Method | Data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study | 162.6 | 5.10 | 3.35 | ResNet | Sentinel-2A Landsat OLI Sentinel-1 VOD |
| Liu et al. [8] | 40.0 | 0.01 | 0.0068 | The empirical relationship of convert VOD to aboveground biomass carbon | VOD |
| Xu et al. [24] | 102.9 | 0.7 | 1.19 | Random forest | GLAS MODIS QuikSCAT WorldClim SRTM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, G.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Xu, J.; Li, S.; Cui, G.; Huang, H. Toward a More Robust Estimation of Forest Biomass Carbon Stock and Carbon Sink in Mountainous Region: A Case Study in Tibet, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091481
Lyu G, Wang X, Huang X, Xu J, Li S, Cui G, Huang H. Toward a More Robust Estimation of Forest Biomass Carbon Stock and Carbon Sink in Mountainous Region: A Case Study in Tibet, China. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(9):1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091481
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Guanting, Xiaoyi Wang, Xieqin Huang, Jinfeng Xu, Siyu Li, Guishan Cui, and Huabing Huang. 2024. "Toward a More Robust Estimation of Forest Biomass Carbon Stock and Carbon Sink in Mountainous Region: A Case Study in Tibet, China" Remote Sensing 16, no. 9: 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091481







