Assessing the Air Quality Impact of Train Operation at Tokyo Metro Shibuya Station from Portable Sensor Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measurement Device
2.2. Description of the Measurement Site and Measurement Setup
2.3. Parameter Selection
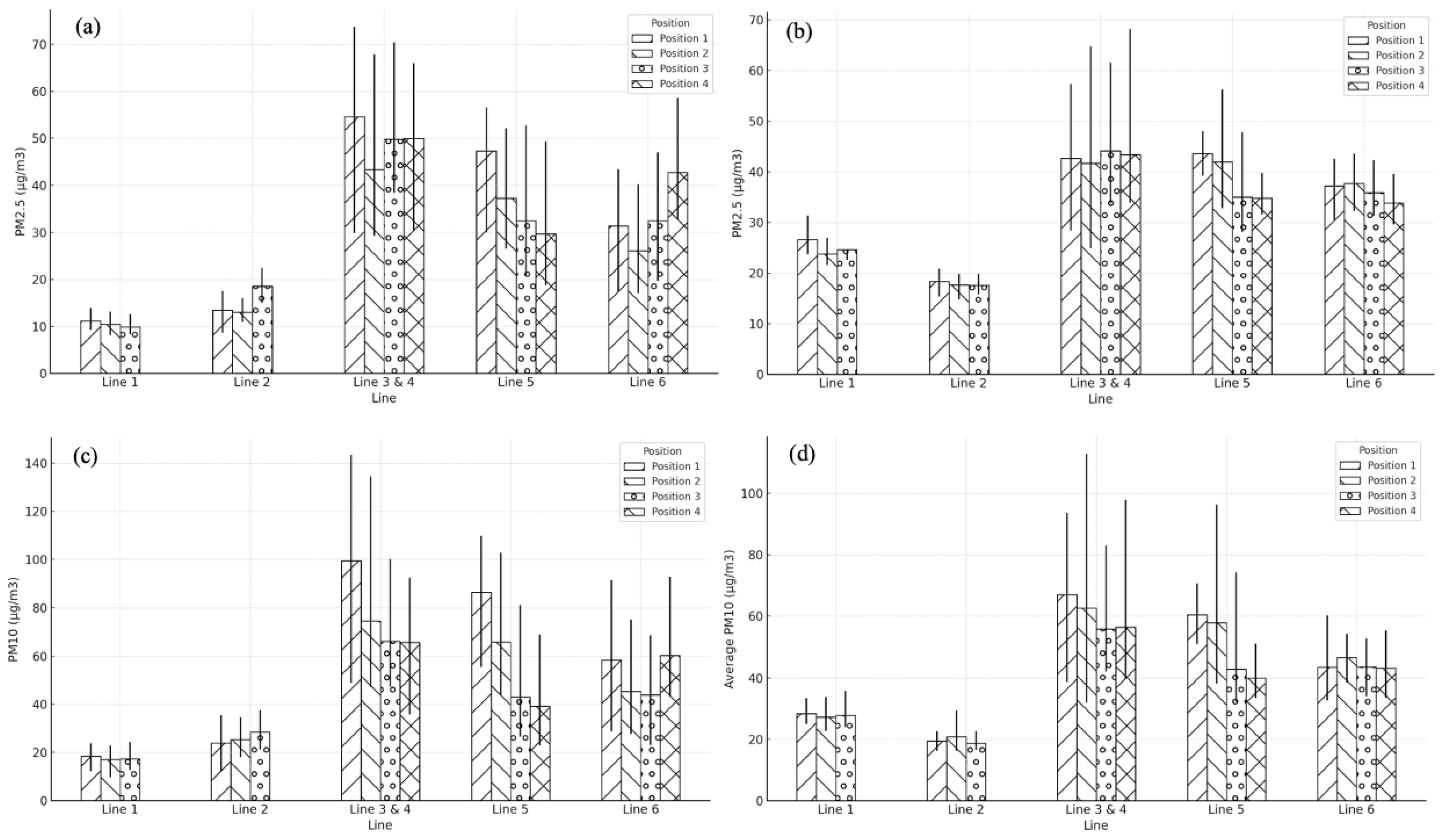
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Particulate Matter Measurements Above-Ground and Underground Lines
3.2. Comparison of PM Level at Different Positions on the Platform
4. Discussion
4.1. PM2.5 Levels at Different Platforms
4.2. PM2.5 Levels at Different Positions on the Platform
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sundell, J. On the History of Indoor Air Quality and Health History. Indoor Air 2004, 14, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centnerová, L.H. On the History of Indoor Environment and It’s Relation to Health and Wellbeing. REHVA J. 2018, 55, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Brunekreef, B.; Holgate, S.T. Air Pollution and Health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.; Suresh, R.; Gupta, A.; Singh, D.; Kulshrestha, P. Indoor Air Quality of Non-Residential Urban Buildings in Delhi, India. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2017, 6, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.O.; Kim, Y.S.; Perry, R. Indoor Air Quality in Homes, Offices and Restaurants in Korean Urban Areas—Indoor/Outdoor Relationships. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Int Panis, L.; de Geus, B.; Vandenbulcke, G.; Willems, H.; Degraeuwe, B.; Bleux, N.; Mishra, V.; Thomas, I.; Meeusen, R. Exposure to Particulate Matter in Traffic: A Comparison of Cyclists and Car Passengers. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Nazelle, A.; Fruin, S.; Westerdahl, D.; Martinez, D.; Ripoll, A.; Kubesch, N.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. A Travel Mode Comparison of Commuters’ Exposures to Air Pollutants in Barcelona. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.; Moreno, T.; Minguillón, M.C.; Amato, F.; de Miguel, E.; Capdevila, M.; Querol, X. Exposure to Airborne Particulate Matter in the Subway System. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, I.; Kumar, P.; Hagen-Zanker, A. Exposure to Air Pollutants during Commuting in London: Are There Inequalities among Different Socio-Economic Groups? Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.S.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Colvile, R.N.; McMullen, M.A.S.; Khandelwal, P. Fine Particle (PM2.5) Personal Exposure Levels in Transport Microenvironments, London, UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 279, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.J.; Kim, B.W.; Malek, M.A.; Koo, Y.S.; Jung, J.H.; Son, Y.S.; Kim, J.C.; Kim, H.K.; Ro, C.U. Chemical Speciation of Size-Segregated Floor Dusts and Airborne Magnetic Particles Collected at Underground Subway Stations in Seoul, Korea. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213–214, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugica-Álvarez, V.; Figueroa-Lara, J.; Romero-Romo, M.; Sepúlvea-Sánchez, J.; López-Moreno, T. Concentrations and Properties of Airborne Particles in the Mexico City Subway System. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 49, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.; Moreno, T.; Minguillón, M.C.; Van Drooge, B.L.; Reche, C.; Amato, F.; De Miguel, E.; Capdevila, M.; Centelles, S.; Querol, X. Origin of Inorganic and Organic Components of PM2.5 in Subway Stations of Barcelona, Spain. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Yu, X.; Gu, H.; Miao, B.; Wang, M.; Huang, H. Commuters’ Exposure to PM2.5 and CO2 in Metro Carriages of Shanghai Metro System. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2016, 47, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, T.; Xiu, G.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Huang, Z. Preliminary Investigation of PM1, PM2.5, PM10 and Its Metal Elemental Composition in Tunnels at a Subway Station in Shanghai, China. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2015, 41, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liu, D.; Zhang, W.; Liu, P.; Fei, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wu, M.; Yu, S.; Yonemochi, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Physico-Chemical Characterization of PM2.5 in the Microenvironment of Shanghai Subway. Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Roh, Y.M.; Lee, C.M.; Kim, C.N. Spatial Distribution of Particulate Matter (PM10 and PM2.5) in Seoul Metropolitan Subway Stations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.U.; Ha, K.C. Characteristics of PM10, PM2.5, CO2 and CO Monitored in Interiors and Platforms of Subway Train in Seoul, Korea. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcassim, M.J.R.; Thurston, G.D.; Peltier, R.E.; Gordon, T. Black Carbon and Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Concentrations in New York City’s Subway Stations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14738–14745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Oliver Gao, H. Exposure to Fine Particle Mass and Number Concentrations in Urban Transportation Environments of New York City. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2011, 16, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, W.; Cheung, K.; Daher, N.; Sioutas, C. Particulate Matter (PM) Concentrations in Underground and Ground-Level Rail Systems of the Los Angeles Metro. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1506–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmparesos, N.; Assimakopoulos, V.D.; Assimakopoulos, M.N.; Tsairidi, E. Particulate Matter Levels and Comfort Conditions in the Trains and Platforms of the Athens Underground Metro. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2016, 3, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Liu, Z.S.; Yan, J.W. Comparisons of PM10, PM2.5, Particle Number, and CO2 Levels inside Metro Trains between Traveling in Underground Tunnels and on Elevated Tracks. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Li, T.; Zhang, L. Estimate Hourly PM2.5 Concentrations from Himawari-8 TOA Reflectance Directly Using Geo-Intelligent Long Short-Term Memory Network. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Kim, J.; Cho, Y.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, D.W.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, F.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, X.; et al. A Synchronized Estimation of Hourly Surface Concentrations of Six Criteria Air Pollutants with GEMS Data. Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 6, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoogman, P.; Liu, X.; Suleiman, R.M.; Pennington, W.F.; Flittner, D.E.; Al-Saadi, J.A.; Hilton, B.B.; Nicks, D.K.; Newchurch, M.J.; Carr, J.L.; et al. Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution (TEMPO). J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2017, 186, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Fan, L.; Liu, J.; Xie, J.; Sun, Y.; Cui, N.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, B. A Review of the Piston Effect in Subway Stations. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2013, 5, 950205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigaki, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Pradana, H.A.; Matsumoto, Y.; Maruo, Y.Y. Citizen Sensing for Environmental Risk Communication. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Cyber-Technologies and Cyber-Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 12–16 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Keio Corporation Shibuya Station Map. Available online: https://www.keio.co.jp/global/routes/stations/shibuya/ (accessed on 8 January 2020).
- Moreno, T.; Reche, C.; Minguillón, M.C.; Capdevila, M.; de Miguel, E.; Querol, X. The Effect of Ventilation Protocols on Airborne Particulate Matter in Subway Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Meteorological Agency. Available online: https://www.data.jma.go.jp/stats/etrn/view/daily_s1.php?prec_no=44&block_no=47662&year=2019&month=08&day=13&view=p1 (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Shibuya Open Data. Available online: https://city-shibuya-data.opendata.arcgis.com/content/24585babf9e84868875ff8509bfad95b/about (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, J. Case Study of Train-Induced Airflow inside Underground Subway Stations with Simplified Field Test Methods. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 37, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripanucci, G.; Grana, M.; Vicentini, L.; Magrini, A.; Bergamaschi, A. Dust in the Underground Railway Tunnels of an Italian Town. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2006, 3, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Gómez-Perales, J.E.; Colvile, R.N. Levels of Particulate Air Pollution, Its Elemental Composition, Determinants and Health Effects in Metro Systems. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7995–8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskell, G.; Salmond, J.A.; Williams, D.E. Use of a Handheld Low-Cost Sensor to Explore the Effect of Urban Design Features on Local-Scale Spatial and Temporal Air Quality Variability. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, T.; Pérez, N.; Reche, C.; Martins, V.; de Miguel, E.; Capdevila, M.; Centelles, S.; Minguillón, M.C.; Amato, F.; Alastuey, A.; et al. Subway Platform Air Quality: Assessing the Influences of Tunnel Ventilation, Train Piston Effect and Station Design. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.B.; Jeong, W.; Park, D.; Kim, K.T.; Cho, K.H. A Multivariate Study for Characterizing Particulate Matter (PM10, PM2.5, and PM1) in Seoul Metropolitan Subway Stations, Korea. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, V.; Minguillón, M.C.; Moreno, T.; Mendes, L.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Alves, C.A.; de Miguel, E.; Querol, X. Characterisation of Airborne Particulate Matter in Different European Subway Systems. Urban Transport Systems. 2017, pp. 89–110. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/52468 (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Wen, Y.; Leng, J.; Shen, X.; Han, G.; Sun, L.; Yu, F. Environmental and Health Effects of Ventilation in Subway Stations: A Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. Urbanization and Global Health: The Role of Air Pollution. Iran J. Public Health 2018, 47, 1644. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.; Du, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Xia, L.; Liu, J.; Pei, F.; Wei, Y. Analysis and Interpretation of the Particulate Matter (PM10 and PM2.5) Concentrations at the Subway Stations in Beijing, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 45, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, A.; Bohn, J.; Groneberg, D.A.; Schulze, J.; Bundschuh, M. Airborne Particulate Matter in Public Transport: A Field Study at Major Intersection Points in Frankfurt Am Main (Germany). J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2014, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnio, P.; Yli-Tuomi, T.; Kousa, A.; Mäkelä, T.; Hirsikko, A.; Hämeri, K.; Räisänen, M.; Hillamo, R.; Koskentalo, T.; Jantunen, M. The Concentrations and Composition of and Exposure to Fine Particles (PM2.5) in the Helsinki Subway System. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 5059–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Kaul, D.; Wong, K.C.; Westerdahl, D.; Sun, L.; Ho, K.-f.; Tian, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Ning, Z. Heterogeneity of Passenger Exposure to Air Pollutants in Public Transport Microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 109, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, Ü.A.; Onat, B.; Stakeeva, B.; Ceran, T.; Karim, P. PM10 Concentrations and the Size Distribution of Cu and Fe-Containing Particles in Istanbul’s Subway System. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2012, 17, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, B.; Stakeeva, B. Assessment of Fine Particulate Matters in the Subway System of Istanbul. Indoor Built Environ. 2014, 23, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartenì, A.; Cascetta, F.; Campana, S. Underground and Ground-Level Particulate Matter Concentrations in an Italian Metro System. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.J.; Vasconcelos, A.; Faria, M. Comparison of Particulate Matter Inhalation for Users of Different Transport Modes in Lisbon. Transp. Res. Procedia 2015, 10, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, M.; Lerma, C.; Infante, O.; Hermosillo, A.G.; Riojas-Rodriguez, H.; Cardenas, M. Personal Exposure to Particulate Matter Less than 2.5 Μm in Mexico City: A Pilot Study. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2004, 14, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ryswyk, K.; Anastasopolos, A.T.; Evans, G.; Sun, L.; Sabaliauskas, K.; Kulka, R.; Wallace, L.; Weichenthal, S. Metro Commuter Exposures to Particulate Air Pollution and PM2.5-Associated Elements in Three Canadian Cities: The Urban Transportation Exposure Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5713–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branǐ, M. The Contribution of Ambient Sources to Particulate Pollution in Spaces and Trains of the Prague Underground Transport System. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Sankararao, B.; Kang, O.; Kim, J.; Yoo, C. Monitoring and Prediction of Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) in Subway or Metro Systems Using Season Dependent Models. Energy Build 2012, 46, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Lian, Z.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, H. Investigation of Indoor Environmental Quality in Shanghai Metro Stations, China. Environ. Monit. Assess 2010, 167, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Johansson, P.Å. Particulate Matter in the Underground of Stockholm. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, M.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L. Particulate Matter Concentrations and Heavy Metal Contamination Levels in the Railway Transport System of Sydney, Australia. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolourchi, A.; Atabi, F.; Moattar, F.; Ehyaei, M.A. Experimental and Numerical Analyses of Particulate Matter Concentrations in Underground Subway Station. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 2569–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Liu, C.C. Levels of PM10 and PM2.5 in Taipei Rapid Transit System. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7242–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Sung, F.C.; Chen, M.L.; Mao, I.F.; Lu, C.Y. Indoor Air Quality in the Metro System in North Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
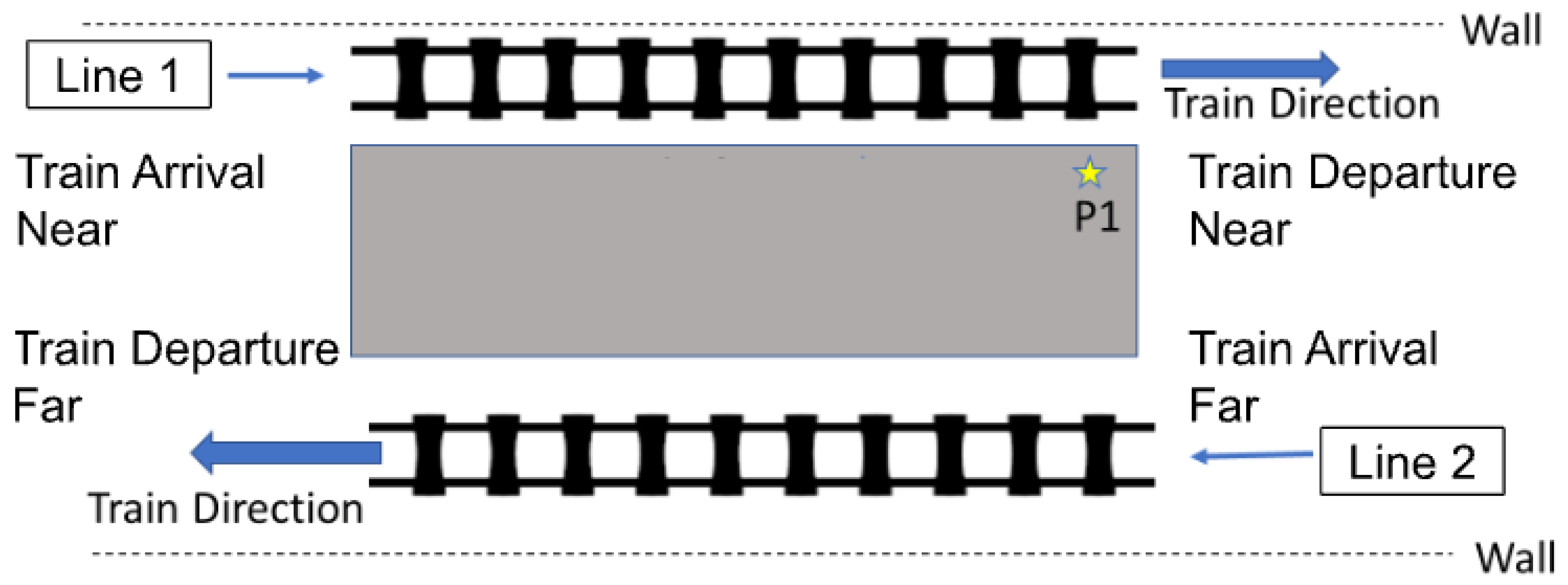





| Line No. | Line Location | Number of Measurement Positions | Measurement Date | Day Type | Measurement Time | Average Intervals Between Trains (Minutes) | Tokyo’s Hourly Average Tempearture (°C) [31] | Tokyo’s Hourly Humidity (%) [31] | Shibuya’s Daily Average SPM (µg/m3) [32] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Above-ground | 3 | 15 August 2019 | Weekday | 14:02–14:46 | 4 | 31.1 | 72 | 29 |
| 17 August 2019 | Weekend | 15:34–16:19 | 4 | 34.2 | 60 | 34 | |||
| 2 | Above-ground | 3 | 15 August 2019 | Weekday | 20:17–20:46 | 1.7 | 27.8 | 92 | 29 |
| 18 August 2019 | Weekend | 16:21–17:22 | 1.5 | 32.7 | 56 | 34 | |||
| 3 and 4 | Underground (B3F) | 4 | 15 August 2019 | Weekday | 19:16–19:54 | 1.6 | 27.5 | 94 | 29 |
| 18 August 2019 | Weekend | 17:37–18:18 | 2.3 | 31.7 | 60 | 34 | |||
| 5 | Underground (B5F) | 4 | 15 August 2019 | Weekday | 15:21–16:01 | 1.9 | 30.4 | 76 | 29 |
| 18 August 2019 | Weekend | 18:57–20:21 | 1.9 | 30.2 | 65 | 34 | |||
| 6 | Underground (B5F) | 4 | 15 August 2019 | Weekday | 16:15–16:55 | 1.9 | 30.3 | 76 | 29 |
| 18 August 2019 | Weekend | 20:45–22:35 (with 25 min rest) | 1.9 | 27.8 | 84 | 34 |
| Position | Line No. | Average PM2.5 Levels (µg/m3) | Average PM10 Levels (µg/m3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weekday | Weekend | Average | Weekday | Weekend | Average | ||
| Above-ground | 1 | 10.45 | 25.03 | 17.09 | 17.57 | 27.79 | 22.73 |
| 2 | 15.00 | 17.87 | 25.89 | 19.66 | |||
| Underground | 3 & 4 | 49.43 | 42.98 | 39.54 | 76.35 | 60.47 | 56.98 |
| 5 | 36.66 | 38.84 | 58.58 | 50.28 | |||
| 6 | 33.17 | 36.18 | 51.99 | 44.22 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agarwal, D.; Trinh, X.T.; Takeuchi, W. Assessing the Air Quality Impact of Train Operation at Tokyo Metro Shibuya Station from Portable Sensor Data. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17020235
Agarwal D, Trinh XT, Takeuchi W. Assessing the Air Quality Impact of Train Operation at Tokyo Metro Shibuya Station from Portable Sensor Data. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(2):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17020235
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgarwal, Deepanshu, Xuan Truong Trinh, and Wataru Takeuchi. 2025. "Assessing the Air Quality Impact of Train Operation at Tokyo Metro Shibuya Station from Portable Sensor Data" Remote Sensing 17, no. 2: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17020235
APA StyleAgarwal, D., Trinh, X. T., & Takeuchi, W. (2025). Assessing the Air Quality Impact of Train Operation at Tokyo Metro Shibuya Station from Portable Sensor Data. Remote Sensing, 17(2), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17020235







