DVIF-Net: A Small-Target Detection Network for UAV Aerial Images Based on Visible and Infrared Fusion
Abstract
Highlights
- A novel visible-infrared fusion network for small-target detection in UAV aerial images, DVIF-Net, is proposed, achieving mAP50 of 85.8% and 62.0% respectively on two cross-modal datasets DroneVehicle and VEDAI, with parameters of only 2.49 M.
- The proposed P4-level cross-modal feature fusion strategy, dual context-guided fusion module (DCGF), and edge information enhancement module (CSP-EIE) have significantly enhanced the ability of visible-infrared feature fusion and the expression ability of small-target edge features.
- The study provides a lightweight and high-precision solution for real-time UAV-based small-target detection in complex environments such as low illumination, fog, and occlusion.
- The proposed fusion strategy and module design offer a valuable reference for deploying multimodal detection models on resource-constrained embedded platforms.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This paper proposes the DVIF-Net, which performs cross-modal feature fusion between the backbone network and the neck network. Unlike other methods that use “Concat” or “Add” to fuse bimodal images, DVIF-Net fuses bimodal information in feature space and focuses on small targets detection task for UAV aerial images.
- A P4-level cross-modal feature fusion strategy is designed, which achieves better fusion effect by performing one fusion at appropriate positions (rather than multiple fusions), and has fewer model parameters.
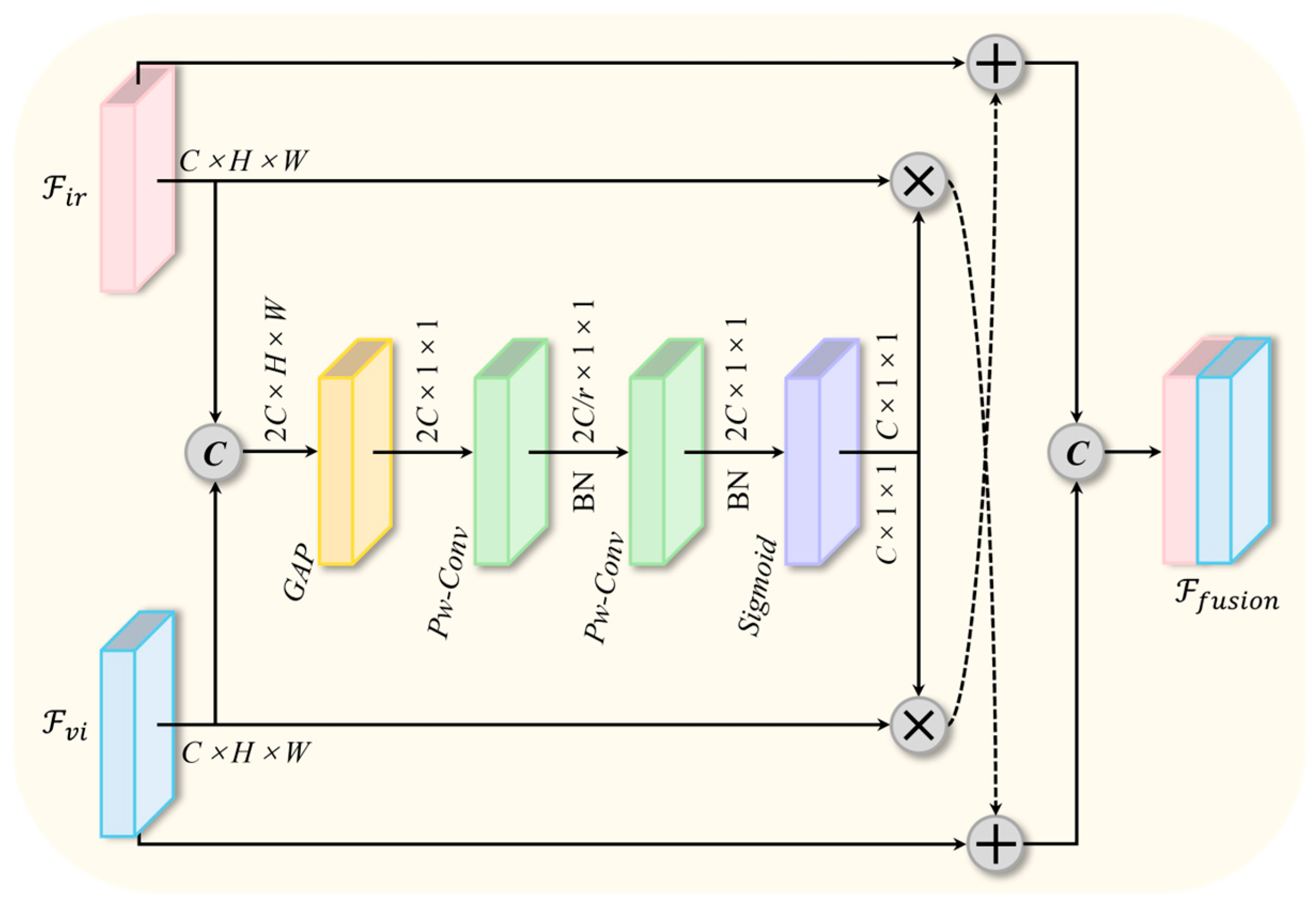
- A novel dual-context information-guided fusion module (DCGF) is proposed, which uses SE attention mechanism to capture and utilize important context information during dual-modal feature fusion, and then guides model to learn this information, thereby enhancing the model’s detection performance. In addition, DCGF employs an element-wise multiplication strategy to enhance the interaction ability between visible and infrared feature information.
- An edge information enhancement module CSP-EIE based on a cross stage partial structure is proposed, which employs AdaptiveAvgPool to expand the receptive field of the network, enabling the extraction of high-frequency image information across different scales. Meanwhile, an edge enhancer is incorporated to extract target edge features, thereby improving the backbone network’s capability in feature extraction for small targets.
2. Related Work
2.1. Small Object Detection Method Based on Deep Learning
2.2. Infrared and Visible Light Image Fusion Method
3. Methodology
3.1. Overall Framework
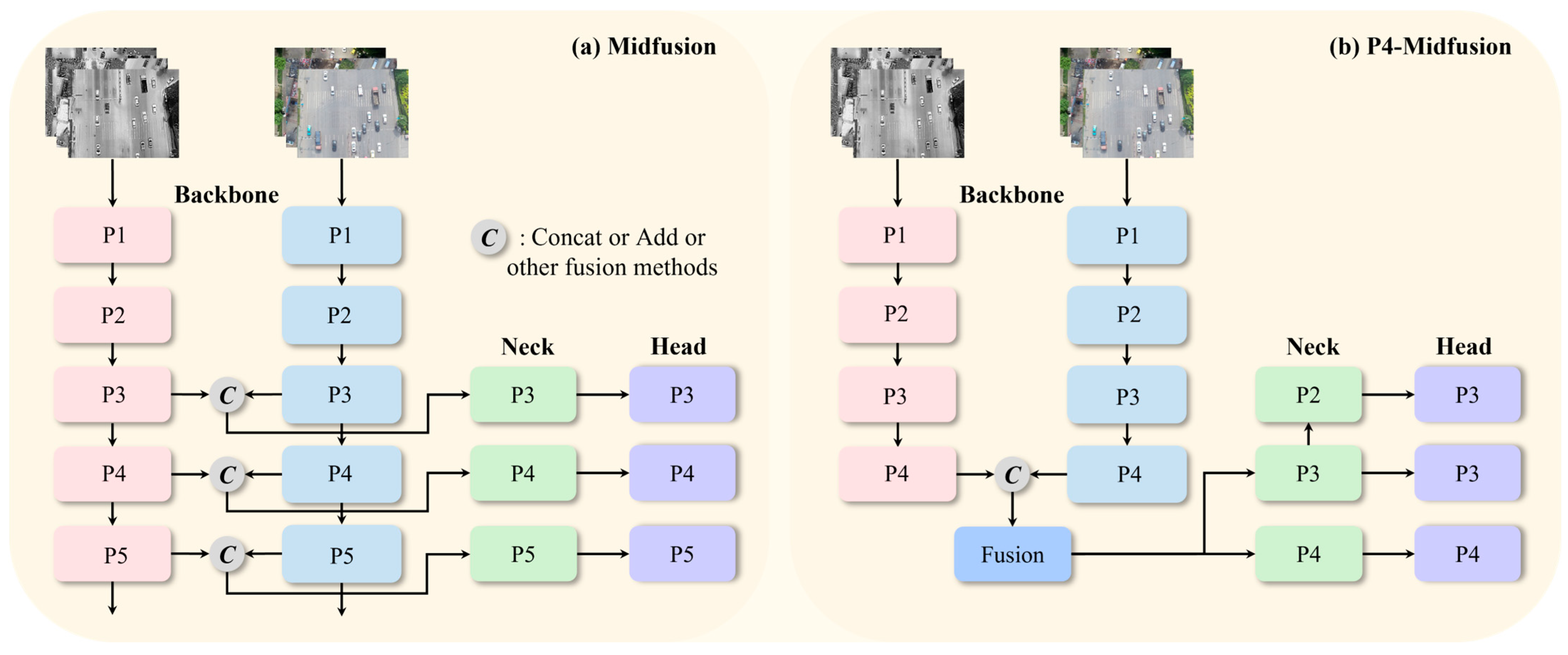
3.2. P4-Level Cross-Modal Feature Fusion Strategy
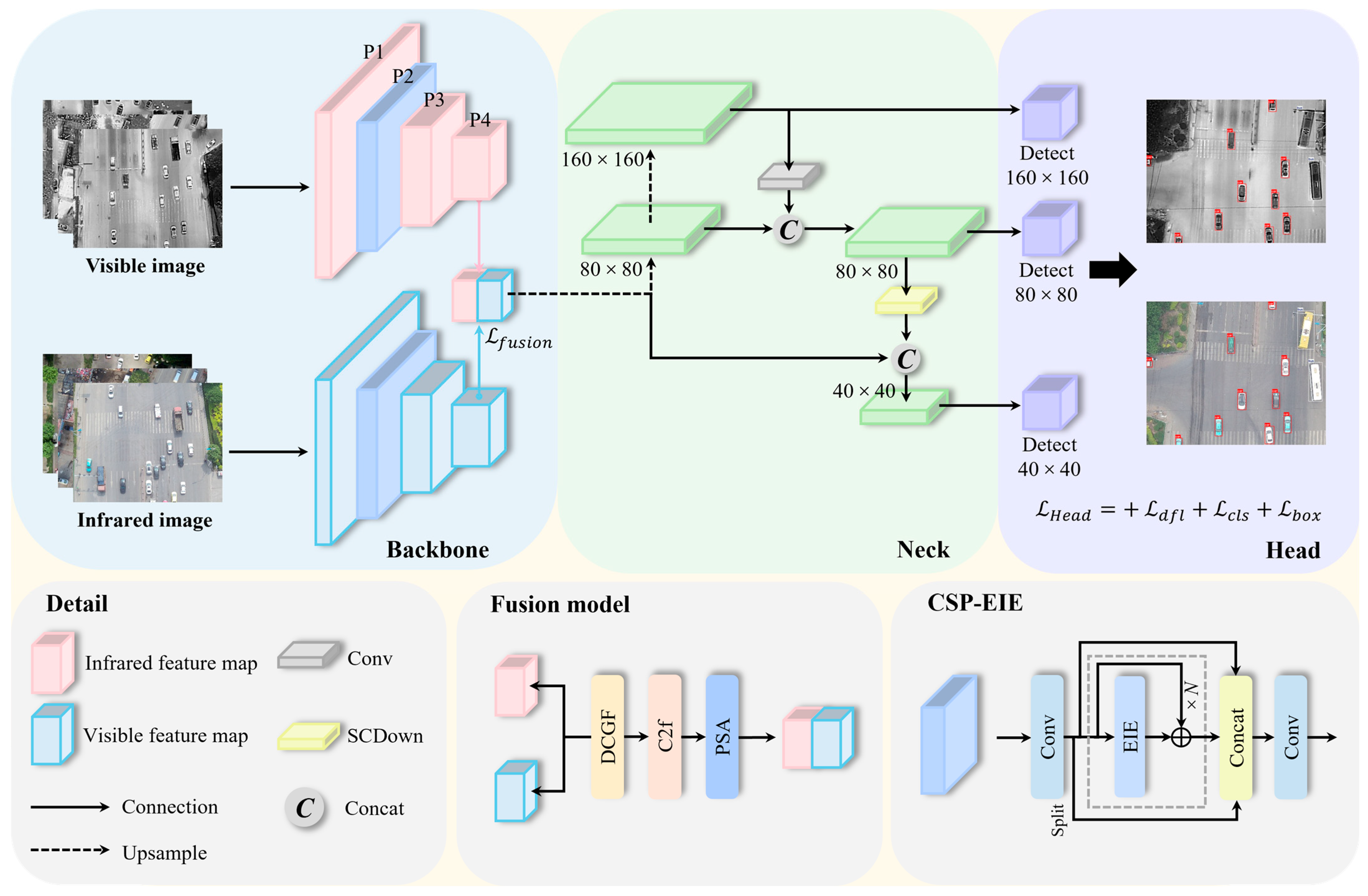

3.3. Dual-Context Information Guide Fusion Module
3.4. Edge Information Enhancement Module
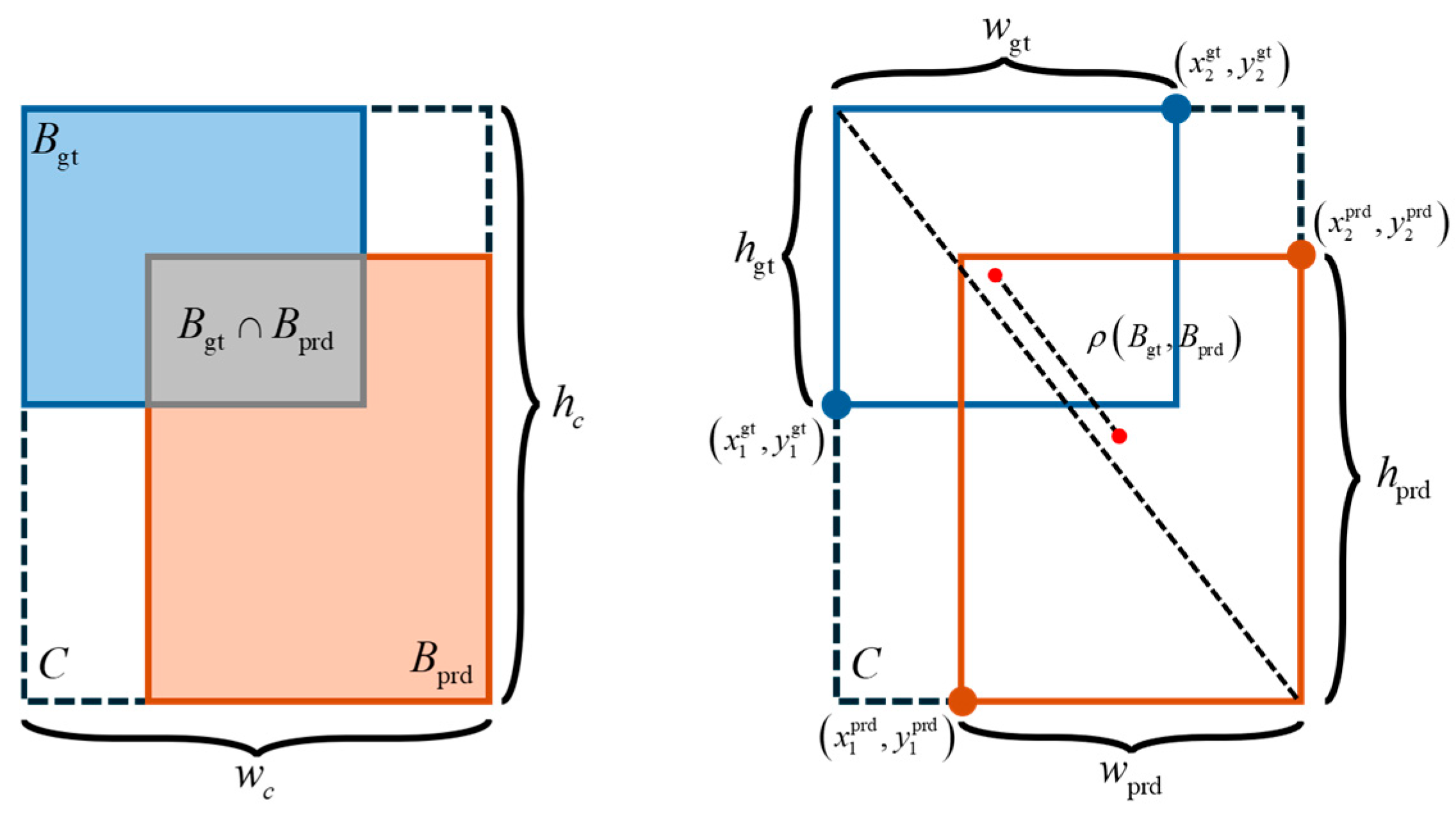
3.5. Loss Function
4. Experiment
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Platform and Parameters
4.3. Assessment Indicators
4.4. Comparison Experiment
4.5. Ablation Experiment
- Compared to the conventional P3–P5 multi-stage fusion approach, the proposed P4-level cross-modal fusion strategy significantly enhances model performance, increasing mAP50 from 81.0% to 81.5% while reducing model parameters by 0.96 M. This improvement demonstrates the effectiveness of the strategy. Performing one-time fusion solely at the P4 level not only decreases computational complexity but also achieves better fusion performance.
- By replacing the “Concat” operation with the DCGF fusion module for feature integration, we observed an overall upward trend in accuracy metrics including P, R, mAP50, and mAP50-95, with a notable improvement of 2.7% in mAP50. This indicates that the DCGF module effectively combines complementary information from visible and infrared images, thereby enhancing feature fusion performance.
- Even without the DCGF module, using CSP-EIE alone still improves model performance, raising mAP50 from 81.9% to 83.4% while the Params of only 2.477 M. This improvement can be attributed to the combined effect of the AdaptiveAvgPool layer and the EdgeEnhancer in CSP-EIE, which enhance the backbone network’s capability to extract edge information of small targets.
- The combination of P4Fusion, DCGF, and CSP-EIE achieves the best performance, yielding mAP50 of 85.8% with a total model parameter of 2.485 M. This result confirms the effectiveness of our proposed strategies, demonstrating a significant improvement in detection accuracy for small targets in UAV aerial images under complex scenarios.
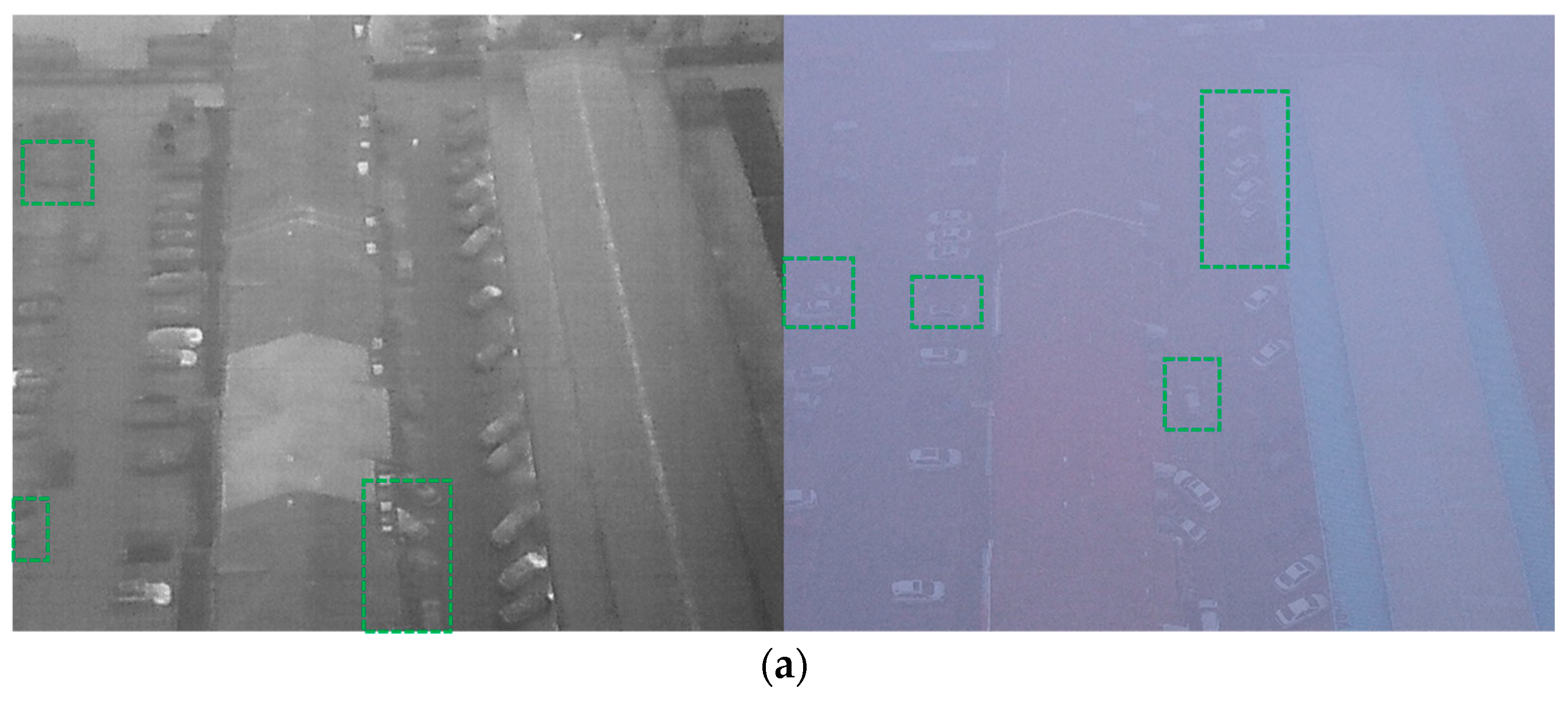
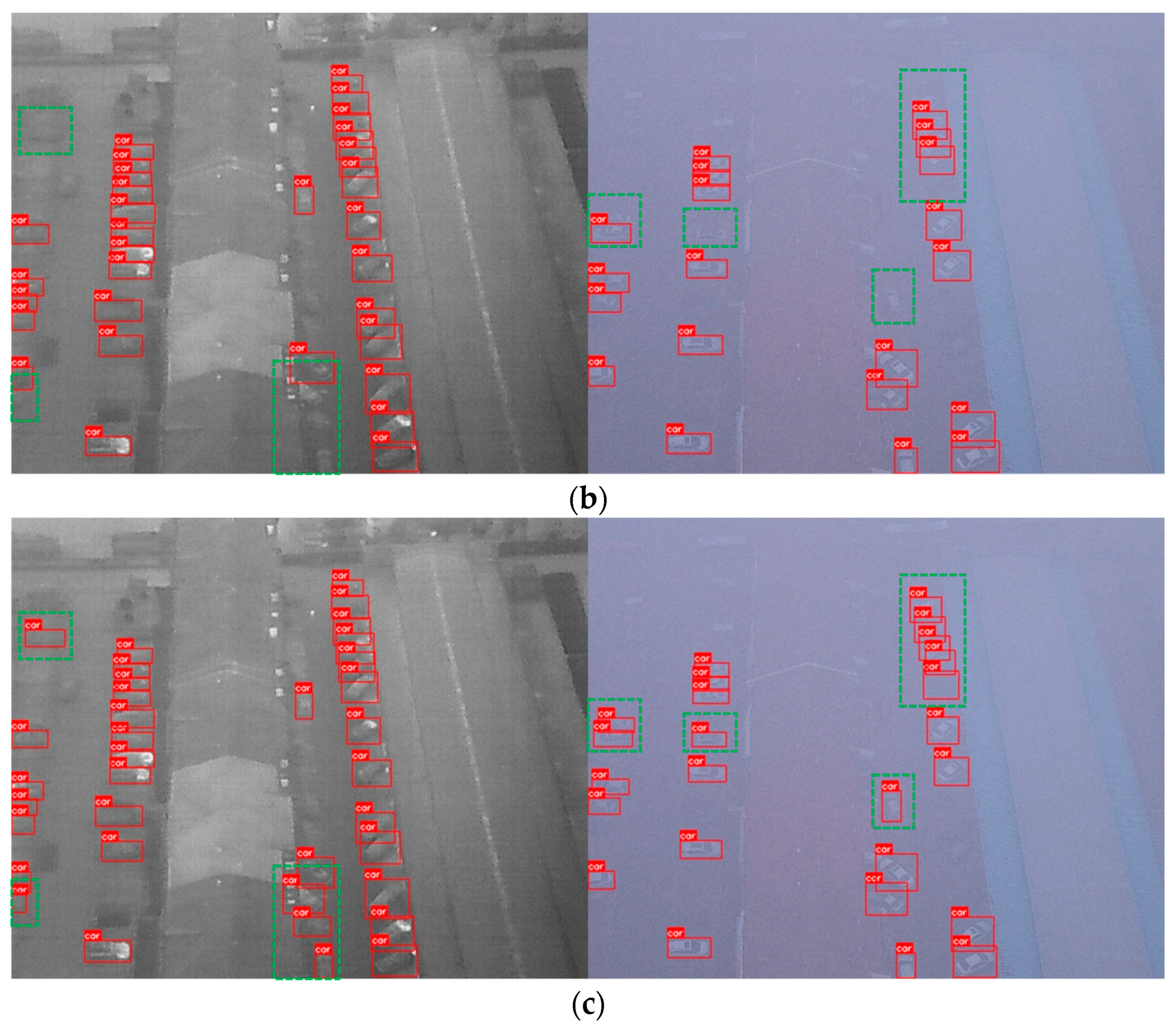
4.6. Visual Experiment
4.7. Comparative Experiments on VEDAI Dataset
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| VIIF | Visible and Infrared Image Fusion |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| DCGF | Dual-Context Information Guide Fusion |
| CSP-EIE | Cross Stage Partial-Edge Information Enhancement |
| HOG | Histogram of Oriented Gradient |
| SVM | Support Vector Machines |
| YOLO | You Only Look Once |
| SSD | Single-Shot MultiBox Detector |
| DFL | Distribution Focal Loss |
| BCE | Binary Cross-Entropy |
| CIoU | Complete Intersection over Union |
| IR | Infrared |
Appendix A. Parameter Settings
| Model | Parameter Settings |
| DCGF | (k = 1) |
| CSP-EIE | Group Convolution (g = 4) |
References
- Wang, Q.; Zhan, Y.; Zou, Y. UAV recognition algorithm for ground military targets based on improved Yolov5n. Comput. Meas. Control 2024, 32, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, S.; Yanmaz, E.; Brown, T.X.; Bettstetter, C. Multi-objective UAV path planning for search and rescue. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 5569–5574. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadra, S.; Sagan, V.; Sarkar, S.; Braud, M.; Mockler, T.C.; Eveland, A.L. PROSAIL-Net: A transfer learning-based dual stream neural network to estimate leaf chlorophyll and leaf angle of crops from UAV hyperspectral images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 210, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, C.; Li, Y.; Gong, W.; Li, B.; Qi, G.; Zhang, J. UAV-aided distribution line inspection using double-layer offloading mechanism. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2024, 18, 2353–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Bai, H.; Chen, T. Special Vehicle Detection from UAV Perspective via YOLO-GNS Based Deep Learning Network. Drones 2023, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zeng, L.; Zhu, W.; Zeng, Z. A Small Object Detection Model for Improved YOLOv8 for UAV Aerial Photography Scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Seminar on Artificial Intelligence, Networking and Information Technology (AINIT), Nanjing, China, 29–31 March 2024; pp. 2099–2104. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W.; Wang, B.; Lei, Y. Technique for infrared and visible image fusion based on non-subsampled shearlet transform and spiking cortical model. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2015, 71, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, S. Multifocus image fusion and restoration with sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Pei, H. The infrared and visible image fusion algorithm based on target separation and sparse representation. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2014, 67, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Zong, H. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 82, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, R.; Wu, G.; Liu, R.; Luo, Z.; Fan, X. CoCoNet: Coupled Contrastive Learning Network with Multi-level Feature Ensemble for Multi-modality Image Fusion. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2024, 132, 1748–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Kittler, J. Infrared and visible image fusion using a deep learning framework. In Proceedings of the 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 20–24 August 2018; pp. 2705–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, G. STDFusionNet: An infrared and visible image fusion network based on salient target detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vs, V.; Valanarasu, J.M.J.; Oza, P.; Patel, V.M. Image fusion transformer. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Bordeaux, France, 16–19 October 2022; pp. 3566–3570. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, D.; Wu, X.J.; Xu, T. TGFuse: An infrared and visible image fusion approach based on transformer and generative adversarial network. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Wan, W.; Wen, W.; Guan, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via texture conditional generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 4771–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Huang, J.; Mei, X.; Fan, F. Correlation-guided discriminative cross-modality features network for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 5002718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Vien, A.G.; Lee, C. Cross-modal transformers for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 770–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Abera, D.E.; Cheng, J. PS-GAN: Pseudo Supervised Generative Adversarial Network with Single Scale Retinex Embedding for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 1766–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–26 June 2005; pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, H.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Wang, C. An overview of object detection and tracking. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Lijiang, China, 8–10 August 2015; pp. 280–286. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Cai, N.; Pacheco, P.P.; Narrandes, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W. Applications of support vector machine (SVM) learning in cancer genomics. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2018, 15, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande, S.D.; Er, M.H.; Venkateswarlu, R.; Chan, P. Max-mean and max-median filters for detection of small targets. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3809, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Zhou, F. Analysis of new top-hat transformation and the application for infrared dim small target detection. Pattern Recogn. 2010, 43, 2145–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liang, K.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, L. Infrared small target detection utilizing the multiscale relative local contrast measure. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.P.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Xia, T.; Tang, Y.Y. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection. IEEE Trans Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Moradi, S.; Faramarzi, I.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, N. Infrared small target detection based on the weighted strengthened local contrast measure. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 1670–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, L.; Zhang, T.; Cao, S.; Peng, Z. Infrared Small Target Detection via Non-Convex Rank Approximation Minimization Joint/2,1 Norm. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection based on partial sum of the tensor nuclear norm. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich Feature Hierarchies for Accurate Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Fang, X.; Meng, X.; Fang, X.; Lv, M.; Zhuo, Y. Real-time semantic segmentation network with an enhanced backbone based on Atrous spatial pyramid pooling module. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intel. 2024, 133, 107988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, D.; Kupec, J.; Hong, J.; Daoudi, A. Real-Time Flying Object Detection with YOLOv8. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.09972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot Multibox Detector. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1512.02325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, M.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Guo, P.; Yan, J. FFCA-YOLO for Small Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Tran. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Cui, K.; Wang, R.-F. Toward Efficient UAV-Based Small Object Detection: A Lightweight Network with Enhanced Feature Fusion. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhu, X. YOLO-SMUG: An Efficient and Lightweight Infrared Object Detection Model for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Drones 2025, 9, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huang, X.; He, C.; Xiao, H.; Luo, S. Infrared Small Target Detection with Swin Transformer-Based Multiscale Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling Network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, Z.; Pan, C.; Zhang, G.; Xu, J. NOC-YOLO: An exploration to enhance small-target vehicle detection accuracy in aerial infrared images. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2025, 149, 105905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ke, Z.; Li, Z.; Wushour, S. Survey of Multimodal Data Fusion. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2021, 57, 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Schnelle, S.R.; Chan, A.L. Enhanced target tracking through infrared-visible image fusion. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Information Fusion, Chicago, IL, USA, 5–8 July 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Xie, S.; Zhao, F.; He, Y.; Lu, H. MetaFusion: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Meta-Feature Embedding from Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 13955–13965. [Google Scholar]
- Que, L.; Zhou, T.; Tao, M.; Che, K.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, J. An efficient method of infrared-visible image fusion. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 34th Wireless and Optical Communications Conference (WOCC), Taipa, Macao, 20–22 May 2025; pp. 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Geng, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Ding, P. SLBAF-Net: Super-Lightweight bimodal adaptive fusion network for UAV detection in low recognition environment. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 47773–47792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liao, X.; Yuan, J.; Yao, Y.; Li, Z. CDC-YOLOFusion: Leveraging Cross-Scale Dynamic Convolution Fusion for Visible-Infrared Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Gao, Q.; Li, Z. Efficient fusion network with label generation and branch transformations for visible and infrared images fusion. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2025, 150, 105916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.-C. Object Detection Based on Decision Level Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Hangzhou, China, 22–24 November 2019; pp. 3257–3262. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Shi, J.; Ye, Z.; Mertz, C.; Ramanan, D.; Kong, S. Multimodal object detection via probabilistic ensembling. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 139–158. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J. YOLOV10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 37, 107984–108011. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Q.; Han, D.; Wang, Z. Cross-modality fusion transformer for multispectral object detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Ma, J. PIAFusion: A progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware. Inf. Fusion 2022, 83–84, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Guo, X.; Zhu, W.; He, J.; Liu, X.; Yuan, J. DEYOLO: Dual-Feature-Enhancement YOLO for Cross-Modality Object Detection. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2412.04931. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Cao, B.; Zhu, P.; Hu, Q. Drone-Based RGB-Infrared Cross-Modality Vehicle Detection Via Uncertainty-Aware Learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 6700–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2999–3007. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxargia, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.06870. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into high quality object detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6154–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Xue, N.; Long, Y.; Xia, G.-S.; Lu, Q. Learning RoI Transformer for Oriented Object Detection in Aerial Images. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 17–24 June 2019; pp. 2844–2853. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, K.; Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, L. RemoteDet-Mamba: A Hybrid Mamba-CNN Network for Multi-modal Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2410.13532. [Google Scholar]
- Razakarivony, S.; Jurie, F. Vehicle detection in aerial imagery: A small target detection benchmark. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2016, 34, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Modality | Car | Truck | Bus | Van | Freight Car |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGB | 339,779 | 22,123 | 15,333 | 11,935 | 13,400 |
| IR | 428,086 | 25,960 | 16,590 | 12,708 | 17,173 |
| Environment | Parameters |
|---|---|
| GPU | Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8488C |
| CPU | NVIDIA A100 |
| GPU memory size | 80 G |
| Operating system | Win 10 |
| Language | Python 3.10.17 |
| Frame | Pytorch 2.1.1 |
| CUDA Version | Cuda 11.8 |
| Parameters | Setup |
|---|---|
| Epochs | 300 |
| Input image size | 640 × 512 |
| Batch size | 32 |
| Worker | 8 |
| Learning rate | 0.01 |
| Momentum | 0.937 |
| Weight decay | 0.0005 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Method | Modality | mAP50 (%) | Params (M) | FLOPs /G | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car | Truck | Bus | Van | Freight Car | All | ||||
| RetinaNet | Visible | 78.5 | 34.4 | 69.8 | 28.8 | 24.1 | 47.1 | 145.0 | 99.9 |
| Faster R-CNN | Visible | 79.0 | 49.0 | 77.0 | 37.0 | 37.2 | 55.9 | 58.30 | 169.5 |
| Mask R-CNN | Visible | 68.5 | 39.8 | 66.8 | 25.4 | 26.8 | 45.5 | 242.0 | 93.5 |
| Cascade R-CNN | Visible | 68.0 | 44.7 | 69.3 | 29.8 | 27.3 | 47.8 | 368.0 | 153.8 |
| RoITransformer | Visible | 61.6 | 55.1 | 85.5 | 27.6 | 42.3 | 61.5 | 273.0 | 123.8 |
| YOLOv5n | Visible | 90.5 | 61.3 | 90.6 | 52.7 | 47.1 | 68.4 | 2.50 | 7.2 |
| YOLOv8n | Visible | 91.2 | 62.3 | 90.2 | 56.0 | 49.2 | 69.8 | 3.01 | 8.1 |
| YOLOv10n | Visible | 91.5 | 63.9 | 90.7 | 55.4 | 51.0 | 70.5 | 2.26 | 6.5 |
| YOLOv11n | Visible | 91.3 | 63.0 | 90.2 | 55.2 | 48.8 | 69.9 | 2.58 | 6.3 |
| YOLOv12n | Visible | 91.3 | 64.5 | 90.5 | 52.4 | 53.0 | 70.3 | 2.51 | 6.6 |
| RetinaNet | Infrared | 88.8 | 35.4 | 76.5 | 32.1 | 39.5 | 54.5 | 145.0 | 99.9 |
| Faster R-CNN | Infrared | 89.4 | 53.5 | 87.0 | 42.6 | 48.3 | 64.2 | 58.30 | 169.5 |
| Mask R-CNN | Infrared | 88.8 | 48.9 | 78.4 | 32.2 | 36.6 | 57.0 | 242.0 | 93.5 |
| Cascade R-CNN | Infrared | 81.0 | 47.2 | 79.3 | 33.0 | 39.0 | 55.9 | 368.0 | 153.8 |
| RoITransformer | Infrared | 89.6 | 51.0 | 88.9 | 44.5 | 53.4 | 65.5 | 273.0 | 123.8 |
| YOLOv5n | Infrared | 97.6 | 67.7 | 94.5 | 50.3 | 70.0 | 75.2 | 2.50 | 7.2 |
| YOLOv8n | Infrared | 98.1 | 72.1 | 96.3 | 61.9 | 71.3 | 79.9 | 3.01 | 8.1 |
| YOLOv10n | Infrared | 98.2 | 71.7 | 95.7 | 63.9 | 70.1 | 79.9 | 2.26 | 6.5 |
| YOLOv11n | Infrared | 98.0 | 71.7 | 95.5 | 61.9 | 70.4 | 79.5 | 2.58 | 6.3 |
| YOLOv12n | Infrared | 98.1 | 70.4 | 95.8 | 62.8 | 69.8 | 79.4 | 2.51 | 6.6 |
| CFT | VI + IR | 91.9 | 67.0 | 92.1 | 56.4 | 55.2 | 72.5 | 44.53 | 123.5 |
| UA-CMDet | VI + IR | 87.5 | 60.7 | 87.1 | 38.0 | 46.8 | 64.0 | 139.70 | 98.1 |
| RemoteDet-Mamba | VI + IR | 98.2 | 81.2 | 95.7 | 52.9 | 67.9 | 81.8 | 71.34 | 84.5 |
| CDC-YOLOFusion | VI + IR | 98.4 | 71.9 | 96.2 | 64.8 | 69.7 | 80.2 | 153.60 | 48.9 |
| DE-YOLO | VI + IR | 98.3 | 78.4 | 96.8 | 68.5 | 76.0 | 83.6 | 6.00 | 18.7 |
| Ours | VI + IR | 98.6 | 82.3 | 97.4 | 71.9 | 78.9 | 85.8 | 2.49 | 8.2 |
| P4Fusion | DCGF | CSP-EIE | P (%) | R (%) | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | Params (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 79.4 | 75.5 | 81.0 | 58.2 | 3.436 | |||
| √ | 80.6 | 75.2 | 81.5 | 59.7 | 2.479 | ||
| √ | √ | 80.4 | 80.3 | 84.2 | 61.1 | 2.487 | |
| √ | √ | 79.4 | 78.6 | 83.4 | 63.1 | 2.477 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 81.6 | 80.3 | 85.8 | 64.4 | 2.485 |
| Method | Modality | mAP50(%) | Params (M) | FLOPs /G | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car | Truck | Boat | Trackor | Camping Van | Pickup | Plane | Van | Others | All | ||||
| YOLOv5n | Visible | 80.5 | 46.1 | 34.7 | 48.6 | 65.4 | 62.6 | 69.1 | 25.2 | 33.2 | 51.7 | 2.50 | 7.2 |
| YOLOv8n | Visible | 79.9 | 55.5 | 48.3 | 47.4 | 67.9 | 65.4 | 70.9 | 25.5 | 31.6 | 54.7 | 3.01 | 8.1 |
| YOLOv10n | Visible | 81.1 | 56.5 | 48.1 | 46.0 | 67.5 | 65.6 | 79.5 | 26.8 | 33.6 | 56.1 | 2.26 | 6.5 |
| YOLOv11n | Visible | 81.1 | 53.8 | 46.4 | 47.0 | 67.7 | 65.1 | 81.2 | 25.6 | 34.3 | 55.8 | 2.58 | 6.3 |
| YOLOv12n | Visible | 80.5 | 58.3 | 35.0 | 48.1 | 61.4 | 69.6 | 69.5 | 15.9 | 34.6 | 52.5 | 2.51 | 6.6 |
| YOLOv5n | Infrared | 76.6 | 43.5 | 36.6 | 45.7 | 58.9 | 59.5 | 31.7 | 15.3 | 24.5 | 43.6 | 2.50 | 7.2 |
| YOLOv8n | Infrared | 74.7 | 57.0 | 40.0 | 38.4 | 56.5 | 60.4 | 26.8 | 19.0 | 26.0 | 44.3 | 3.01 | 8.1 |
| YOLOv10n | Infrared | 77.4 | 52.7 | 45.1 | 44.9 | 56.8 | 57.6 | 46.8 | 18.6 | 27.5 | 47.5 | 2.26 | 6.5 |
| YOLOv11n | Infrared | 77.3 | 53.0 | 45.7 | 45.2 | 54.3 | 63.6 | 46.7 | 18.3 | 25.9 | 47.8 | 2.58 | 6.3 |
| YOLOv12n | Infrared | 77.7 | 50.2 | 39.2 | 46.5 | 62.1 | 59.9 | 44.2 | 18.4 | 24.7 | 47.0 | 2.51 | 6.6 |
| Ours | VI + IR | 81.3 | 60.0 | 58.8 | 58.5 | 67.6 | 70.5 | 92.0 | 27.7 | 42.0 | 62.0 | 2.49 | 8.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Z. DVIF-Net: A Small-Target Detection Network for UAV Aerial Images Based on Visible and Infrared Fusion. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3411. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203411
Zhao X, Zhang H, Li C, Wang K, Zhang Z. DVIF-Net: A Small-Target Detection Network for UAV Aerial Images Based on Visible and Infrared Fusion. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(20):3411. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203411
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiaofeng, Hui Zhang, Chenxiao Li, Kehao Wang, and Zhili Zhang. 2025. "DVIF-Net: A Small-Target Detection Network for UAV Aerial Images Based on Visible and Infrared Fusion" Remote Sensing 17, no. 20: 3411. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203411
APA StyleZhao, X., Zhang, H., Li, C., Wang, K., & Zhang, Z. (2025). DVIF-Net: A Small-Target Detection Network for UAV Aerial Images Based on Visible and Infrared Fusion. Remote Sensing, 17(20), 3411. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203411






