STMSF: Swin Transformer with Multi-Scale Fusion for Remote Sensing Scene Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A multi-scale feature fusion mechanism is designed for a Swin transformer, by which the multi-scale presence of ground objects in remote sensing scenes is encountered for a classification task.
- A spatial attention pyramid network is designed to emphasize spatial context of different scales, which can improve the ability of transformer in multi-scale feature representation.
2. Related Work
2.1. RS Scene Classification with Multi-Scale Features
2.2. Transformer for RS Scene Classification
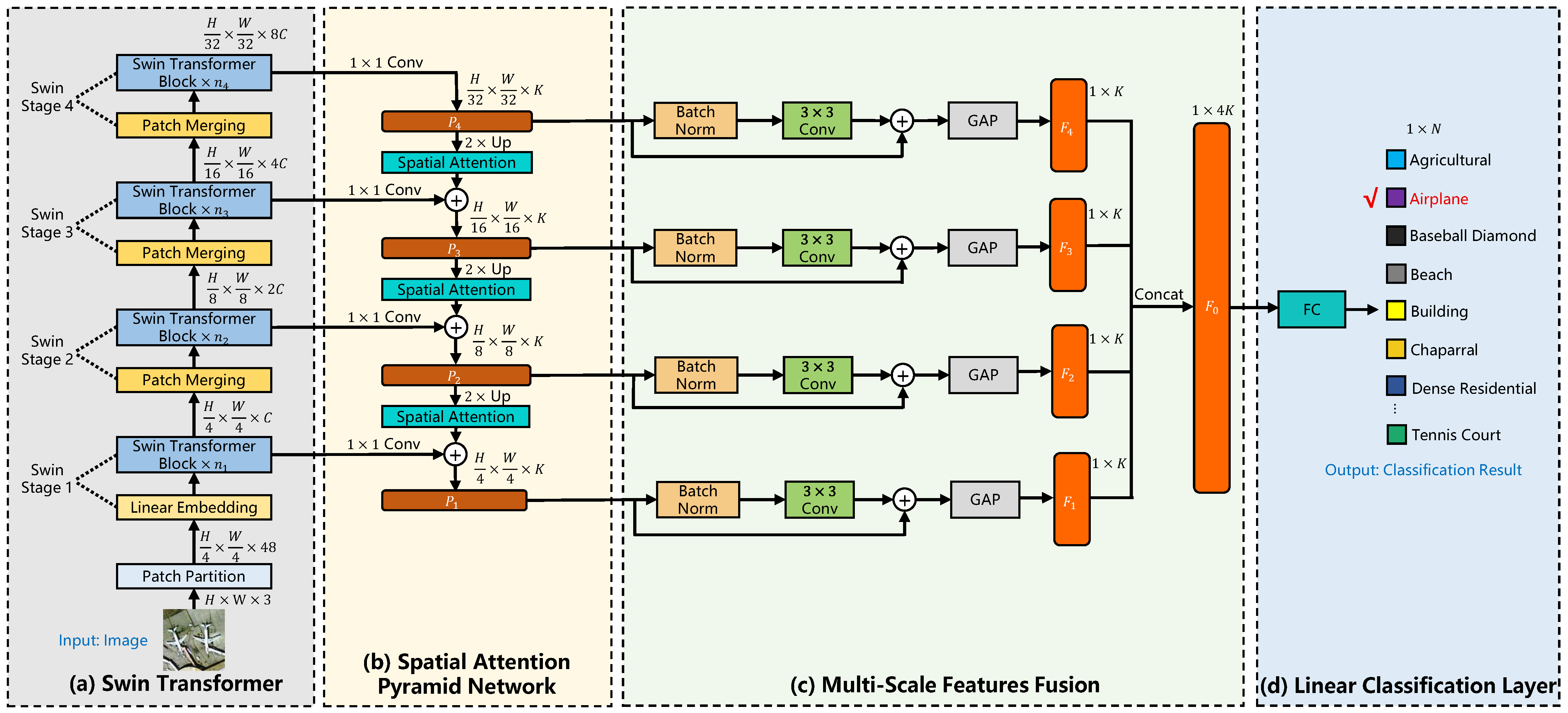
3. Methodology
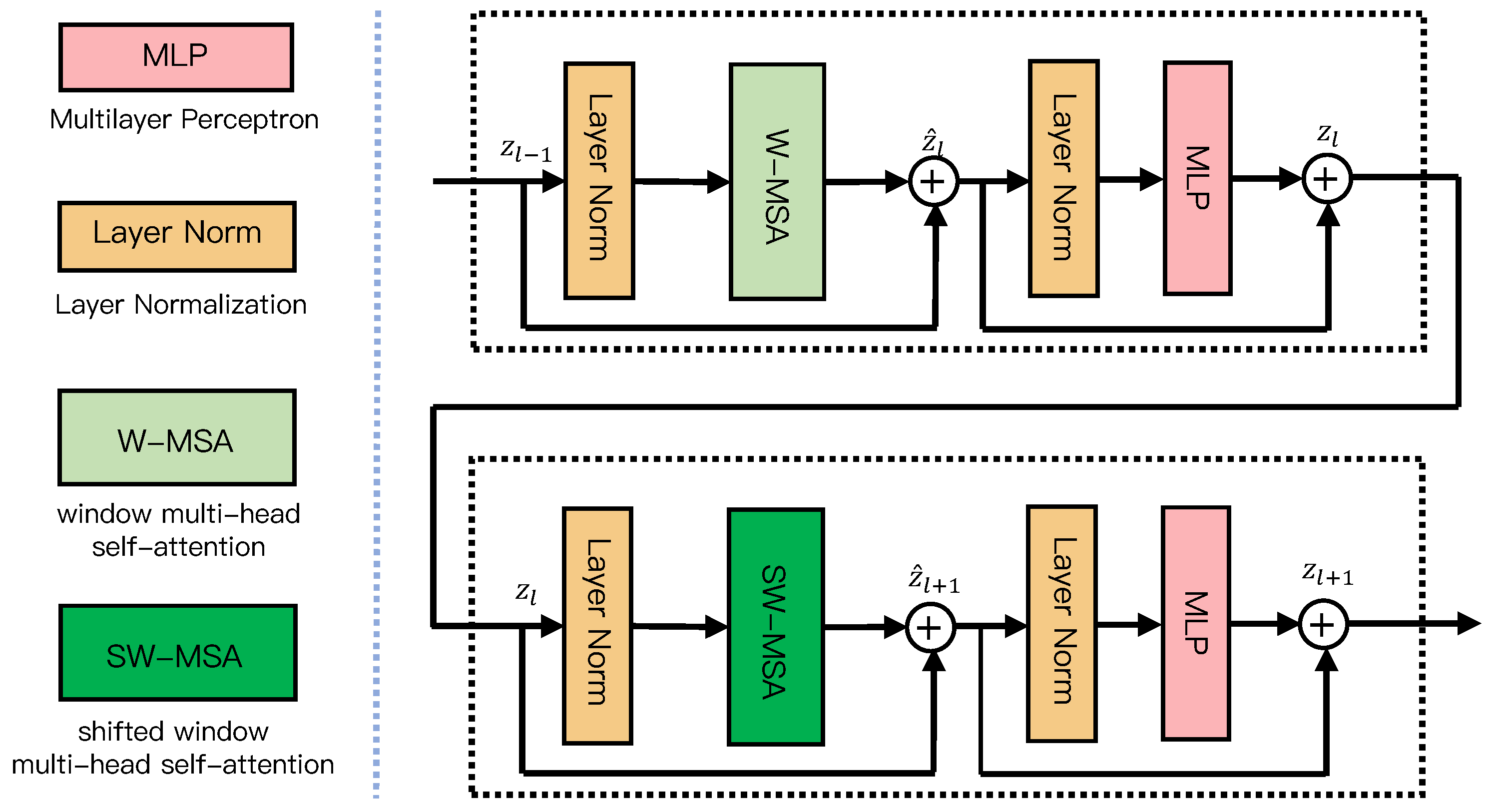
3.1. Swin Transformer
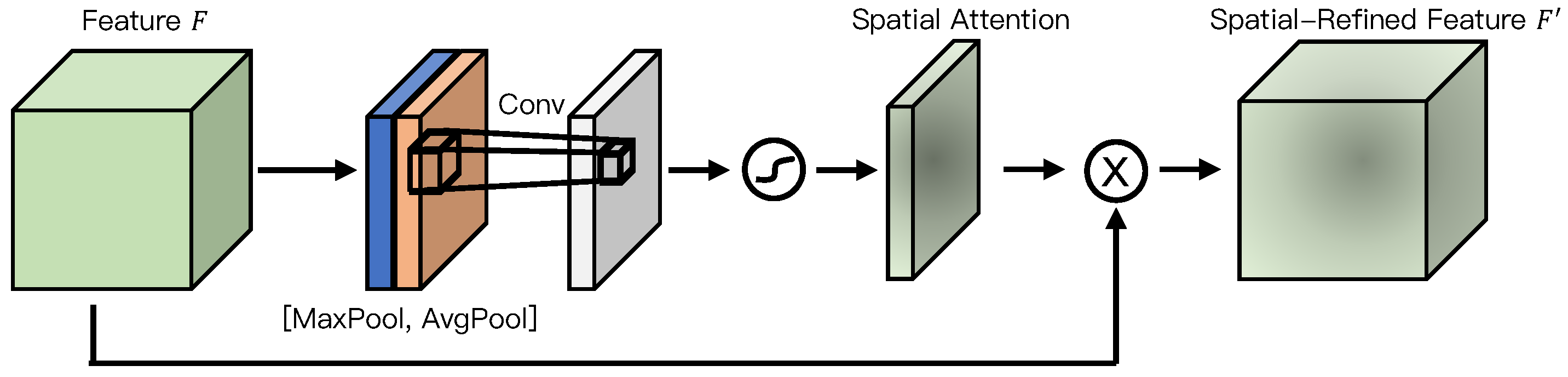
3.2. Spatial Attention Pyramid Network
3.3. Multi-Scale Features Fusion
4. Experimental Results
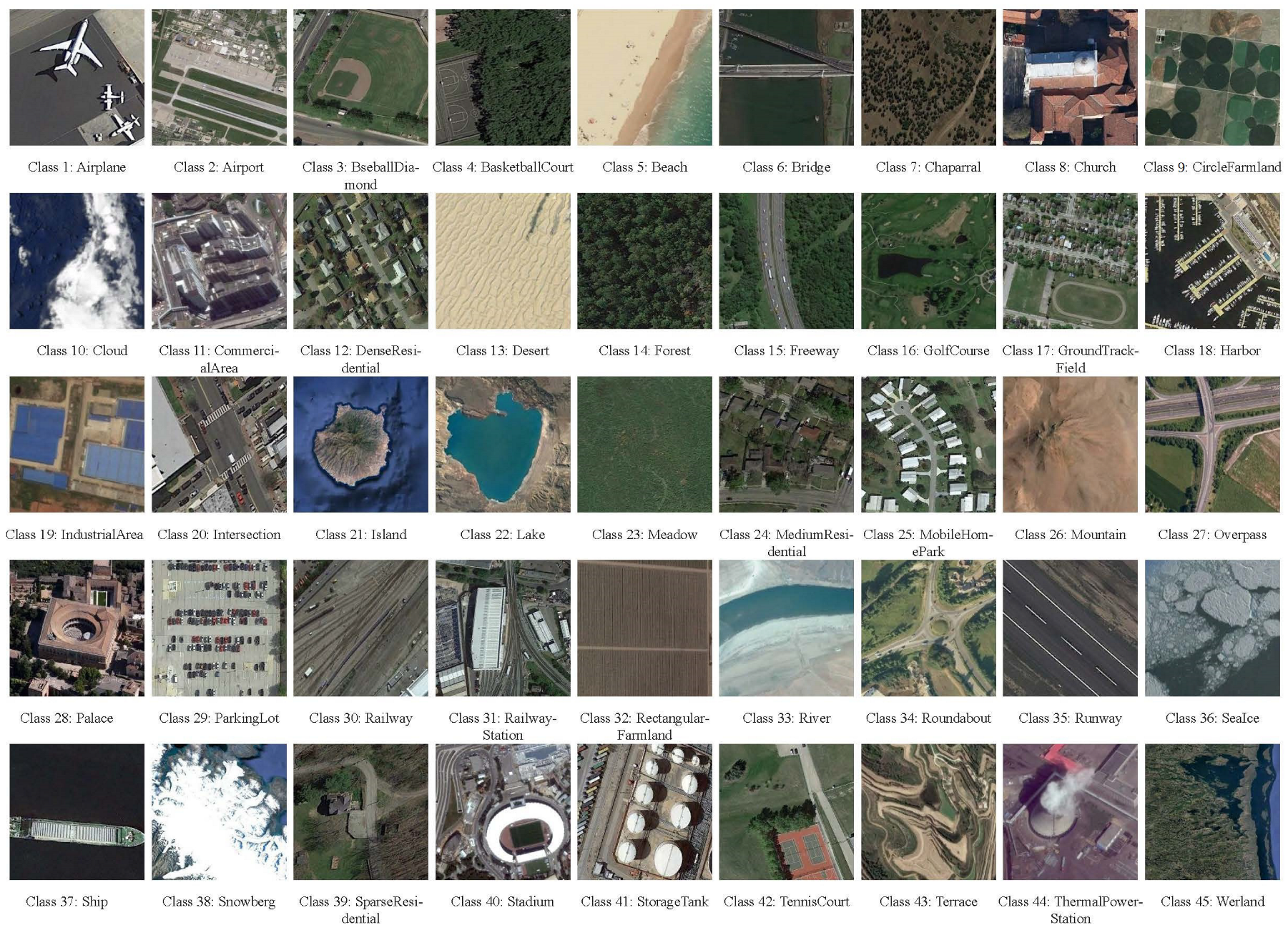
4.1. Dataset Introduction
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.2.1. Data Settings
4.2.2. Implementation Details
4.2.3. Evaluation Metrics
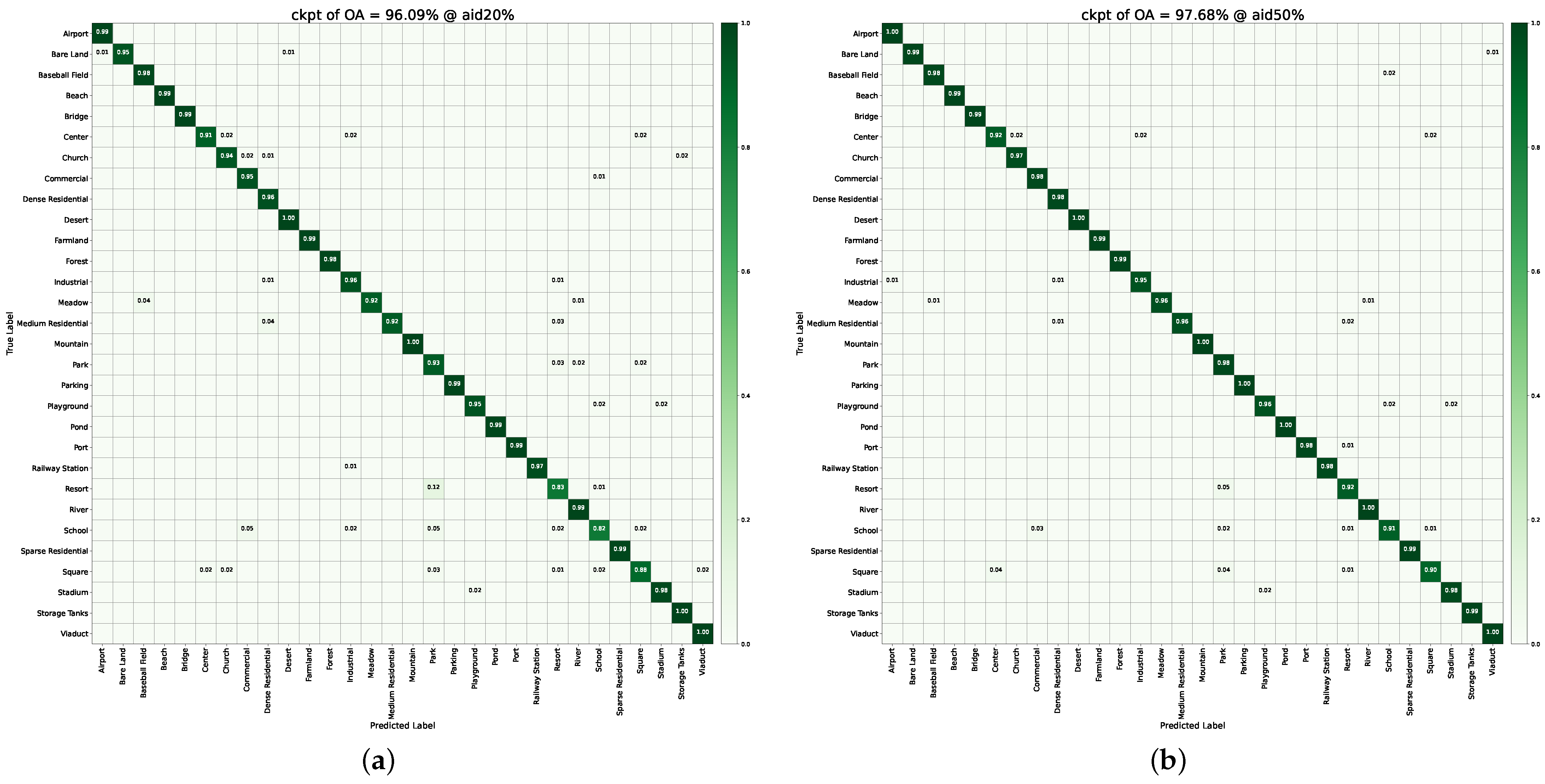
4.3. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.4. Ablation Study
4.5. Complexity Estimation
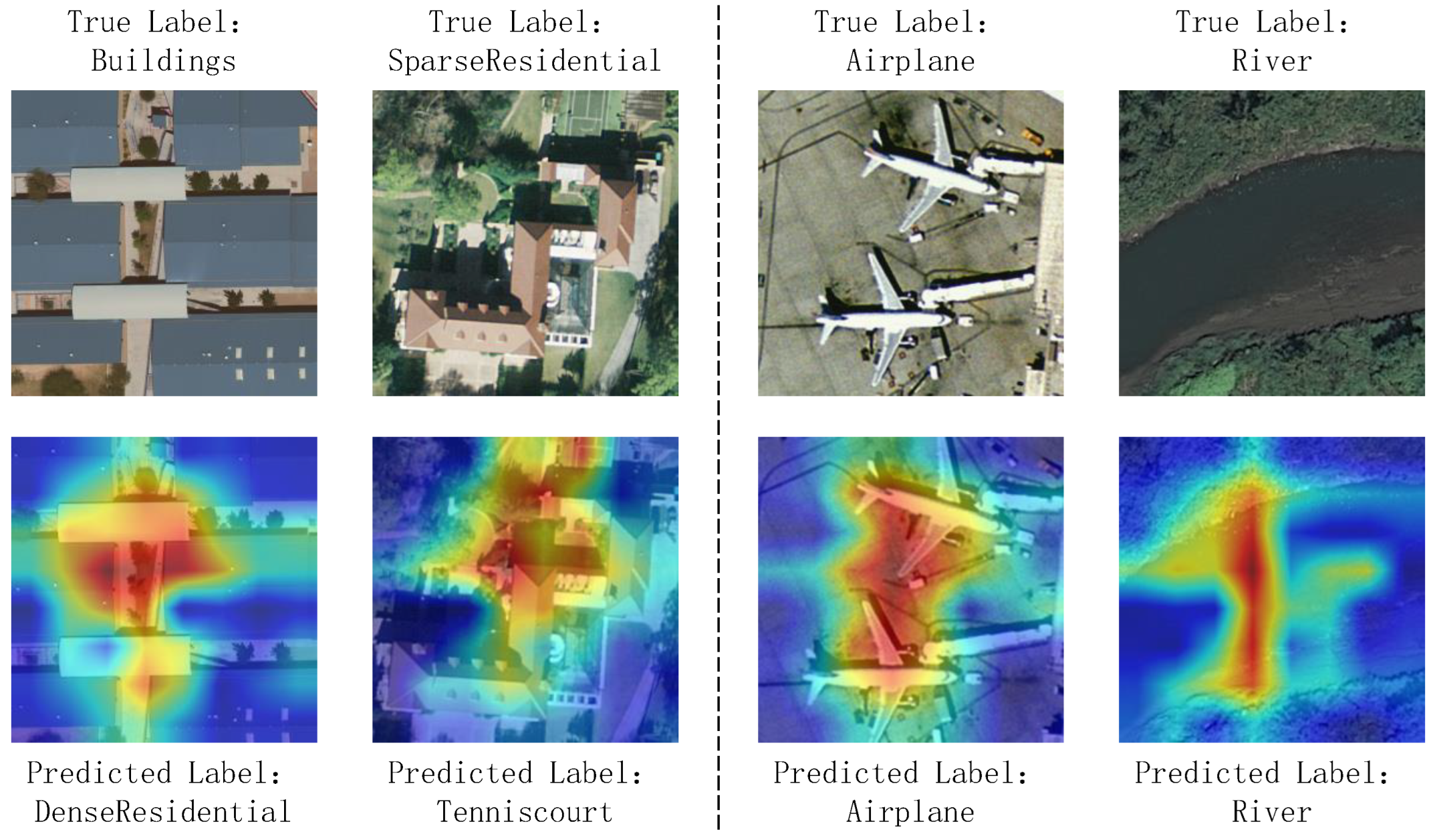
4.6. Explainable Artificial Intelligence Through Feature Visualization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mei, S.; Jiang, R.; Li, X.; Du, Q. Spatial and spectral joint super-resolution using convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 4590–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Geng, Y.; Hou, J.; Du, Q. Learning hyperspectral images from RGB images via a coarse-to-fine CNN. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2022, 65, 152102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Song, C.; Ma, M.; Xu, F. Hyperspectral image classification using group-aware hierarchical transformer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5539014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Gao, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, T. Encoder-free multiaxis physics-aware fusion network for remote sensing image dehazing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4705915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Peng, J.; Zhang, G.; Sun, W.; Du, Q. Deep contrastive learning network for small-sample hyperspectral image classification. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 3, 0025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Jiang, R.; Ma, M.; Song, C. Rotation-invariant feature learning via convolutional neural network with cyclic polar coordinates convolutional layer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5600713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Mei, S. Aerial visible-to-infrared image translation: Dataset, evaluation, and baseline. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 3, 0096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Li, Z.; Wen, Y.; Chen, T.; Niu, Q.; Liu, Z. Attention-free global multiscale fusion network for remote sensing object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5603214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Lian, J.; Wang, X.; Su, Y.; Ma, M.; Chau, L.-P. A comprehensive study on the robustness of deep learning-based image classification and object detection in remote sensing: Surveying and benchmarking. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 4, 0219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tian, Y. Pyramid of spatial relatons for scene-level land use classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1947–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Mao, Z.; Lin, J.; Guo, W. Land-use classification via extreme learning classifier based on deep convolutional features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wen, D.; Li, J.; Qin, R. Multi-level monitoring of subtle urban changes for the megacities of china using high-resolution multi-view satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 196, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Ning, C.; Zhou, H. Enhanced feature pyramid network with deep semantic embedding for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 7918–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Gao, S.; Deng, W.; Wang, W. Improving oriented object detection by scene classification and task-aligned focal loss. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aptoula, E. Remote sensing image retrieval with global morphological texture descriptors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3023–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohrevand, A.; Ahmadyfard, A.; Pouyan, A.; Imani, Z. A sift based object recognition using contextual information. In Proceedings of the 2014 Iranian Conference on Intelligent Systems, Bam, Iran, 4–6 February 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, L.; Liu, P.; Wang, L. Rotation sliding window of the hog feature in remote sensing images for ship detection. In Proceedings of the 2015 8th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design, Hangzhou, China, 12–13 December 2015; pp. 401–404. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J.; Lu, X. Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and state of the art. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1865–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.; Qin, K.; Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Xu, K. APDC-Net: Attention pooling-based convolutional network for aerial scene classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1603–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, L. Branch feature fusion convolution network for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5194–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xu, Q.; Guo, H.; Zhao, C.; Lin, Y.; Li, D. An efficient and lightweight convolutional neural network for remote sensing image scene classification. Sensors 2020, 20, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, W.; Zhao, W.; Huang, C.; Yk, E.N.; Chen, Y.; Su, J. A multiscale attention network for remote sensing scene images classification. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 9530–9545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Li, L.; Chen, W.; Zhou, H. SEMSDNet: A mltiscale dense network with attention for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 5501–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.P.; Alenezi, F.; Thirumoorthy, G.; Dutta, A.K.; You, J. Ensemble of deep learning-based multimodal remote sensing image classification model on unmanned aerial vehicle networks. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lu, X. Pairwise comparison network for remote-sensing scene classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6505105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual, 3–7 May 2021; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, W.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Tay, F.E.; Feng, J.; Yan, S. Tokens-to-token ViT: Training vision transformers from scratch on imagenet. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 538–547. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.-P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 568–578. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, B.; Yun, S.; Han, D.; Chun, S.; Choe, J.; Oh, S.J. Rethinking spatial dimensions of vision transformers. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11936–11945. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Miao, C.; Liu, C.; Tian, Q.; Zhou, Y. Hybrid attention transformer with multi-branch for large-scale high-resolution dense road segmentation. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. MFTransNet: A multi-modal fusion with CNN-transformer network for semantic segmentation of HSR remote sensing images. Mathematics 2023, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolya, D.; Fu, C.-Y.; Dai, X.; Zhang, P.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Hoffman, J. Token merging: Your ViT but faster. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Li, M.; Tang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Jiao, L. Homo–heterogenous transformer learning framework for rs scene classification. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2223–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, M.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Jiao, L. EMTCAL: Efficient multiscale transformer and cross-level attention learning for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5626915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Wu, W.; Zhong, Y.; Du, F.; Zhang, L. SCViT: A spatial channel feature preserving vision transformer for remote sensing image scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4409512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yi, J.; Chen, A.; Jin, Z. EFCOMFF-Net: A multiscale feature fusion architecture with enhanced feature correlation for remote sensing image scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5604917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Li, J.; An, Z.; Fan, H.; Fan, L. CTMFNet: CNN and transformer multiscale fusion network of remote sensing urban scene imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5900314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Feng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yu, C.; Song, B.; Cao, C. Optical remote sensing image target detection based on improved feature pyramid. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 7507–7517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Sehra, S.S.; Chiu, B. Multi-scale and multi-network deep feature fusion for discriminative scene classification of high-resolution remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X. RMFFNet: A reverse multi-scale feature fusion network for remote sensing scene classification. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Yokohama, Japan, 30 June–5 July 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W.; Shi, F.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Yuan, L.; Wen, X. A multi-scale dense residual correlation network for remote sensing scene classification. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, P.; Wu, W.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L. Review of vision transformer models for remote sensing image scene classification. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–22 July 2022; pp. 2231–2234. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Ma, M.; Li, Y.; Mei, S.; Han, Z.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, W. Hierarchical feature fusion of transformer with patch dilating for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4410516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, R.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y. PSCLI-TF: Position-sensitive cross-layer interactive transformer model for remote sensing image scene classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 5001305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Deria, A.; Hong, D.; Rasti, B.; Plaza, A.; Chanussot, J. Multimodal fusion transformer for remote sensing image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5515620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, N.; Liu, W.; Chen, H.; Xie, Y. MFST: A multi-level fusion network for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6516005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Li, N.; Ye, Y. Inductive biased swin-transformer with cyclic regressor for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 6265–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z.; Li, J. MITformer: A multiinstance vision transformer for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6510305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandala, H.; Saha, S.; Banerjee, B.; Zhu, X.X. Exploring transformer and multilabel classification for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6514905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Jia, N.; Bai, J. Transformer based on channel-spatial attention for accurate classification of scenes in remote sensing image. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Lin, S.; Zhou, W.; Huang, H. A lightweight dual-branch swin transformer for remote sensing scene classification. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Lang, C.; Wu, M.; Xie, X.; Yao, X.; Han, J. Feature enhancement network for object detection in optical remote sensing images. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 2021, 9805389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Yan, K.; Ma, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Du, Q. Remote sensing scene classification using sparse representation-based framework with deep feature fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 5867–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Newsam, S. Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification. In Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 2–5 November 2010; pp. 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, G.-S.; Hu, J.; Hu, F.; Shi, B.; Bai, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X. AID: A benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3965–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, Z.; Yao, X.; Guo, L.; Wei, Z. Remote sensing image scene classification using bag of convolutional features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1735–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]





| Dataset | Total | Classes | N per Class | Resolution | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCM | 2100 | 21 | 100 | 0.3m | 256 × 256 |
| AID | 10,000 | 30 | 220–420 | 0.5–8 m | 600 × 600 |
| NWPU | 31,500 | 45 | 700 | 0.2–30 m | 256 × 256 |
| Method | UCM@50% | UCM@80% | AID@20% | AID@50% | NWPU@10% | NWPU@20% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GoogLeNet [18] | 92.70 ± 0.60 | 94.31 ± 0.89 | 83.44 ± 0.40 | 86.39 ± 0.55 | 76.19 ± 0.38 | 78.48 ± 0.26 |
| VGG-16 [18] | 94.14 ± 0.69 | 95.21 ± 1.20 | 86.59 ± 0.29 | 89.64 ± 0.36 | 76.47 ± 0.18 | 79.79 ± 0.15 |
| APDC-Net [19] | 95.01 ± 0.43 | 97.05 ± 0.43 | 88.56 ± 0.29 | 92.15 ± 0.29 | 85.94 ± 0.22 | 87.84 ± 0.26 |
| LCNN-BFF [20] | 94.64 ± 0.21 | 99.29 ± 0.24 | 91.66 ± 0.48 | 94.62 ± 0.16 | 86.53 ± 0.15 | 91.73 ± 0.17 |
| BiMoblieNet [21] | 98.45 ± 0.27 | 99.03 ± 0.28 | 94.38 ± 0.24 | 96.87 ± 0.23 | 92.06 ± 0.14 | 94.08 ± 0.11 |
| MSA-Network [22] | 97.80 ± 0.33 | 98.96 ± 0.21 | 93.53 ± 0.21 | 96.01 ± 0.43 | 90.38 ± 0.17 | 93.52 ± 0.21 |
| PCNet [25] | 98.71 ± 0.22 | 99.25 ± 0.37 | 95.53 ± 0.16 | 96.76 ± 0.25 | 92.64 ± 0.13 | 94.59 ± 0.07 |
| MDRCN [42] | 98.57 ± 0.19 | 99.64 ± 0.12 | 93.64 ± 0.19 | 95.66 ± 0.18 | 91.59 ± 0.29 | 93.82 ± 0.17 |
| T2T-ViT-12 [27] | 95.68 ± 0.61 | 97.81 ± 0.49 | 90.09 ± 0.08 | 93.82 ± 0.55 | 84.91 ± 0.30 | 89.43 ± 0.23 |
| PiT-S [30] | 95.83 ± 0.39 | 98.33 ± 0.50 | 90.51 ± 0.57 | 94.17 ± 0.36 | 85.85 ± 0.18 | 89.91 ± 0.19 |
| PVT-Medium [28] | 96.27 ± 0.42 | 98.48 ± 0.49 | 92.13 ± 0.45 | 95.28 ± 0.23 | 87.40 ± 0.36 | 91.39 ± 0.09 |
| HHTL [34] | 98.87 ± 0.28 | 99.48 ± 0.28 | 95.62 ± 0.13 | 96.88 ± 0.21 | 92.07 ± 0.44 | 94.21 ± 0.09 |
| EMTCAL [35] | 98.67 ± 0.16 | 99.57 ± 0.28 | 94.69 ± 0.14 | 96.41 ± 0.23 | 91.63 ± 0.19 | 93.65 ± 0.12 |
| CSAT [51] | 95.72 ± 0.23 | 97.86 ± 0.16 | 92.55 ± 0.28 | 95.44 ± 0.17 | 89.70 ± 0.18 | 93.06 ± 0.16 |
| ToMe [33] | 98.54 ± 0.10 | 99.20 ± 0.07 | 95.19 ± 0.09 | 97.17 ± 0.12 | 92.56 ± 0.10 | 94.65 ± 0.16 |
| LDBST [52] | 98.76 ± 0.29 | 99.52 ± 0.24 | 95.10 ± 0.09 | 96.84 ± 0.20 | 90.83 ± 0.11 | 93.56 ± 0.07 |
| STMSF | 99.01 ± 0.31 | 99.58 ± 0.23 | 96.15 ± 0.16 | 97.51 ± 0.37 | 92.88 ± 0.16 | 94.95 ± 0.11 |
| Method | F1-Score (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCM | AID | NWPU | ||||
| 50% | 80% | 20% | 50% | 10% | 20% | |
| VGG-16 [18] | 87.85 | 88.12 | 69.90 | 73.34 | 59.99 | 63.29 |
| LCNN-BFF [20] | - | 99.29 | 91.61 | 94.56 | 86.44 | 91.67 |
| Vit-B [26] | 96.79 | 97.74 | 93.39 | 95.38 | 89.43 | 92.10 |
| PVT-Medium [28] | 98.13 | 99.08 | 93.89 | 95.20 | 89.83 | 91.22 |
| STMSF | 98.25 | 99.19 | 94.51 | 96.26 | 91.91 | 92.30 |
| ST | FPN | SAPN | Fusion | NWPU@10% | NWPU@20% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | 88.51 ± 0.19 | 91.60 ± 0.10 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 91.65 ± 0.14 | 93.88 ± 0.23 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 92.88 ± 0.16 | 94.95 ± 0.11 |
| Architecture | Parameters (M) | FLOPs (G) |
|---|---|---|
| GoogLeNet [18] | 6.8 | - |
| VGG-16 [18] | 138 | - |
| APDC-Net [19] | 0.6 | - |
| LCNN-BFF [20] | 6 | - |
| BiMoblieNet [21] | 7.76 | 0.45 |
| PCNet [25] | 32.1 | 3.87 |
| EMTCAL [35] | - | 4.23 |
| CSAT [51] | 85.99 | 16.88 |
| ToMe [33] | - | 4.6 |
| LDBST [52] | 9.3 | 2.6 |
| Swin Transformer | 48.81 | 8.54 |
| STMSF | 48.85 | 8.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, Y.; Song, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, P.; Mei, S. STMSF: Swin Transformer with Multi-Scale Fusion for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17040668
Duan Y, Song C, Zhang Y, Cheng P, Mei S. STMSF: Swin Transformer with Multi-Scale Fusion for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(4):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17040668
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Yingtao, Chao Song, Yifan Zhang, Puyu Cheng, and Shaohui Mei. 2025. "STMSF: Swin Transformer with Multi-Scale Fusion for Remote Sensing Scene Classification" Remote Sensing 17, no. 4: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17040668
APA StyleDuan, Y., Song, C., Zhang, Y., Cheng, P., & Mei, S. (2025). STMSF: Swin Transformer with Multi-Scale Fusion for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. Remote Sensing, 17(4), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17040668









