A VMD-TCN-Based Method for Predicting the Vibrational State of Scaffolding in Super High-Rise Building Construction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. VMD Algorithm
- (1)
- Utilize the Hilbert transform to obtain the one-sided spectrum of the signal:
- (2)
- Convert the spectrum into a baseband by multiplying it with an exponential signal at the estimated center frequency:
- (3)
- Estimate the bandwidth by Gaussian smoothing of the demodulated signal, represented as a constrained variational problem in Equation (3):
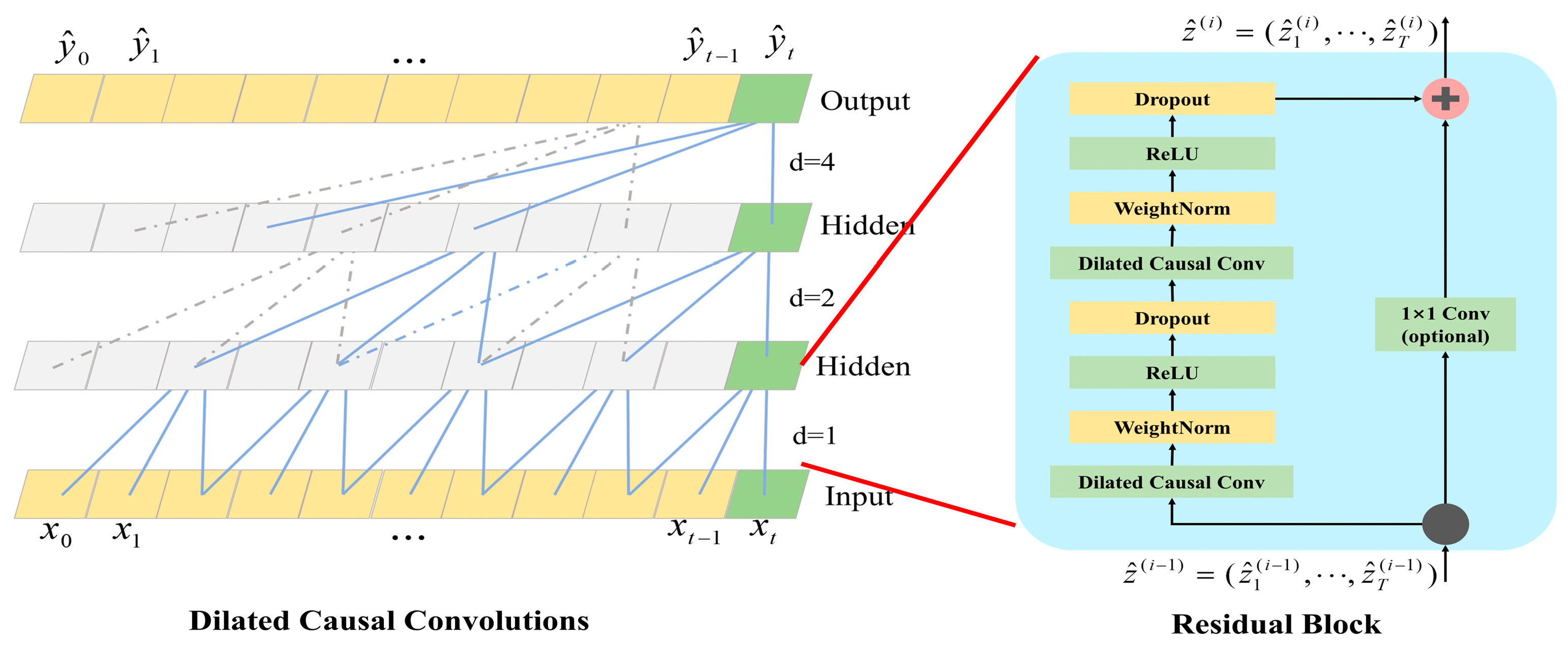
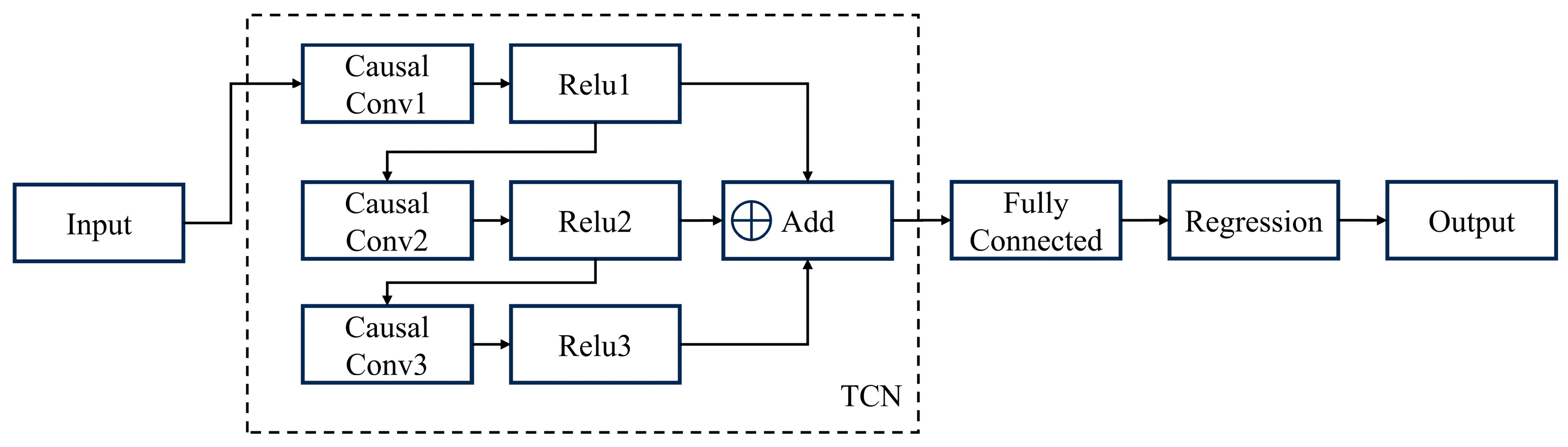
2.2. TCN Algorithm
- (1)
- Causal Convolution
- (2)
- Dilation Convolution
- (3)
- Residual Block
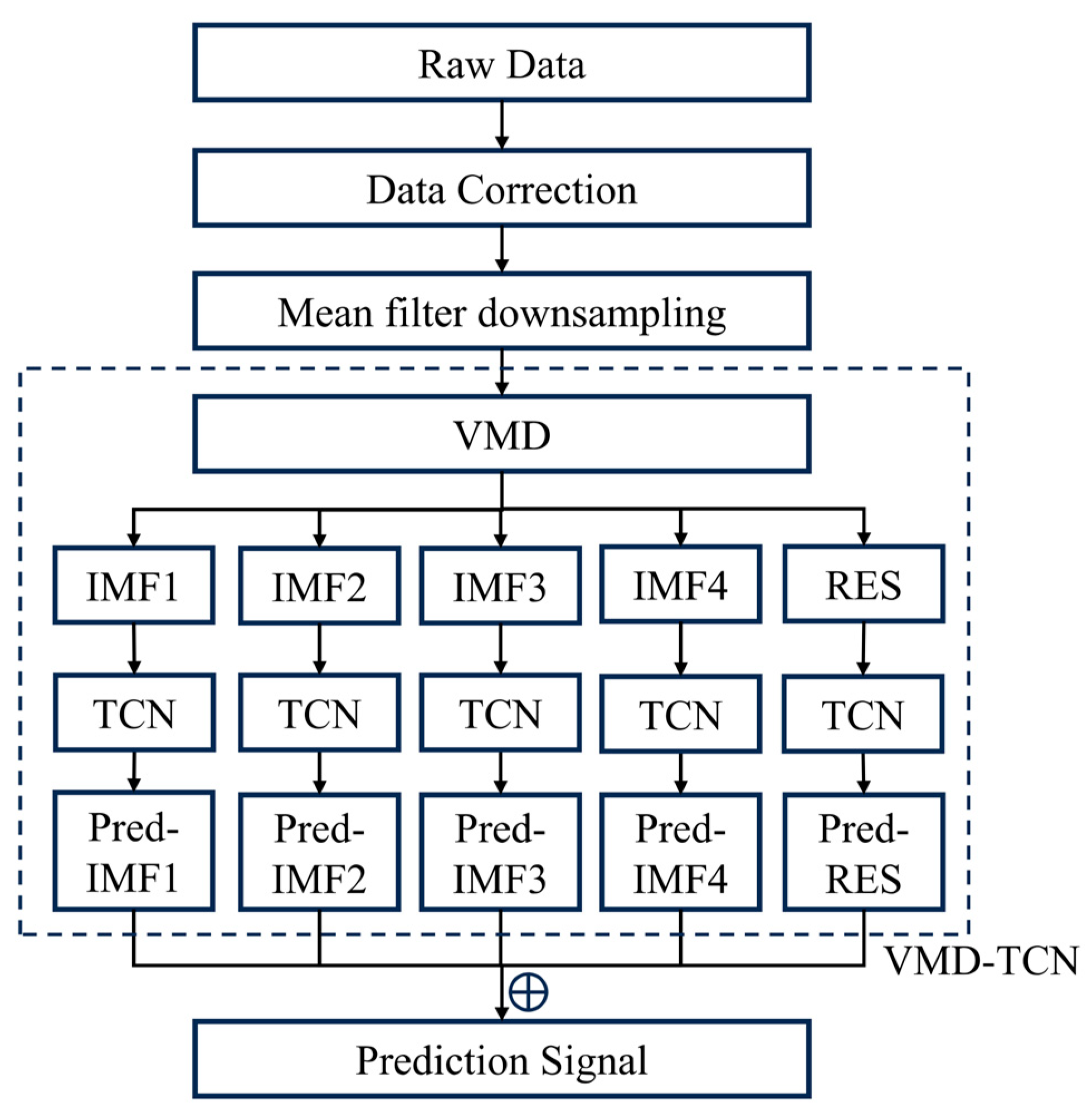
2.3. VMD-TCN Vibration State Prediction Model
3. Experimental Validation
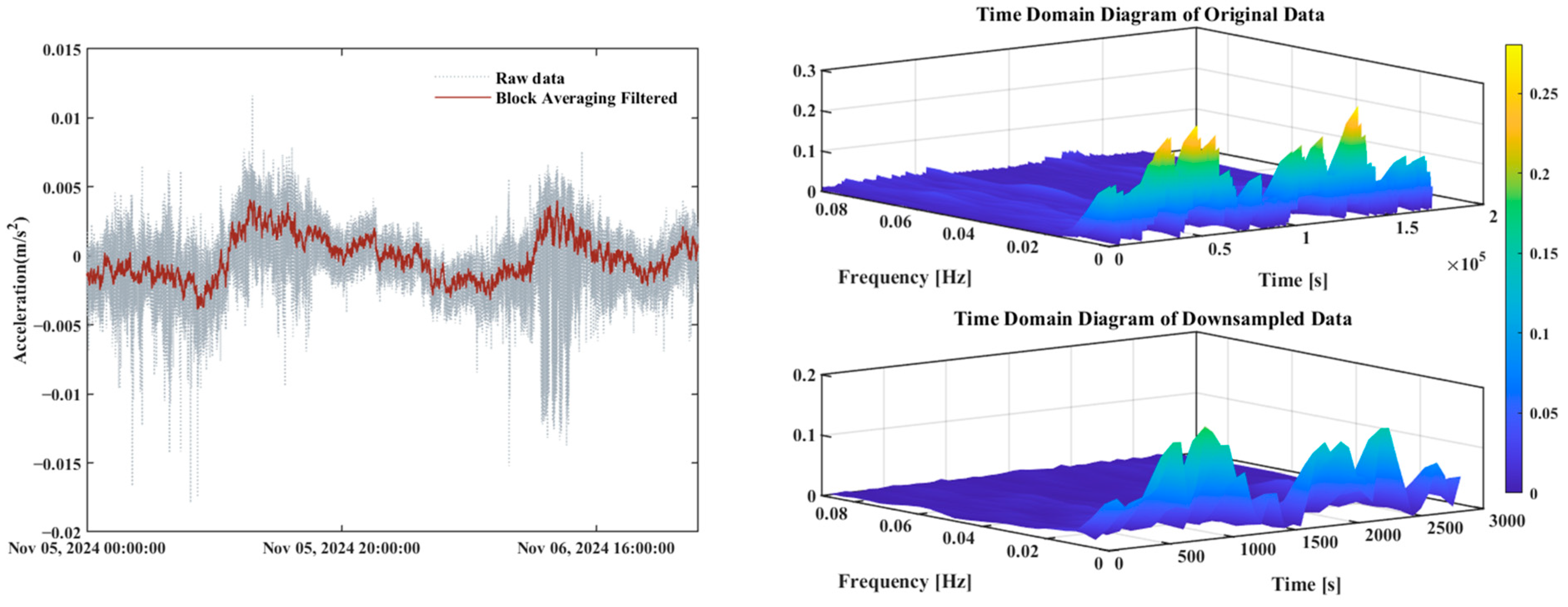
3.1. Collection and Preprocessing of Vibration State Data
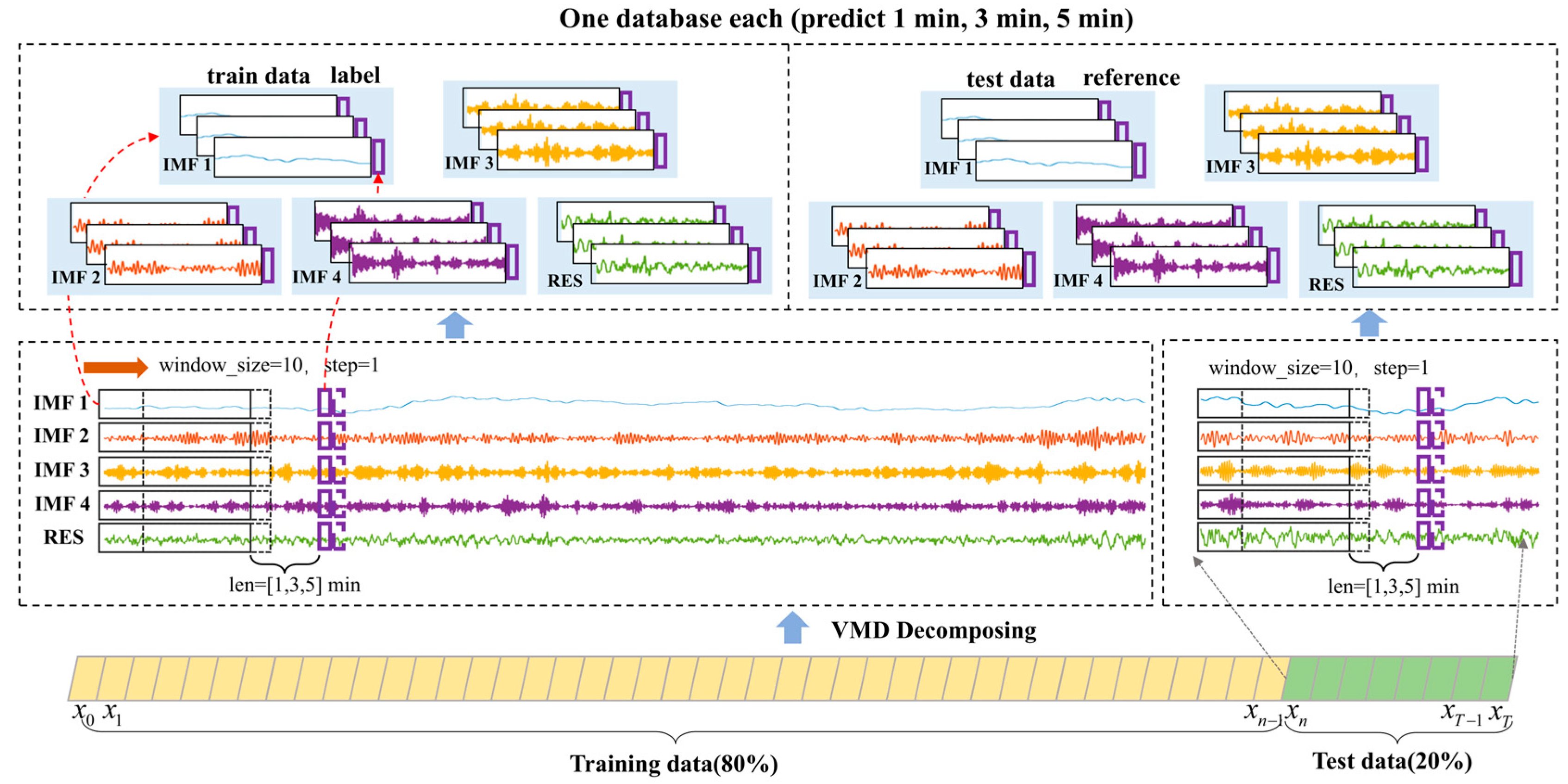
3.2. VMD-TCN Vibration State Prediction Model Database Construction
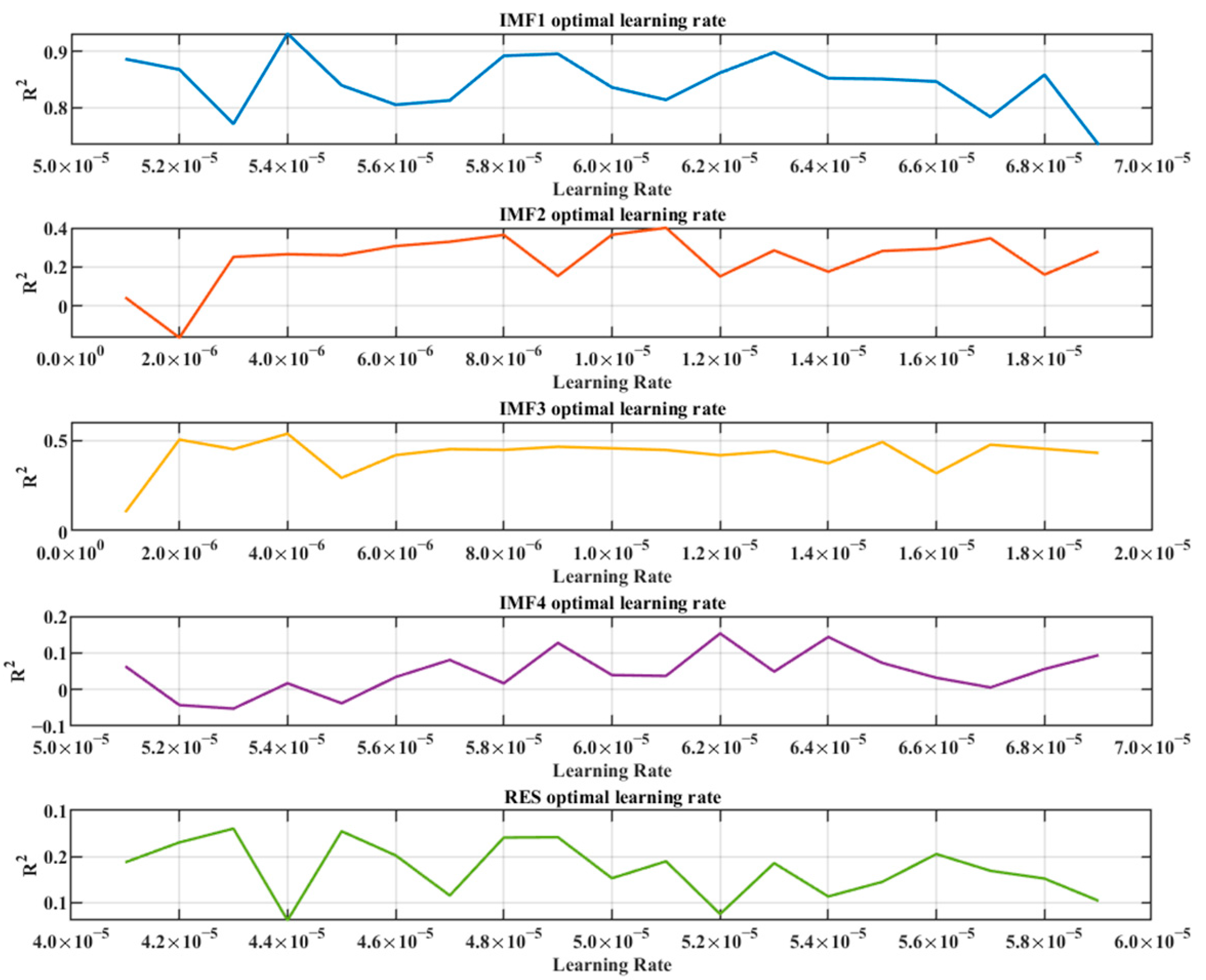
3.3. VMD-TCN Vibration State Prediction Model Training
3.4. Vibration State Prediction Model Performance Analysis
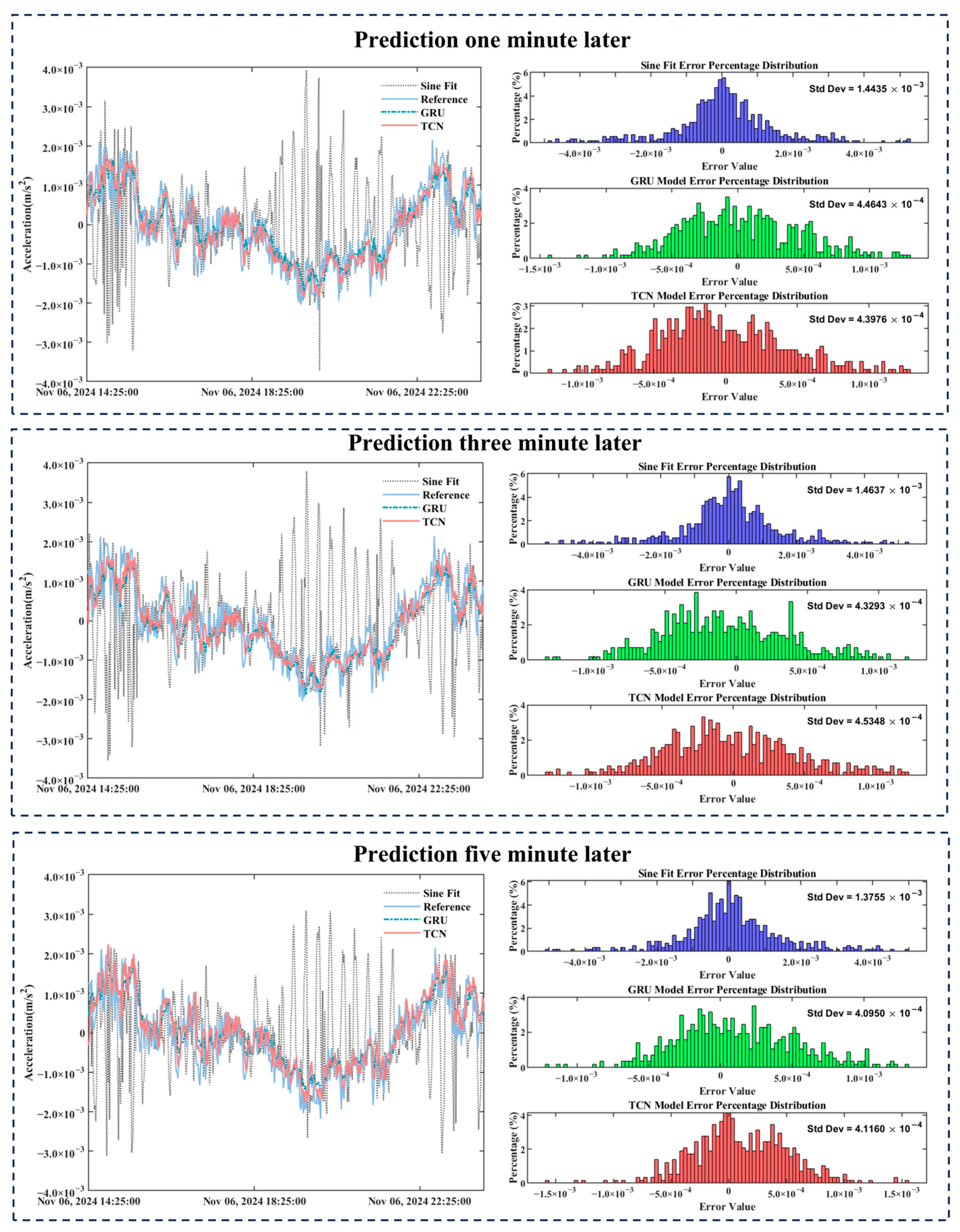
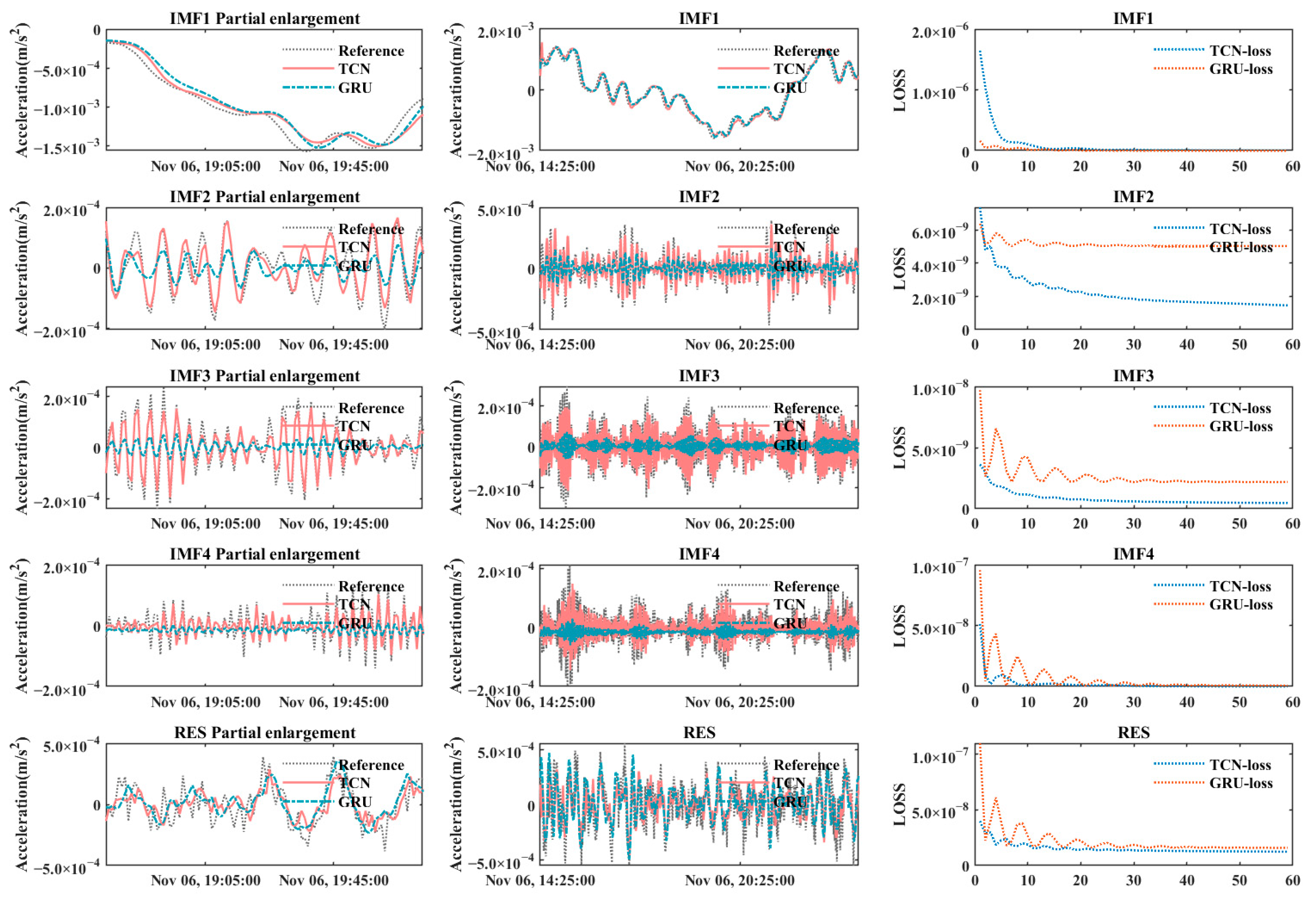
3.4.1. TCNs, GRUs, and Sinusoidal Wave Fitting Vibration State Prediction Model Accuracy Analysis
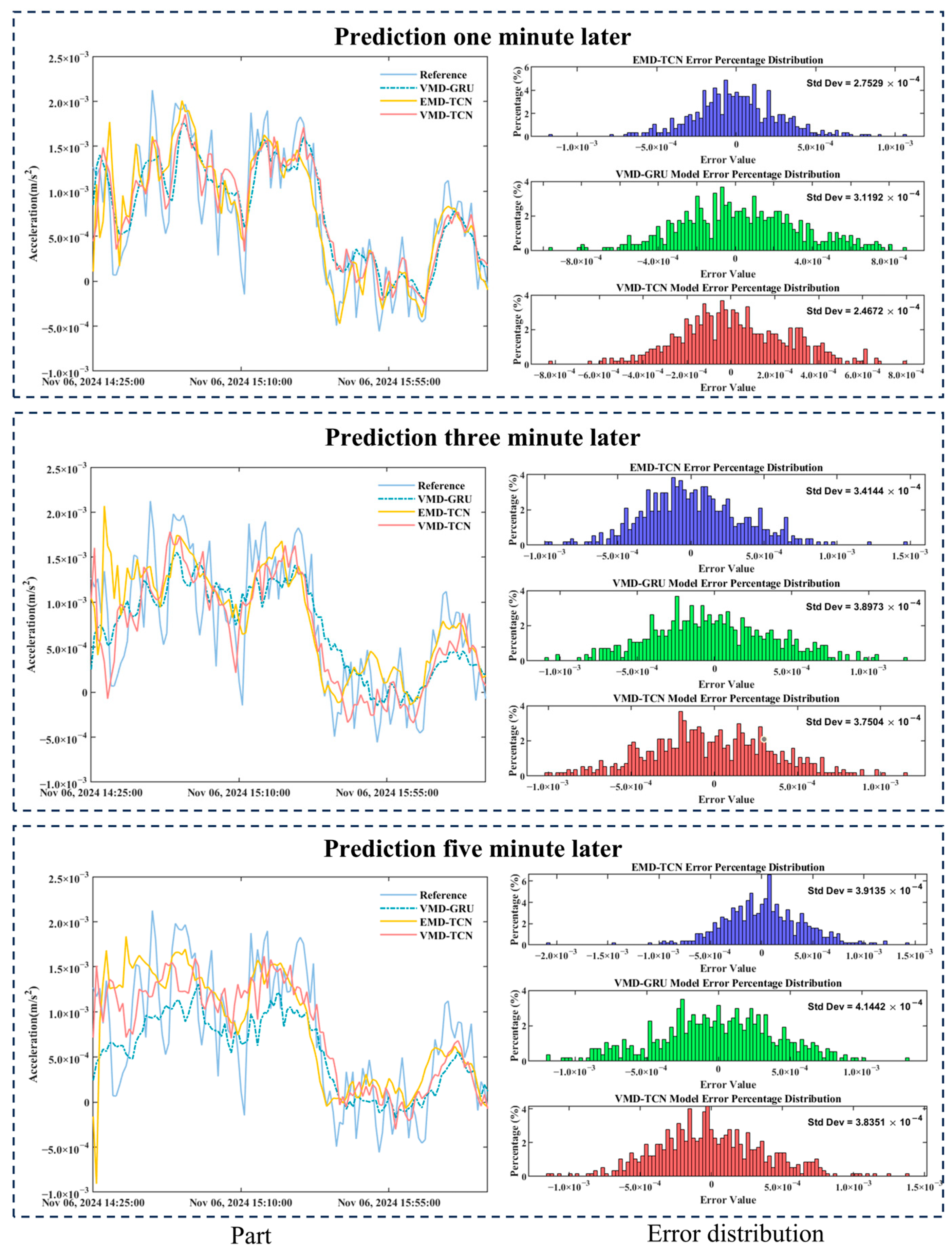
3.4.2. VMD-TCN and VMD-GRU Vibration State Prediction Model Accuracy Analysis
3.4.3. Influence of Different Training Window Lengths on Prediction Accuracy
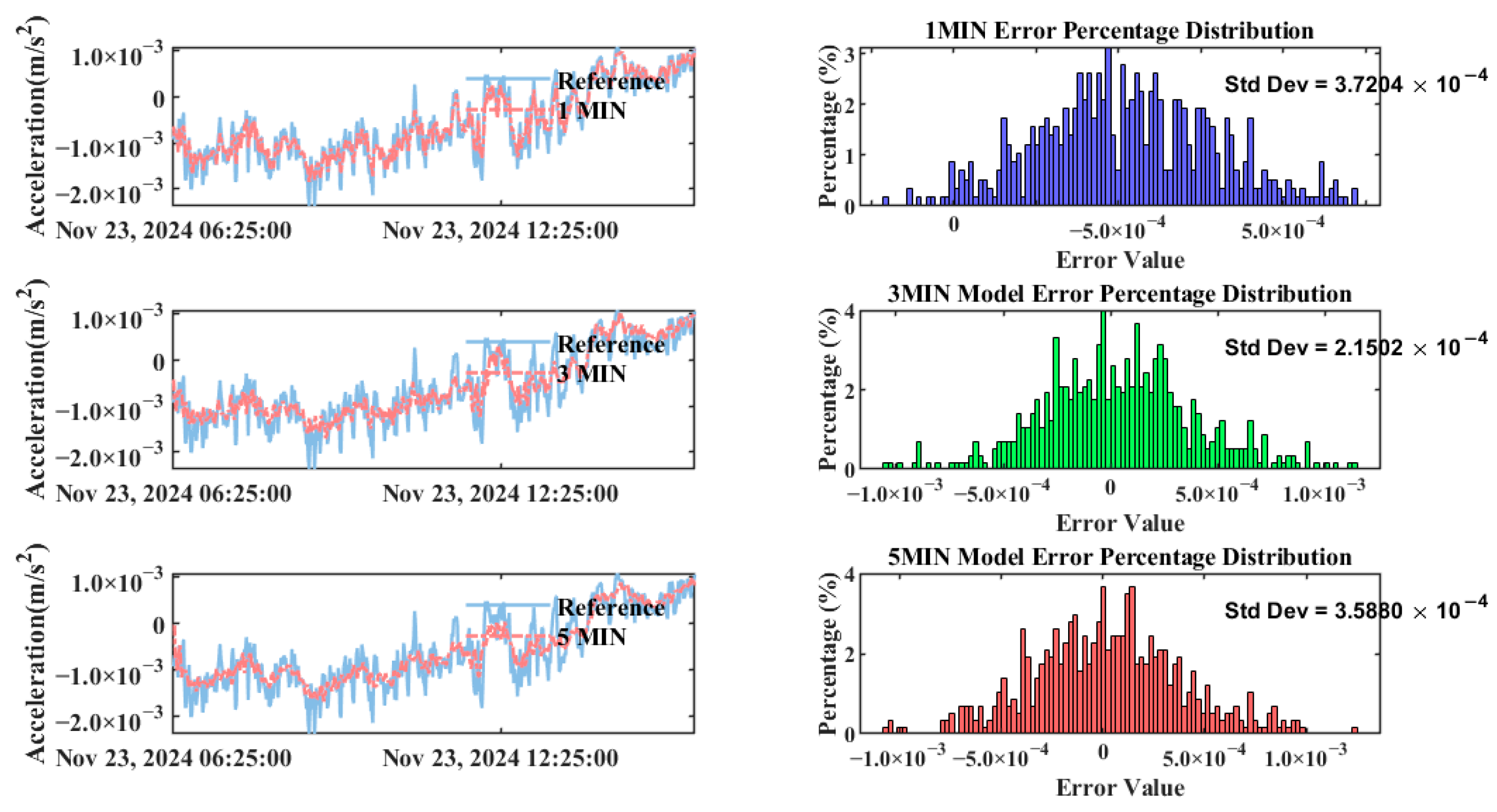
3.4.4. Verification of Model Data Applicability
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- VMD significantly enhances multi-frequency feature extraction capability. Compared to raw vibration signals, VMD modal signals (IMF1~IMF4) better represent low-frequency trends and high-frequency details, providing richer and more accurate feature inputs for deep learning models. Experimental results indicate that VMD effectively reduces mode mixing compared with EMD. Following VMD, the prediction accuracies of TCN and GRU networks improved substantially. Compared to predictions from unprocessed signals, the VMD-TCN model reduced RMSE by 43.9%, 43.2%, and 34.7% at 1 min, 3 min, and 5 min intervals, respectively, while improving R2 by 21.0%, 33.0%, and 37.6%. Similarly, the VMD-GRU model showed RMSE reductions of 29.9%, 26.9%, and 19.1%, with corresponding R2 improvements of 16.2%, 15.14%, and 20.9%.
- (2)
- The TCN model demonstrates superior predictive accuracy and computational efficiency. Compared to the GRU model, the TCN is particularly adept at handling high-frequency features. Specifically, for high-frequency modal components (IMF2, IMF3, and IMF4) obtained through VMD, the TCN achieved R2 values of 81.50%, 86.35%, and 63.18%, respectively—significantly higher than GRU’s corresponding values of 39.36%, 30.22%, and 21.78%. Overall, VMD-TCN achieved RMSE values of 2.47 × 10−4, 2.95 × 10−4, and 3.72 × 10−4 at 1 min, 3 min, and 5 min predictions, representing decreases of 21.1%, 21.9%, and 17.3% compared to VMD-GRU, respectively. Additionally, the training time for VMD-TCN was consistently between 5.58 and 5.72 s, significantly faster than VMD-GRU’s 49.49 to 58.88 s, demonstrating approximately 88–91% improvement in computational efficiency. Therefore, the TCN is more suitable for real-time applications requiring high responsiveness in practical engineering scenarios.
- (3)
- The VMD-TCN model exhibits strong generalization capability. Experimental validation across two independent datasets collected from different sensor locations and acquisition periods demonstrated stable and consistently high prediction accuracy. The new dataset yielded R2 values of 92.47%, 86.86%, and 81.09% for predictions at 1 min, 3 min, and 5 min intervals, respectively, closely matching the original dataset results (92.61%, 89.41%, 83.11%). Furthermore, prediction error distributions were normally distributed with low standard deviations (4.58 × 10−4, 4.01 × 10−4, and 3.47 × 10−4), and computational efficiency remained stable at around 5 s. These findings suggest the VMD-TCN model’s robustness and reliability, making it suitable for broader applications in vibration prediction tasks for super high-rise building construction.
- (1)
- Diversity in environmental conditions and scaffolding types. This study primarily evaluated aluminum climbing scaffolds in Tianjin. Applying the model under varied climatic conditions, materials (e.g., steel or composites), and different scaffolding types requires further investigation. Future research should gather vibration data from various construction sites to thoroughly assess the model’s adaptability and generalization performance in complex scenarios.
- (2)
- Currently, MEMS accelerometers were installed empirically, with only one sensor placed on each face of the scaffold. Systematic studies on the optimal number, placement, and spatial distribution of MEMS accelerometers are lacking. Identifying an optimal sensor deployment strategy will ensure comprehensive and accurate structural vibration monitoring.
- (3)
- Future studies could integrate multi-source heterogeneous data, such as wind speed, temperature, load conditions, and construction progress, with vibration signals. Employing multimodal deep learning models could enhance generalization and predictive accuracy in complex construction environments. Combining threshold-based analysis with trend analysis in a hybrid early-warning framework may further facilitate real-time risk identification and proactive construction safety management.
- (4)
- Determining acceptable vibration thresholds for scaffolding safety. Although the proposed VMD-TCN model significantly reduces prediction errors, practical safety management demands clearly defined vibration safety thresholds. Establishing universally applicable thresholds is challenging, as acceptable vibration levels vary greatly with scaffolding materials, structural design, load conditions, and environmental influences (e.g., wind and seismic forces). Future studies should leverage existing Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) standards and practical engineering insights to define clear vibration safety limits. Developing these thresholds will clarify how prediction accuracy translates into tangible safety improvements, enabling effective risk identification and proactive intervention.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, J.; Fang, T.; Zuo, J. A Review of Key Technologies Development of Super High-Rise Building Construction in China. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022, 2022, 5438917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, S.; Yu, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jing, Z.; Min, L.; Wang, Y. Application of Key Technologies for Multi-Terminal Change of Frame-Double Core Tube Super High-Rise Building. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 692, 22090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Nguyen, K.A.; Nguyen, V.L. An improvement of a hydraulic self-climbing formwork. Arch. Mech. Eng. 2019, 66, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.F.; Ni, Y.Q.; Ko, J.M. A data processing and analysis system for the instrumented suspension Jiangyin Bridge. In Proceedings of the World Forum on Smart Materials and Smart Structures Technology, Nanjing, China, 22–27 May 2008; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; p. 242. [Google Scholar]
- Housner, G.W. Behavior of structures during earthquakes. J. Eng. Mech. Div. 1959, 85, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, E.; Lawrence, J.; Christensen, C.; Chung, A. A novel strong-motion seismic network for community participation in earthquake monitoring. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2009, 12, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, R.; Heaton, T.; Chandy, M.; Krause, A.; Kohler, M.; Bunn, J.; Guy, R.; Olson, M.; Faulkner, M.; Cheng, M. Community seismic network. Ann. Geophys. 2011, 54, 738–747. [Google Scholar]
- Ozer, E.; Feng, M.Q.; Feng, D. Citizen sensors for SHM: Towards a crowdsourcing platform. Sensors 2015, 15, 14591–14614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Tani, A.; Yamabe, Y. Fundamental tests on a structural health monitoring system for building structures using a single-board microcontroller. J. Asian Archit. Build. 2015, 14, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; El-Tawil, S.; Agrawal, A.K. Miami pedestrian bridge collapse: Computational forensic analysis. J. Bridge Eng. 2020, 25, 4019134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin S, Y. Influence of shear deformations on the buckling of reinforced concrete elements. In Proceedings of the Innovations and Technologies in Construction: Selected Papers of BUILDINTECH BIT 2021, Belgorod, Russia, 9–10 March 2021; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Lamonaca, F.; Olivito, R.S.; Porzio, S.; Cami, D.L.; Scuro, C. Structural health monitoring system for masonry historical construction. In Proceedings of the 2018 Metrology for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage (MetroArchaeo), Cassino, Italy, 22–24 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 330–335. [Google Scholar]
- Uva, G.; Sangiorgio, V.; Ruggieri, S.; Fatiguso, F. Structural vulnerability assessment of masonry churches supported by user-reported data and modern Internet of Things (IoT). Measurement 2019, 131, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.; Lin, J. Unit impulse response estimation for structural damage detection under planar multiple excitations. J. Appl. Mech. 2014, 81, 21015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.F.; Xu, Y.L. Two-stage covariance-based multisensing damage detection method. J. Eng. Mech. 2017, 143, B4016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.L.; Lin, J.F.; Zhan, S.; Wang, F.Y. Multistage damage detection of a transmission tower: Numerical investigation and experimental validation. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Barone, G.; Smith, A. A novel multi-level data fusion and anomaly detection approach for infrastructure damage identification and localisation. Eng. Struct. 2023, 292, 116473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha Ribeiro, R.; de Almeida Sobral, R.; Cavalcante, I.B.; Conte Mendes Veloso, L.A.; de Melo Lameiras, R. A Low—Cost Wireless Multinode Vibration Monitoring System for Civil Structures. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2023, 2023, 5240059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarizadehasl, S.; Komary, M.; Alahmad, A.; Lozano-Galant, J.A.; Ramos, G.; Turmo, J. A novel wireless low-cost inclinometer made from combining the measurements of multiple MEMS gyroscopes and accelerometers. Sensors 2022, 22, 5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierleoni, P.; Marzorati, S.; Ladina, C.; Raggiunto, S.; Belli, A.; Palma, L.; Cattaneo, M.; Valenti, S. Performance evaluation of a low-cost sensing unit for seismic applications: Field testing during seismic events of 2016–2017 in Central Italy. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 6644–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragam, P.; Devidas Sahebraoji, N. Application of MEMS-based accelerometer wireless sensor systems for monitoring of blast-induced ground vibration and structural health: A review. IET Wirel. Sens. Syst. 2019, 9, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabato, A.; Niezrecki, C.; Fortino, G. Wireless MEMS-based accelerometer sensor boards for structural vibration monitoring: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 17, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhu, S. Developing iot sensing system for construction-induced vibration monitoring and impact assessment. Sensors 2020, 20, 6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.Y.; Zhou, C.; Deng, Q.X.; Luo, H.B.; Ye, X.W.; Ni, Y.Q.; Guo, P. Real-time safety early warning system for cross passage construction in Yangtze Riverbed Metro Tunnel based on the internet of things. Automat. Constr. 2013, 36, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, M.; Hosoda, A. Application of artificial neural network in predicting maximum thermal crack width of RC abutments using actual construction data. In Proceedings of the fib Symp, Krakow, Poland, 27–29 May 2019; pp. 1339–1346. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, F. Research on classification method of abnormal vibration of pipeline based on SVM. In Proceedings of the Eighth Symposium on Novel Photoelectronic Detection Technology and Applications, Kunming, China, 9–11 November 2022; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2022; Volume 12169, pp. 1184–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Mistikoglu, G.; Gerek, I.H.; Erdis, E.; Usmen, P.M.; Cakan, H.; Kazan, E.E. Decision tree analysis of construction fall accidents involving roofers. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 2256–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; González, A.; Casero, M. A kNN algorithm for locating and quantifying stiffness loss in a bridge from the forced vibration due to a truck crossing at low speed. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 154, 107599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhao, T.; Feng, C.; Zhang, W. Improvement of random forest by multiple imputation applied to tower crane accident prediction with missing data. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 30, 1222–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, T.; Li, X.; Zuo, Z.; Zong, G.; Zhang, L. Automatic identification of the working state of high-rise building machine based on machine learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, Q.; Han, X.; Lu, B.; Wan, J.; Xu, K. Improvement of GPS displacement measurement accuracy for high-rise buildings by machine learning. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 78, 107581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaton, T.; Hernandez, C.; Akhavian, R. Construction activity recognition with convolutional recurrent networks. Automat. Constr. 2020, 113, 103138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Shi, M.; Song, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H. Recurrent neural networks for real-time prediction of TBM operating parameters. Automat. Constr. 2019, 98, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, Q.; Li, Y. Investigation of time-varying natural frequencies of high-rise buildings under harsh excitations using a high-resolution combined scheme. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikumar, R.; Singampalli, R.S. Application of EMD based statistical parameters for the prediction of fault severity in a spur gear through vibration signals. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 8, 2152–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, B. Parallel spatio-temporal attention-based TCN for multivariate time series prediction. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 13109–13118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Mo, X.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J. Recovery Method of Continuous Missing Data in the Bridge Monitoring System Using SVMD-Assisted TCN–MHA–BiGRU. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2025, 2025, 8833186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Kolter, J.Z.; Koltun, V. An empirical evaluation of generic convolutional and recurrent networks for sequence modeling. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.01271. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Wang, B.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Pang, X. Stacking integration algorithm based on CNN-BiLSTM-Attention with XGBoost for short-term electricity load forecasting. Energy Rep. 2024, 12, 2676–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui-Tien, T.; Nguyen-Chi, T.; Le-Xuan, T.; Tran-Ngoc, H. Enhancing bridge damage assessment: Adaptive cell and deep learning approaches in time-series analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 439, 137240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sun, X.; Wang, Q.; Deng, S. Short-term load forecasting using EMD with feature selection and TCN-based deep learning model. Energies 2022, 15, 7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ge, B.; Han, B. Real-time motor fault diagnosis based on tcn and attention. Machines 2022, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justusson, B.I. Median filtering: Statistical Properties. In Two-Dimensional Digital Signal Prcessing II: Transforms and Median Filters; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 161–196. [Google Scholar]
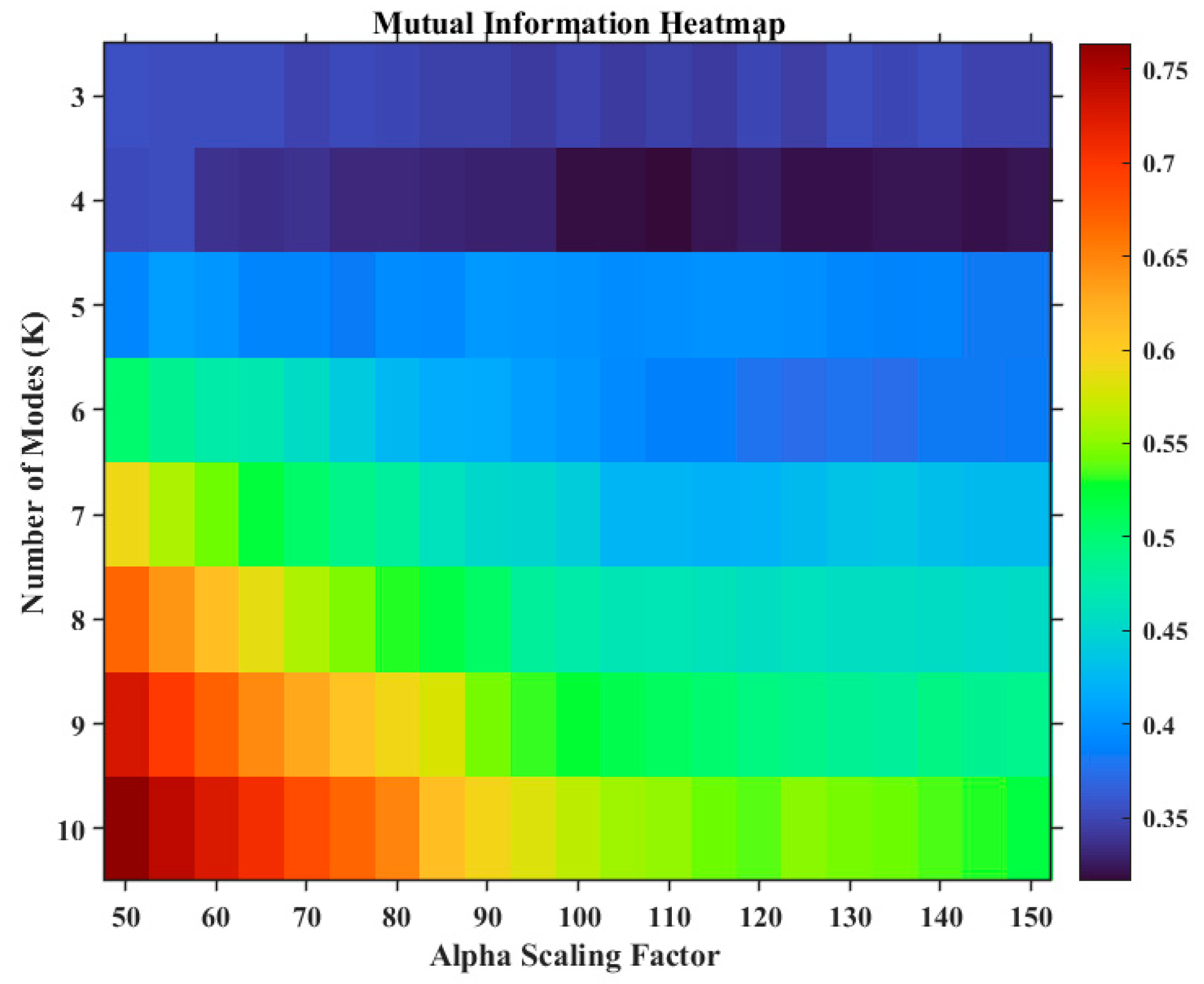
- Kumar, A.; Zhou, Y.; Xiang, J. Optimization of VMD using kernel-based mutual information for the extraction of weak features to detect bearing defects. Measurement 2021, 168, 108402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Händel, P. Evaluation of a standardized sine wave fit algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nordic Signal Processing Symposium, Kolmården, Sweden, 13–15 June 2000. [Google Scholar]


| Model | Metric | 1 min | 3 min | 5 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCN | RMSE | 4.40 × 10−4 | 5.19 × 10−4 | 5.70 × 10−4 |
| MAE | 3.53 × 10−4 | 4.14 × 10−4 | 4.43 × 10−4 | |
| R2 | 76.55% | 67.21% | 60.39% | |
| Time | 1.09 | 1.17 | 1.18 | |
| GRU | RMSE | 4.46 × 10−4 | 5.17 × 10−4 | 5.56 × 10−4 |
| MAE | 3.57 × 10−4 | 4.13 × 10−4 | 4.36 × 10−4 | |
| R2 | 75.87% | 67.53% | 62.32% | |
| Time | 12.48 | −50.45 | 9.35 | |
| SIN | RMSE | 1.44 × 10−3 | 1.46 × 10−3 | 1.40 × 10−3 |
| MAE | 9.97 × 10−4 | 1.03 × 10−3 | 1.00 × 10−3 | |
| R2 | −152.16% | −158.29% | −139.59% | |
| Time | 5.96 | 5.45 | 5.17 |
| Signal | R2 | |
|---|---|---|
| TCN | GRU | |
| IMF1 | 97.45% | 97.36% |
| IMF2 | 81.50% | 39.36% |
| IMF3 | 86.35% | 30.22% |
| IMF4 | 63.18% | 21.78% |
| RES | 43.26% | 25.12% |
| Model | 1 min CI | 3 min | 5 min | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VMD-GRU | (1.54 × 10−6, 5.27 × 10−5) | (−4.25 × 10−5, 2.14 × 10−5) | (−4.49 × 10−5, 2.31 × 10−5) | The CI is the largest, but fluctuations are significant at 3 min and 5 min. |
| EMD-TCN | (−2.45 × 10−5, 2.06 × 10−5) | (−1.24 × 10−5, 4.36 × 10−5) | (−1.54 × 10−5, 4.88 × 10−5) | The CI narrows, but fluctuations remain relatively large at 5 min. |
| VMD-TCN | (−5.39 × 10−6, 3.51 × 10−5) | (−5.17 × 10−5, 9.76 × 10−6) | (−3.50 × 10−5, 2.79 × 10−5) | The CI is the narrowest, with the smallest error and the best stability. |
| Model | Metric | 1 min | 3 min | 5 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMD-TCN | RMSE | 2.75 × 10−4 | 3.41 × 10−4 | 3.79 × 10−4 |
| MAE | 2.11 × 10−4 | 2.67 × 10−4 | 2.95 × 10−4 | |
| R2 | 90.84% | 85.87% | 82.51% | |
| Times (s) | 6.06 | 7.32 | 7.94 | |
| VMD-TCN | RMSE | 2.47 × 10−4 | 2.95 × 10−4 | 3.72 × 10−4 |
| MAE | 1.96 × 10−4 | 2.38 × 10−4 | 2.95 × 10−4 | |
| R2 | 92.61% | 89.41% | 83.11% | |
| Time (s) | 5.72 | 5.58 | 5.67 | |
| VMD-GRU | RMSE | 3.13 × 10−4 | 3.78 × 10−4 | 4.50 × 10−4 |
| MAE | 2.49 × 10−4 | 3.05 × 10−4 | 3.61 × 10−4 | |
| R2 | 88.15% | 82.67% | 75.37% | |
| Time (s) | 58.88 | 50.34 | 49.49 |
| Metric | 5 min | 10 min | 15 min | 20 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 2.50 × 10−4 | 2.47 × 10−4 | 2.89 × 10−4 | 2.90 × 10−4 |
| MAE | 1.97 × 10−4 | 1.96 × 10−4 | 2.25 × 10−4 | 2.33 × 10−4 |
| R2 | 90.78% | 92.61% | 89.88% | 89.79% |
| Times (s) | 6.87 | 5.72 | 4.95 | 5.58 |
| Model | Metric | 1 min | 3 min | 5 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VMD-TCN | RMSE | 2.16 × 10−4 | 2.87 × 10−4 | 3.47 × 10−4 |
| MAE | 1.73 × 10−4 | 2.26 × 10−4 | 2.72 × 10−4 | |
| R2 | 92.47% | 86.86% | 81.09% | |
| Times(s) | 4.89 | 4.98 | 5.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, P.; Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, P. A VMD-TCN-Based Method for Predicting the Vibrational State of Scaffolding in Super High-Rise Building Construction. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061047
Zhu P, Liu G, Wang J, Wang P. A VMD-TCN-Based Method for Predicting the Vibrational State of Scaffolding in Super High-Rise Building Construction. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(6):1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061047
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Ping, Gen Liu, Jian Wang, and Pengfei Wang. 2025. "A VMD-TCN-Based Method for Predicting the Vibrational State of Scaffolding in Super High-Rise Building Construction" Remote Sensing 17, no. 6: 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061047
APA StyleZhu, P., Liu, G., Wang, J., & Wang, P. (2025). A VMD-TCN-Based Method for Predicting the Vibrational State of Scaffolding in Super High-Rise Building Construction. Remote Sensing, 17(6), 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061047






