A Novel Method for PolISAR Interpretation of Space Target Structure Based on Component Decomposition and Coherent Feature Extraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel component decomposition method for electromagnetic simulation of space target components.
- Direct pixel-by-pixel identification of the components of space targets.
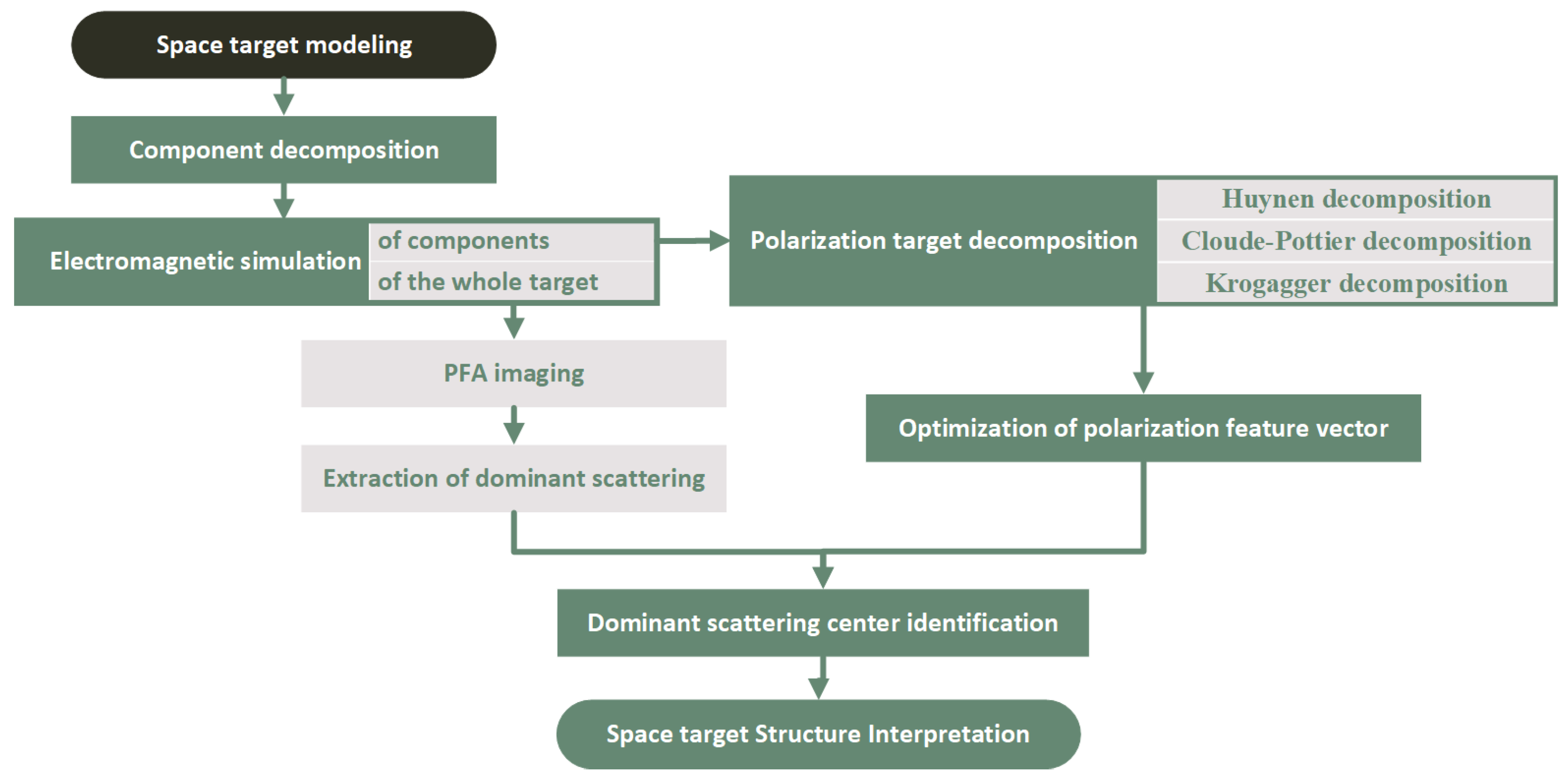
2. Materials and Methods
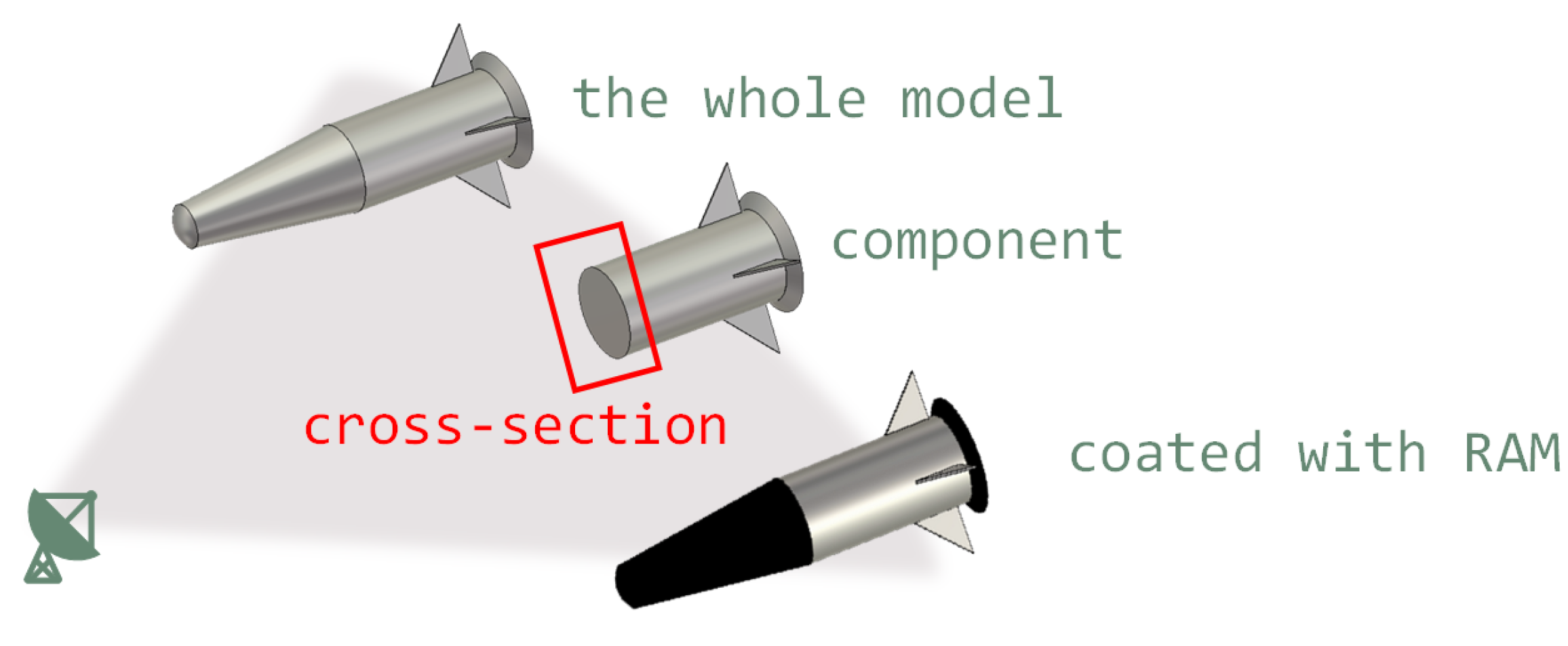
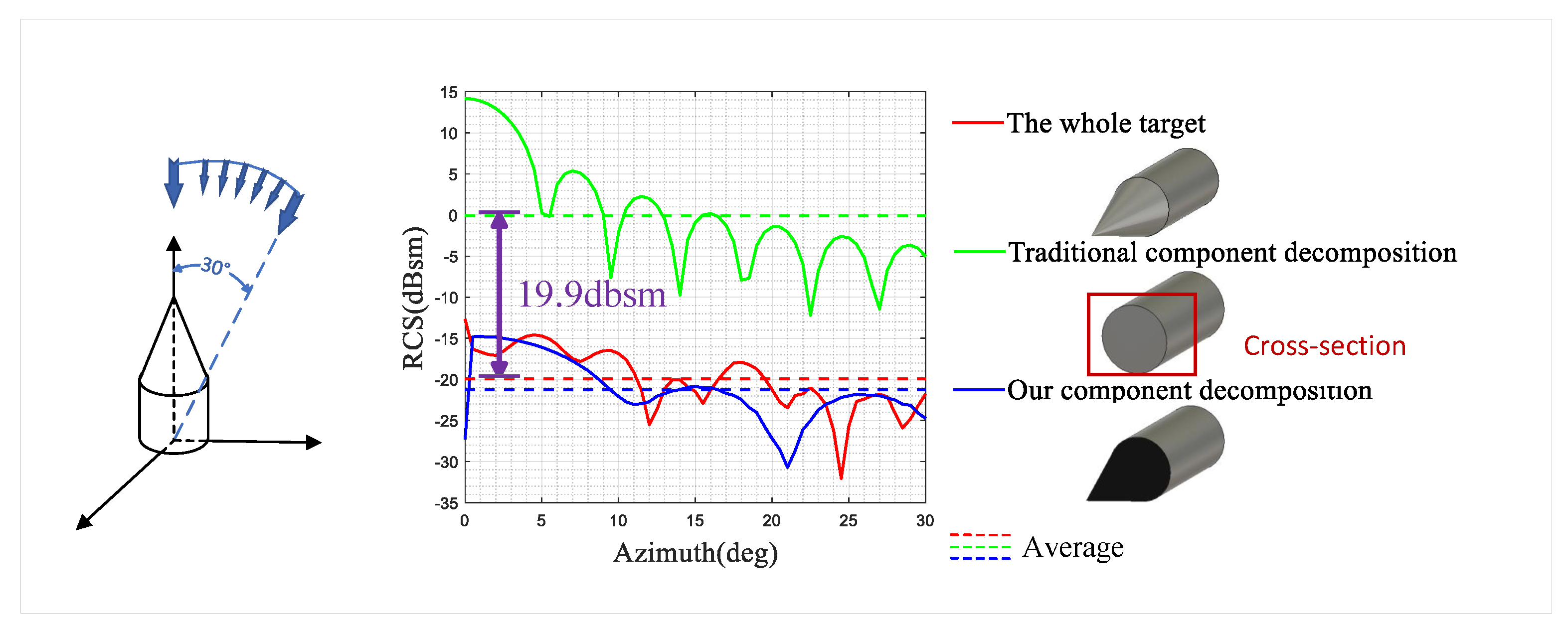
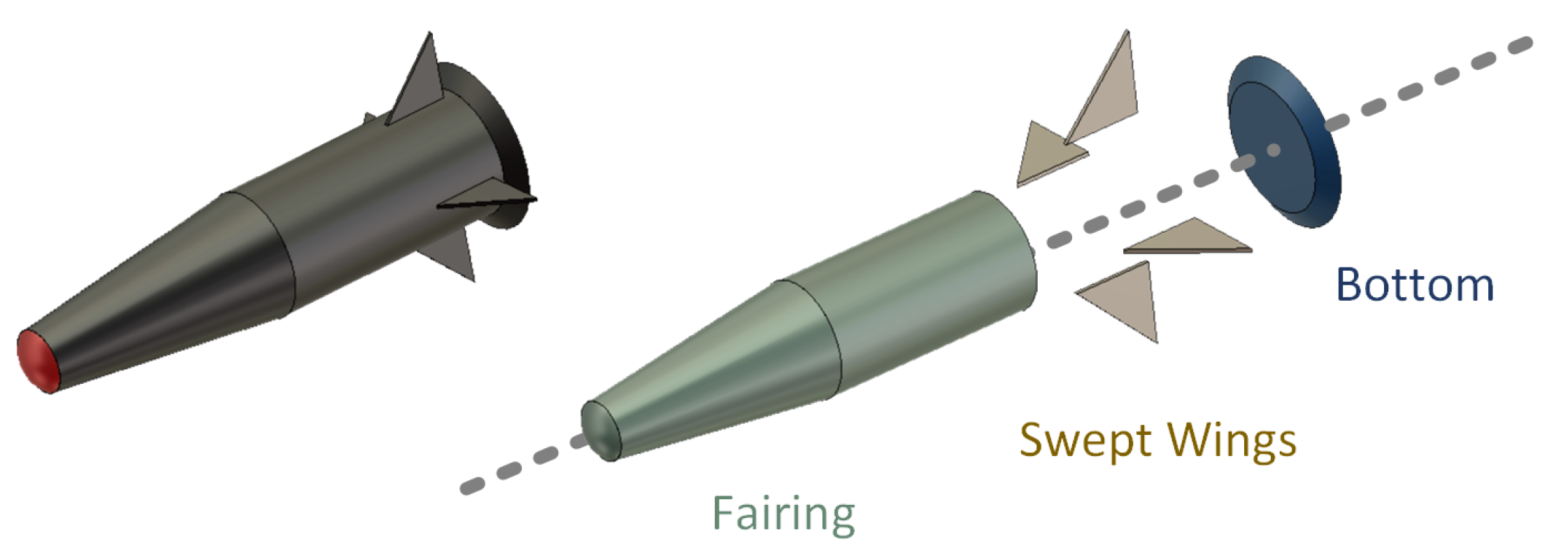
2.1. Component Decomposition
2.2. Polarization Feature Extraction
2.2.1. Huynen Decomposition
2.2.2. Cloude–Pottier Decomposition
2.2.3. Krogager Decomposition
2.3. Feature Selection
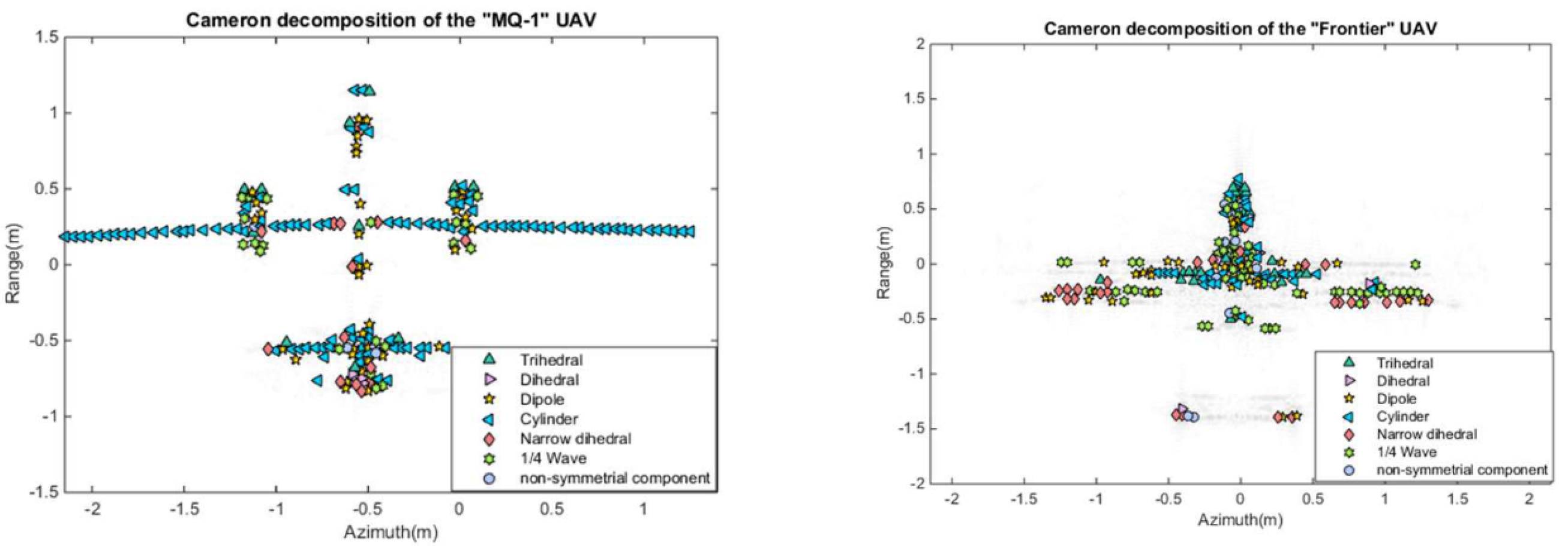
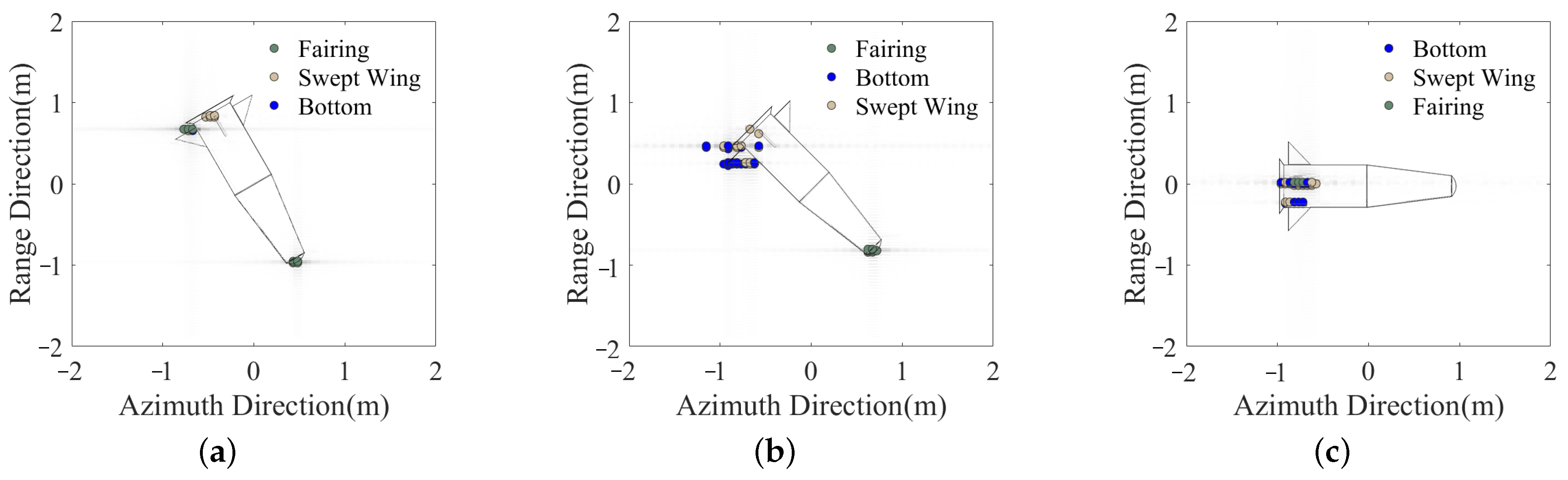
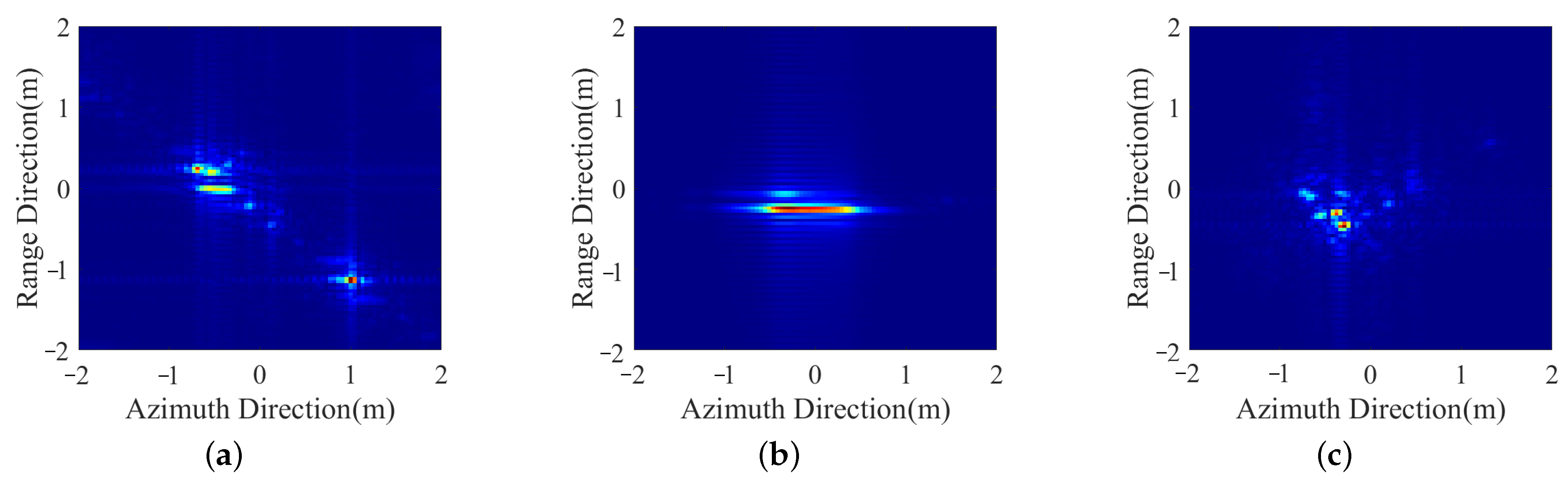
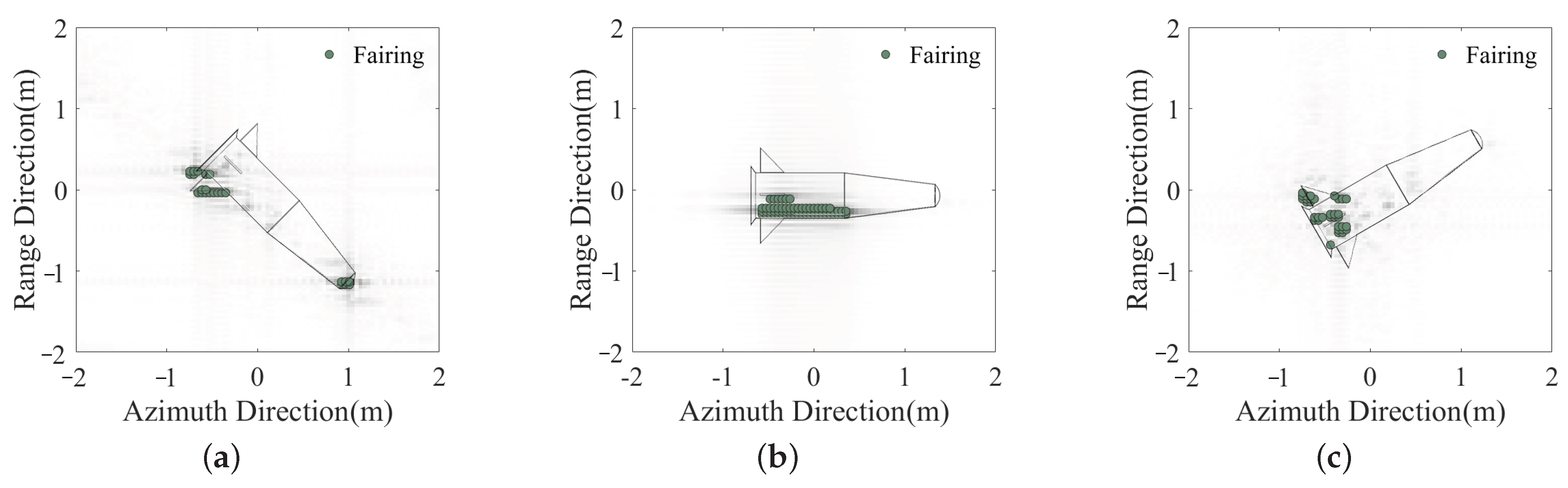
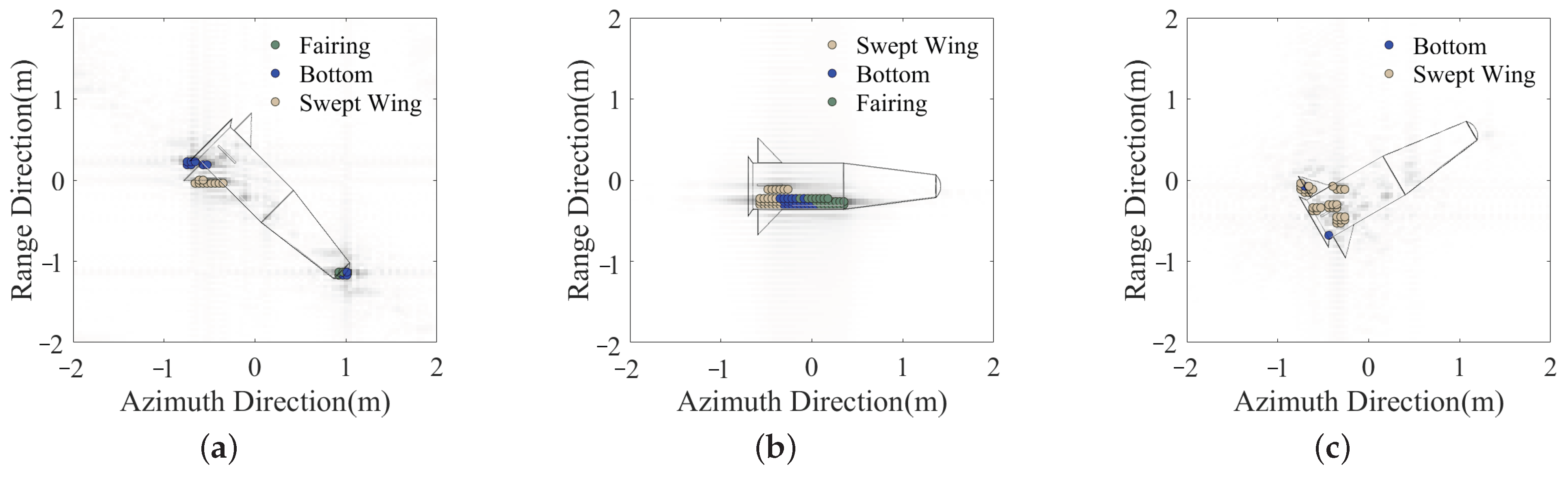
3. Results
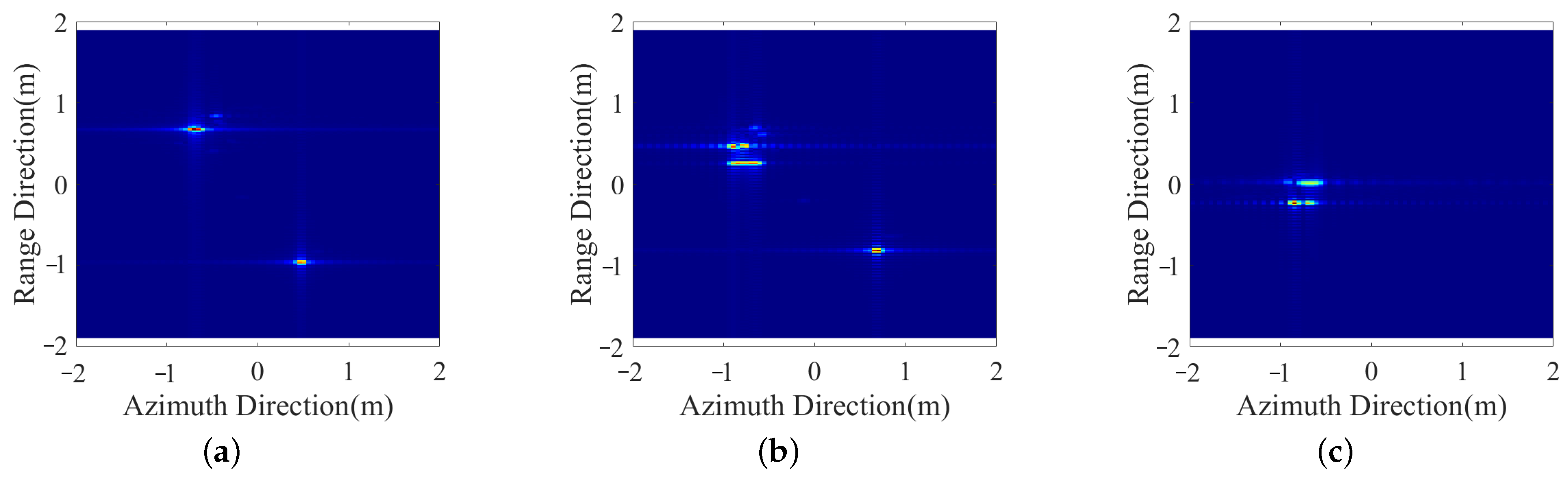
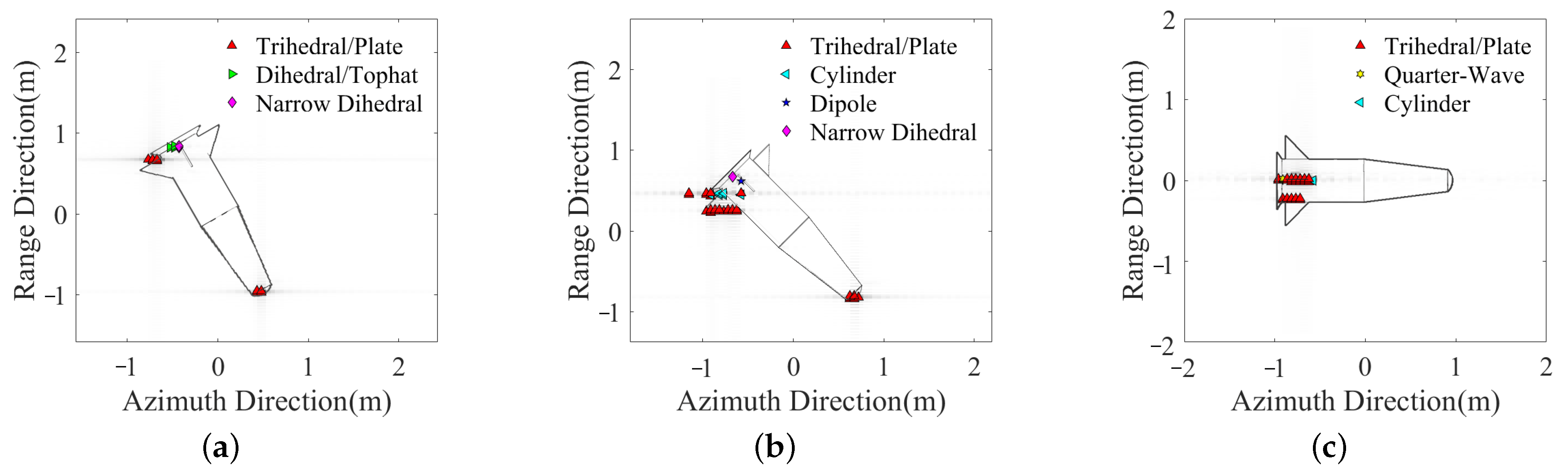
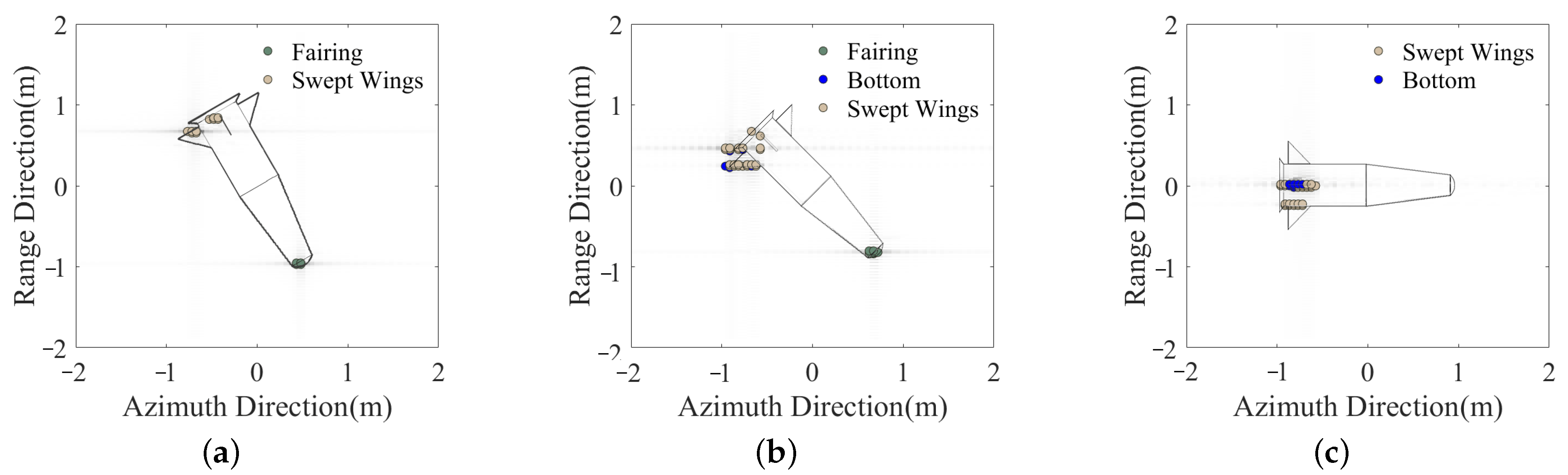
3.1. Experiments with Electromagnetic Simulation Data
3.2. Experiments with Anechoic Chamber Measurement Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Outline
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, X. Application of deep generative networks for SAR/ISAR: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 11905–11983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, K. An Advanced Scheme for Range Ambiguity Suppression of Spaceborne SAR Based on Blind Source Separation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5230112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, F. ISAR Images Segmentation Based on Spatially Variant Mixture Multiscale Autoregressive Model. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 3rd Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 12–14 October 2018; pp. 2170–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L.B. Components segmentation algorithm for space target isar image based on clean. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Wavelet Analysis and Pattern Recognition (ICWAPR), Ningbo, China, 9–12 July 2017; pp. 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Liu, Y.; Pei, H.; Du, H.; Li, H.; Xu, G. CLISAR-Net: A Deformation-Robust ISAR Image Classification Network Using Contrastive Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, L.; Li, Y.; Lyu, G.; Chen, B. Attitude and Size Estimation of Satellite Targets Based on ISAR Image Interpretation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5109015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, P.; Qiu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Li, W.; Zhang, S. ISAR Image Segmentation for Space Target Based on Contrastive Learning and NL-Unet. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 3506105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Huang, W.; Zhang, S. High-resolution remote sensing image semantic segmentation based on a deep feature aggregation network. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 095002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, F.; Shi, X. A New 3-D Geometry Reconstruction Method of Space Target Utilizing the Scatterer Energy Accumulation of ISAR Image Sequence. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8345–8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhi, S.; Li, X. RaNeRF: Neural 3-D Reconstruction of Space Targets From ISAR Image Sequences. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5107215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction From a Multiview Sequence of Sparse ISAR Imaging of a Space Target. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, L.; Du, R.; Zhou, F. Three-Dimensional Geometry Reconstruction Method for Slowly Rotating Space Targets Utilizing ISAR Image Sequence. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xing, M.; Sun, G.C.; Bao, Z. Integrating the Reconstructed Scattering Center Feature Maps with Deep CNN Feature Maps for Automatic SAR Target Recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4009605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Yin, H.; Yan, H. An Automatic and Forward Method to Establish 3-D Parametric Scattering Center Models of Complex Targets for Target Recognition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8701–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; He, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wen, G.J.; Yu, D.F.; Zhu, G.Q. A Forward Approach to Establish Parametric Scattering Center Models for Known Complex Radar Targets Applied to SAR ATR. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 6192–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Bie, B.; Sun, G.C.; Xing, M.; Pascazio, V. ISAR Image Matching and Three-Dimensional Scattering Imaging Based on Extracted Dominant Scatterers. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, D.J.; Jung, H.; Kang, H.; Kim, J.; Park, I.Y.; Lee, H.R.; Kim, Y.D. Scattering Center Extraction for ISAR Image using Deep Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2023 20th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Berlin, Germany, 20–22 September 2023; pp. 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; He, Y.; Li, Y. YOLOv8-based Spatial Target Part Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Information Technology, Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (ICIBA), Chongqing, China, 26–28 May 2023; Volume 3, pp. 1684–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, C.; Lin, C.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X. A Deformation Robust ISAR Image Satellite Target Recognition Method Based on PT-CCNN. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 23432–23453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, W. Multiple Heterogeneous P-DCNNs Ensemble with Stacking Algorithm: A Novel Recognition Method of Space Target ISAR Images Under the Condition of Small Sample Set. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 75543–75570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Ni, P.; Chen, J.; Ma, S.; Zhang, H.; Xu, G. Integrated Convolution Network for ISAR Imaging and Target Recognition. IEEE J. Miniaturization Air Space Syst. 2023, 4, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Su, F. SDRnet: A Deep Fusion Network for ISAR Ship Target Recognition Based on Feature Separation and Weighted Decision. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Shen, Q. A-CGAN based transformation from ISAR to optical image. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Communication, Image and Signal Processing (CCISP), Chengdu, China, 18–20 November 2022; pp. 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y. ISAR Target Recognition Using Pix2pix Network Derived from cGAN. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Radar Conference (RADAR), Toulon, France, 23–27 September 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Wei, S.; Zhang, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X. Joint Target Recognition for Multi-Station ISAR via MIIR Network. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2023—2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; pp. 7074–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Gao, X.; Shen, Q. A Novel Recognition Method of ISAR Image Fusion Based on Botnet and Embracenet. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Nanjing, China, 22–24 October 2021; pp. 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, C.; Gao, R. Complex-Valued Multiscale Vision Transformer on Space Target Recognition by ISAR Image Sequence. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 4008305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cexus, J.C.; Toumi, A.; Riahi, M. Target recognition from ISAR image using polar mapping and shape matrix. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Signal and Image Processing (ATSIP), Sousse, Tunisia, 2–5 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wen, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhu, P.; Mao, L.; Niu, G.; Li, J. Iterative Mamba Diffusion Change-Detection Model for Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Du, B. MambaHSI: Spatial-Spectral Mamba for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5524216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Cheng, X.; Lin, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H. Memory-Augmented Autoencoder with Adaptive Reconstruction and Sample Attribution Mining for Hyperspectral Anomaly Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5518118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, M.; Lin, S.; Zhou, K.; Zhao, S.; Wang, H. Two-Stream Isolation Forest Based on Deep Features for Hyperspectral Anomaly Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 5504205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; p. 422. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Guo, Z.; Li, N. Enhanced PGA for Dual-Polarized ISAR Imaging by Exploiting Cloude-Pottier Decomposition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 4000505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Li, M.D.; Chen, S.W. Man-Made Targets Characterization with Polarimetric Correlation Pattern Interpretation Tool. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 3057–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.C.; Li, H.L.; Chen, S.W. Polarimetric ISAR Image Interpretation Based on Polarimetric Correlation Pattern. In Proceedings of the 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 15–19 December 2021; pp. 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Pang, B.; Dai, D.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Recognition Based on Clustering by Fast Search and Find of Density Peaks (CFSFDP) with Polarimetric Decomposition. Electronics 2018, 7, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.Q.; Chen, S.W.; Li, Y.Z.; Wang, X.S. Null-Pol Response Pattern in Polarimetric Rotation Domain: Characterization and Application. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4503105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ai, X.; Zhao, F.; Xiao, S. A New Bistatic Huynen Target Parameters Extraction Algorithm: Experimental Validation and Data Analysis. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 9694–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.; Pottier, E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaglione, D.; Clemente, C.; Pallotta, L.; Proudler, I.; De Maio, A.; Soraghan, J.J. Krogager decomposition and Pseudo-Zernike moments for polarimetric distributed ATR. In Proceedings of the 2014 Sensor Signal Processing for Defence (SSPD), Edinburgh, UK, 8–9 September 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, H.; Sun, Y.; Kang, J.; Yang, Y.; Liang, X. Application of ReliefF algorithm to selecting feature sets for classification of high resolution remote sensing image. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Alternatives | Feature Vectors | Accuracies |
|---|---|---|
| ReliefF | 91.6% | |
| LASSO | 89.3% | |
| RFFI | 89.4% | |
| PCA | 84.9% | |
| MRMR | 89.3% |
| Components | Frequency Range and Step (GHz) | Theta Range and Step (Deg) | Phi Range and Step (Deg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fairing | 40 to 85, 0.5 | −15 to 15, 1 | |
| Bottom | 8 to 12, 0.04 | 45 to 135, 1 | −15 to 15, 1 |
| Swept Wings | 45 to 90, 0.5 | 30 to 60, 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Xu, Z.; Ai, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, X.; Cheng, J. A Novel Method for PolISAR Interpretation of Space Target Structure Based on Component Decomposition and Coherent Feature Extraction. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061079
Chen Z, Xu Z, Ai X, Wu Q, Liu X, Cheng J. A Novel Method for PolISAR Interpretation of Space Target Structure Based on Component Decomposition and Coherent Feature Extraction. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(6):1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061079
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhuo, Zhiming Xu, Xiaofeng Ai, Qihua Wu, Xiaobin Liu, and Jianghua Cheng. 2025. "A Novel Method for PolISAR Interpretation of Space Target Structure Based on Component Decomposition and Coherent Feature Extraction" Remote Sensing 17, no. 6: 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061079
APA StyleChen, Z., Xu, Z., Ai, X., Wu, Q., Liu, X., & Cheng, J. (2025). A Novel Method for PolISAR Interpretation of Space Target Structure Based on Component Decomposition and Coherent Feature Extraction. Remote Sensing, 17(6), 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061079







