Evaluating the Performance of Irrigation Using Remote Sensing Data and the Budyko Hypothesis: A Case Study in Northwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
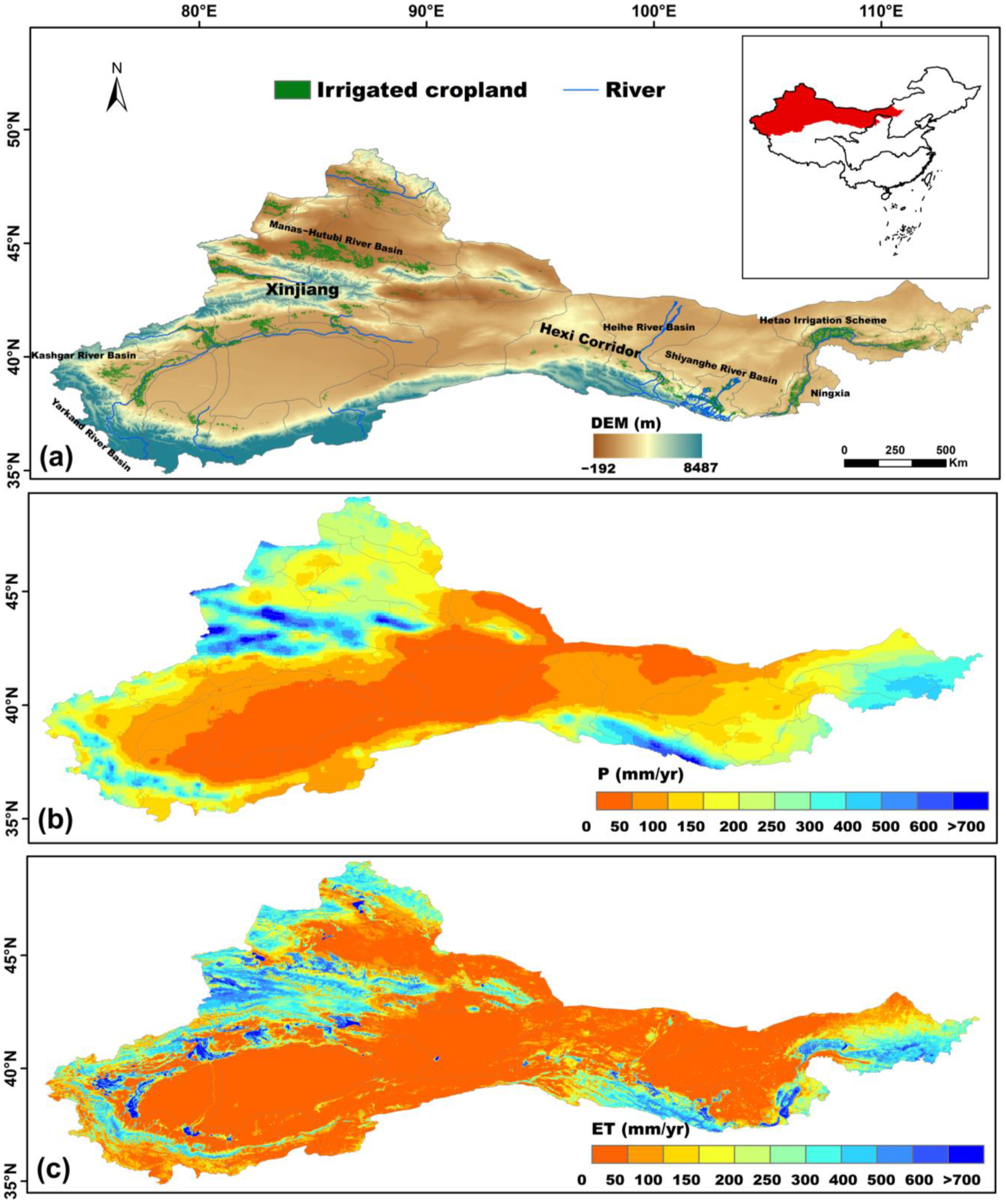
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Pre-Processing
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.2. Statistical Data
3. Methods
4. Results
4.1. Assessment of Crop Water Stress
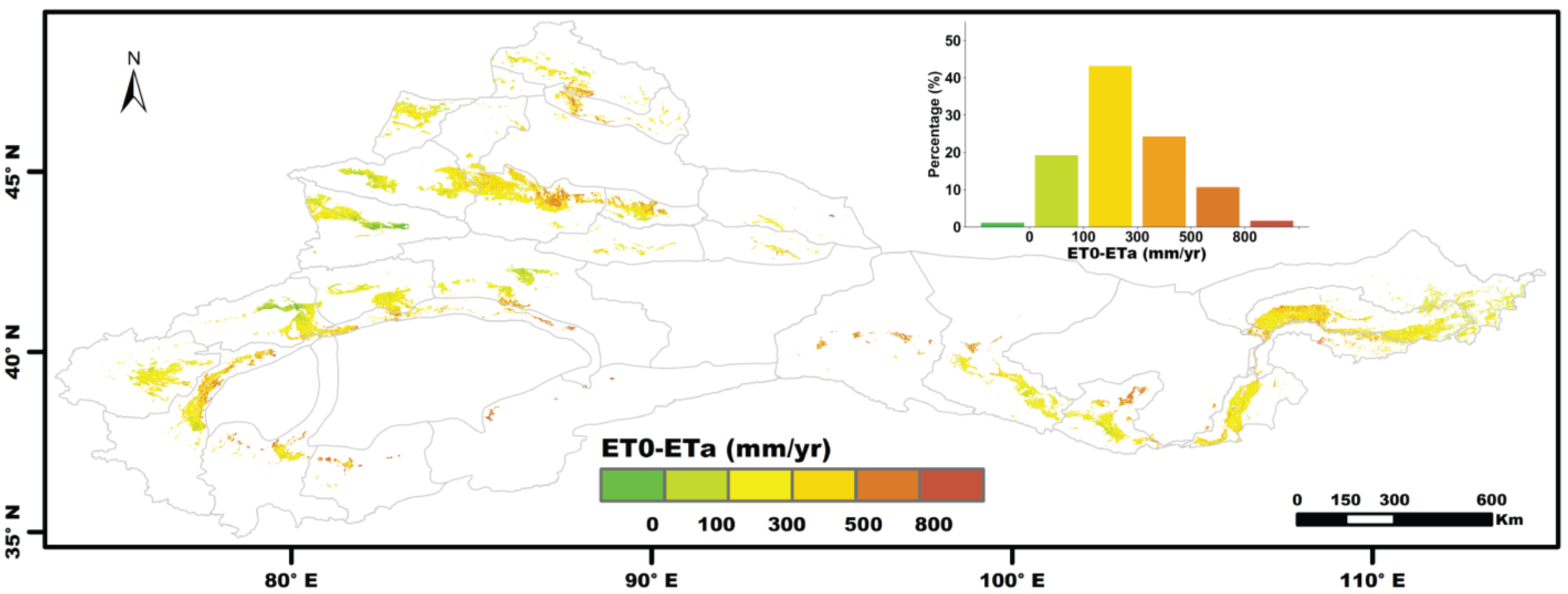
4.2. Is There Enough Water to Overcome the Water Deficit?
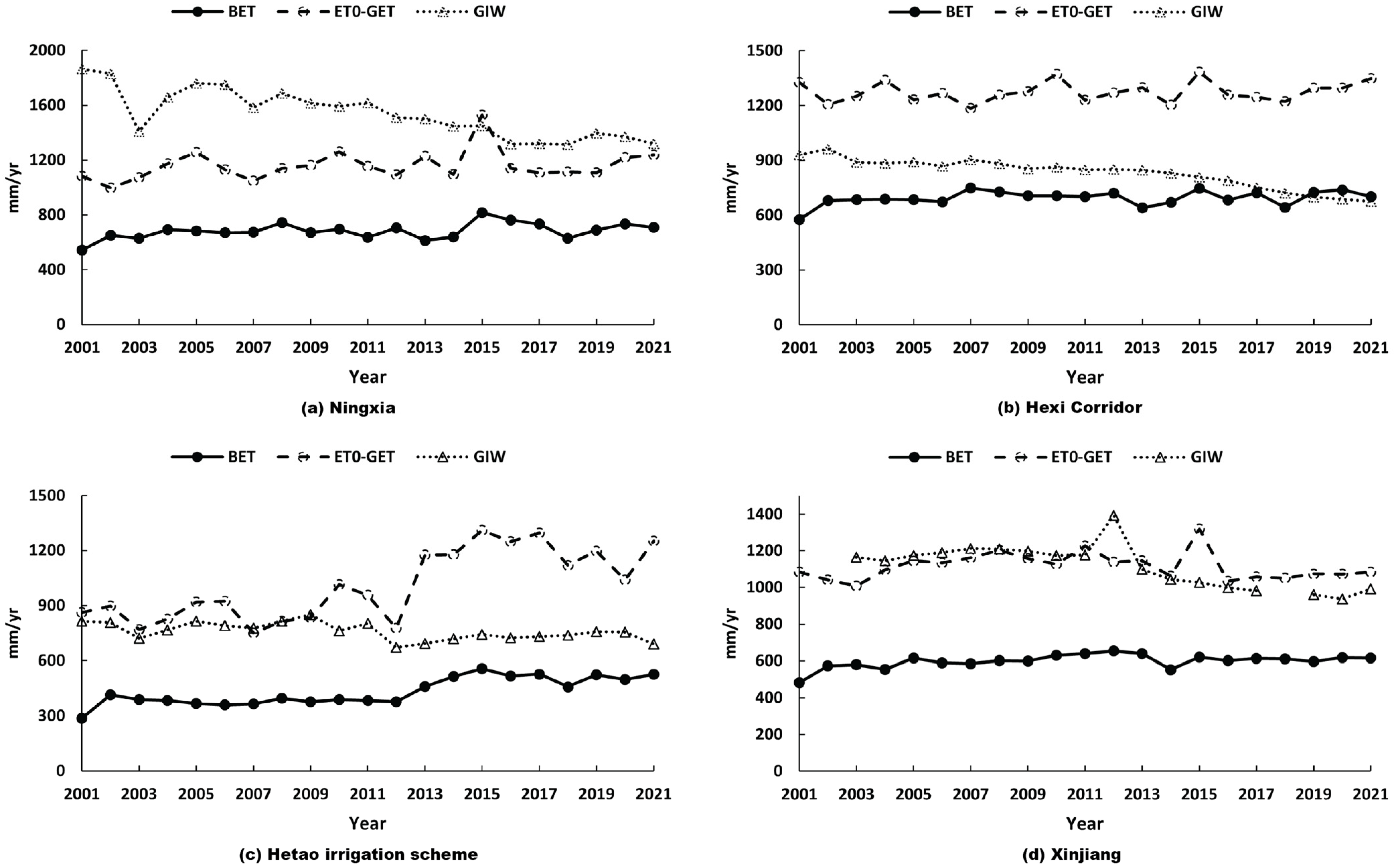
4.3. Is Irrigation Water Sufficient to Overcome the Deficit?
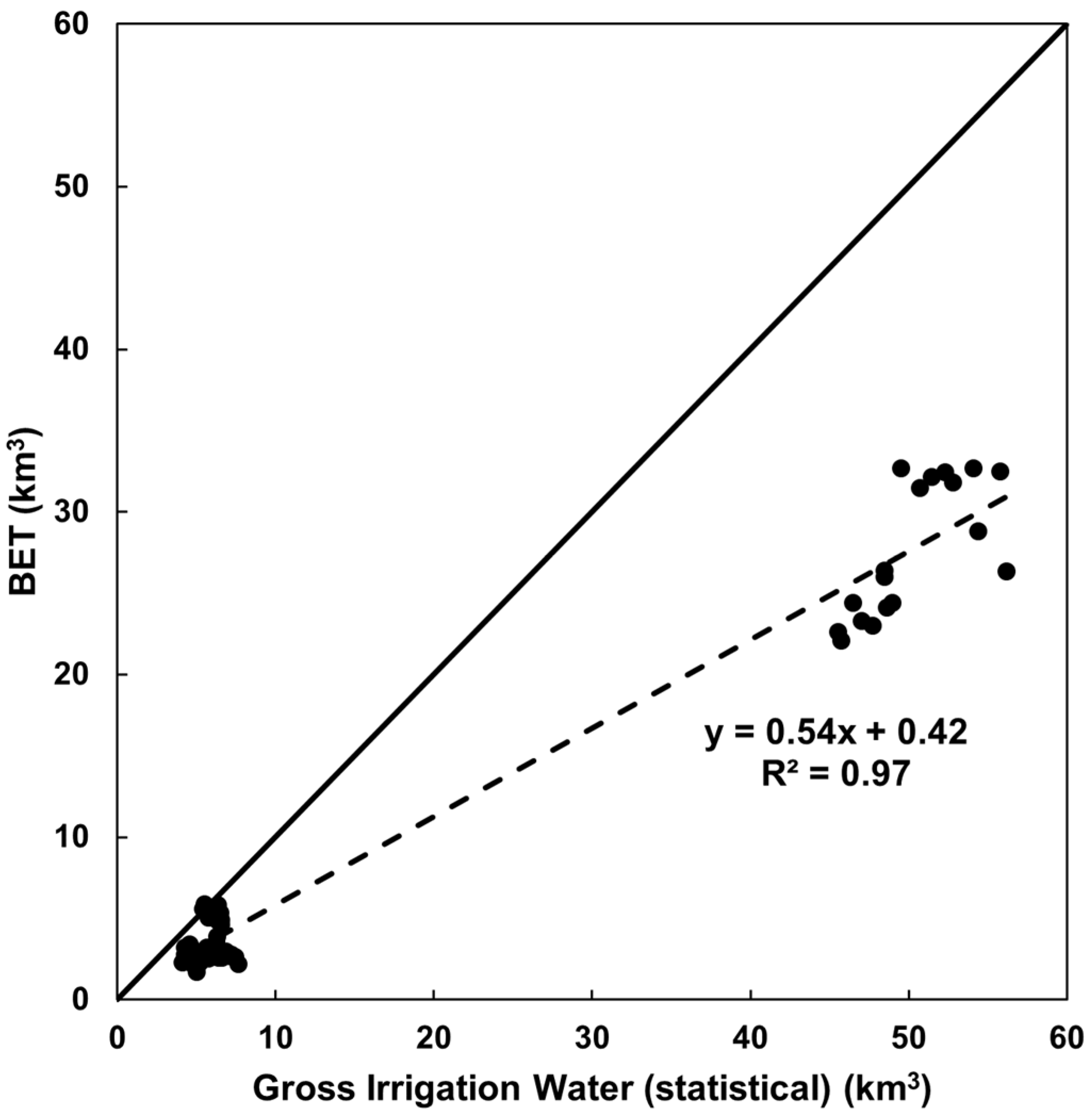
4.4. How Efficient Is the Distribution and Use of Irrigation Water
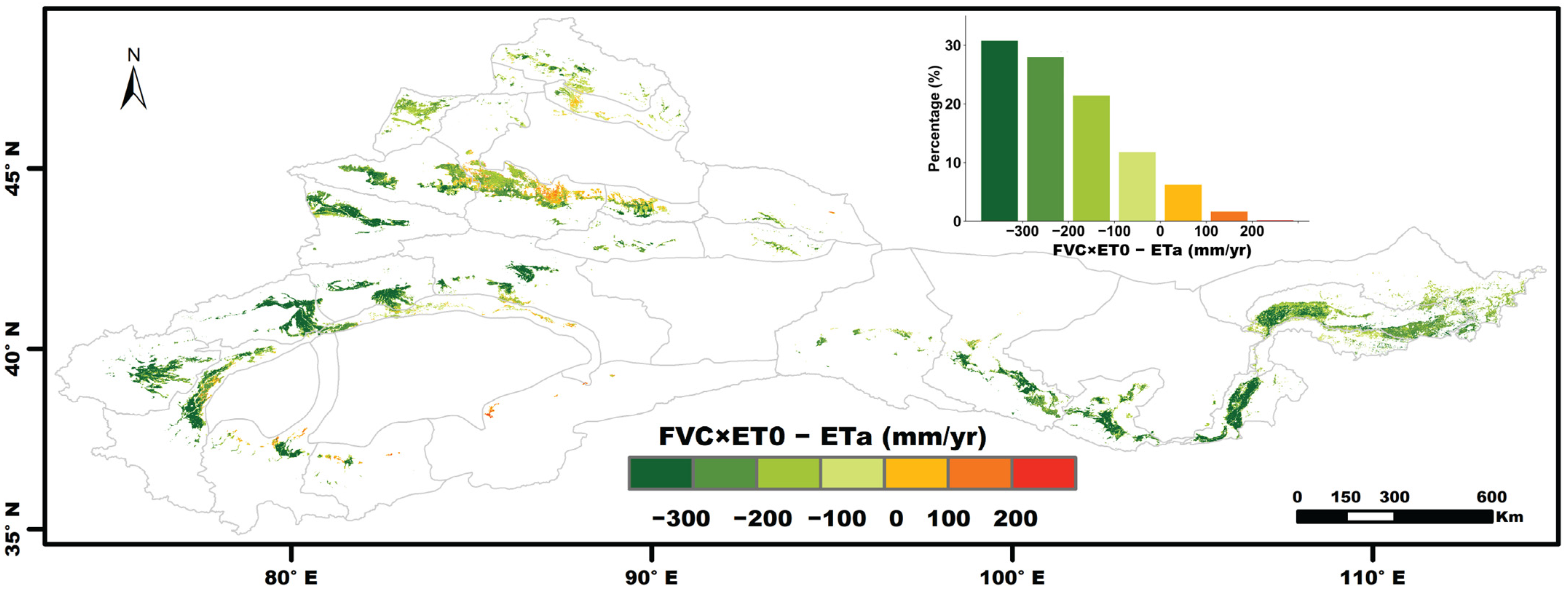
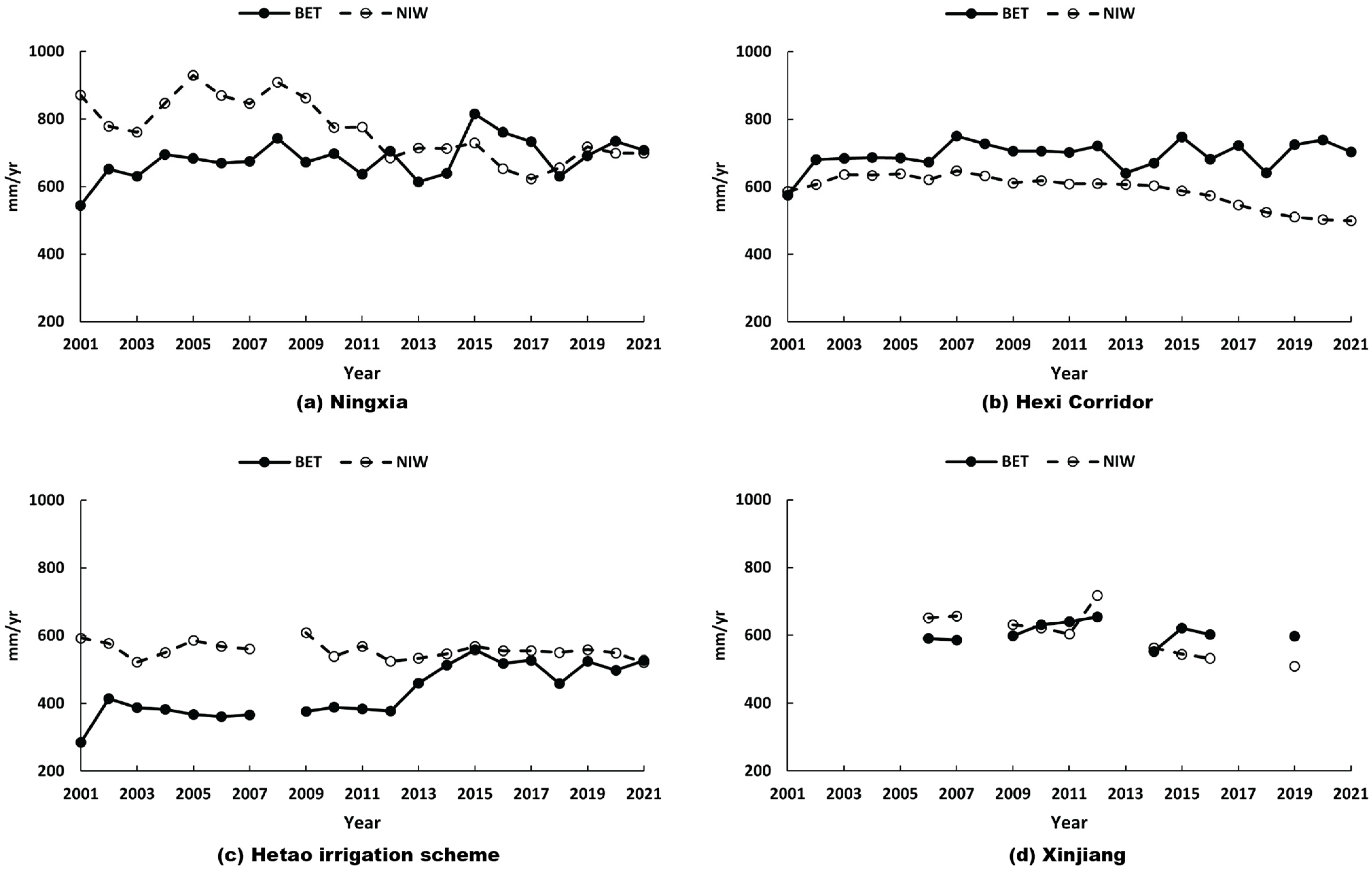
4.5. Is Irrigation Water Used Efficiently by Crops?
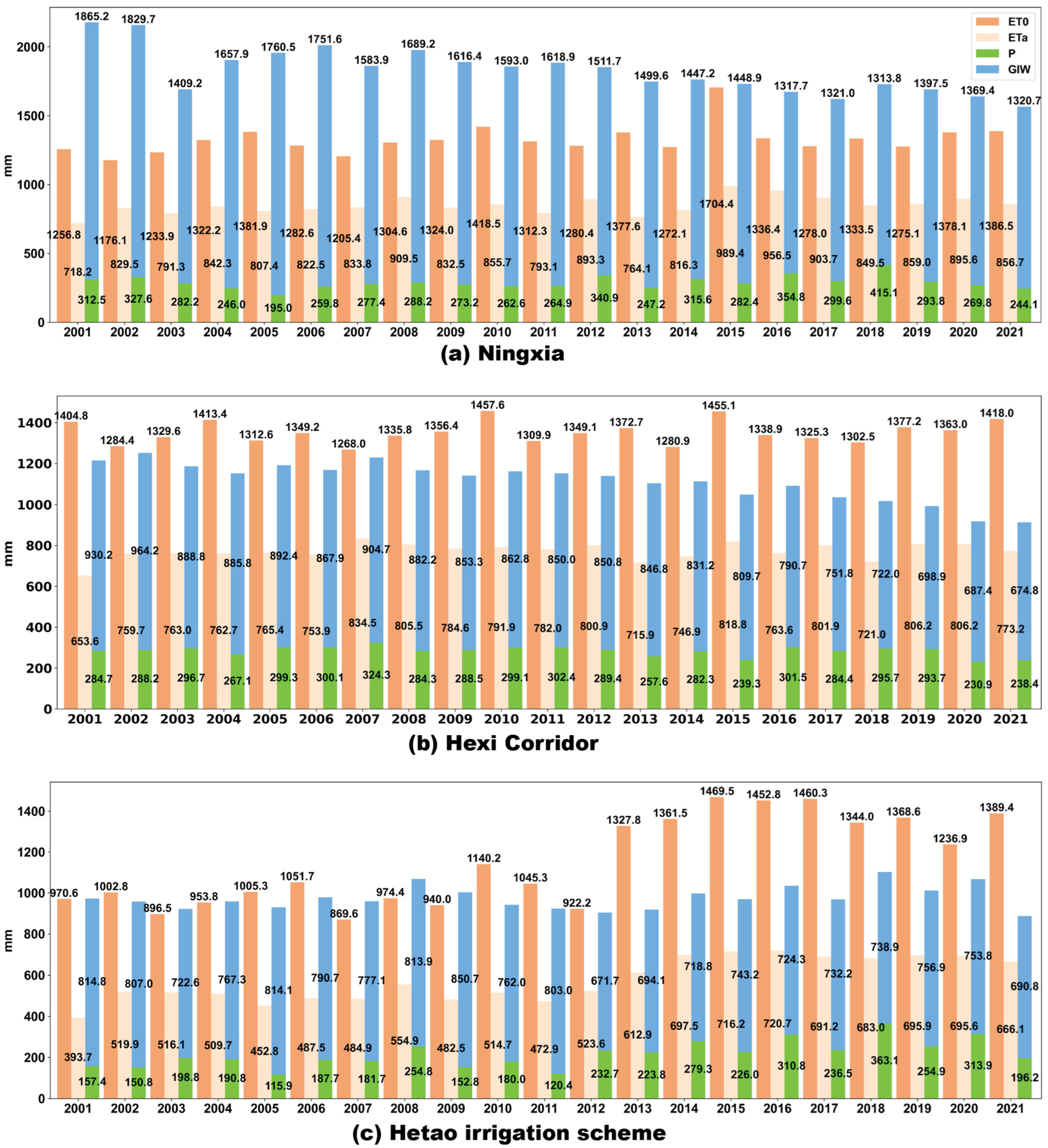
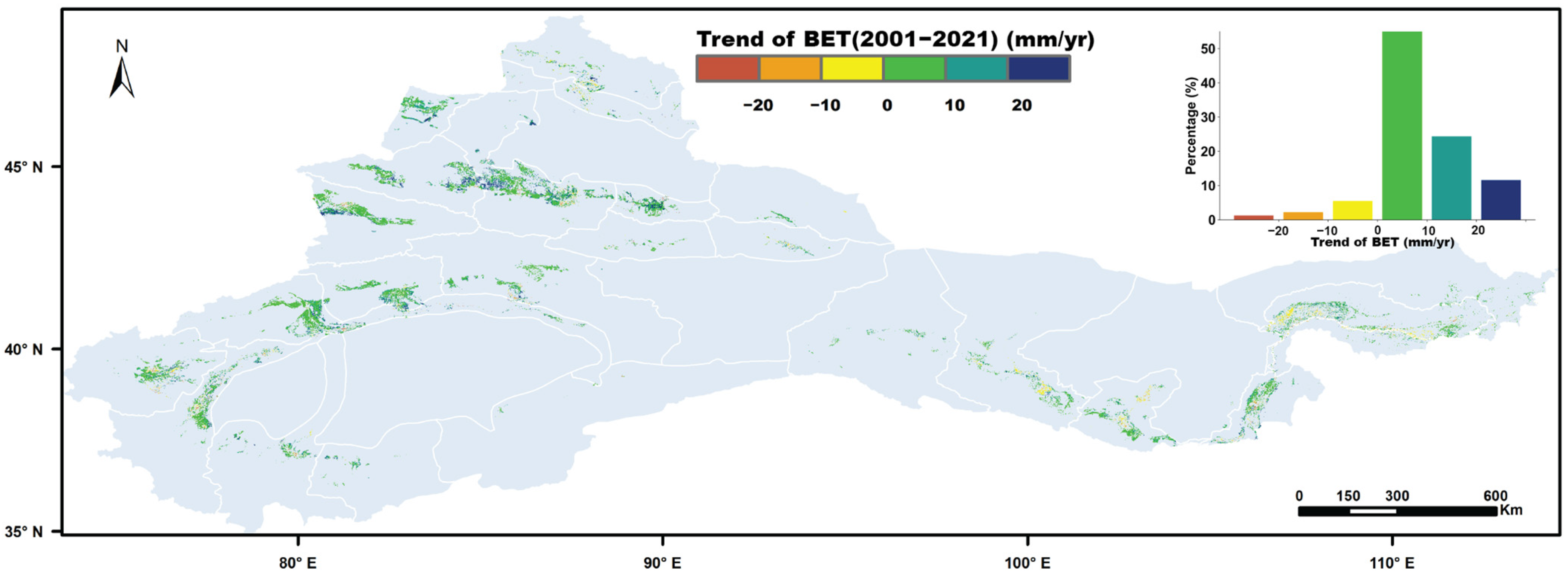
4.6. Trend of Blue Water Evapotranspiration
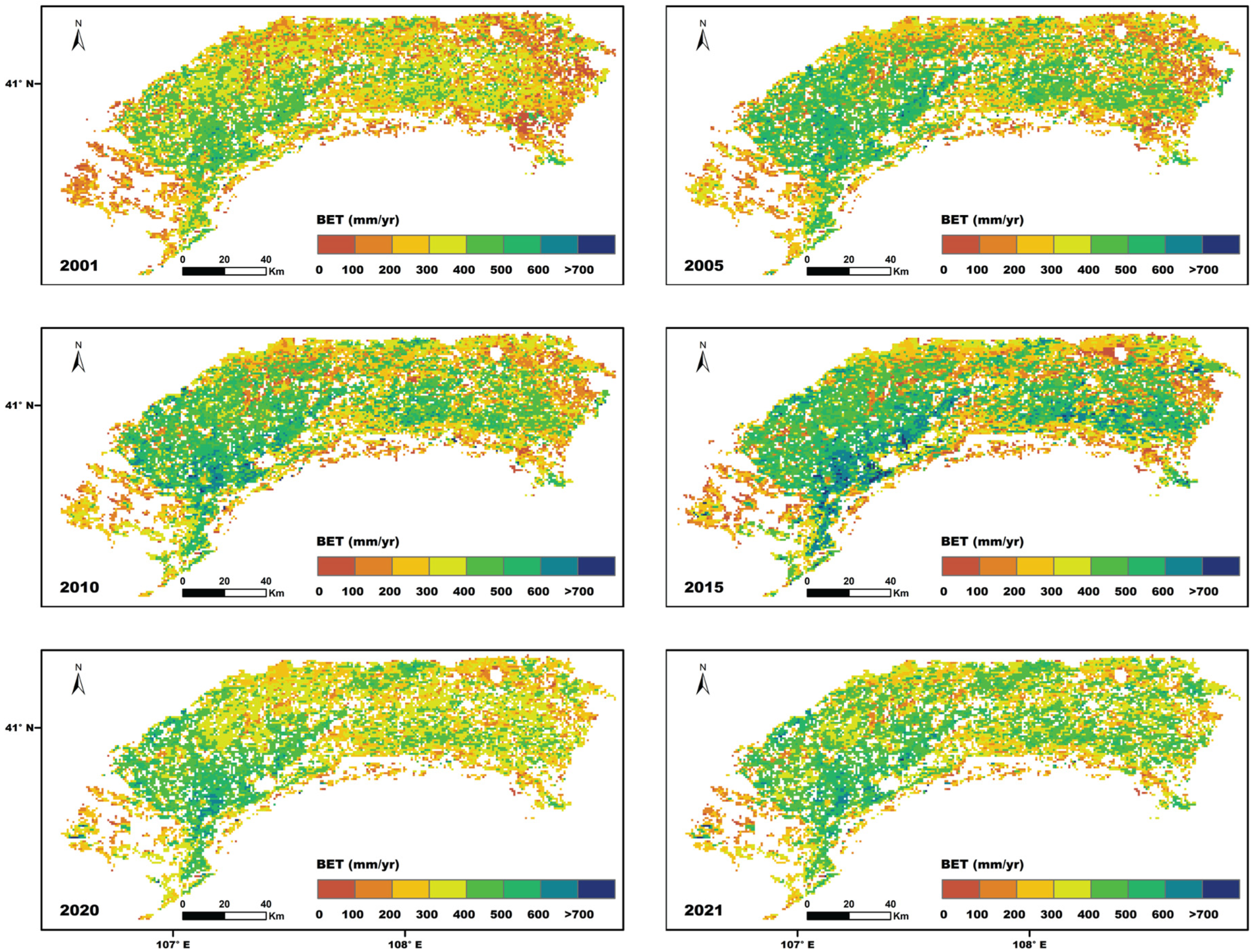
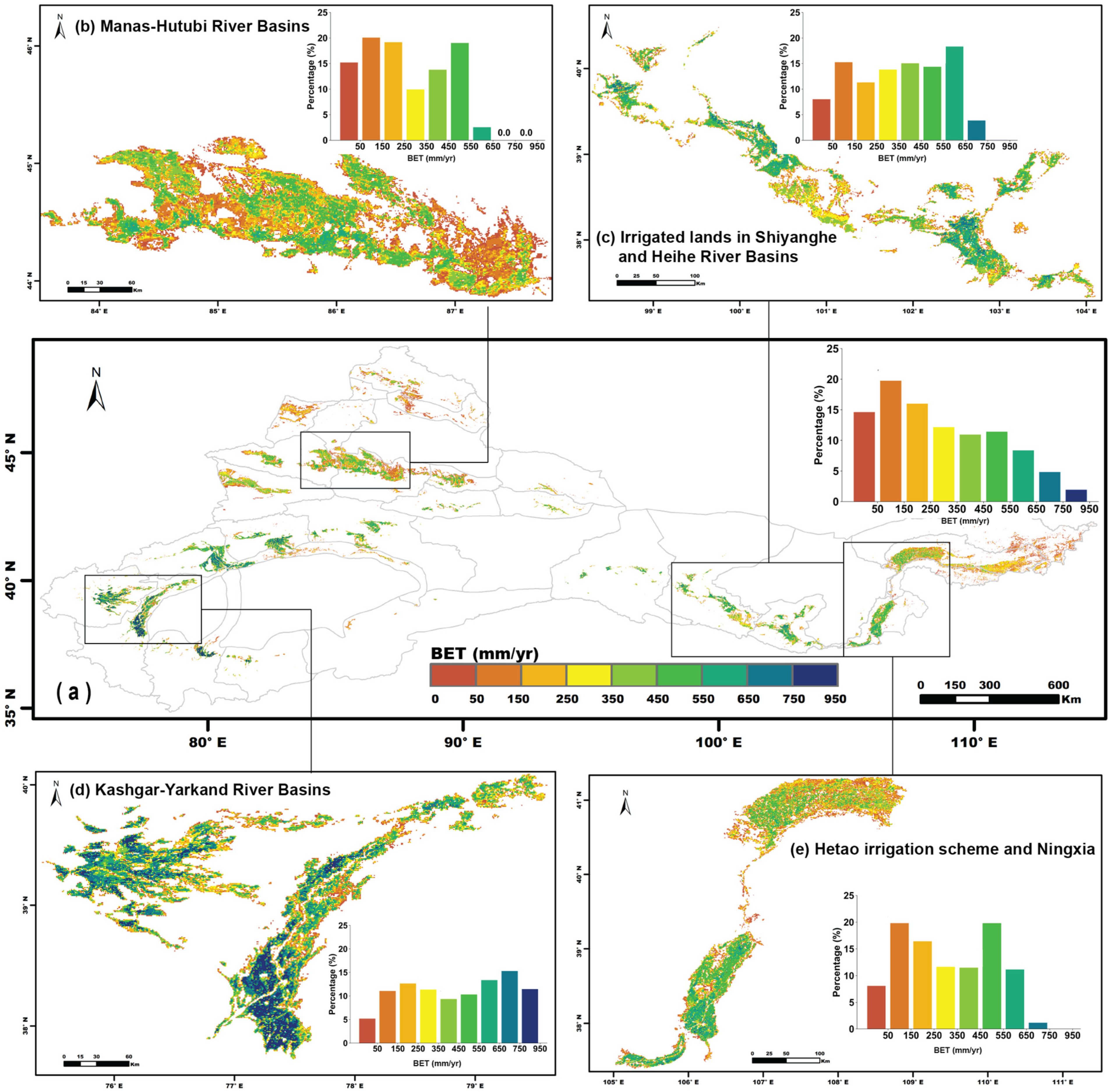
4.7. The Spatial Distribution of Blue Evapotranspiration
5. Discussion
5.1. Indicators of Irrigation Water Use
5.2. Availability of Irrigation Water in the Hexi Corridor
6. Conclusions
- In Ningxia, the total available water resources (precipitation + GIW) were sufficient to meet irrigation demand. Conversely, the Hexi Corridor faced increasing risks of unsustainable water use. The Hetao irrigation scheme shifted from a fragile supply–demand balance to a situation where water demand far exceeded availability. In Xinjiang, the balance between water supply and demand was tight, with irrigation water demand and supply in balance most years;
- The scheme irrigation efficiency, defined as the ratio of the BET to the GIW, was determined to be 0.54. Additionally, the water use efficiency, estimated as the ratio of the BET to the NIW, showed improvements in Ningxia, the Hetao irrigation scheme, and Xinjiang over the last 10 years. However, the Hexi Corridor continued to face severe NIW deficits.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Yan, Y.; Xing, X.; Xie, T.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Xi, H.; Zhu, C.; et al. Changes and Protection Suggestions in Water Resources and Ecological Environment in Arid Region of Northwest China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2023, 38, 385–393. [Google Scholar]
- Hoogeveen, J.; Faurès, J.-M.; Peiser, L.; Burke, J.; van de Giesen, N. GlobWat—A Global Water Balance Model to Assess Water Use in Irrigated Agriculture. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 3829–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, S.; Döll, P. Quantifying Blue and Green Virtual Water Contents in Global Crop Production as Well as Potential Production Losses without Irrigation. J. Hydrol. 2010, 384, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velpuri, N.M.; Senay, G.B. Partitioning Evapotranspiration into Green and Blue Water Sources in the Conterminous United States. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaussinger, F.; Dorigo, W.; Gruber, A.; Tarpanelli, A.; Filippucci, P.; Brocca, L. Estimating Irrigation Water Use over the Contiguous United States by Combining Satellite and Reanalysis Soil Moisture Data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 897–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Long, D. Estimating Spatially Explicit Irrigation Water Use Based on Remotely Sensed Evapotranspiration and Modeled Root Zone Soil Moisture. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2021WR031382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, G. Estimation of Global Irrigation Water Use by the Integration of Multiple Satellite Observations. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappa, L.; Schlaffer, S.; Brocca, L.; Vreugdenhil, M.; Nendel, C.; Dorigo, W. How Accurately Can We Retrieve Irrigation Timing and Water Amounts from (Satellite) Soil Moisture? Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 113, 102979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh, S.J.; Dari, J.; Modanesi, S.; Massari, C.; Brocca, L.; Fensholt, R.; Stisen, S.; Koch, J. An Inter-Comparison of Approaches and Frameworks to Quantify Irrigation from Satellite Data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 28, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Jia, L.; Menenti, M.; Hu, G.; Lu, J.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, M.; Mancini, M.; Corbari, C. Integrating Hydrologic Modeling and Satellite Remote Sensing to Assess the Performance of Sprinkler Irrigation. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 27, 934–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawston, P.M.; Santanello, J.A., Jr.; Kumar, S.V. Irrigation Signals Detected from SMAP Soil Moisture Retrievals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 11860–11867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boser, A.; Caylor, K.; Larsen, A.; Pascolini-Campbell, M.; Reager, J.T.; Carleton, T. Field-Scale Crop Water Consumption Estimates Reveal Potential Water Savings in California Agriculture. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalilvand, E.; Tajrishy, M.; Ghazi Zadeh Hashemi, S.A.; Brocca, L. Quantification of Irrigation Water Using Remote Sensing of Soil Moisture in a Semi-Arid Region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh, S.J.; Fensholt, R.; Stisen, S.; Koch, J. The Precision of Satellite-Based Net Irrigation Quantification in the Indus and Ganges Basins. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 2463–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinders, F.B.; van der Stoep, I.; Backeberg, G.R. Improved Efficiency of Irrigation Water Use: A South African Framework. Irrig. Drain. 2013, 62, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, M.G.; Nugteren, J. On Irrigation Efficiencies, 4th ed.; ILRI: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1990; ISBN 978-90-70260-87-3. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Cui, J.; Wu, Q.; Han, Z. Application of a Monitoring and Evaluation Method in Irrigation Water Efficiency. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menenti, M.; Visser, T.N.M.; Morabito, J.A.; Drovandi, A. Appraisal of Irrigation Performance with Satellite Data and Georeferenced Information. In Irrigation Theory and Practice; Pentech Press: London, UK, 1989; pp. 785–801. [Google Scholar]
- Menenti, M.; Visser, T.; Chambouleyron, J.L. The Role of Remote Sensing in Irrigation Management: A Case Study on Allocation of Irrigation Water; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; pp. 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Van der Wal, T.; Visser, T.N.M. Diagnosis of Regional Evaporation by Remote Sensing to Support Irrigation Performance Assessment. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 1996, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerink, G.J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Chambouleyron, J.; Menenti, M. Relating Crop Water Consumption to Irrigation Water Supply by Remote Sensing. Water Resour. Manag. 1997, 11, 445–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, M.G. Performance Indicators for Irrigation and Drainage. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 1997, 11, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Bos, M.G. Irrigation Performance Indicators Based on Remotely Sensed Data: A Review of Literature. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 1999, 13, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Toomanian, N.; Droogers, P.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Gieske, A. Monitoring Irrigation Performance in Esfahan, Iran, Using NOAA Satellite Imagery. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 88, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.D.; Turral, H.; Nazeer, A. Diagnosing Irrigation Performance and Water Productivity through Satellite Remote Sensing and Secondary Data in a Large Irrigation System of Pakistan. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, U.; Stephen, H.; Ahmad, S. Evaluating Irrigation Performance and Water Productivity Using EEFlux ET and NDVI. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Falkenmark, M.; Karlberg, L.; Hoff, H.; Rost, S.; Gerten, D. Future Water Availability for Global Food Production: The Potential of Green Water for Increasing Resilience to Global Change. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W00A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Hao, Z.; Tong, K. Discharge Regime and Simulation for the Upstream of Major Rivers over Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 8500–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Shang, H.; Hu, G.; Menenti, M. Phenological Response of Vegetation to Upstream River Flow in the Heihe Rive Basin by Time Series Analysis of MODIS Data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1047–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zheng, C.; Jia, L.; Menenti, M. Partitioning Green and Blue Evapotranspiration by Improving Budyko Equation Using Remote Sensing Observations in an Arid/Semi-Arid Inland River Basin in China. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Jia, L. Monitoring of Evapotranspiration in a Semi-Arid Inland River Basin by Combining Microwave and Optical Remote Sensing Observations. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3056–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Jia, L.; Hu, G. Global Land Surface Evapotranspiration Monitoring by ETMonitor Model Driven by Multi-Source Satellite Earth Observations. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 300. [Google Scholar]
- Funk, C.C.; Peterson, P.J.; Landsfeld, M.F.; Pedreros, D.H.; Verdin, J.P.; Rowland, J.D.; Romero, B.E.; Husak, G.J.; Michaelsen, J.C.; Verdin, A.P. A Quasi-Global Precipitation Time Series for Drought Monitoring; U.S. Geological Survey Data Series 832; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2014; p. 4.
- Zhang, C.; Dong, J.; Ge, Q. IrriMap_CN: Annual Irrigation Maps across China in 2000–2019 Based on Satellite Observations, Environmental Variables, and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tian, J.; Rong, Y.; Long, A. Monitoring Spatial Patterns of Vegetation Phenology in Heihe River Basin based on Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2012, 27, 282–288. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Yan, D.; Xu, X.; Gao, Y. Effects of Climate Change on Spring Wheat Phenophase and Water Requirement in Heihe River Basin, China. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 126, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Guan, X.; Liu, H.; Yin, F. Status and Countermeasures of Agricultural Water Saving Development in Irrigation Areas of Xinjiang. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2024, 43, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, D.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Qu, Z. Thresholds of Irrigated Farmland Area in the Hexi Corridor Region. Arid. Arid. Arid. Land Geogr. 2024, 47, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningxia Water Conservancy. Ningxia Water Resources Bulletin (2021); Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Water Conservancy Bureau: Yinchuan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bayannur Water Conservancy. Bayannur Water Resources Bulletin (2021); Bayannur Water Conservancy Bureau: Bayannur, China, 2022.
- Han, S.; Tian, F.; Gao, L. Current Status and Recent Trend of Irrigation Water Use in China. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calera, A.; Campos, I.; Osann, A.; D’Urso, G.; Menenti, M. Remote Sensing for Crop Water Management: From ET Modelling to Services for the End Users. Sensors 2017, 17, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, G.; Menenti, M.; Santini, A. Regional Application of One-Dimensional Water Flow Models for Irrigation Management. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 40, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, A.N.; Hunsaker, D.J.; Sanchez, C.A.; Saber, M.; Gonzalez, J.R.; Anderson, R. Satellite-Based NDVI Crop Coefficients and Evapotranspiration with Eddy Covariance Validation for Multiple Durum Wheat Fields in the US Southwest. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 239, 106266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pôças, I.; Calera, A.; Campos, I.; Cunha, M. Remote Sensing for Estimating and Mapping Single and Basal Crop Coefficientes: A Review on Spectral Vegetation Indices Approaches. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 233, 106081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzali, S.; Menenti, M.; Meuwissen, I.J.M.; Visser, T.N.M. Mapping Crop Coefficients in an Argentinian Irrigation Scheme. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing in Evaluation and Management of Irrigation, Mendoza, Argentina, 20–25 November 1989; pp. 79–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hunsaker, D.J.; Pinter, P.J.; Kimball, B.A. Wheat Basal Crop Coefficients Determined by Normalized Difference Vegetation Index. Irrig. Sci. 2005, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchemin, B.; Hadria, R.; Erraki, S.; Boulet, G.; Maisongrande, P.; Chehbouni, A.; Escadafal, R.; Ezzahar, J.; Hoedjes, J.C.B.; Kharrou, M.H.; et al. Monitoring Wheat Phenology and Irrigation in Central Morocco: On the Use of Relationships between Evapotranspiration, Crops Coefficients, Leaf Area Index and Remotely-Sensed Vegetation Indices. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 79, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, H.; Neale, C.M.U.; Wright, J.L. Development and Validation of Canopy Reflectance-Based Crop Coefficient for Potato. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 88, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, L.; González-Dugo, M.P.; Testi, L.; Villalobos, F.J. Monitoring Evapotranspiration of Irrigated Crops Using Crop Coefficients Derived from Time Series of Satellite Images. I. Method Validation. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 125, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Ge, Y.; Li, H.; Han, F.; Hu, X.; Tian, W.; Tian, Y.; Pan, X.; Nian, Y.; et al. Hydrological Cycle in the Heihe River Basin and Its Implication for Water Resource Management in Endorheic Basins. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 890–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Regions | Years of GIW Collected | Years of NIW Collected | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hetao irrigation scheme | 2001–2007, 2009–2021 | 2001–2021 | Bayannur Water Resources Bulletin |
| Ningxia | 2001–2021 | 2001–2021 | Ningxia Water Resources Bulletin |
| Hexi Corridor | 2001–2021 | 2001–2021 | Gansu Water Resources Bulletin |
| Xinjiang | 2006–2012, 2014–2016, 2019 | 2003–2017, 2018–2021 | Xinjiang Water Resources Bulletin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, D.; Zheng, C.; Jia, L.; Menenti, M.; Lu, J.; Chen, Q. Evaluating the Performance of Irrigation Using Remote Sensing Data and the Budyko Hypothesis: A Case Study in Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061085
Zhou D, Zheng C, Jia L, Menenti M, Lu J, Chen Q. Evaluating the Performance of Irrigation Using Remote Sensing Data and the Budyko Hypothesis: A Case Study in Northwest China. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(6):1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061085
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Dingwang, Chaolei Zheng, Li Jia, Massimo Menenti, Jing Lu, and Qiting Chen. 2025. "Evaluating the Performance of Irrigation Using Remote Sensing Data and the Budyko Hypothesis: A Case Study in Northwest China" Remote Sensing 17, no. 6: 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061085
APA StyleZhou, D., Zheng, C., Jia, L., Menenti, M., Lu, J., & Chen, Q. (2025). Evaluating the Performance of Irrigation Using Remote Sensing Data and the Budyko Hypothesis: A Case Study in Northwest China. Remote Sensing, 17(6), 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061085










