FQDNet: A Fusion-Enhanced Quad-Head Network for RGB-Infrared Object Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Main Contributions
- We propose FQDNet, an end-to-end RGB-IR object detection network that integrates optimized feature fusion with a dynamic-weighted Quad-Head detection framework. Extensive experiments on benchmark RGB-IR datasets (M3FD, VEDAI, LLVIP) demonstrate that FQDNet achieves state-of-the-art performance in multi-modal detection.
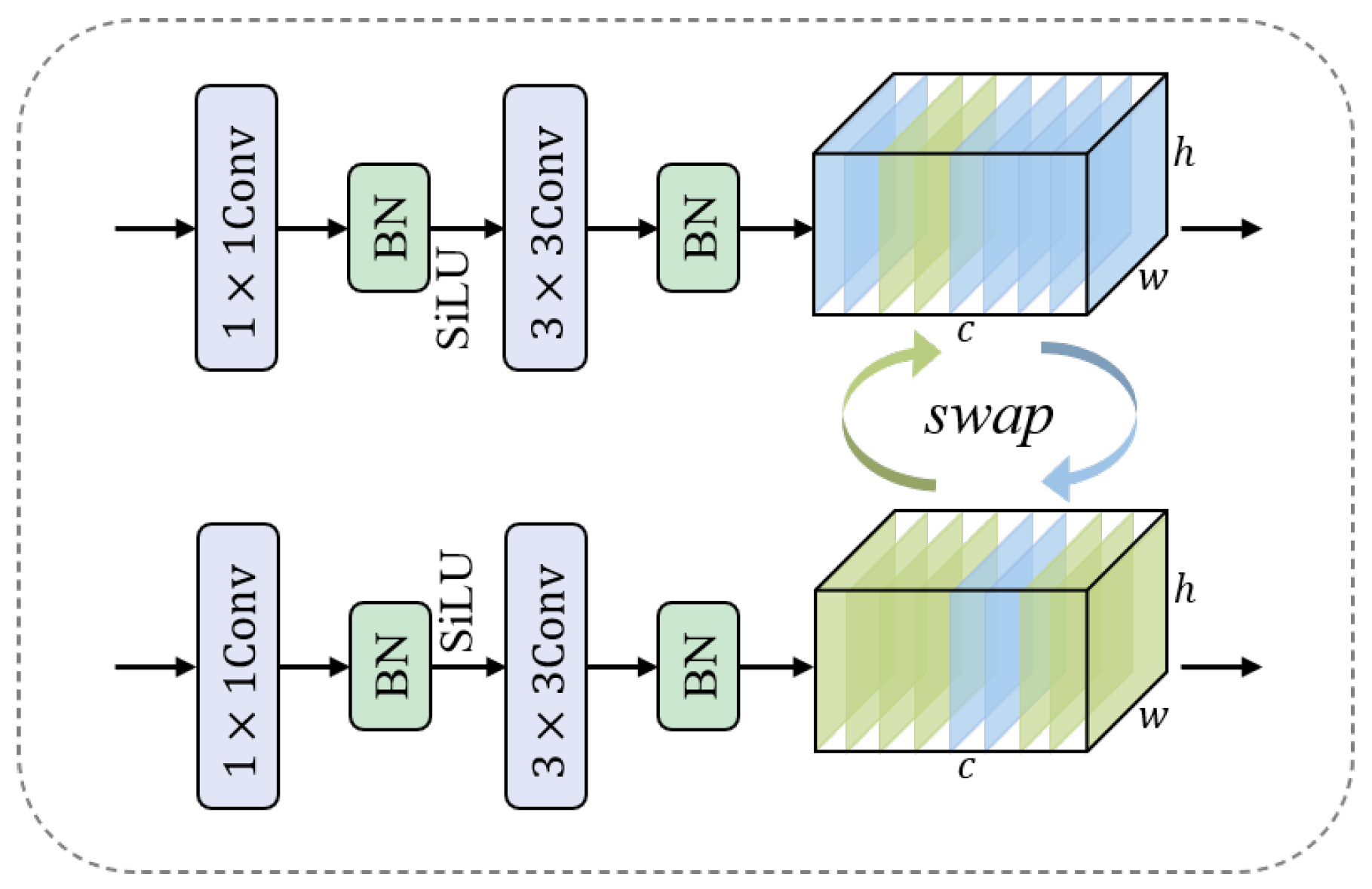
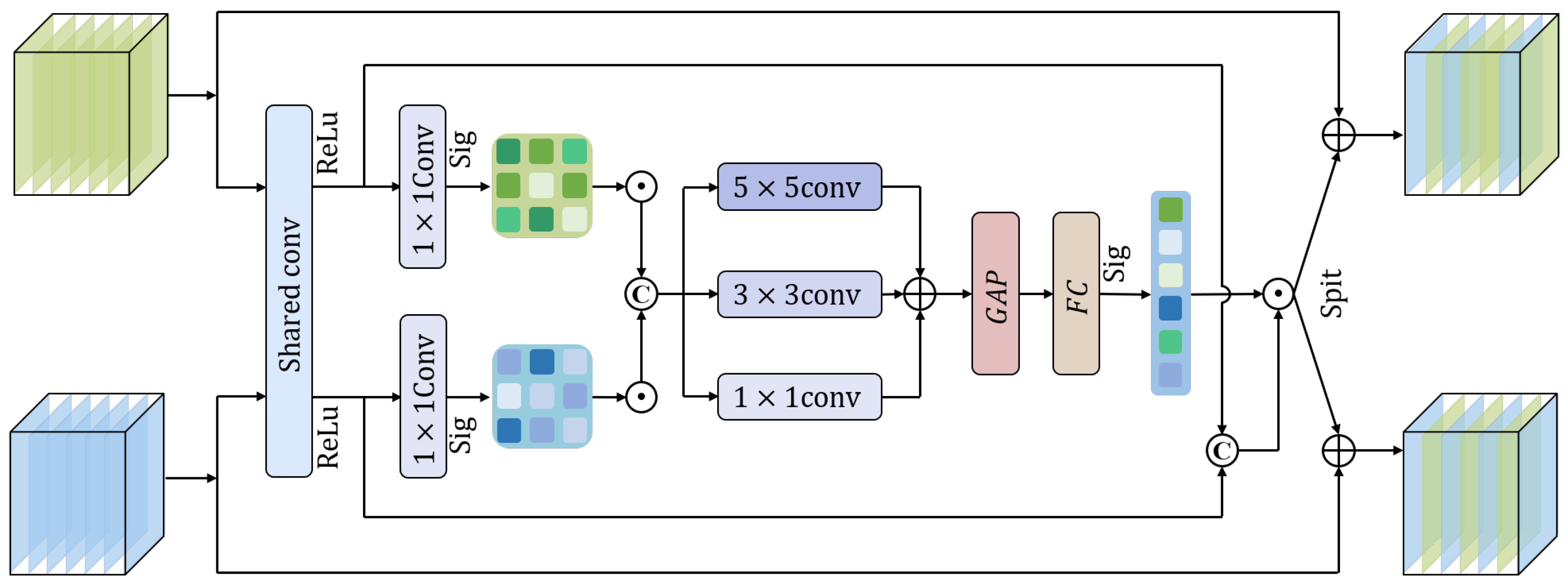
- To improve feature integration, we introduce the Channel Swap SCDown Block (CSSB) for initial pre-fusion and a Spatial Channel Attention Fusion Module (SCAFM) to refine multi-modal fusion, resulting in more effective feature representation.
- We designed the Dynamic-Weight-based Quad-Head Detector (DWQH) to address multi-scale object detection, dynamically adjusting multi-scale feature weights to improve detection accuracy for objects of various sizes.
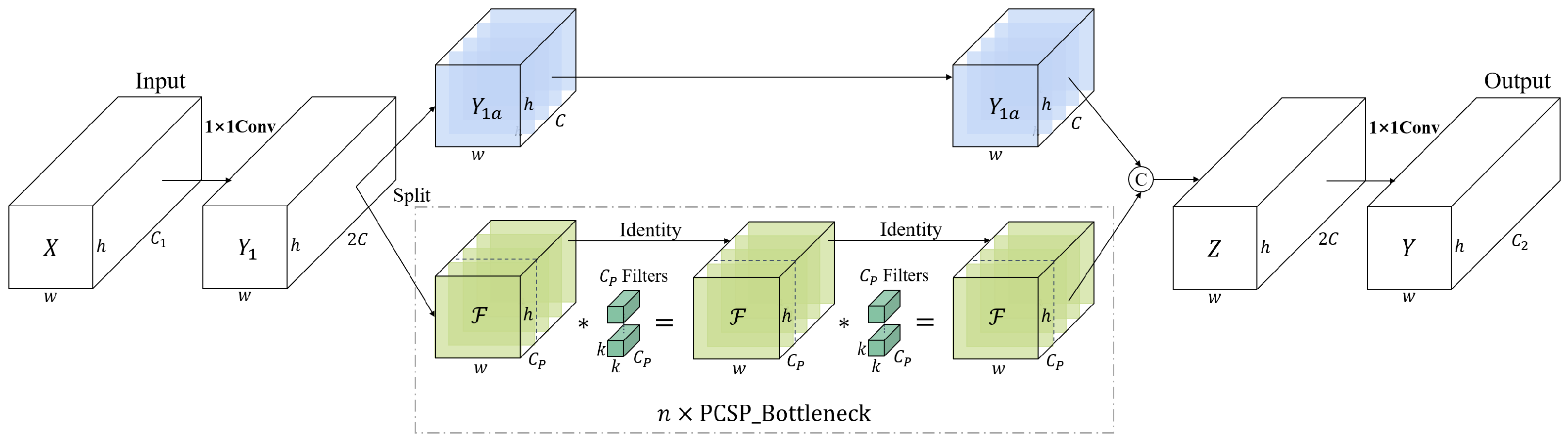
- To meet real-time application needs, we optimized the network with lightweight modules, including the Partial Cross-Stage Pyramid (PCSP) and SCDown, reducing computational complexity while preserving detection accuracy.
2. Related Works
2.1. Traditional Object Detection Algorithms
2.2. Visible-Infrared Object Detection Methods
2.3. Lightweight Models for Object Detection
3. Method
3.1. Overall Architecture
3.2. Dual-Stream Feature Extraction and Fusion Backbone
3.3. Dynamic-Weight-Based Quad-Head Detector (DWQH)
3.4. Lightweight Optimization
3.5. Focaler–Inner IoU (FI-IoU)
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
4.1.1. Datasets
4.1.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Implementation Details
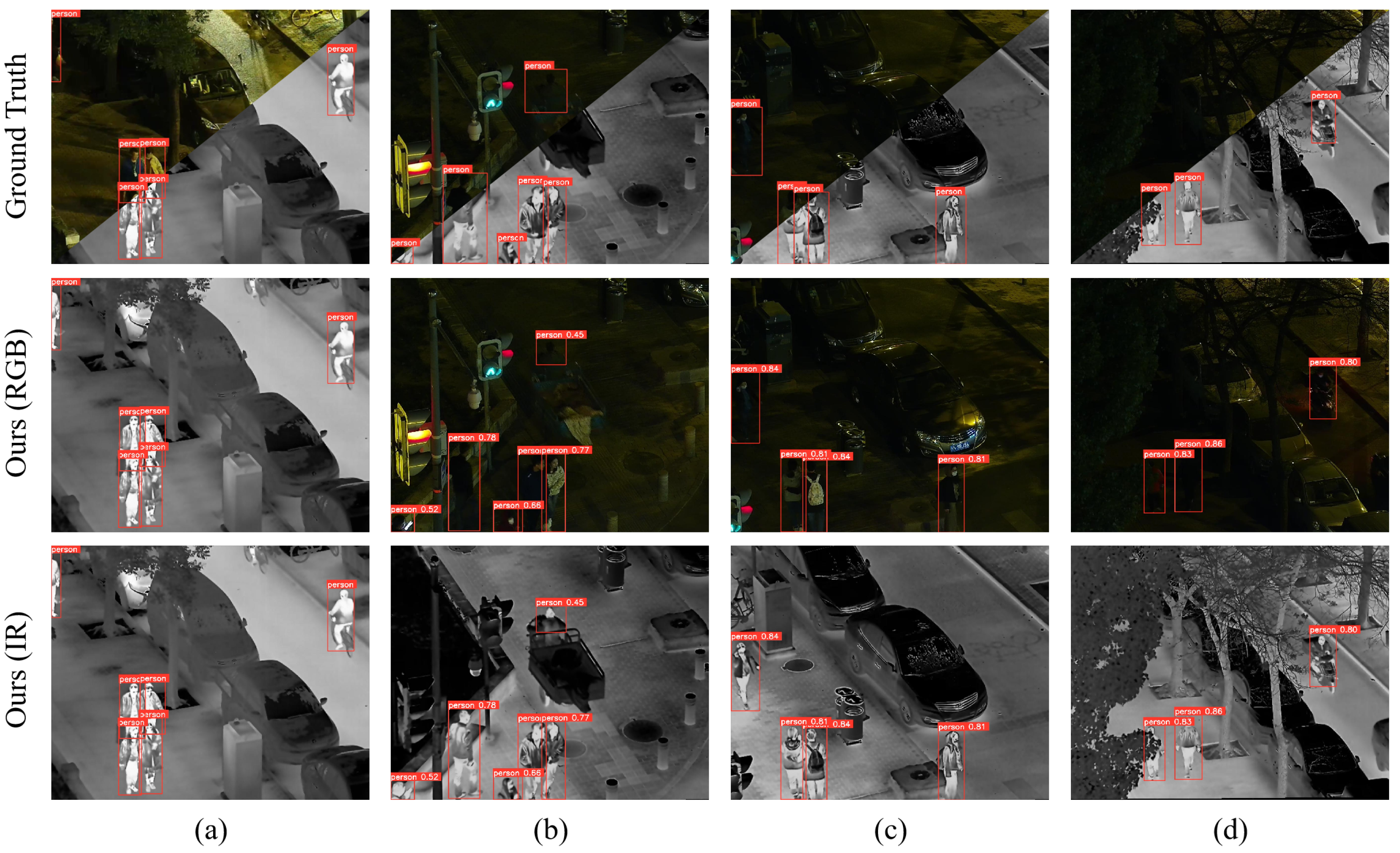
4.3. Algorithm Performance Experiment
4.4. Ablation Experiment
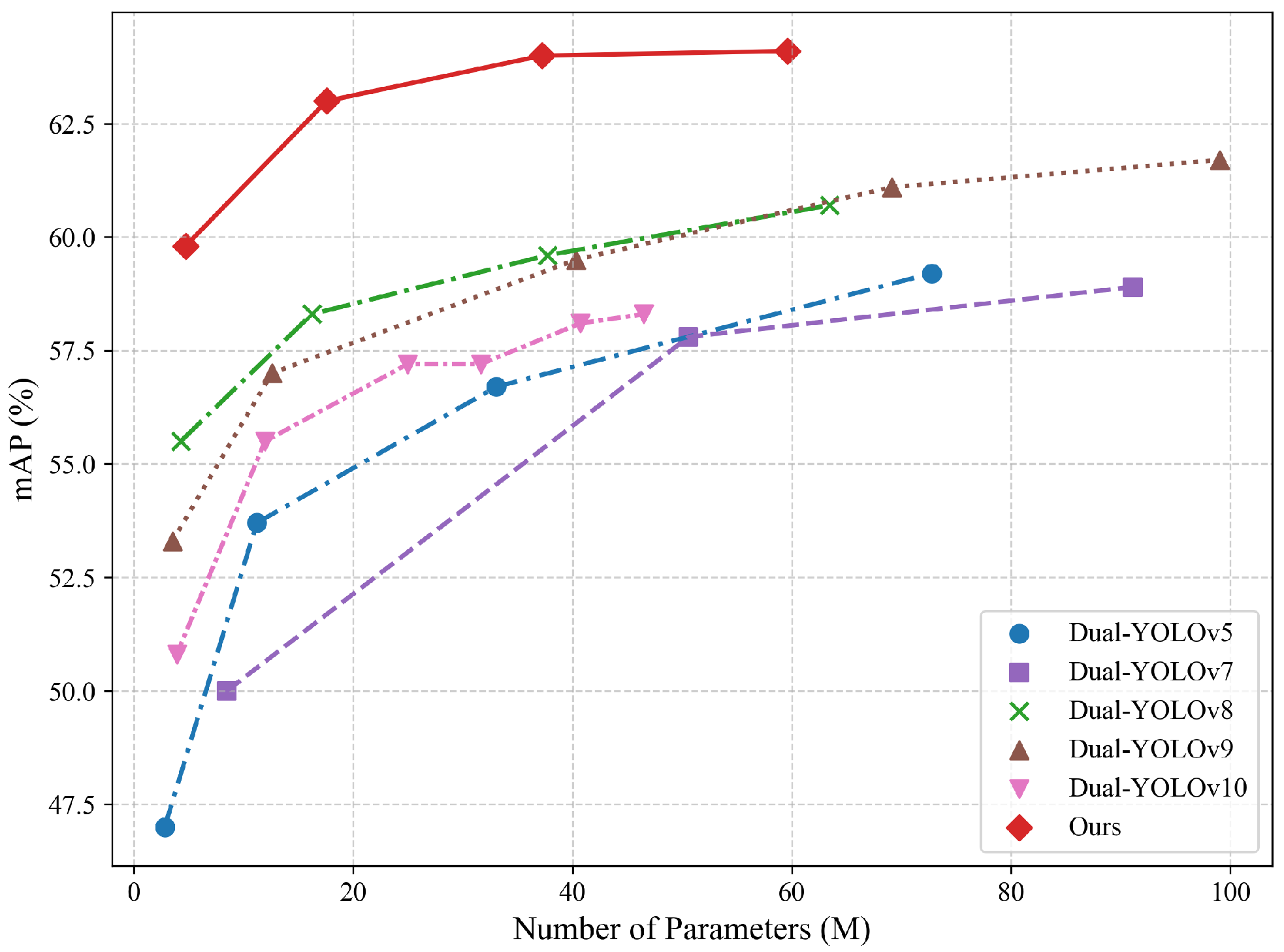
4.5. Comparative Experiments
4.6. Generalization Experiments
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gui, S.; Song, S.; Qin, R.; Tang, Y. Remote Sensing Object Detection in the Deep Learning Era—A Review. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payghode, V.; Goyal, A.; Bhan, A.; Iyer, S.S.; Dubey, A.K. Object Detection and Activity Recognition in Video Surveillance using Neural Networks. Int. J. Web Inf. Syst. 2023, 19, 123–138. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Li, J.; Zeng, T. A Review of Environmental Perception Technology Based on Multi-Sensor Information Fusion in Autonomous Driving. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chu, K.; Zhang, J.; Feng, C. YOLO-FSD: An Improved Target Detection Algorithm on Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 30751–30764. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Lai, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, Z.; Yao, Y. Poly Kernel Inception Network for Remote Sensing Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 27706–27716. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Tu, W.; Yu, H. DDEYOLOv9: Network for Detecting and Counting Abnormal Fish Behaviors in Complex Water Environments. Fishes 2024, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M. YOlOv1 to v8: Unveiling each variant–A comprehensive review of yolo. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 42816–42833. [Google Scholar]
- Krišto, M.; Ivasic-Kos, M.; Pobar, M. Thermal Object Detection in Difficult Weather Conditions using YOLO. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 125459–125476. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Hu, J.; Ma, P.; Tao, R. Single-Frame Infrared Small-Target Detection: A survey. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2022, 10, 87–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hong, D.; Gao, L.; Yao, J.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, B.; Chanussot, J. Deep Learning in Multimodal Remote Sensing Data Fusion: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102926. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Yin, M.; Wang, Z.; Xie, T.; Bei, S. Multispectral Object Detection Based on Multilevel Feature Fusion and Dual Feature Modulation. Electronics 2024, 13, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Fischer, V.; Herman, M.; Behnke, S. Multispectral Pedestrian Detection using Deep Fusion Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 24th European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning, Bruges, Belgium, 27–29 April 2016; pp. 509–514. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Q.; Han, D.; Wang, Z. Cross-modality Fusion Transformer for Multispectral Object Detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00273. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Huang, Q. MOD-YOLO: Multispectral Object Detection based on Transformer Dual-stream YOLO. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2024, 183, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.; Chen, X.; Tang, H.; Wang, C.; Tong, G. B2MFuse: A Bi-branch Multi-scale Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Network based on Joint Semantics Injection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, W. Illumination-guided RGBT Object Detection with Inter-and Intra-modality Fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Gu, W.b.; Ai, Y.b.; Li, W.; Wang, D. Adaptive Spatial Pixel-level Feature Fusion Network for Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 116, 103770. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich Feature Hierarchies for Accurate Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 27th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1504.08083. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayakumar, A.; Vairavasundaram, S. Yolo-based Object Detection Models: A Review and Its Applications. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 83535–83574. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot Multibox Detector. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, T.Y.; Dollár, G. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Lv, W.; Xu, S.; Wei, J.; Wang, G.; Dang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. DETRs Beat YOLOs on Real-time Object Detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.08069. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Ni, L.M.; Zhang, L. Dn-detr: Accelerate Detr Training by Introducing Query Denoising. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 13619–13627. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7263–7271. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Yeh, I.H.; Mark Liao, H.Y. YOlOv9: Learning What You Want to Learn using Programmable Gradient Information. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 26–27 March 2025; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. YOlOv10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Shen, S.; Cao, W.; Li, X.; Wang, D. Improved YOLOv8-CR network for detecting defects of the automotive MEMS pressure sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 26935–26945. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-freebies Sets New state-of-the-art for Real-time Object Detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Dong, X.; Cheng, C.; Ou, X.; He, X. Research on Improved Semantic SLAM Adaptation to Dynamic Environment Based on YOLOv8. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference, Kaifeng, China, 17–19 May 2024; pp. 772–776. [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, J.E.; Oughton, E.J. Surveying You Only Look Once (YOLO) Multispectral Object Detection Advancements, Applications and Challenges. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 7366–7395. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, C.; Cao, J.; Hao, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Ning, Y.; Zhao, T. Dual-YOLO Architecture From Infrared and Visible images for Object Detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lei, J.; Xie, W.; Fang, Z.; Li, Y.; Du, Q. SuperYOLO: Super Resolution Assisted Object Detection in Multimodal Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Li, X.; Zhu, B.; Shi, Y.; Xie, B. Drone Detection Method based on MobileViT and CA-PANet. Electronics 2023, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ye, J. Edge-YOLO: Lightweight Infrared Object Detection Method Deployed on Edge Devices. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Mi, W.; Wang, Y. EDGS-YOLOv8: An Improved YOLOv8 Lightweight UAV Detection Model. Drones 2024, 8, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Chen, Y.; Cai, W.; Niu, M.; Li, J. LD-YOLOv10: A Lightweight Target Detection Algorithm for Drone Scenarios based on YOLOv10. Electronics 2024, 13, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Jiang, X.; Dong, L. Gated Weighted Normative Feature Fusion for Multispectral Object Detection. Vis. Comput. 2024, 40, 6409–6419. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.; Wei, X. C²Former: Calibrated and Complementary Transformer for RGB-Infrared Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M. Mobilevit: Light-weight, General-purpose, and Mobile-friendly Vision Transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.02178. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, H. LGADet: Light-weight Anchor-free Multispectral Pedestrian Detection with Mixed Local and Global Attention. Neural Process. Lett. 2023, 55, 2935–2952. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Fu, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Xue, M.; Cui, Y. Lightweight Cross-Modal Multispectral Pedestrian Detection Based on Spatial Reweighted Attention Mechanism. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2024, 78, 4071–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Wang, W.; Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wen, Z. A Lightweight Coal Gngue Detection Method based on Multispectral Imaging and Enhanced YOLOv8n. Microchem. J. 2024, 199, 110142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Wang, Z. Cross-modality Attentive Feature Fusion for Object Detection in Multispectral Remote Sensing Imagery. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 130, 108786. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Sun, F.; Xu, T.; Rong, Y.; Huang, J. Deep Multimodal Fusion by Channel Exchanging. Adv. Neural Inf. Proces. Syst. 2020, 33, 4835–4845. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Learning Spatial Fusion for Single-shot Object Detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.09516. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Kao, S.h.; He, H.; Zhuo, W.; Wen, S.; Lee, C.H.; Chan, S.H.G. Run, don’t walk: Chasing higher FLOPS for faster neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 12021–12031. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Fang, J.; Song, X.; Guan, C.; Yin, J.; Dai, Y.; Yang, R. Iou Loss for 2D/3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on 3D Vision, Quebec, QC, Canada, 15–18 September 2019; pp. 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Focaler-IoU: More Focused Intersection over Union Loss. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.10525. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Zhang, S. Inner-IoU: More Effective Intersection over Union Loss With Auxiliary Bounding Box. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.02877. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Huang, Z.; Wu, G.; Liu, R.; Zhong, W.; Luo, Z. Target-aware Dual Adversarial Learning and a Multi-scenario Multi-modality Benchmark to Fuse Infrared and Visible for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 5802–5811. [Google Scholar]
- Razakarivony, S.; Jurie, F. Vehicle Detection in Aerial Imagery: A small Target Detection Benchmark. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2016, 34, 187–203. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, M.; Tang, W.; Zhou, W. LLVIP: A Visible-infrared Paired Dataset for Low-light Vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3496–3504. [Google Scholar]
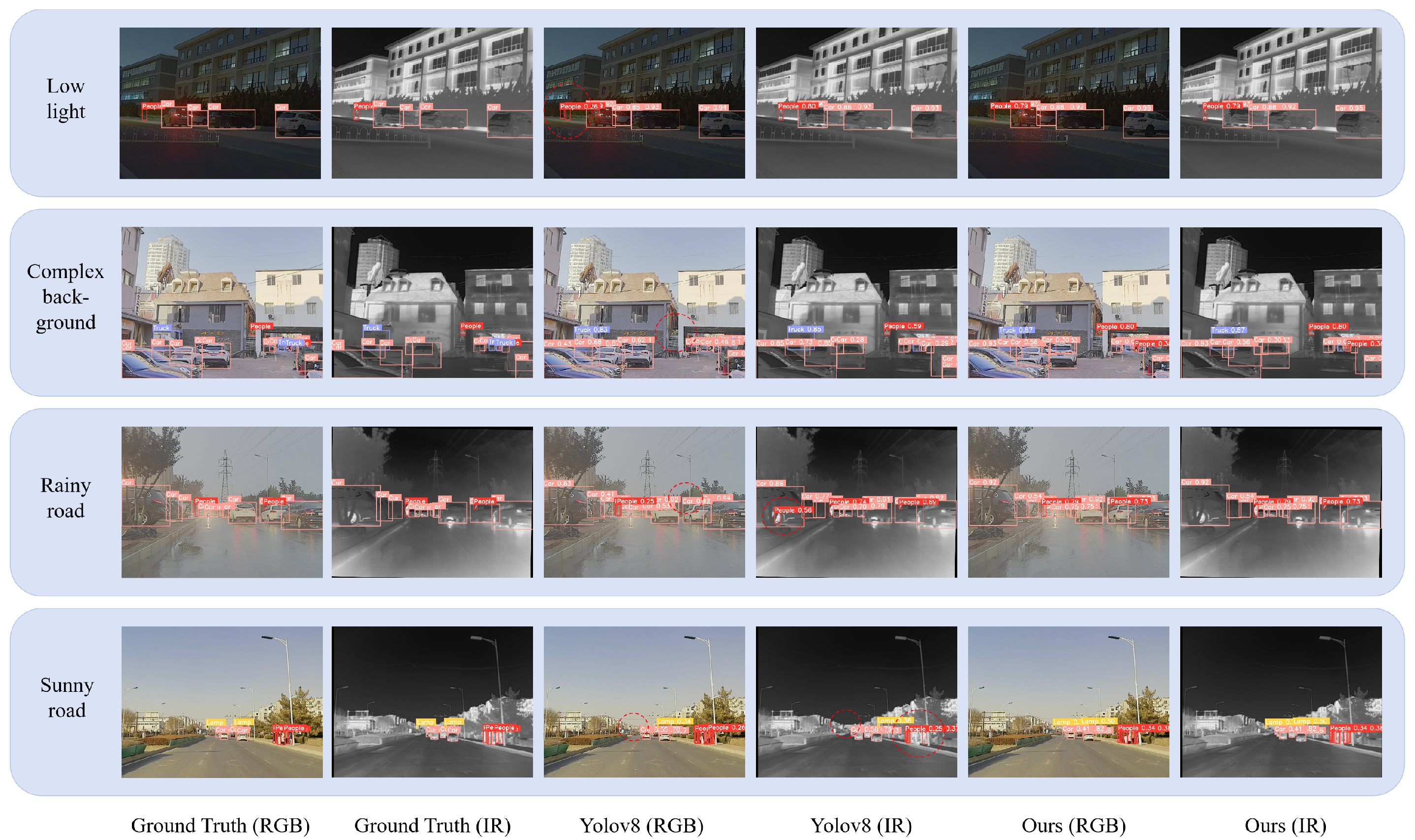




| Method | FT | DWMH | LW | Param (M) | FLOPs (G) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@[0.5:0.95] (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | - | - | - | 4.3 | 11.4 | 89.1 | 74.1 | 81.9 | 55.5 |
| 1 | ✓ | 4.4 | 12.1 | 85.7 | 76.5 | 82.6 (+0.7) | 56.0 (+0.5) | ||
| 2 | ✓ | 5.6 | 18.6 | 87.7 | 81.6 | 88.4 (+6.5) | 60.2 (+4.7) | ||
| 3 | ✓ | 3.0 | 9.5 | 88.3 | 73.1 | 81.1 | 53.4 | ||
| 4 | ✓ | ✓ | 5.7 (+1.4/32.6%) | 19.3 (+7.9/69.3%) | 87.4 | 82.0 | 89.0 (+7.1) | 60.5 (+5.0) | |
| 5 | ✓ | ✓ | 3.4 | 10.2 | 88.2 | 74.8 | 82.4 | 54.8 | |
| 6 | ✓ | ✓ | 4.3 | 16.2 | 86.8 | 80.9 | 87.4 | 59.4 | |
| 7 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 4.7 (+0.4/9.3%) | 16.9 (+5.5/48.2%) | 87.2 | 82.1 | 88.8 (+6.9) | 59.9 (+4.4) |
| Method | Param (M) | FLOPs (G) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@[0.5:0.95] (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual-YOLOv5n | 2.8 | 7.0 | 85.7 | 71.3 | 78.2 | 47.0 |
| Dual-YOLOv7tiny | 8.5 | 20.4 | 85.7 | 73.6 | 80.4 | 50.0 |
| Dual-YOLOv8n | 4.3 | 11.4 | 89.1 | 74.1 | 81.9 | 55.5 |
| Dual-YOLOv9t | 3.5 | 14.9 | 88.0 | 71.9 | 79.6 | 53.3 |
| Dual-YOLOv10n | 3.9 | 11.8 | 83.5 | 70.2 | 77.8 | 50.8 |
| FQDNet_n (Ours) | 4.7 | 16.9 | 87.2 | 82.1 | 88.8 | 59.9 |
| Dual-YOLOv5s | 11.2 | 26.5 | 89.7 | 77.1 | 84.6 | 53.7 |
| Dual-YOLOv8s | 16.2 | 41.0 | 87.6 | 77.3 | 83.6 | 58.3 |
| Dual-YOLOv9s | 12.6 | 51.5 | 90.2 | 77.6 | 84.4 | 57.0 |
| Dual-YOLOv10s | 12.0 | 36.6 | 88.5 | 74.5 | 83.1 | 55.5 |
| FQDNet_s (Ours) | 17.6 | 53.8 | 91.3 | 86.2 | 91.9 | 63.0 |
| Dual-YOLOv5m | 33.1 | 79.6 | 89.7 | 79.0 | 86.1 | 56.7 |
| Dual-YOLOv7 | 50.6 | 171.9 | 89.0 | 81.9 | 87.8 | 57.8 |
| Dual-YOLOv8m | 37.7 | 117.6 | 89.0 | 77.7 | 85.8 | 59.6 |
| Dual-YOLOv9m | 40.3 | 165.5 | 90.3 | 78.6 | 85.4 | 59.5 |
| Dual-YOLOv10m | 25.0 | 100.1 | 88.1 | 78.3 | 84.0 | 57.2 |
| Dual-YOLOv10b | 31.6 | 159.2 | 88.8 | 77.4 | 84.4 | 57.2 |
| FQDNet_m (Ours) | 37.2 | 134.3 | 90.5 | 85.4 | 91.3 | 64.0 |
| Dual-YOLOv5l | 72.7 | 178.1 | 91.1 | 80.9 | 87.6 | 59.2 |
| Dual-YOLOv7x | 91.1 | 290.4 | 90.8 | 82.8 | 87.3 | 58.9 |
| Dual-YOLOv8l | 63.4 | 251.0 | 88.9 | 80.0 | 86.3 | 60.7 |
| Dual-YOLOv9c | 69.1 | 330.8 | 91.1 | 80.8 | 88.1 | 61.1 |
| Dual-YOLOv9e | 99.0 | 362.4 | 89.3 | 82.4 | 88.6 | 61.7 |
| Dual-YOLOv10l | 40.7 | 209.0 | 91.0 | 77.4 | 85.9 | 58.1 |
| Dual-YOLOv10x | 46.5 | 271.2 | 88.8 | 80.3 | 86.4 | 58.3 |
| FQDNet_l (Ours) | 59.6 | 267.5 | 89.6 | 86.3 | 92.1 | 64.1 |
| Method | Data Modality | Param (M) | FLOPs (G) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@[0.5:0.95] (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | RGB | 3.0 | 8.2 | 84.0 | 71.8 | 78.3 | 51.4 |
| YOLOv8n | IR | 3.0 | 8.2 | 79.0 | 68.6 | 74.6 | 49.1 |
| Dual-YOLOv8n | RGB+IR | 4.3 | 11.4 | 89.1 | 74.1 | 81.9 | 55.5 |
| CFT [13] | RGB+IR | 44.9 | 17.9 | 90.3 | 77.7 | 85.1 | 53.9 |
| YOLOFusion [46] | RGB+IR | 12.5 | 28.6 | 86.0 | 82.1 | 87.7 | 53.8 |
| SuperYOLO [35] | RGB+IR | 4.9 | 56.3 | 90.1 | 80.1 | 88.0 | 54.8 |
| MOD-YOLO [14] | RGB+IR | 24.9 | 35.7 | 88.1 | 79.6 | 84.5 | 57.7 |
| FQDNet_n (Ours) | RGB+IR | 4.7 | 16.9 | 87.2 | 82.1 | 88.8 (+6.9) | 59.9 (+4.4) |
| FQDNet_s (Ours) | RGB+IR | 17.6 | 53.8 | 91.3 | 86.2 | 91.9 (+10.0) | 63.0 (+7.5) |
| Method | Data Modality | Param (M) | FLOPs (G) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@[0.5:0.95] (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | RGB | 3.0 | 8.2 | 59.0 | 67.8 | 66.8 | 39.5 |
| YOLOv8n | IR | 3.0 | 8.2 | 61.3 | 56.1 | 62.4 | 37.4 |
| Dual-YOLOv8n | RGB+IR | 4.3 | 11.4 | 71.0 | 63.6 | 67.1 | 40.8 |
| CFT [13] | RGB+IR | 44.9 | 17.9 | 68.6 | 65.7 | 70.5 | 42.6 |
| YOLOFusion [46] | RGB+IR | 12.5 | 28.6 | 75.8 | 64.8 | 73.3 | 43.8 |
| SuperYOLO [35] | RGB+IR | 4.9 | 56.3 | 67.2 | 71.1 | 72.4 | 44.2 |
| MOD-YOLO [14] | RGB+IR | 24.9 | 35.7 | 70.1 | 65.3 | 71.8 | 41.9 |
| FQDNet_n (Ours) | RGB+IR | 4.7 | 16.9 | 62.3 | 77.0 | 73.0 (+5.9) | 44.2 (+3.5) |
| FQDNet_s (Ours) | RGB+IR | 17.6 | 53.8 | 73.9 | 65.0 | 75.9 (+8.8) | 47.7 (+6.9) |
| Method | Data Modality | Param (M) | FLOPs (G) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@[0.5:0.95] (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | RGB | 3.0 | 8.2 | 87.4 | 79.3 | 86.9 | 48.5 |
| YOLOv8n | IR | 3.0 | 8.2 | 90.3 | 88.5 | 92.6 | 58.9 |
| Dual-YOLOv8n | RGB+IR | 4.3 | 11.4 | 92.4 | 89.4 | 94.6 | 58.2 |
| CFT [13] | RGB+IR | 44.9 | 17.9 | 93.5 | 90.7 | 95.4 | 61.5 |
| YOLOFusion [46] | RGB+IR | 12.5 | 28.6 | 89.7 | 90.5 | 93.1 | 57.9 |
| SuperYOLO [35] | RGB+IR | 4.9 | 56.3 | 89.2 | 89.2 | 93.2 | 58.5 |
| MOD-YOLO [14] | RGB+IR | 24.9 | 35.7 | 94.0 | 90.3 | 95.2 | 60.6 |
| FQDNet_n (Ours) | RGB+IR | 4.7 | 16.9 | 94.6 | 89.7 | 95.5 (+0.9) | 61.3 (+3.1) |
| FQDNet_s (Ours) | RGB+IR | 17.6 | 53.8 | 94.1 | 91.3 | 96.4 (+1.8) | 64.1 (+5.9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, F.; Hong, A.; Tang, H.; Tong, G. FQDNet: A Fusion-Enhanced Quad-Head Network for RGB-Infrared Object Detection. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061095
Meng F, Hong A, Tang H, Tong G. FQDNet: A Fusion-Enhanced Quad-Head Network for RGB-Infrared Object Detection. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(6):1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061095
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Fangzhou, Aoping Hong, Hongying Tang, and Guanjun Tong. 2025. "FQDNet: A Fusion-Enhanced Quad-Head Network for RGB-Infrared Object Detection" Remote Sensing 17, no. 6: 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061095
APA StyleMeng, F., Hong, A., Tang, H., & Tong, G. (2025). FQDNet: A Fusion-Enhanced Quad-Head Network for RGB-Infrared Object Detection. Remote Sensing, 17(6), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061095








