Bayesian Model Averaging for Satellite Precipitation Data Fusion: From Accuracy Estimation to Runoff Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
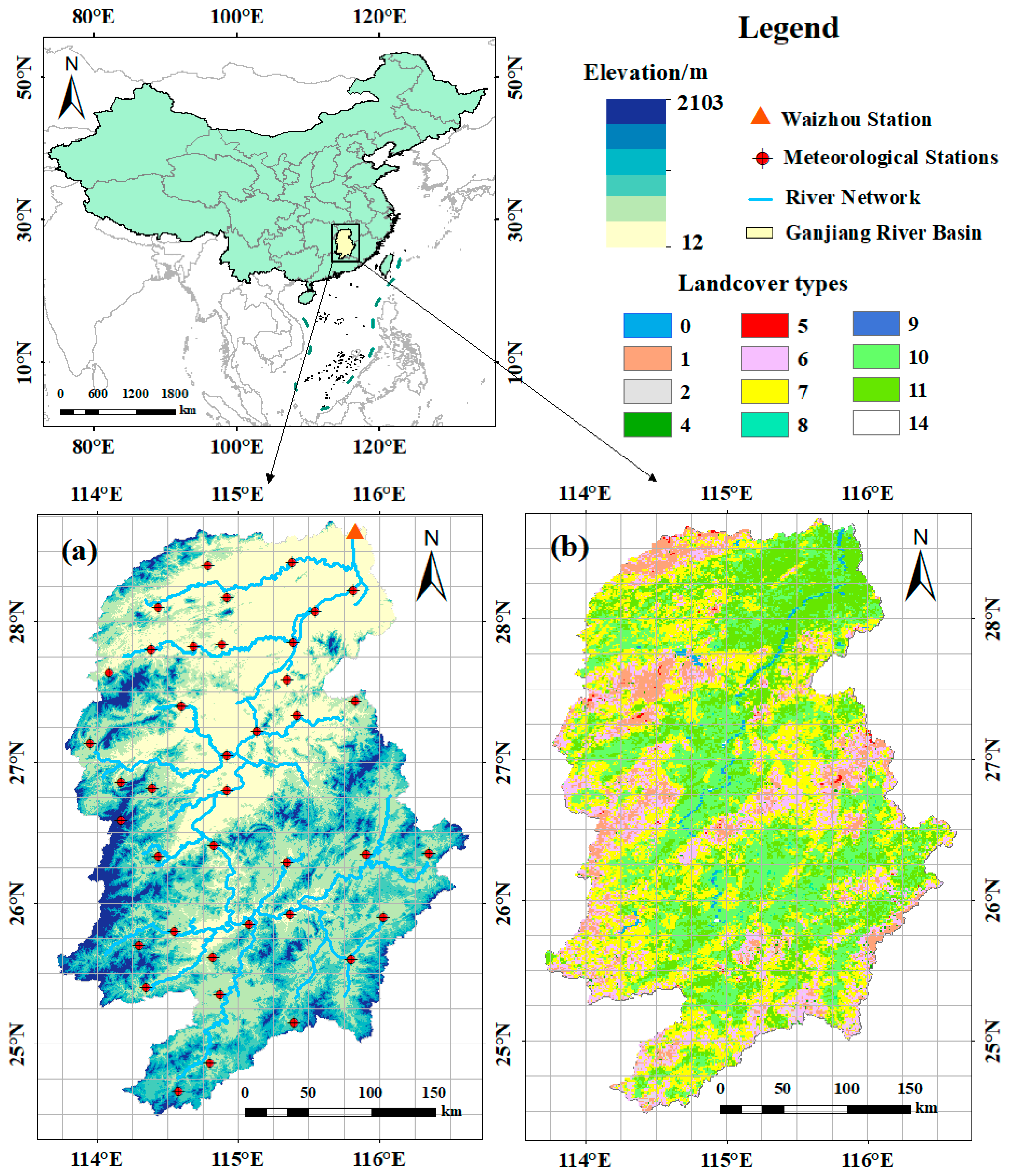
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Ground Observation Data
2.2.2. Satellite, Reanalysis, and Ensemble Precipitation Products
| Products | Spatial Coverage | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Coverage | Temporal Resolution | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHIRPS | 50°N-S | 0.05° | 1981–present | 24 h | [34] |
| ERA5 | Global | 0.25° | 1950–present | 1 h | [36] |
| GSMaP-G | 60°N-S | 0.1° | 2000–present | 1 h | [38] |
| IMERG-F | 60°N-S | 0.1° | 2000–present | 0.5 h | [40] |
| MSWEP | Global | 0.1° | 1979–present | 3 h | [42] |
2.2.3. Runoff Data and Others
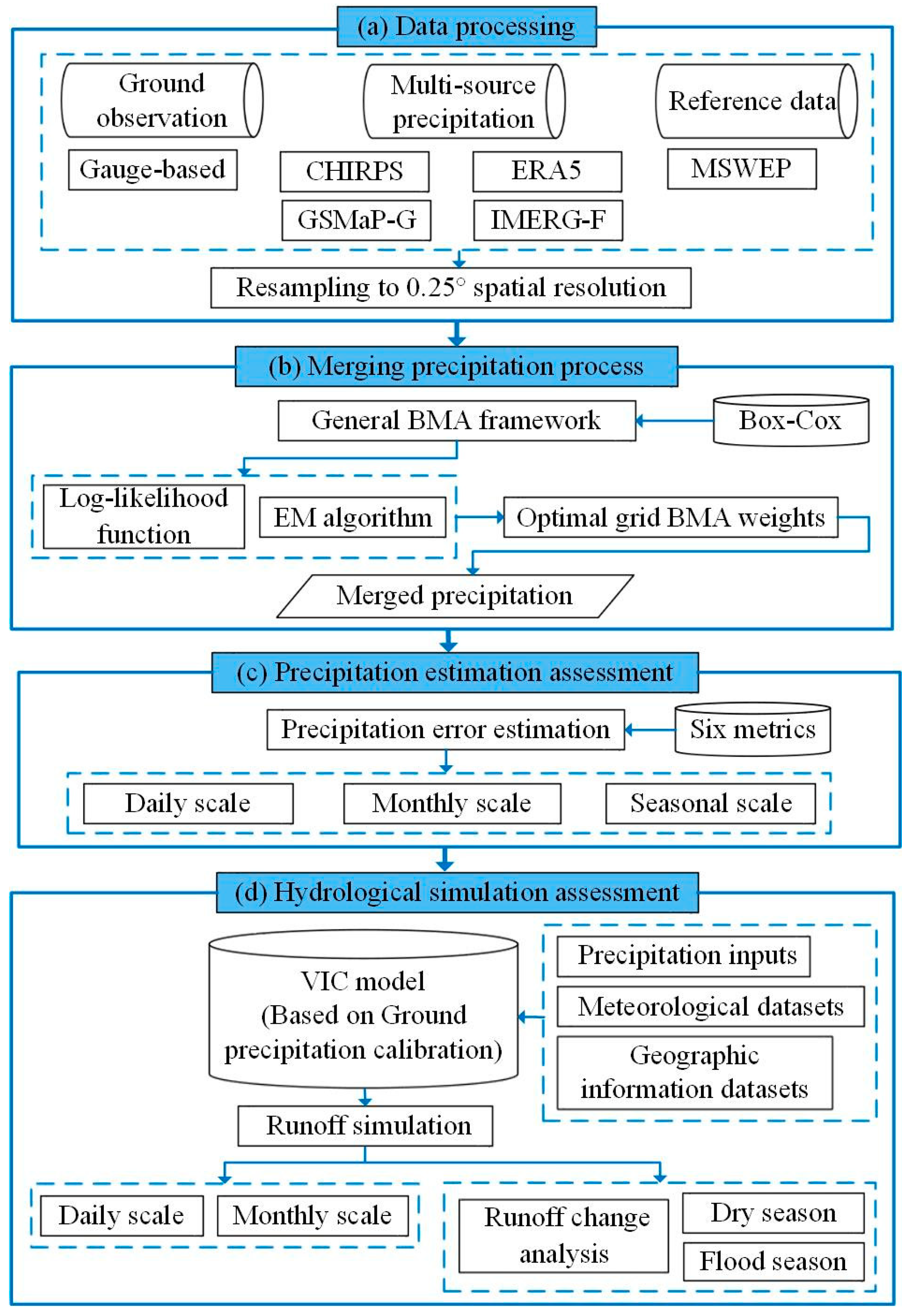
3. Methods
3.1. Bayesian Model Averaging (BMA)
3.2. VIC Hydrological Model
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
4. Results
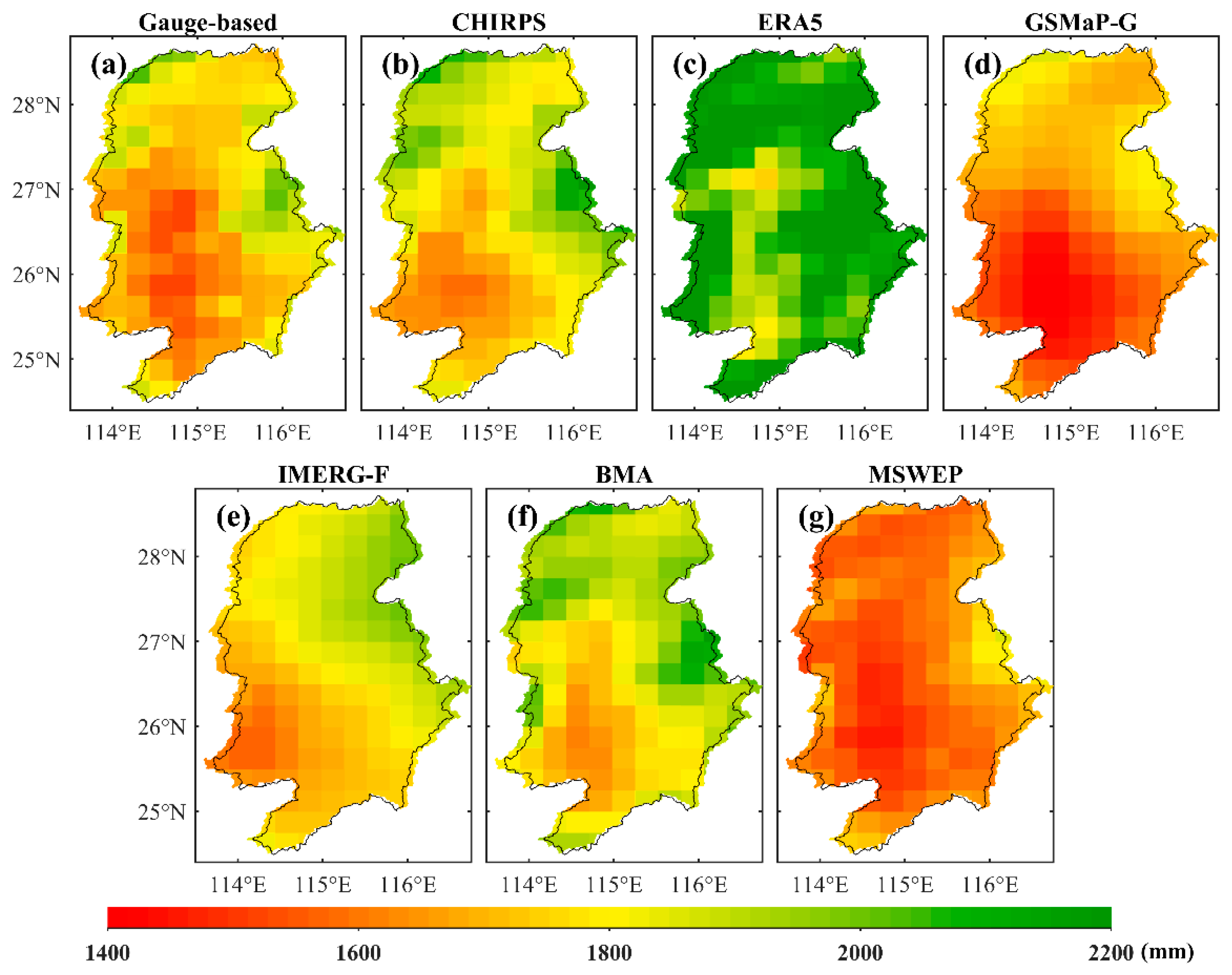
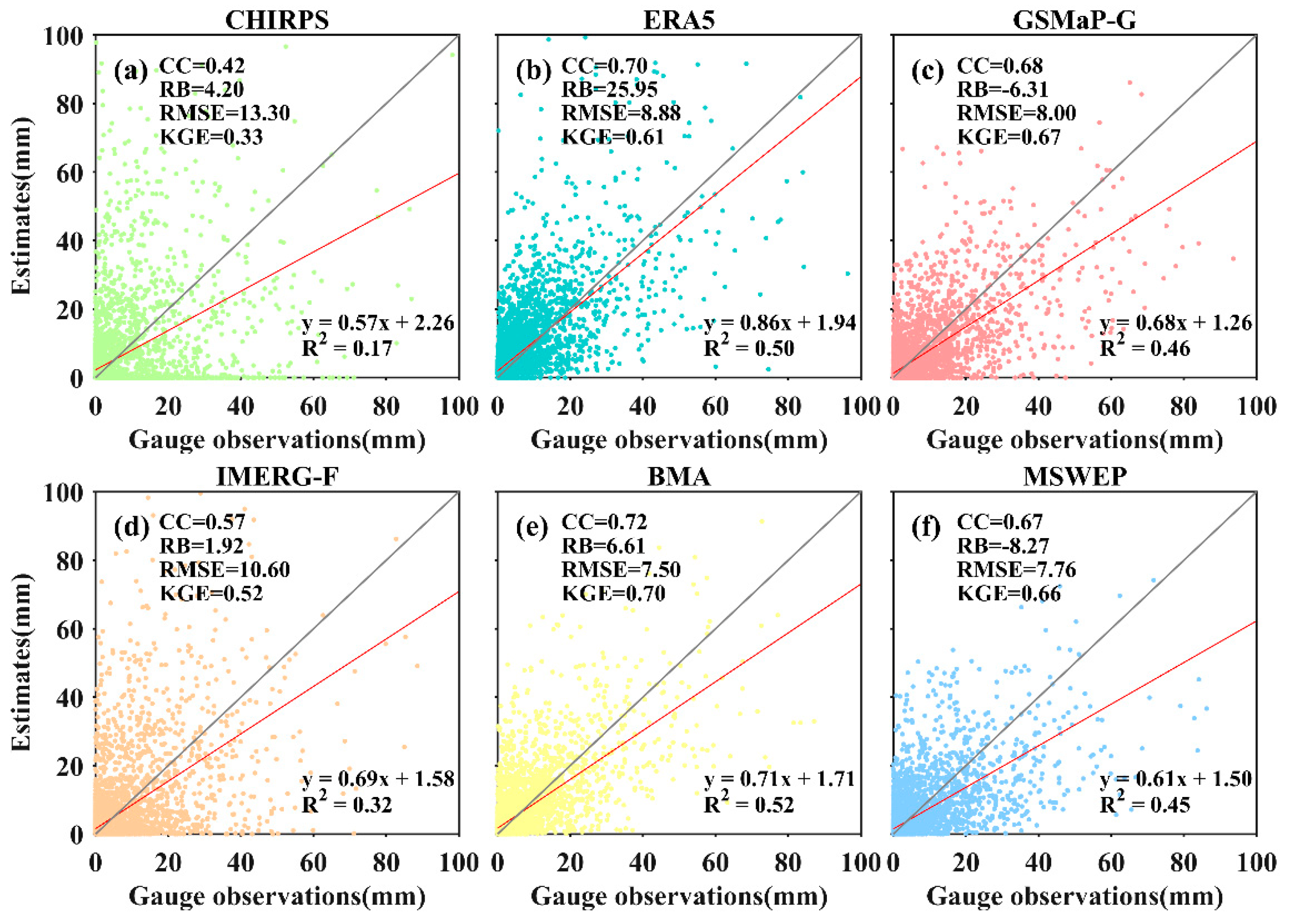
4.1. Accuracy Evaluation of Precipitation Estimation for Different Products
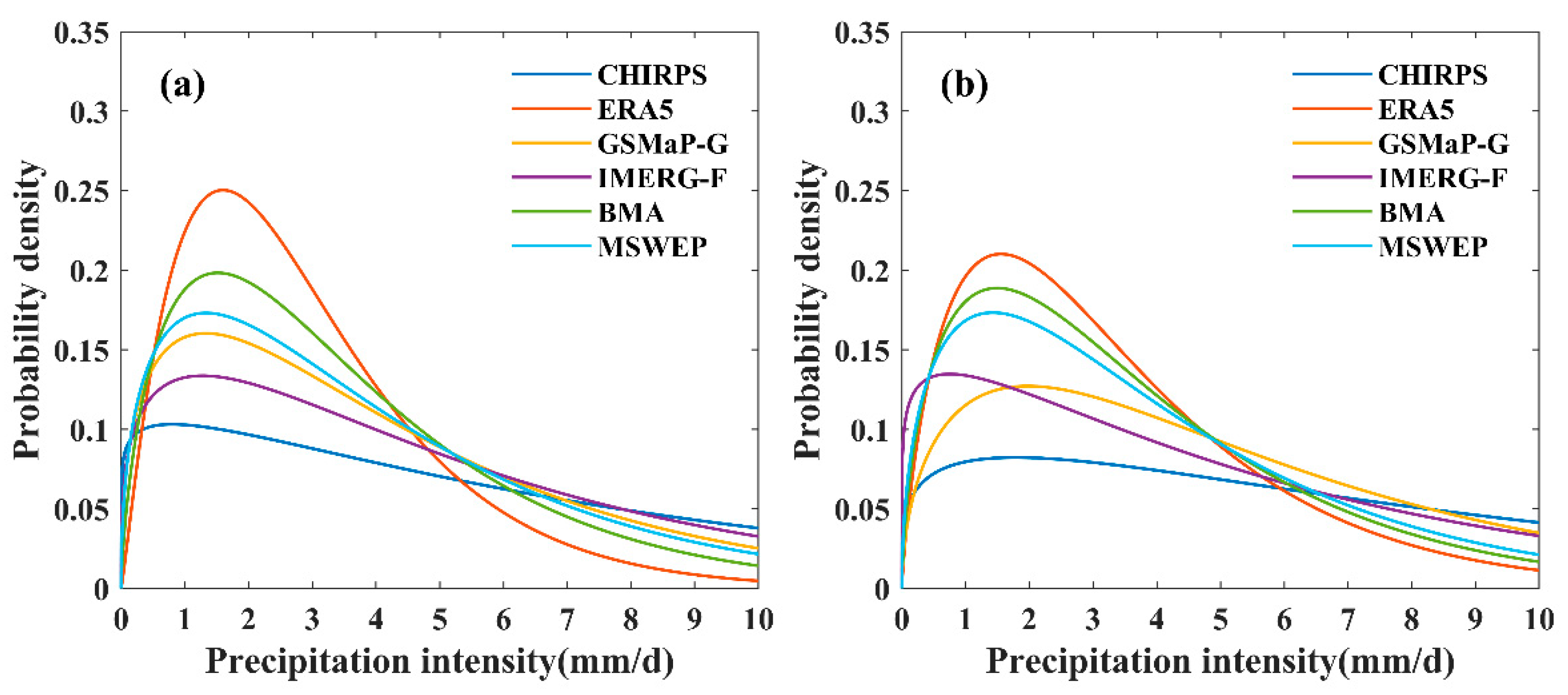
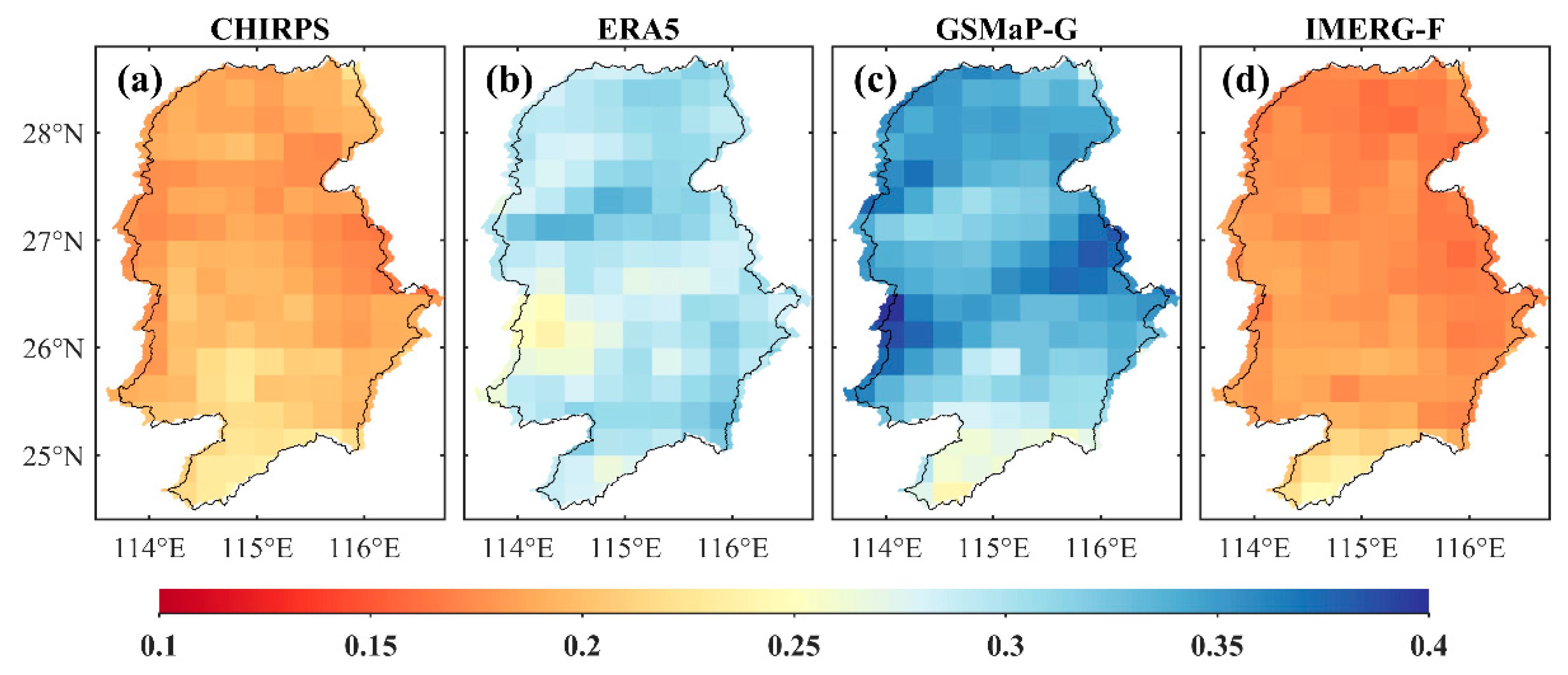
4.1.1. Daily Scale Evaluation
4.1.2. Monthly Scale Evaluation
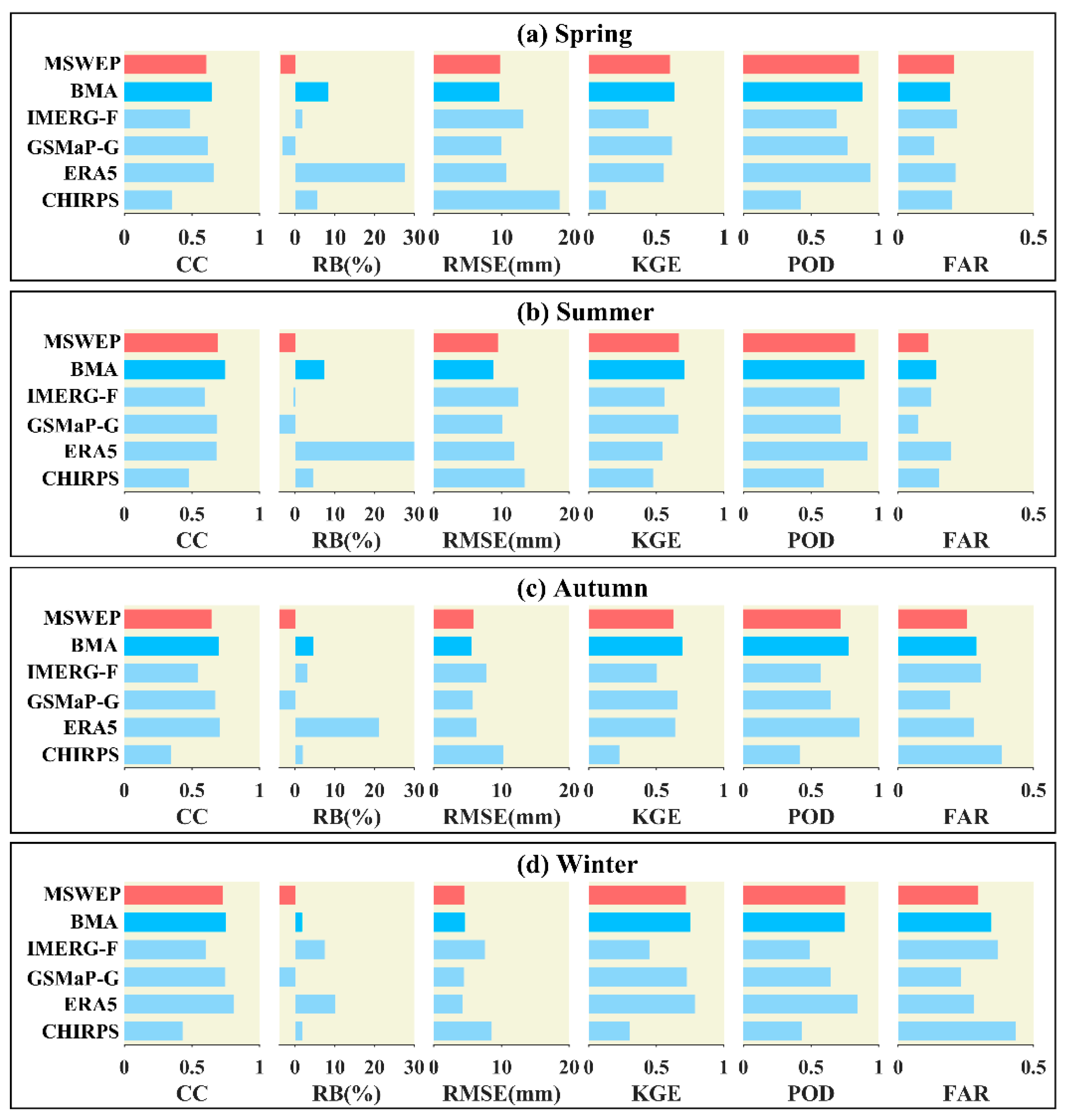
4.1.3. Seasonal Scale Evaluation
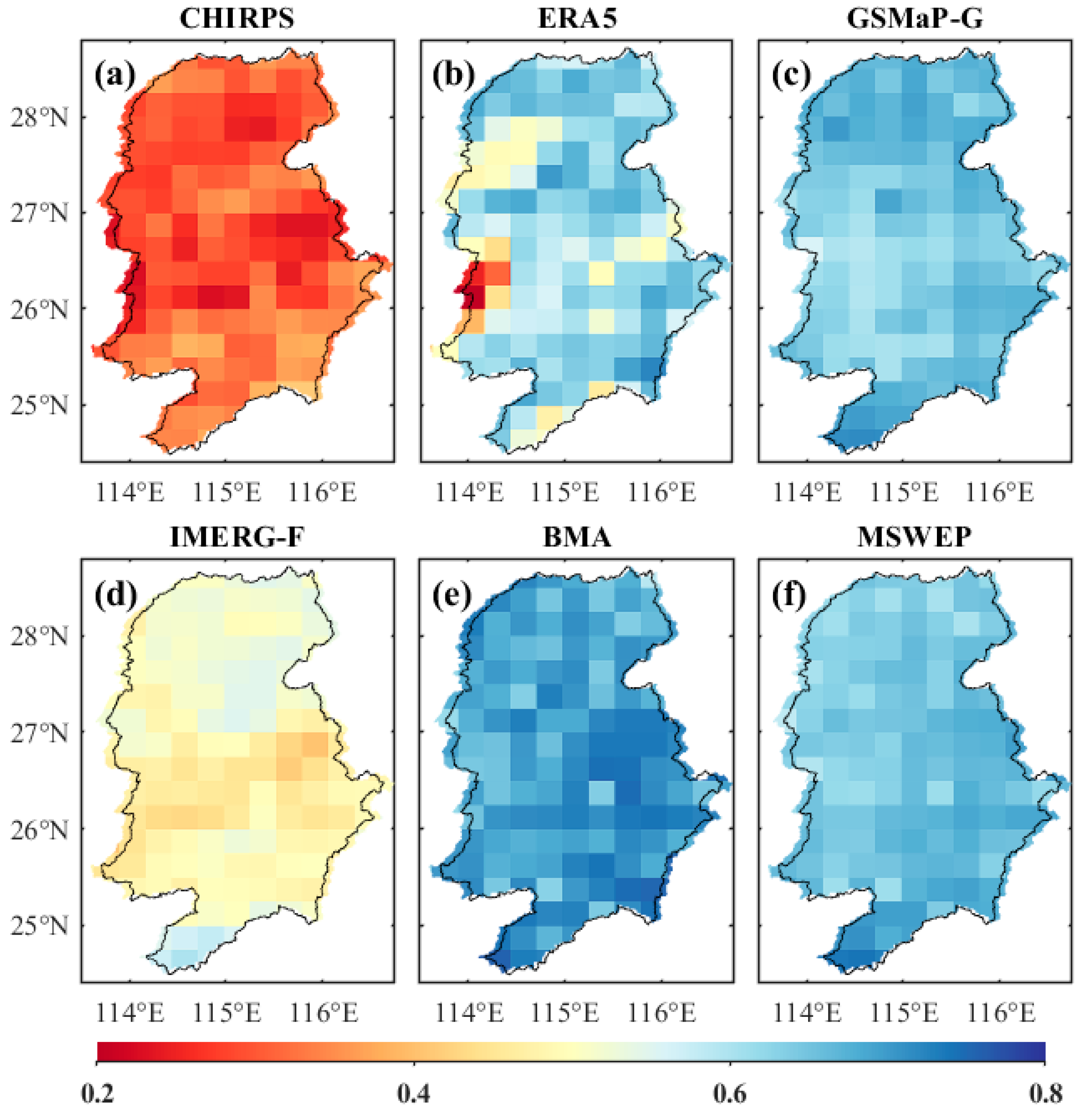
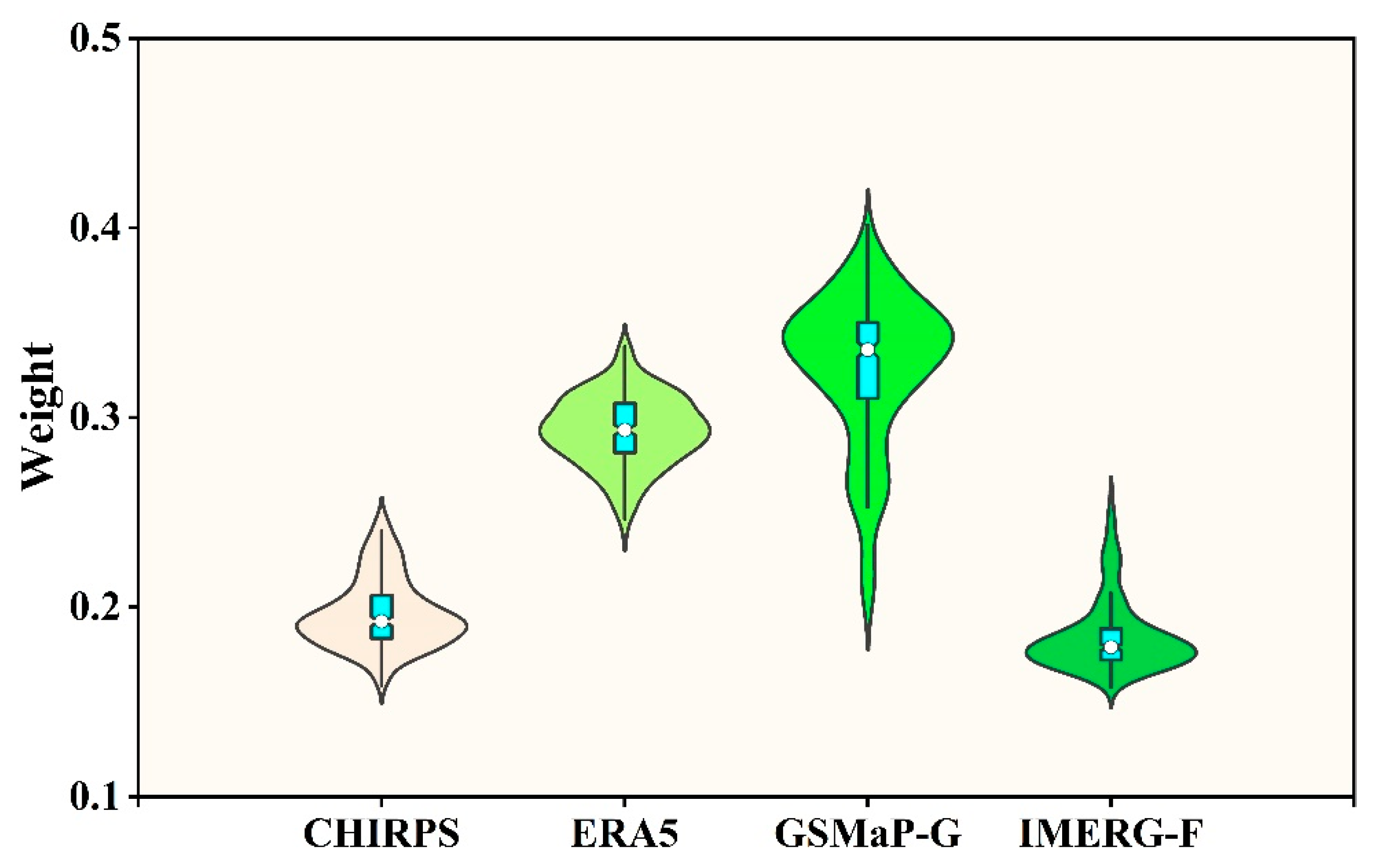
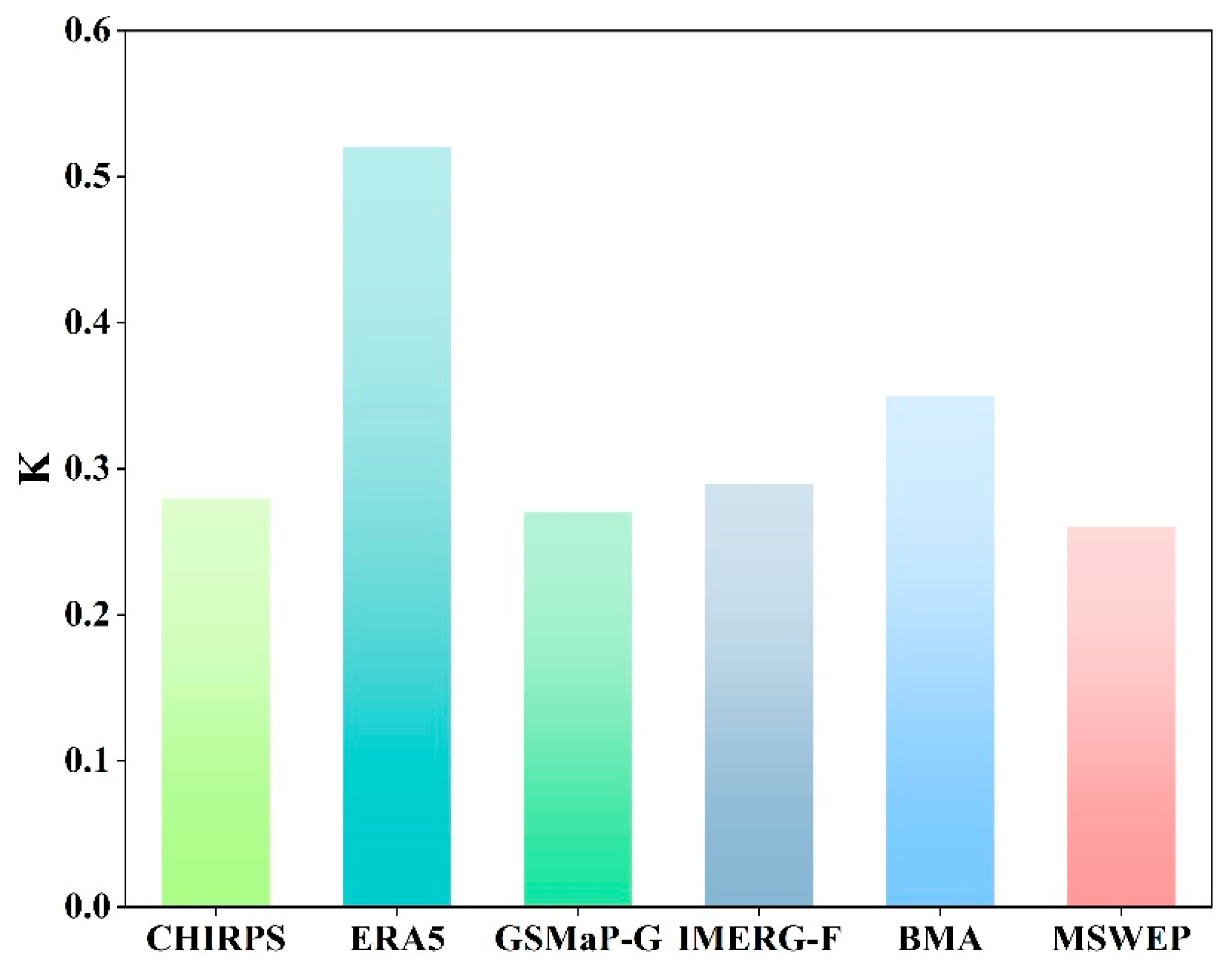
4.2. Weight Analysis of BMA Ensemble Members
4.3. Hydrological Simulation Driven by Different Precipitation Products
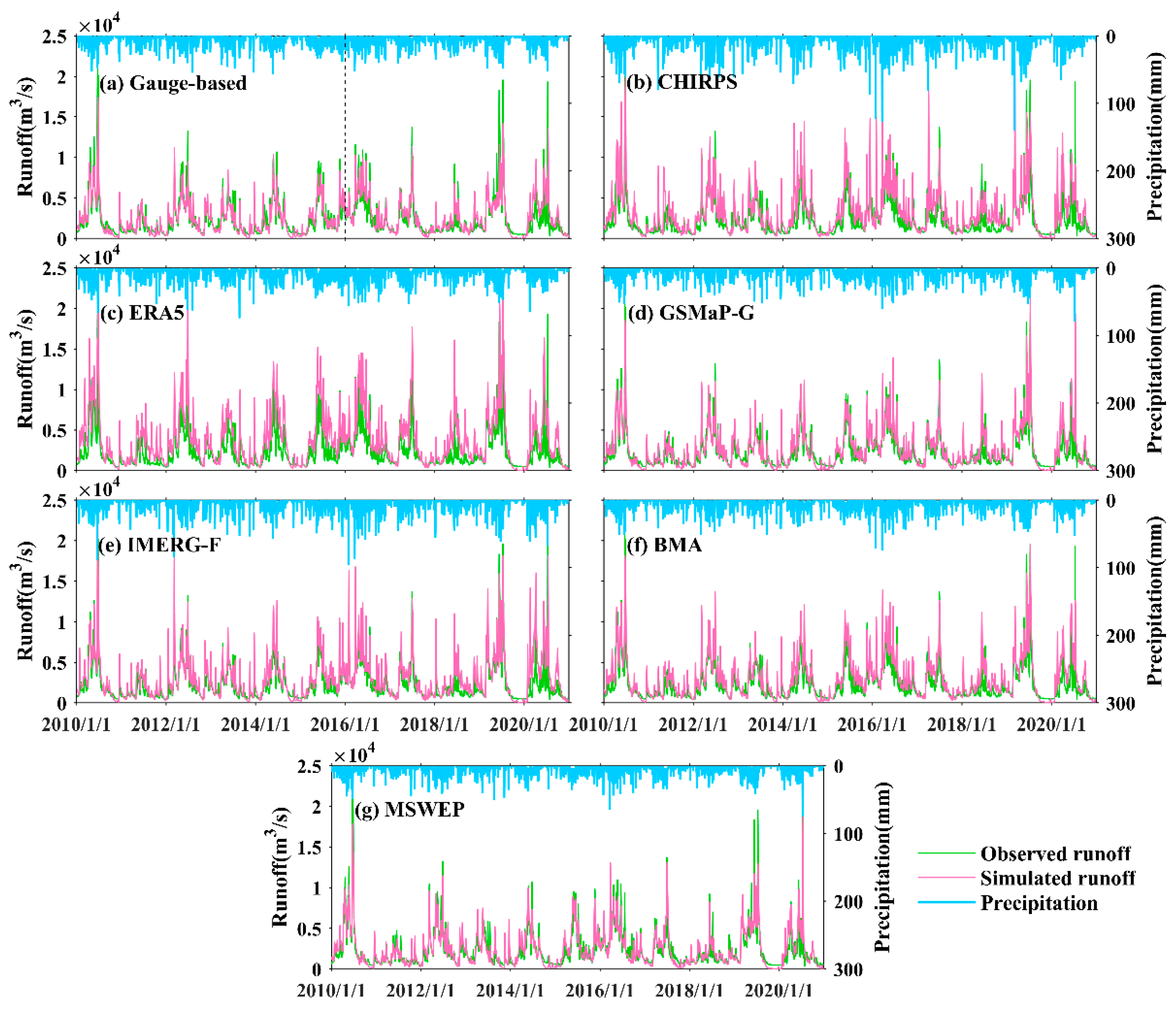
4.3.1. Daily Scale Simulation
4.3.2. Monthly Scale Simulation
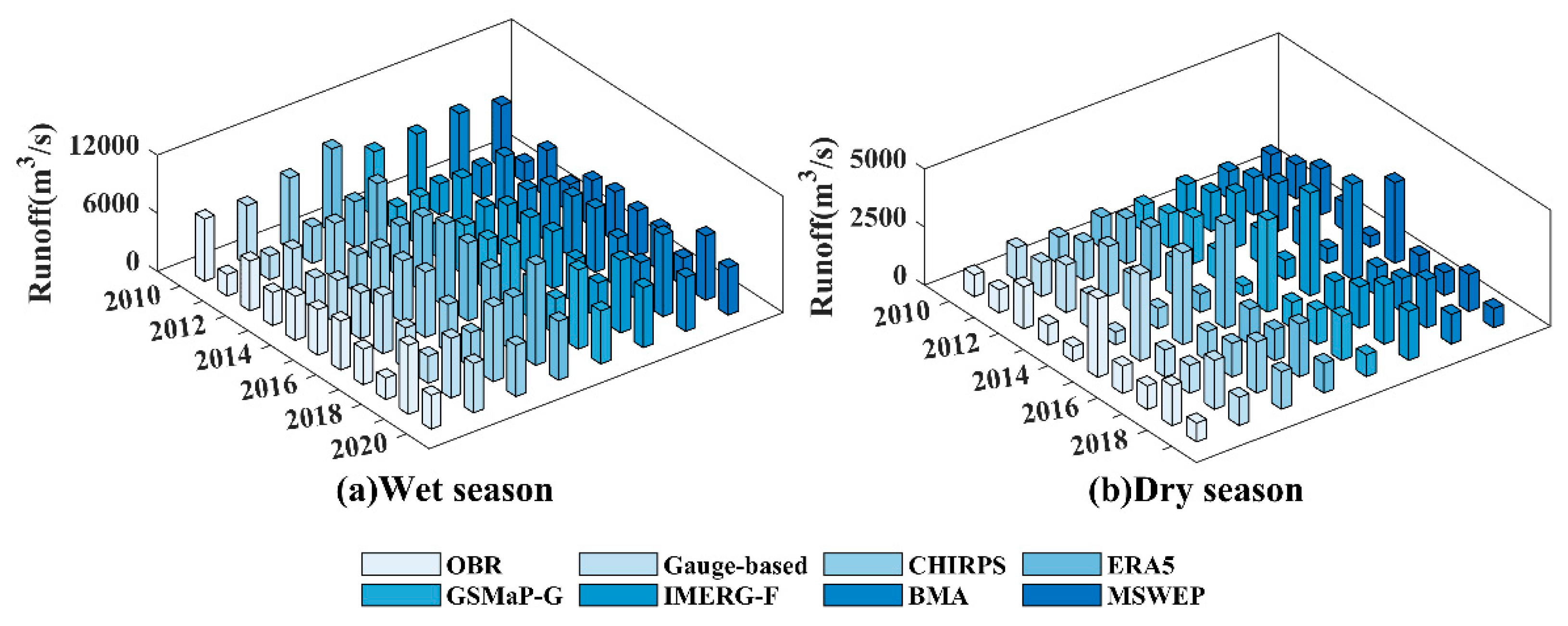
4.3.3. Analysis of Runoff Changes During Wet and Dry Periods
5. Discussion
5.1. Strengths and Contributions of the BMA in This Study
5.2. Influence of Precipitation Inputs on BMA
5.3. Extreme Runoff Analysis
5.4. Analysis of Error Propagation from Precipitation to Runoff
5.5. Improvements in Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Nam, W.-H.; Huang, T.; Gu, X.; Zeng, J.; Huang, S.; Chen, N.; Yan, Z.; Niyogi, D. Data fusion of satellite imagery and downscaling for generating highly fine-scale precipitation. J. Hydrol. 2024, 631, 130665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, H.; Taflan, G.Y.; Yaldiz, S.G.; Akgül, M.A. Evaluation of IMERG for GPM satellite-based precipitation products for extreme precipitation indices over Turkiye. Atmos. Res. 2023, 291, 106826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanshahi, A.; Roshun, S.H.; Booij, M.J. Comparison of satellite-based and reanalysis precipitation products for hydrological modeling over a data-scarce region. Clim. Dynam. 2024, 62, 3505–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuo, L.; Han, D.; Liu, Y.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A. Hydrological model adaptability to rainfall inputs of varied quality. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR032484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, S.; Tan, M.L.; Pan, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; He, R.; Wang, Z. Correcting the bias of daily satellite precipitation estimates in tropical regions using deep neural network. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Z. Comprehensive evaluation of IMERG, ERA5-Land and their fusion products in the hydrological simulation of three karst catchments in Southwest China. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2024, 52, 101671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Nguyen, D.L.; Nguyen, H.H. Assessing applicability of two gridded precipitation datasets for hydrological simulation in a poorly gauged river basin towards supporting sustainable water resources management. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; He, Q.; Li, Y. Downscaling and merging multiple satellite precipitation products and gauge observations using random forest with the incorporation of spatial autocorrelation. J. Hydrol. 2024, 632, 130919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Chen, M.; Yang, S.; Yatagai, A.; Hayasaka, T.; Fukushima, Y.; Liu, C. A gauge-based analysis of daily precipitation over East Asia. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A. Validation and comparison of a new gauge-based precipitation analysis over mainland China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Deng, Z. Multi-source precipitation products assessment on drought monitoring across global major river basins. Atmos. Res. 2023, 295, 106982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ma, Z.; Yan, S.; Peng, J. Do ERA5 and ERA5-land precipitation estimates outperform satellite-based precipitation products? A comprehensive comparison between state-of-the-art model-based and satellite-based precipitation products over mainland China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Xu, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, S.; He, K.; Zhang, S.; Ma, W.; Xu, X. AERA5-Asia: A long-term asian precipitation dataset (0.1°, 1-hourly, 1951–2015, Asia) anchoring the ERA5-land under the total volume control by APHRODITE. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 103, E1146–E1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hsu, K.-L.; Aghakouchak, A.; Sorooshian, S. Object-based assessment of satellite precipitation products. Rem. Sens. 2016, 8, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhou, L.; Du, J.; Yue, J.; Ao, T. Accuracy evaluation and comparison of GSMaP series for retrieving precipitation on the eastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2024, 56, 102017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wen, D.; Du, Y.; Xiong, L.; Wang, L. Errors of five satellite precipitation products for different rainfall intensities. Atmos. Res. 2023, 285, 106622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Van Dijk, A.I.; Levizzani, V.; Schellekens, J.; Miralles, D.G.; Martens, B.; De Roo, A. MSWEP: 3-hourly 0.25 global gridded precipitation (1979–2015) by merging gauge, satellite, and reanalysis data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 589–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Yong, B. A novel Double Machine Learning strategy for producing high-precision multi-source merging precipitation estimates over the Tibetan Plateau. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR035643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavahi, K.; Foroumandi, E.; Moradkhani, H. A deep learning-based framework for multi-source precipitation fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Clark, M.P.; Knoben, W.J.; Liu, H.; Gharari, S.; Arnal, L.; Beck, H.E.; Wood, A.W.; Newman, A.J.; Papalexiou, S.M. The impact of meteorological forcing uncertainty on hydrological modeling: A global analysis of cryosphere basins. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR033767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, Y.-T.; Ma, S.-G.; Kang, Y.; Li, Y.-Q.; Chen, H.; Xu, C.-Y. Uncertainty estimation of hydrological modelling using gridded precipitation as model inputs in the Gandaki River Basin. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2024, 53, 101825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, A.; Tran, T.-N.-D.; Kumar, B.; Lakshmi, V. Evaluation of Satellite-Derived Precipitation Products for Streamflow Simulation of a Mountainous Himalayan Watershed: A Study of Myagdi Khola in Kali Gandaki Basin, Nepal. Rem. Sens. 2023, 15, 4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Tang, G.; Jing, W.; Hou, Z.; Yang, J.; Sun, J. Evaluation of Multiple Satellite, Reanalysis, and Merged Precipitation Products for Hydrological Modeling in the Data-Scarce Tributaries of the Pearl River Basin, China. Rem. Sens. 2023, 15, 5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Wood, E.F.; Pan, M.; Fisher, C.K.; Miralles, D.G.; Van Dijk, A.I.; Mcvicar, T.R.; Adler, R.F. MSWEP V2 global 3-hourly 0.1 precipitation: Methodology and quantitative assessment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 473–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, E.; Lee, H.; Gibson, P.; Loikith, P.; Waliser, D. Bayesian model averaging of climate model projections constrained by precipitation observations over the contiguous United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 2401–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, S.; Bhat, M.S.; Alam, A.; Farooq, H.; Shiekh, H.A. Complementary use of multi-model climate ensemble and Bayesian model averaging for projecting river hydrology in the Himalaya. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 38898–38920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tang, G.; Yao, Y.; Long, D.; Li, C.; Han, Z.; Liu, R. Performance of optimally merged multisatellite precipitation products using the dynamic Bayesian model averaging scheme over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2018, 123, 814–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumnam, K.; Guntu, R.K.; Rathinasamy, M.; Agarwal, A. Quantile-based Bayesian Model Averaging approach towards merging of precipitation products. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Jiang, S.; Dong, J.; Ren, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Duan, Z. Fusion of gauge-based, reanalysis, and satellite precipitation products using Bayesian model averaging approach: Determination of the influence of different input sources. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yong, B.; Gourley, J.J.; Qi, W. Real-time bias adjustment for satellite-based precipitation estimates over Mainland China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ju, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xu, C.-Y.; Lai, X. Evaluation and hydrological application of four gridded precipitation datasets over a large Southeastern Tibetan Plateau Basin. Rem. Sens. 2022, 14, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Zhao, H.; Ao, T.; Hu, W. Quantifying the reliability and uncertainty of satellite, reanalysis, and merged precipitation products in hydrological simulations over the topographically diverse basin in Southwest China. Rem. Sens. 2022, 15, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Iqbal, M.F.; Mahmood, I. Validation of CHIRPS satellite-based precipitation dataset over Pakistan. Atmos. Res. 2021, 248, 105289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Xu, T.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zou, J. Multiple spatial and temporal scales evaluation of eight satellite precipitation products in a mountainous catchment of south China. Rem. Sens. 2023, 15, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorolog. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Guo, B.; Xing, W.; Zhou, J.; Xu, F.; Xu, Y. Comprehensive evaluation of latest GPM era IMERG and GSMaP precipitation products over mainland China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 246, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Guo, H.; Tian, Y.; Meng, X.; Bao, A.; De Maeyer, P. Evaluation of GSMaP Version 8 Precipitation Products on an Hourly Timescale over Mainland China. Rem. Sens. 2024, 16, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Letu, H.; Shang, H.; Ri, X.; Tang, C.; Ji, D.; Shi, C.; Teng, Y. Rainfall Area Identification Algorithm Based on Himawari-8 Satellite Data and Analysis of its Spatiotemporal Characteristics. Rem. Sens. 2024, 16, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retalis, A.; Katsanos, D.; Tymvios, F.; Michaelides, S. Comparison of GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B43 Products over Cyprus. Rem. Sens. 2020, 12, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ruan, H.; Lin, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Duan, W.; Deng, H. The magnitude and frequency of detected precipitation determine the accuracy performance of precipitation data sets in the high mountains of Asia. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.; Song, W.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, K.; Chen, L.; Feng, T.; Linghu, S.; Alam, M. Validation of CRU TS v4. 08, ERA5-Land, IMERG v07B, and MSWEP v2. 8 Precipitation Estimates Against Observed Values over Pakistan. Rem. Sens. 2024, 16, 4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Ajami, N.K.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S. Multi-model ensemble hydrologic prediction using Bayesian model averaging. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 1371–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y.; Yong, B.; Yang, X.; Yuan, F.; Ma, M. Comprehensive evaluation of multi-satellite precipitation products with a dense rain gauge network and optimally merging their simulated hydrological flows using the Bayesian model averaging method. J. Hydrol. 2012, 452, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftery, A.E.; Gneiting, T.; Balabdaoui, F.; Polakowski, M. Using Bayesian model averaging to calibrate forecast ensembles. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2005, 133, 1155–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Kong, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Pang, C. Reliability of satellite-derived precipitation data in driving hydrological simulations: A case study of the upper Huaihe River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; He, D.; Guo, R.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Yue, C.; Liu, C. Evaluation of bias correction methods for APHRODITE data to improve hydrologic simulation in a large Himalayan basin. Atmos. Res. 2020, 242, 104964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhong, R.; Lai, C.; Chen, J. Evaluation of the GPM IMERG satellite-based precipitation products and the hydrological utility. Atmos. Res. 2017, 196, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Yuan, H. Impacts of precipitation uncertainty on hydrological ensemble simulations over the Ganjiang River Basin. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2024, 51, 101617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaowei, N.; Jie, W.; Juliang, J.; Xiaoyan, X.; Yuliang, Z.; Fan, S.; Linlin, Z. Comprehensive evaluation of satellite-derived precipitation products considering spatial distribution difference of daily precipitation over eastern China. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 101242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloughter, J.M.L.; Raftery, A.E.; Gneiting, T.; Fraley, C. Probabilistic quantitative precipitation forecasting using Bayesian model averaging. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2007, 135, 3209–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourian, M.J.; Saemian, P.; Ferreira, V.G.; Sneeuw, N.; Frappart, F.; Papa, F. A copula-supported Bayesian framework for spatial downscaling of GRACE-derived terrestrial water storage flux. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, W.; Xia, J.; Fisher, J.B.; Dong, W.; Zhang, X.; Liang, S.; Ye, A.; Cai, W.; Feng, J. Using Bayesian model averaging to estimate terrestrial evapotranspiration in China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; De Maeyer, P.; Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Li, L. Spatiotemporal variability of the precipitation concentration and diversity in Central Asia. Atmos. Res. 2020, 241, 104954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, D.; Xing, C.; Tiexi, C.; Xing-Wu, C. Relationship between extremes of precipitation and discharge in the Huaihe River Basin. J. Nanjing Univ. (Nat. Sci.). 2009, 45, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, C.M.; Pham, H.T.; Marshall, L.A.; Johnson, F.M. Which Rainfall Errors Can Hydrologic Models Handle? Implications for Using Satellite-Derived Products in Sparsely Gauged Catchments. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2020WR029331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanding, N.; Wu, H.; Tao, J.; Maggioni, V.; Beck, H.E.; Zhou, N.; Huang, M.; Huang, Z. Assessment of precipitation error propagation in discharge simulations over the contiguous United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2021, 22, 1987–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Miao, C.; Sorooshian, S.; Duan, Q.; Guo, X.; Su, T. Satellite-based precipitation error propagation in the hydrological modeling chain across China. J. Hydrol. 2024, 632, 130906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Guo, S.; Gu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Shen, Y.; Xu, C.-Y. Blending multi-satellite, atmospheric reanalysis and gauge precipitation products to facilitate hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, D. A multiple-step scheme for the improvement of satellite precipitation products over the Tibetan Plateau from multisource information. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K.U.; Shang, S.; Shahid, M.; Wen, Y.; Khan, Z. Application of a dynamic clustered bayesian model averaging (DCBA) algorithm for merging multisatellite precipitation products over Pakistan. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Han, Z.; Tang, G.; Maguire, L.; Chu, Z.; Hong, Y. Comprehensive evaluation of ensemble multi-satellite precipitation dataset using the dynamic bayesian model averaging scheme over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, S. Evaluating the TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis for extreme precipitation and streamflow in Ganjiang River basin, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 2902493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, K.; Dong, N.; Wang, H. Optimally integrating multi-source products for improving long series precipitation precision by using machine learning methods. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.Y.; Lee, S.-I. Fusion of Multi-Satellite Data and Artificial Neural Network for Predicting Total Discharge. Rem. Sens. 2020, 12, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | Unit | Description | Value Range | Perfect Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| b_infilt | - | Variable infiltration capacity curve | [0.1, 0.4] | 0.39 |
| Dsmax | mm/day | Maximum velocity of base flow | [0, 30] | 27.79 |
| Ds | - | Fraction of Dsmax where non-linear baseflow begins | [0.1, 1] | 0.95 |
| Ws | - | Fraction of maximum soil moisture where non-linear baseflow occurs | [0.1, 1] | 0.50 |
| D2 | m | The second soil-layer thickness | [0.1, 1] | 0.27 |
| D3 | m | The third soil-layer thickness | [0.1, 3] | 1.67 |
| Evaluation Metrics | Equation | Value Range | Perfect Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient (CC) | [−1, 1] | 1 | |
| Relative bias (RB) | (−∞, +∞) | 0 | |
| Root mean square error (RMSE) | [0, +∞) | 0 | |
| Kling–Gupta efficiency (KGE) | (−∞, 1] | 1 | |
| Probability of detection (POD) | [0, 1] | 1 | |
| False alarm ratio (FAR) | [0, 1] | 0 | |
| Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE) | (−∞, 1] | 1 |
| Products | CC | RB (%) | RMSE (mm) | KGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHIRPS | 0.94 | 4.19 | 38.43 | 0.90 |
| ERA5 | 0.91 | 25.98 | 75.90 | 0.71 |
| GSMaP-G | 0.96 | −6.31 | 30.73 | 0.91 |
| IMERG-F | 0.96 | 1.93 | 29.65 | 0.95 |
| BMA | 0.97 | 6.62 | 28.85 | 0.93 |
| MSWEP | 0.95 | −8.24 | 35.01 | 0.90 |
| Products | Calibration | Verification | Entire Study Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gauge-based | 0.86 | 0.74 | 0.80 |
| CHIRPS | 0.48 | 0.29 | 0.39 |
| ERA5 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| GSMaP-G | 0.87 | 0.69 | 0.79 |
| IMERG-F | 0.73 | 0.40 | 0.57 |
| BMA | 0.77 | 0.61 | 0.70 |
| MSWEP | 0.87 | 0.77 | 0.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, J.; Thapa, B.R. Bayesian Model Averaging for Satellite Precipitation Data Fusion: From Accuracy Estimation to Runoff Simulation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071154
Ning S, Cheng Y, Zhou Y, Wang J, Zhang Y, Jin J, Thapa BR. Bayesian Model Averaging for Satellite Precipitation Data Fusion: From Accuracy Estimation to Runoff Simulation. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(7):1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071154
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Shaowei, Yang Cheng, Yuliang Zhou, Jie Wang, Yuliang Zhang, Juliang Jin, and Bhesh Raj Thapa. 2025. "Bayesian Model Averaging for Satellite Precipitation Data Fusion: From Accuracy Estimation to Runoff Simulation" Remote Sensing 17, no. 7: 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071154
APA StyleNing, S., Cheng, Y., Zhou, Y., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Jin, J., & Thapa, B. R. (2025). Bayesian Model Averaging for Satellite Precipitation Data Fusion: From Accuracy Estimation to Runoff Simulation. Remote Sensing, 17(7), 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071154





